Stability Study and Strengthening Strategy of Spiral Case-Encased Concrete Structure of Pumped Storage Power Station
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Object
2.2. High-Density Steel and Concrete Ratio
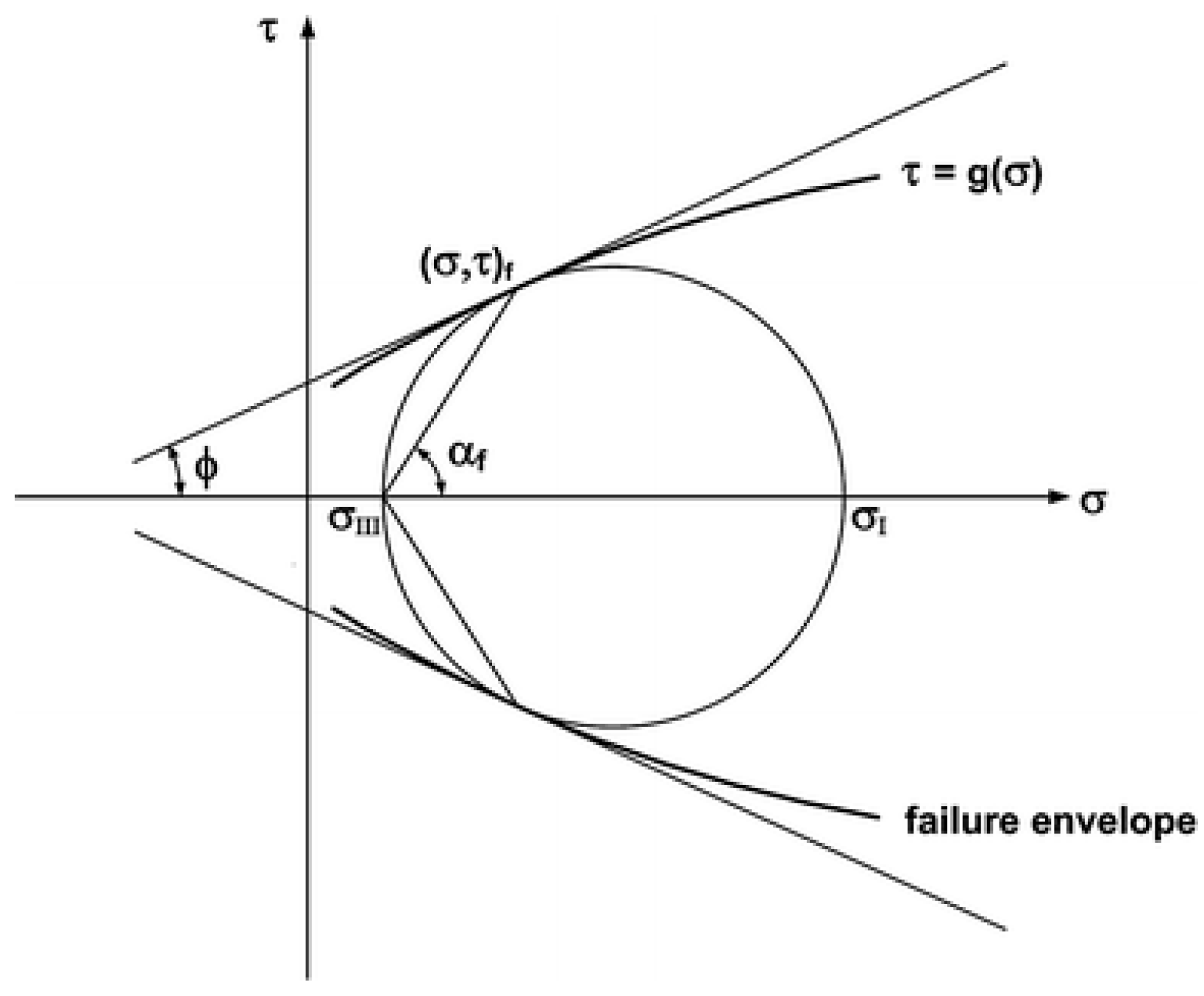
2.3. Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion
3. Results and Discussion
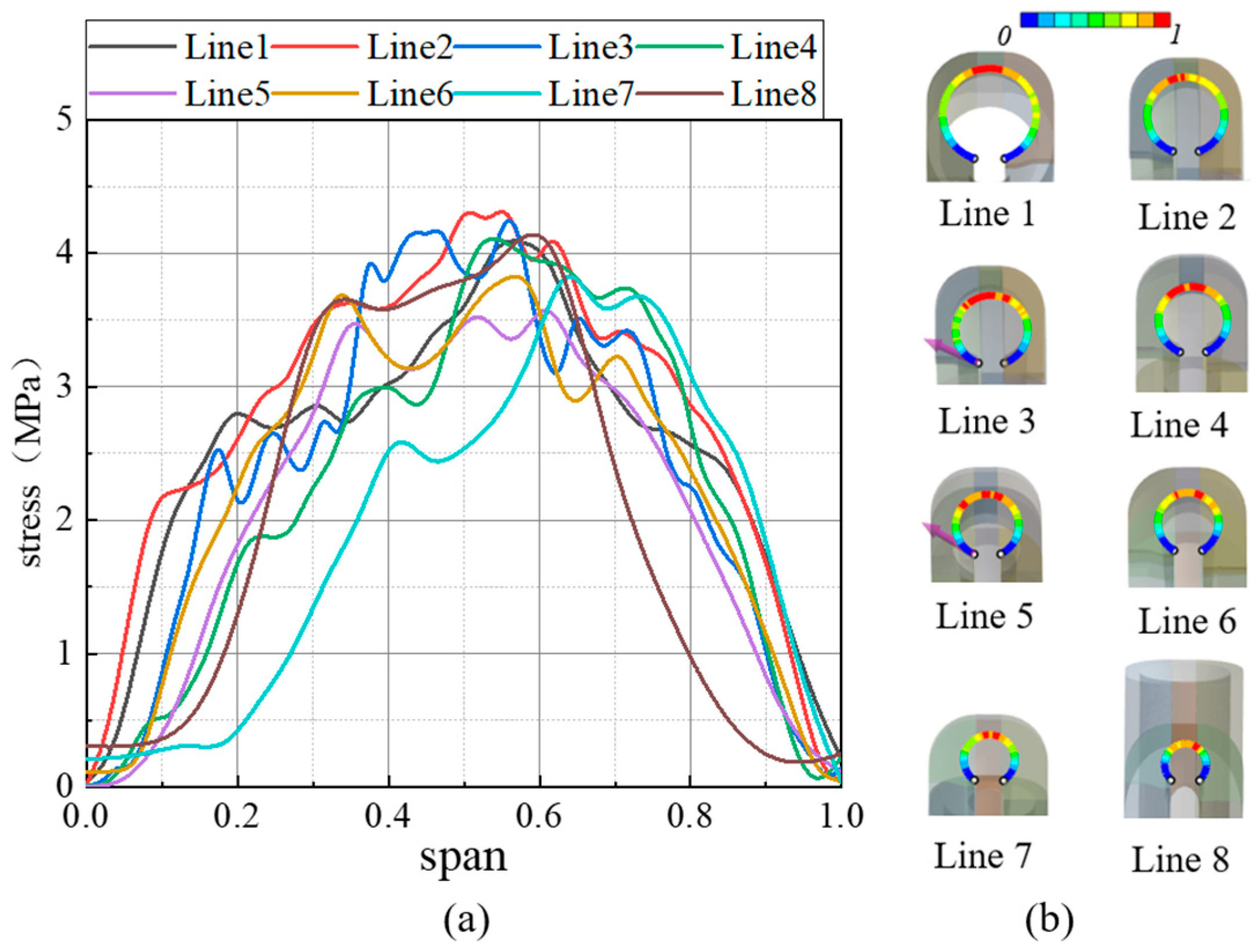
