Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Deterioration of Powder Crystal Dolomite under Dissolution
Abstract
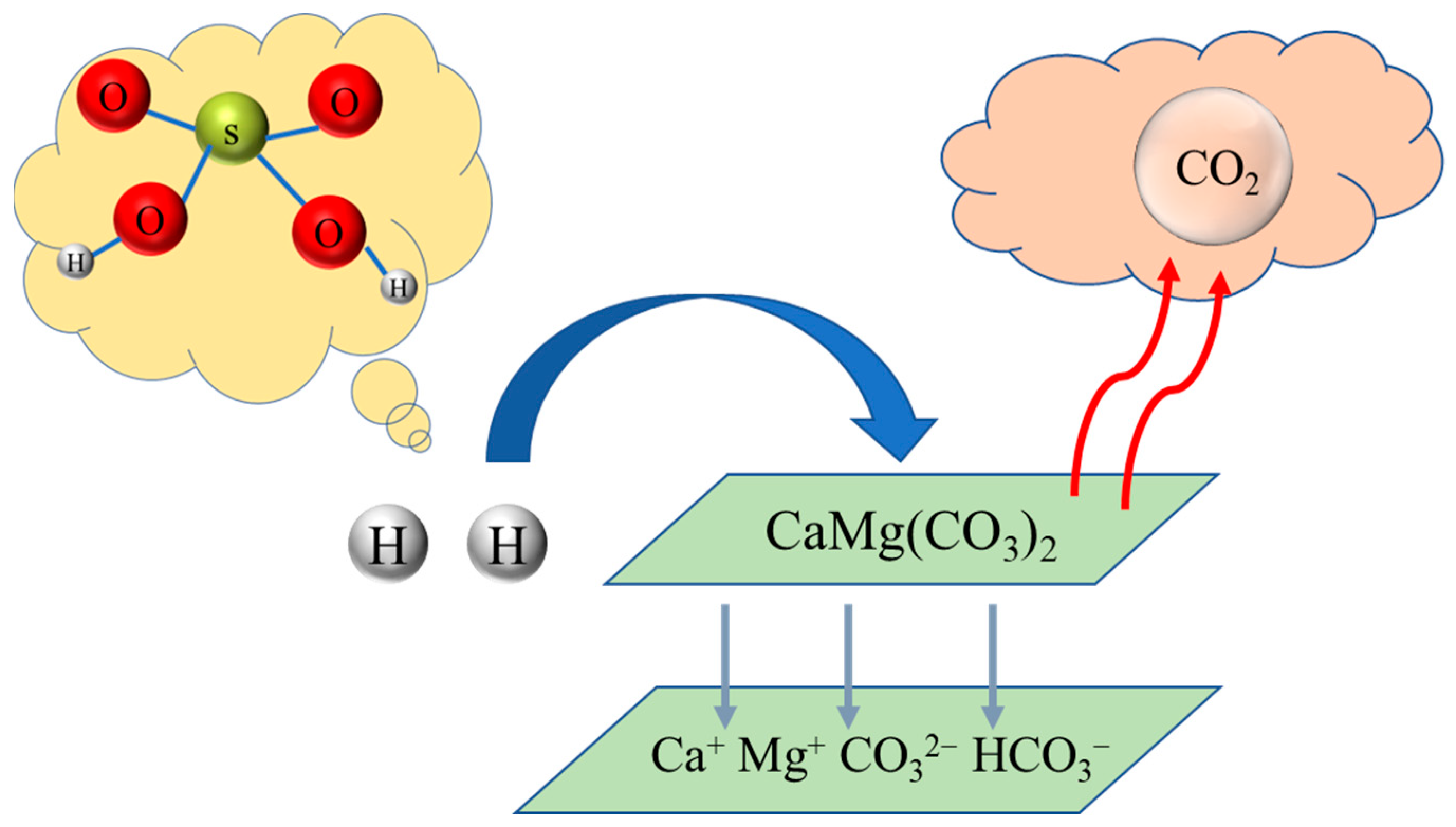
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
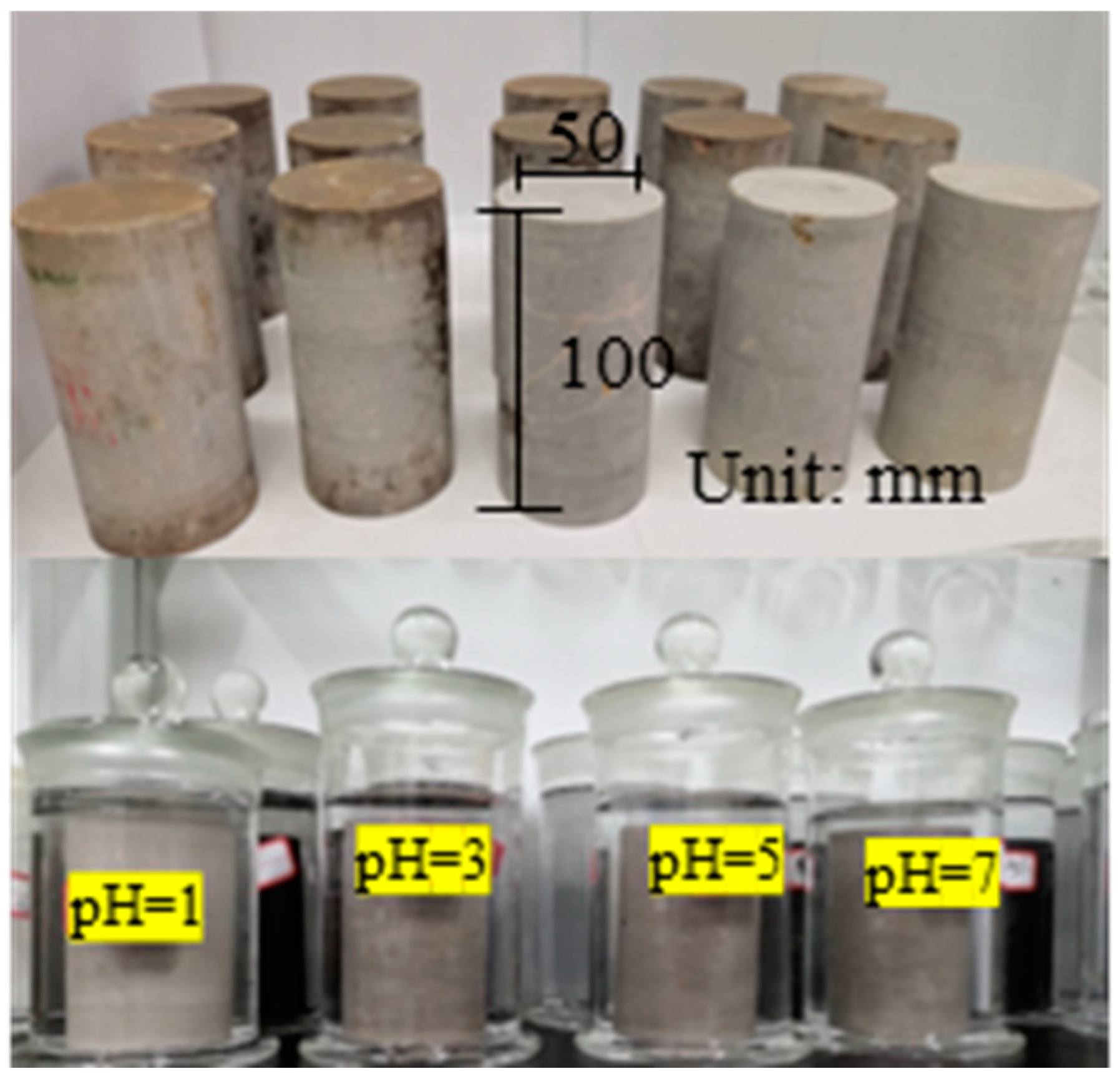
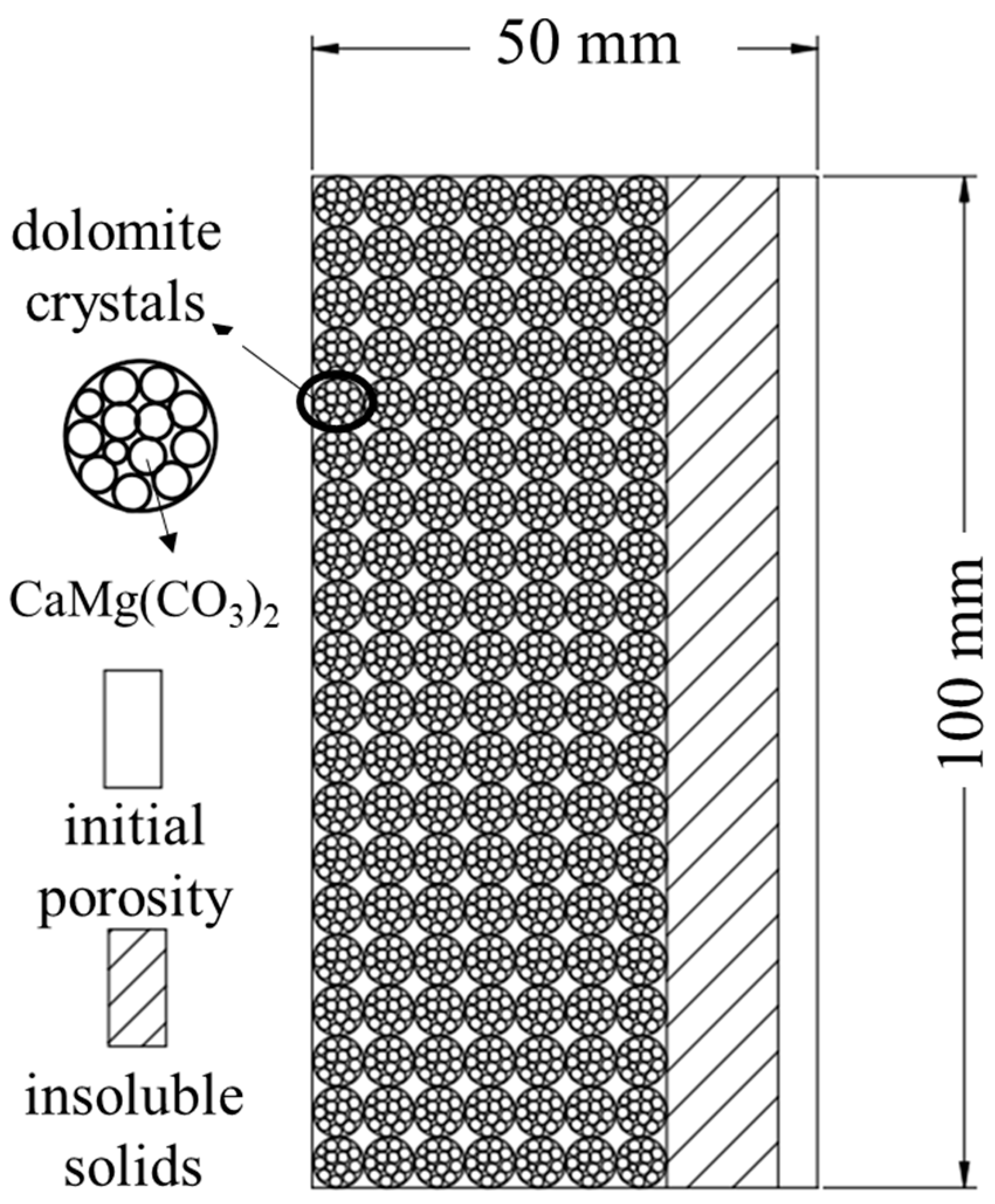
2.1. Materials and Instruments
2.2. Dissolution Test
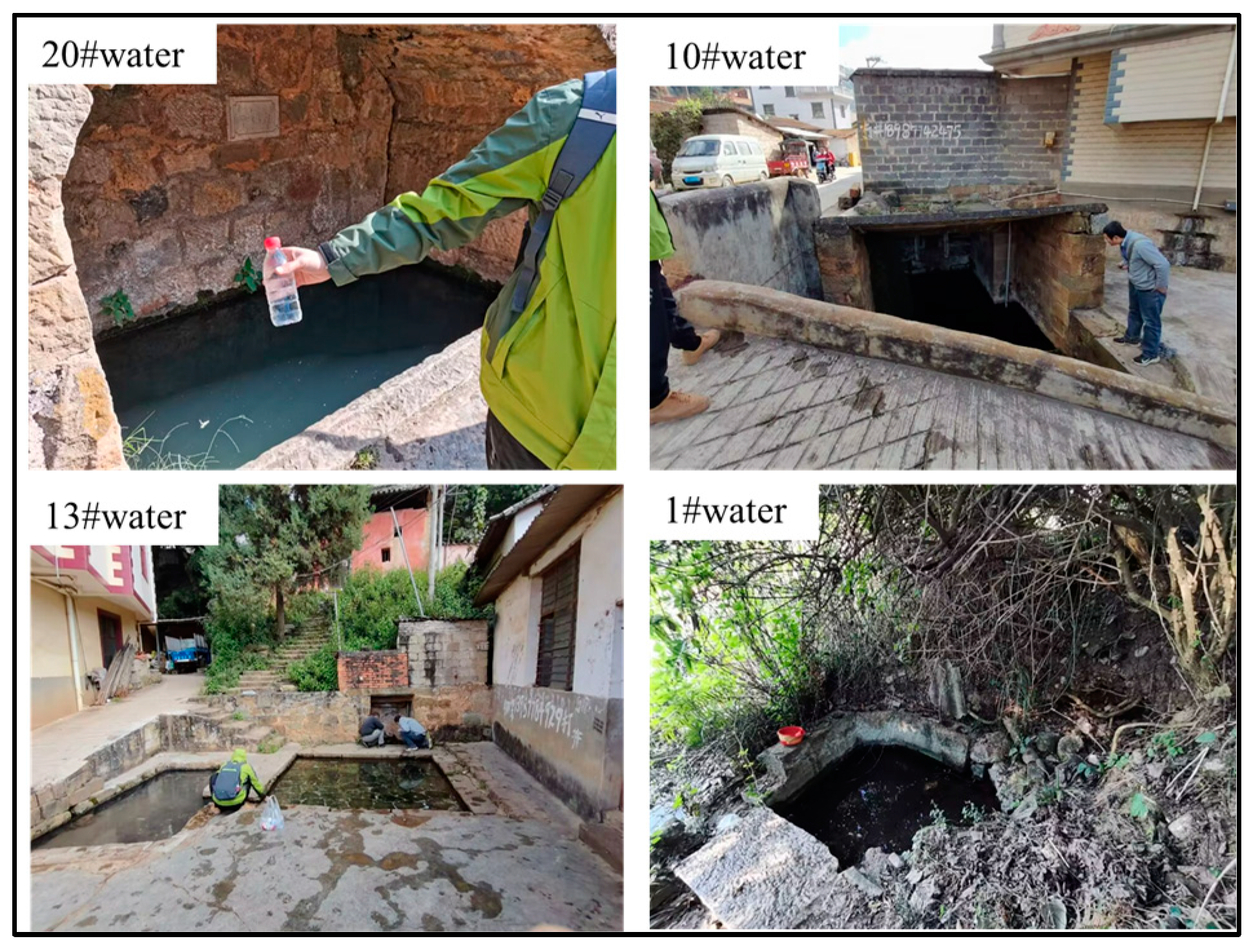
2.3. Water Chemical Analysis
3. Results
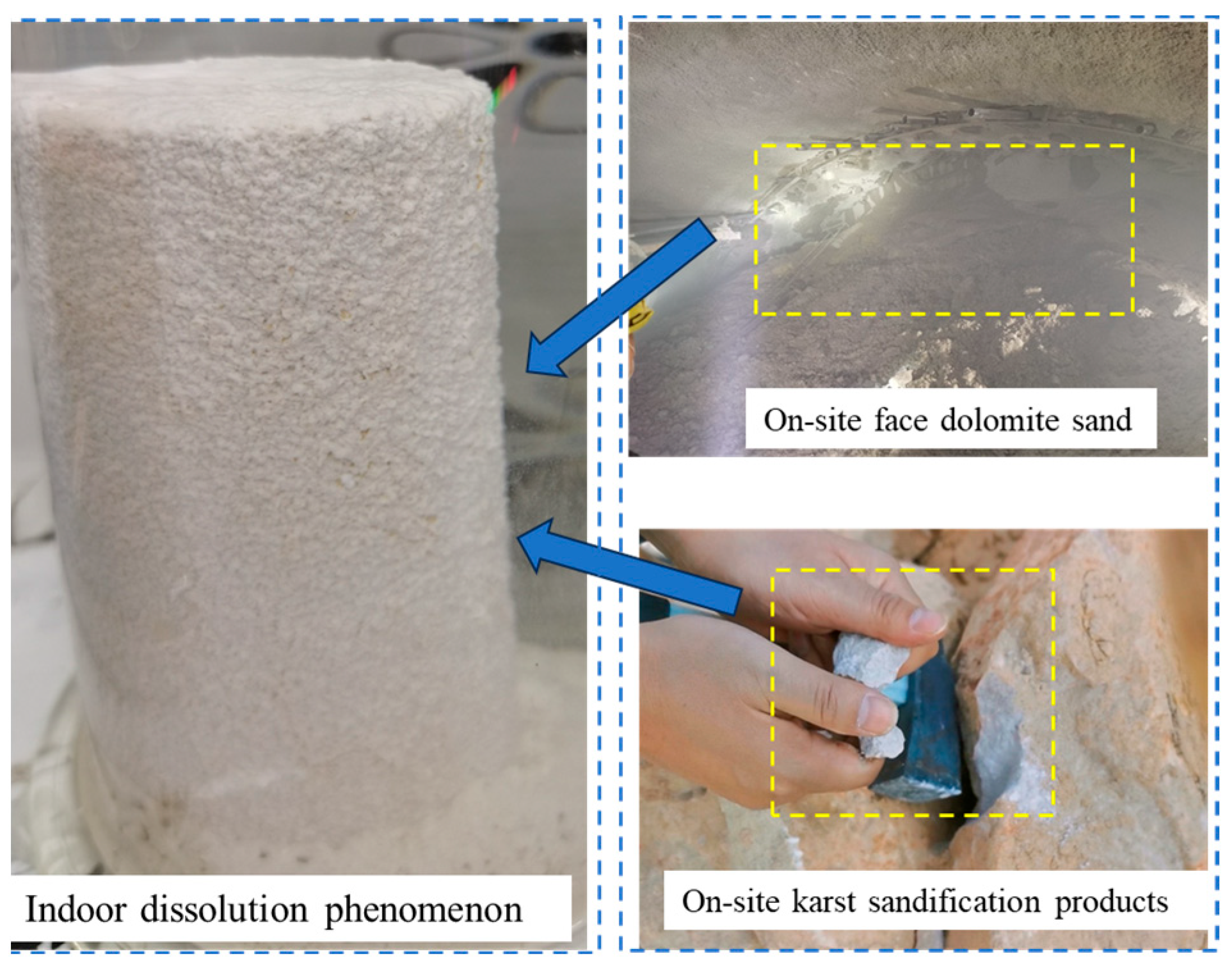
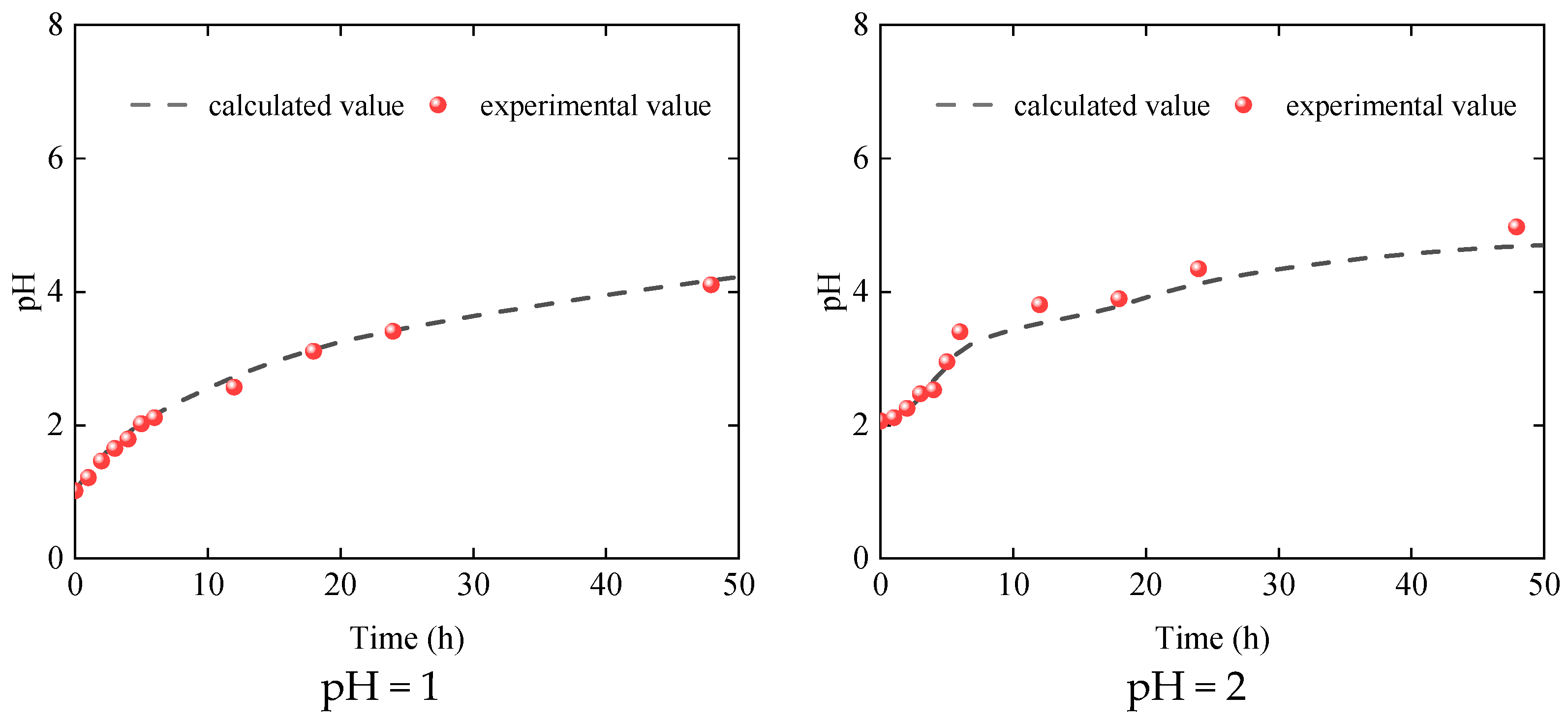
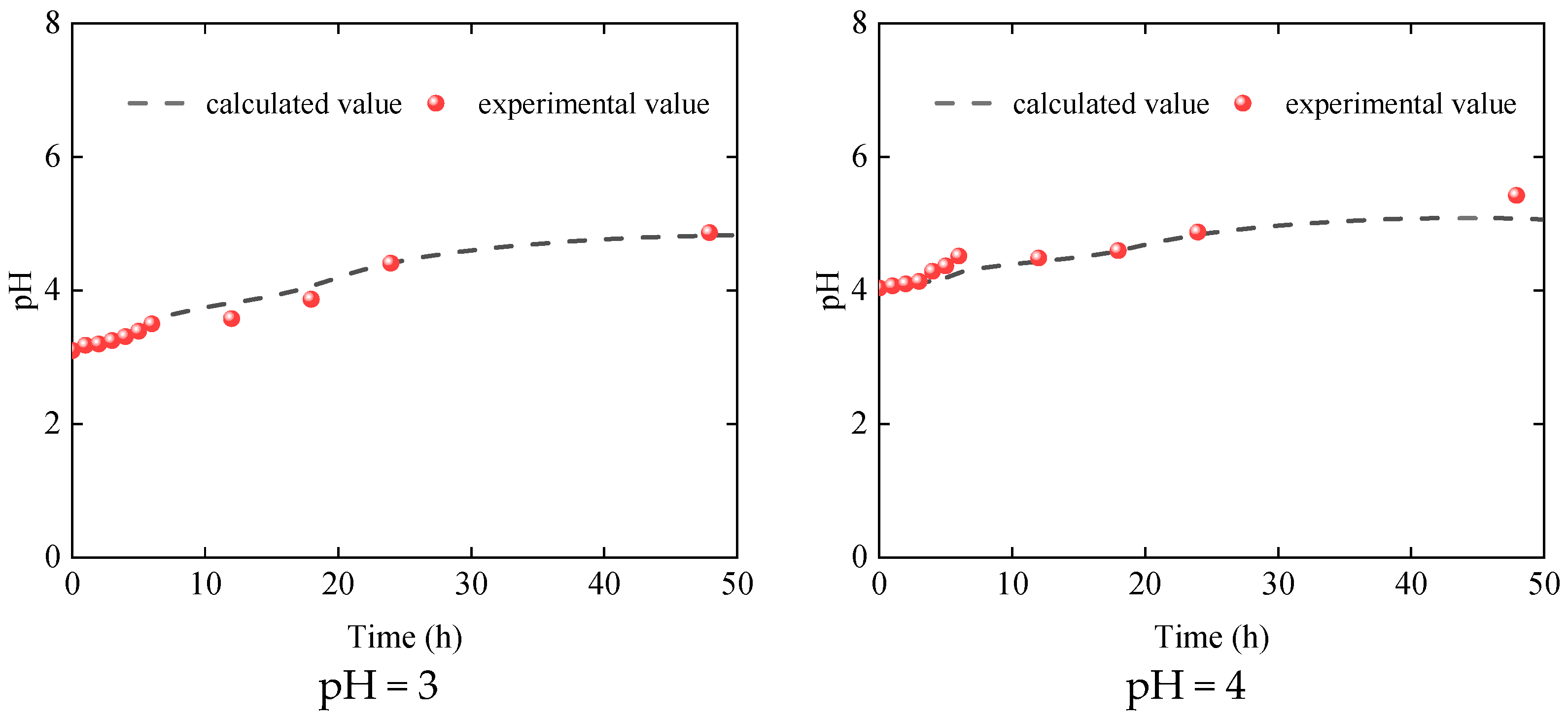
3.1. Dissolution Characteristics of Dolomite
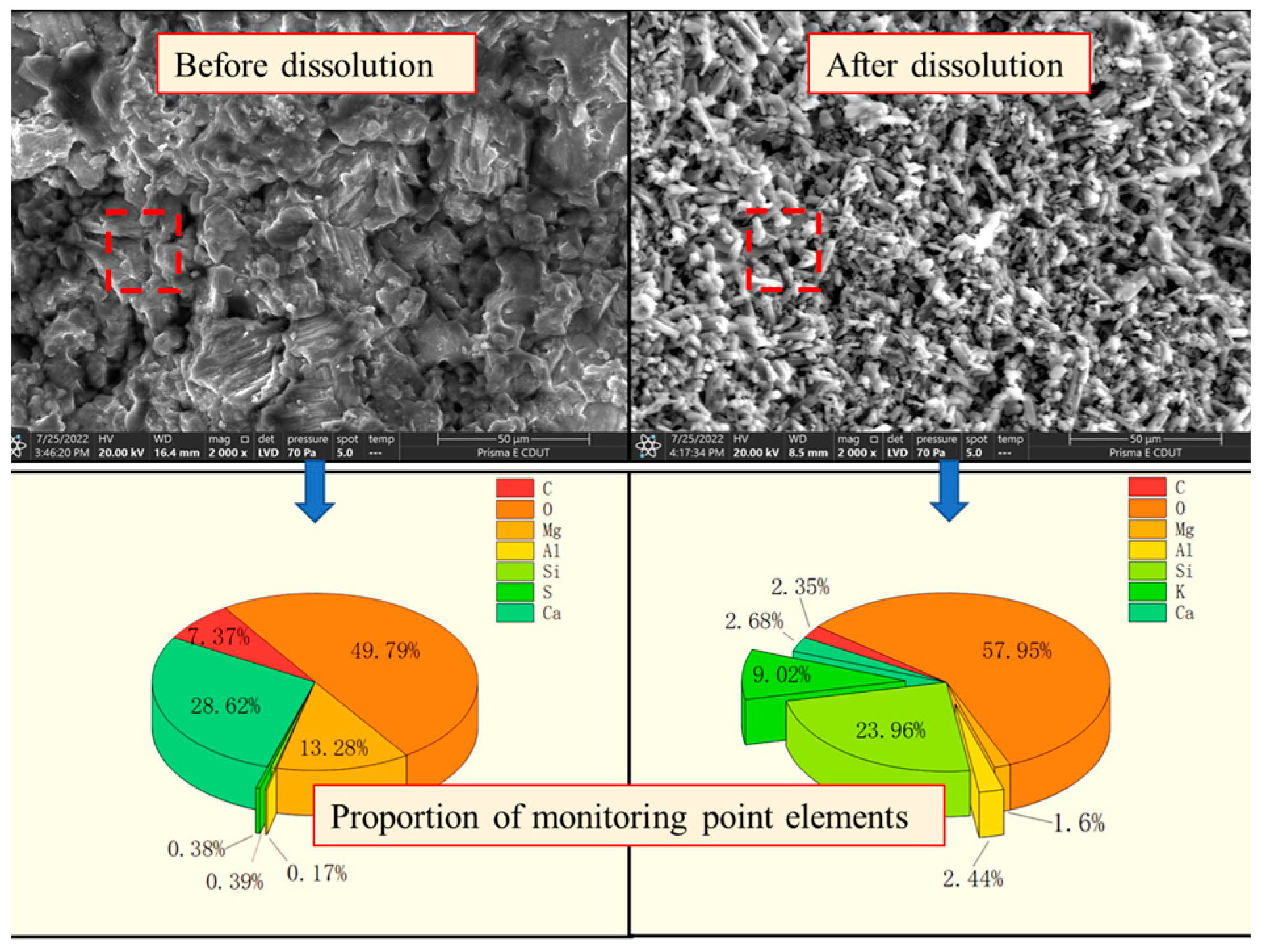
3.2. Microstructure Evolution and Element Migration Change
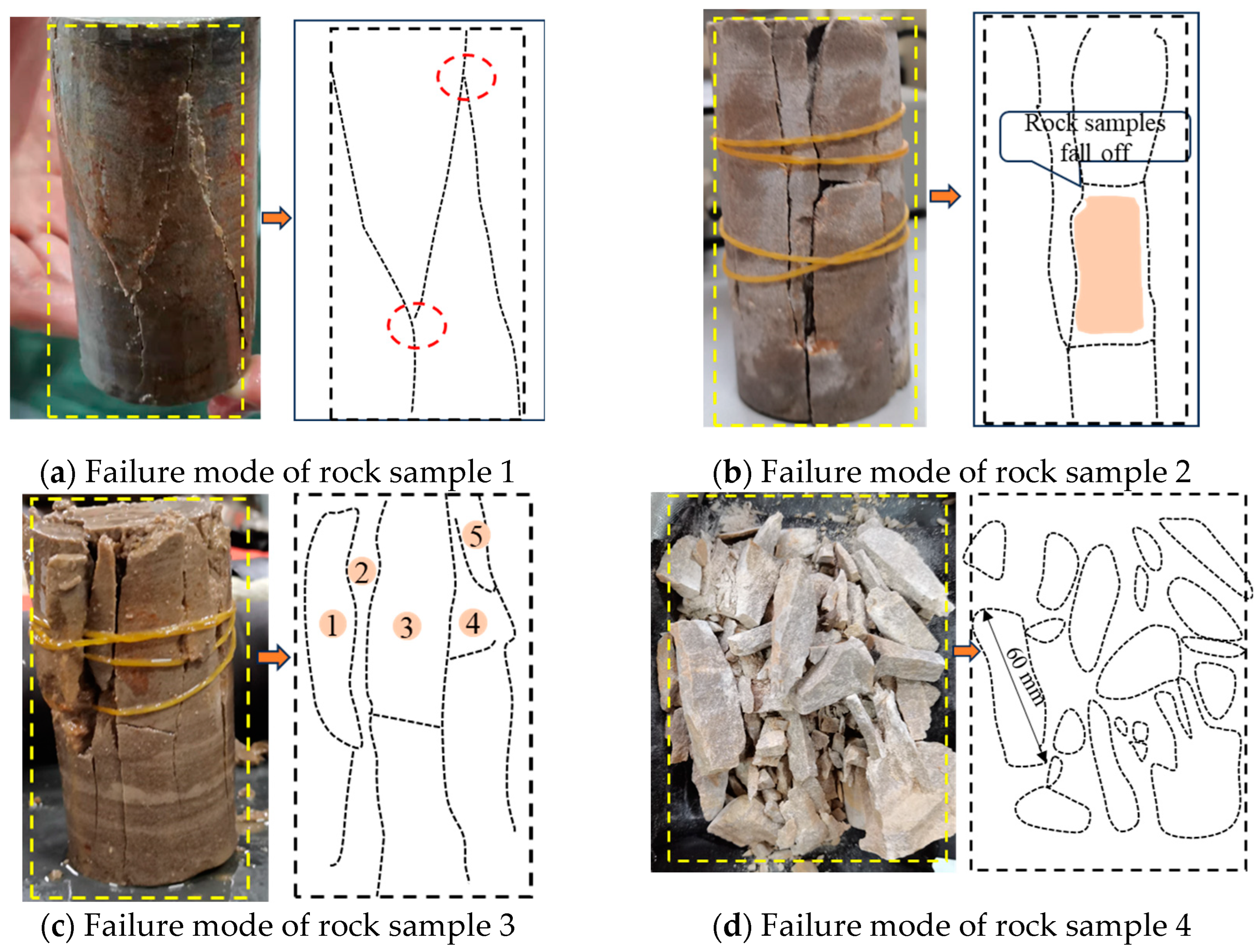
3.3. Failure Characteristics
4. Discussion
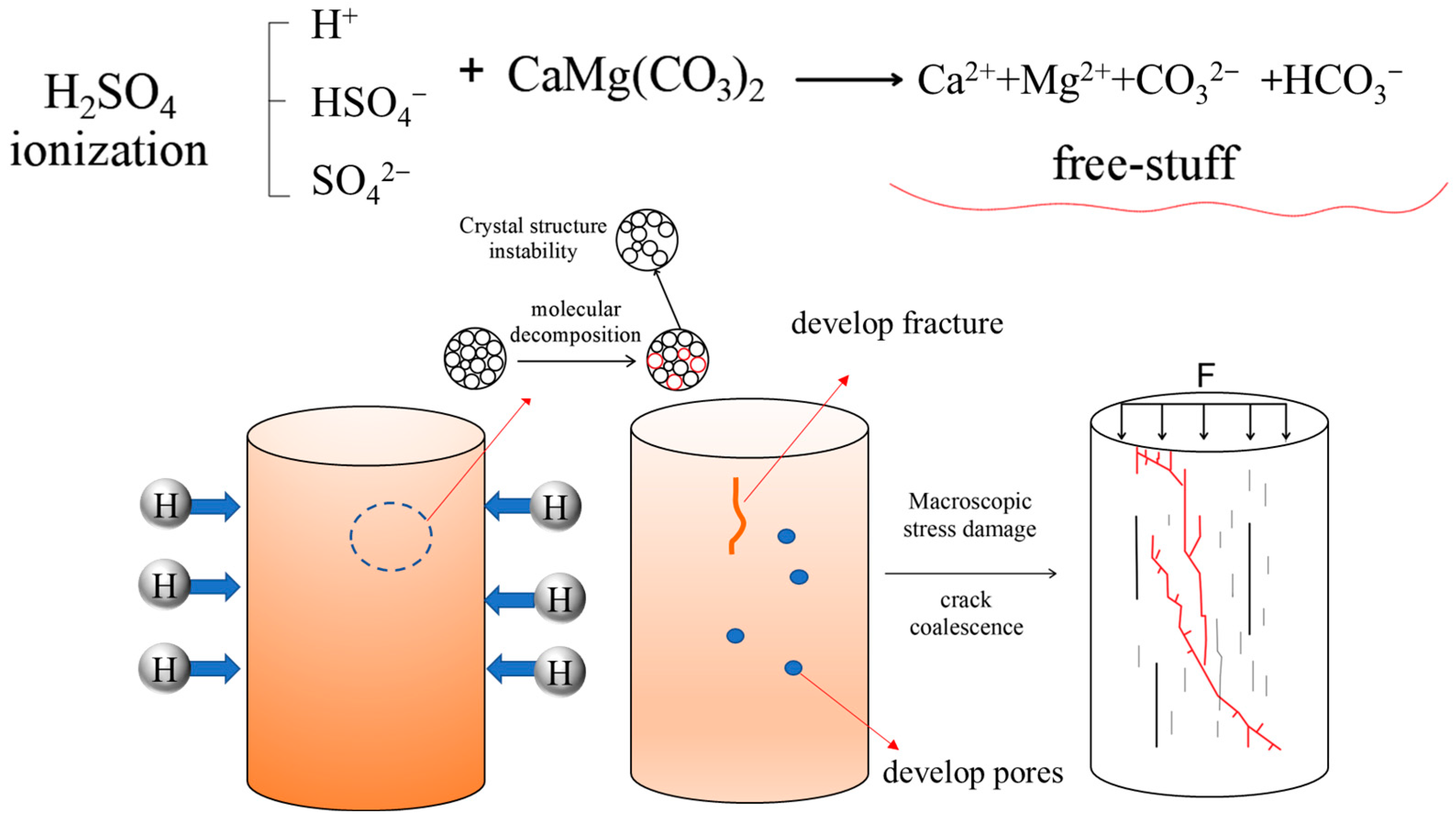
4.1. Analysis of Dissolution Effect on Microstructure Damage
4.2. Strength Degradation and Evolution Model of Dolomite
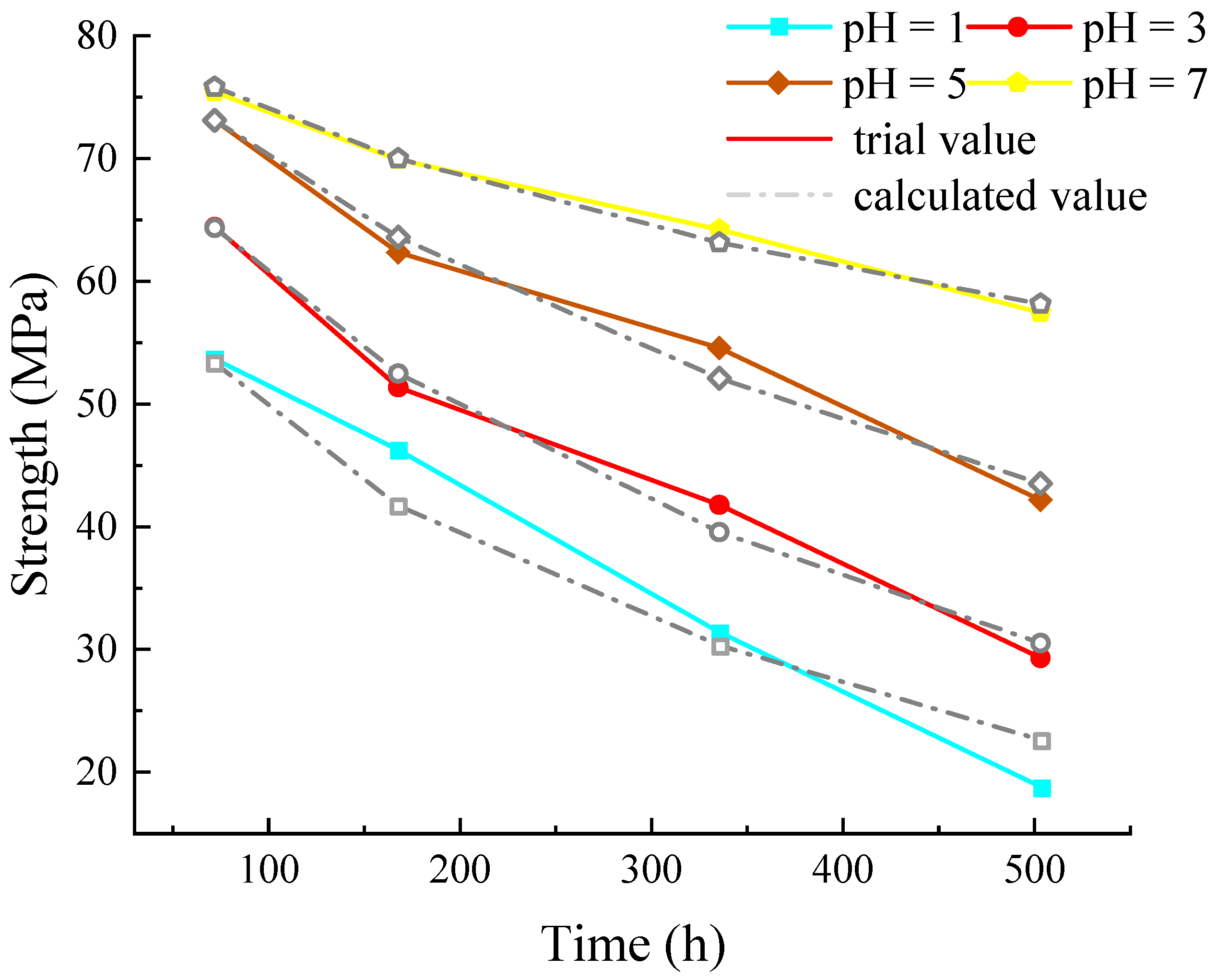
