Abstract
The Qinling region in central China, known as the ‘Dragon Vein of China’, is a vital ecological barrier facing significant soil erosion challenges. This study aims to enhance soil erosion management and analyse the spatiotemporal changes of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains. We collected data on precipitation, terrain, land use types, and soil in the designated region. Using GIS technology and the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model, we created a detailed soil erosion map and analysed its evolution from 2018 to 2022. Results show a significant reduction in soil erosion in 2020–2021 despite a general upward trend in other years. Innovation includes integrating remote sensing with RUSLE for high-precision mapping and introducing a hierarchical approach for erosion risk assessment. The study found erosion peaks in summer and autumn, with higher levels in the southern parts compared to the northern parts. Influential factors include climate variables, human activities, soil, and vegetation types. The average soil erosion modulus in 2023 is 233.515 t/(km2·a), with total soil erosion of 85,233.046 t/a, mainly concentrated in the valley and mountain basin areas. This research provides a theoretical basis for improving the natural environment and implementing comprehensive soil and water conservation measures in the Qinling region, offering a model for similar ecological regions globally.
1. Introduction
Water-induced soil erosion is a major worldwide problem, reducing soil fertility and land degradation and compromising the long-term sustainability and productivity of agricultural regions. Soil erosion is a natural process influenced by natural factors and accelerated by human activities such as deforestation, construction, agriculture, and mining. Erosion is a natural part of the Earth’s geological development. However, it becomes a problem when human activities speed up erosion. This is especially concerning when excessive soil loss affects the quality of the soil and reduces crop yield [,]. It is worth mentioning that almost 85% of land degradation worldwide is caused by soil erosion, with much of it happening in the last five decades, resulting in a 17% decrease in crop yield []. Soil erosion is the process by which soil or its parent material is disrupted, displaced, transported, and deposited by external forces, which leads to land deterioration []. The adverse consequences of soil erosion have profound effects on various aspects, including land use, agricultural productivity, water resource management, and the sustainable development of human societies. It has developed into a significant cause of concern that incorporates both societal and environmental factors [,]. Water-induced soil erosion is a significant global problem that reduces soil fertility, causes land degradation, and adversely affects the sustainability and productivity of agricultural regions.
The Qinling region in central China is called the ‘Dragon Vein of China.’ It serves as a fundamental ecological barrier in the central and western regions of the country, playing a significant role in maintaining China’s ecological security and biodiversity []. However, due to prolonged unsustainable development, the natural environment in the Qinling region witnessed a period of deterioration, which had an essential impact on the overall viability of the area [,,]. In recent years, there has been a significant enhancement in the efficiency of ecological governance, which may be linked to the implementation of the ‘Two-Mountain Theory’ and increased focus on ecological conservation efforts in the Qinling region. Although there has been some progress in terms of overall soil erosion, controlling current levels of soil erosion remains challenging in particular agricultural and environmentally vulnerable areas [,]. Models developed to anticipate the soil erosion process are essential for analysing the structure and advancement of soil erosion. Currently, the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model thoroughly analyses the factors affecting soil erosion. It is a powerful tool for quantitatively studying soil erosion processes and has been widely used in various applications [,]
There are extensive research and experimental records on soil erosion analysis at home and abroad [,,,]. The United States Department of Agriculture developed the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) in the 1960s. It was based on extensive small-scale observations and simulated rainfall experiment data. In order to overcome the limitations of the USLE’s applicability to moderate slopes, the United States Department of Agriculture introduced the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in the 1990s []. Huang, Li [] investigated the changes in soil erosion in Henan Province over the past 10 years using the RUSLE model and revealed that the severely eroded areas were primarily concentrated in the western portions of Henan, including Sanmenxia and Luoyang.
Dang, Liu [] revealed a steady decline in the overall area impacted by the effects of soil and water erosion in Longnan City. The decrease continued to happen at a faster annual speed. Gao and Li [] showed a decline in soil erosion within the Han River Basin from 2000 to 2015. Regarding geospatial analysis, areas with high erosion rates were concentrated in the centre core of the basin, and lower rates were spread along its eastern and western sides. Guo, Han [] revealed significant differences in soil erosion severity across the east–west dimension of the Qinling region. The Jialing River Basin was mainly affected by severe soil erosion issues. The prior soil erosion investigations mainly concentrated on regional studies in provinces, cities, counties, and river basins. It has led to a fragmented and fragmented research landscape. However, there is a lack of comprehensive investigation of regional soil erosion [,]. Soil erosion modelling involves mathematically modelling the separation of soil particles, sediment transport, and sediment deposition on the ground surface []. The integration of 3S technology and soil erosion model has greatly improved the monitoring of large-scale soil erosion and is conducive to the quantification of soil erosion rate.
Several empirical models have been developed to evaluate soil erosion, such as the USLE (Universal Soil Loss Equation) by Wischmeier [], the WEPP (Water Erosion Prediction Project) proposed by Nearing, Foster [], EUROSEM (European Soil Erosion Model) by Morgan, Quinton [], and Perović, Životić []. The USLE and its upgraded version, RUSLE, are the leading models for assessing soil erosion hazards. Due to their simple structure and low data requirements, they are widely used in underdeveloped countries. Using satellite data, geographic information systems, and RUSLE models together, soil erosion can be estimated at regional scales with greater accuracy and reasonable cost [,,,]. Researchers have efficiently used the USLE/RUSLE, remote sensing, and GIS methods to assess soil erosion and sediment production, leading to favourable outcomes. However, these studies mainly concentrate on regions with frequent water and soil erosion and agricultural areas, and there are few studies on soil erosion in runoff plots or small and medium-sized basins, mountains, and forest lands [].
