Abstract
Water quality and usability are global concerns due to microbial and chemical pollution resulting from anthropogenic activities. Therefore, strategies for eliminating contaminants are required. In this context, the removal and decrease in antibiotic activity (AA) associated with levofloxacin (LEV), using TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 catalysts, with and without sunlight and peroxydisulfate, was evaluated. Additionally, the disinfection capacity of catalytic systems was assessed. The catalysts were synthesized and characterized. Moreover, the effect of Ag doping on visible light absorption was determined. Then, the photocatalytic treatment of LEV in water was performed. The materials characterization and EPR analyses revealed that LEV degradation and AA decrease were ascribed to a combined action of solar light, sulfate radical, and photocatalytic activity of the TiO2-based materials. Also, the primary byproducts were elucidated using theoretical analyses (predictions about moieties on LEV more susceptible to being attacked by the degrading species) and experimental techniques (LC-MS), which evidenced transformations on the piperazyl ring, carboxylic acid, and cyclic ether on LEV. Moreover, the AA decrease was linked to the antibiotic transformations. In addition, the combined system (i.e., light/catalyst/peroxydisulfate) was shown to be effective for E. coli inactivation, indicating the versatility of this system for decontamination and disinfection.
1. Introduction
The presence of antibiotics in aquatic environments poses a significant risk by potentially causing irreversible long-term changes in bacterial genomes, leading to the development of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms, a serious public health concern. Levofloxacin (LEV), a widely used antibiotic for treating various bacterial infections, exemplifies this issue. After consumption, approximately 87% of LEV is excreted unchanged, eventually reaching municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) [1]. However, due to its strong antimicrobial properties, LEV resists degradation by conventional WWTP methods, highlighting the need for more effective treatments to eliminate it from wastewater.
In parallel, Escherichia coli (E. coli) serves as a universal indicator of microbiological water contamination and is commonly detected in wastewater and WWTP effluents [2]. The limitations of classical WWTP treatments in effectively addressing E. coli contamination underscore the necessity for alternative approaches. These could include advanced treatments at primary pollution sources, such as hospital wastewater or even the urine from patients harboring such bacteria, to mitigate the spread of resistant microorganisms and safeguard public health. Therefore, seeking effective ways to deeply eliminate the environmental risk caused by LEV and microbial contaminants is of great importance.
Heterogeneous photocatalysis has been widely studied to deal with chemical and microbiological pollutants in aqueous samples [3,4]. Indeed, during the last five decades, TiO2 photocatalysis has been applied; it is a well-known system able to produce degrading/disinfecting species such as hydroxyl radicals. However, the application at large scale of this system is questioned [5]. Despite this limitation of the TiO2-based processes, some niche applications of the TiO2-based photocatalytic systems for treating small volumes of polluted water (e.g., some tens of liters) could be found. Then, studies on fundamental aspects of photocatalytic systems for future developments and applications are still relevant.
Treatment methods based on photocatalysis with TiO2 have been attractive, as they can operate under UV radiation, including solar light. Interaction of UV light with TiO2 initiates a sequence of oxidative processes, generating reactive oxygen species, e.g., HO●, (Equations (1)–(3)) that favors the degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutants (OP, Equation (4)), including mineralization [6,7,8] (Equation (5)). However, photocatalysis with TiO2 has several drawbacks: (i) its relatively high band gap (3.2 eV for anatase), which makes it active in the ultraviolet (UV) light region that constitutes only about 5–7% of the solar spectrum [9], thus demanding the use of lamps that involves adjustments to the configuration of the reactor, (ii) TiO2 has a high recombination rate of the electron-hole pairs, leading to low exploitation of the absorbed photons [10]. Therefore, strategies such as the deposition of noble metal (e.g., Ag) on TiO2 could enhance the photo-response of TiO2 to the visible light range (i.e., narrow band gap energy allows absorption of photons at lower energy, near the visible region), due to the localized surface plasmon effects (LSPR) [11,12]. On the other hand, the presence of oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide or persulfates (e.g., S2O82−) can enhance the performance of photocatalysis toward the degradation of pollutants. Such an enhancement is associated with the production of extra radical species by the interaction of the added oxidant with electrons of the conduction band (Equation (6), [13]); which at the same time can also limit the hole-electron recombination.
TiO2 + hv → TiO2 (h+ ... e−),
h+ + H2O → HO● + H+,
e− + O2 → O2●−,
h+, HO●, or O2●− + OP → primary byproducts,
h+, HO●, or O2●− + primary byproducts →→→ CO2 + H2O + inorganic ions,
e− + S2O82− → SO4●− + SO42−,
Some previous works have studied the use of TiO2-based photocatalysis to degrade LEV [14,15,16,17,18]. These works have tested the degrading efficiency (even some have shown the disinfecting capability of the process) of TiO2/UV light systems, but they did not report the incorporation of peroxydisulfate into the photocatalytic system to deal with LEV and inactivate E. coli. Thereby, such topics were developed in this research. On the other hand, it can be mentioned that sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation technologies (considering the peroxydisulfate activation) have been widely applied to organic pollutants treatment due to their high degradation efficiency and eco-friendly nature. It must be mentioned that the advanced oxidation processes based on peroxydisulfate have also been used for bacteria inactivation [19,20]. These oxidation processes involve the generation of sulfate radicals (SO4●−), a species with a high oxidation potential (2.5–3.1 V), and a half-life of 30–40 µs, far longer than HO● (20 ns), the radical reference in advanced oxidation processes [21]. Direct oxidation of organic pollutants by peroxydisulfate (PDS) alone is difficult to occur and it needs to be activated to generate SO4●−. Typical activation strategies comprise ultraviolet C (UVC) light, ultrasound (US), electrochemical oxidation, heat, alkali, transition metals, carbon-based materials, and photogenerated electrons [21]. Hence, the possibility of activating PDS through photocatalysts was explored herein.
In this work, TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 were initially synthesized and characterized by TEM/EDS, XRD, XPS, SEM, and BET. Afterward, these materials were used under solar light as photocatalysts and activators of PDS, to eliminate a model antibiotic (LEV) and to inactivate a relevant microorganism (E. coli). The capability of the photocatalytic systems to eliminate the antimicrobial activity was also assessed. Then, the degradation routes (radicals involved in the process) related to the possible synergistic relationships between the materials, sunlight, and PDS were determined. The role of the identified oxidizing species (e.g., HO●) in the degradation of LEV and the inactivation of E. coli was discussed. Furthermore, using theoretical tools, the moieties on LEV more susceptible to attacks by the oxidizing species were identified, and the by-products were experimentally elucidated. Also, the evolution of the AA was followed and linked to the LEV changes caused by the photocatalytic treatment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Levofloxacin (LEV, purity > 99%) was provided by Chemo Laboratories. Formic acid (98.0%), hydrogen fluoride (HF) (48 wt.% in H2O), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (97.0%), silver nitrate (AgNO3) (99.9%), titanium tetraisopropoxide ([Ti(OCH(CH3)2]4) (≥ 97.0%) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Acetonitrile (HPLC grade) was supplied by Sharlab (Europe); 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (TEMP) (≥ 98.0%) was acquired from Thermo Scientific (Germany); 5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) (≥ 97.0%) was obtained from Cayman Chemical (Europe) and potassium peroxydisulfate (PDS) (≥ 99.0%) purchased from ITW Reagents PanReac (Spain).
2.2. Catalyst Synthesis
TiO2 was prepared using a volume ratio of titanium tetraisopropoxide/HF 25:4 v/v. Then, such a solution was submitted to hydrothermal treatment at 200 °C for 24 h [22]. To obtain the Ag/TiO2, a suspension of the prepared TiO2 sample was modified by silver addition, using the AgNO3 photo-deposition method under an inert atmosphere (N2). Thereby, the appropriate amount of metal precursor was added to obtain 5% Ag nominal loading from the weighted total of the catalyst. Photochemical deposition of Ag was then performed by illuminating the suspensions for 2 h [22].
2.3. Reaction System
Experiments were carried out at a laboratory scale in a solar simulator (Hanau Suntest) equipped with an air-cooled xenon lamp (1500 W) and proper filters to obtain a cutoff at 300 nm. The illumination intensity for the UVA component was measured using an LS126C radiometer (light intensity of 44.3 W m−2 was found). The temperature in the reactor never exceeded 35 °C. The experiments were carried out in equilibrium with the air under 360 rpm of agitation. Pyrex reactors of 500 mL were used for all tests with 200 mL of the sample (distilled water containing the target compound or microorganism). The addition of photocatalyst or PDS was conducted in a single dosage and the light source was turned on to start the tests. Each experiment was carried out at least in duplicate to verify the reproducibility of the measurements. In the figures/plots, the average values of the experimental replicates are reported, and the coefficients of variation for such repetitions were lower than 5% in the case of LEV degradation were lower than 10% for the microbiological tests.
2.4. Analyses
The catalysts were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption (BET measures), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM-EDS), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Also, the effect of Ag doping on the visible light absorption of TiO2 was determined by UV-vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS). XRD analyses were conducted using a Siemens D-501 diffractometer, equipped with a nickel filter and copper Kα radiation (ʎ = 1.541874 Å). Scanning was performed over a 2θ angle range of 10° to 80°, with a step size of 0.05° and a total acquisition time of 1 second [22]. TEM-EDS analyses were performed with FEI Titan 80–300 kV FEG S/TEM equipped with an EDAX EDX detector. The BET was measured via N2 physisorption at 77.35 K employing a Micromeritics ASAP 2010 apparatus. UV–vis (UV–vis DRS) measurements were conducted using a Varian spectrophotometer model Cary 100, which was equipped with an integrating sphere, and BaSO4 served as the reference compound. The band-gap value was determined using the Kubelka–Munk F(R∞) function, which is proportional to the radiation absorption; for these calculations, the graphical function was (F(R∞) × hν)1/2 vs. hν. The morphology for all the samples was analyzed using a Hitachi S 4800 microscope field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). X-ray photoelectron spectra (XPS) were recorded on a SPECS spectrometer working with a constant pass energy of 40 eV. The spectrometer was equipped with an ultra-high vacuum (UHV) system operating at 5–6·10−10 bar; the instrument was equipped with a PHOIBOS 150 9MCD hemispherical electron analyzer, using Al Kα (hμ) 1486.6 eV at 250W and 12.5 kV. Binding energy correction was performed by fixing the C 1s level at 284.6 eV.