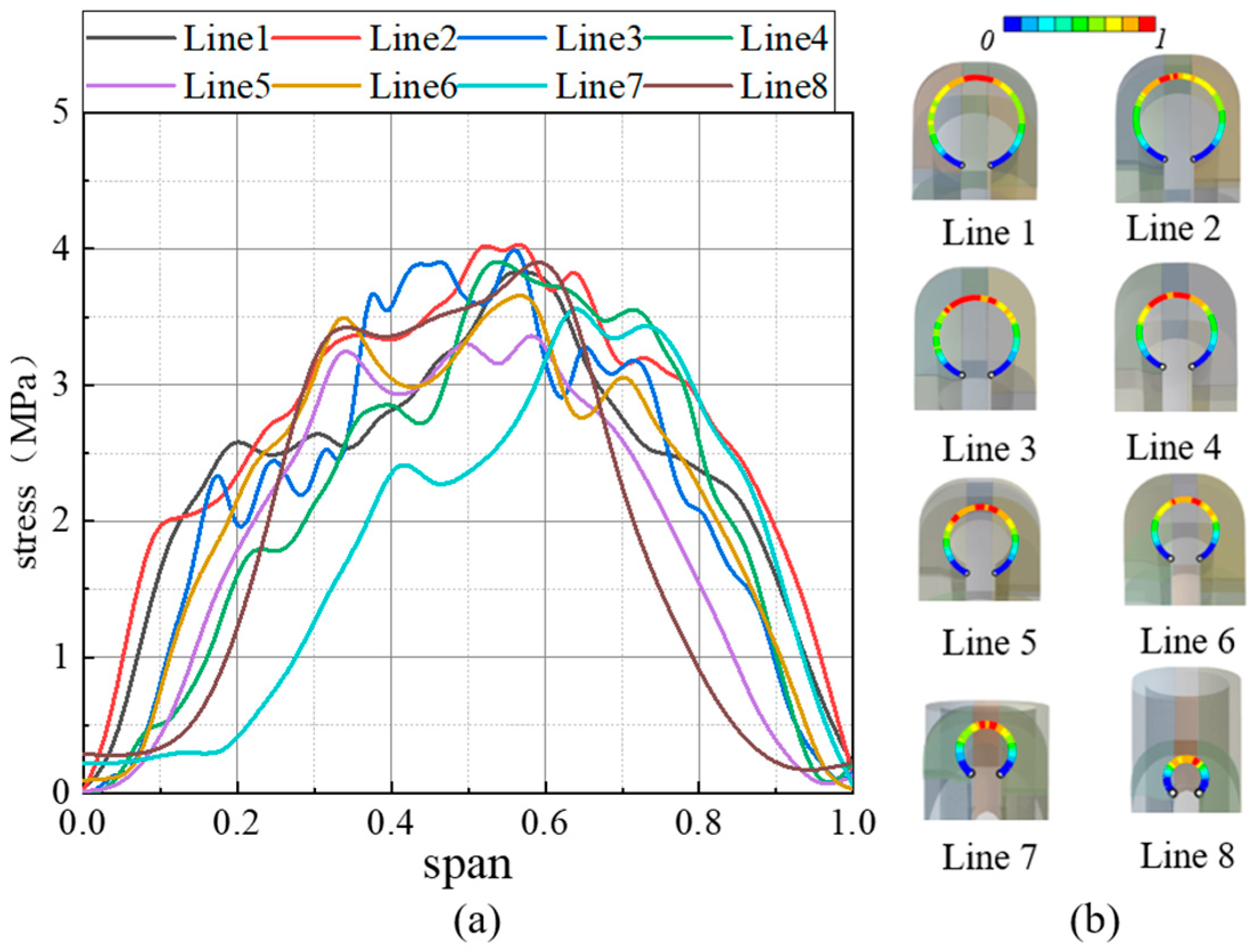
3.1. Stress Distribution of Concrete
3.2. Structure without Reinforcement Arrangement
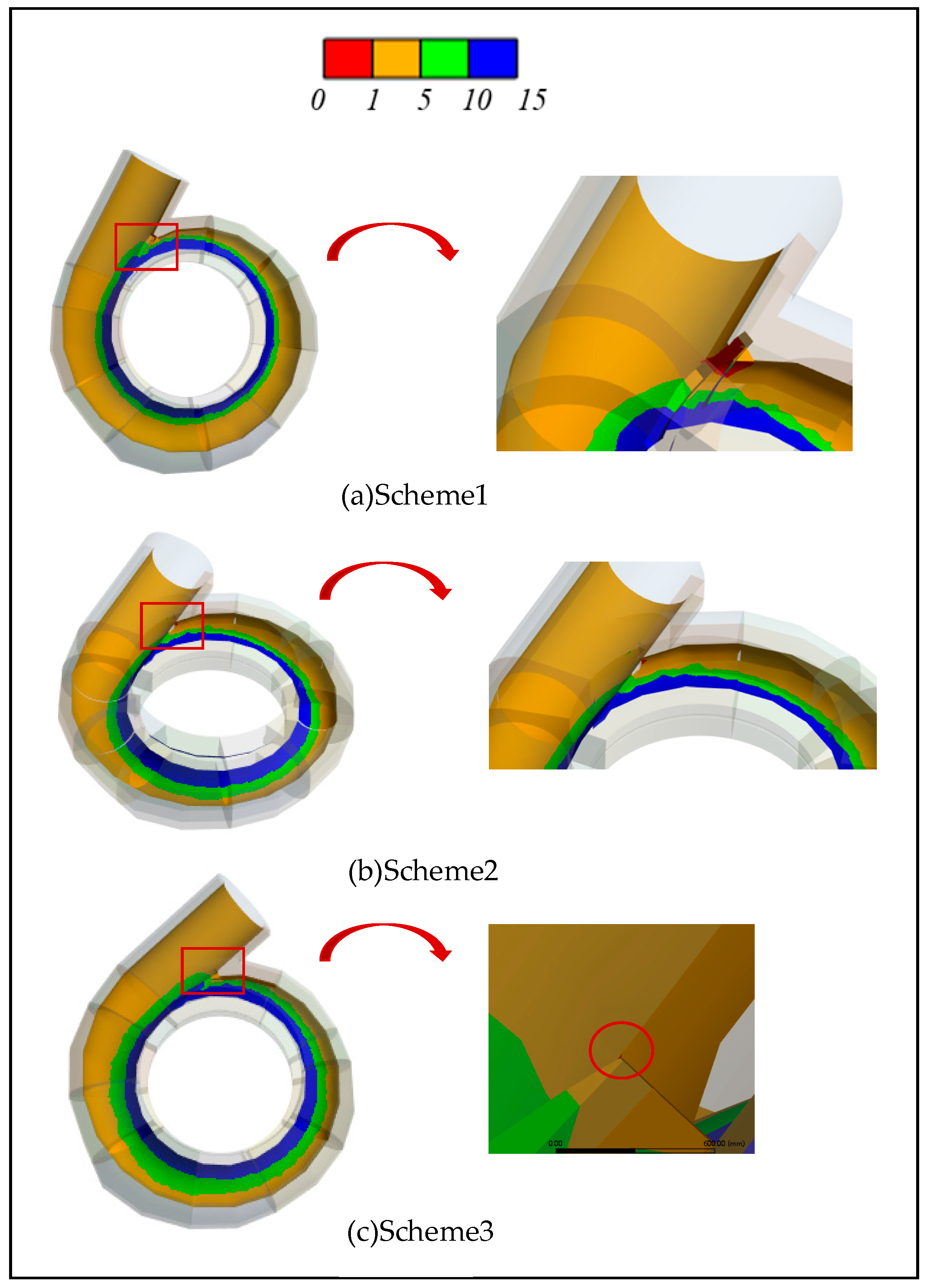
3.3. The Influence of Steel Bar Arrangement Structure on Concrete
