Abstract
Water conservation efforts and studies receive special attention, versatile and constantly developing remote sensing methods especially so. The quality and quantity of algae fundamentally influence the ecosystems of water bodies. Inland lakes are less-frequently studied despite their essential ecological role compared to ocean and sea waters. One of the reasons for this is the small-scale surface extension, which poses challenges during satellite remote sensing. In this study, we investigated the correlations between remote-sensing- (via Seninel-2 satellite) and laboratory-based results in different chlorophyll-a concentration ranges. In the case of low chlorophyll-a concentrations, the measured values were between 15 µg L−1 and 35 µg L−1. In the case of medium chlorophyll-a concentrations, the measured values ranged between 35 and 80 µg L−1. During high chlorophyll-a concentrations, the results were higher than 80 µg L−1. Finally, under extreme environmental conditions (algal bloom), the values were higher than 180 µg L−1. We also studied the accuracy and correlation and the different algorithms applied through the Acolite (20231023.0) processing software. The chl_re_mishra algorithm of the Acolite software gave the highest correlation. The strong positive correlations prove the applicability of the Sentinel-2 images and the Acolite software in the indication of chlorophyll-a. Because of the high CDOM concentration of Lake Naplás, the blue–green band ratio underestimated the concentration of chlorophyll-a. In summer, higher chlorophyll-a was detected in both laboratory and satellite investigations. In the case of extremely high chlorophyll-a concentrations, it is significantly underestimated by satellite remote sensing. This study proved the applicability of remote sensing to detect chlorophyll-a content but also pointed out the current limitations, thus assigning future development and research directions.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, accessible water resources play an increasingly critical role in society and the ecosystem. The monitoring of surface water resources is a top priority in most countries. Within the European Union, the conservation of water resources is primarily governed by the Water Framework Directive [1], which states that the Member States of the European Union should aim to achieve at least a good water quality status for their water resources, and where a good water quality status already exists, it should be maintained. For this, it is essential to monitor the relevant parameters of the water bodies.
Different kinds of ecosystem services connect to inland water resources. Water quality is a complex and important part of hydrology that refers to water’s hydrological, chemical, physical, and biological characteristics [2]. Collected information about water quality—more precisely, its physical, chemical, and biological parameters—is indispensable for proper water resource management. The quantity and quality of the information are important factors because these datasets can be used for further analysis.
As for the biological water quality parameters, the chlorophyll-a content of the water influences its usability for drinking, agricultural purposes (irrigation), economic and industrial purposes, and recreational activities. The chlorophyll-a concentration of water provides information about the vertical and horizontal distribution of phytoplankton. Several authors have studied phytoplankton’s horizontal and vertical distribution with different methods, for example, using submersible fluorescence spectrometers or other laboratory-based and remote sensing techniques [3,4,5,6]. They found that the submersible fluorescence probes were particularly suitable for analyzing the vertical distribution of algae. This technique provides rapid and accurate data about the chlorophyll-a concentration of the water column.
The spatial distribution of the phytoplankton is inhomogeneous, depending on numerous influencing factors, for example, the underwater light conditions, available nutrients, physical and chemical water quality parameters, thermal stratification, predator–prey relationship, weather conditions (especially wind), currents, and water temperature [7,8]. Our research team has also focused on the vertical distribution of algae in a previous study [9]. After statistical analysis of collected physical, chemical, biological, and spectral parameters, we found that the UV radiation, available light, and water temperature significantly affected the vertical distribution of phytoplankton.
The dissolved organic matter (DOC) content in water provides an effective protection against UV radiation. Therefore, a significant part of the UV-B radiation is absorbed in the upper 20–50 cm layer [10,11]. Within the total suspended solids content, it is important to know the organic and inorganic suspended solids content and their relative proportions because these parameters interact with the spectral properties of water. Within this recent study, 85% of total suspended solids originated from organic components. In a previous study, Mirnasab et. al. [12] examined the relationship between water quality and natural organic matter in water. Their data suggest that the organic matter content plays a significant role in water quality and the spectral properties of the water.
Concerning the horizontal distribution of algae, different remote sensing techniques, such as satellite- or UAV-based systems, provide a good monitoring solution. The advantage of these methods is that we can quickly and cost-efficiently obtain data from large areas.
Several studies have compared different measuring methods, on-site submersible fluorescence spectrometers, conventional laboratory measurements, and remote sensing techniques with different observatory levels [13,14,15,16,17]. Their findings reveal that the adequate environmental assessment of an area requires the simultaneous application of different analytical techniques. To obtain high-quality and large amounts of data for the investigated water parameters, we need to combine on-site measurements and remote sensing.
The significance and relevance of the research project presented here relies on two main points. First, climate change poses many challenges for humanity. Therefore, proper water resource management is essential on a local, regional, and global scale. This is why we used combined data collection methods for environmental monitoring. Second, comparing the different methods, focusing on usability and accuracy, opens possibilities for new ways to take advantage of the techniques. Our study focuses on the chlorophyll-a content of the water and two different data collection and measuring methods, namely, conventional and remote sensing techniques. As for the biological water quality measurements in the laboratory, the chlorophyll-a content signifies a vital parameter. We used the ISO 10260:1992 [18] (water quality) measurement of biochemical parameters, and we used the spectrometric determination of the chlorophyll-a concentration method to determine the chlorophyll-a concentration.
The utilized remote sensing analyses relied on Sentinel 2 data from the European Space Agency. The database is built upon a long-term in situ sampling campaign and complex remote sensing data analysis in a selected nutrient-rich shallow lake in Hungary. Most sensors have been developed for land or ocean applications, not considering the possible and particular demands of lakes, which means that lake applications are somewhat restricted [19]. Sentinel-2 data and the Acolite (20231023.0) software were used to investigate algae formerly [20,21,22], with appropriate results.
Since, during remote sensing, the detected rays are reflected from the surface or emitted from it, the small investigated surface area carries some challenges. Radar altimetry is a commonly used technique for observing large lakes, and laser altimetry is commonly used to track changes in smaller lakes. The best choice for accurately quantifying lakes is to use instruments that work in the visible/infrared bands with high spatial resolution [23]. Sentinel-2, with its appropriate band, spatial resolution, and five-days revisiting time, is a potentially appropriate tool, which, together with Acolite, was successfully used in the case of a large surface lake to determine chlorophyll-a concentration [24].
Previous research found that the blue/green and the near-infrared/red ratio correlates well with the concentration of chlorophyll-a [25,26,27,28,29].
Several different phytoplankton types can cause problems in the aquatic ecosystem. There are three types (cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates, and diatoms) that can cause harmful algal bloom and health issues for people and animals. Cyanobacteria cause harmful algal blooms in freshwater. Dinoflagellates and diatoms are common types in salt water. Some types of cyanobacteria, including the harmful genus Microsystis, can produce hazardous cyanotoxins such as microcystins, which are hepatotoxins that cause liver problems in mammals. Other types of cyanobacteria can also produce harmful hepatotoxins, for example: neurotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. Combined monitoring methods (in situ and remote sensing approaches) can help us to detect harmful algae blooms in time.
This study’s main objective is to compare laboratory and remote sensing chlorophyll-a measurements, especially their accuracy and the different algorithms used in the calculation process.
To achieve the described main objective, we took the following steps:
- Creation of a complex sampling and measuring program based on remote sensing, on-site, and laboratory measurements.
- Establishment of correlations between the laboratory and remote sensing chlorophyll-a measurements.
- Comparison between the different applied chlorophyll-a concentration algorithms based on remote sensing data.
- Investigating the effect of chlorophyll-a’s vertical and horizontal distribution on remote sensing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Measurements
The study area is Lake Naplás, a small, shallow (the average depth is 3 m) reservoir on the Szilas Creek in Budapest, Hungary. The area of the lake is 22 hectares, and it is primarily used for recreational activities. Lake Naplás and its connectional areas have been under environmental protection since 1997, and it is the largest open-surface urban lake and wetland area in Central Europe [30]. This protected area in the urban region provides a unique habitat for its complex ecosystem. It allows migratory birds (150 different bird species) and other animals and plants to survive.
For creating the database, we fulfilled two on-site data collection periods to record the following parameters:
- Chlorophyll-a concentration: vertical distribution of phytoplankton by taking water samples for further laboratory analysis.
- Water temperature: water temperature profile of the sampling points for further analysis.
- Depth of the water: depth profile of the sampling points for further analysis.
The sampling program was divided into two periods: the first sampling period was between 2016 and 2018, and the second was in 2022. The program included eighty-five wholly performed sampling campaigns during the first period and thirteen in the second. As for the data collection, we used a submersible sampler for the sampling process carried out from a boat. We designated three sampling points in the study area. During the designation process of the sampling points, the main point of interest was to represent the different basin characteristics and habitat conditions of the study area, based on our previous research [9]. We determined the chlorophyll-a content at different depths in all three sampling points. Table 1 lists the detailed information about the sampling campaigns.

Table 1.
Detailed information about the sampling points.
