Abstract
Plans are prepared to provide direction, set goals, manage risks, and ensure timely and successful implementation to achieve desired outcomes. However, plans fail to deliver desired outcomes when an unexpected event occurs. The adaptive planning process is known for its ability to respond to an unexpected event with pre-emptive preparation. The adaptive planning approach seeks to minimise uncertainties and associated risks during each stage of the planning process by (re)assessing the feasibility of water supply needs and the effectiveness of planning decisions. The two most prevalent concepts in the integration of adaptiveness in planning processes are the dynamic adaptive policy planning and the adaptive planning cycle (Mobius loop) frameworks; these frameworks are used to address the uncertainties and associated risks at the planning stage. The Mobius loop, or infinity loop, is gaining momentum, as it clearly illustrates the iterative and continuous nature of adaptation to changing conditions. However, the data on the successful implementation of ‘adaptive’ planning practices are limited, and there is little knowledge about these practices. This study reviews the literature in this field and discusses the different interpretations of adaptiveness and its benefits and challenges while developing long-term strategic plans. The findings identify gaps for future research and recommend the way forward for policymakers to promote adaptive planning practices.
1. Introduction
Plans are prepared to provide direction, set goals, manage risks, and ensure timely and successful implementation to achieve desired outcomes. However, plans are often prepared and followed strictly. This is the main cause of plans failing when an unexpected event occurs. Water management planning and population growth projections are subject to deep uncertainties in a complex system with competing priorities [1]. To ensure that water management plans achieve their desired outcomes, Brinckmann (2015) [2] recommended that decision makers critically reflect upon their predispositions while pursuing the imminent task of planning and that they explore an informative approach to planning. Schoemaker (2022) [3] recommended that planners reduce the sources of challenges related to the climate change-related uncertainties that complicate the planning process. In particular, uncertain population growth is a human-induced source of uncertainty in water planning processes, and it needs attention if the impacts of structural land use changes on water management needs are to be included and understood [4]. The challenges of uncertainty are not limited to climate change but extend to the circular economy, fast-paced technological changes, and institutional, social, and political upheavals.
Traditional planning practices are ill-equipped to address multi-faceted uncertainties in an increasingly dynamic and unpredictable environment [5]. These uncertainties drive the need for an alternative approach to planning, an approach that is flexible enough to adapt to changes and can be applied with minimum changes to the original plan [6]. The three major approaches used to adapt to a shock or disruptive condition are adaptation management, adaptation planning, and adaptive planning. Adaptation management and adaptation planning are reactive approaches. In particular, adaptation management is a passive form of planning acknowledged for its ability to respond to a condition after it occurs with little or no preparation to create change [7]. The adaptive planning process, however, is a proactive approach, which seeks to minimise the risks related to uncertainty at each stage of the planning process by (re)assessing the feasibility and effectiveness of the planning decisions [8]. Learning by doing [9] and multi-option scenario planning [10] are suggested as alternative planning methods for addressing uncertainties. These were found to achieve a small degree of success at the local water utility level.
The terms ‘adaptation’ or ‘adaptive planning’ are usually associated with challenges related to climate change. However, the circular economy [11,12], the increased reliance on technology [13], and the global drive towards equity [14,15] are the global challenges that create uncertainties that have an adverse impact on a local water utility’s planning considerations. According to Erfani (2018) [16], the adaptation pathway approach by Haasnoot (2013) [17] was designed for policymakers so that they could make informed decisions. Adaptive planning is generally about being prepared for transformation during times of change and in the face of uncertainties [16]. However, the concept of adaptive planning is not just limited to addressing water management challenges; preparation and the capacity to imagine alternative futures can turn a crisis into an opportunity [16]. Atwater (2015) [17] studied the extent of resource integration within water utilities and found that under uncertain conditions, the water utilities do more to integrate resources and adapt to a rapidly changing world to manage water management challenges.
Despite an increasing awareness of the adaptive planning concept, there is limited publicly available information, whether it is in the grey literature or in peer-reviewed studies. This study reviews the interpretations of the adaptive planning concept from the early 2000s, as it was found to be the most relevant in today’s context. Attempts to search for versions of adaptive planning concepts prior to the early 2000s were unsuccessful due to accessibility issues and organisational confidentiality. The ability of an adaptive planning approach to adapt to the changing environment with minimum disruption drives this literature review; the aim is also to better understand its potential to address uncertainties. An analytical review was carried out in this study to gain a better understanding of the different adaptive planning interpretations.
Section 2 outlines the methodology; Section 3 reviews the abilities of the adaptive planning pathway; and Section 4 examines the existing literature that considers how the emerging adaptive planning process can provide a response to planning challenges under uncertain conditions. Section 5 discusses the conclusions and provides a future research direction, and it recommends the way forward for policymakers.
2. Methodology
The method used to carry out this literature review involved the exploratory research of peer-reviewed studies and grey literature. To gather intelligence on the different ways of adapting to shocks and disruptions in plans with minimum changes, keywords were used to explore the scientific journals and grey literature. The grey literature search included the use of Google and Google Scholar. The lack of diversity in the publicly available information and the similarities in the conceptual adaptive planning approaches designed to incorporate adaptiveness in long-term strategic plans emphasise the need for a literature review on adaptive planning to improve water management at the governance level. The different versions of the adaptive planning concept are represented as either a circle or a Mobius loop to visualise adaptiveness and the need to revisit and improve plans in an iterative manner. This initial finding triggered the review of the grey literature.
The literature review was carried out in two stages. The initial short review was conducted to check the viability of the approach and the knowledge gaps in this field. This short review included referenced material from 29 peer-reviewed studies and government documents. In the second stage of the literature review, the top five (5) keywords used to explore the peer-reviewed studies were adaptive planning, adaptive pathways, scenario planning, planning for uncertainty, and risk mitigation in water governance. These keywords were selected as a result of the research and literature review of the drivers and challenges involved in developing a long-term water management strategy [18] and an integrated water cycle management (IWCM) strategy, which were used in this research as examples of long-term strategic planning [19]. The resulting publication lists from these searches were then reviewed and shortlisted to include those with the most relevant information related to water management, strategic planning, and water governance. Many peer-reviewed studies and Google links had overlapping information; for example, a study by Erfani (2018) [16] not only discusses the DAPP concept but also reviews the use of the real options analysis (ROA) concept to plan for multiple pathways (scenario planning) and to minimise and manage the risks of long-term planning. Thus, a total of 417 papers, government documents, and grey literature articles were reviewed and downloaded; of these, 111 with publicly available information are referenced in this review. The information is collated in the logical–analytical format of a literature review. The explanation of the concept, benefits, and challenges of an adaptive planning process is discussed for the available interpretations, and the ways in which adaptive planning can overcome uncertainties is deliberated in the subsequent sections of this review.
3. Adaptive Planning Pathway—An Emerging Concept
It is a bad plan that cannot be changed—Publilius Syrus (c. 43 BC)
The initial academic reference to the mixed-conditional adaptive planning process was made by Cooper (1971) [20] regarding a systems approach to urban planning. Then, in the following year, the use of this adaptive planning process was identified as a decision-making tool in a dissertation by Bellaschi (1972) [21]. The Defense Technical Information Center in the United States also developed and applied an unknown version of an adaptive planning model in a number of their operations. However, this interpretation of the adaptive planning process remains an internal confidential process [22,23]. Then, in the early 2000s, adaptation pathways were conceptualised by Haasnoot (2013) [17] to address the increasing uncertainties at the planning stage.
The adaptation pathways are a series of actions to be implemented; their implementation depends on the extent of our knowledge as the future unfolds [24]. Organisations should modify their traditional action plans to: (a) accept uncertainty as a norm and (b) value the changing environment [25]. In preparing plans, Williams (2011) [26] identifies four types of uncertainties influencing the management of natural resource systems: environmental variation; the partial observability or partial controllability of conditions; and structural or process uncertainty. For a water utility, the management of external and internal risks while developing a long-term water management plan involves deep uncertainty. These risks range from individual capacity-related risks to global risks related to climate change or shocks such as COVID-19, which affect the entire world. The management of the risks requires: (a) decision-making under deep uncertainty; (b) embracing uncertainty, and (c) the consideration of alternative adaptation planning pathways [27]. In reducing the ‘causes’ of the challenges related to uncertainty that complicate the planning process, the study by Schoemaker (2022) [3] serves as a primary driver for the adaptive approach. The adaptive planning approach seeks to challenge and minimise the uncertainty and risks related to uncertainty at each stage of the planning process by (re)assessing the feasibility of water infrastructure needs and the effectiveness of planning decisions [3,8].
Before adaptive planning, adaptive management was viewed as a tool for implementing integrated water resource management (IWRM) strategies and for coping with the challenges of ‘uncertainty’. Adaptive management aims to increase the adaptive ability to manage disruptions; it is based on a sound understanding of the critical factors involved in determining vulnerability [28]. The IPCC (2014) [29] studied the impacts following the improvement of the adaptive capacity of plans and found that, for the success of long-term strategic plans, the effective selection of adaptation options was crucial for implementation. As such, adaptive management is about managing the situation after it occurs, and it provides a reactive solution to a disruptive condition. This is the less desired option for addressing uncertainties, as it does not consider the time factor or the financial implications of the solution.
Adaptive planning represents a fundamental, systemic reform of how we think about water management planning [30]. In adaptive planning, predictive modelling for developing scenarios is a collaborative exercise involving different disciplines and stakeholders [31]. Though the benefits of adaptive planning are well known, the complexities of incorporating flexibility and adaptive planning principles [32] into planning have yet to be achieved successfully [33]. An adaptive approach provides discretionary authority to the decision makers with relatively strong capacity, who are working in a mature and trusted system of recognised ‘good governance’ [34]. Thus, adaptive planning is a proactive solution to a disruptive condition. This is the desired option for addressing uncertainties, as it considers all options, prepares scenarios, and develops multiple pathways. The adaptive planning pathway duly considers the time factor and the financial needs of the selected solution to future-proof the water infrastructure plans, which are expensive to implement and operate.
Many researchers have found that developing infrastructure too soon can lead to unnecessary, expensive, and irreversible investments, but waiting too long can threaten water supply reliability [35,36,37,38,39]. However, should the infrastructure development be deferred, it could mitigate the risk of overbuilding or underbuilding infrastructure while maintaining water supply reliability in the face of uncertainty [16,40]. Another study by Gurung (2017) [40] highlights the cost implications of delaying infrastructure investment, operating the existing deteriorating infrastructure, and the (in)ability of the utilities to provide adequate levels of services to their water user communities. Thus, there is recognition of the need for proactive solutions. The adaptive planning process provides a proactive solution that identifies the potentially disruptive condition and proposes various scenarios, including risk management and mitigation, that may be implemented as required.
Considerable efforts have been made to implement adaptive planning in practice. The main approaches proposed by researchers to implement an adaptive planning process over the last decade and a half consider macro-level governance, local planning pathways, and the stakeholder mindset. The approaches are as follows:
- An analytical framework proposed to map three-dimensional politics around reflexive governance at the micro-, meso-, and macro-planning levels [41];
- Six practice-based adaptive planning approaches: (i) requirement-based planning, (ii) cost–benefit-based planning, (iii) multi-objective planning, (iv) conflict resolution planning, (v) market-based planning, and (vi) muddling through [31];
- The perspectives of (i) researchers and (ii) planning practitioners who influence the interpretations of scenario analysis as a tool [42];
- Two scenario planning approaches: (i) exploratory scenarios—extrapolating projective and prospective future trends and (ii) the anticipatory scenario—is a policy response that is based on experts’ judgement and stakeholder-defined [43].
These four multiple-pathway options are designed to mitigate the planning risks in an uncertain environment. Collectively, these four approaches and frameworks are parts of a whole (adaptive planning concept). Each approach addresses a major component of the adaptiveness of the multi-level governance of the planning process, the water management and practices, the different perspectives on water governance, and the detailed scenario planning.
The adaptive planning process centres on prioritising the risk-based pathways developed using scenario planning (Available at: https://flevy.com/blog/scenario-planning-for-consultants-strategizing-the-uncertainties/, accessed on 3 October 2023) as a tool. The risk-based approach triggers the need for the selection of the pathway on a case-by-case basis [44]. These planning tools address a specific issue but cannot mitigate multiple risks in an uncertain environment, nor do these frameworks consider the complexities associated with the non-stationary nature of the hydrological parameters that now exists due to climate change [45]. This raises a clear need to manage water demand in the face of multiple risks in an uncertain environment and complex climate change challenges. Thus, it is necessary to improve water use efficiencies and promote conservation to respond to climate-induced impacts on the water sector. As with adaptive planning, adaptive governance is about being prepared for change and surprise and enhancing adaptability when dealing with disturbances [46] and social capitalism [47]. The basic principles of sustainable adaptive governance include exploring a broad range of uncertainties and planning for long-term goals while targeting short-term objectives, where listed options can be adjusted to respond to problems and opportunities. To implement adaptive governance measures, adaptive pathways, according to Haasnoot (2013) [17], must involve being prepared for a wide range of scenarios. This can be achieved by selecting from the reviewed options and by increasing the ability to revise plans.