4. Conclusions
- 1.
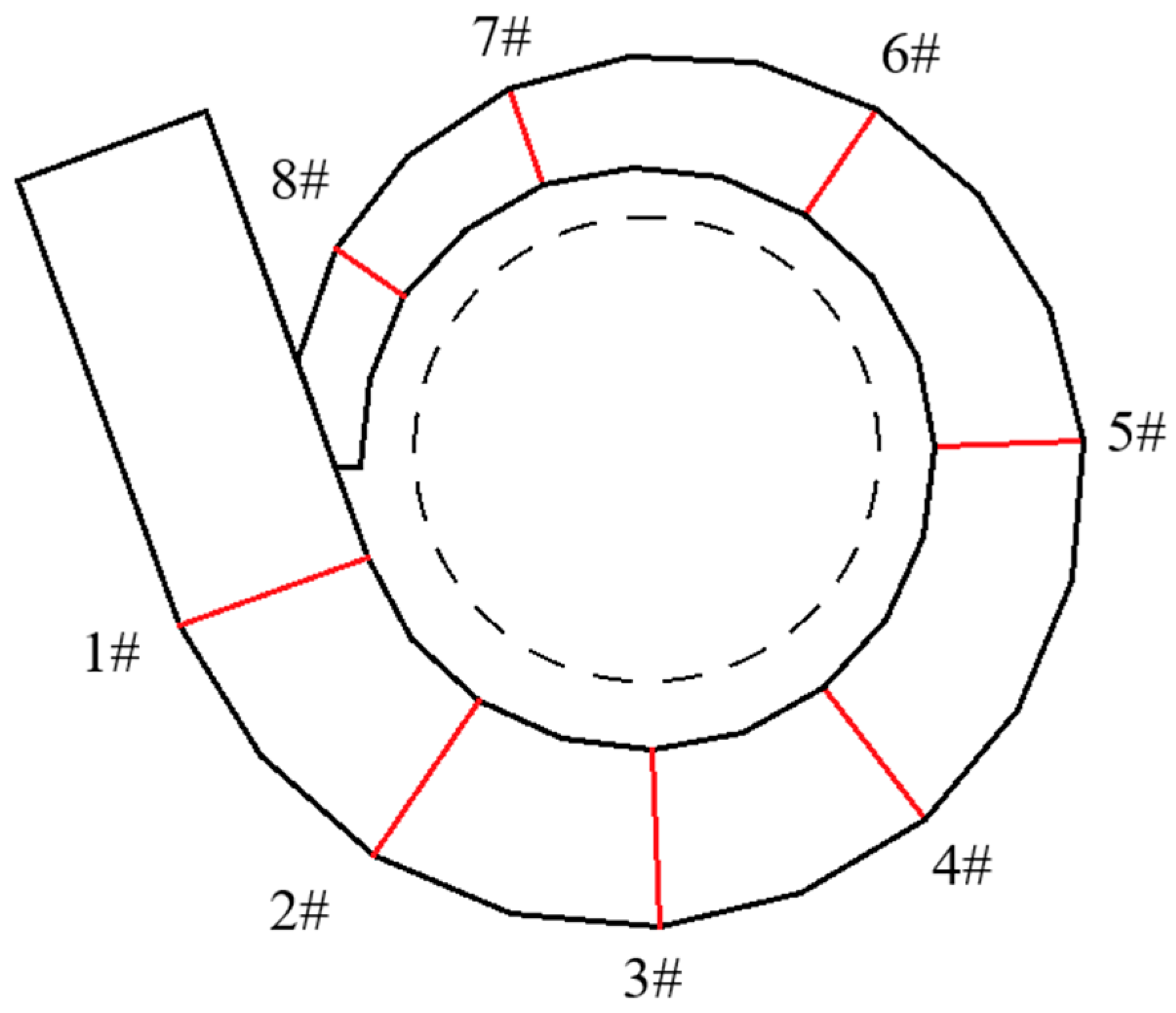
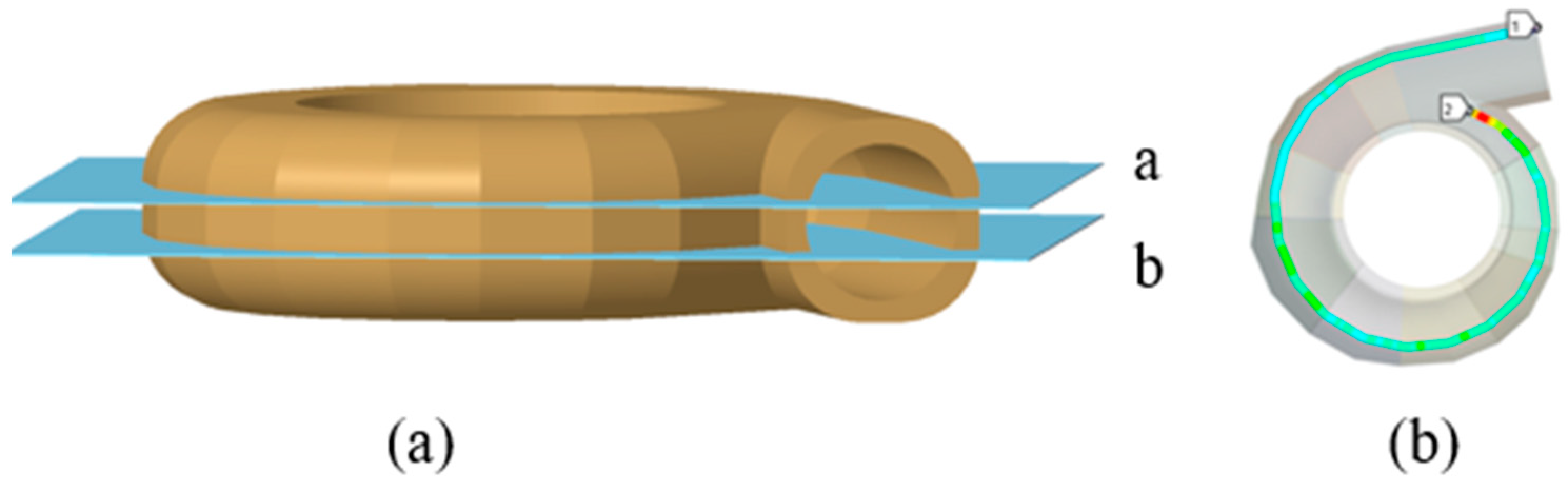
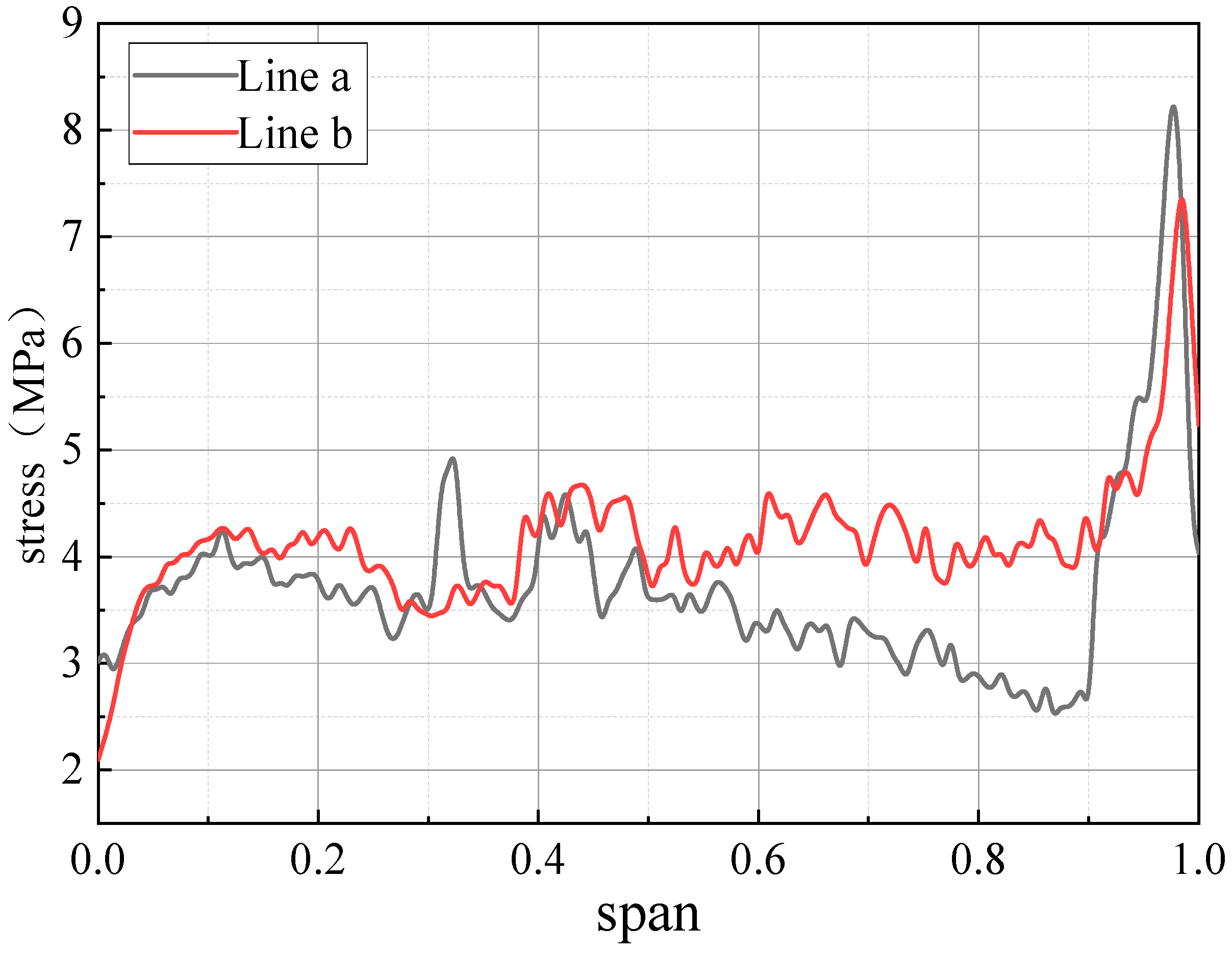
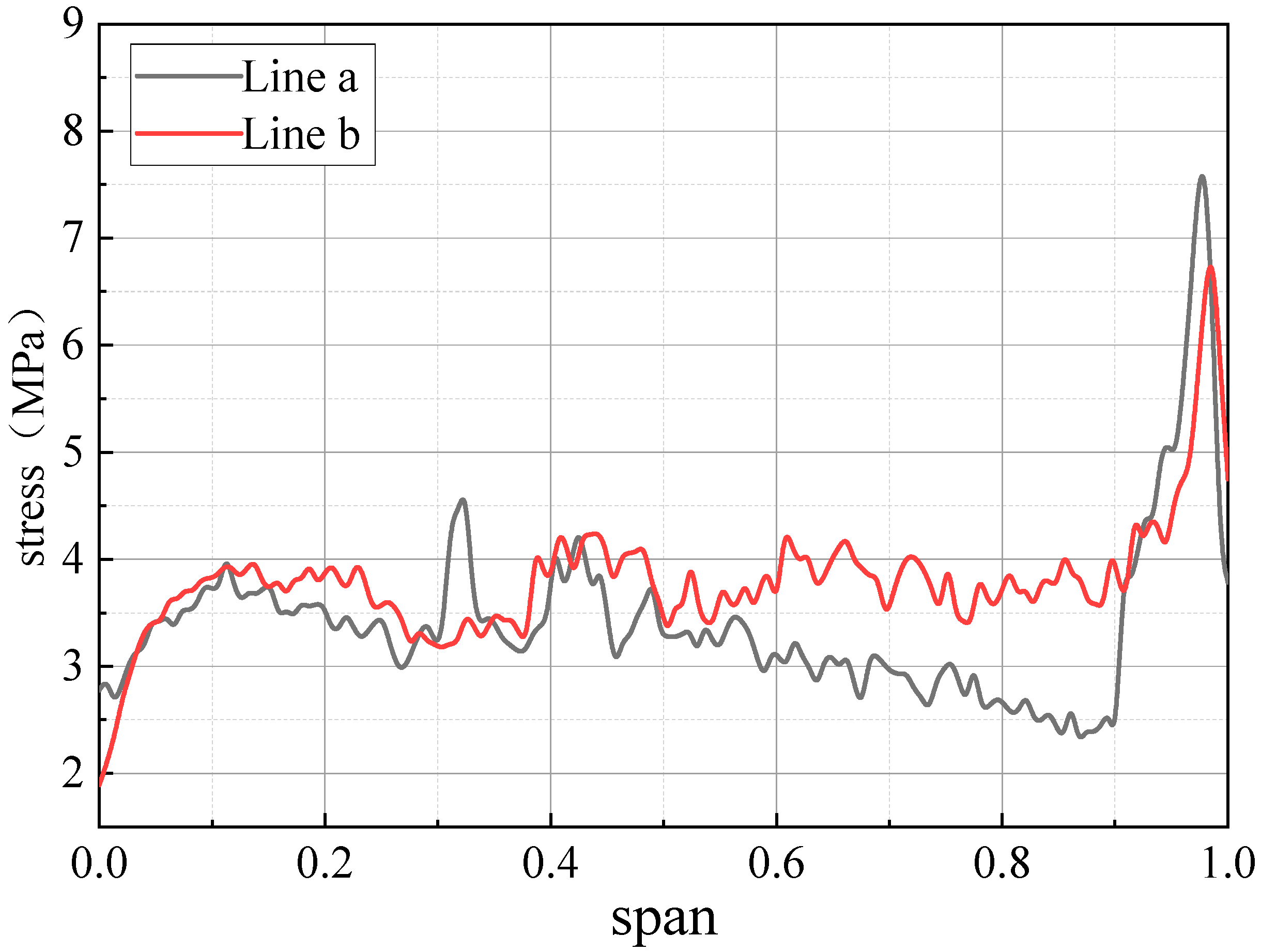