LEV transformation was monitored using an HPLC instrument from Waters (model 2695), featuring a C-18 superxcel reverse phase column (100 × 4.6 mm, 3 μm). Optimal separation was achieved with an isocratic mobile phase consisting of 0.02% formic acid and acetonitrile (85:15 v/v) at a temperature of 30 °C. UV detection at 280 nm was used for quantification, with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min and an injection volume of 10 μL. Identification of transformation products was performed via UPLC/MS analysis using a Waters Acquity instrument coupled with a Waters Acquity QDa single quadrupole instrument. The chromatographic conditions were similar to those of the HPLC instrument, with the eluent comprising water and acetonitrile doped with 0.1% formic acid (85/15 v/v). The detector operated in positive ESI mode with a scan range of 130–1500 m/z.
The antibacterial activity (AA) was determined using the disk diffusion method. Mueller–Hinton agar plates were prepared, and a suspension of Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) with an optical density of 0.6 at 580 nm was evenly spread across the plates to inoculate them. Filter paper discs containing the sample (5.0 μL) were placed onto the agar plates, followed by incubation for 16–24 h. After incubation, the growth of microorganisms was assessed, and the diameters of the inhibition zones were measured in millimeters to assess the reduction in antibiotic potency during the treatments [23].
To determine the degradation pathways, analysis of the radical-trapping reaction adducts by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) was performed using an X-band Bruker EleXsys E580 spectrometer (manufactured by Bruker Biospin, Ettlingen, Germany) equipped with an ELEXSYS Super High Sensitivity Probehead, The HO● and SO4●− trapping reactions were performed using 5,5-Dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO, Cayman Chemical, Europe). To trap 1O2, 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine (TEMP, Thermo Scientific, Germany) was used. The spin trap was mixed at room temperature with an aqueous dispersion of the catalyst at final concentrations of 5.0 mmolL−1 for DMPO or TEMP and 1.0 mg mL−1 for the catalyst, in the presence or absence of PDS (final concentration of 1 mmol L−1). The mixture was transferred to a Petri dish and illuminated in the solar simulator. Subsequently, the sample was transferred to a glass capillary that was introduced in the center of the spectrometer resonator. The EPR instrument was operated at a microwave (mw) frequency of 9.84 GHz and an mw power of 19 mW. The magnetic field was modulated at 100 kHz and the modulation amplitude was set to 0.1 mT after having checked that no overmodulation effects were observed at this modulation amplitude.
The atomic charge calculation (ACC) provides an initial approach to the electron density [24]. For LEV, the ACC was performed through the AtomicChargeCalculator II © freeware by uploading the structure of the antibiotic in an SDF format [25]. Predictions of the antimicrobial biological activity of LEV and a representative degradation byproduct were calculated using the PASS software (free online version), having structure-activity relationships as conceptual bases [26]. To perform the theoretical calculations, the chemical structure is uploaded to the PASS software in the SMILE format. Subsequently, the values of the probability of biological activities (Pa) for the tested compounds are obtained.
Preparation and Enumeration of Escherichia coli
Disinfection experiments were performed with the Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 variant. Strains that grow in aerobic conditions were routinely streaked from frozen stocks to nutritive agar until their stationary phase by cultivation at 37 °C. The bacterial colonies were suspended in distilled water, and the suspension concentration was controlled considering the optical density of 0.35 at λ = 625 nm, which generates a concentration of around 109 CFU mL−1, from which test water spiking to an initial concentration of 106 CFU mL−1. The samples collected during the experiments were quantified using the standard plate counting method, involving serial 10-fold dilutions in sterile saline solution. Diluted samples of 100 μL were then plated on MacConkey agar, and the colonies were counted after incubation for 24 hours at 37 °C. If the bacterial concentration was below 10 CFU mL−1, the samples underwent filtration method. A 10 mL sample was filtered using cellulose nitrate membranes with a pore size of 0.45 µm in a filtration ramp. The resulting membranes were placed on MacConkey agar and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. The detection limit (DL) of this technique is 10 CFU 100 mL−1, the minimum disinfection level required by EU 2020/741, the European regulation on water reuse for Class A treated municipal wastewater.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of the Materials
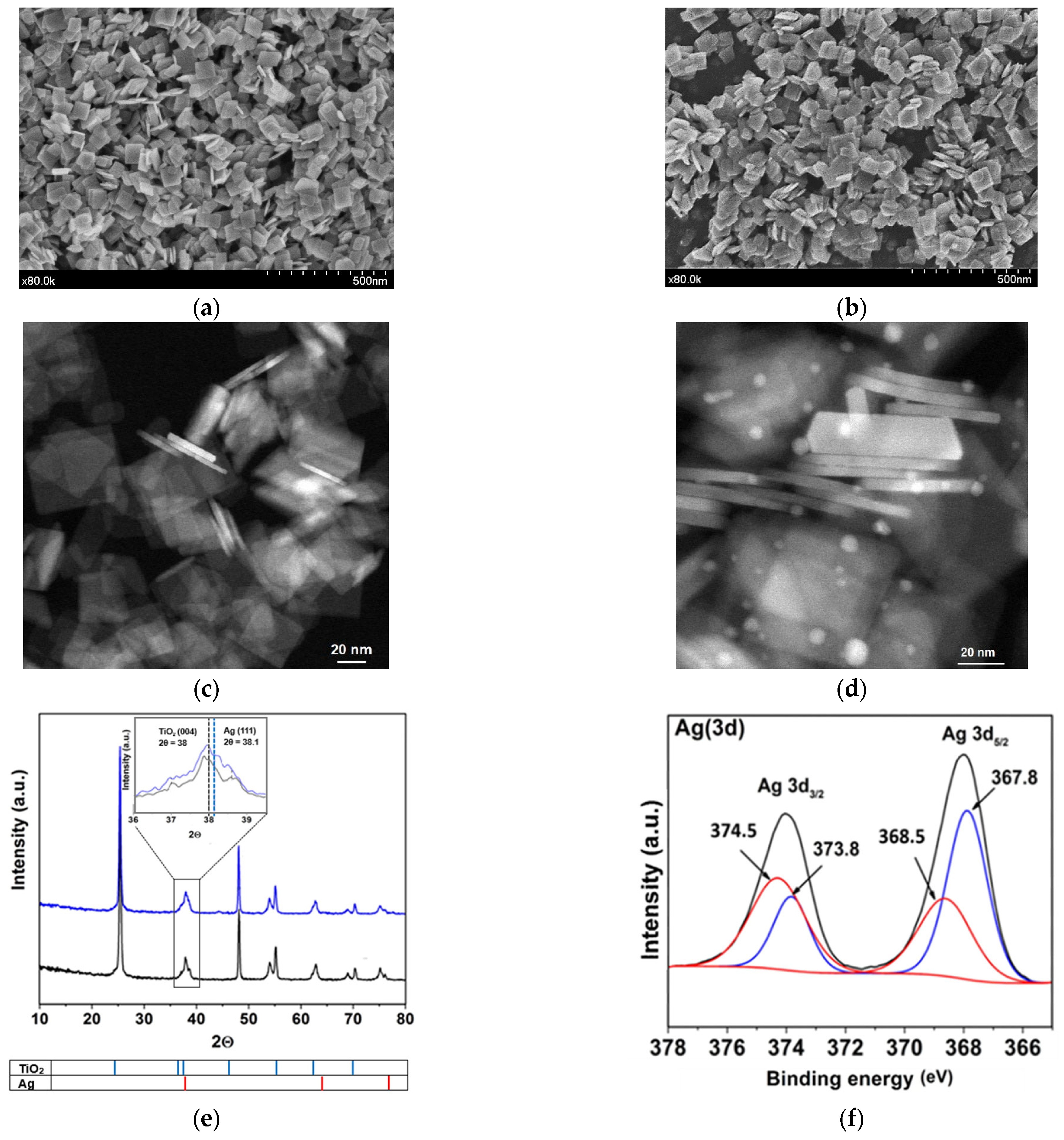
The synthesized TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 materials were initially characterized (Figure 1). The study of morphological characteristics started with SEM and TEM analyses. From Figure 1a,b, it was observed that both materials are nanoplatelets. Figure 1c,d show the dimensions of materials; crystals measure nearly 70 nm in length, 80 nm in height, and 5–6 nm in thickness. In a previous study, 76% of {001} facet was reported for the TiO2 material [22]. This crystalline form favors the photocatalytic processes considering the higher surface energy of {001} facets, which allows more efficient dissociative adsorption of reactant molecules as compared with that of {101} facets [27,28]. Those aspects are linked to the low atomic coordination numbers of exposed atoms, a high density of active unsaturated coordination Ti atoms, and active surface oxygen atoms with wide bond angles of Ti–O–Ti [29]. Moreover, 2D nanostructures enhance the efficiency of light collection by multiple light scattering and also favor the electron transfer rates [30]. Therefore, the synthesis of high-energy facets of TiO2 composites is desired to improve the optical properties and extend the catalytic applications. Furthermore, the TEM images of TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) revealed the presence and distribution of Ag nanoparticles on the nanoplates of the TiO2 structure. TEM image also evidenced the spherical shape of Ag NPs, with a size range from 2 to 10 nm (Figure 1d).
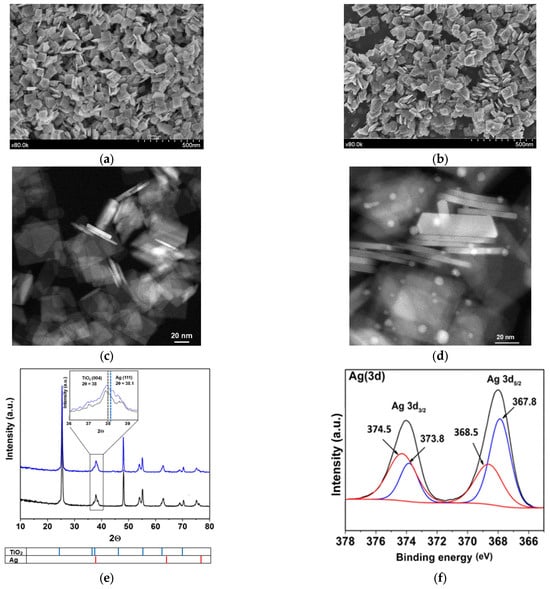
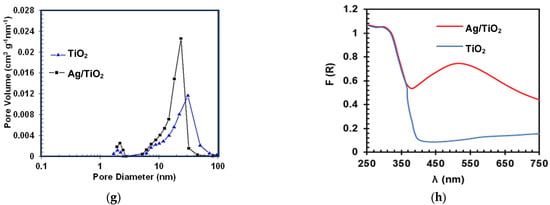
Figure 1.