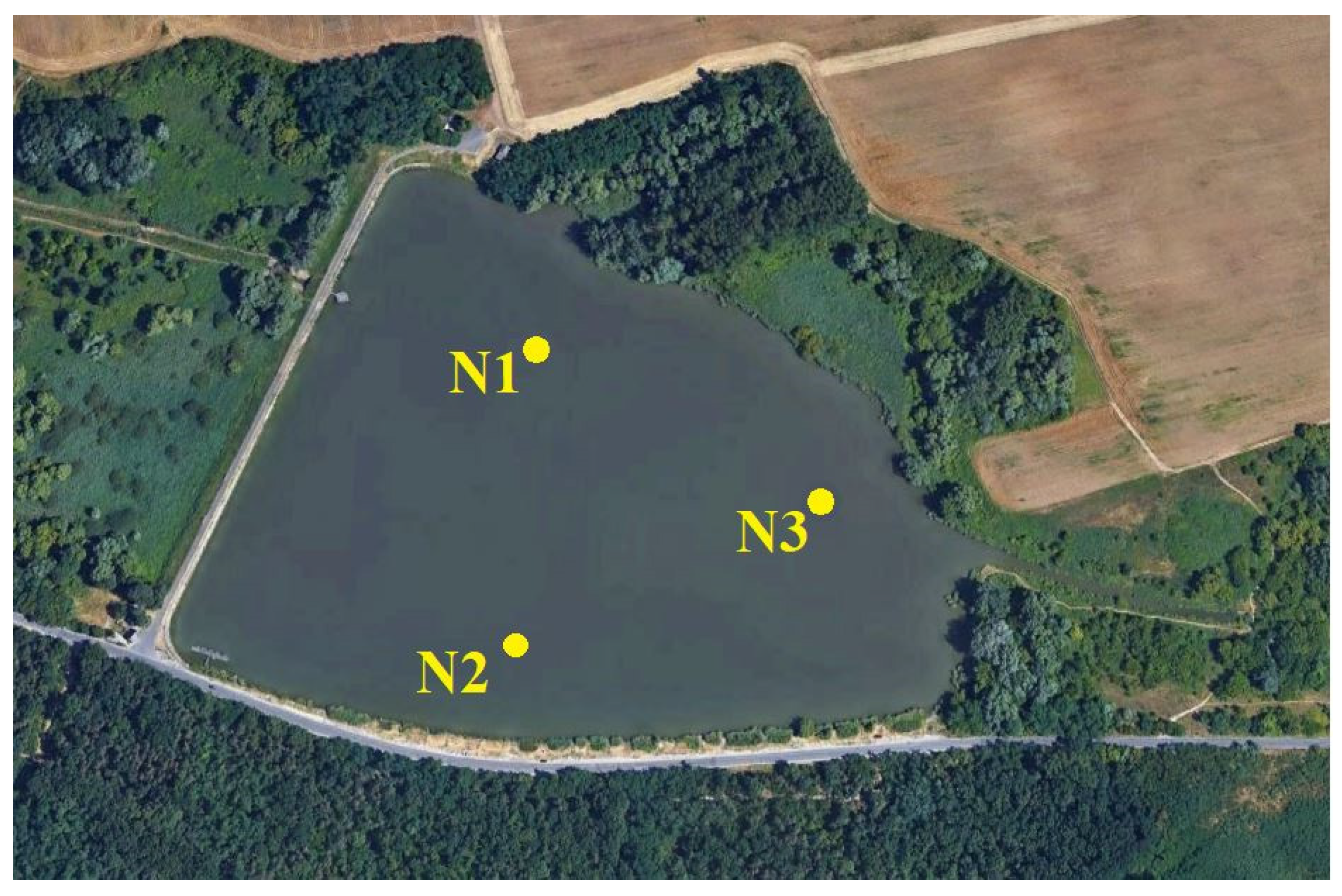
The first sampling point (N1) is on the northern side of the lake. Within this area, the local currents are moderate, and the water column is hardly disturbed. We used this location almost throughout the year, except in winter when the lake is frozen and walking on the ice is not permitted.
The N2 sampling point is on the southern side of the lake. The currents are negligible because it is far from the in- and outflow.
The third sampling point (N3) was located on the lake’s western side, close to the inflow of the Szilas creek. The lake’s bed is shallow and partly covered by reeds along the coast. Around this location, high-velocity flows are frequent.
The locations of the sampling points are shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Locations of sampling points (source: Google Earth).
The main objective of the laboratory analysis was to determine the chlorophyll-a concentration of the water samples with high accuracy to compare the results with the remotely sensed data. The conventional method of phytoplankton concentration determination, the ISO 10260:1992 method [18], was applied during the analysis. We applied a laboratory spectrometer (Jenway 6405 UV/VIS Spectrophotometer, Cole-Parmer, Stone, UK) to determine the chlorophyll-a concentration of the water samples. Biological parameters were measured from each collected 250 mL water sample.
2.2. Source of the Dataset
Sentinel-2 is a constellation of two satellites: Sentinel-2A (launched: 23 June 2015) and Sentinel-2B (7 March 2017). Sentinel-2 has the multispectral imager (MSI) on board, an optical imager with 13 spectral bands spanning from the blue to the shortwave infrared (SWIR), with 10, 20, or 60 m ground resolution. Sentinel-2 images rely on two sources: USGS EarthExplorer [31] and Copernicus Open Access Hub [32]. The processing level of the images was 1C, which is characterized by top-of-atmosphere (TOA) reflectance, radiometric correction, and orthorectification.
Several different studies have examined the accuracy of remote sensing determinations [33,34,35]. The accuracy of the remote-sensing-based chlorophyll-a determination is between 80 and 95%, depending on the satellite system and algorithm used. Alongside these mentioned parameters, a very important point is the vertical distribution of the phytoplankton.
2.3. Data Processing
Data processing included three pieces of software: Acolite [36] to obtain chlorophyll-a data; QGIS Desktop 3.14.15 software [37] to visualize the results, making the dataset clearly understandable and creating chlorophyll-a maps and zonal statistics; and IBM SPSS v25 [38] statistical software to perform statistical analysis.
Acolite is a program developed by the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences (RBINS) specifically designed to process satellite water imagery. It also offers seven different algorithms for determining the content of chlorophyll-a in Sentinel-2. Chlorophyll-a content was determined via remote sensing using a method and equation developed by Vanhellemont and Ruddick [39] (see p. 3., Equations (2)–(4)).
The following algorithms we used during the recent study:
- chl_oc2, chl_oc3: Chlorophyll-a concentration (µg/L) using the blue–green ratio algorithm. The oc2 and oc3 use two and three bands, respectively. Results should be used with care in coastal and inland waters, especially in the presence of sediments and CDOM [40].
- chl_re_gons, chl_re_gons740: Chlorophyll-a concentration (µg/L) using the red edge algorithm by Gons et al. [41], with published coefficients and a mass-specific chlorophyll-a absorption of 0.015. By default, 780 nm (band 6) was used as a reference, but the chl_re_gons740 product uses 740 nm (band 5) on MSI [40].
- chl_re_moses3b, chl_re_moses3b740: Chlorophyll-a concentration (µg/L) using the three-band red edge algorithm by Moses et al. [42]. By default, we relied on 780 nm (band 6) as a reference, but the chl_re_moses3b740 product uses 740 nm (band 5) on MSI [40].
- chl_re_mishra: Chlorophyll-a concentration (µg/L) using the normalized difference chlorophyll index algorithm by Mishra and Mishra [40,43].
QGIS zonal statistics were applied to obtain datasets of the lake’s mean, maximum, and minimum chlorophyll-a values. We used the mean chlorophyll-a data for statistical analyses. Data visualization applied the four different classes with different chlorophyll-a rates (0–8; 8–25; 25–75; >75 µg/L), as defined by the OECD (Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development) [44].
To reveal the correlation between chlorophyll-a concentration of Lake Naplás, we used Pearson’s correlation after performing the Shapiro–Wilk normality test.
We also investigated the average chlorophyll-a content of the lake and the chlorophyll-a concentration of the exact sampling points. To obtain the chlorophyll-a data of each point, we used QGIS’s “zoom-to-coordinate” function.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overall Comparison of Laboratory-Based Chlorophyll-a Values with Remote Sensing Data
When choosing adequate sampling dates, we had to consider the satellite revisit period and the atmospheric weather conditions. Based on these circumstances, a few sampling dates fell out of the 98 sampling occasions. The analyzed dataset was set up on 22 sampling dates when the environmental and weather conditions were adequate to compare the laboratory measurements with the remotely sensed data.
Many images showed the study site covered by clouds, so we had to exclude many laboratory results because of the missing satellite data. Furthermore, three measurements were excluded from statistical analysis because of the >100 µg/L chlorophyll-a concentration given that extremely high chlorophyll-a values lead to saturation.
We applied the Shapiro–Wilk test of normality to prove the Pearson correlation’s applicability. The results are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Results of the Shapiro–Wilk normality test.