Adaptive planning is used in metropolitan NSW councils to address the uncertainties of water resource management and is becoming increasingly popular in the regional NSW councils (Water Utility Strategic Planning; NSW Department of Planning, Environment and Industry—Available at: https://water.dpie.nsw.gov.au/our-work/local-water-utilities/water-utility-strategic-planning, accessed on 14 March 2024). The metropolitan water utilities of Sydney Water (Eastern SydneyWater Strategy—Available at: https://www.sydneywater.com.au/content/dam/sydneywater/documents/eastern-sydney-regional-master-plan-final.pdf, accessed on 25 January 2024; Western SydneyWater Strategy—Available at: https://www.sydneywater.com.au/content/dam/sydneywater/documents/western-sydney-regional-master-plan.pdf, accessed on 25 January 2024) and Hunter Water (Draft Lower Hunter Water Security Plan: At a glance, Available at: https://www.hunterwater.com.au/documents/assets/src/uploads/documents/Plans--Strategies/lower-hunter-water-security-plan.pdf, accessed on 25 January 2024) in NSW lead the way in adopting the adaptive planning process in their strategic plans. Water utility alliances and joint organisations in regional NSW are adopting the adaptive planning process in their strategic plans, both at the utility and joint organisation levels. A proactive planning approach, as suggested by Smet (2017) [48], can create opportunities for water utilities to develop robust cross-disciplinary solutions as a part of good governance measures. The integration of finance, water resource planning, engineering, operations, and facilities management decision-making into a single collaborative effort was found to be fundamental to the success of the adaptive planning approach [48]. Fletcher (2019) [35] also suggested exploring various engineering options and identifying future applications of these options to build a theory around the drivers and limits of adaptive plans. Then, Fletcher (2019) [35] demonstrated that the adaptive infrastructure planning approach allows planners in data-scarce regions to assess the conditions when initial plans are made. However, identifying infrastructure needs in practice under uncertain conditions and future-proofing the infrastructure are major challenges for the water utilities in NSW [18]. The challenge facing the inclusion of adaptive planning in rural and regional councils is the limited access to the already-limited resources [31], whether natural, human, or financial [49,50,51]. The challenges and benefits of an adaptive planning process are deliberated in Section 4.
4. Adaptive Planning Processes—Benefits and Challenges
Introducing the ‘adaptive planning’ concept to develop long-term strategic plans can mitigate the risks associated with semi-coherent shocks and disruptive conditions with minimum changes to achieve higher degrees of efficiency at the time of implementation. Adaptive planning, however, is viewed as a complex process that is difficult for the resource-poor councils to undertake and implement [32]. Understanding the existing strengths and challenges of the adaptive process is imperative in overcoming the challenges of water management at the water utility level.
The key benefits of an adaptive planning process are the ‘Decision Making under Deep Uncertainty’ approach [5] and the flexibility to select from multiple pathways as a proactive planning approach; these benefits enable dynamic decision-making as the future unfolds. The process explores different decision-making pathways for multiple-scenario planning and alternative strategies for overcoming policy paralysis due to deep uncertainty. As such, the adaptive planning process drives the design of long-term options that help to indicate when to implement the planned long-term options and revisit decisions as required [5]. This is particularly useful for water utilities when exploring long-term options for critical water infrastructure and managing increasing water use demands. In the following subsections, the current approaches used to incorporate adaptiveness in long-term plans are discussed, including the benefits and challenges they pose.
4.1. Dynamic Adaptive Policy Planning
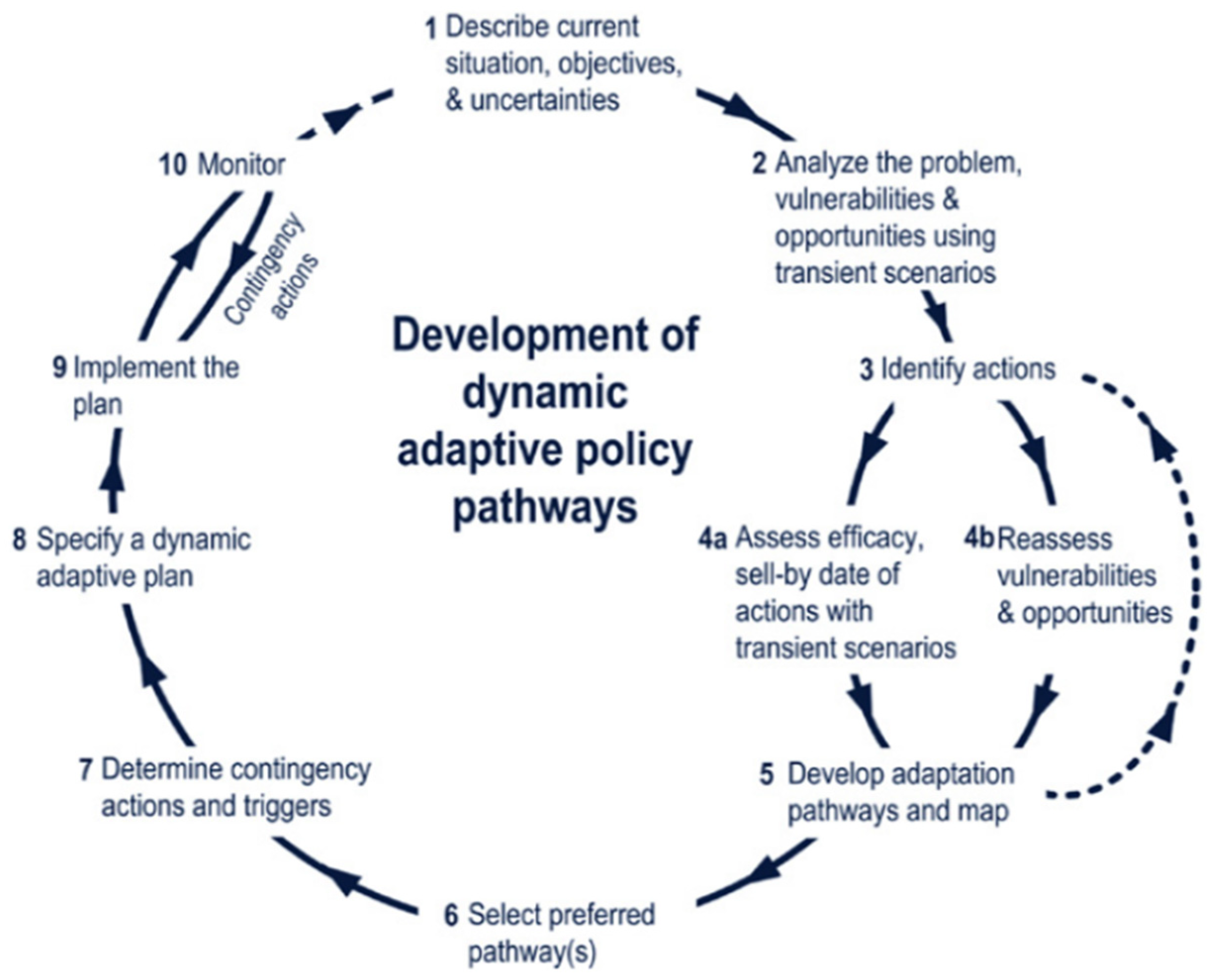
The ‘Dynamic Adaptive Policy Pathway’ (DAPP) concept (Figure 1) was developed by Haasnoot (2013) [17] to address the issue of uncertainties at the global and regional scales. According to Kwadijk (2010) [52], the DAPP combines two adaptive approaches to design policies. Nyamekye (2018) [53] proposed a slightly different approach and provided specific details that defined the DAPP as a combination of adaptive policy (visionary, implicit, comprehensive, specific, and distinctive) and the adaptation pathway (exploratory, explicit, and limited to an application and multiple pathways). Alternatively, Kwakkel (2010) [54] proposed a structured approach for designing dynamic plans, whereas the adaptation pathway approach specified the conditions under which the plans met the goals [54,55,56]. The DAPP has the much-needed capabilities to analyse the strengths and weaknesses of policy impacts over a long period through scenario planning for multiple uncertainties [57]. Alternative paths are designed through the dynamic adaptive planning process to address weaknesses and build upon the strengths of uncertainties [16,58,59]. From a water management viewpoint, climate change impacts trigger the need to change current plans and identify new actions to ensure secure water supplies. Identifying the triggers for successfully designing and implementing the DAPP approach is challenging [16]. The DAPP and real options analysis (ROA) are both decision-making processes, but they use different techniques to prepare adaptive plans [16]. The DAPP uses multi-path scenario planning in the absence of information [60,61], and ROA focuses on the cost–benefit analysis of the options using probability information to prepare for uncertain future conditions [62]. These differences in approach make the DAPP a more viable option in a constantly changing environment, where the absence of information is a more regular occurrence. The adaptive planning approach, however, integrates the two approaches to planning in the absence of information and develops options using probability.
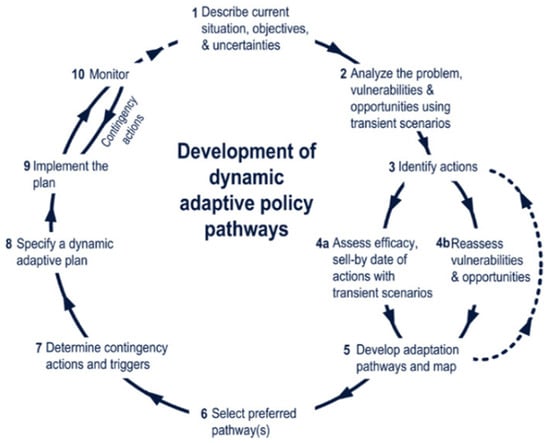
Figure 1.
DAPP framework, Haasnoot (2013) [17].
According to a study by Lawrence (2017) [59] on implementing the DAPP, there are four intervention phases for incorporating adaptiveness while implementing the long-term strategic plans: (1) creating interest through framing the science, (2) increasing awareness using the game, (3) experimenting with the DAPP, and (4) taking up the DAPP. The catalysts for the uptake of adaptive planning pathways are (a) the knowledge broker introducing new frameworks to reduce risk levels, (b) facilitating the DAPP approach in a real-life decision-making setting, and (c) providing contextual assistance from events and (inter)national reports [59]. However, publicly available information on the successful implementation of the DAPP process using these intervention methods is missing.
In contrast to Haasnoot’s DAPP theory, Malekpour (2020) [60] found that interwoven multi-dimensional challenges and adaptation pathways are barriers to the uptake of the DAPP at the planning stage. Another study by Giezen (2012) [61] found that including all the options to address uncertainties is hard to manage. Project planning becomes manageable when there are fewer unknowns and variables to predict and the complexities are reduced. However, limiting the scope of the project to the minimum means
- Less intense stakeholder engagement;
- A reduced number of external influences;
- Limited feedback about alternatives;
- Limited uncertainties and related risk management;
- A reduced need to adapt.
Such a minimalistic approach, which limits the scope of a project, tends to exclude uncertainties that could potentially put the desired outcomes of the project itself at risk. Therefore, scaling down the project is not an option. Adaptive plans should be designed to incorporate changes, new knowledge, and information to enable the improved management of future changes, deal with uncertainties, and guide future actions [45]. Erfani (2021) [62] encourages the use of decision rule (decision rule is the method used in statistical analysis to reject options with null impacts), as it is easy to use and tractable, and its applicability at all decision stages assists in the optimisation of the solution. Thus, analysts should consider using decision rules to optimise adaptive planning models [6]. These cumulative findings highlight the fact that, though adaptive planning is complex, there is a definite need to include and address uncertainties and risks in the plans.