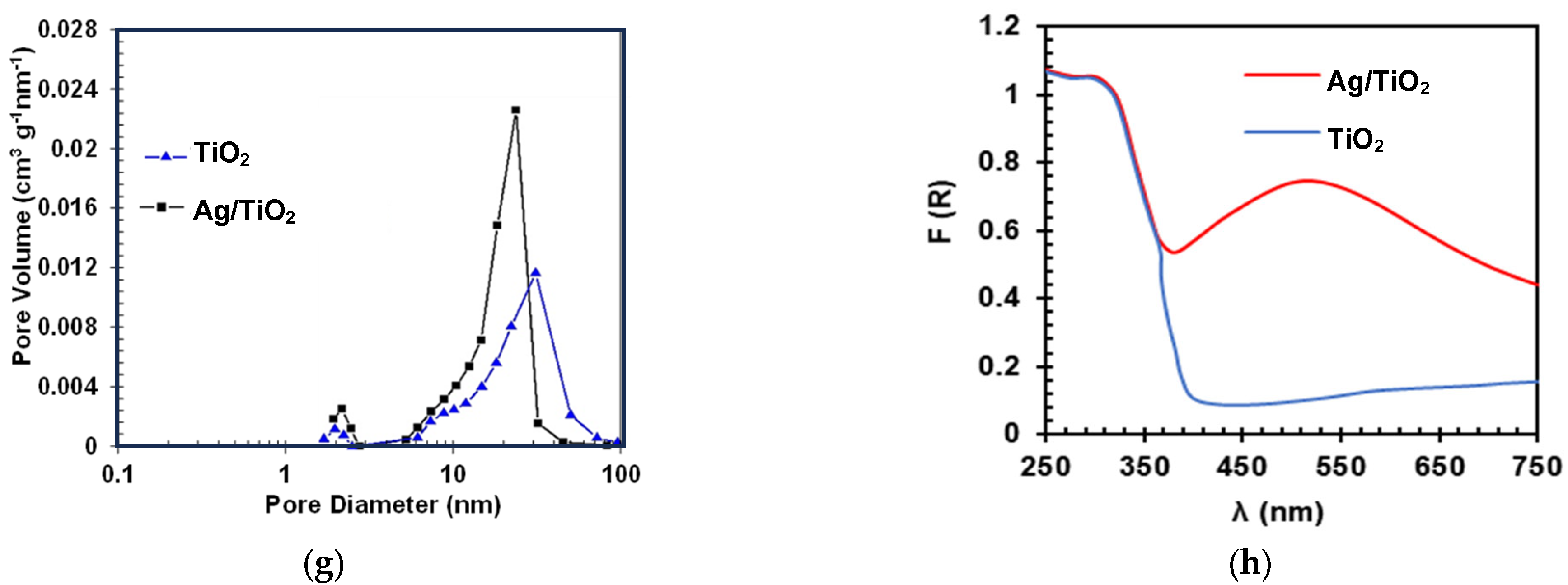
Images of the synthesized materials. SEM TiO2 (a) and Ag/TiO2 (b); TEM TiO2 (c) and Ag/TiO2 (d); XRD patterns: TiO2 (black) and Ag/TiO2 (blue) (inset: amplification between 36° and 39.5° in the 2θ angle (e) (For readers’ clarity, a zoomed-in version of this figure was added to the Supporting Information as Figure S1d); XPS results after Ag metallization in TiO2 (f) (more details about XPS are provided in Figure S1e–g and Text S1); Pore size distribution of synthesized TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 (g) and UV-Vis DRS for TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 samples (h).
The EDS results for the synthesized photocatalysts are presented in Figure S1 (in Supplementary Materials). These results confirmed that the surface of the prepared material is composed of Ti and O in the case of TiO2 (Figure S1a). In turn, Ag, Ti, and O are effectively present in the Ag/TiO2 surface (Figure S1b). In fact, the elemental distribution mapping (Figure S1c) shows a heterogeneous distribution of Ag (red) deposited on the plates and their sides. The XRD diffraction for TiO2 (Figure 1e) shows signals at 2θ values of 25°, 37°, 38°, 48°, 55°, 62°, and 70°, that correspond to the characteristic peaks of anatase at (101), (004), (112), (200), (211), (213) and (220) planes, respectively (JCPDS card file No. 021-1272). For Ag/TiO2, Ag nanoparticles (NPs) appear, having peaks at 2θ of 38°, 64°, and 77°, corresponding to (111), (220), and (311) planes of Ag, respectively (JCPDS card file No. 04-0783). The graph amplification between 36° and 39.5° in the 2θ angle of the XRD diffractogram range indicates a noticeable alteration in the peak shapes of (Ag/TiO2) in comparison to the untreated material (TiO2) (inset on Figure 1e) [31]. This alteration could be linked to the presence of the primary plane (111) of cubic silver (JCPDS No. 087-0717). Moreover, within this analyzed region, the planes associated with the anatase TiO2 phase, such as (103), (004), and (112), are also visible.
To identify the oxidation states of Ag, XPS analysis was performed for the surface of the silver metalized catalyst. Figure 1f reveals a doublet of doublets in the deconvolution. The first doublet showed the Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2 signals at 368.5 eV and 374.5 eV, respectively, which are attributed to Ag0 deposits. Meanwhile, the second doublet, with signals at 367.8 eV and 373.8 eV for Ag 3d5/2 and Ag 3d3/2, typically corresponds to Ag+. The presence of Ag+ possibly occurs due to precursor remnants or oxidized silver species (Ag2O or AgF) [32]. These results could be associated with photo-deposition and change of silver from Ag+ to Ag0. As previously mentioned, there is a reducing face {101}, places where the Ag0 deposition could occur preferentially, while the silver precursor species could be adsorbed on the oxidative face {001}. Other details about XPS regions of Ti(2p), O(1s) and F(1s) and F (1s) in Ag/TiO2 are pre-sented in Figure S1e-g and Text S1 [30,33].
Regarding BET, superficial areas of 56.80 m2g−1 and 50.98 m2g−1 were found for TiO2 and Ag/TiO2, respectively. The slight decrease in the surface area would correspond to the obstruction of some pores on the TiO2 by the incorporation of Ag particles. In fact, after metallization, there is a decrease in the pore volume (Figure 1g) and, consequently, in the specific surface area of the metalized sample concerning the non-metalized one. In turn, UV–vis DRS analysis for TiO2 (Figure 1h) shows an absorption in the UV range (λ ≤ 400 nm) associated with the intrinsic band-gap transition of the anatase-TiO2 [34]. From Figure 1h, it can also be noted that the presence of Ag nanoparticles on the materials leads to an increase in the absorption in the visible light range (λ > 400 nm). This is associated with an LSPR effect, which facilitates an enhancement of the excitation of electrons at the material surface. Furthermore, we should mention that noble metals (such as Ag) have unusually high Schottky barriers (SBs). When noble metals are attached to semiconductors, the SBs help to trap electrons and facilitate the separation of electron-hole pairs [11,35]. Therefore, the lifetime of electron and hole pairs upon irradiation of Ag/TiO2 could be increased, which can enhance the photocatalytic efficiency. Thus, considering these characteristics of the prepared materials, they were tested in a photocatalytic system to degrade LEV and inactivate E. coli in water, as detailed below.
3.2. Degradation and Disinfection Using the Photocatalytic System
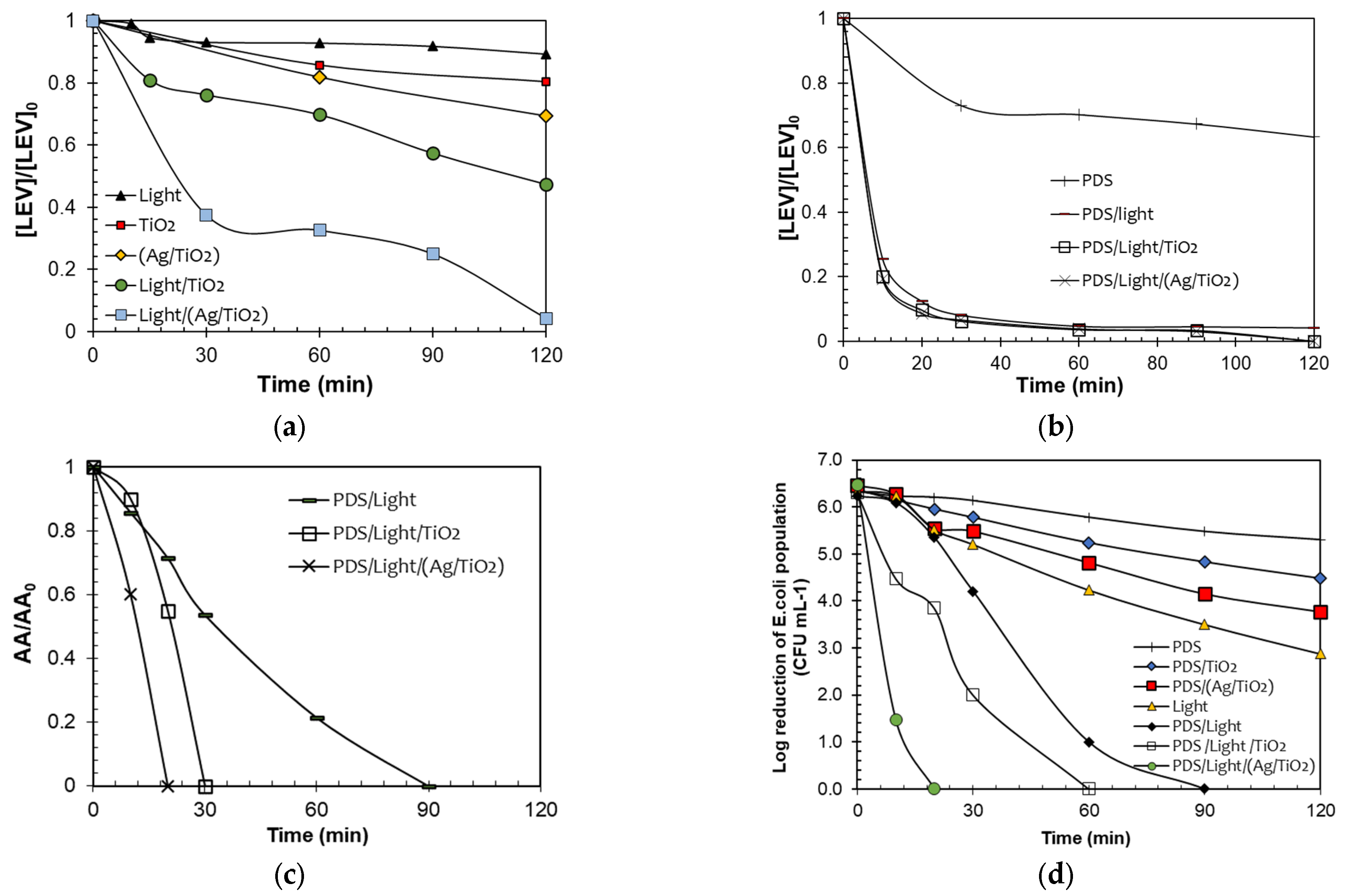
Figure 2a compares the photolysis and LEV elimination by the materials (TiO2 and Ag/TiO2) in both the presence (photocatalysis) and the absence of light (adsorption) and under illumination alone. The LEV photodegradation by the sunlight alone is small (~10% after 120 min). According to Albini et al., the main pathway of direct photo-transformation of fluoroquinolones is the cleavage of the C–F bond [36]. However, this pathway is dependent on the electron-withdrawing nature of the substituent in the meta position concerning the fluorine atom. As the electron-withdrawing nature of the substituent is augmented, the efficiency of the direct photodecomposition is increased. Thus, the photolysis of LEV is low, considering that this antibiotic contains an electron-donating substituent (i.e., the O-alkyl group) in the meta position to the C–F bond, which limits the fluoride-losing pathway [37].