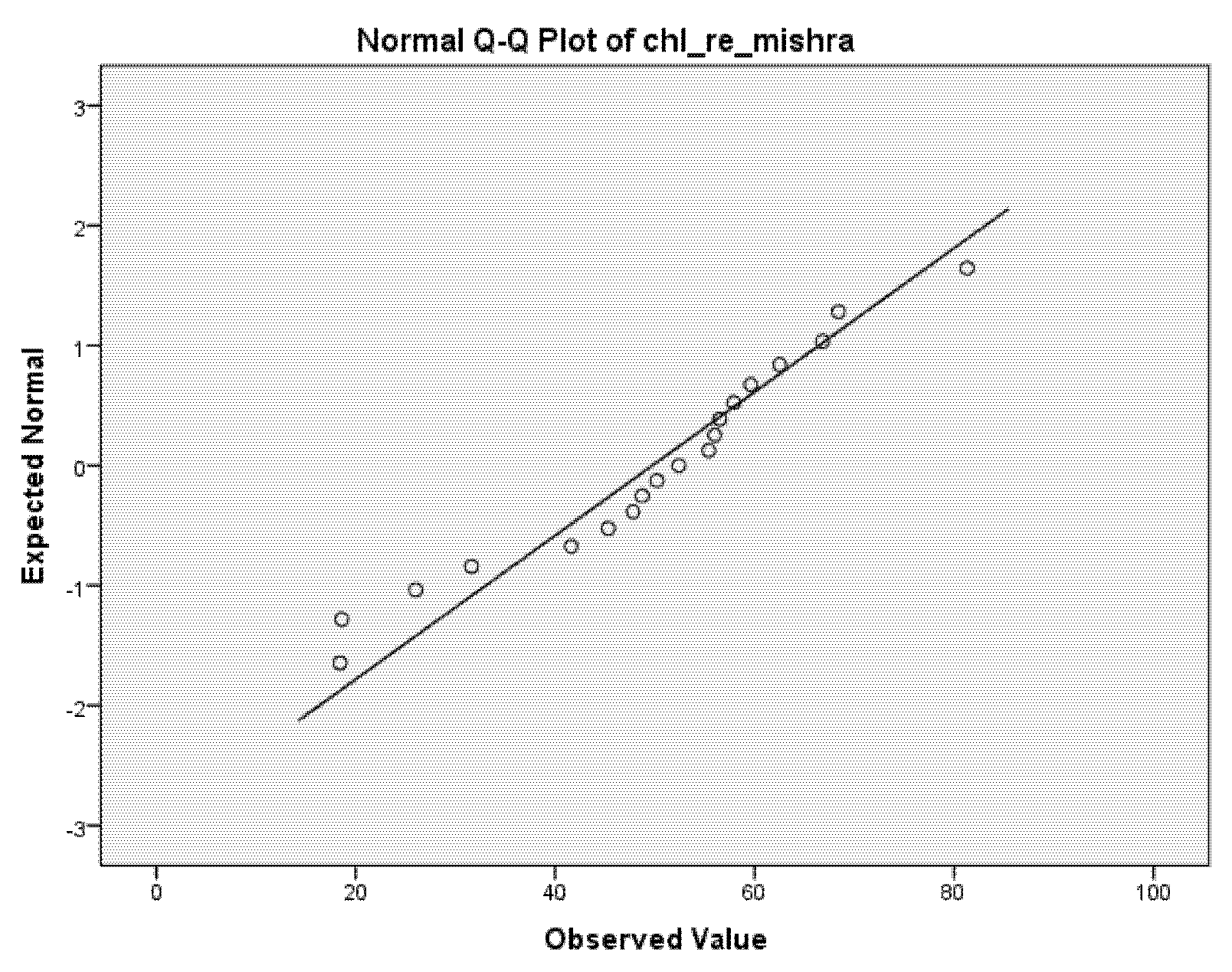
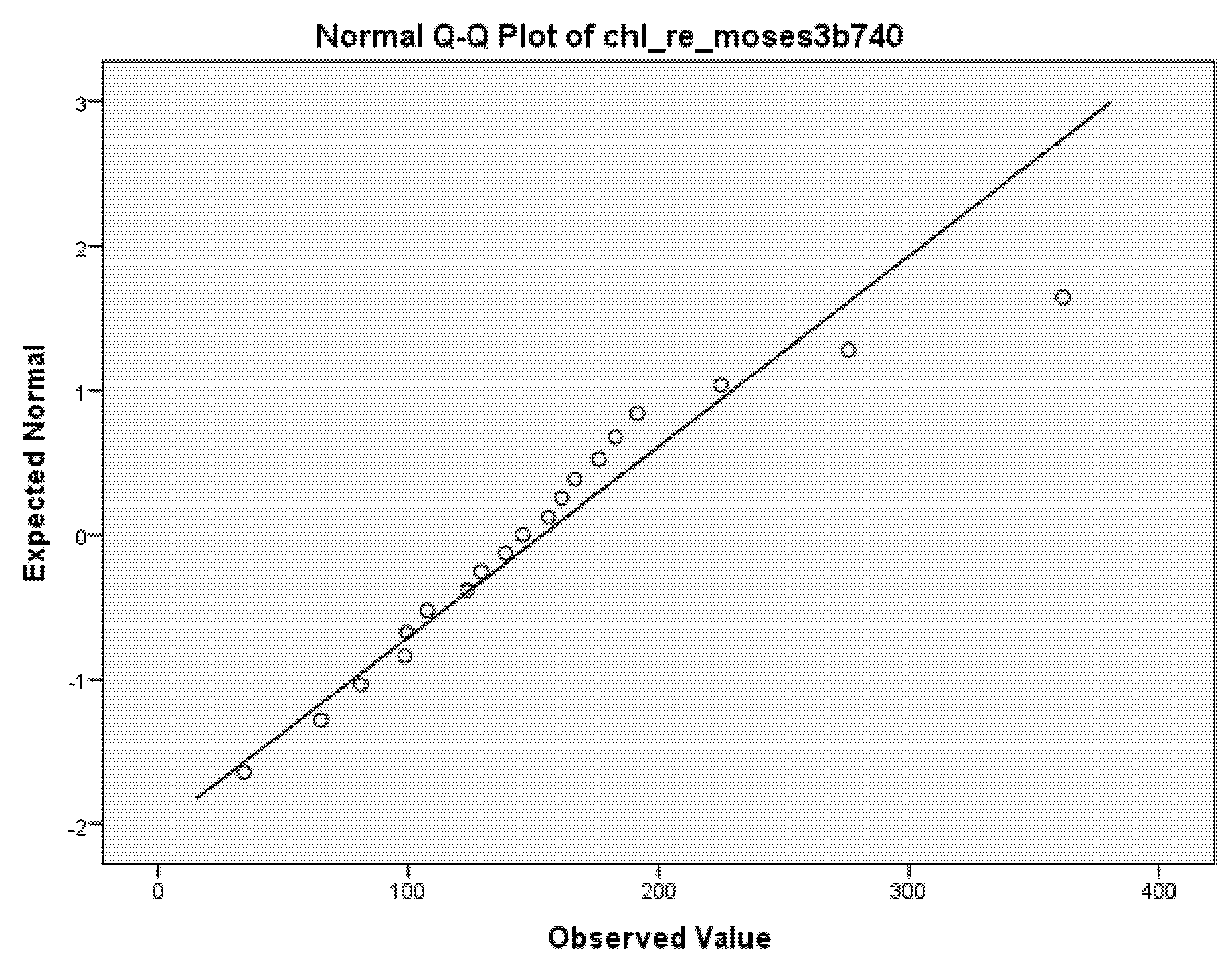
The results of laboratory measurements (spectrometer) and the Acolite algorithms chl_re_mishra and chl_re_moses3b740 fulfilled the condition of normality (p > 0.05); thus, we investigated these two algorithms further. The Q-Q plots of the two algorithms are presented in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
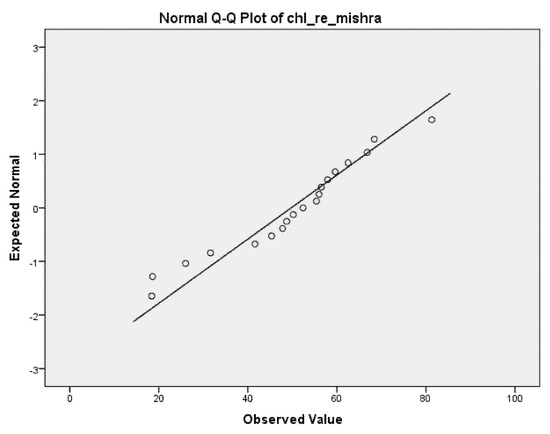
Figure 2.
Q-Q plot of chl_re_mishra algorithm.
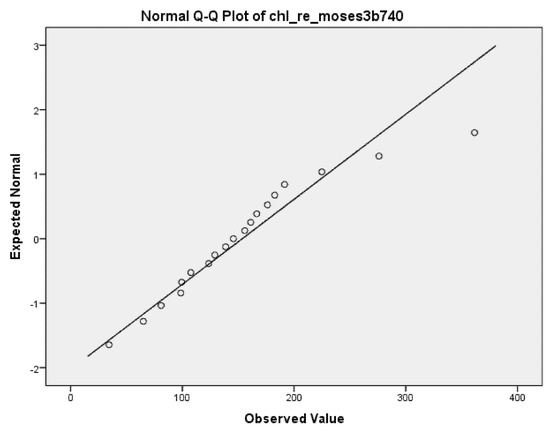
Figure 3.
