A Comprehensive Review on Ecological Buffer Zone for Pollutants Removal
Abstract
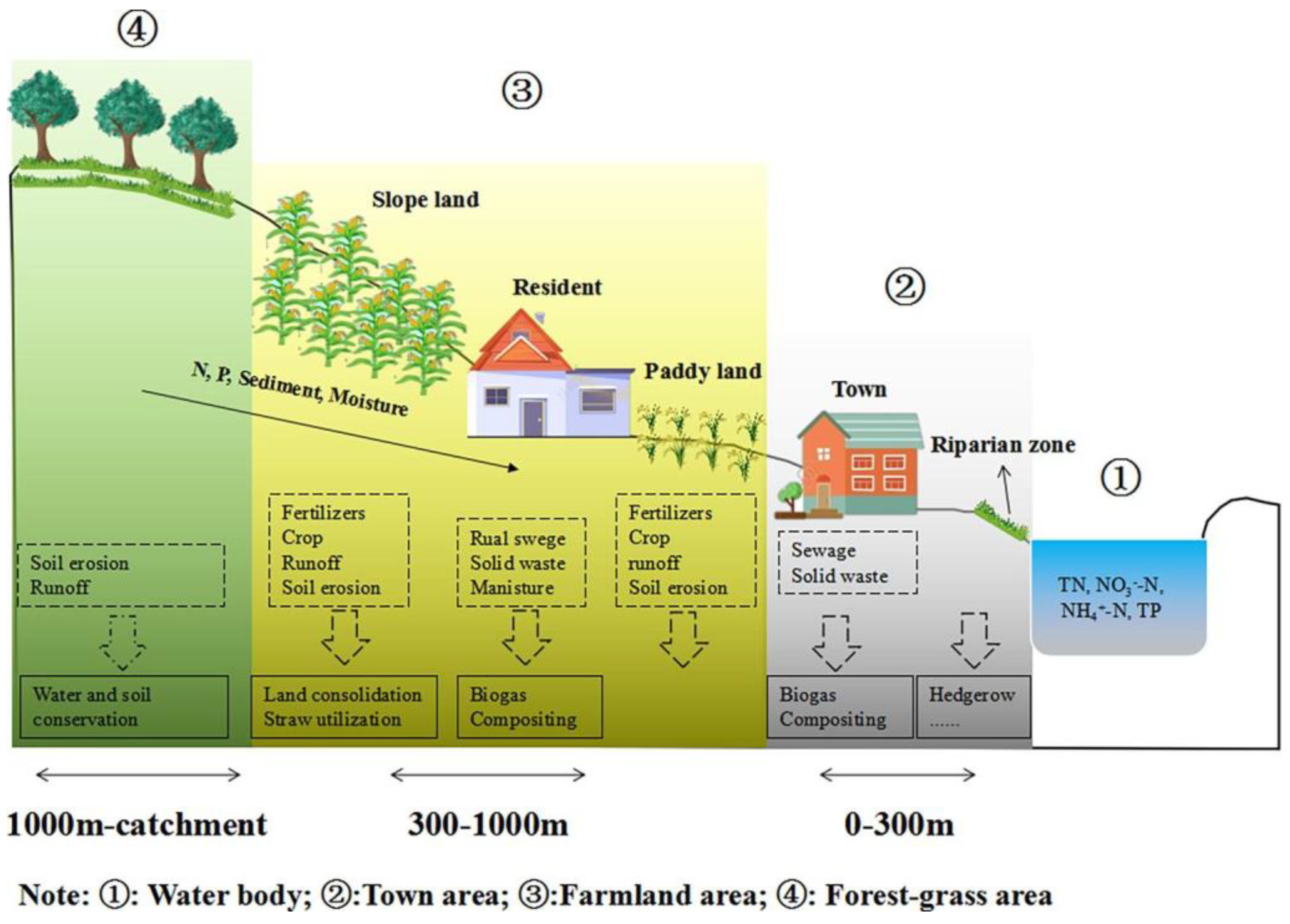
1. Introduction
2. Methods
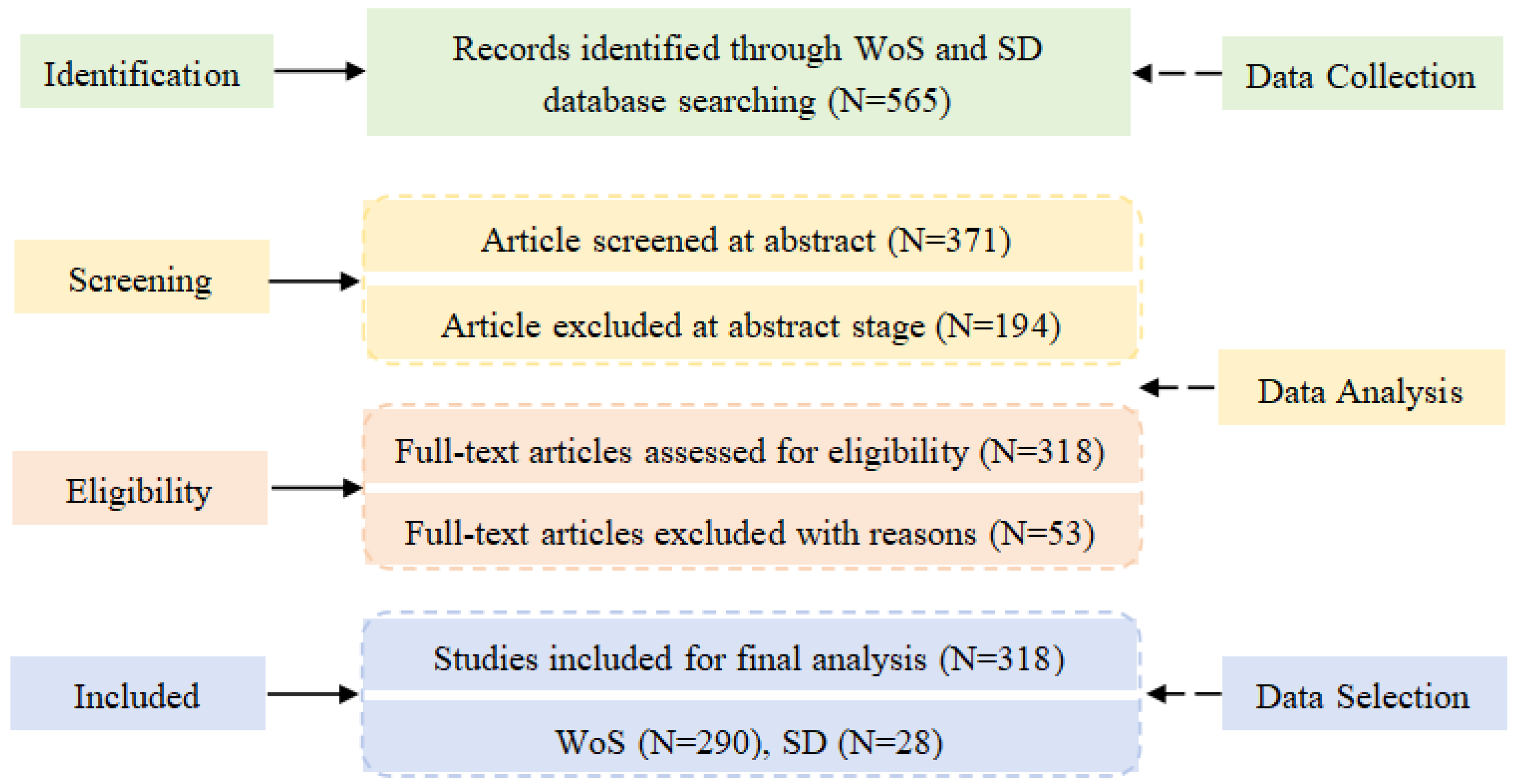
2.1. Literature Acquisition Sources
2.2. Literature Selection Criteria and Classification
3. Mechanism of Buffer Zones in Removing Pollutants
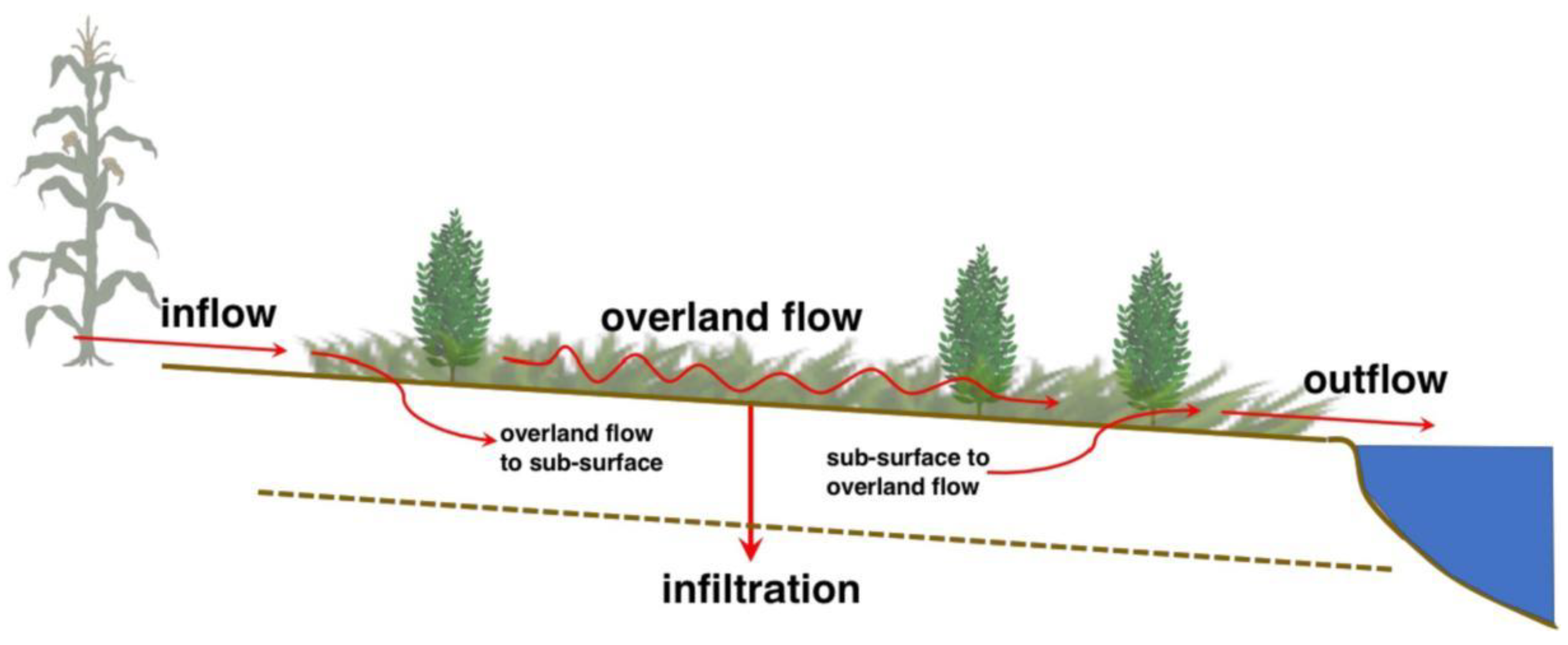
3.1. Physical Processes
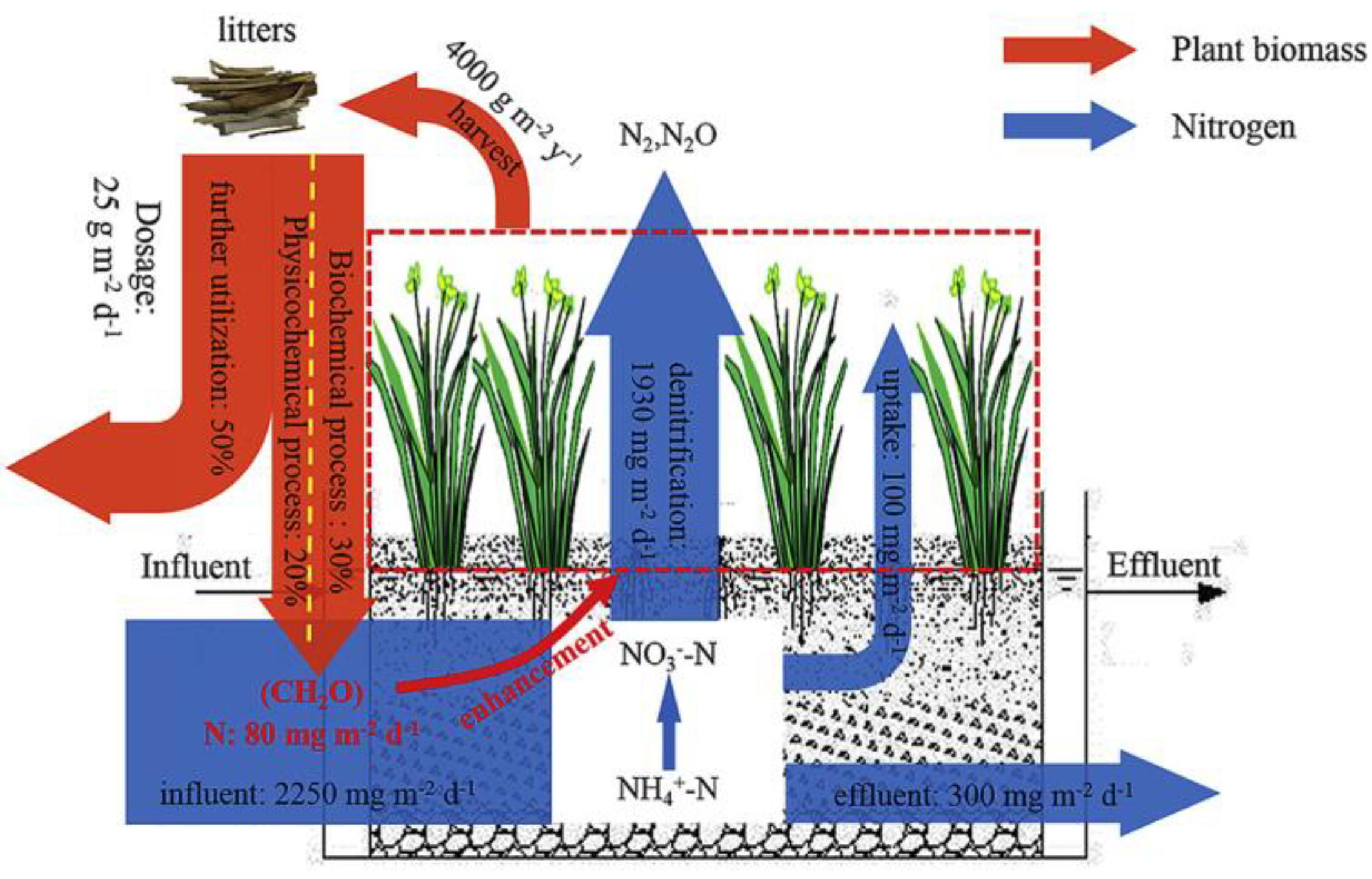
3.2. Absorption and Assimilation Process by Plants
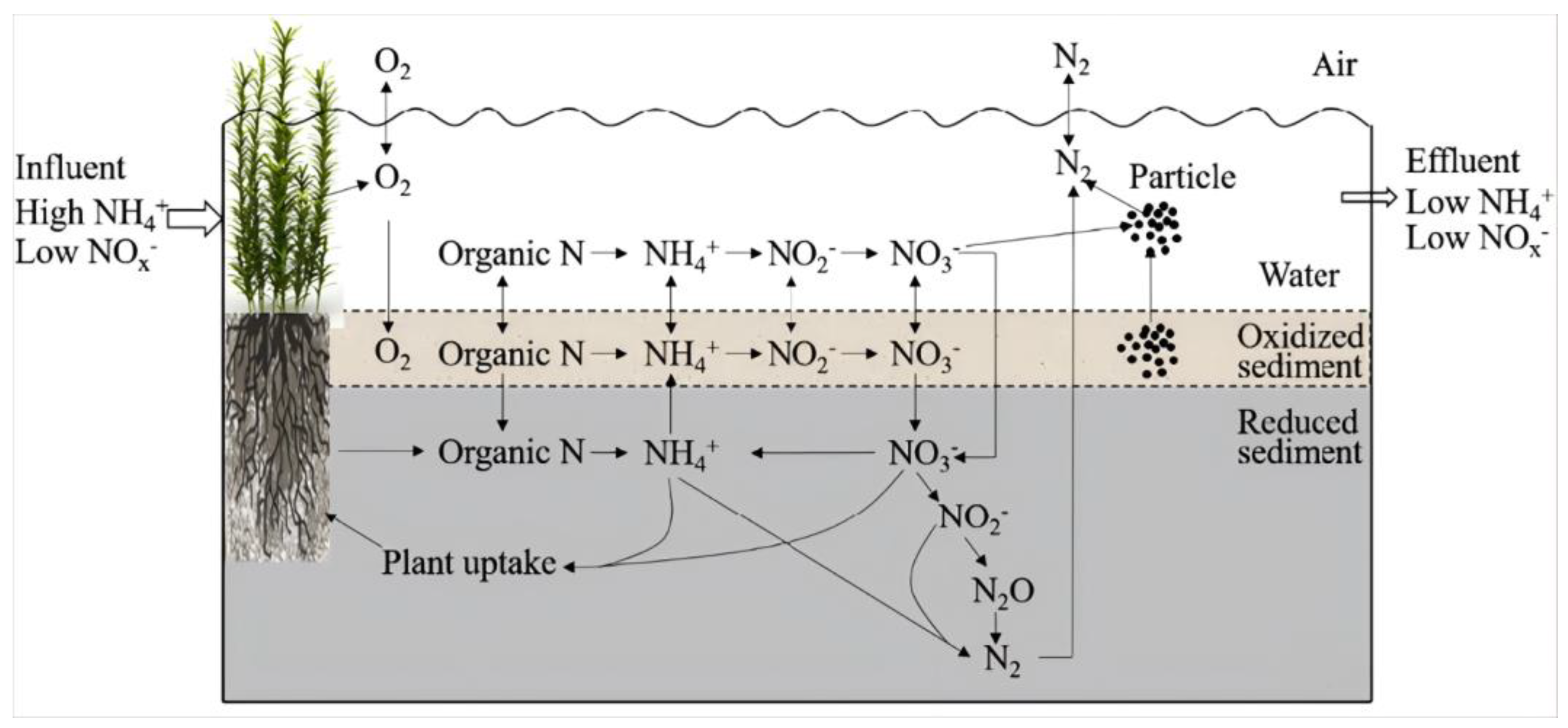
3.3. Microbiological Effects
4. Affecting Factors for Pollutants Removal
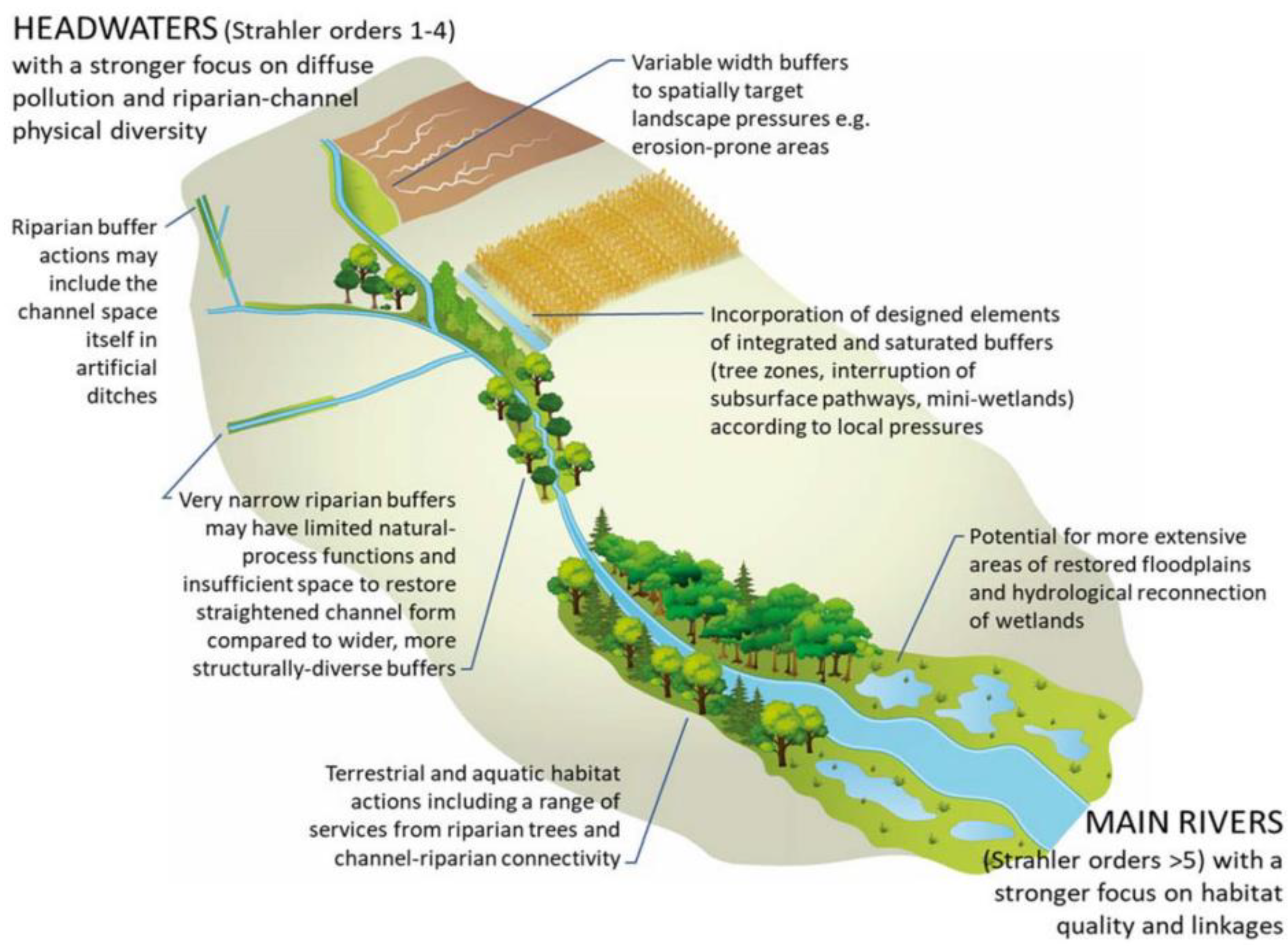
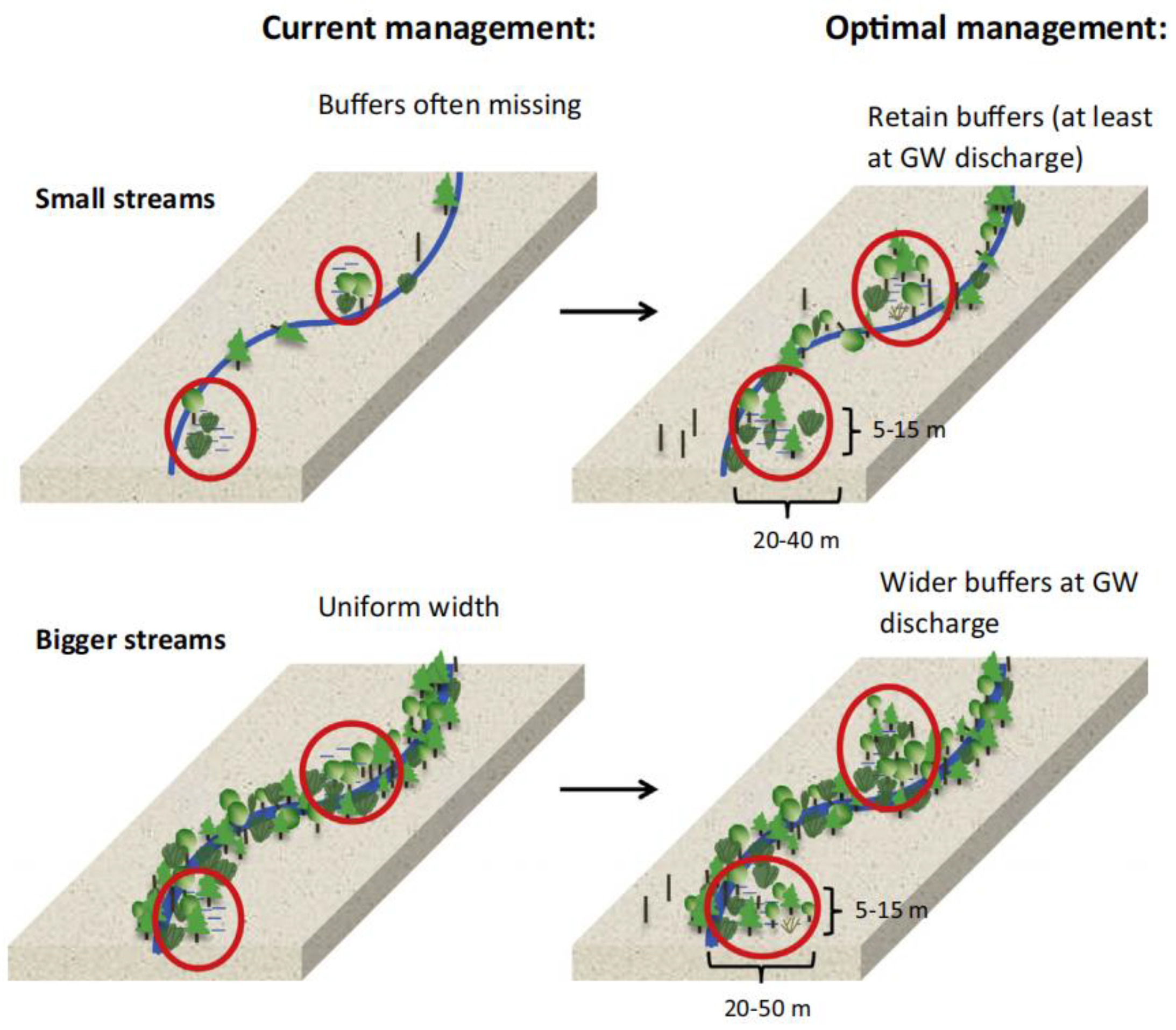
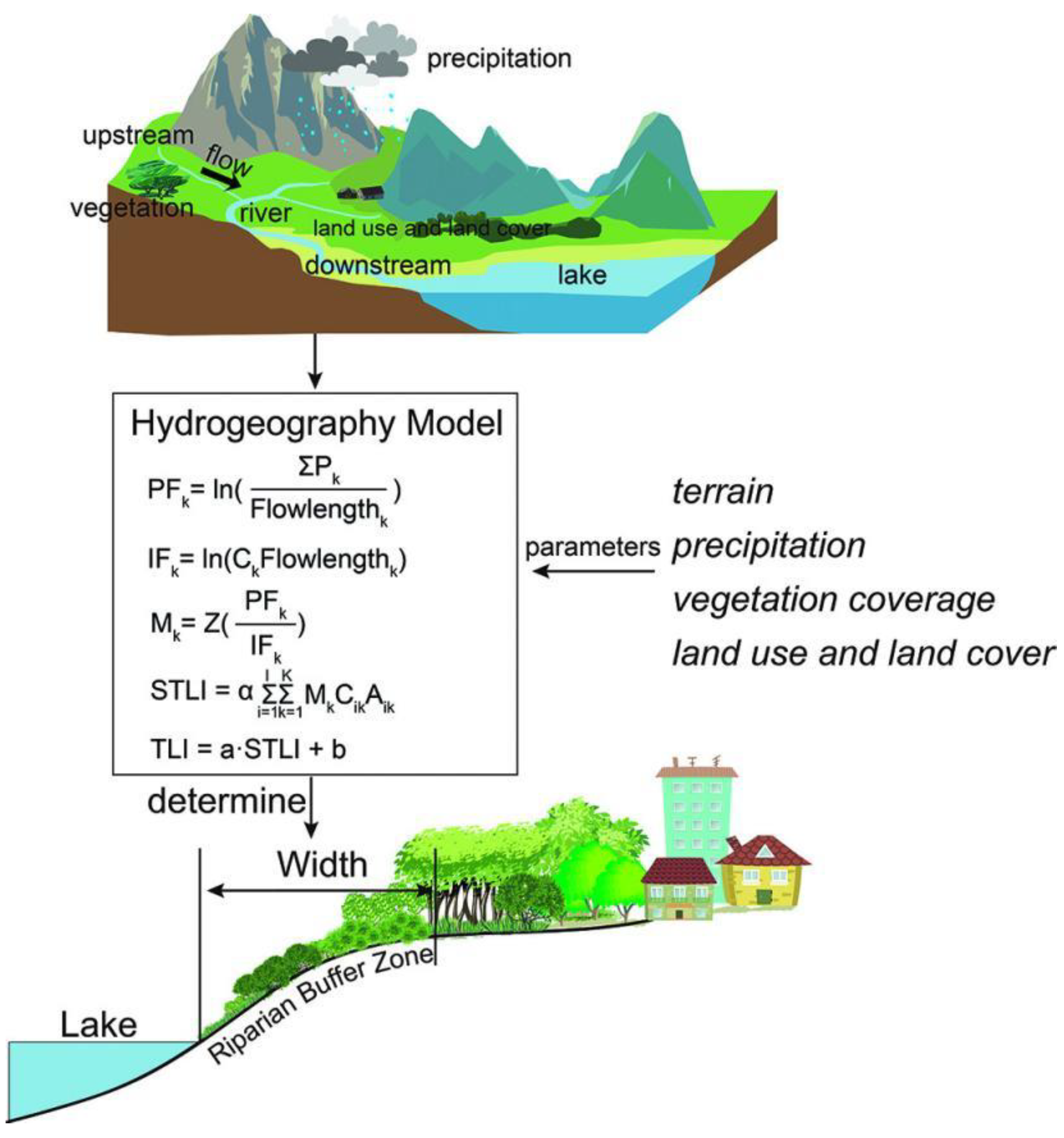
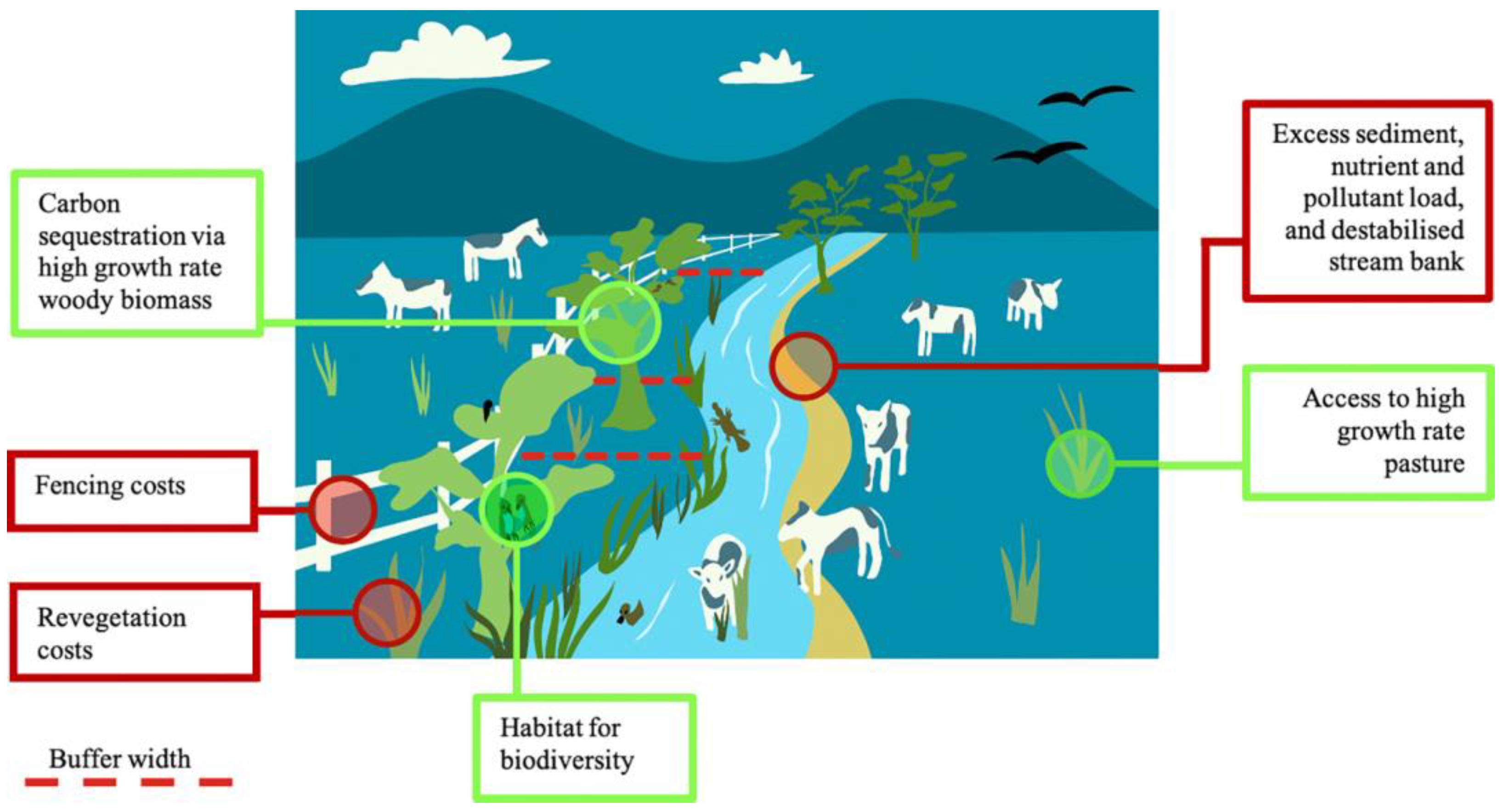
4.1. Buffer Zone Width
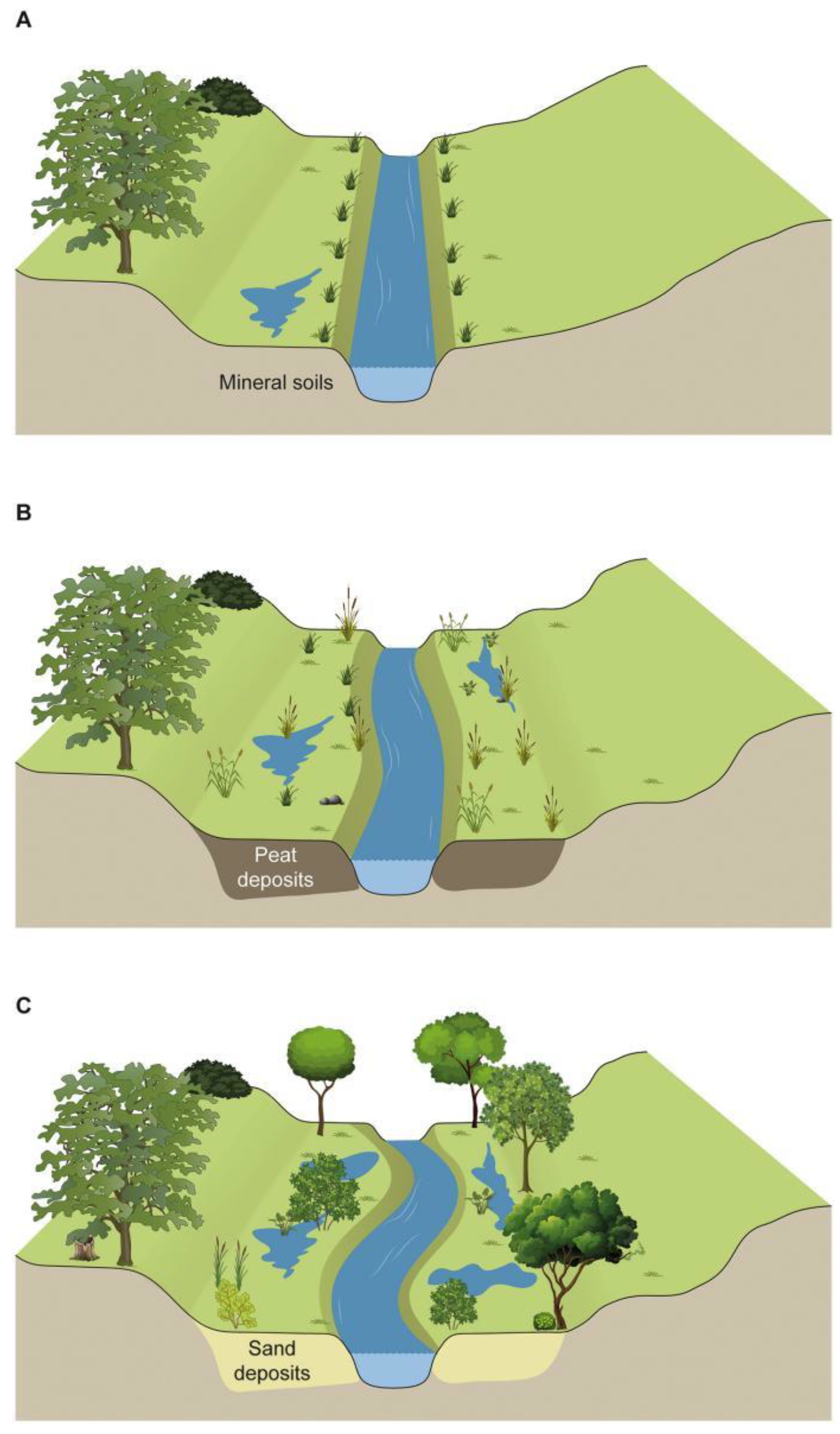
4.2. Vegetation Type
4.3. Slope and Runoff Intensity
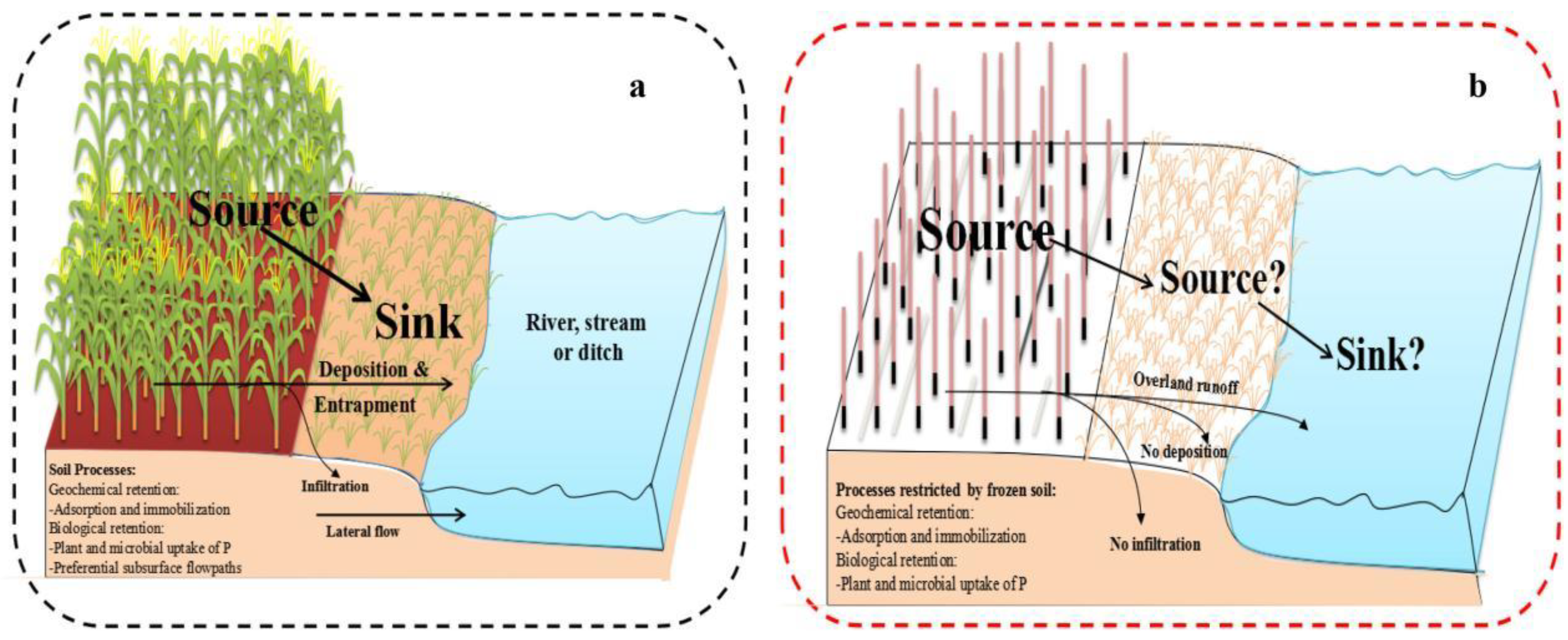
4.4. Seasonal Variation
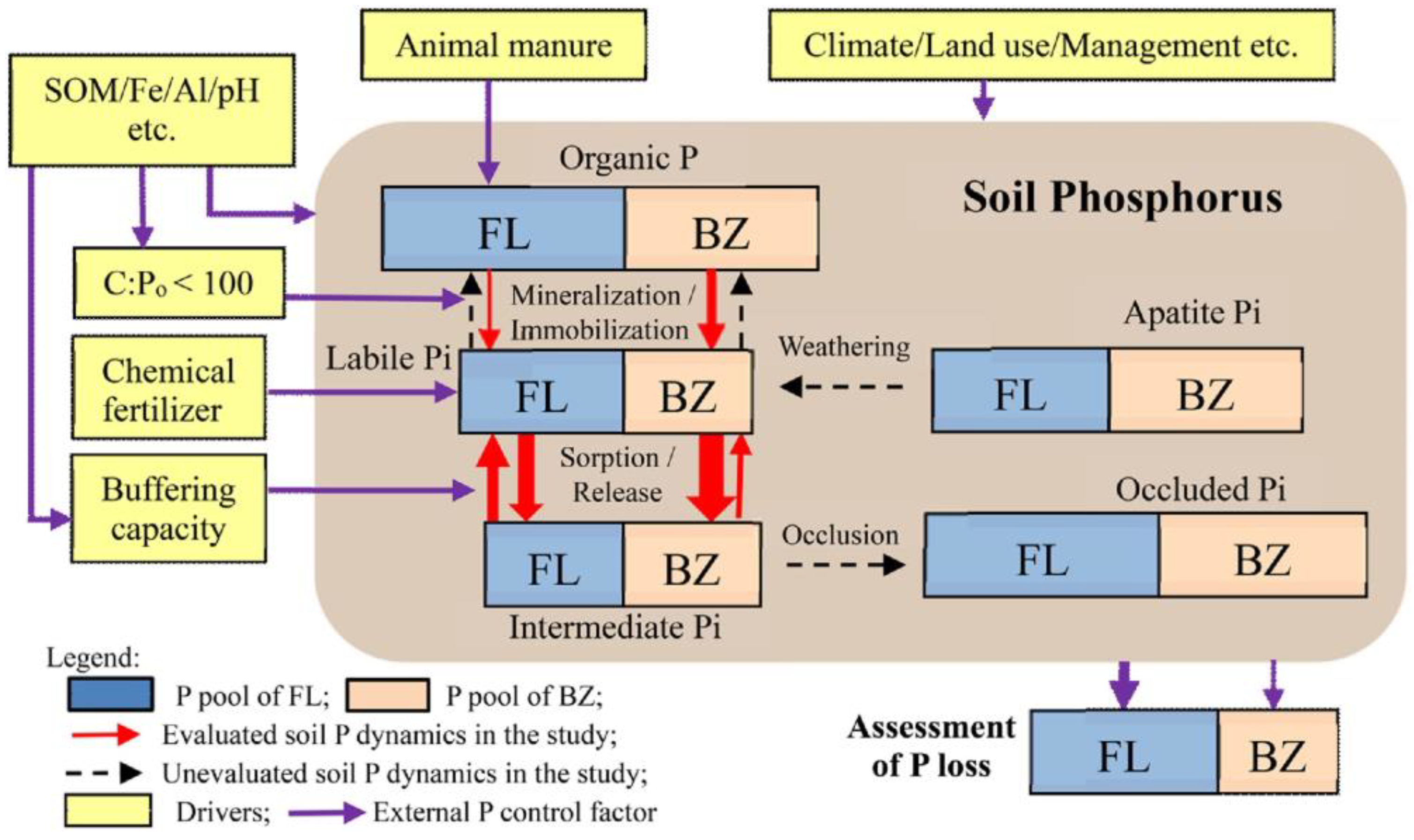
4.5. Soil Composition
4.6. Vegetation Density
4.7. Other Factors
4.7.1. Types and Contents of Pollutants
4.7.2. Microbial Activity
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| TN Total nitrogen | TP Total phosphorus |
| NH4+-N Ammonia nitrogen | PO43−-P Phosphate |
| NO3−-N Nitrate nitrogen | WWTPs Wastewater treatment plants |
| NO2−-N Nitrite nitrogen | SSF CWS Subsurface flow constructed wetlands |
| N2O Nitrous oxide | GW Groundwater |
| NOX Nitrogen oxides | CH2O Formaldehyde |
| N2 Nitrogen |
References
- Yang, C.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, X.; Cui, Z.; Tao, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Huang, Q. Driving forces and recovery potential of the macrophyte decline in East Taihu Lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Qu, X.; Liu, Y.; Rudstam, L.G.; Anderson, J.T.; Ni, L.; Chen, Y. Climate, hydrology, and human disturbance drive long-term (1988–2018) macrophyte patterns in water diversion lakes. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X. Assessment and analysis of agricultural non-point source pollution loads in China: 1978–2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Bashir, M.A.; Raza, Q.U.A.; Rehim, A.; Geng, Y.; Cao, L. Application of riparian buffer zone in agricultural non-point source pollution control—A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 985870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Long, H.; Li, Y.; Tu, S.; Jiang, T. Non-point source pollution in response to rural transformation development: A comprehensive analysis of China’s traditional farming area. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 83, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, F.K.; Grote, K. Statistical assessment of nonpoint source pollution in agricultural watersheds in the Lower Grand River watershed, MO, USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 26, 1487–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, J.; Qiang, Y.; Fang, S.; Gao, M.; Fan, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, B.; Feng, Y. Analysis of the environmental behavior of farmers for non-point source pollution control and management in a water source protection area in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.; Zheng, J.; Cui, X.; He, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, C.; Tan, B. Suitable coverage and slope guided by soil and water conservation can prevent non-point source pollution diffusion: A case study of grassland. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiao, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Xu, M.; Ge, T.; Meersmans, J.; Zhang, W. Manuring improves soil health by sustaining multifunction at relatively high levels in subtropical area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 353, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, D.; Goldhammer, T.; Cabezas, A.; Gelbrecht, J.; Gurke, R.; Wagner, C.; Reuter, H.; Augustin, J.; Klimkowska, A.; McInnes, R.; et al. Top soil removal reduces water pollution from phosphorus and dissolved organic matter and lowers methane emissions from rewetted peatlands. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 55, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Hasselquist, E.M.; Laudon, H. Towards ecologically functional riparian zones: A meta-analysis to develop guidelines for protecting ecosystem functions and biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Fu, Z.; Song, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, F. Application performance and nutrient stoichiometric variation of ecological ditch systems in treating non-point source pollutants from paddy fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 299, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.L.; Patel, N.; Rani, L.; Kumar, P.; Dutt, I.; Maddodi, B.S.; Chaudhary, V.K. Sustainable options for fertilizer management in agriculture to prevent water contamination: A review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 8303–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.R.; Zak, D.; Audet, J.; Petersen, R.J.; Lange, J.; Oehmke, C.; Wichtmann, W.; Kreyling, J.; Grygoruk, M.; Jabłońska, E.; et al. Wetland buffer zones for nitrogen and phosphorus retention: Impacts of soil type, hydrology and vegetation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yan, X.; Xie, H.; Qiu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Yan, X.; Xia, Y. Incorporating a new landscape intensity indicator into landscape metrics to better understand controls of water quality and optimal width of riparian buffer zone. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutter, M.; Kronvang, B.; Ó hUallacháin, D.; Rozemeijer, J. Current Insights into the Effectiveness of Riparian Management, Attainment of Multiple Benefits, and Potential Technical Enhancements. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, S.R.; Nayak, A.C.; Corona, J.; Parmar, R.; Srinivasan, R.; Mendoza, K.; Johnston, J.M. Holistic Sustainability Assessment of Riparian Buffer Designs: Evaluation of Alternative Buffer Policy Scenarios Integrating Stream Water Quality and Costs. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieta, K.A.; Owens, P.N.; Lobb, D.A.; Vanrobaeys, J.A.; Flaten, D.N. Phosphorus dynamics in vegetated buffer strips in cold climates: A review. Environ. Rev. 2018, 26, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.P.; Deguire, A.K.; Surasinghe, T.D. Riparian Buffers as a Critical Landscape Feature: Insights for Riverscape Conservation and Policy Renovations. Diversity 2022, 14, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosser, R.S.; Hoekstra, P.F.; Gene, S.; Truman, C.; White, M.; Hanson, M.L. A review of the effectiveness of vegetated buffers to mitigate pesticide and nutrient transport into surface waters from agricultural areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, K.; Cao, W. Simulation effects of clean water corridor technology on the control of non-point source pollution in the Paihe River basin, Chaohu lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23534–23546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dlamini, J.C.; Cardenas, L.M.; Tesfamariam, E.H.; Dunn, R.M.; Loick, N.; Charteris, A.F.; Cocciaglia, L.; Vangeli, S.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Upadhayay, H.R.; et al. Riparian buffer strips influence nitrogen losses as nitrous oxide and leached N from upslope permanent pasture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 336, 108031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, S.W.; Baskerville, M.; Oelbermann, M.; Gordon, A.M.; Thevathasan, N.V.; Isaac, M.E. Plant Diversity and Agroecosystem Function in Riparian Agroforests: Providing Ecosystem Services and Land-Use Transition. Sustainability 2020, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, H.I.; Nair, S.S.; Efroymson, R.A.; DeRolph, C.R.; Parish, E.S.; Wang, G. Ecosystem services from partially harvested riparian buffers can offset biomass production costs. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 889, 164199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, C.; Li, X.; Yuan, P.; Song, Y.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Yu, H. Nitrogen retention effect of riparian zones in agricultural areas: A meta-analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Zhang, D.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; Chen, A.; Wang, H. Shift of lakeshore cropland to buffer zones greatly reduced nitrogen loss from the soil profile caused by the interaction of lake water and shallow groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutter, M.; Costa, F. The interactions of site-specific factors on riparian buffer effectiveness across multiple pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsenga Kumwimba, M.; Huang, J.; Dzakpasu, M.; De Silva, K.; Ohore, O.E.; Ajibade, F.O.; Li, X.; Jing, J.S.; Muyembe, D.K.; Kaixuan, H. An updated review of the efficacy of buffer zones in warm/temperate and cold climates: Insights into processes and drivers of nutrient retention. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.F.; Li, J.K.; Liu, Y.W.; Peng, K.; Zhang, K. Evaluation of ecological buffer zone based on landscape pattern for non-point source pollution control: A case study in Hanjiang River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisandro, A.; Angel, V.G. Spatial modeling tool to assess and rank peri-urban land use in an agricultural region of the Midwestern United States. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshunsanya, S.O.; Li, Y.; Yu, H. Vetiver grass hedgerows significantly reduce nitrogen and phosphorus losses from fertilized sloping lands. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundersen, P.; Laurén, A.; Finér, L.; Ring, E.; Koivusalo, H.; Sætersdal, M.; Weslien, J.O.; Sigurdsson, B.D.; Högbom, L.; Laine, J.; et al. Environmental Services Provided from Riparian Forests in the Nordic Countries. Ambio 2010, 39, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulch, H.M.; Elliott, J.A.; Cordeiro, M.R.C.; Flaten, D.N.; Lobb, D.A.; Wilson, H.F. Soil and water management: Opportunities to mitigate nutrient losses to surface waters in the Northern Great Plains. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 447–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Mo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, M. Water quantity and quality changes from forested riparian buffer in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 29041–29051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weatherill, J.J.; Krause, S.; Ullah, S.; Cassidy, N.J.; Levy, A.; Drijfhout, F.P.; Rivett, M.O. Revealing chlorinated ethene transformation hotspots in a nitrate-impacted hyporheic zone. Water Res. 2019, 161, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene, S.M.; Hoekstra, P.F.; Hannam, C.; White, M.; Truman, C.; Hanson, M.L.; Prosser, R.S. The role of vegetated buffers in agriculture and their regulation across Canada and the United States. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Cai, C.; Zhang, J. Discussing on “source-sink” landscape theory and phytoremediation for non-point source pollution control in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44797–44806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goloran, J.B.; Phillips, I.R.; Chen, C. Forms of Nitrogen Alter Plant Phosphorus Uptake and Pathways in Rehabilitated Highly Alkaline Bauxite Processing Residue Sand. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moset, V.; Hille, S.; Rubæk, G.H.; Møller, H.B.; Wahid, R.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A. Indicators of biomass and methane yields in vegetated buffer strips. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Q.; Xiong, L.J.; Sha, C.Y. Removal of N, P from seepage and runoff by different vegetated and slope buffer strips. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, T.; Bahrndorff, S.; Alemayehu, E.; Ambelu, A. Agricultural sediment reduction using natural herbaceous buffer strips: A case study of the east African highland. Water Environ. J. 2017, 31, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Xue, J.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y.; Han, F.; Zhu, L. Sediment and nutrient removal by integrated tree-grass riparian buffers in Taihu Lake watershed, eastern China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Tian, R.; Li, H. Coupling of surface charges, adsorbed counterions and particle-size distribution on soil water infiltration and transport. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpley, A.N.; Kleinman, P.J.A.; Flaten, D.N.; Buda, A.R. Critical source area management of agricultural phosphorus: Experiences, challenges and opportunities. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 64, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorioz, J.M.; Wang, D.; Poulenard, J.; Trévisan, D. The effect of grass buffer strips on phosphorus dynamics—A critical review and synthesis as a basis for application in agricultural landscapes in France. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 117, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, S.; Andersen, D.K.; Kronvang, B.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A. Structural and functional characteristics of buffer strip vegetation in an agricultural landscape—High potential for nutrient removal but low potential for plant biodiversity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefting, M.M.; Clement, J.C.; Bienkowski, P.; Dowrick, D.; Guenat, C.; Butturini, A.; Topa, S.; Pinay, G.; Verhoeven, J.T.A. The role of vegetation and litter in the nitrogen dynamics of riparian buffer zones in Europe. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 24, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Hsu, T.C.; Huang, X.F.; Lin, H.J.; Kao, S.J. Nitrogen transformations and removal efficiency enhancement of a constructed wetland in subtropical Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Forestry Measures for Ecologically Controlling Non-Point Source Pollution in Taihu-Lake, China; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peterjohn, W.T.; Correll, D.L. Nutrient dynamics in an agricultural watershed: Observations on the role of a riparian forest. Ecology 1984, 65, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Yue, K.; Ni, X. Global Positive Effects of Litter Inputs on Soil Nitrogen Pools and Fluxes. Ecosystems 2022, 26, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadani, O.; Jebara, S.H.; Fatnassi, I.C.; Chiboub, M.; Mannai, K.; Zarrad, I.; Jebara, M. Effect of Vicia faba L. var. minor and Sulla coronaria (L.) Medik associated with plant growth-promoting bacteria on lettuce cropping system and heavy metal phytoremediation under field conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 8125–8135. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ding, B.; Li, Z. Impact of sand mining on the carbon sequestration and nitrogen removal ability of soil in the riparian area of Lijiang River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Hefting, M.M.; Schwark, L.; Zhu, G. Anammox and denitrification separately dominate microbial N-loss in water saturated and unsaturated soils horizons of riparian zones. Water Res. 2019, 162, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, F.; He, S.; Huang, J. Recycled utilization of Iris pseudacorus in constructed wetlands: Litters self-consumption and nitrogen removal improvement. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.L.; Kaushik, N.K.; Trevors, J.T.; Whiteley, H.R. Review: Denitrification in Temperate Climate Riparian Zones. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 111, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüsch, W.; Nilsson, B. Nitrate transformation and water movement in a wetland area. Hydrobiologia 1993, 251, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchithanantham, S.; English, B.; Wilson, H. Seasonality of Phosphorus and Nitrate Retention in Riparian Buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.; Frings, J.; Lennartz, B. Effect of grass buffer strips on nitrate export from a tile-drained field site. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Feng, L.; Yang, N.; Sun, Z.; Luo, Q. Effectiveness of Riparian Vegetated Filter Strips in Removing Agricultural Nonpoint Source Pollutants in Agricultural Runoff from the Liao River Area, China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 4709–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.M.; Julien, G.; Ernst, W.R.; Cook, A.; Doe, K.G.; Jackman, P.M. Evaluation of buffer zone effectiveness in mitigating the risks associated with agricultural runoff in Prince Edward Island. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Preisendanz, H.E.; Veith, T.L.; Cibin, R.; Drohan, P.J. Riparian buffer effectiveness as a function of buffer design and input loads. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, T.R., Jr.; Rasera, K.; Parron, L.M.; Brito, A.G.; Ferreira, M.T. Nutrient removal effectiveness by riparian buffer zones in rural temperate watersheds: The impact of no-till crops practices. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 149, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Qu, L.; Clausen, J.; Lei, T.; Yang, X. Impact of Riparian Buffer Zone Design on Surface Water Quality at the Watershed Scale, a Case Study in the Jinghe Watershed in China. Water 2023, 15, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, T.R.; Bortolozo, F.R.; Hansel, F.A.; Rasera, K.; Ferreira, M.T. Riparian buffer zones as pesticide filters of no-till crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10618–10626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, D.T.; MacDougall, A.S.; Levison, J. Impacts of soil, climate, and phenology on retention of dissolved agricultural nutrients by permanent-cover buffers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izydorczyk, K.; Michalska-Hejduk, D.; Jarosiewicz, P.; Bydałek, F.; Frątczak, W. Extensive grasslands as an effective measure for nitrate and phosphate reduction from highly polluted subsurface flow—Case studies from Central Poland. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo-Bescós, M.A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Kiker, G.A.; Bodah, B.W.; Ullman, J.L. Watering or buffering? Runoff and sediment pollution control from furrow irrigated fields in arid environments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 205, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xie, H.; Cao, Y. Effects of land use types on dissolved trace metal concentrations in the Le’an River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, H. Finite Element Simulation of Total Nitrogen Transport in Riparian Buffer in an Agricultural Watershed. Sustainability 2016, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Meng, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Multi-spatial scale effects of multidimensional landscape pattern on stream water nitrogen pollution in a subtropical agricultural watershed. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, C.; Jim, C.Y.; Johnson, V.C.; Tan, M.L. Determining the main contributing factors to nutrient concentration in rivers in arid northwest China using partial least squares structural equation modeling. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 343, 118249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Mao, J.; Zhu, D.; Lin, C. Impacts of Land Use and Land Cover on Water Quality at Multiple Buffer-Zone Scales in a Lakeside City. Water 2019, 12, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Bruijnzeel, L.A.; Mao, Z.; Yang, X.; Cardinael, R.; Meng, F.R.; Sidle, R.C.; Seitz, S. Reductions in water, soil and nutrient losses and pesticide pollution in agroforestry practices: A review of evidence and processes. Plant Soil 2019, 453, 45–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwimana, A.; van Dam, A.A.; Irvine, K. Effects of conversion of wetlands to rice and fish farming on water quality in valley bottoms of the Migina catchment, southern Rwanda. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 125, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salceda-Gonzalez, M.; Udawatta, R.P.; Anderson, S.H. Agroforestry on runoff nitrogen and phosphorus losses from three paired watersheds after 25 years of implementation. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 98, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, F.; Qiao, H.; Bi, Y. Effects of substrate improvement on winter nitrogen removal in riparian reed (Phragmites australis) wetlands: Rhizospheric crosstalk between plants and microbes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 95931–95944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Eitzel, M. A Review of Vegetated Buffers and a Meta-analysis of Their Mitigation Efficacy in Reducing Nonpoint Source Pollution. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Cao, L.; Zhang, X. Study on the planning and influential factors of the safe width of riparian buffer zones in the upper and middle reaches of the Ziwu River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 103703–103717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Li, Z.; Luo, C.; Wu, M.; Chao, L.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, H. The reduction effects of riparian reforestation on runoff and nutrient export based on AnnAGNPS model in a small typical watershed, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5934–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Duan, L.; Wang, J.; Peng, J.; Zheng, B. Determining the width of lake riparian buffer zones for improving water quality base on adjustment of land use structure. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 158, 106001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirabahenda, Z.; St-Hilaire, A.; Courtenay, S.C.; Van Den Heuvel, M.R. Assessment of the effective width of riparian buffer strips to reduce suspended sediment in an agricultural landscape using ANFIS and SWAT models. Catena 2020, 195, 104762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.R.; Burchell, M.R., II; Evans, R.O.; Osmond, D.L.; Gilliam, J.W. Riparian buffer located in an upland landscape position does not enhance nitrate-nitrogen removal. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds, S.K.; McCutchen, M.D.; Canfield, T.J. Meta-Analysis of Nitrogen Removal in Riparian Buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Wu, Y. Nitrogen removal by different riparian vegetation buffer strips with different stand densities and widths. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3541–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkama, E.; Usva, K.; Saarinen, M.; Uusi-Kämppä, J. A Meta-Analysis on Nitrogen Retention by Buffer Zones. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanyama, J.; Kristoff, H.; Isabirye, M.; Kahimba, F.; Maetens, W.; Kimaro, D.; Deckers, S. Evaluation of runoff and sediment trapping effectiveness of vegetative filter strips in the riparian zone of Lake Victoria. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 2011, 13, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, T.; Dosskey, M.G.; Hoagland, K.D. Filter strip performance and processes for different vegetation, widths, and contaminants. J. Environ. Qual. 1999, 28, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindaroğlu, T.; Reis, M.; Akay, A.E.; Tonguç, F. Hydroecological approach for determining the width of riparian buffer zones for providing soil conservation and water quality. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffney, P.M.; Richardson, J.S.; Bull, J.P. Responses of periphyton and insects to experimental manipulation of riparian buffer width along forest streams. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 1060–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, M.B.C.; Doran, B. A review of the efficiency of buffer strips for the maintenance and enhancement of riparian ecosystems. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 2004, 39, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuglerová, L.; Ågren, A.; Jansson, R.; Laudon, H. Towards optimizing riparian buffer zones: Ecological and biogeochemical implications for forest management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 334, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcher, J.; Critchell, K.; Matthews, T.G.; Lester, R.E. How wide, how much? A framework for quantifying the economic and ecological outcomes of altering riparian width on agricultural land. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 897, 165342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, I.; Kavian, A.; Habibnezhad Roushan, M.; Jafarian, Z. The efficiency of vegetative buffer strips in runoff quality and quantity control. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 15, 811–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, R.L.B.; Ziembowicz, T.; Torres, G.N.; Guzha, A.C.; Amorim, R.S.S.; Cardoso, D.; Johnson, M.S.; Santos, T.G.; Couto, E.; Gerold, G. Ecosystem services of a functionally diverse riparian zone in the Amazon–Cerrado agricultural frontier. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 21, e00819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, S.; Srinivas, R.; Magner, J. Using fuzzy logic-based hybrid modeling to guide riparian best management practices selection in tributaries of the Minnesota River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Y. Vegetated Buffer Zone Restoration Planning in Small Urban Watersheds. Water 2021, 13, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellaiah, D.; Yule, C.M. Effect of riparian management on stream morphometry and water quality in oil palm plantations in Borneo. Limnologica 2018, 69, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Schoonover, J.E.; Williard, K.W.J.; Sweet, A.L.; Stewart, J. Giant Cane Vegetative Buffer for Improving Soil and Surface Water Quality. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.M.; Hawkins, J.M.B.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Zhang, Y.; Collins, A.L. Impacts of different vegetation in riparian buffer strips on runoff and sediment loss. Hydrol. Process. 2022, 36, e14733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, S.; Li, X.; Dzakpasu, M.; Ifon, B.E.; Manirakiza, B.; Muyembe, D.K.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guadie, A. Nutrient and sediment retention by riparian vegetated buffer strips: Impacts of buffer length, vegetation type, and season. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 369, 109050. [Google Scholar]
- Haukos, D.A.; Johnson, L.A.; Smith, L.M.; McMurry, S.T. Effectiveness of vegetation buffers surrounding playa wetlands at contaminant and sediment amelioration. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 181, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Gao, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, C. The Comprehensive Reduction Capacity of Five Riparian Vegetation Buffer Strips for Primary Pollutants in Surface Runoff. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusi-Kämppä, J.; Braskerud, B.; Jansson, H.; Syversen, N.; Uusitalo, R. Buffer zones and constructed wetlands as filters for agricultural phosphorus. J. Environ. Qual. 2000, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, C.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Zheng, R.; Que, X. Effectiveness of narrow grass hedges in reducing atrazine runoff under different slope gradient conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 25, 7672–7680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Cao, M. Removal efficiencies of vegetation-specific filter strips on nonpoint source pollutants. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Deng, L.; Gao, H. Effects of rainfall intensity, slope angle, and vegetation coverage on the erosion characteristics of Pisha sandstone slopes under simulated rainfall conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 17458–17467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, O.; Rojas, C.; Avendaño, F.; Realini, P.; Nájera, F.; Tapia, Y. Inorganic nitrogen losses from irrigated maize fields with narrow buffer strips. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 102, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, G.; Lin, X.; Cheng, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, X. Evidence of Nitrogen Loss from Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation Coupled with Ferric Iron Reduction in an Intertidal Wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11560–11568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieta, K.A.; Owens, P.N.; Vanrobaeys, J.A.; Lobb, D.A. Seasonal Changes in Phosphorus in Soils and Vegetation of Vegetated Filter Strips in Cold Climate Agricultural Systems. Agriculture 2022, 12, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.M.; Griffiths, S.W.; Ormerod, S.J. Beyond cool: Adapting upland streams for climate change using riparian woodlands. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 22, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, A.; Duan, C.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Land use effects on soil phosphorus behavior characteristics in the eutrophic aquatic-terrestrial ecotone of Dianchi Lake, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Liu, X.; Tan, J.; Shao, X.; Cheng, J. Effect of Plant Buffer Zone–Antifouling Curtain Wall on Reducing Non-Point Source Pollution in Paddy Fields, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibiandehkordi, R.; Quinton, J.N.; Surridge, B.W.J. Enhancing soluble phosphorus removal within buffer strips using industrial by-products. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12257–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, C.J.; Bryant, R.B.; Callahan, M.P.; McGrath, J.M. Use of Industrial By-products to Sorb and Retain Phosphorus. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, A.; Zhao, J. Effectiveness of vegetation cover pattern on regulating soil erosion and runoff generation in red soil environment, southern China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ma, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, Q.; Zheng, J. Combining infiltration hole and mulching techniques with fish-scale pits effectively improved soil water storage in semiarid areas with shallow buried bedrock (Pisha Sandstone) in China. Catena 2023, 230, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.X.; Römkens, M.J.M. Experimental studies of factors in determining sediment trapping in vegetative filter strips. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 277. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Xiang, K.; Zeng, Y.; Gu, H.; Guan, Y.; Chen, S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in air, foliage, and litter in a subtropical forest: Spatioseasonal variations, partitioning, and litter-PAH degradation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 328, 121587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hénault-Ethier, L.; Lucotte, M.; Smedbol, É.; Gomes, M.P.; Maccario, S.; Laprise, M.E.L.; Perron, R.; Larocque, M.; Lepage, L.; Juneau, P.; et al. Potential Efficiency of Grassy or Shrub Willow Buffer Strips against Nutrient Runoff from Soybean and Corn Fields in Southern Quebec, Canada. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Zhao, G.; Peng, C.; Ye, W.; Xie, D.; Chen, F.; Ni, C.; Shao, J.; Zheng, L.; Ni, J. Multi-scale effects of landscape on nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) in a subtropical agricultural watershed: A case of Qi river basin (QRB), China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L.J.; Stockan, J.; Helliwell, R. Managing riparian buffer strips to optimise ecosystem services: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 296, 106891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, H.Y.; Rao, C.; Jiang, C.; Tan, Y.C.; Yu, T.; Yu, E.J.; Wu, P. Soil microbial community dynamics indicate disruption of nitrogen cycling by pollution in vegetation buffer zones. Pedobiologia 2021, 85, 150722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzetti, L.L.; Jones, R.C.; Murphy, R.F. Stream condition in Piedmont streams with restored riparian buffers in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2010, 46, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, C.M.; Neils, A.; Hooper, D. Impacts of land use at the catchment scale constrain the habitat benefits of stream riparian buffers. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