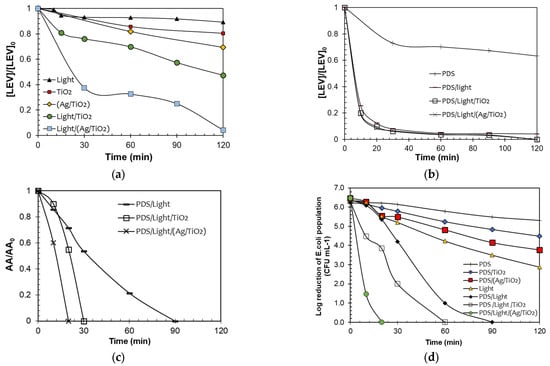
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the photocatalytic activity of the materials. LEV degradation by the processes (a,b). Note: Red dots (TiO2) and yellow diamonds (Ag/TiO2) in Figure 2a represent the LEV adsorption on the catalysts. AA removal (c) and disinfection (d). Note: Ag/TiO2 in dark achieved a reduction of the E. coli population of only 1.5-log units after 120 min, which is associated with adsorption or toxicity of Ag species in the material. Experimental Conditions Figure (a–c): [LEV] = 0.05 mmol L−1, [PDS] = 0.01 mmol L−1. [TiO2] = [Ag/TiO2] =10.0 mg L−1, pH = 6.5. Figure (d). [E. coli] = 106 CFU L−1, [PDS] = 0.01 mmol L−1. [TiO2] = [Ag/TiO2] =10.0 mg L−1, pH = 6.5.
LEV underwent partial adsorption, with 15% and 30% adsorbed on TiO2 and Ag/TiO2, respectively (Figure 2a). LEV exhibits two distinct pKa values (6.0 and 7.5). In acidic environments, it predominantly exists in its cationic form, while in basic conditions, it is primarily in the anionic form. At the pH range of 6.0 to 7.5, LEV predominantly exists in its zwitterionic form. Additionally, the measurements of the Point of Zero Charge (PZC) of the materials show a lower value for TiO2 (6.3) compared to Ag/TiO2 (7.3). Therefore, at the experimental pH of the solution (6.5), the LEV molecules may be attracted differentially by the electrostatic interactions on the surface of TiO2, compared to the surface of Ag/TiO2. Considering the experimental pH and PZC of both catalysts, the interaction of TiO2 (predominantly charged negatively) with LEV occurs through the positively charged bulky methyl-piperazyl ring, whereas in the case of Ag/TiO2 (which mainly has positive charges on the surface), it interacts with LEV via the negative carboxylate group. Thus, as the TiO2/LEV interaction occurs through a bulkier group than the interaction of Ag/TiO2 with LEV, the adsorption of the antibiotic is more favored on the second material.
According to Figure 2a, the two photocatalytic systems (i.e., Light-TiO2 and Light-Ag/TiO2) achieved a superior elimination of the pollutant. Moreover, the test performed under Light-(Ag/TiO2) led to a higher removal of the antibiotic regarding the non-modified TiO2. This can be explained by considering the plasmonic effects. Plasmonic nanomaterials, such as Ag, have excellent electromagnetic field-concentrating properties [38]. Therefore, they can enhance photoreactions by increasing the local field. Additionally, the plasmonic particles can also enhance chemical reactions by increasing electron-hole-pair generation in a nearby semiconductor, which will then transfer the charge carriers to the available states in the organic molecules (e.g., pollutants), inducing their transformation [38,39]. However, it is crucial to mention that factors such as the concentration of the contaminant, its reactivity, as well as the concentration of the photocatalysts, the irradiation source, and the pH among others, can play a significant role in the efficiency of the processes using TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 [40]. Therefore, there is an interest in developing methodologies that allow for improving the function of the materials in the removal of recalcitrant contaminants.
As a strategy to enhance the degrading performance of the photocatalytic processes, the addition to both systems of PDS was assessed (Figure 2b). The direct action of PDS toward LEV was also tested. Furthermore, another control test (PDS combined with solar light) was evaluated. As seen in Figure 2b, after 120 min PDS alone was able to degrade ~36% of LEV by direct oxidation. Interestingly, the elimination of LEV under PDS and sunlight demonstrates a fast degradation of the antibiotic. Around 80% of the antibiotic concentration was removed after 10 min of treatment. The PDS/sunlight combination could promote the formation of sulfate radicals, thus enhancing the degradation efficiency regarding PDS alone [21].
From Figure 2b, it can also be noted that the PDS/light/catalyst systems led to close degradation percentages to the PDS/sunlight one. However, in the treatment of antibiotics, it is very relevant to go beyond pollutant removal, because in some cases, despite the antibiotic being degraded, the antimicrobial activity could remain, representing a risk for the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms. Thus, the removal of the evolution of the antimicrobial activity (AA) was followed (Figure 2c). Despite the LEV degradations being similar, the AA removal is faster by the action of the photocatalytic processes. These last results suggest that different primary by-products, having different AA, could be formed in the considered treatment systems [41]. Indeed, the PDS/light/(Ag/TiO2) system was more efficient in removing the AA, indicating that this system could produce less biologically active byproducts than those obtained by the other treatments.
In addition to the degradation of the target antibiotic and determination of the AA evolution, the considered photochemical systems were used to deal with E. coli. The corresponding control tests were also carried out (Figure 2d). It can be remarked that the inactivating capability of the PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2) system was superior to the PDS/sunlight combination or simpler components (e.g., light alone). The best disinfecting action suggests that in the PDS/light/(Ag/TiO2) system, diverse degrading agents (e.g., light and radicals) could be involved [42,43]. It is important to mention that for materials such as Ag/TiO2 in aqueous media, the released amount of Ag is low (less than 4% of the initial load of silver in the catalyst or equivalently ~20 µg L−1); however, some disinfecting effects by the leached Ag are plausible, which complement the stronger inactivating action of other species (e.g., radicals) that are participating in the process. Therefore, all the above results show that the Ag/TiO2 material is a very versatile photocatalyst able to promote degradative processes, elimination of AA, and bacteria inactivation.