The primary aims of this study are to assess the spatial and temporal patterns of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains, to identify the key factors influencing these patterns, and to propose effective soil and water conservation strategies based on our findings.
2. Material and Methods
In this study, we employed the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) model, integrated with GIS technology, to accurately assess the geographical distribution and intensity of soil erosion. Data on precipitation, terrain, land use types, and soil characteristics were collected and analysed to create high-precision maps of soil erosion and to evaluate its spatial and temporal evolution.
2.1. Study Area
The study area is located in the northern part of the Qinling Mountains (Xi’an region) in Central China, adjacent to the southern side of the Guanzhong Basin. It lies within longitude 107.667°–109.808° E, latitude 33.683°–34.444° N and has an area of about 9267.53 km2 (Figure 1). Located in China’s transition zone, the Qinling Mountains region is known for its diverse natural conditions, geographical landscape, and agricultural productivity. This region has complex topography, diverse landforms, and significant differences in climate characteristics. The population is primarily concentrated in the low-lying plains at the base of the hills and the basins of the valleys, demonstrating a significant population density. The northern foot of Qinling Mountain (Xi’an region) has a typical monsoon climate with obvious seasonal changes and uneven rainfall distribution. The elevated terrain of the Qinling Mountains produces a unique alpine phenomenon. Elevations beyond 1700.00 m experience a frigid and damp climate, with an average yearly temperature ranging from 6 to 8 °C, whereas regions below 1700.00 m enjoy a temperate and rainy environment, with an average annual temperature of 10 to 12 °C. The northern foot of the Qinling Mountains (Xi’an region) has developed water conservancy infrastructure, including 50 river basins. At higher elevations, the valley mouth shows vertical arrangements of several natural flora, including alpine shrubs, grasslands, coniferous forests, mixed coniferous and broadleaf forests, and deciduous broadleaf forests. According to different topographic features, the study area is divided into 10 unique units of protection, integrated management, and ecological restoration (Table 1).
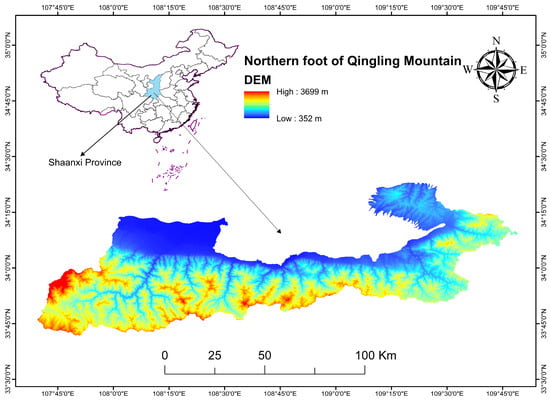
Figure 1.
Location of study area.

Table 1.
Ecological restoration unit.
2.2. Data Source
The dataset includes data relating to elevation, vegetation cover, land classification, soil categorisation, precipitation, and other variables, as specified in Table 2. The study adopted the WGS_1984 geographic coordinate system, and the projection data was WGS_1984_UTM_Zone_49N. The region has a warm, temperate, semi-humid continental monsoon climate, which is characterised by noticeable changes in temperature and precipitation throughout the seasons. Low temperatures, minimal wind, frequent fog and haze, and limited precipitation in the form of rain or snow characterise the winters. Mild temperatures, low humidity, strong winds, and unpredictable weather patterns characterise spring. Summers are characterised by high temperatures and heavy rainfall, often accompanied by prolonged periods of drought and frequent occurrences of thunderstorms and strong winds. A decrease in temperature and substantial precipitation characterises autumns.

Table 2.
Data sources.
According to climate data spanning the last three decades (1991–2020), the yearly mean temperature fluctuates between 13.5 °C and 14.9 °C. The mean temperature during the coldest month, January, falls within the range of −1.2 °C to 0.7 °C, while in the warmest month, July, it varies from 26.9 °C to 27.8 °C. The lowest temperature recorded at Lantian on 28 December 1991, was −21.2 °C, while the highest temperature recorded in Chang’an on 17 June 2006, was 43.3 °C.
The yearly rainfall varies between 506.1 and 690.3 mm, with the highest amount of rainfall recorded in Lintong in 2003 at 954.9 mm and the lowest amount recorded in Xi’an in 2013 at 277.6 mm. The highest daily rainfall was 138.9 mm in Gaoling in 2007. July and September are the two separate periods when precipitation reaches its highest point. The yearly amount of time that the sun is visible ranges from 1679.9 to 2062.6 h.
The primary meteorological catastrophes that occur during the year encompass droughts, extreme heat, powerful gusts, sandstorms, thunderstorms, hailstorms, torrential downpours, frost damage from low temperatures, prolonged periods of cloudy and rainy weather, dense fog, and haze.
2.3. RUSLE Model
This study used the RUSLE to evaluate soil erosion in the Qinling Mountains region quantitatively. The mathematical equation is delineated as follows:
where A is the average amount of soil erosion , known as the soil erosion modulus.