4.2. Mobius Loop or Infinity Loop
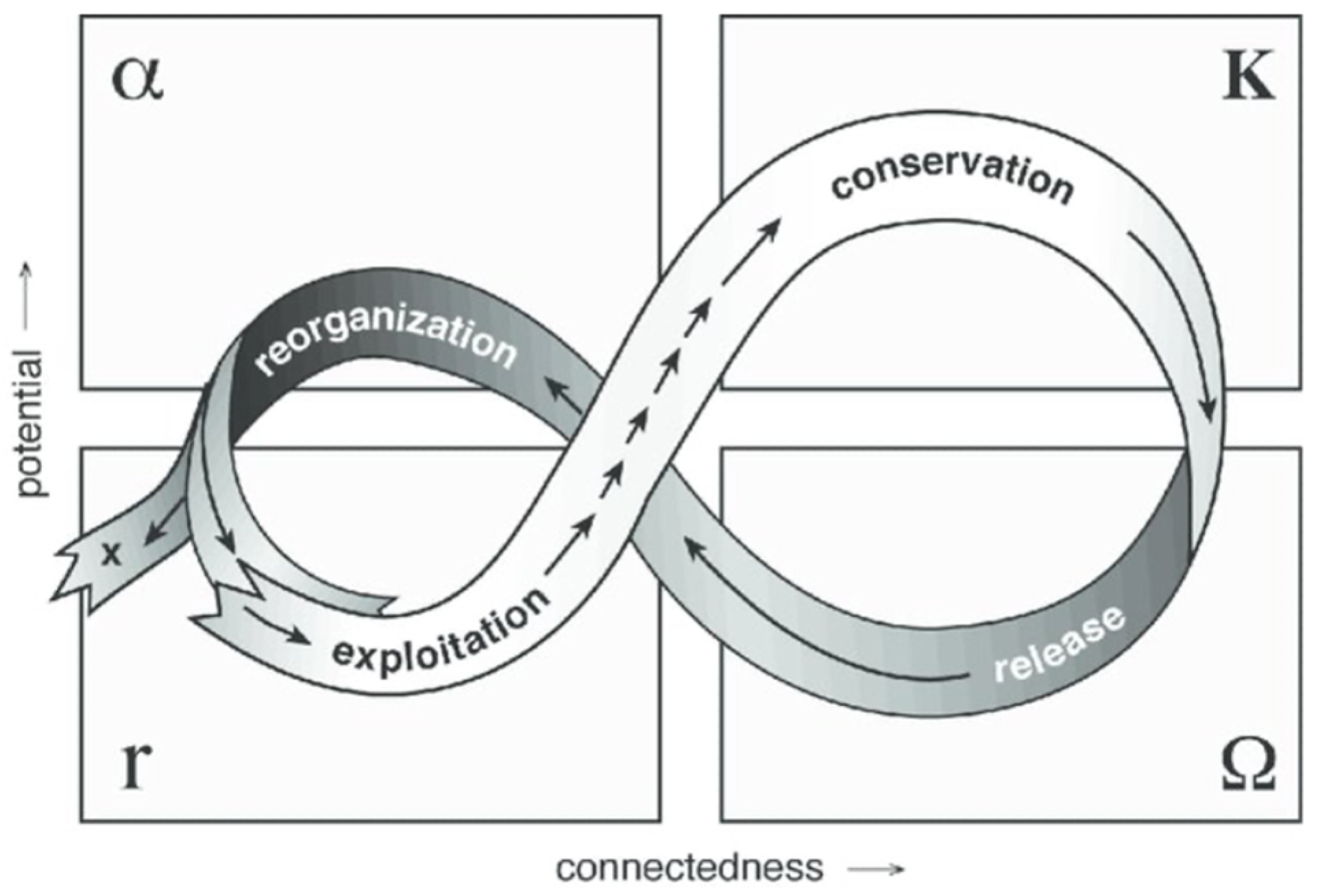
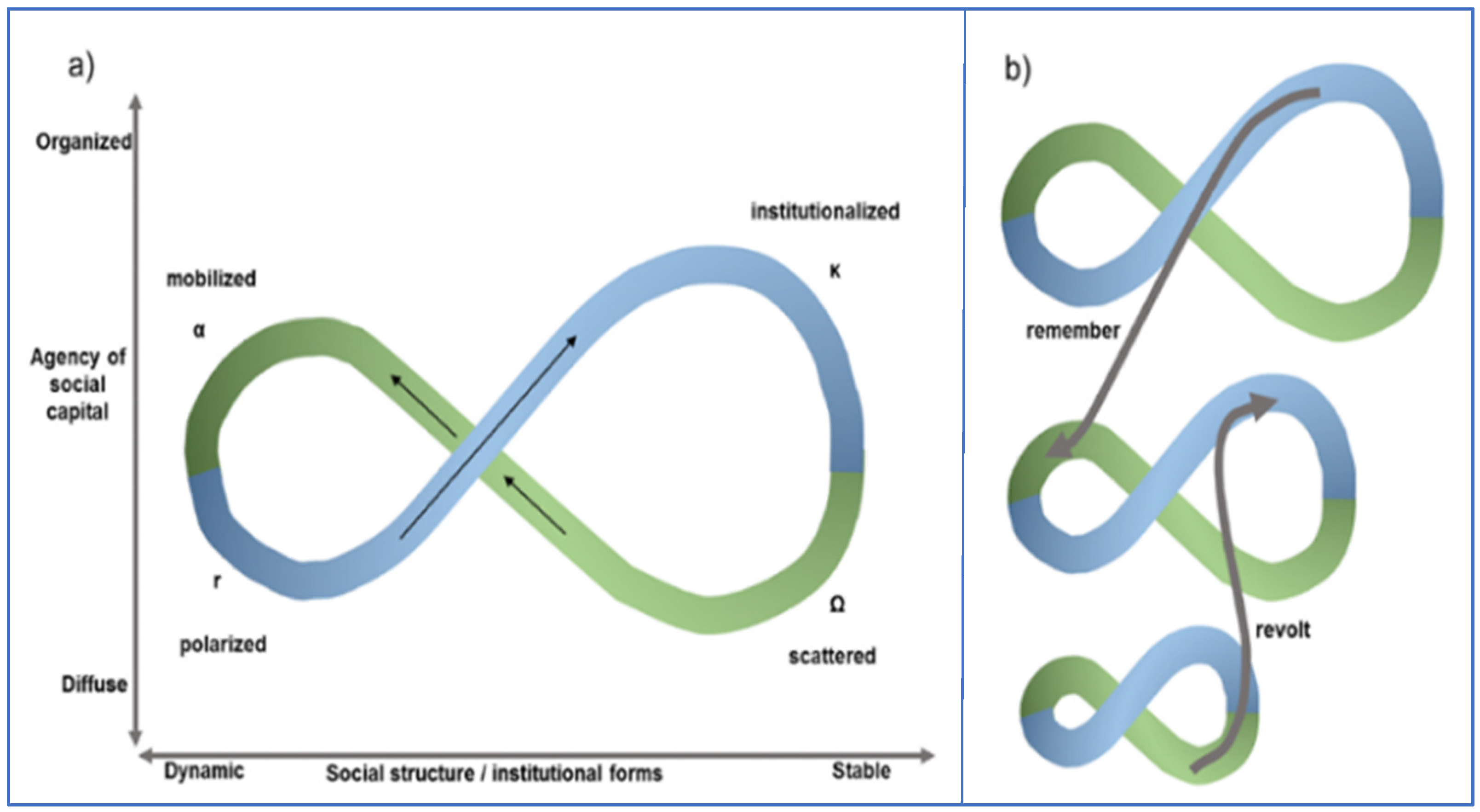
The study of adaptive planning interpretations by Wahl (2016) [63] found that they are often represented as a Mobius loop or an infinity loop to capture the iterative process of the adaptation. Gunderson (2002) [64] proposed the adaptive cycle as an infinity loop (Figure 2), divided into four distinct phases representing the ecosystem and the socio-ecological system dynamics of: ‘growth or exploitation’ (r); ‘conservation’ (K) of established patterns and resource distribution or ‘release’ (Ω) of information; and reorganisation (α) of the plans to adapt to the altered conditions. These four phases are presented as a two-stage transition process: (1) foreloop and (2) backloop. Foreloop, the first stage (denoted by gamma (r) and kappa (K)), is a slow, incremental phase of growth and accumulation. Backloop, the second stage (denoted by omega (Ω) and alpha (α)), is the rapid phase of reorganisation leading to renewal. This transition process forms an infinity loop or Mobius loop that highlights the need for an iterative process to reach the desired goals and objectives of the plan or to address the uncertain condition efficiently and effectively.
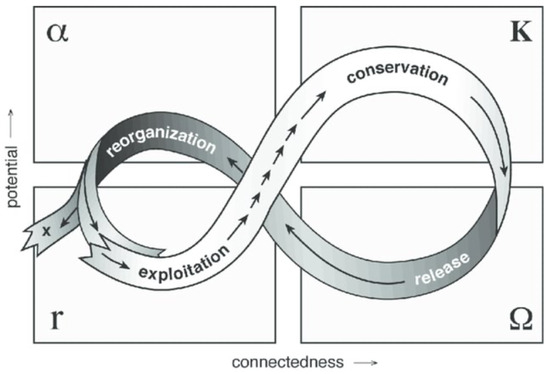
Figure 2.
Adaptive Cycle design for developing plans under uncertainty by Gunderson (2002) [64].
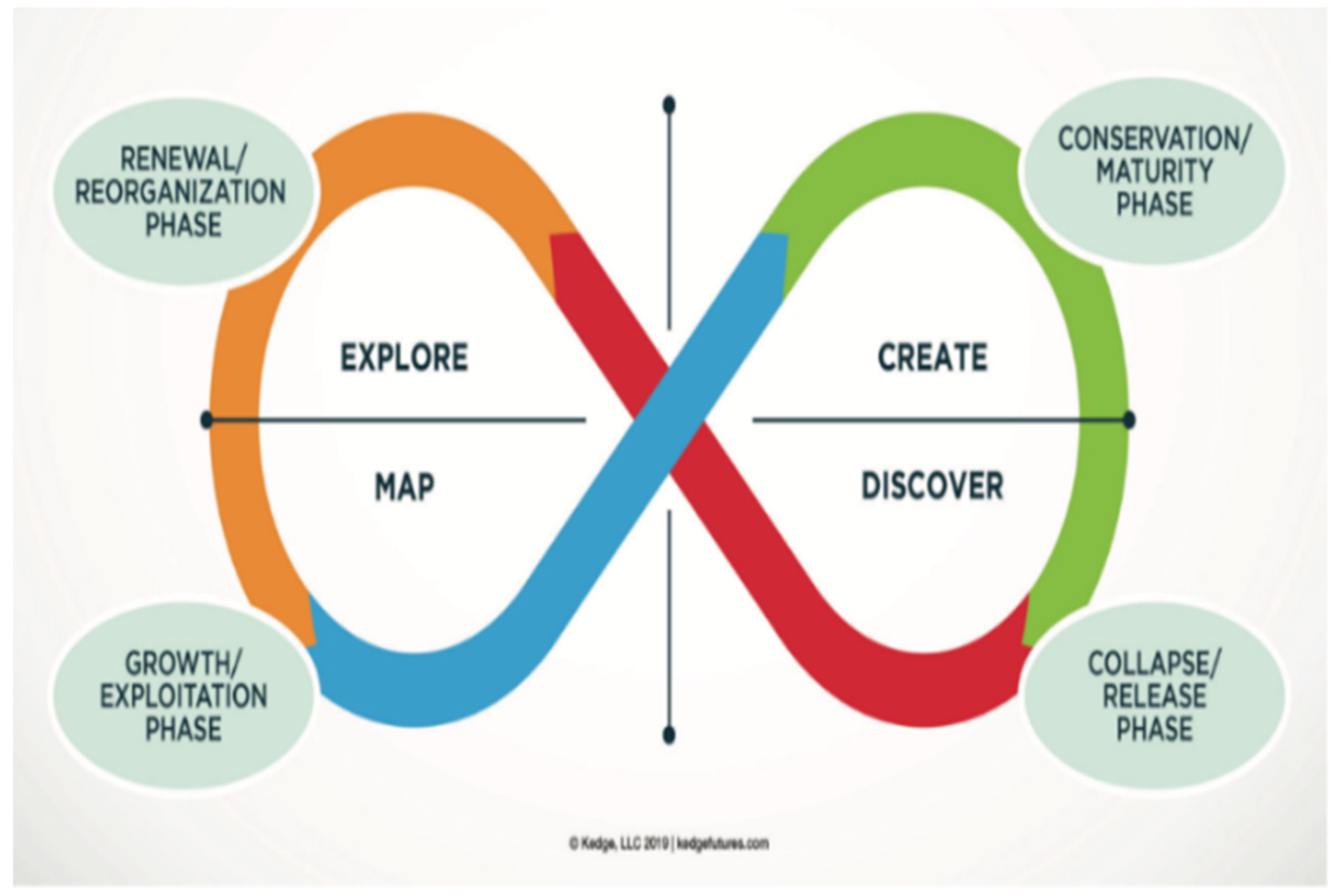
Natural Foresight (https://tfsx.com/2021/07/natural-foresight-as-a-panarchy/, accessed on 1 June 2024; Free open-access copyright permission available at: https://tfsx.com/nff/, accessed on 1 June 2024) proposes the panarchy model from an ecological or environmental perspective. The concept of panarchy was explored from a planning perspective and is divided into four phases: exploring, mapping, discovering, and creating (Figure 3).
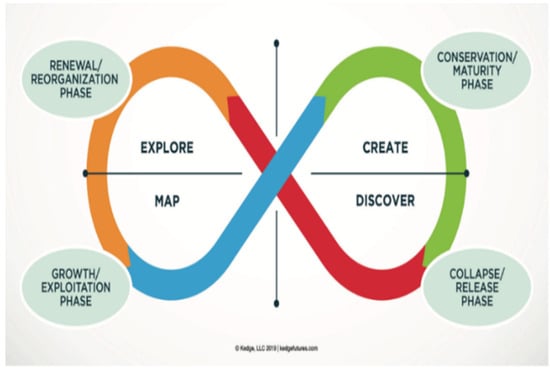
Figure 3.
Panarchy of interconnected adaptive cycle. Each section of the cycle is tagged (Green = conservation, Red = Collapse, Orange = Renewal and Blue = Growth) to show overlaps with the four phases of planning (extracted from Natural Foresight).