3.3. Principal Degradation Routes and Transformations Involved in the Photocatalytic Systems
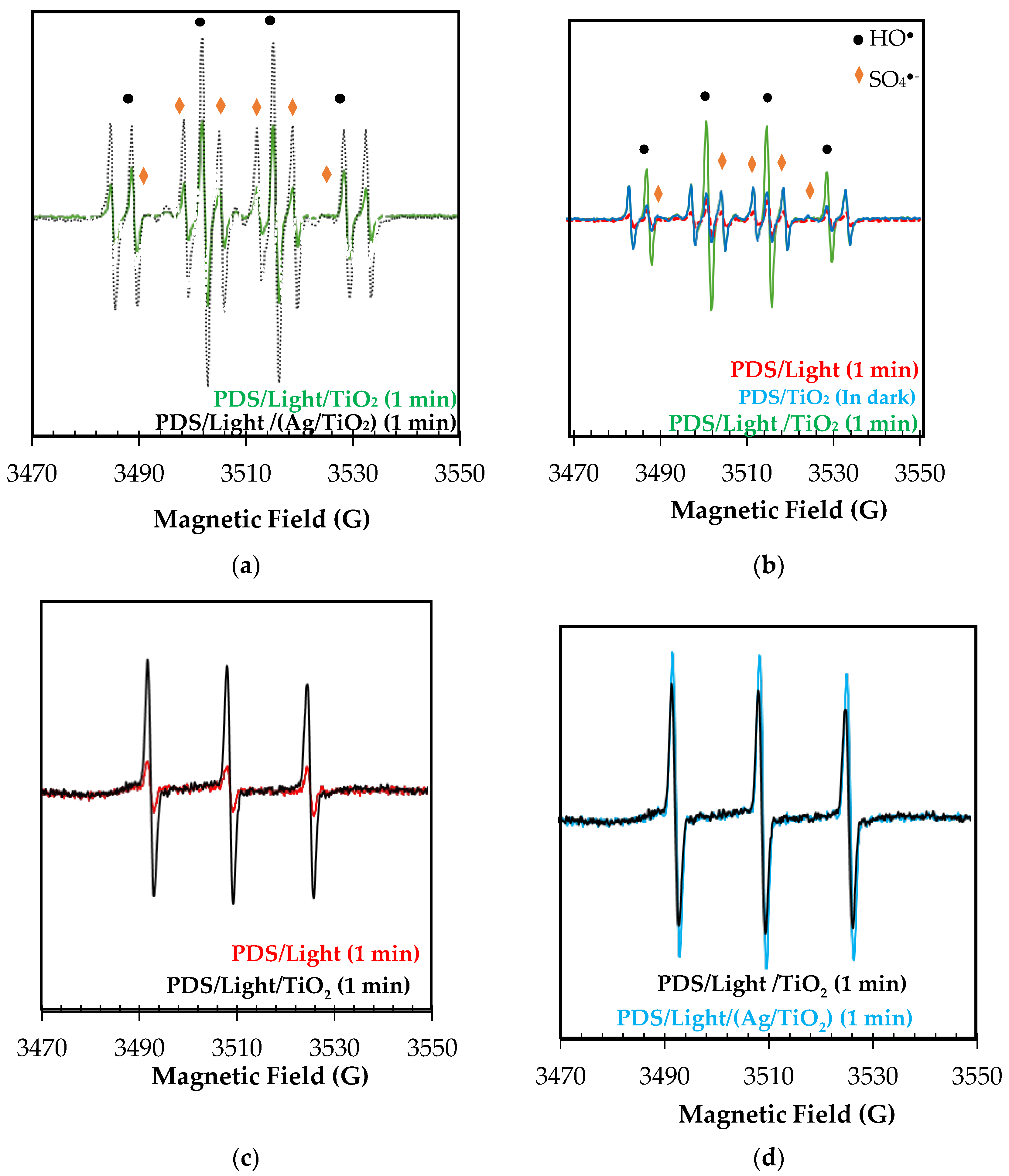
As a first approximation to the understanding of degradation routes that participate in the PDS/Light/TiO2 and PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2) systems, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) spectroscopy analyses were performed (Figure 3). Using the spin traps DMPO and TEMP, oxidizing species generated in the PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2) processes were determined. DMPO was used to trap hydroxyl and sulfate radicals, and TEMP was used to trap singlet oxygen. The DMPO results (Figure 3a, black markers) show four characteristic signals of the DMPO●-HO adduct (AN = 14.8 G, AH = 14.8 G) [44], confirming the formation of HO● in both PDS/Light/TiO2 and PDS/Light/Ag/TiO2 systems. The six representative lines of the DMPO●-SO4− adduct signals, marked with blue, (AN = 13.8 G, AH = 10.1 G) are less pronounced and partially covered by radicals centered in carbon (AN = 15.8 G, AH = 22.8 G), characteristics of DMPO interaction with radical species. To confirm the presence of sulfate radicals, additional measurements were performed using Ag/TiO2 photocatalyst and increasing PDS concentration, from 1 mM to 100 mM (changing the DMPO:PDS ratio, from 5:1 to 5:100). As can be seen in Figure S2, radicals DMPO●-SO4- adduct signals appear in the experimental EPR spectrum and align with the EPR spectrum simulation. Furthermore, across all measurements with DMPO, there is a superior capacity of Ag/TiO2 to activate PDS compared to the TiO2 photocatalyst. In turn, in the EPR spectrum using TEMP (Figure 3c), the three characteristic lines with high intensity for the adduct of TEMP-1O2 demonstrated the participation of singlet oxygen during the degradation process [45]. As can be seen in Figure 3d, the intensity of the signals for TEMP-1O2 is also lightly higher for PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2), suggesting higher radical adduct formation than in PDS/Light/TiO2 under these conditions.
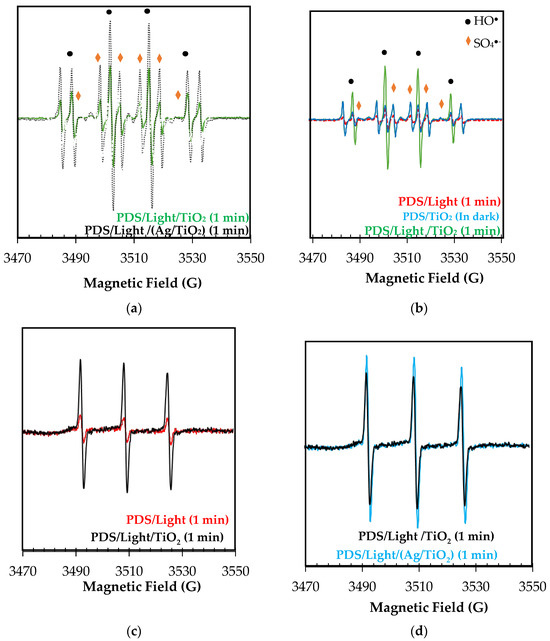
Figure 3.
EPR spectrum of adducts formed upon exposure of PDS/Light/TiO2 and PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2) systems to sunlight with (a,b) DMPO, and (c,d) TEMP in water.
The results from the EPR can be used to rationalize the photocatalytic behavior of the materials. Then, we can propose that the light with TiO2 and Ag/TiO2 generates electron-hole pairs, and the photogenerated holes produce hydroxyl radicals from water oxidation (Equations (1) and (2)). Consecutively, the electrons in the conduction band could interact with PDS, leading to the formation of sulfate radicals (Equation (6)) [13]. Additionally, nanoparticles and species of silver in the modified TiO2 enhance the production of oxidizing species due to: (i) the plasmonic effect (which promotes better charge carrier separations), which leads to superior hydroxyl radical formation; (ii) the diminution of electron-hole pairs recombination, which also allows PDS to react more easily to produce sulfate radical (Equation (6)); (iii) the oxidative and reductive cycle of silver species, which promote the PDS activation through electron transference processes (Equations (7)–(10)) [46,47,48]:
Ag+ + S2O82− → Ag2+ + SO4•− + SO42−
SO4•− + H2O → SO42− + •OH + H+
Ag2+ + H2O → Ag+ + •OH + H+
Ag2+ + S2O82− → Ag+ + S2O8•−
(iv) the higher lifetime of the electrons in the conduction band, which could have more chance to interact with oxygen to produce superoxide radical anion and then singlet oxygen (Equations (11) and (12)) [49,50]. Also, the UV components of the simulated solar light induce the homolysis of PDS, yielding SO4●− (Equation (13)). Then, the oxidizing species (i.e., SO4●−, HO●, or 1O2) produced through the aforementioned pathways are primarily responsible for the degradation of LEV and its AA removal.
e− + O2 → O2●−
hv + O2●− → 1O2 + e−
S2O82− + hv → 2SO4●−
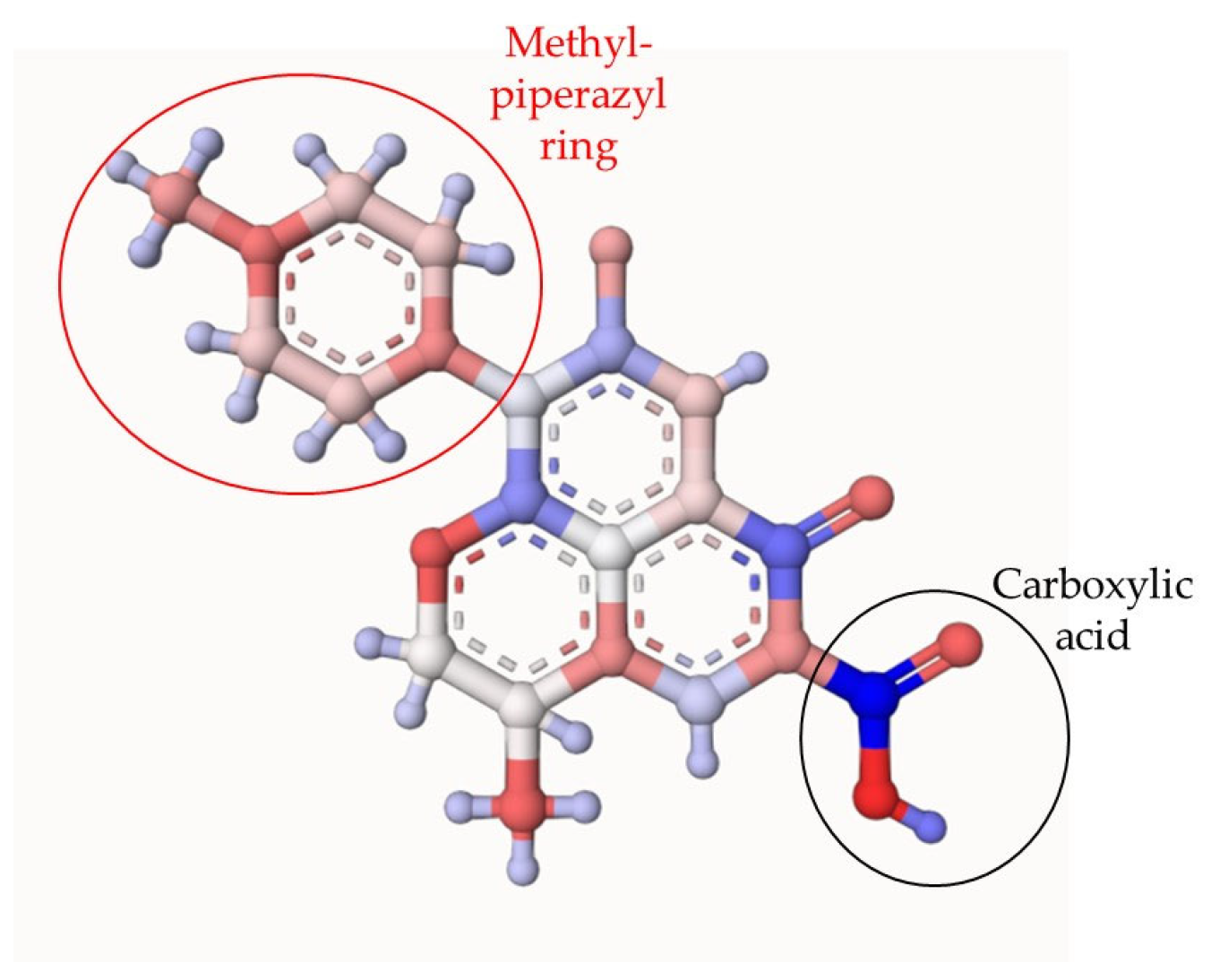
In addition to the EPR analyses, theoretical atomic charges calculation (ACC) on LEV was also carried out. Figure 4 shows the results of ACC for LEV. The ACC analysis allowed us to identify the moieties of the target pollutant that are more susceptible to attacks by the degrading species [41]. The ACC presents in red color the electro-rich atoms, while in blue color are represented the electron-deficient atoms. The methyl-piperazyl group on LEV had a predominantly red color, indicating that this region of the antibiotic is more susceptible to the attack of hydroxyl radical, sulfate radical, or singlet oxygen. Also, the methyl group attached to the cyclic ether and carboxylic acid could be attacked by HO● and SO4●- generated in the photocatalytic process. The formation of primary transformation by-products having modifications on the mentioned functional groups on LEV was evidenced experimentally (the main stable primary degradation products were determined by LC-MS analyses). Indeed, the information provided by the ACC analysis is consistent with the primary transformations observed for LEV (Figure 5 and Table S1). In Figure 6, red labels correspond to products generated using the PDS/Light/TiO2 system, green labels were only detected in PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2), and underlined labels correspond to products detected in both systems. Table S1 contains some details of these transformation products.