The rainfall erosion factor is denoted by R , whereas the soil erodibility factor is represented by K . LS represents the combined value of slope length and slope factor (dimensionless). C represents the vegetation cover and management factor (dimensionless). P represents the factor associated with soil conservation measures (dimensionless). Using the ArcGIS 10.3V software, these components are transformed into raster images. The soil erosion modulus A can be obtained by performing a multiplication operation on each factor.
2.4. The Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R)
The rainfall erosivity factor (R) is calculated using monthly rainfall data, following the Ministry of Water Resources guidelines titled ‘Guidelines for Soil Erosion Calculation in Production and Construction Projects’. The R factor was specifically computed for the period from 2018 to 2022 to capture the temporal variations in rainfall erosivity over these years, ensuring accurate representation in our analysis as shown in Formula (2):
where Rm represents the rainfall erosivity factor for the m-th month, and Pm denotes the m-th month precipitation measured in mm.
The rainfall erosivity factor R is closely related to factors such as rainfall amount, intensity, and duration and size and falling speed of raindrops, and it reflects the potential ability of rainfall to erode soil. This study used the representative method of Wischmeier [,], and the R factor is calculated using a linear algorithm that takes into account annual precipitation and monthly rainfall:
pi represents the monthly rainfall; p represents annual rainfall (unit: mm).
The formula (3) was employed in this study to compute the R values for the Qinling northern foothills and 20 surrounding stations. The unit is . The spatial distribution data of rainfall erosion factor R in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains in 2023 were obtained by using the distance-weighted inverse interpolation method, as depicted in Figure 2a.
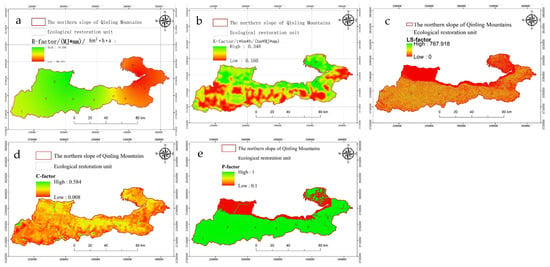
Figure 2.
Erosion factors in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains ((a–e) represent R, K, LS, C, and P factors, respectively).
2.5. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
The soil erodibility factor K reflects the susceptibility of soil to erosion and its ability to be hydraulically divided and transported []. The present study utilises the EPIC model, as formulated by Williams, Nearing [], to estimate the K factor based on soil organic matter and particle composition ratios. The computation formula is as stated:
K is the soil erodibility, and the unit is in the American system. To convert to an international system unit, we must multiply by 0.1317, with the unit ; Sd and Cl denote the percentages of sand, silt, and clay content, (%); C is the organic carbon content (%); SN is calculated as , shown in Figure 2b.
2.6. Slope Length Slope Factor (LS)
The slope length–slope steepness factor (LS) is used to quantify the influence of terrain on soil erosion. Typically, greater slope steepness and longer slope length result in more pronounced soil erosion. The slope length and steepness factor (LS) was calculated using a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) with a spatial resolution of 12.5 m. The higher resolution of 12.5 m was chosen to enhance the accuracy of the topographical representation. The LS factor algorithm stated in the Chinese Soil Erosion Model (CSLE) was employed, along with the LS factor calculation tool produced by []. The computation formula is as follows:
where the slope factor is denoted as S (dimensionless), represents the slope value (degrees), the variable L denotes the factor that represents the length of the slope (dimensionless), and λ denotes the measurement of slope length (m). The variable ‘m’ represents the exponent that determines the length of the slope.
The slope length (L) and slope steepness (S) parameters reflect how topography affects soil erosion and contributes to the rapid rate of erosion. The study calculates the slope steepness (S) factor using Equation (5). It produces a raster map of the downhill slope factor.
The more precise slope length (L) factor is computed through the utilisation of Equations (6), (8), (9), and (10) within the Raster Calculator tool in the ArcGIS software. The raster layer for the slope length (L) factor is obtained. It is crucial to emphasise that the slope angle (θ) must be translated to radians while calculating.
In the equation, ‘m’ is the slope length, exponent, ‘λ’ is the horizontal projection slope length, ‘flowacc’ is the raster layer obtained after filling sinks, calculating flow direction, and flow accumulation using DEM data in ArcGIS software. ‘cellsize’ is the original pixel value of the flowacc raster layer, ‘β’ is the ratio of rill erosion to interracial erosion, and ‘θ’ is the slope angle.
Analysing the LS factor in the USLE model initially requires calculating the slope length factor []. The DEM data are processed, and the gradient is initially calculated, including filling the flume, determining the flow direction, calculating the flow length, and estimating the length of the horizontal projection slope. The variable slope length exponent is determined by applying the con function in the ArcGIS raster calculator, and then the power function is used to calculate the slope length factor. Subsequently, the slope factor is calculated via the con conditional function. Ultimately, the LS factor is derived by multiplying the two estimated outcomes, as depicted in Figure 2c.
2.7. Vegetative Cover and Management Factor (C)
The vegetation cover factor (C) is used to evaluate the influence of different land use types and vegetation cover degrees on soil erosion. Currently, the methods to determine the C value consist of manual assignment, quantitative estimation of remote sensing data, and experimental approaches within specified locations []. Nevertheless, the prevailing approach requires the computation of the C factor through Normalised Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) calculations.