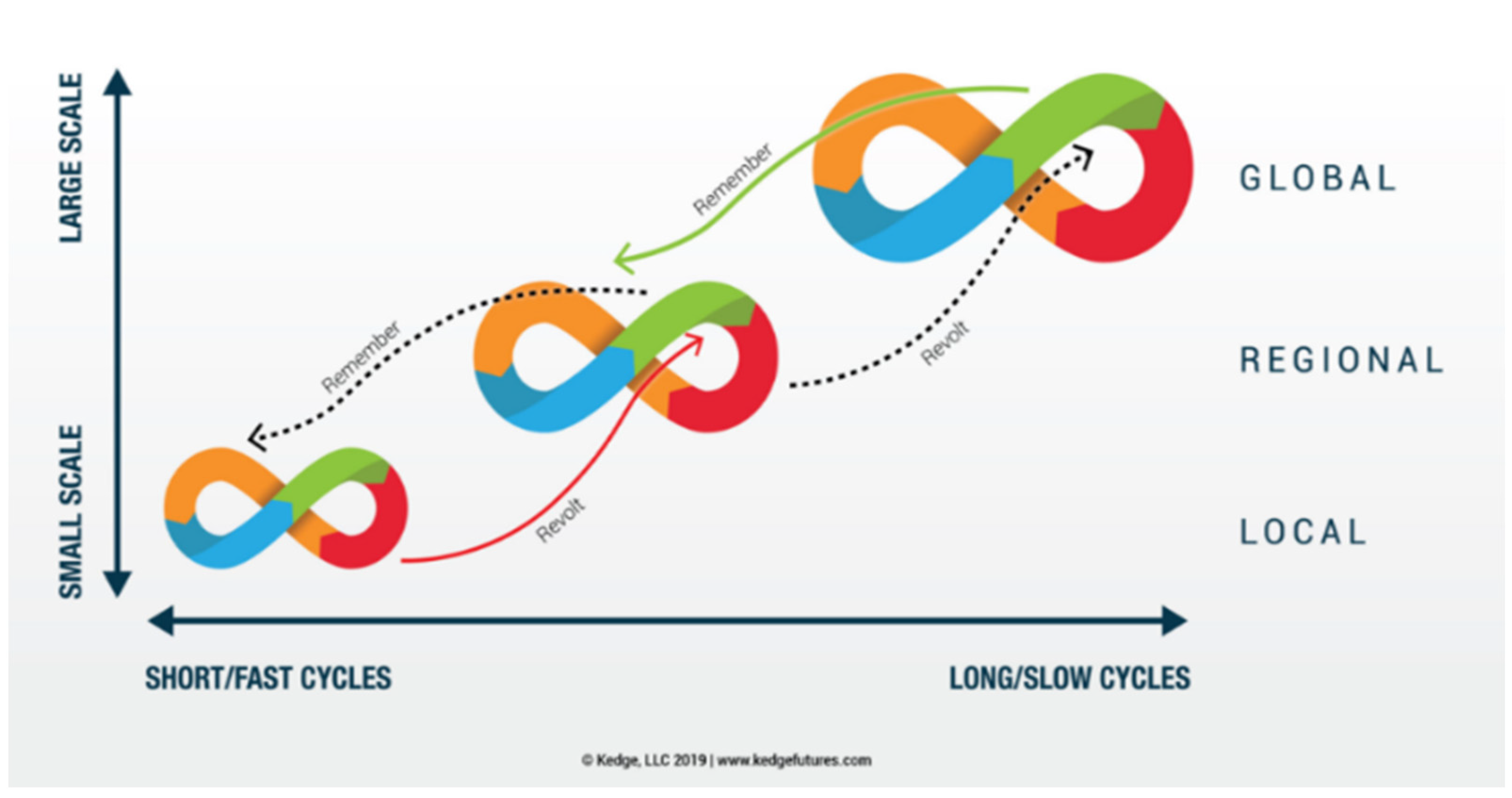
It was found that the adaptiveness of the action plans was best leveraged by an iterative (double-looped) process rather than a linear process [64] or a single-loop process. Figure 4 shows the interconnectedness of these iterative cycles at different levels of governance, illustrating the scalability of the model. A linear process does not facilitate feedback and learning from previous processes, which potentially increases the risks of planning and developing plans through an adaptive process. The circular process and the single-loop process do not facilitate changes to a disruptive or unpredicted situation. Thus, a double-loop process or a process presented as a Mobius loop has a better chance of successfully integrating adaptiveness in the traditional planning practices.
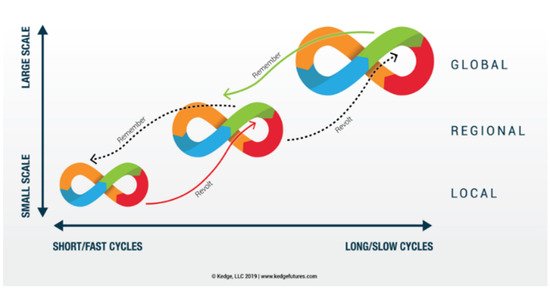
Figure 4.
Panarchy process with spatial and temporal scalability. Each section of the cycle is tagged (Green = conservation, Red = Collapse, Orange = Renewal and Blue = Growth) to show overlaps with the four phases of planning, reiterated at all scales. Red arrow denotes an upward cycle and green arrow denotes downward trends of planning challenges. (extracted from Natural Foresight).
The traditional ‘predict and plan’ model is where future trends are forecasted using scenarios, as a planning tool, for a desired outcome [65,66]. The infrastructure and land use requirements needed to accommodate and future-proof population growth are identified to achieve the desired outcomes. Quay (2010) [67] finds that the ‘predict and plan’ model works conditionally when the social and environmental systems are stable and predictable over short periods of time. When the uncertainties and complexities are high, forecasting is difficult; so, the predict and plan model does not work as anticipated. Thus, anticipatory governance measures offer a new decision-making model for planning under conditions of high uncertainty [68] and are emerging in the literature on climate change and socio-technological governance [69]. Anticipatory governance is based on concepts of foresight and adaptation and on scenarios of multiple possible futures [67] in which planners not only evaluate alternatives for their communities but also consider possibilities that they may not fully control. Uncertainty as an integral part of a planning and implementation process is new [68], but the concept of scenario planning as an integral part of planning for uncertainties is not new.
Scenario planning is found to be a versatile planning method used by water utilities to achieve stability in transformation landscapes; its applicability in addressing a wide range of challenges, not just climate change challenges, is recognised [3,9,10]. Scenario planning also has the capability to consider risks and possible solutions for a range of alternative futures [70]. According to Schoemaker (2022) [3], achieving the balance between the known and unknown aspects of the future that necessitate risk mitigation and require a degree of certainty was the main challenge of implementing an adaptive plan. The use of probabilities to assess risks—of certainty (definite need), between certainty and uncertainty (the available information is sufficient to make decisions), and uncertainty (nearly impossible to assess)—can balance the known and unknown scenarios of the future, according to Schoemaker (2022) [3]. Thus, scenario planning can lead to better-informed decision-making by understanding and bridging the gap between the different approaches used by the stakeholders and by making plans adaptive [50].
Another interpretation of the adaptive cycle in a Mobius loop formation, by Räsänen (2021) [71], builds upon the adaptive planning cycle (Figure 5a) developed by Iii (2009) [72]; it uses the perspectives of social structure and social capital and then charts them as multiple loops. These multiple loops (Figure 5b) refer to shocks—forward-looped as ‘revolt’ and historical knowledge and back-looped as ‘remember’. Figure 5b shows the alternative views of the spatial and temporal scales of connectivity in an increasing scale to demonstrate the extent of the planning regions.
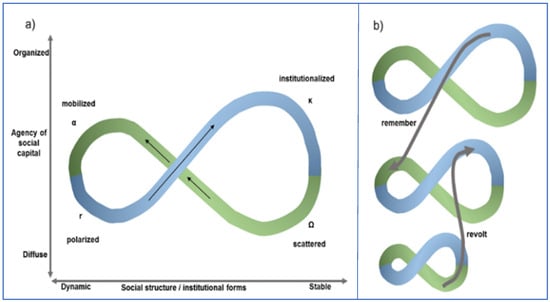
Figure 5.
Adaptive planning cycle interpretation from social structure and social capital perspectives (a). The upward arrows denote the forward loop and green broken arrows denote a back loop of interconnectedness in a social capitalism context. (b) highlights the multi-planar projection of the interpretation and the connections between the different scales by Räsänen (2021) [71].
The planning process ultimately leads to infrastructure investment decisions regarding the several available options for coping with uncertainties related to climate change. The consequences of climate change are extensive enough to question the risks and uncertainties associated with a specific project, the infrastructure investment needs, and the design process. Integrating climate change uncertainties is essential at the planning stage [30,55,73]. To assist in planning for future infrastructure needs, it is imperative for all stakeholders within the water industry, including policymakers, regulatory governments, practitioners, and professionals, to integrate the uncertainties related to water availability and changing water needs [48]. However, integrating what is not known is a difficult and confusing exercise, and these plans do not get approved. Thus, implementing an adaptive planning process is not a viable option.
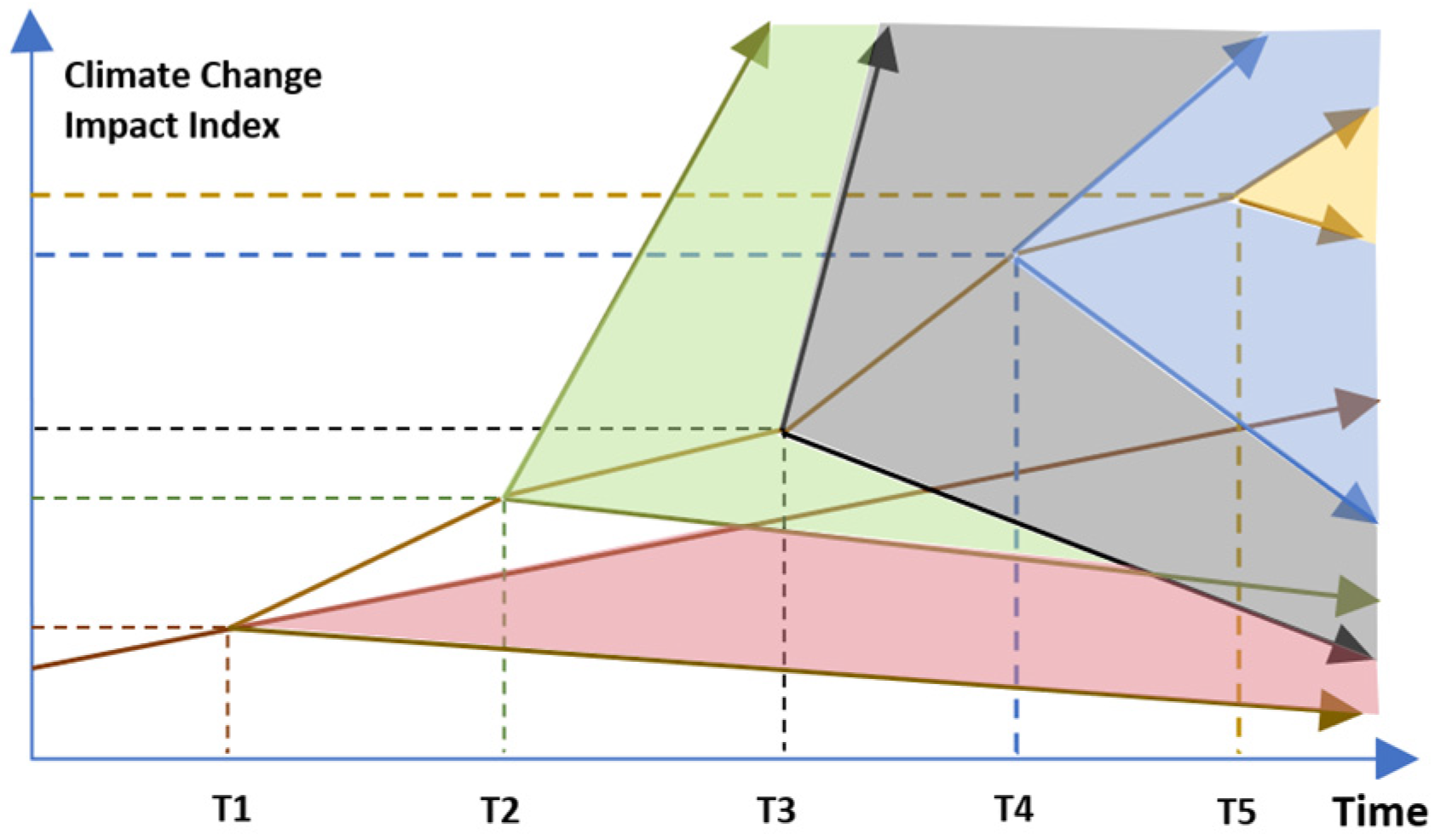
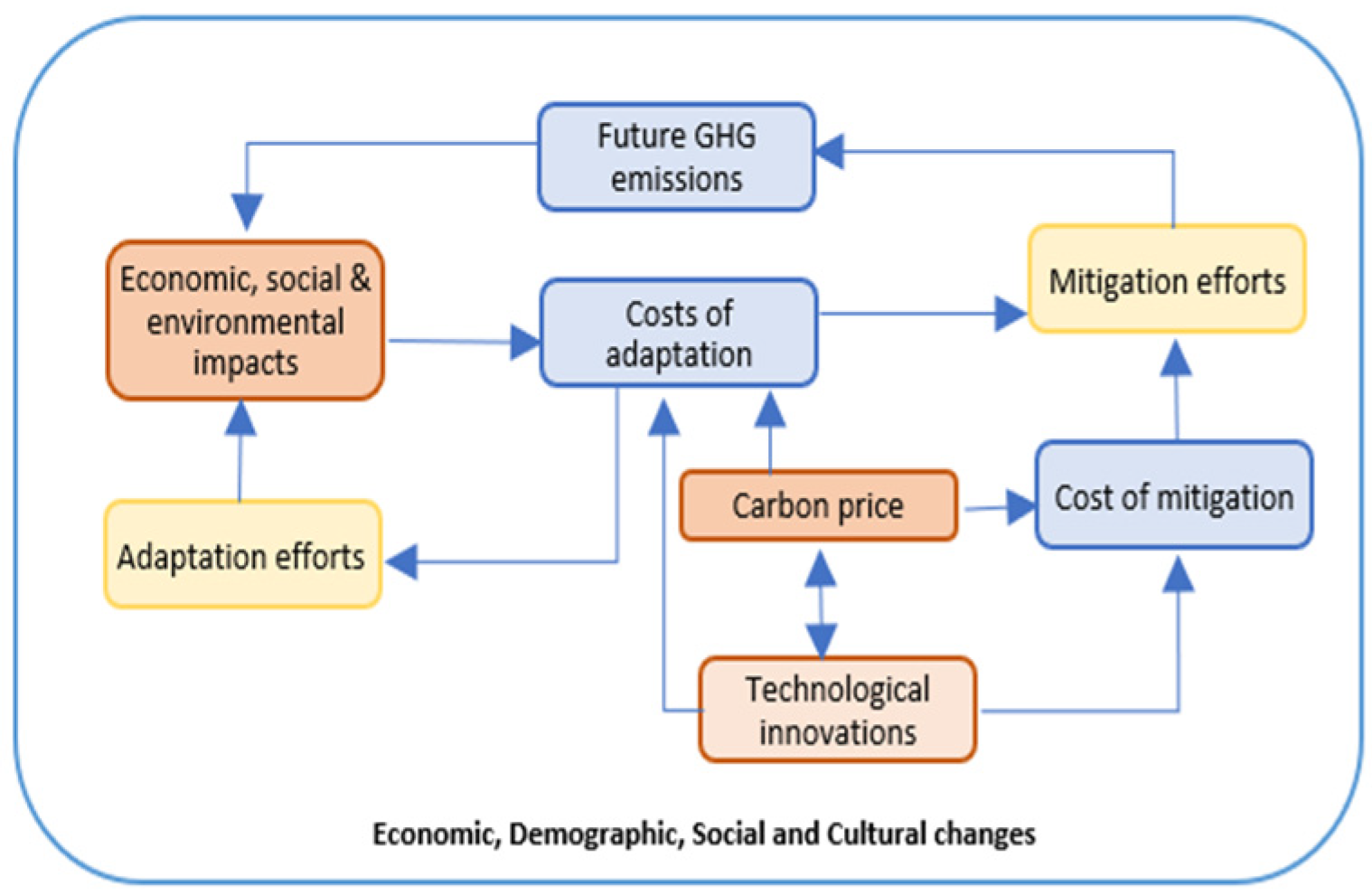
As more research is being conducted on the uncertainties related to climate change, new and more complex challenges are being identified [74]. Figure 6 shows an increase in the number of uncertainties, which evolve, expand, and fragment to varying degrees over time. Figure 7 maps the interconnectedness of the adaptation efforts and the stakeholder’s efforts [75] to reduce the risks associated with the uncertainties related to climate change. While Figure 6 highlights the complexities of climate change challenges, Figure 7 shows the connections between the social, economic, and cultural efforts to mitigate the impacts of increasing climate change challenges.