Q-Q plot of chl_re_moses3b740.
The chl_re_mishra algorithm showed a higher correlation (0.618) with laboratory results than the chl_re_moses3b740 (0.322). A result of 0.618 represents a moderately strong correlation. Results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results of the Pearson correlation test.
The chl_re_mishra algorithm uses the normalized difference chlorophyll index algorithm, using red and red edges, by Mishra and Mishra [43]. In the case of Sentinel-2, the calculation used the red spectral band B4 with the red edge spectral band B5. The chl_re_mishra algorithm used the normalized difference chlorophyll Index, which has been created to predict chlorophyll-a (chl-a) concentration from remote sensing data in estuarine and coastal turbid productive waters.
Additionally, algorithms that employ wavebands in the red and near-infrared (NIR) range (650–800 nm) are less sensitive than traditional blue–green (440–550 nm) ratio algorithms to absorption by colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) and scattering by mineral particles; both CDOM absorption and particulate scattering decrease rapidly with the wavelength and are small in the red–NIR part of the spectrum [26]
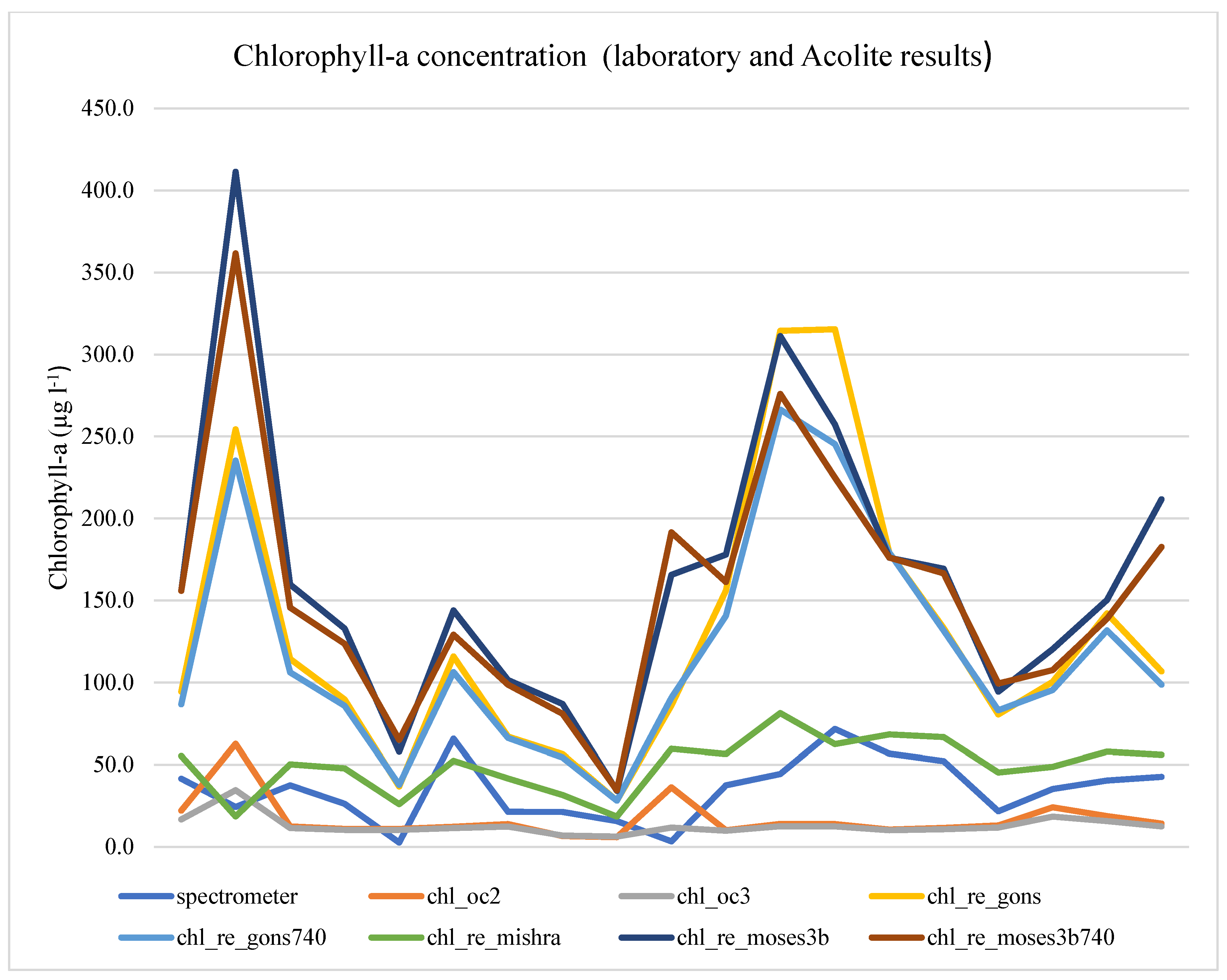
The chl_re_gons, chl_re_gons740, chl_re_moses3b, and chl_re_moses3b740 algorithms overestimate the concentration of chlorophyll-a. We used the red edge algorithm, relying on the published coefficients, and a mass-specific chlorophyll-a absorption of 0.015 (after Gons et al. [41], so chl_re_gons and chl_re_gons740 estimate chlorophyll-a concentration (µg/L). By default, 780 nm (band 6) was used as a reference, but the chl_re_gons740 product uses 740 nm (band 5) on Sentinel-2 MSI. Chlorophyll-a concentration (µg L−1) uses Moses et al.’s three-band red edge algorithm [42]. By default, 780 nm (band 6) is used as a reference, but the chl_re_moses3b740 product uses 740 nm (band 5) on Sentinel-2 MSI.
As expected, based on the high CDOM concentration of Lake Naplás, the chl_re_oc2 and chl_re_oc3 algorithms (using blue/green band ratio) underestimated the concentration of chlorophyll-a, as displayed in Figure 4.
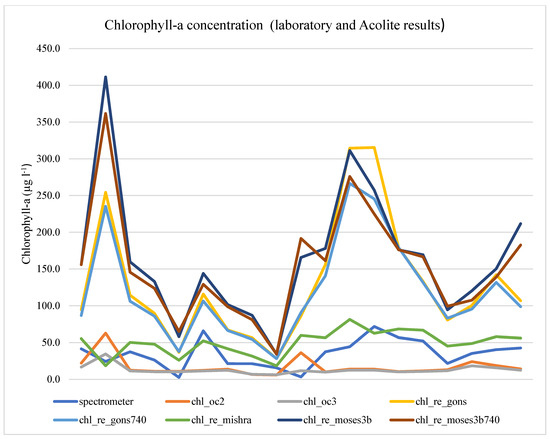
Figure 4.
Chlorophyll-a concentration (laboratory and Acolite results).
3.2. Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Phytoplankton
The horizontal and vertical distribution of phytoplankton are inhomogeneous on the surface and in the water column, influencing the optical properties of the system. Multiple processes and parameters influence the distribution.
Based on our and other in situ and laboratory measurements [9,44], the underwater light conditions, available nutrients, physical and chemical water quality parameters, thermal stratification of the lakes, wind conditions, parts of the day, predator–prey relationship, currents, water temperature, and finally, UV radiation could be mentioned as necessary influencing factors.