This work adopted a quantitative estimating technique that utilises remote sensing data to compute the C factor. Using Landsat 8 imagery enables the acquisition of NDVI values, facilitating the calculation of vegetation coverage. This study used Landsat 8 satellite data to assess the vegetation coverage (fc) on the northern slope of the Qinling Mountains from 2018 to 2022. The C factor was estimated by considering seasonal and annual vegetation changes. Specifically, vegetation data were collected and averaged over multiple months each year to accurately reflect the dynamic nature of vegetation cover. This approach ensures that the C factor represents the average vegetation cover for the entire year, providing a more accurate estimation of its impact on soil erosion. The vegetation status in April of each year serves as an indicator of the vegetation cover. The formula is as stated:
The term refers to the normalised index that measures the presence of bare rock, soil, and vegetation-covered pixels. Additionally, reflects the normalised index only for pure vegetation-covered pixels.
The study shows that there is no significant soil erosion in the construction area with the solidification of cement ground and water bodies subjected to material deposition. Therefore, the default assumes that the C value is set to 0. On the other hand, certain areas utilise the method developed by Cai, Ding [], which calculates the C value by considering the relationship between vegetation cover, management C factor, and the extent of vegetation cover (f). The C value is calculated utilising an equation written as follows, with the result falling within the range of 0 to 1:
where fc represents the degree of vegetation cover.
Surface erosion can be disregarded when the plant cover surpasses 78.3%. When the value is negative, it has no erosion-reducing impact. Figure 2d depicts the regional distribution of the C factor in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains.
2.8. Soil and Water Conservation Measures Factor (P)
The factor represented by P in soil and water conservation indicates the ratio between soil erosion with particular conservation measures and soil erosion without any measures. Regions where soil erosion does not occur after implementing water conservation measures are assigned a p value of 0, while areas without any such measures are designated a p value of 1.00. In alternative situations, the variable P takes on values ranging from 0 to 1.00. The determination of values for the factor P, which represents soil and water conservation measures in the Qinling Mountains region, is derived from the U.S. Department of Agriculture manual and related studies []. These values are adjusted to account for local conditions, as specified in Table 3.

Table 3.
p values for different land uses.
3. Results and Outcomes
The soil erosion modulus results for the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains from 2018 to 2023 were obtained by performing overlay operations on raster layers for each factor. Then, the geographical distribution characteristics of soil erosion in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains during a specific period were studied. The results were classified into six levels according to the ‘Soil Erosion Classification Criteria’ (SL 190-2007) [] set by the Ministry of Water Resources. These levels are slight erosion, mild erosion, moderate erosion, intense erosion, extremely intense erosion, and severe erosion (Table 4). Figure 3 identifies concentrated erosion source locations in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains.

Table 4.
Water erosion intensity classification standard.
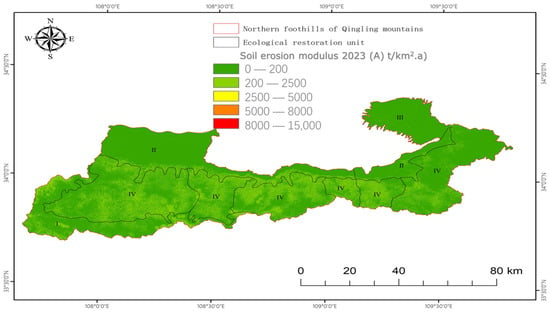
Figure 3.
Graded distribution map of soil erosion modulus.
Upon conducting calculations on soil erosion levels in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains, it was noted that the soil erosion modulus exhibited a steady decrease over time. The observed phenomena had significant spatial differences, with higher values primarily concentrated in the eastern and southern regions, progressively decreasing as one moved toward the western and northern portions.
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics of Soil Erosion in the Northern Foothills of the Qinling Mountains
Figure 3 depicts soil erosion intensity in the research region. Refer to Figure 3 to observe the geographic fluctuations in soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains between 2018 and 2023. Based on the soil erosion intensity classification standards provided by the Ministry of Water Resources [], the soil erosion levels in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains in 2023 are classified into six categories: slight, mild, moderate, severe, extremely severe, and drastic erosion.
The soil erosion modulus in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains in 2023 is measured at an average of 233.515 t/(km2·a), resulting in a total soil erosion of 85,233.046 t/a within the watershed. Based on the data in Table 5, the most significant area with little erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains is 601,154.995 km2, which represents 92.958% of the total watershed area. Subsequently, the extent of light erosion covers an area of 43,880.839 km2, while the overall erosion in the minimal category is at its peak, amounting to 60,279.329 metric tonnes per annum. The prevailing soil erosion in the research region is primarily classified as light and minor, accounting for 96.661% of the total, with an erosion area extending to 644,822.560 km2. The soil and water conservation initiatives in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains have yielded notable accomplishments, as indicated by a decrease in the soil erosion modulus compared to prior evaluations [].

Table 5.
Statistical classification of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains.
Soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains is mainly distributed in river valleys and mountain basins, and the soil erosion modulus increases while the slope erosion decreases steadily. Furthermore, the central region, characterised by elevated terrain in hilly areas affected by vegetation, also escalates the soil erosion modulus. The soil erosion modulus positively correlates with parameters such as slope and elevation, displaying apparent geographical and temporal fluctuations. Various land-use categories exhibit a declining pattern in soil erosion, with the most notable decrease noted in unutilised land.