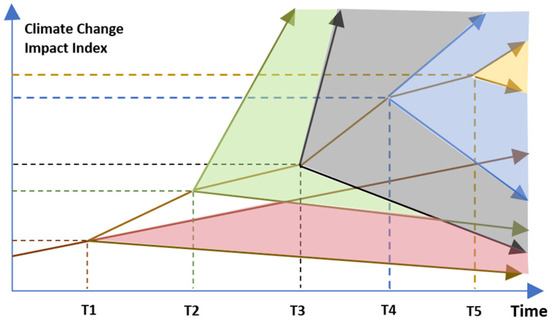
Figure 6.
Impacts of climate change over time; Giordano (2012) [75].
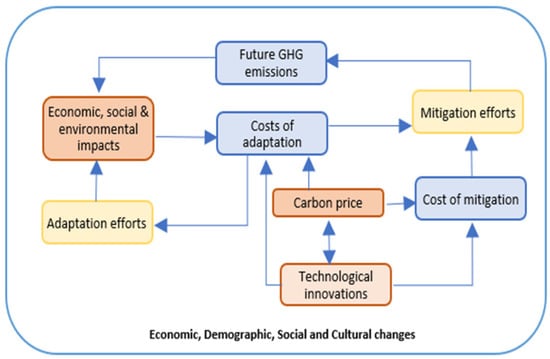
Figure 7.
Interconnectedness of adaptation efforts; Giordano (2012) [75].
The colours in Figure 6 and Figure 7 are co-related and illustrate the areas of impacts, responses, and efforts. To prepare adaptive plans with multiple scenarios, a planning process should demonstrate a high level of flexibility to be able to respond to the expanding uncertainties and employ a robust decision-making process [75,76]. The resulting adaptive plans could potentially measure the performances of various investment plans [36]. Adaptive plans are referred to as coping mechanisms for policy changes that aim to limit the negative impacts and exploit the positive impacts of climate change on the quality and level of services for the planned infrastructures [75].
Policymakers play a vital role in facilitating the inclusion of uncertainties related to climate change at the planning stage for resilience while developing long-term strategic plans. Resilience is the capacity of a system to ‘continually change and adapt yet remain within critical thresholds’ [77] and the capability to transform from one ‘stability’ landscape to another. Transformations are referred to as novelty and innovation, and crises are used as an opportunity to gather sources of knowledge and experience to navigate socio-ecological transitions between landscapes [77,78]. The impact of transformation is rationalised as promoting change at smaller scales and enabling resilience at larger scales [79]. Deliberate transformation is a two-stage process that involves breaking down the resilience of the old and then building the resilience of the new [77].
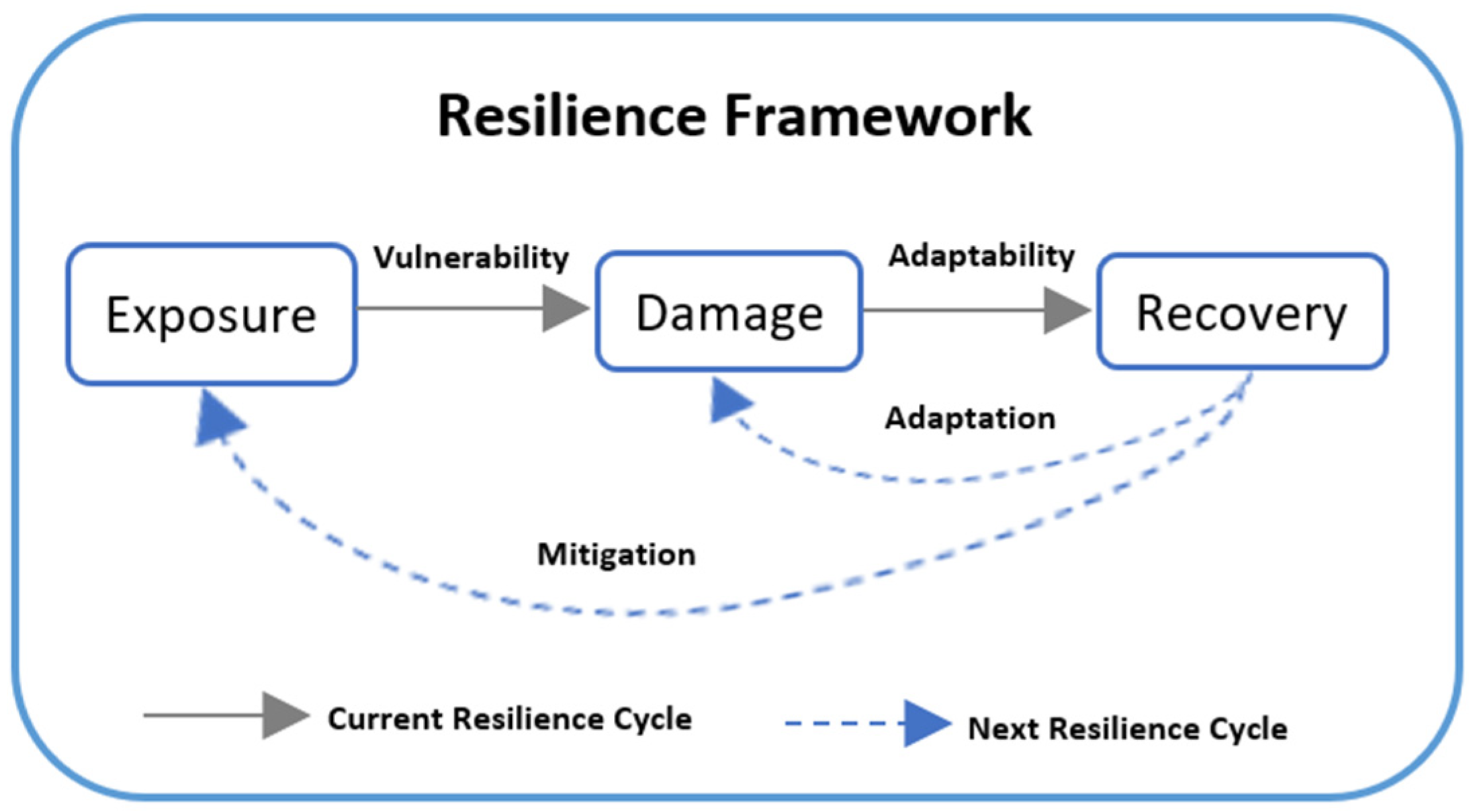
Planning for resilience [80] is carried out by adapting to damaging conditions and mitigating impacts by reducing exposure to vulnerable conditions, as shown in the resilience inference measurement (RIM) model. As shown in Figure 8, the RIM model, developed by Lam (2015) [81], serves as a basis for the implementation of adaptive planning.
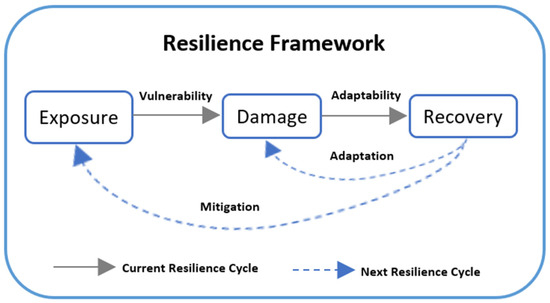
Figure 8.
Resilience inference model adapted by Lam (2015) [81].
The adequacy of the current mechanisms for tackling complex planning issues is still under debate. Traditional planning is mainly focused on fostering desired change under given and certain conditions [82]. The adaptive planning process introduces an additional level of intervention to achieve the desired change [83,84]. Skrimizea (2019) [84] defined the adaptive rationale as both a normative and analytical trajectory in the planning theory, which interacts with certainties and uncertainties. Such non-linear or adaptive rationale refers to adaptive planning as being vital for driving the co-evolution of temporal and spatial processes. In the non-linear or adaptive rationale, the adaptability component formulates both responsive and proactive integrated strategies [85,86] for a mix of certain and uncertain conditions. The decision-making responsibilities regarding which path to take lie with the planners, and their decisions are influenced by their personality traits, knowledge, and experience in the field of application.
Nearly four decades ago, Alterman (1988) [87] drew attention to the habits of a planner prevailing at the planning stage; Alterman’s observations still hold true. They are especially relevant for the adaptive planning process, where knowledge, experience, and the unique interpretations of a planner in the action plans are foregrounded. The risks associated with the individual perspective of a planner [80] could be minimised by appropriate levels of access to the organisation’s knowledge storage and by collaborating with internal teams and external stakeholders [62,88,89] to build the capacity to deal with long-term disaster recovery in a socially inclusive manner [62,90]. However, studies on urban development find that stakeholders tend to undermine the capabilities of the adaptive rationale under uncertain conditions [62,91] nestled within the strategic action plans. Such diverse findings create confusion (uncertainty) amongst the planners about the extent of stakeholder engagement and the design of the long-term strategic plans. Section 5 highlights the different ways of integrating the adaptive planning process.