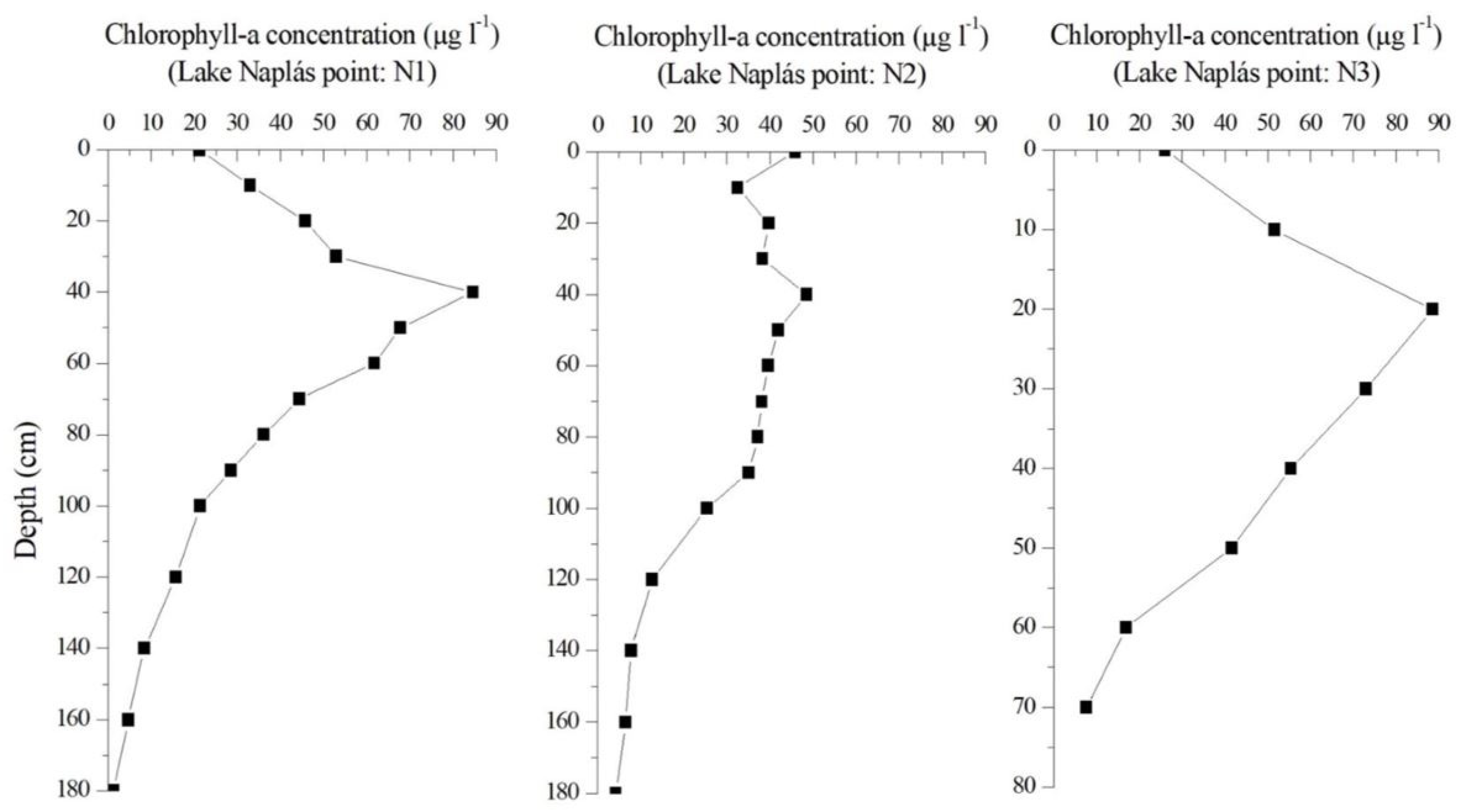
In this study, the vertical distribution of chlorophyll-a content is a significant parameter because it allows for further analysis of which layer correlates best with the remote sensing data. The results of laboratory measurement provided two main distribution patterns during the study. In the first case, the maximum chlorophyll-a content was on the surface. Meanwhile, the maximum chlorophyll-a content in the second case was in the deeper layer (more than 50 cm below the water surface). These two cases are displayed in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
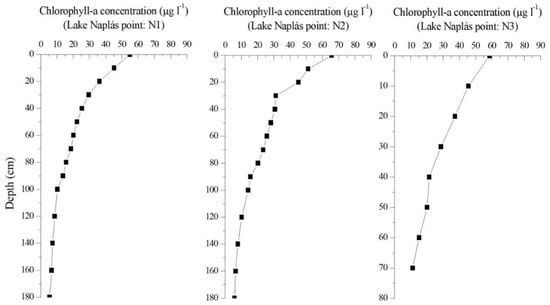
Figure 5.
Vertical distribution of phytoplankton in Case 1 (12 October 2017).
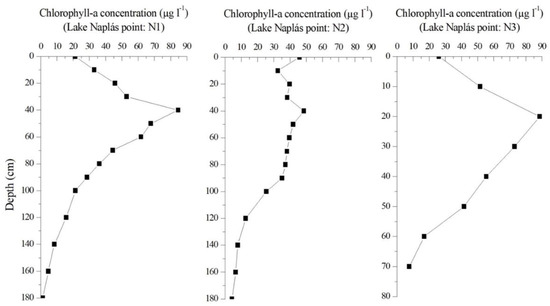
Figure 6.
Vertical distribution of phytoplankton in Case 2 (5 August 2022).
In a former study [9], we found that the placement depth of the maximum chlorophyll-a content could influence the remote sensing reflectance. Based on these results, the difference in the vertical distribution of chlorophyll-a concentration provided different remote sensing reflectance curves.
Within the framework of this recent study, we analyzed and compared the laboratory-based data with the satellite-based data regarding vertical distribution. Table 4 compares the laboratory measurements and the remote sensing data regarding the vertical distribution of phytoplankton at sampling point N1.

Table 4.
Results of laboratory- and remote-sensing-based measurements at sampling point N1. Different colors indicate the different levels of statistical correlations between the laboratory- and satellite-based reflectance measurements. Key of the colors: blue, no statistical correlation; red, poor (>0.584) correlation; pink, good (>0.795) correlation; orange, strong (>0.816) correlation; green, very strong (>0.853) correlation (for more explanation, see the text).
Based on the statistical analyses, we have found that in the case of high surface chlorophyll-a concentration (above 35 µg L−1), the remotely sensed maximum chlorophyll-a value showed a strong correlation (0.795) with the surface chlorophyll-a content (marked with pink in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The reason was that the high surface chlorophyll-a content modified the surface reflectance. In this case, the in-situ-measured maximum chlorophyll-a concentration occurs in a deeper layer, generally below 40 cm depth. A similar case happened when the maximum chlorophyll-a content was close to the water surface (marked green in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The correlation between the in situ and remote sensing data was robust (0.853).

Table 5.
Results of laboratory- and remote-sensing-based measurements at sampling point N2. Different colors indicate the different levels of statistical correlations between the laboratory- and satellite-based reflectance measurements. Key of the colors: blue, no statistical correlation; red, poor (>0.584) correlation; pink, good (>0.795) correlation; orange, strong (>0.816) correlation; green, very strong (>0.853) correlation (for more explanation, see the text).

Table 6.
Results of laboratory- and remote sensing-based measurements in sampling point N3. Different colors indicate the different levels of statistical correlations between the laboratory- and satellite-based reflectance measurements. Key of the colors: blue, no statistical correlation; red, poor (>0.584) correlation; pink, good (>0.795) correlation; orange, strong (>0.816) correlation; green, very strong (>0.853) correlation (for more explanation, see the text).
During extremely high surface chlorophyll-a concentration (during massive algal bloom), poor correlation was identified between the two methods (marked with red in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). A possible explanation is that the floating algal mass has highly modified and distorted the water column’s surface reflectance and optical properties. In these cases, chl_re_gons and chl_re_gons740 algorithms correlated better (0.584) with the laboratory-measured surface chlorophyll-a content.
During the winter season, the chl_re_mishra algorithm did not correlate with the laboratory data (marked in blue in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The reason for this was the ice crust on the lake, which was between 10 and 15 cm thick. The ice crust strongly influenced the remote sensing reflectance. Thus, the analyses reveal that the chl_oc2 algorithm correlated better (0.508) with the laboratory measurements.
In another case, when the chlorophyll-a concentration of the surface water layer was lower than 25 µg L−1, the remotely sensed maximum chlorophyll-a concentration strongly correlated (0.816) with the laboratory-measured maximum chlorophyll-a concentration in the water column. Analyzing the vertical distribution pattern of phytoplankton, the placement depth of maximum chlorophyll-a concentration was between 20 and 40 cm in depth (marked in orange in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6). The data suggest that the chl_re_mishra algorithm detected maximum chlorophyll-a concentration at the 40 cm depth when the surface layer chlorophyll-a content was in a low range.
As predicted, the moderate wind speed modified the surface reflection, so satellite-based measurements were inadequate. Therefore, remote sensing values did not correlate with any of the laboratory measurements (marked in blue in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6).