Figure 4a–e presents the comprehensive time series of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains, demonstrating the significant changes in soil erosion modulus throughout time. The findings demonstrate a progressive and marginal decrease in the soil erosion modulus between 2018 and 2022, indicating a positive trend in the area’s current soil erosion condition.
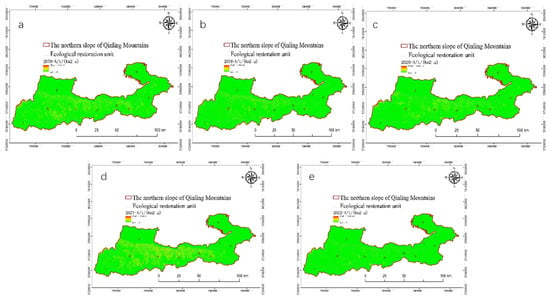
Figure 4.
Presents the comprehensive time series of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains (a–e) present annual average soil erosion from 2018 to 2022.
As can be seen from Figure 5 and Figure 6, the soil erosion modulus of the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains increased slightly in general from 2018 to 2022, with an upward slope of 0.119. The soil erosion modulus changed correspondingly with the change in annual average rainfall from 2018 to 2020. The soil erosion modulus decreased from 11.58 t/(km2·a) to 7.94 t/(km2·a), while the average annual rainfall increased slightly from 2020 to 2022, and the soil erosion modulus also increased from 7.94 t/(km2·a) to 13.18 t/(km2·a). The variation of soil erosion modulus is consistent with the annual average rainfall. The main reason is that the north foot of the Qinling Mountains has complex topography, a wide variety of soil types, and abundant and concentrated rainfall. During the formation, collection, and transfer of slope surfaces, rainfall interacts with the surface soil, resulting in changes in the physical structure of the surface soil and the occurrence of soil loss.
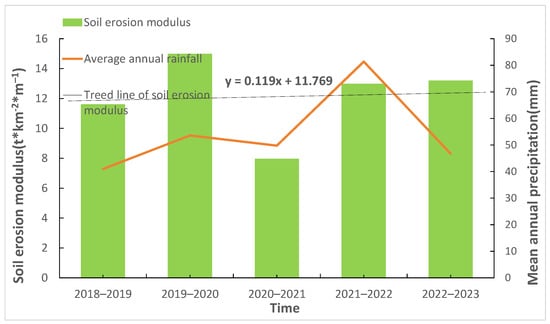
Figure 5.
Histogram of average annual soil erosion from 2018 to 2022.
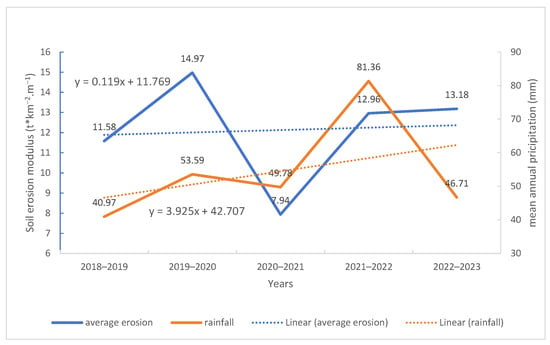
Figure 6.
The line graph of annual average rainfall and soil erosion.
3.2. Soil Erosion in Various Restoration Units in the Northern Foothills of the Qinling Mountains
In order to effectively evaluate the geographical variability of soil erosion in different restoration units in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains, this study categorised the various restoration units into regions for statistical analysis. The study identified and analysed soil erosion in various levels of sub-restoration and management regions in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains. The results are summarised in Table 6.

Table 6.
The average soil erosion statistics for various restoration units from 2018 to 2022.
Table 6 indicates that soil erosion in the Heihe River Basin constitutes 29.490% of the northern slopes of the Qinling Mountains. The erosion quantity in the Foping River Basin, specifically on soil and habitat restoration, accounts for 14.629% of the whole basin. The erosion quantity in the water conservation and maintenance unit in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains constitutes 14.456% of the total basin. The average erosion modulus in the Heihe River Basin exceeds 19 t/(km2·a). The considerable amount of erosion in the Heihe River Basin suggests a significant concentration of erosion patches of higher calibre. The indicated area continues to experience a significant problem with soil and water loss, indicating that regulatory actions should be given priority in the planning process. Taking immediate action to implement appropriate solutions in the upstream areas adjacent to the convergence nodes of the selected region is expected to lead to a more significant decrease in erosion.
The erosion modulus in the Foping River Basin is among the highest three, while the total erosion quantity ranks second. It suggests that areas with more severe erosion are located near the river channels in the Foping River Basin. According to the model results, the erosion modulus calculated for the Lahe River Basin’s water conservation and habitat restoration unit can be as high as 20.62 t/(km2·a). However, the erosion quantity proportion is ranked fifth, a position that might be attributed to the comparatively small size of the basin area. Hence, the Lahe River Basin’s soil and water loss condition in the area committed to soil and habitat conservation is highly critical, indicating the imperative for targeted endeavours in soil and water conservation and habitat restoration.