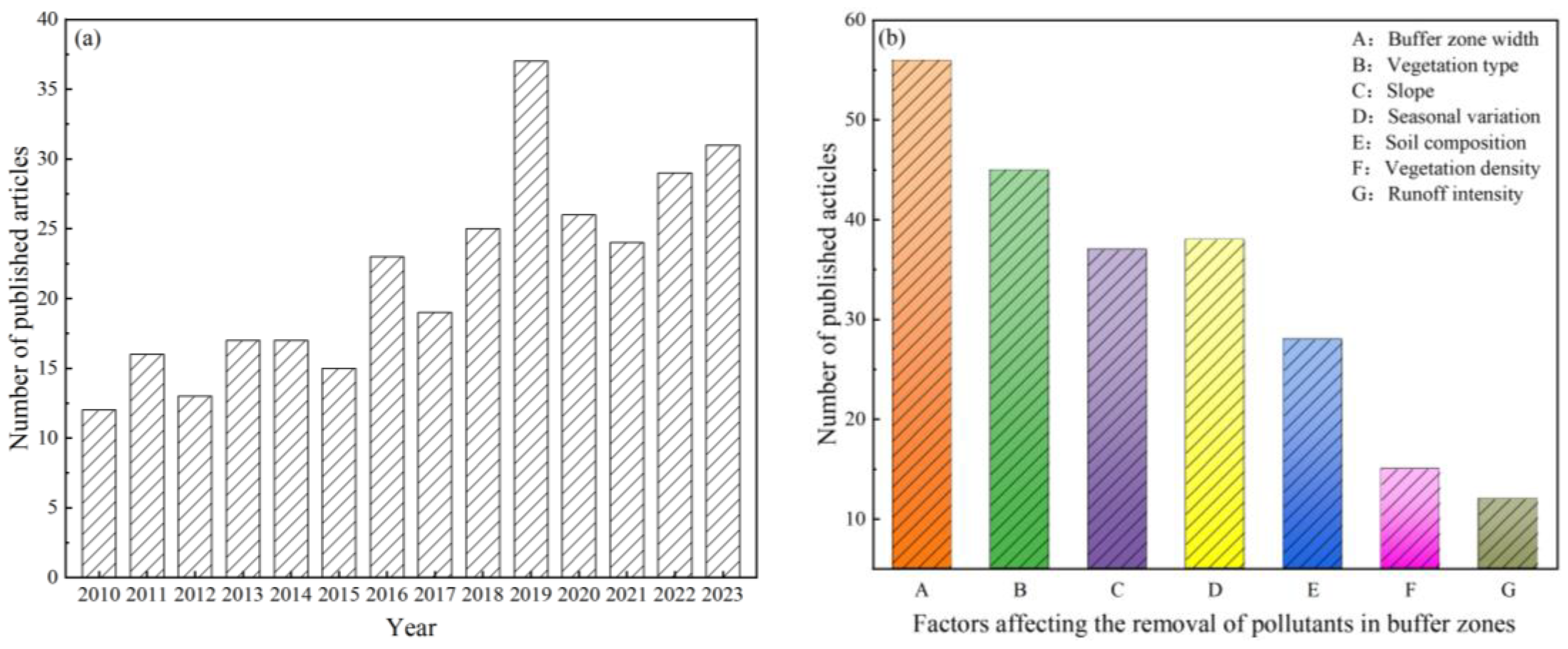
| Database | Retrieval String | Number | Search Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| Web of Science | First search string: buffer zone, second search string: water pollution, third search string: agriculture | 364 | 30 June 2024 |
| First search string: buffer zone, second search string: water pollution, third search string: mechanism | 138 | 30 June 2024 | |
| ScienceDirect | Keywords in the title or abstract: buffer zone, pollution | 28 | 30 June 2024 |
| Keywords in the title or abstract: buffer zone, agriculture | 35 | 30 June 2024 | |
| Total | — | 565 | 30 June 2024 |
| Retrieval String | Number of Articles in the Initial Searching | Number of Relevant Articles Based on the Exacting Screening |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | 52 | 28 |
| Buffer zone width | 83 | 56 |
| Vegetation type | 67 | 45 |
| Slope | 58 | 37 |
| Seasonal variation | 48 | 38 |
| Soil composition | 201 | 28 |
| Vegetation density | 22 | 15 |
| Runoff intensity | 20 | 12 |
| Others | — | — |
| Buffer Zone Width | Vegetation Type | Slope | Soil Composition | Average Annual Precipitation | Average Temperature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1, 3, 7 m | Grass | <3% | — | 665 mm | 8.2 °C | [59] |
| 5, 9, 13 m | Weeds, sweet clover, and sweet clover/Chinese wingnut | 10–20% | Sand, clay, and silt | 665 mm | Minus 13.7 °C to 23.7 °C | [60] |
| 10, 30 m | White clover, meadow fescue, and timothy | 1–14% | Fine sand | — | — | [61] |
| 10, 15, 30 m | Grass, deciduous trees, and trees | — | Hagerstown and Opequon | 1050 mm | — | [62] |
| 12, 24, 36, 48, 60 m | Woody vegetation, shrubs, or grass | 8–9% | Clay | 1650 mm | 18 °C | [63] |
| 0, 10, 20 m | Willows and poplars | — | Loess soil | 350–600 mm | 8 °C | [64] |
| 12, 36, 60 m | Grass vegetation, shrubs, and woody vegetation | 8–9% | — | 1650 mm | 18 °C | [65] |
| 2, 4, 8 m | Native tallgrass prairie grasses and forbs | 5–10% | Sand or clay | 1035.8 mm | 8 °C | [66] |
| 25, 45 m | Tall forbs or swamp non-forest communities | 0.5–3.0% | Soil, fine sands, grits, and coarse sand | 600 mm | 8.6 °C | [67] |
| 3.05, 6.1, 9.14 m | Ordeum vulgare, medicago sativa, | 0.5–2.0% | Loamy sand, sandy loam, loam, and silty loam | 150 mm | 0–23.1 °C | [68] |
| bromus marginatus, and pascopyrum smithii | ||||||
| 0–200, 200–500, | Agriculture, forest, grassland, and urban | 0–5% | — | 1900 mm | 17 °C | [69] |
| 500–1000 m | ||||||
| 1, 3, 4, 6 m | Forest and tillage crops | 8% | Loamy soils | 450–700 mm | 6.25 °C | [70] |
| 100–700 m | Forest, paddy field, and tea field | 0–80.30° | Ultisols, anthrosols, and inceptisols | 1340 mm | 17.5 °C | [71] |
| 500, 1000 m | Site buffer, riparian buffer, and catchment buffer | — | — | — | — | [72] |
| 500, 800, 1000 | Forest land, water area, agricultural land, | — | — | 1680 mm | 17.5 °C | [73] |
| 1200, 1500, 1800 m | bare land, construction land | |||||
| — | Silvopastoral systems, silvoarable agroforestry, and | — | — | — | — | [74] |
| linear tree plantings | — | |||||
| — | Rice plant and grass samples | — | Ponds, rice fields, and natural wetlands | 1200 mm | 20 °C | [75] |
| — | Arboraceous, herbaceous, and aerenchymous | — | Organic and mineral | — | — | [14] |
| 4.5 m | Trees and grasses | 1–5%, 5–9% | Putnam silt loam soil and armstrong loam soil | 978 mm | — | [76] |
| — | Phragmites australis | — | Gravel, gravel + biochar, ceramsite + biochar, | 1191.5 mm | 16.1 °C | [77] |
| and modified ceramsite + biochar | ||||||
| 30 m | — | ≤10%, >10% | — | — | — | [78] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Gao, X.; Wu, S.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C. A Comprehensive Review on Ecological Buffer Zone for Pollutants Removal. Water 2024, 16, 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152172
Wang D, Gao X, Wu S, Zhao M, Zheng X, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Fan C. A Comprehensive Review on Ecological Buffer Zone for Pollutants Removal. Water. 2024; 16(15):2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152172
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dongsheng, Xing Gao, Suqing Wu, Min Zhao, Xiangyong Zheng, Zhiquan Wang, Yejian Zhang, and Chunzhen Fan. 2024. "A Comprehensive Review on Ecological Buffer Zone for Pollutants Removal" Water 16, no. 15: 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152172
APA StyleWang, D., Gao, X., Wu, S., Zhao, M., Zheng, X., Wang, Z., Zhang, Y., & Fan, C. (2024). A Comprehensive Review on Ecological Buffer Zone for Pollutants Removal. Water, 16(15), 2172. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16152172