5. Adaptive Planning Process—Dealing with Uncertainties
In water resource planning, dealing with uncertainty is problematic, as inadequate (over- or underused) infrastructure can have social, economic, and environmental costs [56]. The uncertainty arising from the interactions between humans and nature is amplified during the decision-making process of identifying adaptation pathways today for emerging and future risks due to natural disasters [57]. Deep uncertainty includes the surprises and proliferating uncertainties associated with changes in global emissions [57], such as the potential to trigger polar ice melts and create thermal instabilities [5]. Such uncertainties need to be considered, as adaptation too early or too late can be costly. Tools that do not rely upon assigning the levels of uncertainties (likelihoods) and can represent changing community preferences over generations are required [57,85]. However, there is a need to understand the source of deep uncertainties. Marchau (2019) [5] found the three main causes of deeply uncertain conditions, where the experts do not know or the parties taking decisions cannot agree; these are as follows: (a) the interaction of a system’s variables with appropriate models; (b) probability distributions to represent uncertainty in a model; and (c) valuing the desirability of alternative outcomes. The cautious appraisal of the situation is proposed by researchers for such scenarios [70,92]. It is still necessary to examine the trending nature and impact of current practices, prompted by policy/ies, more closely [48].
Policymaking is rife with uncertainties [57], including partial knowledge of deep uncertainties that cannot be known or agreed upon and can be contested [5]. Such uncertainties affect our ability to assess the risks of climate change impacts, including how we plan and respond to those impacts. Thus, long-term planning is often challenged by cost–benefit considerations, value propositions, and local preferences. The hybrid approach involving integrating certain and uncertain scenarios creates awareness amongst policymakers and communities, which steers them towards taking longer-term views while planning to address immediate threats [57]. Through this process, a wide range of adaptation actions are considered to transition towards threat avoidance or mitigation before the threat becomes a pervasive reality. The processes for implementing adaptive plans are anticipated to reinforce anticipatory long-term thinking by building the community’s capacity to deal with the change [59,93]. One of the most consistent trends is increasing transparency and the broader involvement of citizens in the planning process, although this engagement remains relatively weak in a sizeable proportion of countries, illustrating the need for the further development of participatory planning practices [48]. Reforms, while developing planning tools to influence the shaping of urban development, may have unintended consequences. For example, increased integration may lead to a dilution of important environmental policies in favour of economic priorities. A fully adaptable planning system may allow powerful interests to manipulate the discretion of decision makers in their favour [94], while the widespread and active engagement of citizens may not deliver community-sensitive decisions [95] nor deliver equitable water supply services. It is clear that there is a need for interventions to appropriately address and mitigate the risks in order to deliver equitable water supply services.
Appropriate intervention measures should be included to secure an acceptable and reliable water supply while planning for water supply infrastructure [16,27]. Climate change is a major cause of uncertainty in water resource planning, as source yields and their impacts are uncertain. Adaptability to changing weather conditions is increasingly viewed as a valuable design principle for strategic water planning. The decisions made in the present at a water utility impact the system’s ability to: (a) adapt to future needs [24], (b) be flexible in activating, delaying, and or replacing engineering projects [30], and (c) consider least-cost water supply intervention scheduling [30,96]. Water utilities are required to maintain efficient and reliable water supply services [97] while maintaining affordability [98]. They do so by optimising the schedule of supply augmentation projects, combined with demand reduction policies [99]. The strategic plans that perform well under a wide range of plausible scenarios [100,101] and investment plans with the least sensitivity to significant uncertainties [39,102] have robust decision-making processes [56].
A study by Groves (2015) [103] recognises the importance of a water utility’s need to prepare flexible plans and meet the organisation’s goals and objectives under the multiple uncertainties of future supply–demand management, changes in climate conditions, limited funds, and legal constraints. They also find that competition between water utilities to best one another and construct state-of-the-art infrastructure makes it difficult to integrate flexibility and to ensure the robustness of plans. Water utilities, however, simultaneously need to offer system-based technical solutions to adequately address a contested future [104,105] by improving the adaptive capacity of the strategic plans.
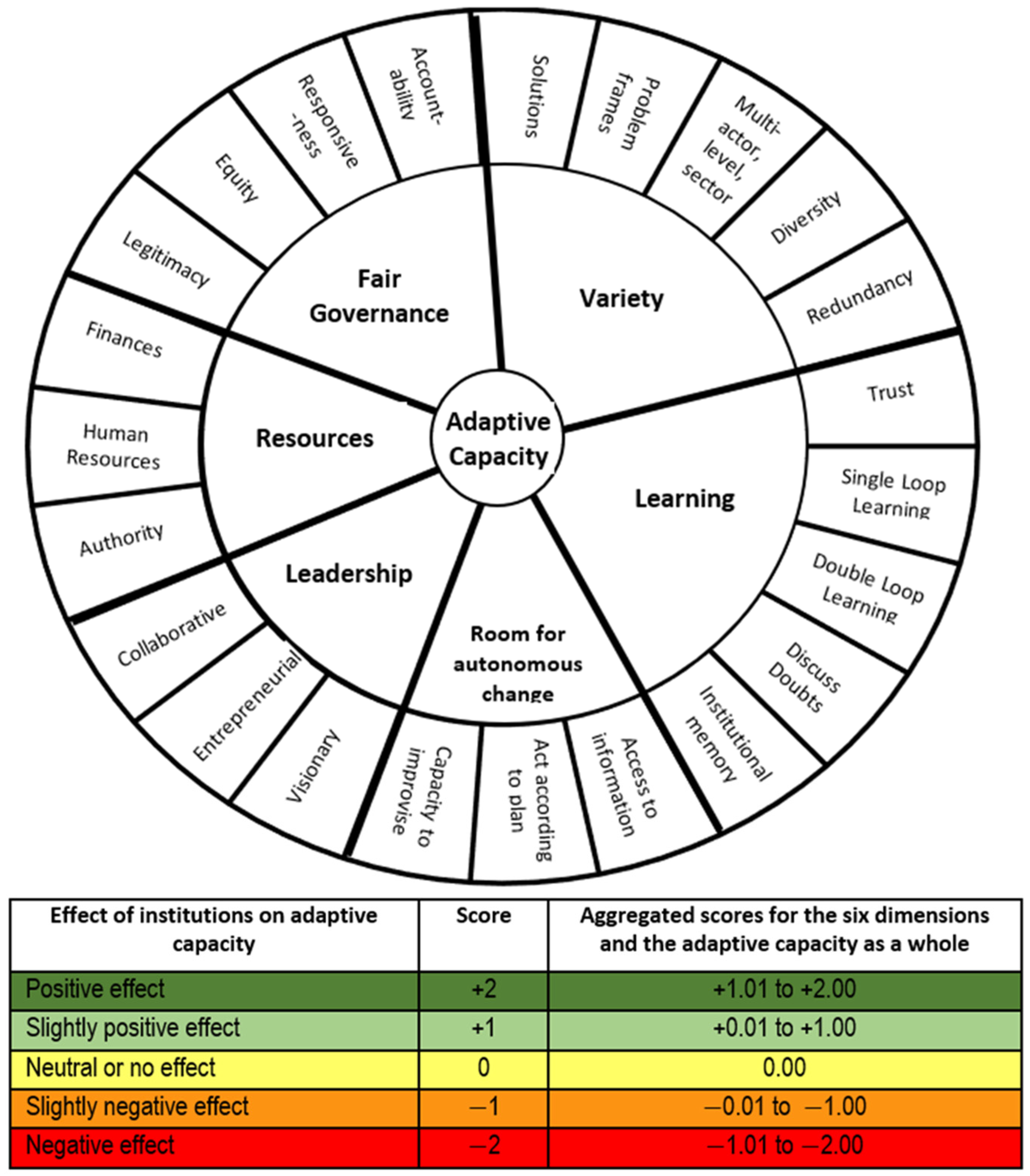
The adaptive capacity wheel (Figure 9), proposed by van den Brink (2014) [106], provides a methodological framework for improving the adaptiveness of action plans by identifying the strengths and weaknesses of each action in the plan. The colour-coded scoring chart that sits beneath the adaptive capacity wheel was designed by van den Brink (2014) [106] to understand the adaptive capacity of 6 thematic risk-prone criteria and 22 sub-criteria to measure, monitor, and improve adaptive planning practice. This colour-coding system enabled the planning process to focus on the weaker actions, improving the overall adaptive capacity of the plans to address deep uncertainties. The process of identifying the level of adaptiveness involves finding the level of impact from the scoring of the 22 actions of the outer circle using the chart (Figure 9). The score of each cluster is then averaged to obtain the level of adaptiveness of the six thematic risk-prone criteria. The average scoring of the six thematic risk-prone criteria is the level of adaptiveness of the action plan.
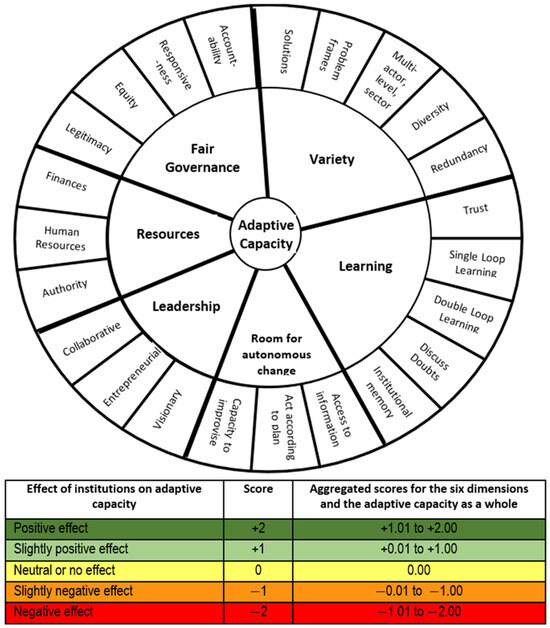
Figure 9.
Adaptive capacity wheel for checking the adaptiveness of action plans using the colour-coded score chart by van den Brink (2014) [106].
‘Learning by doing’ is another adaptive approach used by water utilities to cope with uncertainties as a part of green infrastructure planning; it involves adapting to changing conditions by improving the efficacy of management plans. However, the value (of learning) vs. cost (of providing the learning opportunity) is a challenge for both the water practitioners when delivering the learning and the water utilities when procuring the learnings. To overcome these cost implications, Hung (2022) [107] studied the stepwise approach of learning from direct and indirect investments in building capacity and multi-level learning processes. Hung (2022) [107] also proposed quantifying the value of learning and adaptability in systems performance and categorised the adaptiveness of decision-making into three major types: (1) non-adaptive—no learning between decisions; (2) passive adaptive—accidental learning; and (3) active adaptive—a considered learning approach that actively seeks potential learning opportunities when choosing from an available option.
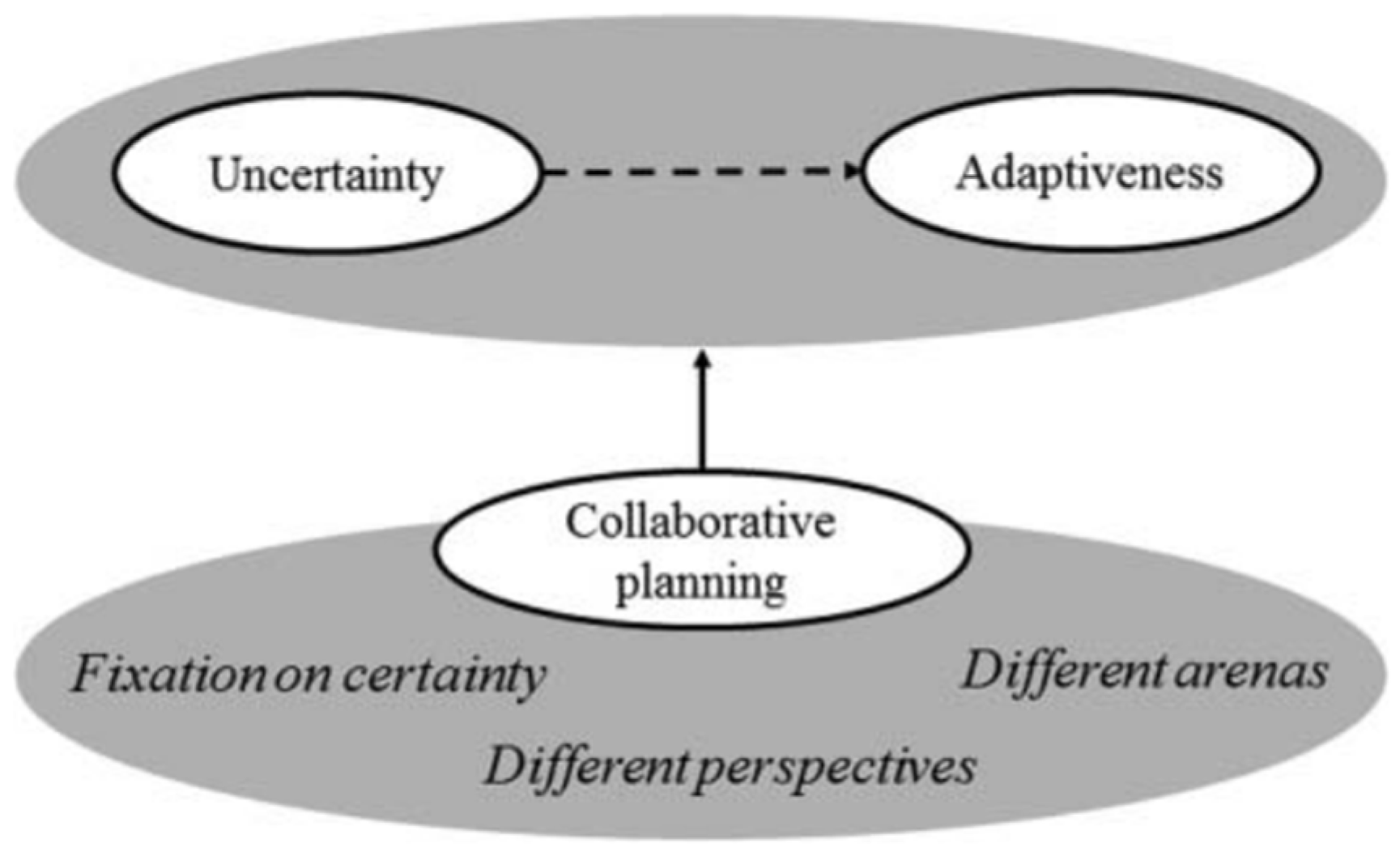
The collaborative governance model is yet another emerging approach that is often used to deal with uncertainties in managing water resources and developing adaptive strategies. Collaboration is deemed to be difficult to carry out due to the vast number of diverse stakeholders involved in the decision-making process. The collective responsibility of the decision-making group dissolves the impact of ownership, putting the implementation at risk. However, when collaborative efforts are successful, the outcomes achieved are exemplified. However, the influence of collaboration on managing uncertainties has not been researched in greater depth [105,108]; Figure 10 illustrates a simplified version of collaborative planning as a pathway from uncertain future conditions to adaptive plans that address uncertainties.