3.3. Study on the Key Factors Affecting Soil Erosion
The northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains are situated in a region characterised by a convergence of different variables, including climate and vegetation, in China. The area has intricate topography and a wide range of soil compositions and has been significantly impacted by human interventions. Rainfall is a crucial natural component that significantly influences the process of soil erosion, impacting both the yearly and seasonal fluctuations of soil erosion at a large spatial scale. The leading cause of soil erosion is the soil itself, while the types of plants play a crucial role in soil conservation. In addition, humans alter or disrupt the original surface vegetation conditions or growth cycles through agriculture, steep slope development, construction of highways, and urban development, which results in heightened soil erosion in specific regions [].
The influence of terrain factors on soil erosion is significant. However, using Digital Elevation Models (DEM) for calculations can introduce some errors in determining the actual slope and slope length, thereby affecting the accuracy of the results [,]. In this study, the temporal and spatial characteristics of soil erosion in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains were analysed. However, the influence of height and slope on soil erosion was not measured. Future research should prioritise investigating the effects of individual and multiple factors on soil erosion, including ecological and socioeconomic factors.
The combination of climate change and a rise in intense precipitation events might potentially amplify soil erosion. This intensification can result in the deterioration, movement, and accumulation of soil organic carbon, modifying the extent and spatial arrangement of terrestrial carbon sources and sinks []. Given the sensitivity of the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains to climate, further investigation can focus on the effects of global climate change and extreme weather events on the spatial and temporal distribution of soil erosion in this region. This exploration aims to augment the region’s ability to adapt to climate change.
For future studies, it is recommended to gather empirical data from specific sub-areas of runoff and soil conservation stations in comparable regions. The combination of experience and measurable data can effectively calibrate the parameters of various erosion variables and improve the reliability of the model results. This measure will effectively mitigate the adverse effects of soil erosion on the biological and hydrological resources of the region.
4. Discussion
The Qinling Mountains are an important ecological barrier in China, with basic functions such as regulating temperature and protecting water sources in the Yellow and Yangtze River basins, representing an important aspect of Chinese culture and tradition. The northern slopes of the Qinling Mountains are crucial in supplying water for the core route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project. The soil erosion in this area has significant consequences for China’s water security, the preservation of rare plants and animals, and the region’s socioeconomic growth. Hence, it is imperative to investigate this region’s spatiotemporal patterns of soil erosion to ensure future soil and water conservation and facilitate sustainable resource planning.
In recent years, there has been a noticeable reduction in soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains, with the extent and severity of erosion showing a consistent downward trend, which is consistent with the research conducted by Li Yanhong []. Guo, Han [] analysed the spatiotemporal variations in soil erosion in the Qinling region. They showed a gradual decrease in soil erosion from west to east and south to north, which aligns with the spatial distribution of soil erosion observed in this study.
The spatial distribution of soil erosion in the Qinling region shows that the eastern sections have much higher values, while the middle and western regions have predominantly lower values. The observed distribution pattern corresponds to the precipitation distribution and provides evidence that precipitation circumstances substantially impact soil erosion in the area. We have analysed the changes in soil erosion from 1985 to 2021 to understand long-term trends and the impact of various factors over time. Our analysis integrates both our primary research data from 2018 to 2022 and historical data from previous studies. Specifically, we utilised data from Zhao and Zhao [], which provided insights into erosion patterns starting from 1985. Additionally, we incorporated findings from Yanhong [] and Guo, Han [], with Yanhong’s research covering data from 2005 onwards and Guo et al.’s work offering valuable historical context.
Analysis of soil erosion patterns in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains over the past three decades reveals that around 70% of the area has witnessed a modest reduction in soil erosion. This showed a positive trend towards mitigating soil and water loss in the region. Nevertheless, around 30% of the land in the Qinling region, which accounts for nearly 30% of the total area, has exhibited a discernible level of soil erosion. The Qinling region, which is environmentally sensitive, continues to face the threat of soil and water loss due to global climate change and unsustainable human activities [].
Over the past 30 years, the soil erosion modulus in the Qinling region has gradually decreased, suggesting that soil and water conservation conditions in the area have improved. Nevertheless, precipitation has a substantial impact on the fluctuations within a year. Soil erosion escalates during periods of anomalous precipitation due to increased rainfall. Furthermore, the combination of periodic intense rainfall and persistent precipitation exacerbates the likelihood of soil erosion.
The intricate topography and capricious climatic circumstances in the Qinling region render it vulnerable to fluctuations in water and thermal conditions, particularly in abnormal climate years. This can hinder the simultaneous development of vegetation, affecting its regular growth. Given the importance of vegetation in soil and water conservation, any limitations on its growth are likely to have adverse effects on soil and water conservation in the area.
The disparities between the findings of this study and the prior studies conducted by Yanhong [] and Yao and Jiao [] can be ascribed to discrepancies in the utilised model, data kinds, and methodologies employed for computing erosion factors. Nevertheless, the findings of this investigation are deemed trustworthy. Regarding spatial distribution, moderate and higher levels of soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains are shifting and concentrating towards the ecologically more susceptible western regions. According to the results of this study, the ecological protection and restoration work in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains should focus on the areas with rapid soil erosion and soil erosion. By increasing vegetation cover, improving farming methods, and preventing farmland pollution, land regulation measures should be taken to protect soil resources and alleviate ecological and environmental problems. Based on the diagnosis of regional ecological and environmental problems and regional identification of soil erosion, a comprehensive assessment of ecosystem service functions from climate, terrain, human activities, vegetation cover, and other aspects, proposed from different spatial and temporal scales of ecological problems in the northern foot of the Qinling Mountains, will be of great significance to restore ecosystem biodiversity and improve the quality of ecological environment.