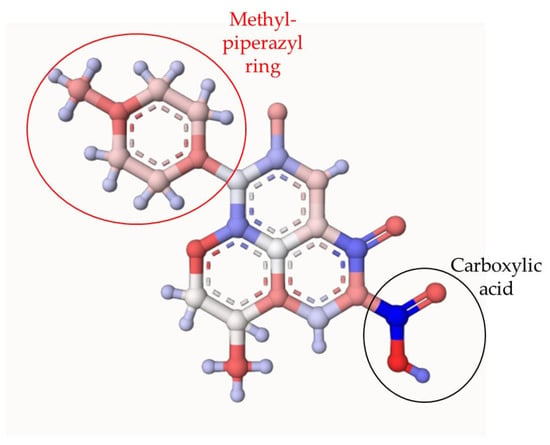
Figure 4.
Theoretical atomic charges calculation (ACC) for LEV. The ACC2 software: Version: ACC II was used (https://acc2.ncbr.muni.cz/ (accessed on 2 November 2023)), The ACC presents in red color the electro-rich atoms, while in blue color are represented the electron-deficient atoms.
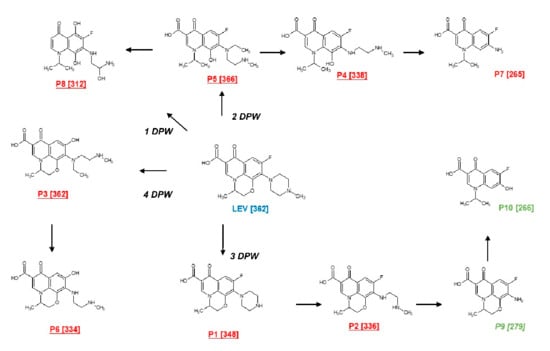
Figure 5.
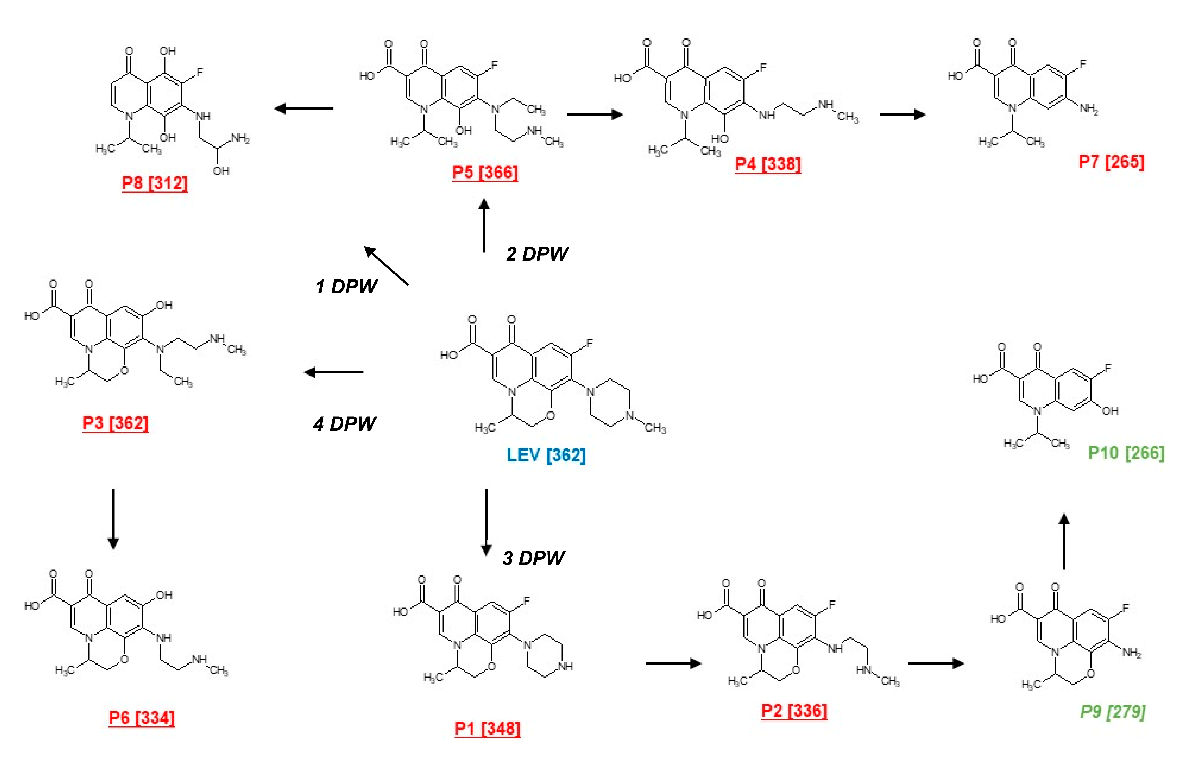
Primary transformation of LEV under the action of the photocatalytic processes. DPW represents the suggested degradation pathways of LEV.
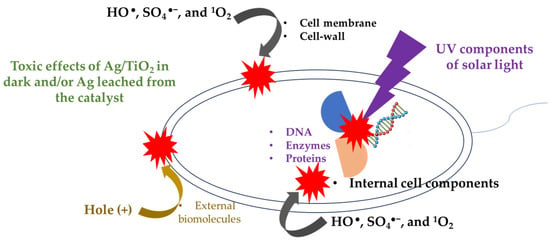
Figure 6.
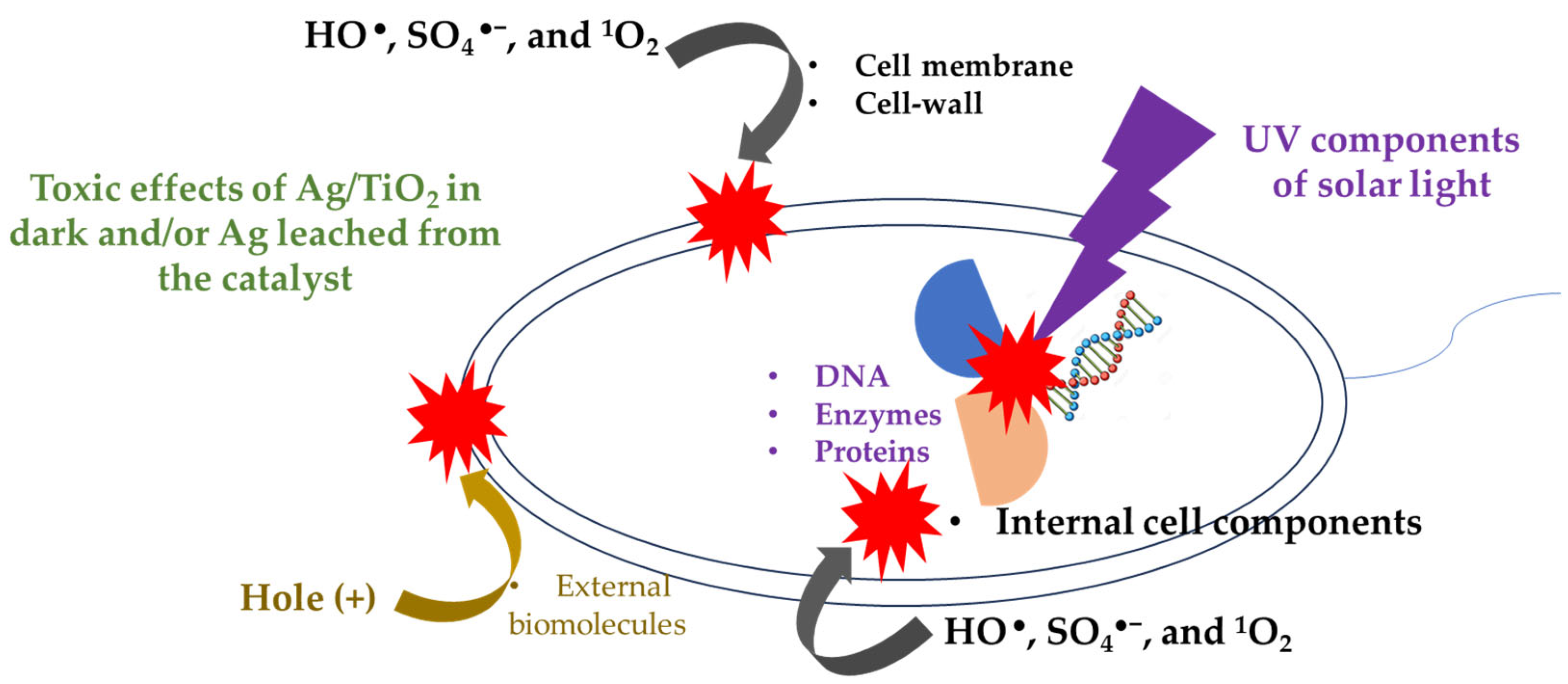
Scheme of the possible interaction of the bacteria with light and oxidizing species generated in the photocatalytic system.
The elucidated transformation products can be generated from four degradation pathways (PDW). The first degradation pathway (1-DPW) consists of the breaking of the piperazyl and morpholine rings, followed by hydroxylations, leading to the formation of an intermediate product with m/z 312. The second route (2-DPW) occurs also as a consequence of the opening of the piperazyl and morpholine rings, but with the subsequent loss of an ethyl group and N-methylethanamine, generating the products with m/z 366, m/z 338, and m/z 265, respectively. In turn, the products having m/z 348 (reported before in [51,52]), m/z 336, m/z 279 (also finding in [51,53] ), and m/z 266 (described by [54]) were obtained through the successive loss of groups associated with the piperazyl ring (third pathway, 3-DPW); the last two products, shown in green color, owing to the superior formation of reactive oxygen species, were only detected in the presence of PDS/Light/(AgTiO2). Finally, the cleavage of the C-F bond followed by hydroxylation and cleavage of the piperazyl ring (the fourth pathway, 4-DPW) generates the products with m/z 362 and m/z 344 (Figure 5).