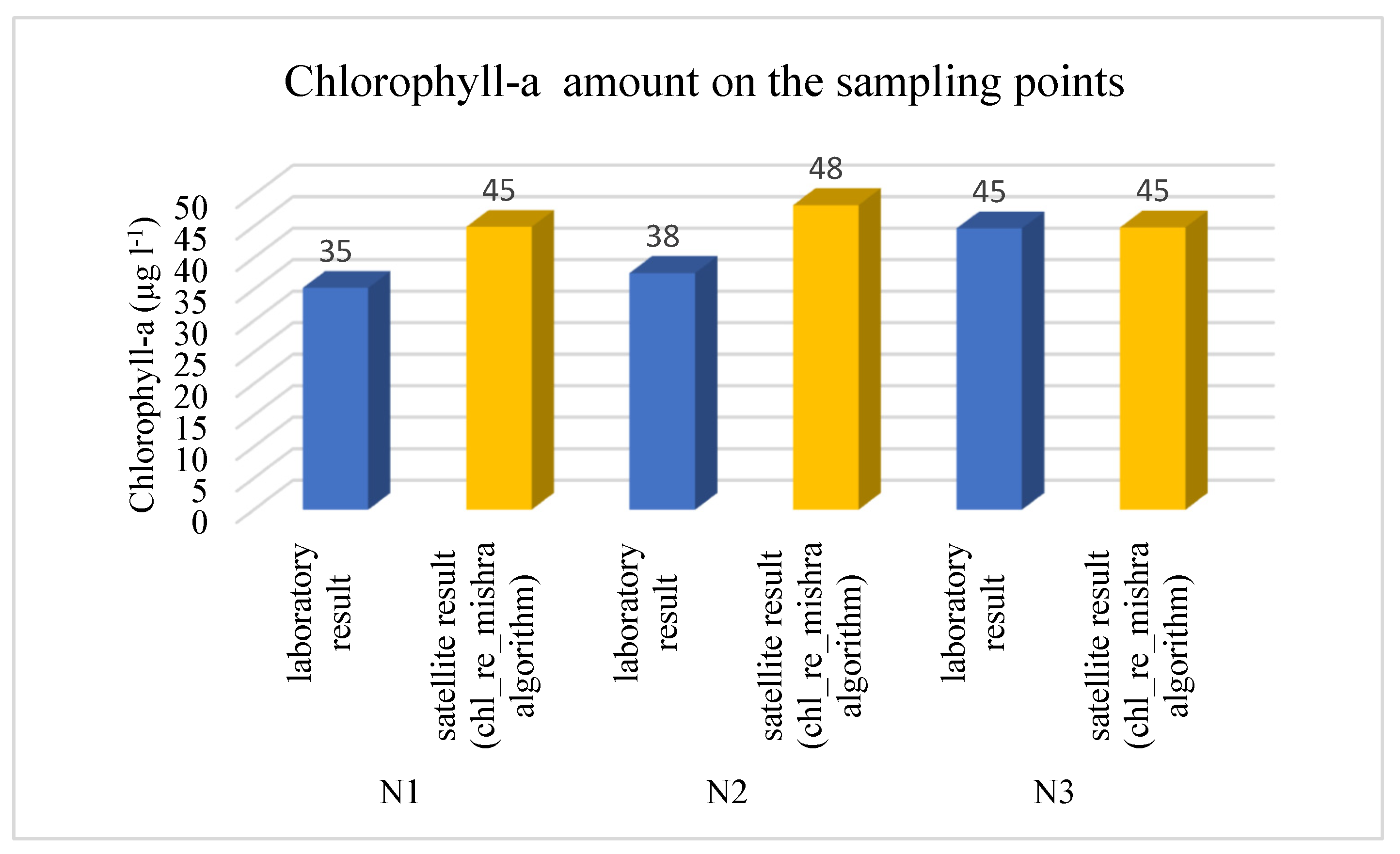
We also investigated the laboratory and satellite data at the sampling points. Each point has chlorophyll-a values in different depths, and the average of these values was compared to the satellite data. Figure 7 presents the results.
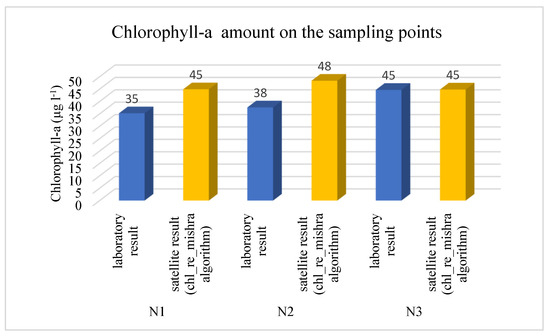
Figure 7.
Chlorophyll-a concentration at the sampling points (laboratory and satellite).
According to laboratory measurements, the average chlorophyll-a concentration was similar in the three sampling points (N1: 35; N2: 38; N3: 45).
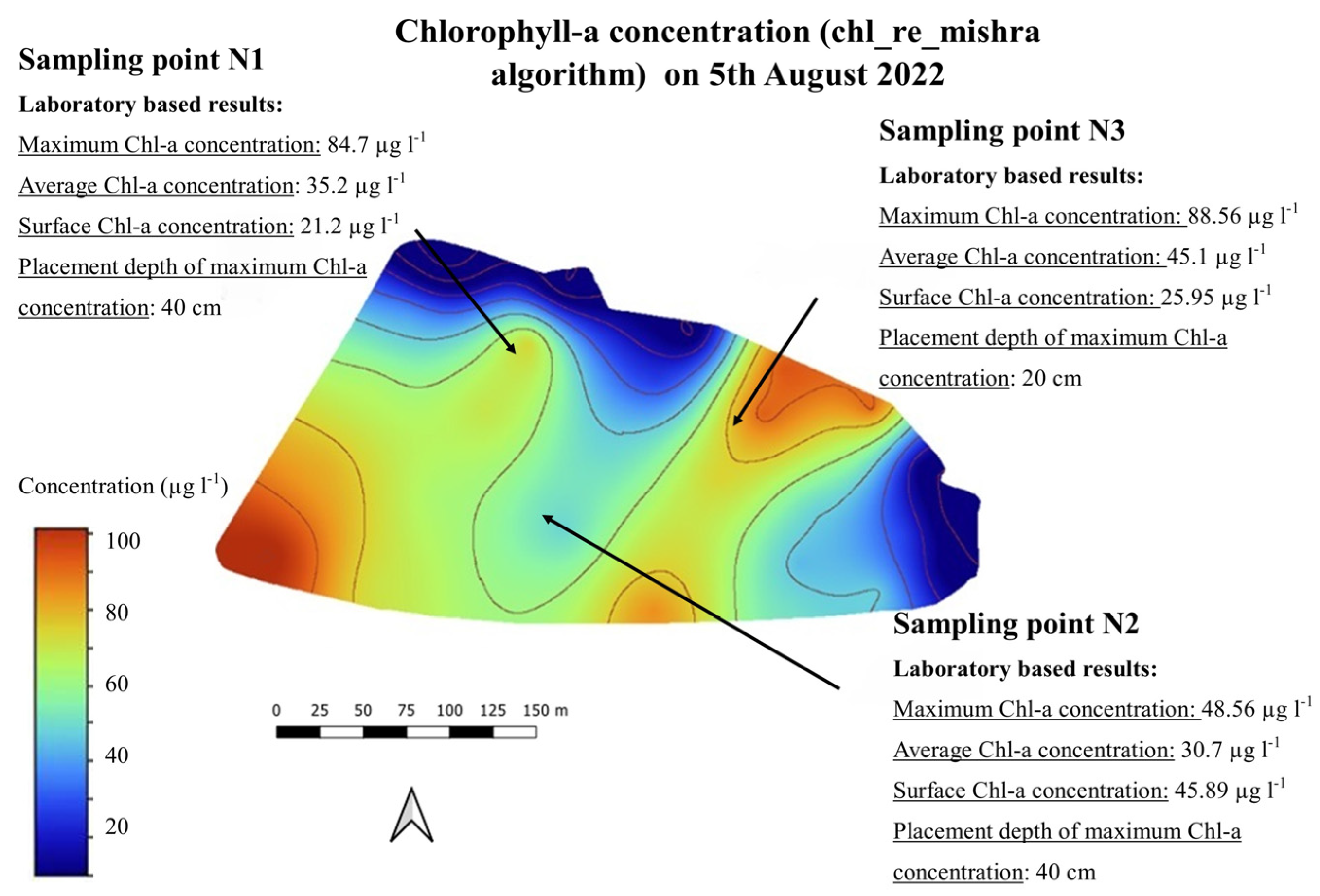
Analyzing the horizontal distribution of phytoplankton, the different applications of remote sensing—UAV, aerial imaging, and satellite-based techniques—provide an appropriate solution for monitoring the surface distribution patterns. Figure 8 shows one sample of the chlorophyll-a maps on 5 August 2022 (chl_re_mishra algorithm).
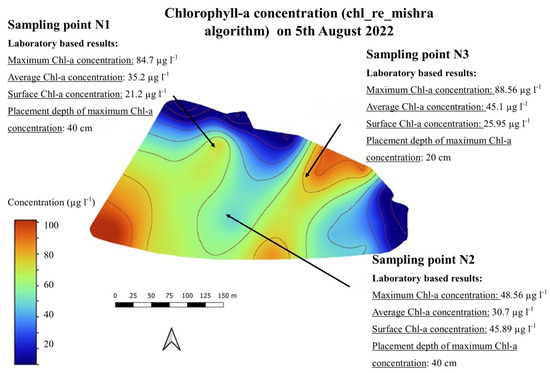
Figure 8.
Chlorophyll-a map (chl_re_mishra) on 5 August 2022.