5. Conclusions
The primary achievements of this research are as follows:
- Soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains is predominantly characterised by moderate and gentle erosion. In 2023, the average soil erosion modulus is 233.515 tonnes per square kilometre per year, resulting in a total soil erosion amount of 85,233.046 tonnes per year. Between 2018 and 2023, there has been an improvement in the soil erosion situation in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains. Both the area affected by erosion and the intensity of erosion have shown a consistent decrease. The process of soil erosion, specifically of moderate and higher grades, has progressively moved from the research area’s northeastern and southwestern sections to the northern foothills’ western region. The centre region displays reduced soil erosion, predominantly characterised by minimal and moderate erosion.
- Topographic features, including height and slope, strongly influence soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains. The soil erosion area in the study region has a declining tendency on both sides as elevation increases, primarily due to variations in slope. The centre area, characterised by slopes ranging from 15° to 25°, experiences the most significant decrease in soil erosion. The concentrated region for erosion, which plays a significant role in soil erosion prevention and control, has been discovered to have an elevation range of 500–1500 m and a slope range of 15°–25°. The river valleys and mountain basins are the main areas affected by soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains. In these areas, the soil erosion modulus is higher, while the slopes of the mountains show a gradual decrease in soil erosion. In the Heihe River Basin, 29.49% of the erosion quantity in the entire region is attributed to biodiversity conservation and habitat units. The Laohe River Basin exhibits the highest soil erosion modulus, measuring 20.620 t/(km2·a), underscoring the importance of implementing soil and water conservation measures and habitat restoration initiatives in this region.
- The main land use categories contributing to soil erosion in the northern foothills of the Qinling Mountains are forests, grasslands, and cultivated land. The erosion occurring on cultivated land and woods at a small scale is diminishing, and there is a declining tendency in erosion at other levels. In grasslands, there is a rising pattern in both micro-scale and severe erosion, while other levels of erosion show a declining tendency.
Measures such as hierarchical coordination, timely storage, and sand interception can ensure ‘sufficient water quantity and clear water quality,’ and the measures are based on the priority identification and ranking of erosion modulus and erosion quantity and the results of rainfall-runoff forecasting. It will be of great significance for biodiversity conservation, soil and water conservation, and habitat quality restoration in watershed systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, Y.C.; Data curation, A.A., M.E.-S.A. and A.E.; Investigation, F.L.; Methodology, Y.C.; Software, F.L.; Supervision, A.H.; Validation, A.H., F.L. and D.E.K.; Writing—original draft, A.A.; Writing—review and editing, A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42261144749 and 42377158), National Natural Science Foundation of China: Evolution and Disaster Risk Management of Eco-Geological Environment System in Qinling Mountains (42341101), and International Science and Technology Cooperation Program of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2024GH-ZDXM-24).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors of this study would like to thank all anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mandal, D.; Sharda, V. Assessment of permissible soil loss in India employing a quantitative bio-physical model. Curr. Sci. 2011, 100, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Mosaffaie, J.; Jam, A.S. Economic assessment of the investment in soil and water conservation projects of watershed management. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angima, S.; Stott, D.E.; O’neill, M.K.; Ong, C.K.; Weesies, G.A. Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Meng, P.; Ba, Y.; Zhang, J. Quantitative attribution analysis of soil erosion driving factors in the Xiaolangdi reservoir area of the Yellow River. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 155–163+171. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W. Research on the Mechanism and Prevention and Control Technology of Mining Water Damage under Runoff in Loess Gullies in Northern Shaanxi; China University of Mining: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, Q.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Peng, J. Evolution of an arid social-ecosystem with different water utilization spanning 12,000 years. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Lü, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F. Characteristics of runoff and sediment produced by typical grass cover in loess hilly and gully areas and its influencing factors. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 30, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, A.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Li, C.; Xie, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Multispectral remote sensing inversion for city landscape water eutrophication based on Genetic Algorithm-Support Vector Machine. Water Qual. Res. J. 2014, 49, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huo, A.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Rebouh, N.Y.; Luo, C. Spatial Differentiation and Influencing Factors Analysis of Drought Characteristics Based on the Standardized Precipitation Index: A Case Study of the Yellow River Basin. Water 2024, 16, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, A.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.-S.; Ganjidoust, H. Habitat Quality Assessment and Driving Factor Analysis of Xiangyu in Feng River Basin Based on InVEST Model. Water 2023, 15, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Meng, J. The relationship between soil hydraulic erosion and land use spatiotemporal changes in Ordos City from 1988 to 2000. J. Nat. Resour. 2009, 10, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, P.; Meng, J. Relationship between soil hydraulic erosion and land use change in Ordos City during 1988–2000. J. Nat. Resour. (Chin. Engl. Abstr.) 2009, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Temporal and spatial changes in soil erosion and landscape pattern in the Qinling area. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 2167. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.J.; Deng, L.W.; Zhang, J.P. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes in soil erosion in Henan Province in the past ten years. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2021, 38, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, I.; MacDonald, L. Predicting post-fire sediment yields with RULSE, WEPP, and ERMiT: Accuracy and limitations. AGU Fall Meet. Abstr. 2006, H31C-1437. [Google Scholar]
- Akinmolayan, A.; Adepoju, K.; Adelabu, S.; Osunmadewa, A. Estimating Potential Annual Soil Loss of Watershed in Nigeria Using Rulse in a GIS and Remote Sensing Environment. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, W.; Shen, Z.; Duan, X. Spatiotemporal patterns and drivers of soil erosion in Yunnan, Southwest China: RULSE assessments for recent 30 years and future predictions based on CMIP6. Catena 2023, 220, 106703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Wu, P.; Yin, X. Research progress on soil erosion models. Sichuan For. Technol. 2014, 35, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, G.; Liu, S.; Song, Z. Analysis on changing trends and causes of soil and water loss in Longnan City. Agric. Sci. Technol. Inf. 2022.