On the other hand, the removal of AA can be linked to the transformations of LEV by the photocatalytic processes. Indeed, structural modifications of moieties such as the piperazyl ring (which controls the antibacterial potency, efflux inhibition, and the acid/base speciation of the antibiotic) or the carboxylic acid (responsible for the antibiotic binding to bacterial DNA topoisomerases or DNA gyrase) [55,56,57] can be associated with the AA decrease. Thus, to better understand the removal of AA associated with LEV shown in Figure 2c, theoretical estimations of the biological activity were performed for LEV and one illustrative product (P9), m/z: 279, which is also very common in several photochemical and photocatalytic processes [18,51,58]. Then, the probability of being active (Pa) for LEV and the illustrative by-product were obtained (Figure S3). Pa values for biological activities of topoisomerase II inhibitor, such as anti-infective substance, DNA synthesis inhibitor, and antibiotic quinolone-like (i.e., the main antimicrobial action mechanisms of fluoroquinolone antibiotics [59]) were calculated. Figure S3 contains the results, where a higher Pa value means a higher probability of having the biological activity. From Figure S3, it can be noted that the illustrative by-product had lower Pa values than the parent antibiotic.
This last aspect fits well with the decrease in the AA observed in Figure 2c. Additionally, it is important to remark that the elimination of AA could have a positive environmental impact. The AA removal can contribute to decreasing the interaction of the antibiotic with bacteria in the aqueous medium, thus limiting the proliferation of antibiotic-resistant microorganisms in the environment.
Regarding the inactivation of E. coli (Figure 2d), it can also be explained considering its interaction with the oxidizing species identified by EPR analyses, in addition to the direct action of the solar light on this microorganism (as schematized in Figure 6). It must be mentioned that HO●, SO4●−, and 1O2 (coming from the photocatalytic process) can induce external damage on E. coli such as oxidation of the lipid membrane and cell-wall components [60,61]. The formed ROS also are able to attack and damage internal cell components, including organelles, proteins, enzymes, and DNA. Even the photogenerated holes on the catalysts could also take electrons from the external biomolecules of the bacteria [62,63], thus promoting the inactivation of E. coli. Furthermore, the UVA and UVB components of solar light are able to induce damage inside bacteria [64]. For instance, the UVB component promotes the alteration of DNA strains and deactivation of enzymes/proteins. Meanwhile, the UVA component can lead to internal photo-oxidation reactions, plus the generation of DNA dimers [65]. Furthermore, some disinfecting effects caused by Ag/TiO2 in dark and/or leached Ag are plausible, and these complement the inactivating action of the other species (e.g., ROS) that are participating in the process. Thereby, we propose that all these pathways address the water disinfection in the photocatalytic systems (i.e., PDS/light/TiO2 and PDS/Light/(Ag/TiO2)).
4. Conclusions
After performing this research, it can be concluded that two TiO2-based materials were effectively synthesized. The presence of Ag on the surface of TiO2 promoted “local surface plasmon resonance”, and its effects significantly enhanced the absorption of light at wavelengths greater than 400 nm compared to unmodified TiO₂ under the studied conditions. The photocatalytic results showed that the Ag/TiO2 material improved the LEV degradation regarding TiO2. Moreover, the Ag/TiO2 in the light presence enhanced the PDS activation, leading to faster removal of the AA. The LEV degradation was associated with the attacks of hydroxyl, sulfate radicals, and singlet oxygen (which were identified by EPR analyses). Consequently, the AA was decreased, which was associated with attacks on and changes of the methyl-piperazyl ring and carboxylic acid on LEV (the most electron-rich moieties according to the ACC analyses and the experimental results). Moreover, E. coli disinfection can occur through the action of oxidizing species (HO●, SO4●−, and 1O2), in addition to the direct action of the solar light and the toxic effects of Ag/TiO2 or the leached Ag on this microorganism. We can mention that the good catalytic performance of Ag/TiO2 is favored by the role of Ag, which could act as a sink for the photogenerated electrons, retarding electron-hole recombination, thus increasing the presence of diverse degrading and disinfecting species in water. Finally, we suggest developing in future research experimental tests of photostability and reuse of the Ag/TiO2 in the photocatalytic systems to degrade organic pollutants and inactivate microorganisms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w16172434/s1, Figure S1: EDS analyses, XRD, and XPS results; Text S1: Discussion of XPS results; Figure S2. EPR spectrum of radicals generated by the Ag/TiO2-sunlight system, captured using DMPO. Signals: Black: experimental results, blue: simulated DMPO-●OH and red: simulated DMPO-SO4. Test conditions: DMPO = 5 mM; PDS = 100 mM. Simulation software: EasySpin in the MATLAB. (Exp. = in the experiment; Sim. = in the simulation); Figure S3: predicted biological activity; Table S1: Characteristics of the identified by-products of Levofloxacin (LEV).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: S.D.J.-S., J.A.N., E.A.S.-G., R.A.T.-P. and R.M.; methodology: S.D.J.-S., I.G.-R. and C.J.-P.; software: E.A.S.-G.; formal analysis: S.D.J.-S. and E.A.S.-G.; investigation: S.D.J.-S., C.J.-P. and E.A.S.-G.; resources: M.P.O., I.G.-R., R.M. and M.C.H.; writing—original draft preparation: S.D.J.-S. and E.A.S.-G.; writing—review and editing: R.M., R.A.T.-P., C.J.-P., I.G.-R. and J.A.N.; supervision: R.M., M.C.H. and R.A.T.-P.; project administration: R.M., M.P.O. and M.C.H.; funding acquisition: R.M., M.P.O., M.C.H., I.G.-R. and J.A.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by: “European Union Next Generation EU/PRTR” through MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033, grant TED2021-129267B-I00 and grant PID2021-127287NB-100, MCIN with funding from European Union NextGenerationEU (PRTR-C17.I1) promoted by the Government of Aragon. This work was also financed by Gobierno de Aragon (Spain): Research Reference Team Water and Environmental Health B43_23R, and MINCIENCIAS-COLOMBIA (grant project No. 1115-852-69594).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available on request to the authors.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge research services of the CITIUS University of Seville and SAI University of Zaragoza. We would like to thank the Universidad del Tolima for financial support in the study commission of César Augusto Jaramillo Páez.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fish, D.N.; Chow, A.T. The Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Levofloxacin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 32, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotto, C.; Bissa, M.; Illiano, E.; Mezzanotte, V.; Marazzi, F.; Turolla, A.; Antonelli, M.; De Giuli Morghen, C.; Radaelli, A. Identification of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia Coli Isolated from a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wu, H.; Cai, M.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, C.; Han, Y.; Zhang, L. Valorization of Biomass-Derived Polymers to Functional Biochar Materials for Supercapacitor Applications via Pyrolysis: Advances and Perspectives. Polymers 2023, 15, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengyu, C.; Hongmiao, L.Y.; Caiyun, Y.; Yuting, Z.; Hao, W. Activated Sludge Incineration Ash Derived Fenton-like Catalyst: Preparation and Its Degradation Performance of Methylene Blue. J. Inorg. Mater. 2024, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengifo-Herrera, J.A.; Pulgarin, C. Why Five Decades of Massive Research on Heterogeneous Photocatalysis, Especially on TiO2, Has Not yet Driven to Water Disinfection and Detoxification Applications? Critical Review of Drawbacks and Challenges. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 146875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, K.; Lim, T.M.; Tsen, L.; Lee, C.C. Photocatalytic Degradation and Mineralization of Bisphenol A by TiO 2 and Platinized TiO2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 261, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulou, D.; Rethemiotaki, I.; Frontistis, Z.; Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Venieri, D.; Mantzavinos, D. Degradation, Mineralization and Antibiotic Inactivation of Amoxicillin by UV-A/TiO2 Photocatalysis. J. Env. Manag. 2012, 98, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xekoukoulotakis, N.P.; Xinidis, N.; Chroni, M.; Mantzavinos, D.; Venieri, D.; Hapeshi, E.; Fatta-Kassinos, D. UV-A/TiO2 Photocatalytic Decomposition of Erythromycin in Water: Factors Affecting Mineralization and Antibiotic Activity. Catal. Today 2010, 151, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, L.E.; Ray, M.B. Degradation of Paracetamol in Aqueous Solutions by TiO2 Photocatalysis. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangeneh, H.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.L.; Habibi, M.; Akia, M.; Hasnain Isa, M. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Organic Dyes and Pollutants in Wastewater Using Different Modified Titanium Dioxides: A Comparative Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangamuthu, M.; Raziman, T.V.; Martin, O.J.F.; Tang, J. Review—Origin and Promotional Effects of Plasmonics in Photocatalysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 036512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraju, D.; anak Kutiang, F.D.; Lim, Y.C.; Goh, P.S. Recent Progress of Ag/TiO2 Photocatalyst for Wastewater Treatment: Doping, Co-Doping, and Green Materials Functionalization. Appl. Mater. Today 2022, 27, 101500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Giannakis, S.; Marjanovic, M.; Kohantorabi, M.; Gholami, M.R.; Grandjean, D.; de Alencastro, L.F.; Pulgarín, C. Solar-Assisted Bacterial Disinfection and Removal of Contaminants of Emerging Concern by Fe2+-Activated HSO5- vs. S2O82− in Drinking Water. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 248, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansal, S.K.; Kundu, P.; Sood, S.; Lamba, R.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K. Photocatalytic Degradation of the Antibiotic Levofloxacin Using Highly Crystalline TiO2 Nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Salunke, D.B.; Umar, A.; Mehta, S.K.; Sinha, A.S.K.; Kansal, S.K. Visible Light Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Fluoroquinolone Levofloxacin Drug Using Ag2O/TiO2 Quantum Dots: A Mechanistic Study and Degradation Pathway. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12079–12090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.G.; Gandhi, V.G.; Modi, K.; Shukla, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Levofloxacin by GO-TiO2 under Visible Light. Mater. Today Proc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandaghian, F.; Ebrahimian Pirbazari, A.; Tavakoli, O.; Asasian-Kolur, N.; Sharifian, S. Comparison of the Per-formance of Ag-Deposited ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles in Levofloxacin Degradation under UV/Visible Radia-tion. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Ibhadon, A.O.; Grazia Francesconi, M.; Mehta, S.K.; Elumalai, S.; Kansal, S.K.; Umar, A.; Baskoutas, S. Bi2WO6/C-Dots/TiO2: A Novel z-Scheme Photocatalyst for the Degradation of Fluoroquinolone Levofloxacin from Aqueous Medium. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; An, T.; Zhao, H.; Wong, P.K. Catalyst-Free Activation of Persulfate by Visible Light for Water Disinfection: Efficiency and Mechanisms. Water Res. 2019, 157, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Wong, P.K.; An, T. Visible Light Activation of Persulfate by Magnetic Hydrochar for Bacterial Inactivation: Efficiency, Recyclability and Mechanisms. Water Res. 2020, 176, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y. A Comprehensive Review on Persulfate Activation Treatment of Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, M.A.; Sayagués, M.J.; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C. A Facile Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Highly Photoactive Fluorine Containing TiO2 Nanosheets with High {001} Facet Exposure. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Giraldo, A.L.; Flórez, O.A.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Comparison of Route, Mechanism and Extent of Treatment for the Degradation of a β-Lactam Antibiotic by TiO2 Photocatalysis, Sonochemistry, Electrochemistry and the Photo-Fenton System. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, C.M.; Sehnal, D.; Falginella, F.L.; Pant, P.; Pravda, L.; Bouchal, T.; Svobodová Vařeková, R.; Geidl, S.; Koča, J. AtomicChargeCalculator: Interactive Web-Based Calculation of Atomic Charges in Large Biomolecular Complexes and Drug-like Molecules. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehnal, D. AtomicChargeCalculator. Available online: https://webchem.ncbr.muni.cz/Platform/ChargeCalculator (accessed on 28 July 2022).