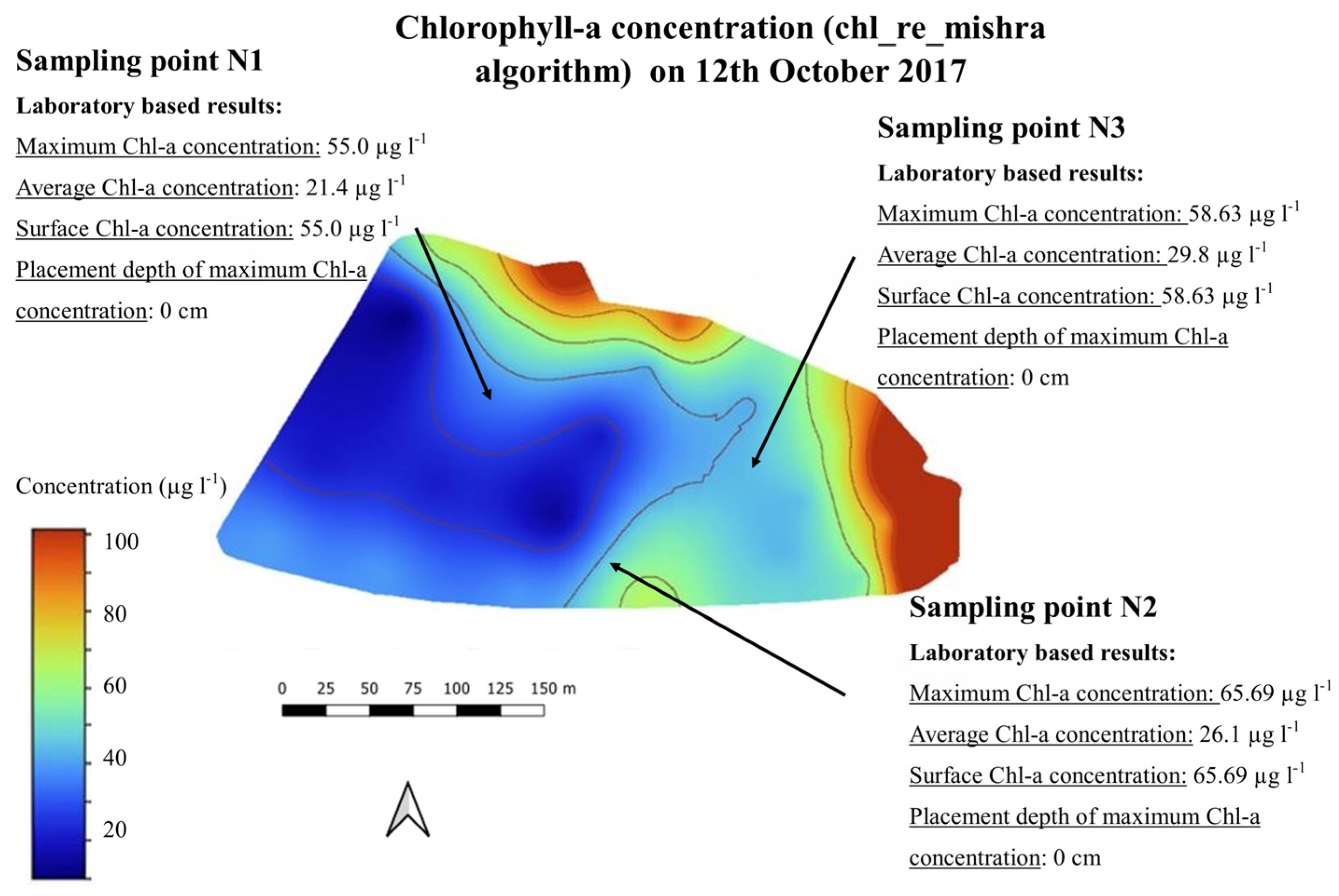
Figure 9 presents another example of the horizontal distribution of chlorophyll-a content.
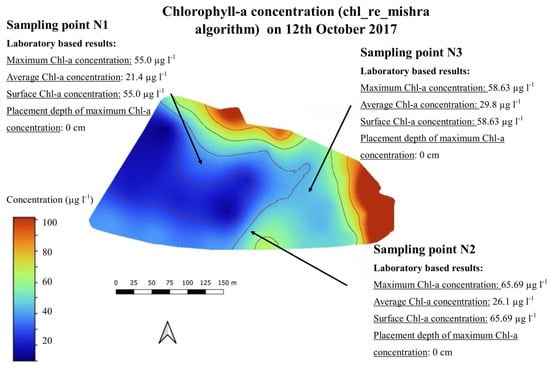
Figure 9.
Chlorophyll-a map (chl_re_mishra) on 12 October 2017.
Both examples represent the correlation between the laboratory-based and the satellite-based results well.
3.3. Seasonal Trends
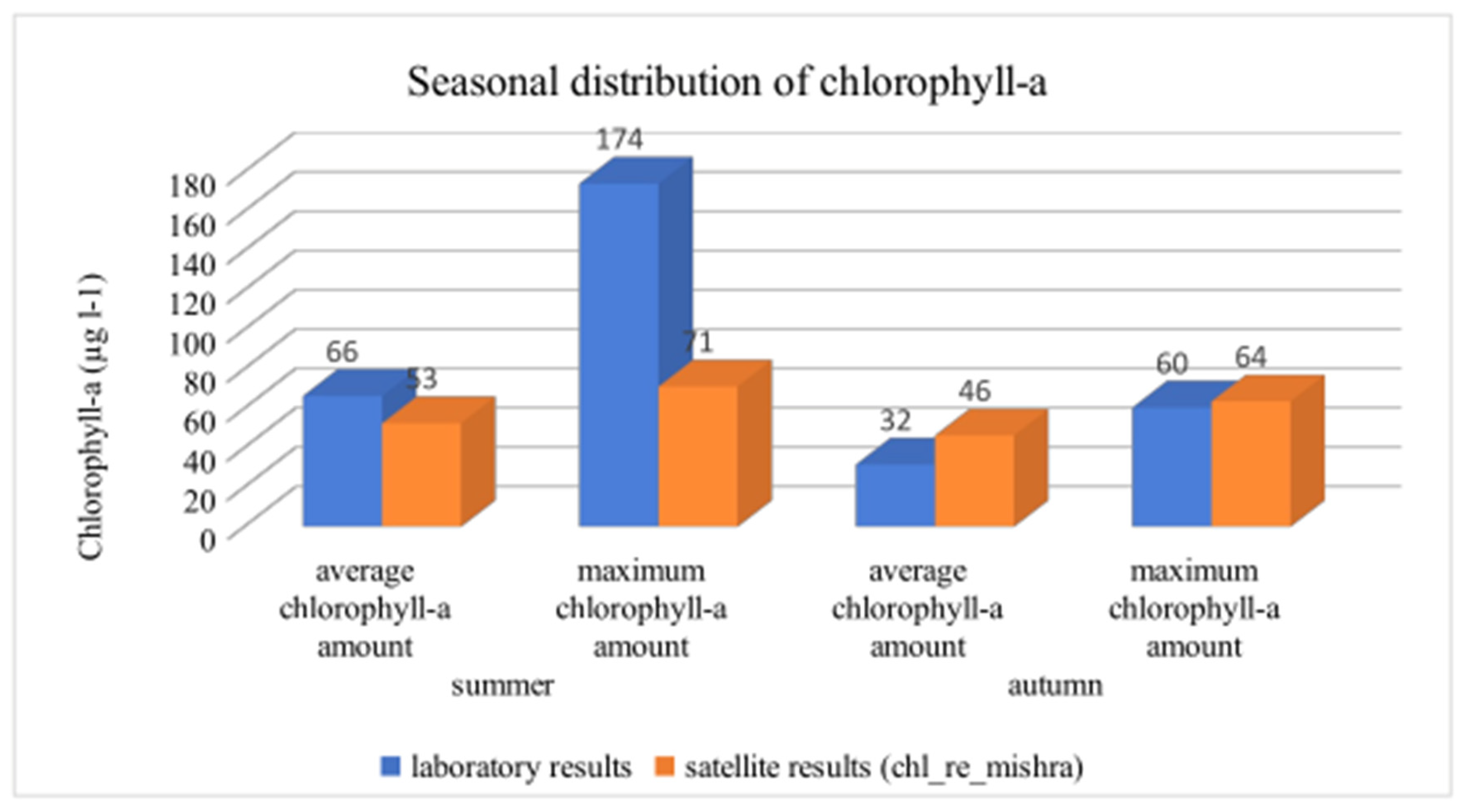
The chlorophyll-a concentration was investigated and divided into summer and autumn (spring and winter were excluded because of insufficient data). Figure 10 shows the related results.
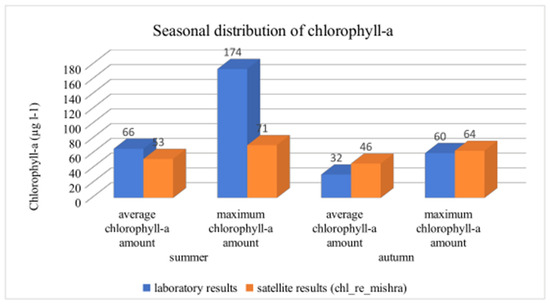
Figure 10.
Seasonal distribution of chlorophyll-a.
The laboratory and the satellite results show that the average chlorophyll-a concentration is higher in summer than in autumn. The difference is lower in the case of satellite measurements. The significant difference between maximum chlorophyll-a content in summer can be explained by the very high chlorophyll-a concentration (174 µg L−1), which leads to saturation, as we presented above. This phenomenon has also appeared in the case of Kis-Balaton, West Hungary, in previous studies [24].