- Gao, Y.; Li, H. Effects of landscape pattern changes in the Han River Basin on soil erosion. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Yanhong, L. Research on Multi-Dimensional Changes of Soil Erosion in Qinling Mountains; Henan University: Kaifeng, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Huo, A.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, P.; Peng, J.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.-S.; Mokhtar, A.; Ahmed, A. Impacts of Different Gully Consolidation and Highland Protection Models on the Runoff and Sediment Yield in Small Watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau—A Case Study of Fengbugou in Qingyang City of Gansu. Water 2023, 15, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Water management in various crop production systems related to soil tillage. Soil Tillage Res. 1994, 30, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Predicting rainfall erosion loss-a guide to conservation planning. Agric. Handb. 1978, 537, 1–58. [Google Scholar]
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A process-based soil erosion model for USDA-Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. J. Br. Geomorphol. Group 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perović, V.; Životić, L.; Kadović, R.; Đorđević, A.; Jaramaz, D.; Mrvić, V.; Todorović, M. Spatial modelling of soil erosion potential in a mountainous watershed of South-eastern Serbia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millward, A.A.; Mersey, J.E. Adapting the RUSLE to model soil erosion potential in a mountainous tropical watershed. Catena 1999, 38, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, A.; Singh, R. Modeling runoff and soil erosion in a catchment area, using the GIS, in the Himalayan region, India. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huo, A.; Liu, Q.; Peng, J.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.-S.; Abu-Hashim, M.S.D. Spatiotemporal Variation in the Coupling Relationship between Human Activities and Soil Erosion—A Case Study in the Weihe River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Huo, A.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, P.; Peng, J.; Elbeltagi, A.; Abuarab, M.E.-S.; Mokhtar, A. Experimental study on slope morphological characteristics and stability analysis of GCHP engineering in the loess plateau. Adv. Space Res. 2023, 72, 4324–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Analysis and research on temporal and spatial patterns of soil erosion in Qinling area. Agric. Technol. 2023, 21, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Predicting rainfall erosion losses from cropland east of the Rocky Mountain. Agric. Handb. 1965, 282, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture, Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Fang, N.; Yue, Z. Research progress and prospects on soil erosion and soil and water conservation in the past ten years. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 57, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Nearing, M.; Nicks, A.; Skidmore, E.; Valentin, C.; King, K.; Savabi, R. Using soil erosion models for global change studies. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Baartman, J.E.; Gai, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. An improved method for calculating slope length (λ) and the LS parameters of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation for large watersheds. Geoderma 2017, 308, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Li, C.; Wu, L.; Xie, X.; Lü, J.; Zhou, X. Study on soil erosion in northwest Gannanchuan River based on USLE. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W. Research progress on vegetation cover and management factors in USLE/RUSLE. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 4461–4472. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Ding, S.; Shi, Z.; Huang, L.; Zhang, G. Application of USLE Model and Geographic Information System IDRISI in Predicting Soil Erosion in Small Watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2000, 14, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R. Special Investigation and Research Report on the Classification of Soil Erosion Types and Regional Changes in the Loess Area of Western Henan Province (Problems on the Sources of Yellow Coarse Sediment); Henan Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Hydrogeology Team 2: Zhengzhou, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- SL 190-2007; Soil Erosion Classification Criteria. Ministry of Water Resources: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Zhao, Q.; Zhao, Y. Spatial and Temporal Pattern Analysis of Soil Erosion in the Qinling Mountain Region. Agric. Technol. 2023, 43, 103–106. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, F. Xi’an Soil and Water Conservation Plan (2016–2030); Xi’an Water Conservancy and Soil Conservation Work Station: Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, F. Soil erosion and sensitivity analysis in the upper reaches of the Zuli River basin based on RUSLE. Teppes Turfgrass 2022, 42, 128–135. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X. Research on the Accuracy of Extracting Ground Slope from DEM at Different Scales. Soil Water Conserv. Bull. 2001, 21, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- He, S.; Zhu, W.; Cui, Y.; He, C.; Ye, L.; Feng, X.; Zhu, L. Study on Soil Erosion Characteristics of Qihe River Basin in Taihang Mountains Based on InVEST Model. Yangtze River Basin Resour. Environ. 2019, 28, 426–439. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Zhang, X.; Chen, A.; Liu, Q.; Lian, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Wu, X. Impact of extreme climate events on the carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystems. Chin. Sci. Earth Sci. 2019, 49, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.; Jiao, P. Analysis on spatial balance of comprehensive management of soil and water conservation in the Yellow River Basin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 1–7+22. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).