- W2D Team—PharmaExpert PASS Online. Available online: http://www.pharmaexpert.ru/passonline/index.php (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- Khalil, M.; Anggraeni, E.S.; Ivandini, T.A.; Budianto, E. Exposing TiO2 (001) Crystal Facet in Nano Au-TiO2 Heterostructures for Enhanced Photodegradation of Methylene Blue. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Yang, J. Surface Heterojunction between (001) and (101) Facets of Ultrafine Anatase TiO2 Nanocrystals for Highly Efficient Photoreduction CO2 to CH4. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 198, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.J.; Tan, L.L.; Chai, S.P.; Yong, S.T.; Mohamed, A.R. Highly Reactive {001} Facets of TiO2-Based Composites: Synthesis, Formation Mechanism and Characterization. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1946–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.C.; Yu, J.; Ho, W.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Effects of F-Doping on the Photocatalytic Activity and Microstructures of Nanocrystalline TiO2 Powders. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3808–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia, J.J.; Hernández, J.S.; Rojas, H.; Moreno-Cascante, J.; Sánchez-Cid, P.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Navío, J.A.; Jaramillo-Páez, C. Evaluation of Au–ZnO, ZnO/Ag2CO3 and Ag–TiO2 as Photocatalyst for Wastewater Treatment. Top. Catal. 2020, 63, 1286–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Kowalska, E.; Sobczak, J.W.; Łacka, I.; Gazda, M.; Ohtani, B.; Hupka, J.; Zaleska, A. Silver-Doped TiO2 Prepared by Microemulsion Method: Surface Properties, Bio- and Photoactivity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 72, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, F.; Navío, J.A.; Paulete-Romero, M.A.; Córdoba, J.M.; Hidalgo, M.C. Exploring the Photocatalytic Activities of a Highly {0 0 1} Faceted TiO2 Sensitized by Coupling with AgBr or Ag3PO4. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2022, 276, 115555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshay, V.R.; Arun, B.; Mukesh, M.; Chanda, A.; Vasundhara, M. Tailoring the NIR Range Optical Absorption, Band-Gap Narrowing and Ferromagnetic Response in Defect Modulated TiO2 Nanocrystals by Varying the An-nealing Conditions. Vacuum 2021, 184, 109955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlalhmingmawia, C.; Lee, S.M.; Tiwari, D. Plasmonic Noble Metal Doped Titanium Dioxide Nanocomposites: Newer and Exciting Materials in the Remediation of Water Contaminated with Micropollutants. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albini, A.; Monti, S. Photophysics and Photochemistry of Fluoroquinolones. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2003, 32, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Jojoa-Sierra, S.D.; Berrio-Perlaza, K.E.; Ferraro, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Structure-Reactivity Rela-tionship in the Degradation of Three Representative Fluoroquinolone Antibiotics in Water by Electrogenerated Active Chlorine. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, H.; Naik, B. Hot Electron and Surface Plasmon-Driven Catalytic Reaction in Metal-Semiconductor Nanostructures. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 1996–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pillai, S.C.; Ho, S.H.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Dionysiou, D.D. Plasmonic-Based Nanomaterials for Environmen-tal Remediation. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 237, 721–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norouzi, M.; Fazeli, A.; Tavakoli, O. Phenol Contaminated Water Treatment by Photocatalytic Degradation on Electrospun Ag/TiO2 Nanofibers: Optimization by the Response Surface Method. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jojoa-Sierra, S.D.; Herrero-Albillos, J.; Ormad, M.P.; Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Mosteo, R. Wüstite as a Catalyst Source for Water Remediation: Differentiated Antimicrobial Activity of by-Products, Action Routes of the Process, and Transformation of Fluoroquinolones. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Hu, Z.; Wei, J.; He, Q.; He, Z. Recent Advances in Persulfate-Assisted TiO2-Based Photocatalysis for Wastewater Treatment: Performances, Mechanism and Perspectives. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 888, 161625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Giannakis, S.; Li, D.; Yan, B.; Lin, T. Efficient and Sustainable Photocatalytic Inactivation of E. Coli by an Innovative Immobilized Ag/TiO2 Photocatalyst with Peroxymonosulfate (PMS) under Visible Light. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Villamena, F.A.; Weavers, L.K. Kinetics and Mechanism of Ultrasonic Activation of Persulfate: An in Situ EPR Spin Trapping Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Y. Non-Photochemical Production of Singlet Oxygen via Activation of Persulfate by Carbon Nanotubes. Water Res. 2017, 113, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Gou, J.; Cheng, X. Degradation of Sulfamethoxazole by Peroxymonosulfate Acti-vated by Waste Eggshell Supported Ag2O-Ag Nano–Particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Huo, W.; Wang, M.; Wei, H.; Lu, Z.; Li, K. Visible-Light-Assisted Peroxydisulfate Activation over Ag6Si2O7/Cu(II)-Modified Palygorskite Composite for the Effective Degradation of Organic Pollutants by Radical and Nonradical Pathways. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.M.; Heo, J.; Wang, D.; Su, C.; Yoon, Y. Heterogeneous Activation of Persulfate by Reduced Graphene Ox-ide–Elemental Silver/Magnetite Nanohybrids for the Oxidative Degradation of Pharmaceuticals and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Water. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 225, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demyanenko, A.V.; Bogomolov, A.S.; Dozmorov, N.V.; Svyatova, A.I.; Pyryaeva, A.P.; Goldort, V.G.; Kochubei, S.A.; Baklanov, A.V. Singlet Oxygen 1O2 in Photocatalysis on TiO2. Where Does It Come From? J. Phys. Chem. 2019, 123, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolov, A.S.; Demyanenko, A.V.; Selishchev, D.S.; Kozlov, D.V.; Baklanov, A.V. Photogeneration of Singlet Oxygen on the Surface of TiO2, Doped by Nitrogen and Non-Doped, under UV- and VIS-Irradiation. High. Energy Chem. 2023, 57, S391–S396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T.; Xi, B. Degradation Difference of Ofloxacin and Levofloxacin by UV/H2O2 and UV/PS (Persulfate): Efficiency, Factors and Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 123987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.M.; Pang, S.Y.; Song, Y.; Guo, Q. A Comparison Study of Levofloxacin Degra-dation by Peroxymonosulfate and Permanganate: Kinetics, Products and Effect of Quinone Group. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.W.; Mabury, S.A. Photodegradation of the Pharmaceuticals Atorvastatin, Carbamazepine, Levofloxacin, and Sulfamethoxazole in Natural Waters. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 67, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameel, M.I.; Wali, M.; Al-Humaidi, J.Y.; Liaqat, F.; Khan, M.A. Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Levofloxacin over Heterostructured C3N4/Nb2O5 System under Visible Light. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, M.I.; MacGowan, A.P. Development of the Quinolones. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51 (Suppl. 1), 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Dodd, M.C.; Strathmann, T.J. Photolytic and Photocatalytic Decomposition of Aqueous Ciprofloxacin: Transformation Products and Residual Antibacterial Activity. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3121–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alovero, F.L.; Pan, X.; Morris, J.E.; Manzo, R.H.; Fisher, L.M. Engineering the Specificity of Antibacterial Fluoro-quinolones: Benzenesulfonamide Modifications at C-7 of Ciprofloxacin Change Its Primary Target in Streptococ-cus Pneumoniae from Topoisomerase IV to Gyrase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, K.S.; Shukla, A.D.; Tayade, R.J.; Joshi, P.A.; Das, A.K.; Modi, K.B.; Gandhi, V.G. Photocatalytic Perfor-mance and Interaction Mechanism of Reverse Micelle Synthesized Cu-TiO2 Nanomaterials towards Levofloxa-cin under Visible LED Light. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2022, 21, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DrugBank Ciprofloxacin. Available online: https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00537 (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Zhen, W.; Li, S.; Jiang, X. Generation of Singlet Oxygen via Iron-Dependent Lipid Peroxidation and Its Role in Ferroptosis. Fundam. Res. 2022, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S. Lipid Peroxidation: Production, Metabolism, and Signaling Mechanisms of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2014, 2014, 360438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, H.; Zhao, J.; Jian, X.; Liu, C.; Gao Supervison, Z.; Song, Y.Y. Enhanced Inactivation of Bacteria on Capacitive Semiconductor Nanotubes by Self-Discharging Triggered Photoelectrocatalysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 611, 155660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbasi, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Raeissi, K.; Rtimi, S.; Kiwi, J.; Giannakis, S.; Pulgarin, C. Insights into the Photocata-lytic Bacterial Inactivation by Flower-like Bi2WO6 under Solar or Visible Light, through in Situ Monitoring and Determination of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Water 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, J.; Prakash, H. Photo-Disinfection Processes for Bacterial Inactivation and Underlying Principles for Water Constituents’ Impact: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2023, 14, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Polo López, M.I.; Spuhler, D.; Sánchez Pérez, J.A.; Fernández Ibáñez, P.; Pulgarin, C. Solar Disinfec-tion Is an Augmentable, in Situ-Generated Photo-Fenton Reaction—Part 1: A Review of the Mechanisms and the Fundamental Aspects of the Process. Appl. Catal. B 2016, 199, 199–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).