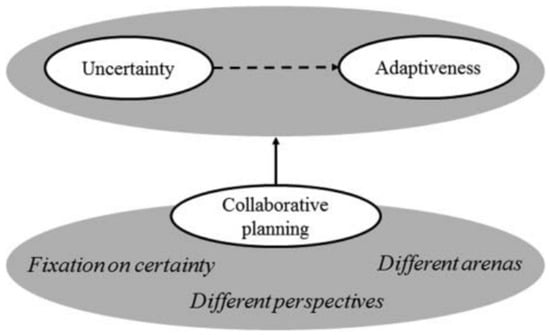
Figure 10.
Co-relation between uncertainty, adaptiveness, and collaborative planning; Zandvoort (2019) [105].
Zandvoort (2019) [105] also identified a conceptual relationship between uncertainty, adaptiveness, and collaborative planning, where collaborative planning provides a different viewpoint on the fixations of certainty prevailing in planners and the different areas of water management to understand uncertainty and improve adaptiveness. However, the success of this collaborative governance model is highly dependent on their relationships and the position or rank of the collaborators [109,110].
The different ways of integrating adaptiveness in plans discussed in this section highlight its needs and at the same time present the barriers to implementation. Section 6 discusses and provides conclusive remarks.
6. Discussion and Conclusions
Dealing with deep uncertainty is multifaceted and complex. The concept of adaptive planning is an emerging solution that deals with the deep uncertainties that are usually associated with climate change. However, uncertainties are not limited to changes in the climate and also include changes in the society, economy, political agendas, institutional mindset, and personal approach. It is vital to understand the interconnectedness of the sources and sinks of emissions that impact planning and the impacts of climate change on water resources (e.g., on water availability). This process of adaptive planning includes stakeholder involvement in designing adaptation pathways and mitigation measures to achieve resilience. The adaptive planning framework can be described, operationalised, and implemented by the decision makers and planners even without achieving a consensus in the theoretical and empirical literature [80]. Though the existing interpretations of adaptive planning processes aim to address the challenges of climate change and the uncertainties prevailing in the governance, the regulatory and resource management bodies play a vital role at the planning stage, which cannot be overlooked.
The two main conceptual frameworks of adaptive planning processes are
- (1)
- The DAPP concept;
- (2)
- The panarchy model or Mobius loop concept:
- The basic concept [64];
- The panarchy model by ‘Natural Foresight’;
- The social structure and social capital perspective [71].
- (3)
- The DAPP concept was found to be the most widely used framework for designing adaptive plans. Lawrence (2017) [59] identified four main intervention methods for incorporating adaptiveness at the implementation stage and three catalysts for the uptake of the DAPP. However, the implementation experience or the levels of success of the DAPP are not known in the peer-reviewed literature.
- (4)
- The panarchy model represented by the Mobius loop or infinity loop was the only model illustrated as a scalable model, connecting the past to the future.
- (a)
- The ‘Panarchy model’ was developed by Gunderson (2002) [64] to identify the patterns of change in the ecosystem and eco-social systems.
- (b)
- Natural Foresight builds upon this basic concept of panarchy developed by Gunderson (2002) [64] to integrate adaptability in the action plans using a Mobius loop approach through four main steps: explore, discover, create, and map, in order to drive the implementation of the adaptive planning concept not just at a local level but also in temporal and spatial dimensions to assist in progressive adaptation.
- (c)
- Iii (2009) [72] re-interprets the panarchy model developed by Gunderson (2002) [70] and provides us with the social structure and social capitalism perspective. Räsänen (2021) [71] then builds upon the adaptive planning cycles (Figure 3) developed by Iii (2009) [72] and charts them as a multi-loop structure. The social capitalism perspective is used to organise priorities and social structure to diffuse knowledge, ultimately assisting the move from dynamic to stable conditions [72]. The four steps of panarchy are adapted to the terminology of the social structures as polarised, institutionalised, scattered, and mobilised.
These different versions of the panarchy model highlight the need for an iterative process to ensure that current and emerging issues are included in the plans and are flexible enough to weather intense changes in managing water supply requirements. The ‘adaptability’ of plans can also be achieved through intervention techniques [59,84], the collaborative approach [31,105], and the use of score charts to quantify and map the level of adaptability in a plan [106].
The major factors contributing to the success of the adaptive plans are resilience under unstable climatic conditions; flexibility in implementation; the ability to address urgent needs; and early infrastructure trend detection [111] to predict disruptions or shocks. The adaptiveness of decision-making is categorised into three major types: (1) non-adaptive (no learning between decisions); (2) passive adaptive (accidental learning); and (3) active adaptive (considered learning) to quantify the value of learning and system performance when choosing from the available options [107]. Collaboration is used as an intervention tool to move from uncertainty to adaptiveness [105].
The adaptive capacity wheel by van den Brink (2014) [106] provides a methodological framework for identifying the strengths and weaknesses of the action plans and improving the adaptiveness of these action plans. Research and thorough risk assessments form the basis for a robust plan and monitoring techniques, bringing us a step closer to dealing with uncertainties.
The adaptive planning concept is still in its infancy and is being progressively improved as new challenges come to light. Although researchers have proposed many versions of adaptation methods for over a decade, as discussed in this study, each researcher has focussed on one particular area in great detail and lacks comprehensive guidance to integrate adaptiveness in the traditional planning practice. The unavailability of a comprehensive adaptive planning process integrated in the traditional planning practice is a gap for future research.
Furthermore, there is little or no knowledge of success in practice for the existing adaptive planning concepts and models. This is a gap that can be managed by ‘policymakers’ by collating the statistical data as a check to determine how many utilities used the adaptive planning process and what the outcomes were. The case studies of successful and unsuccessful adaptive planning practice have formed a strong experiential foundation. The lessons from the successful and unsuccessful cases—to understand the factors driving successful implementation and the periodic evaluations of the adaptive planning practiced at the different governance levels or regional scales—provide a strong foundation with which to either build upon the current adaptive planning concepts or design a new framework by eliminating the redundant problems of the past and including the new and emerging challenges.
Funding
This is an independent PhD research program at the Institute of Sustainable Futures, University of Technology, Sydney. No funds have been provided to support the publication of this study.
Data Availability Statement
This is a desktop research study and does not involve any external stakeholder engagement. All interpretations provided in this study either reference the original source or are the author’s own analytical interpretation.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge my mentors Simon Fane and Pierre Mukheibir for their guidance and support in my PhD journey. I would like to acknowledge Fiona Lord for reviewing and providing vital comments to improve the readability of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fu, Z.H.; Zhao, H.J.; Wang, H.; Lu, W.T.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.C. Integrated planning for regional development planning and water resources management under uncertainty: A case study of Xining, China. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinckmann, J.; Kim, S.M. Why We Plan: The Impact of Nascent Entrepreneurs’ Cognitive Characteristics and Human Capital on Business Planning. Strat. Entrep. J. 2015, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoemaker, P.J.H. Advanced Introduction to Scenario Planning; Edward Elgar Publishing Limited: Cheltenham, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shirmohammadi, B.; Malekian, A.; Salajegheh, A.; Taheri, B.; Azarnivand, H.; Malek, Z.; Verburg, P.H. Scenario analysis for integrated water resources management under future land use change in the Urmia Lake region, Iran. Land Use Policy 2020, 90, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchau, V.A.W.J.; Walker, W.E.; Bloemen, P.J.T.M.; Popper, S.W. Decision Making under Deep Uncertainty: From Theory to Practice; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pilz, M.; Kunzmann, K.; Herrmann, C.; Rauch, G.; Kieser, M. Optimal planning of adaptive two-stage designs. Stat. Med. 2021, 40, 3196–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, R. Can Adaptive Comanagement Help to Address the Challenges of Climate Change Adaptation? Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Ahern, J. ‘Learning by doing’: Adaptive planning as a strategy to address uncertainty in planning. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2008, 51, 543–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadnis, S.S.; Sheffi, Y.; Caplice, C.G. Strategic Planning for Dynamic Supply Chains: Preparing for Uncertainty Using Scenarios; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C.A.; Bailey, C.J.; Marra, R.P.; Woods, G.J.; Ormerod, K.J.; Lansey, K. Scenario Planning to Address Critical Uncertainties for Robust and Resilient Water–Wastewater Infrastructures under Conditions of Water Scarcity and Rapid Development. Water 2012, 4, 848–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Utility Pathways in a Circular Economy; IWA: Nuremberg, Germany, 2016.
- Jazbec, M.; Mukheibir, P.; Turner, A. Transitioning the Water Industry with the Circular Economy FINAL 12102020; Water Services Association of Australia, Institute of Sustainable Futures, University of Technology Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhabitskii, M.G.; Andryenko, A.Y.; Malyshev, V.N.; Chuykova, S.V.; Zhosanov, A.A. Digital transformation model based on the digital twin concept for intensive aquaculture production using closed water circulation technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 723, 032064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, T. What kind of governance for what kind of equity? Towards a theorization of justice in water governance. Water Int. 2014, 39, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, F.A.; Pulido-Velázquez, M. Efficiency, equity, and sustainability in a water quantity–quality optimization model in the Rio Grande basin. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 66, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, T.; Pachos, K.; Harou, J.J. Real-Options Water Supply Planning: Multistage Scenario Trees for Adaptive and Flexible Capacity Expansion Under Probabilistic Climate Change Uncertainty. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 5069–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haasnoot, M.; Kwakkel, J.H.; Walker, W.E.; ter Maat, J. Dynamic adaptive policy pathways: A method for crafting robust decisions for a deeply uncertain world. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanpurwala, T. Drivers and Challenges of Implementing Integrated Water-Cycle Management Strategy in Regional NSW. Ph.D. Thesis, Macquarie University, Macquarie Park, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwala, T.; Mukheibir, P.; Fane, S. A Review and Comparative Analysis of IWCM Concepts in Australia and Similar Jurisdictions. Water 2023, 15, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, W.W.; Eastman, C.; Johnson, N.; Kortanek, K. Systems approaches to urban planning: Mixed, conditional, adaptive and other alternatives. Policy Sci. 1971, 2, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellaschi, J.J. The Design and Simulation of Selected Aspects of an Adaptive Planning Andcontrol System Incorporating Managerial Decision Rules; ProQuest Dissertations Publishing: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Blevins; Ramamoorthy. Aspects of a Dynamically Adaptive Operating System. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1972, 100, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylander, W.C., III; Pearson, J.D. CHAMP: A Chance Constrained Adaptive Planning Model; Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Werners, S.E.; Wise, R.M.; Butler, J.R.A.; Totin, E.; Vincent, K. Adaptation pathways: A review of approaches and a learning framework. Environ. Sci. Policy 2021, 116, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOBL. An Adaptive Approach to the Strategic Planning Process. 2023. Available online: https://academy.nobl.io/an-adaptive-approach-to-the-strategic-planning-process/ (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Williams, B.K. Adaptive management of natural resources—Framework and issues. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwater, R.; Atwater, P.; Atwater, D.; Cruz, J. Adaptation, Integration, and Connection—How Water Utilities Can Plan for Uncertainty. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2015, 107, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukheibir, P. Small Towns Water Access and Climate Change—Towards Sustainable Access to Urban Water Services under Projected Climate Change Impacts; Lambert Academic Publishing: Saarbrucken, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report; Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Greig, L.A.; Marmorek, D.R.; Murray, C.; Robinson, D.C.E. Insight into Enabling Adaptive Management. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, J.R. Approaches to Planning Water Resources. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2021, 147, 04021058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.; Costantino, N.; Giustolisi, O. Flexible investment planning for water distribution networks. J. Hydroinform. 2018, 20, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, C. Challenges in adaptive management of riparian and coastal ecosystems. Ecol. Soc. 1997, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadin, V.; Stead, D.; Dąbrowski, M.; Fernandez-Maldonado, A.M. Integrated, adaptive and participatory spatial planning: Trends across Europe. Reg. Stud. 2021, 55, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S.; Strzepek, K.; Alsaati, A.; de Weck, O. Learning and flexibility for water supply infrastructure planning under groundwater resource uncertainty. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 114022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.R.; Uddin, W.; Haas, R.C.G. Public Infrastructure Asset Management, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, S.-R.; Suh, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, H.S. Urban water infrastructure optimization to reduce environmental impacts and costs. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSW Auditor General’s Report. Support for Regional Town Water Infrastructure; Performance Audit Report; Audit Office of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 2020.