4. Conclusions
A shallow lake, Lake Naplás, Budapest, characterized by a small open water surface area and reeds along the coast, was investigated. Laboratory and satellite data were analyzed, applying Sentinel-2 images and Acolite software to acquire chlorophyll-a data and maps. Of the seven Acolite algorithms, two fulfilled the requirement of normal distribution. From the two algorithms, chl_re_mishra showed a moderately strong correlation, proving the applicability of satellite remote sensing in the case of an optically complex lake. Because of the high CDOM concentration of Lake Naplás, the blue–green band ratio underestimated the content of chlorophyll-a. In the case of large chlorophyll-a concentrations, it is significantly underestimated by satellite remote sensing.
It was found that in the case of high surface chlorophyll-a concentration (above 30 µg L−1), the remotely sensed maximum chlorophyll-a value was strongly correlated with the surface chlorophyll-a content. The chl_re_mishra algorithm detected the maximum chlorophyll-a concentration in the 40 cm depth when the surface layer chlorophyll-a content was in a low range, i.e., under 25 µg L−1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, J.G., V.Z.T., and Z.V.; software, J.G. and V.Z.T.; validation, I.W.; formal analysis, J.G. and V.Z.T.; investigation, J.G. and V.Z.T.; resources, J.G. and V.Z.T.; data curation, J.G., V.Z.T., and G.H.; writing—original draft preparation, J.G. and V.Z.T.; writing—review and editing, G.H.; visualization, J.G. and V.Z.T.; funding acquisition, J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was granted the ÚNKP-22-4-II, the New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Culture and Innovation from the National Research, Development, and Innovation Fund.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to local computer storage.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Hungarian University of Agriculture and Life Sciences.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Veronika Zsófia Tóth was employed by the company K-Konstrukt Kft. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- European Community: Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2000 establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy. Off. J. Eur. Communities 2000, 43, 1–74.
- Padisák, J. Általános Limnológia; ELTE Eötvös Kiadó: Budapest, Hungary, 2005. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- Parésys, G.; Rigart, C.; Rousseau, B.; Wong, A.; Fan, F.; Barbiere, J.; Lavaud, J. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of phytoplankton communities by trichromatic chlorophyll fluorescence excitation with special focus on cyanobacteria. Water Res. 2005, 39, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babichenko, S.; Poryvkina, L.; Arikese, V.; Kaitala, S.; Kuosa, H. Remote sensing of phytoplankton using laser-induced fluorescence. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 45, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poryvkina, L.; Babichenko, S.; Leeben, A. Analysis of Phytoplankton Pigments by Excitation Spectra of Fluorescence. In Proceedings of the EARSeL-SIG-Workshop LIDAR, Dresden, Germany, 16–17 June 2000; pp. 224–232. [Google Scholar]
- Gregor, J.; Maršálek, B. Freshwater phytoplankton quantification by chlorophyll-a: A comparative study of in vitro, in vivo and in situ methods. Water Res. 2004, 38, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalf, J. Limnology: Inland Water Ecosystems; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grósz, J.; Waltner, I.; Vekerdy, Z. First analysis results of in situ measurements for algae monitoring in Lake Naplás (Hungary). Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 14, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.; Brando, V.; Anstee, J.; Pinnel, N.; Kutser, T.; Hoogenboom, E.; Peters, S.; Pasterkamp, R.; Vos, R.; Olbert, C.; et al. Imaging Spectrometry of Water. Imaging Spectrom. Basic Princ. Prospect. Appl. 2001, 4, 307–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mirnasab, M.A.; Hashemi, H.; Samaei, M.R.; Azhdarpoor, A. Advanced removal of water NOM by Pre-ozonation, Enhanced coagulation and Bio-augmented Granular Activated Carbon. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganf, G.G.; Oliver, R.L. Vertical Separation of Light and Available Nutrients as a Factor Causing Replacement of Green Algae by Blue-Green Algae in the Plankton of a Stratified Lake. J. Ecol. 1982, 70, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Szilágyi, F.; Mittenzwey, K.H. Improving quantitative remote sensing for monitoring of inland water quality. Water Res. 1993, 27, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.; Lavender, S.; Castaing, P. Spectral signature of highly turbid waters: Application with SPOT data to quantify suspended particulate matter concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, B.M.; Bicudo, C.E.M. Phytoplankton seasonal variation in a shallow stratified eutrophic reservoir (Garças Pond, Brazil). Hydrobiologia 2008, 600, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, R.; Thakur, R.; Singh, U.; Ahluwalia, A. Phytoplankton dynamics and water quality of Prashar Lake, Himachal Pradesh, India. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2014, 3–4, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10260:1992; Water Quality. Measurement of Biochemical Parameters. Spectrometric Determination of the Chlorophyll-a Concentration. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992.
- Jönsson, L. Satellite Data and Lakes. In Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs; Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Bengtsson, L., Herschy, R.W., Fairbridge, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Sandoval, M.; Ruiz-Verdú, A.; Tenjo, C.; Delegido, J.; Urrego, P.; Pena, R.; Vicente, E.; Soria, J.; Soria, J.; Moreno, J. Calibration and Validation of Algorithms for the Estimation of Chlorophyll-A in Inland Waters with Sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018–2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 9276–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alba, G.; Anabella, F.; Marcelo, S.; Andrea, G.A.; Ivana, T.; Guillermo, I.; Sandra, T.; Michal, S. Spectral monitoring of algal blooms in an eutrophic lake using sentinel-2. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Bramich, J.; Bolch, C.J.; Fischer, A. Improved red-edge chlorophyll-a detection for Sentinel 2. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.I. (Eds.) Hydrologic Remote Sensing: Capacity Building for Sustainability and Resilience; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tóth, V.Z.; Ladányi, M.; Jung, A. Adaptation and Validation of a Sentinel-Based Chlorophyll-a Retrieval Software for the Central European Freshwater Lake, Balaton. PFG—J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2021, 89, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R.; Morel, A.Y. Remote Assessment of Ocean Color for Interpretation of Satellite Visible Imagery: A Review; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, C.; Xu, H.; Fischer, A.M. Chlorophyll-a estimation around the Antarctica peninsula using satellite algorithms: Hints from field water leaving reflectance. Sensors 2016, 16, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.T.T.; Thao, N.T.P.; Koike, K.; Nhuan, M.T. Selecting the Best Band Ratio to Estimate Chlorophyll-a Concentration in a Tropical Freshwater Lake Using Sentinel 2A Images from a Case Study of Lake Ba Be (Northern Vietnam). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Rundquist, D.C. Comparison of NIR/RED ratio and first derivative of reflectance in estimating algal-chlorophyll concentration: A case study in a turbid reservoir. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, B.-H.; Fu, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, M.; Chen, G.; Pan, X. Estimation of Chlorophyll-A Concentration with Remotely Sensed Data for the Nine Plateau Lakes in Yunnan Province. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bognár, A.L. Védett Természeti Értékek a Fővárosban. (‘Environmental Protected Values in the Capital [of Budapest, Hungary]’); Főpolgármesteri Hivatal: Budapest, Hungary, 2008; p. 38. (In Hungarian) [Google Scholar]
- USGS. Available online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 6 August 2022).
- Copernicus. Available online: https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Ha, N.T.T.; Koike, K.; Nhuan, M.T. Improved Accuracy of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Estimates from MODIS Imagery Using a Two-Band Ratio Algorithm and Geostatistics: As Applied to the Monitoring of Eutrophication Processes over Tien Yen Bay (Northern Vietnam). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, W.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.-K.; Chon, K.; Kang, E.T.; Park, Y.; Kim, S. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 Based Chlorophyll-a Estimation in a Small-Scale Reservoir: Assessing Accuracy and Availability. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, X. Improving lake chlorophyll-a interpreting accuracy by combining spectral and texture features of remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 83628–83642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acolite. Available online: https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/remsem/software-and-data/acolite (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- QGIS.org: QGIS 3.14. Geographic Information System API Documentation. QGIS Association. Available online: https://api.qgis.org/api/3.14/ (accessed on 28 November 2023).
- IBM Corp. Released 2017. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows; Version 25.0; IBM Corp: Armonk, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://www.ibm.com/support/pages/how-cite-ibm-spss-statistics-or-earlier-versions-spss (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Acolite for Sentinel-2: Aquatic applications of MSI imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 ESA Living Planet Symposium, Prague, Czech Republic, 9–13 May 2016; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Alcolite User Manual. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/650829066/acolite-manual-20221114-0 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Ruddick, K.G. A chlorophyll-retrieval algorithm for satellite imagery (Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer) of inland and coastal waters. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Saprygin, V.; Povazhnyi, V. Operational MERIS-based NIR-red algorithms for estimating chlorophyll-a concentrations in coastal waters—The Azov Sea case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.R. Normalized difference chlorophyll index: A novel model for remote estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in turbid productive waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryding, S.O.; Rast, W.; Uhlmann, D.; Clasen, J.; Somlyody, L.; Schorscher, J. (Eds.) Le Contrôle de L’eutrophisation des Lacs et des Reservoirs; Masson: Singapore, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Giripunje, M.; Fulke, A.; Khaimar, K.; Mesharam, P.; Paunikar, W. A review of phytoplankton ecology in freshwater lakes of India. Lakes Reserv. Ponds 2013, 7, 127–141. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).