4.3. Model Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhao, Q.H.; Hu, X.B.; Han, G.; Zhao, X. Laboratory dissolution test on dolomite and its microdissolution mechanism. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 20, 576–584. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, F.K.; Wang, H.R.; Liu, G.; Yin, P.S.; Hou, Z.Y.; Cheng, Q.L.; Zhao, W.H. Study on the whole process model of rock creep considering damage factors. Coal Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Bai, Y.E.; Gu, Z.F.; Lu, Y.R.; Sheng, Z.P. Experimental study on dissolution-creep characteristics of limestone and dolomite in rocky desertification area—A case study of Zhenfeng-Guanling Huajiang karst area in Guizhou. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 2017, 37, 399–404. [Google Scholar]
- Gautelier, M.; Schott, J.; Oelkers, E.H. An experimental study of dolomite dissolution rates at 80 °C as a function of chemical affinity and solution composition. Chem. Geol. 2007, 242, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.S.; Wang, S.J. Discussion on mechanism and quantification method of chemical damage of rock water. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2002, 3, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Liu, T.G.; Lv, J.; Wang, R.B.; Xu, W.Y.; Jian, B. Experimental study of influence of water-rock chemical interaction on mechanical characteristics of sandstone. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 3607–3617. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.C.; Fang, J.N.; Zhou, H. Experimental study of rock salt dissolving characteristics under triaxial stress. Rock Soil Mech. 2012, 33, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.H.; Ma, T.T.; Wang, J.; Ye, H.Z. Simulation study on the effect of aqueous solution with different pH values on the dissolution of limestone. J. Foshan Univ. 2013, 31, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W. Experimental simulation of dissolution process of the Lower Paleozoic carbonate rocks in Zhuanghai Area under supergene conditions. Acta Mineral. Sin. 2019, 39, 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Huo, R.; Yoshiaki, F.; Ren, D.; Song, Z. Effect of acid-temperature-pressure on the damage characteristics of sandstone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 122, 104079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Xu, H.; Gong, B.; Ji, F. Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Damage Mechanism of Dolomite under Dissolution Condition. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Y.; Shao, J.F.; Xu, W.Y. Influences of chemical degradation on mechanical behaviour of a limestone. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, S.; Wang, H.; Cai, M.; Song, Y.; Ma, J. Damage constitutive model and variables of cracked rock in a hydro-chemical environment. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Y.M.; Zhang, P.; Ge, X.R. A chemical damage model of sandstone in acid environment. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2003, 4, 395–399. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.L.; Feng, X.T. Study on triaxial meso-failure mechanism and damage variables of sandstone under chemical erosion. Geotechnical mechanics. Geotech. Mech. 2004, 9, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.X.; Feng, X.T. Testing study on mechanical effect for limestone under chemical erosion. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2004, 21, 3571–3576. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.P.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.T. Study on damage mechanism of sandstone under hydro-physico-chemical effects. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2007, 10, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Qu, J.J.; Chen, X.; Qin, Y.H. Study of time scale and strength model of yichang sandstone under different ph values of acidic solution immersion. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2010, 29, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.F.; Hu, A.L.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Hu, Y.; Chang, D.L.; Zhu, M. Statistical damage constitutive model of sandstone under water-rock interaction. Rock Soil Mech. 2017, 38, 631–639. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.W.; Wang, W.; Wang, R.B.; Yuan, S.S.; Zhu, Q.Z. Ontogenetic model of rheological damage in sandstone considering water chemical damage. Rock Soil Mech. 2018, 39, 3340–3346+3354. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Xiong, F.; Lin, Y.; Cao, C.; Liu, X. Softening Damage Analysis of Gypsum Rock With Water Immersion Time Based on Laboratory Experiment. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 125575–125585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhou, K.; Gao, R.; Guo, H. Mechanical Properties and Statistical Damage Constitutive Model of Rock under a Coupled Chemical-Mechanical Condition. Geofluids 2019, 2019, 7349584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuva, J.; Sammaljärvi, J.; Parkkonen, J.; Siitari-Kauppi, M.; Lehtonen, M.; Turpeinen, T.; Timonen, J.; Voutilainen, M. Imaging connected porosity of crystalline rock by contrast agent-aided X-ray microtomography and scanning electron microscopy. J. Microsc. 2018, 270, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.F. Study on prediction model for rock immersion time scale and deterioration under effect of acidic solution. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2021, 52, 162–171. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.L.; Chen, Q.J.; Xiao, P.; Du, X.; Wang, S.R. Rock chemical corrosion-confining pressure damage constitutive model and discrete element simulation. Chin. J. Solid Mech. 2022, 43, 703–715. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.H. An Outline of the Establishment and Development of Chemical Kinetics. Univ. Chem. 2007, 3, 28–36+66. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.S.; Yang, G.S.; Ren, J.X. New study of damage variable and constitutive equation of rock. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2003, 1, 30–34. [Google Scholar]






| Essential Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Original porosity /% | 4.28 |
| Crystal size R/mm | 0.03 |
| Initial acid solution volume Vs/L | 0.8 |
| Initial volume of specimen V0/m3 | 1.96 × 10−4 |
| Single axis compressive strength /MPa | 78.6 |
| Grain volume V/m3 | 1.62 × 10−13 |
| Parameter | pH = 1 | pH = 3 | pH = 5 | pH = 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | 1.26 | 0.611 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| a | 0.0025 | 0.004 | 0.013 | 0.012 |
| b | 0.00729 | 0.0012 | −0.0158 | −0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Ji, F.; Liu, P.; Xu, H.; Meng, X. Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Deterioration of Powder Crystal Dolomite under Dissolution. Water 2024, 16, 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141989
Liu W, Ji F, Liu P, Xu H, Meng X. Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Deterioration of Powder Crystal Dolomite under Dissolution. Water. 2024; 16(14):1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141989
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wenlian, Feng Ji, Pengen Liu, Hanhua Xu, and Xiansen Meng. 2024. "Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Deterioration of Powder Crystal Dolomite under Dissolution" Water 16, no. 14: 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141989
APA StyleLiu, W., Ji, F., Liu, P., Xu, H., & Meng, X. (2024). Study on the Microstructure Evolution and Strength Deterioration of Powder Crystal Dolomite under Dissolution. Water, 16(14), 1989. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16141989