- Huskova, I.; Matrosov, E.S.; Harou, J.J.; Kasprzyk, J.R.; Lambert, C. Screening robust water infrastructure investments and their trade-offs under global change: A London example. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2016, 41, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kc, B.K.; Wu, X.; Suwal, B.; Whittington, D. The costs of delay in infrastructure investments: A comparison of 2001 and 2014 household water supply coping costs in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 7078–7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, J.-P.; Bornemann, B. The Politics of Reflexive Governance—Challenges for Designing Adaptive Management and Transition Management. Ecol. Soc. 2011, 16, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J. The Practice of Environmental Scenario Analysis. In Environmental Futures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.; Liu, Y.; Hartmann, H.; Stewart, S.; Wagener, T.; Semmens, D.; Stewart, R.; Gupta, H.; Dominguez, D.; Dominguez, F.; et al. A formal framework for scenario development in support of environmental decision-making. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berner, C.L.; Flage, R. Creating risk management strategies based on uncertain assumptions and aspects from assumption-based planning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2017, 167, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; Herman, J.; Lund, J.; Madani, K. Adaptive water infrastructure planning for nonstationary hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 118, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termeer, C.J.A.M.; Dewulf, A.; van Lieshout, M. Disentangling Scale Approaches in Governance Research: Comparing Monocentric, Multilevel, and Adaptive Governance. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, J.; Vengosh, A.; Weinthal, E. Climate change, water resources, and the politics of adaptation in the Middle East and North Africa. Clim. Chang. 2010, 104, 599–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, K.S.M. Engineering Options: A Proactive Planning Approach for Aging Water Resource Infrastructure under Uncertainty. Ph.D. Thesis, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, H. FactorX-Challenges Implementation strategies and examples for a sustainable use of natural resources. In Eco-Efficiency in Industry and Science; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Loucks, D.P.; van Beek, E. Water Resource Systems Planning and Management—An Introduction to Methods, Models, and Applications; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Xu, X. Can resource policy adjustments effectively curb regional “resource curse”? New evidences from the “energy golden triangle area” of China. Resour. Policy 2021, 73, 102146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwadijk, J.C.J.; Haasnoot, M.; Mulder, J.P.M.; Hoogvliet, M.M.C.; Jeuken, A.B.M.; van der Krogt, R.A.A.; van Oostrom, N.G.C.; Schelfhout, H.A.; van Velzen, E.H.; van Waveren, H.; et al. Using adaptation tipping points to prepare for climate change and sea level rise: A case study in the Netherlands. WIREs Clim. Chang. 2010, 1, 729–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamekye, A.B.; Dewulf, A.; Van Slobbe, E.; Termeer, K.; Pinto, C. Governance arrangements and adaptive decision-making in rice farming systems in Northern Ghana. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2018, 86, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakkel, J.H.; Walker, W.E.; Marchau, V.A. Classifying and communicating uncertainties in model-based policy analysis. Int. J. Technol. Policy Manag. 2010, 10, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessai, S.; van der Sluijs, J.P. Uncertainty and Climate Change Adaptation: A Scoping Study; Copernicus Institute for Sustainable Development and Innovation, Department of Science Technology and Society: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, W.E.; Rahman, S.; Cave, J. Adaptive policies, policy analysis, and policy-making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 128, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Bell, R.; Stroombergen, A. A Hybrid Process to Address Uncertainty and Changing Climate Risk in Coastal Areas Using Dynamic Adaptive Pathways Planning, Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis & Real Options Analysis: A New Zealand Application. Sustainability 2019, 11, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, L.M.; Haasnoot, M.; ter Maat, J.; Kwakkel, J.H. Designing monitoring arrangements for collaborative learning about adaptation pathways. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 69, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.; Haasnoot, M. What it took to catalyse uptake of dynamic adaptive pathways planning to address climate change uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Policy 2017, 68, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekpour, S.; Newig, J. Putting adaptive planning into practice: A meta-analysis of current applications. Cities 2020, 106, 102866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giezen, M. Navigating Mega Projects through Complexity and Uncertainty: Strategic and Adaptive Capacity in Planning and Decision-Making; Institutional Repository of the University of Amsterdam (UvA): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/11245/2.106042 (accessed on 13 May 2024).
- Erfani, T.; Harou, J.J. Adaptive water resource planning using decision-rules. Adv. Water Resour. 2021, 154, 103961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.C. Designing Regenerative Cultures; Triarchy Press: Axminster, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gunderson, L.H.; Holling, C.S. Panarchy: Understanding Transformations in Human and Natural Systems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brotchie, R.; Brooks, K.; Plas, G.; Williams, K. Planning for uncertainty: Scenarios & adaptive pathways. In Proceedings of the OZ WATER 2019, Melbourne, Australia, 7–9 May 2019; Australian Water Association: Chatswood, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, C.; Schoups, G.; van de Giesen, N. Scenario development for water resource planning and management: A review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quay, R. Anticipatory Governance: A Tool for Climate Change Adaptation. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2010, 76, 496–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berke, P.; Cooper, J.; Aminto, M.; Grabich, S.; Horney, J. Adaptive Planning for Disaster Recovery and Resiliency: An Evaluation of 87 Local Recovery Plans in Eight States. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2014, 80, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guston, D.H. Innovation policy: Not just a jumbo shrimp. Nature 2008, 454, 940–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, A.; Garnett, K.; Pollard, S.J.T.; Lickorish, F.; Jude, S.; Leinster, P. Fusing strategic risk and futures methods to inform long-term strategic planning: Case of water utilities. Environ. Syst. Decis. 2021, 41, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räsänen, A. Cross-scale interactions in flood risk management: A case study from Rovaniemi, Finland. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 57, 102185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin Iii, F.S.; Folke, C.; Kofinas, G. A Framework for Understanding Change; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, P.A.; Ray, P.A.; Brown, C.M. Confronting Climate Uncertainty in Water Resources Planning and Project Design: The Decision Tree Framework, 1st ed.; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dessai, S.; Hulme, M.; Lempert, R.; Pielke, R., Jr. Do We Need Better Predictions to Adapt to a Changing Climate? Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2009, 90, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, T. Adaptive planning for climate resilient long-lived infrastructures. Util. Policy 2012, 23, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalau, J.; Torabi, E.; Edwards, N.; Howes, M.; Morgan, E. A critical exploration of adaptation heuristics. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 32, 100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.R.; Walker, B.; Scheffer, M.; Chapin, T.; Rockström, J. Resilience Thinking: Integrating Resilience, Adaptability and Transformability. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.J.Z.; Carenzo, S.; Charles, G.; Gutberlet, J.; Kain, J.-H.; Oloko, M.O.; Reynosa, J.P.; Zapata, P. Grassroots innovations in ‘extreme’ urban environments. The inclusive recycling movement. Environ. Plan. C Politi Space 2023, 41, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaniotou, A.; Pritsa, A.; Kyriakou, E.-A. Observational Evidence of the Need for Gender-Sensitive Approaches to Wildfires Locally and Globally: Case Study of 2018 Wildfire in Mati, Greece. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudec, O. Cities of Resilience: Integrated Adaptive Planning. Kvalita Inovácia Prosperita 2017, 21, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.S.-N.; Qiang, Y.; Arenas, H.; Brito, P.; Liu, K.-B. Mapping and assessing coastal resilience in the Caribbean region. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 42, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.R.; Farrelly, M.A. Delivering sustainable urban water management: A review of the hurdles we face. Water Sci. Technol. 2009, 59, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauws, W. Embracing Uncertainty Without Abandoning Planning: Exploring an Adaptive Planning Approach for Guiding Urban Transformations. DISP Plan. Rev. 2017, 53, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrimizea, E.; Haniotou, H.; Parra, C. On the ‘complexity turn’ in planning: An adaptive rationale to navigate spaces and times of uncertainty. Plan. Theory 2018, 18, 122–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.E.; Haasnoot, M.; Kwakkel, J.H. Adapt or Perish: A Review of Planning Approaches for Adaptation under Deep Uncertainty. Sustainability 2013, 5, 955–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelens, L.; de Roo, G. Planning of undefined becoming: First encounters of planners beyond the plan. Plan. Theory 2016, 15, 42–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterman, R. Adaptive planning. Cogn. Sci. 1988, 12, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmouch, A.C.; Stakeholder, D. Engagement for Inclusive Water Governance: “Practicing What We Preach” with the OECD Water Governance Initiative. Water 2016, 8, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoradeniya, B.; Maheshwari, B. Strategies and Frameworks for Effective Stakeholders Engagement for Water Governance Leadership: A Review. New Water Policy Pr. 2018, 4, 19–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, D.R.; Plummer, R.; Berkes, F.; Arthur, I.R.; Charles, A.T.; Davidson-Hunt, I.J.; Diduck, A.P.; Doubleday, N.C.; Johnson, D.S.; Marschke, M.; et al. Adaptive co-management for social–ecological complexity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savini, F. Self-Organization and Urban Development: Disaggregating the City-Region, Deconstructing Urbanity in Amsterdam. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2016, 40, 1152–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rouquette, J.; Lerner, D.N. Integrated modelling for Sustainability Appraisal of urban river corridors: Going beyond compartmentalised thinking. Water Res. 2013, 47, 7221–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, R.; Hunter, S.; Christoff, T.; Rehring, J.; Courtney, B. Adaptive Planning: A Resilience Model for Communities. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2023, 115, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Round, J.; Paulden, M. Incorporating equity in economic evaluations: A multi-attribute equity state approach. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2018, 19, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, C. Strategic Stakeholder Engagement, 1st ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Padula, S.; Harou, J.J.; Papageorgiou, L.G.; Ji, Y.; Ahmad, M.; Hepworth, N. Least Economic Cost Regional Water Supply Planning—Optimising Infrastructure Investments and Demand Management for South East England’s 17.6 Million People. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 5017–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NSW Government. Water Management (General) Regulation 2018—Regulatory Impact Statement; NSW Government: Sydney, Australia, 2018.
- IPART. IPART—Final Report—LG Regulatory Burdens; IPART: Sydney, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mortazavi-Naeini, M.; Kuczera, G.; Cui, L. Application of multiobjective optimization to scheduling capacity expansion of urban water resource systems. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 4624–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, T.; Pachos, K.; Harou, J.J. Decision-dependent uncertainty in adaptive real-options water resource planning. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 136, 103490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempert, R.J.; Groves, D.G.; Popper, S.W.; Bankes, S.C. A General, Analytic Method for Generating Robust Strategies and Narrative Scenarios. Manag. Sci. 2006, 52, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.W.; Lempert, R.J.; Keller, K.; Hackbarth, A.; Mijere, C.; McInerney, D.J. Robust Climate Policies Under Uncertainty: A Comparison of Robust Decision Making and Info-Gap Methods. Risk Anal. 2012, 32, 1657–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, D.G.; Bloom, E.; Lempert, R.J.; Fischbach, J.R.; Nevills, J.; Goshi, B. Developing Key Indicators for Adaptive Water Planning. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2015, 141, 05014008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butsch, C.; Hermans, L.M.; Farrelly, M.A.; Zandvoort, M. Editorial: Actors and adaptive planning in water management. Front. Water 2022, 4, 991338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandvoort, M.; van der Brugge, R.; van der Vlist, M.J.; Brink, A.v.D. Dealing with uncertainty in collaborative planning: Developing adaptive strategies for the IJsselmeer. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2019, 62, 248–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, D.; Meijerink, S.; Termeer, C.; Gupta, J. Climate-proof planning for flood-prone areas: Assessing the adaptive capacity of planning institutions in the Netherlands. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 981–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, F.; Hobbs, B.F.; McGarity, A.; Chen, X. A Modeling Framework for Assessing the Value of Learning in Dynamic Adaptive Planning: Application to Green Infrastructure Investment Evaluation. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinagre, V.; Fidélis, T.; Luís, A. How Can We Adapt Together? Bridging Water Management and City Planning Approaches to Climate Change. Water 2023, 15, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blythe, J.L.; Cohen, P.J.; Eriksson, H.; Harohau, D. Do governance networks build collaborative capacity for sustainable development? Insights from Solomon Islands. Environ. Manag. 2022, 70, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cisneros, P. What makes collaborative water governance partnerships resilient to policy change? A comparative study of two cases in Ecuador. Ecol. Soc. 2019, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeuken, A.; Haasnoot, M.; Reeder, T.; Ward, P. Lessons learnt from adaptation planning in four deltas and coastal cities. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2015, 6, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).