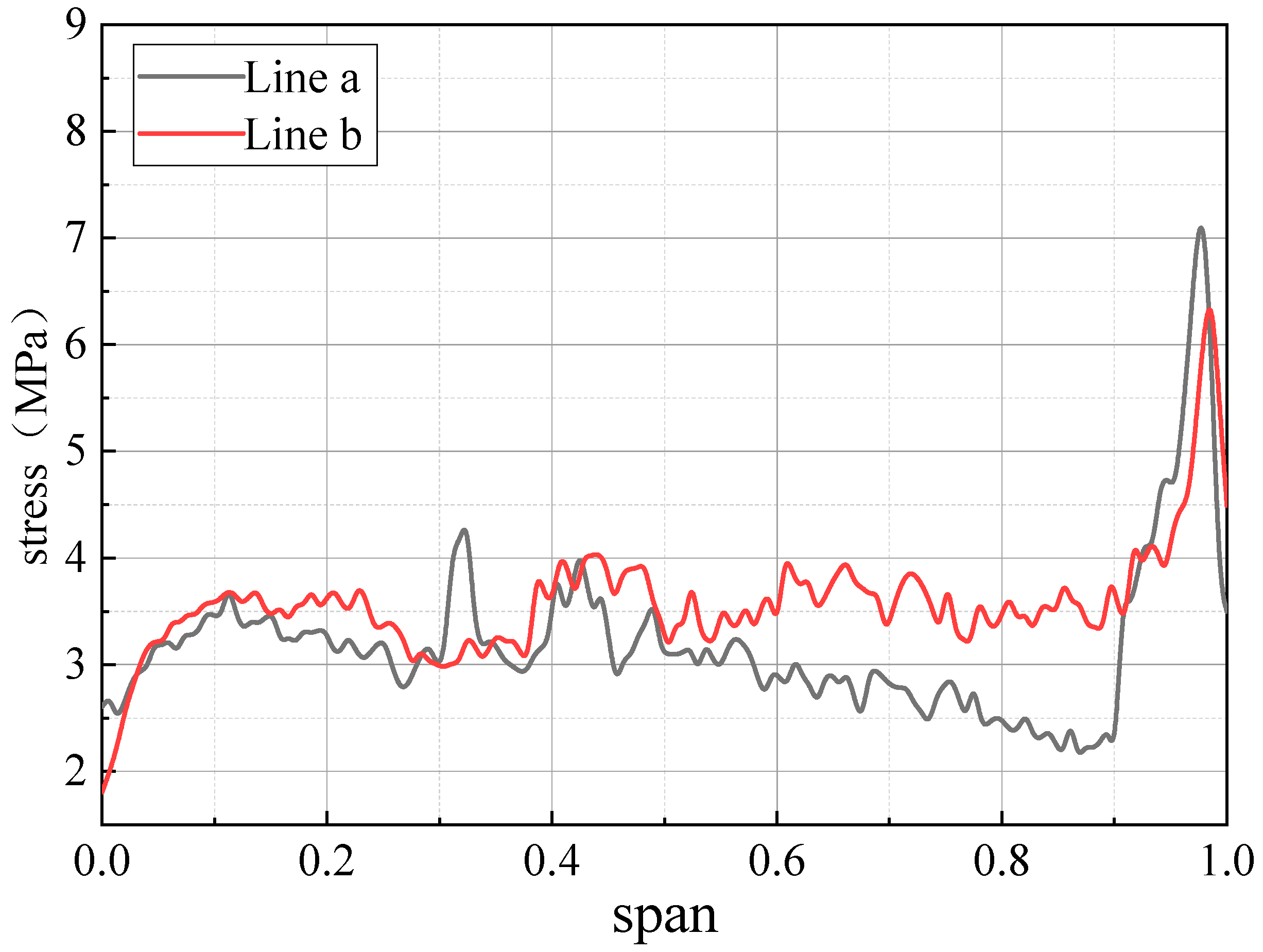
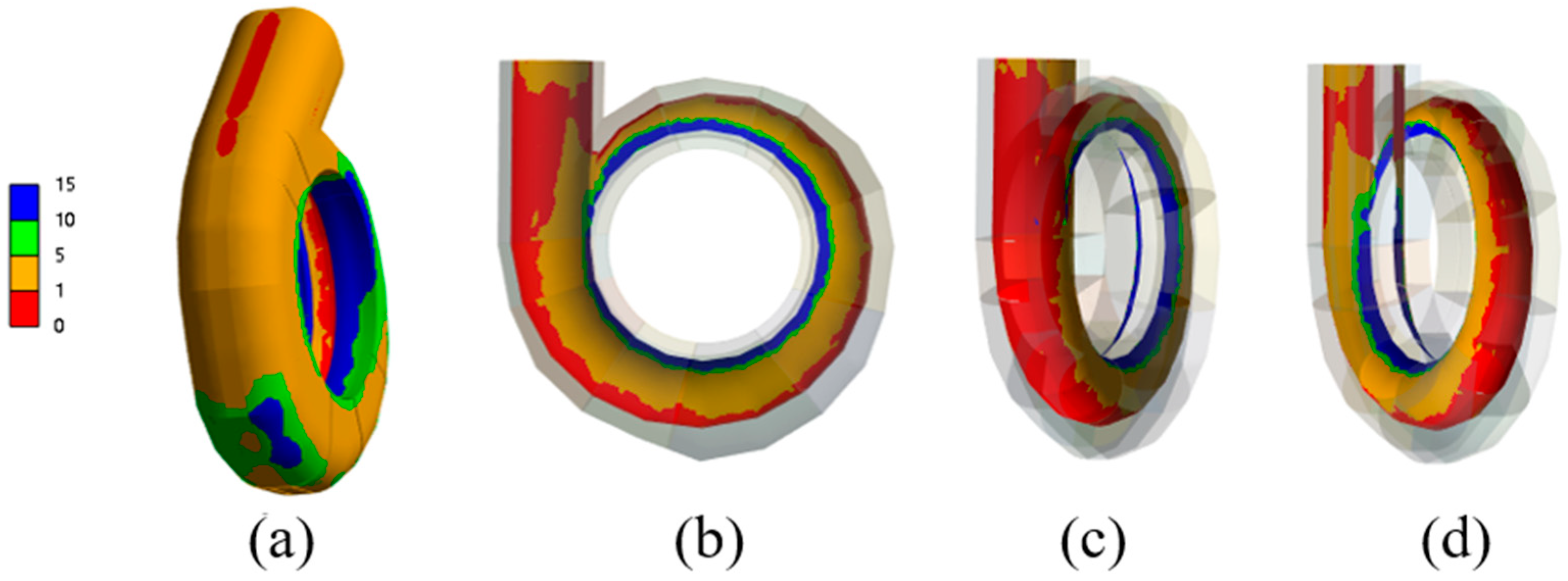
- In the vertical direction, the maximum stress of the concrete inner surface decreases from 0.5 span to both sides. In the horizontal direction, the maximum stress of the concrete inner surface is concentrated at the volute inlet and the tongue. Along the spiral line, the stress of the volute section away from the inlet is small. Under the condition of throwing off the load, the stress fluctuates mainly around 4 MPa along the spiral line, not exceeding 5 MPa. The stress is the largest near the tongue, reaching 8.3 MPa.
- 2.
- The variation law of inner surface stress under different working conditions is consistent, and the stress depends on the stability of the operating conditions of the turbine unit.
- 3.
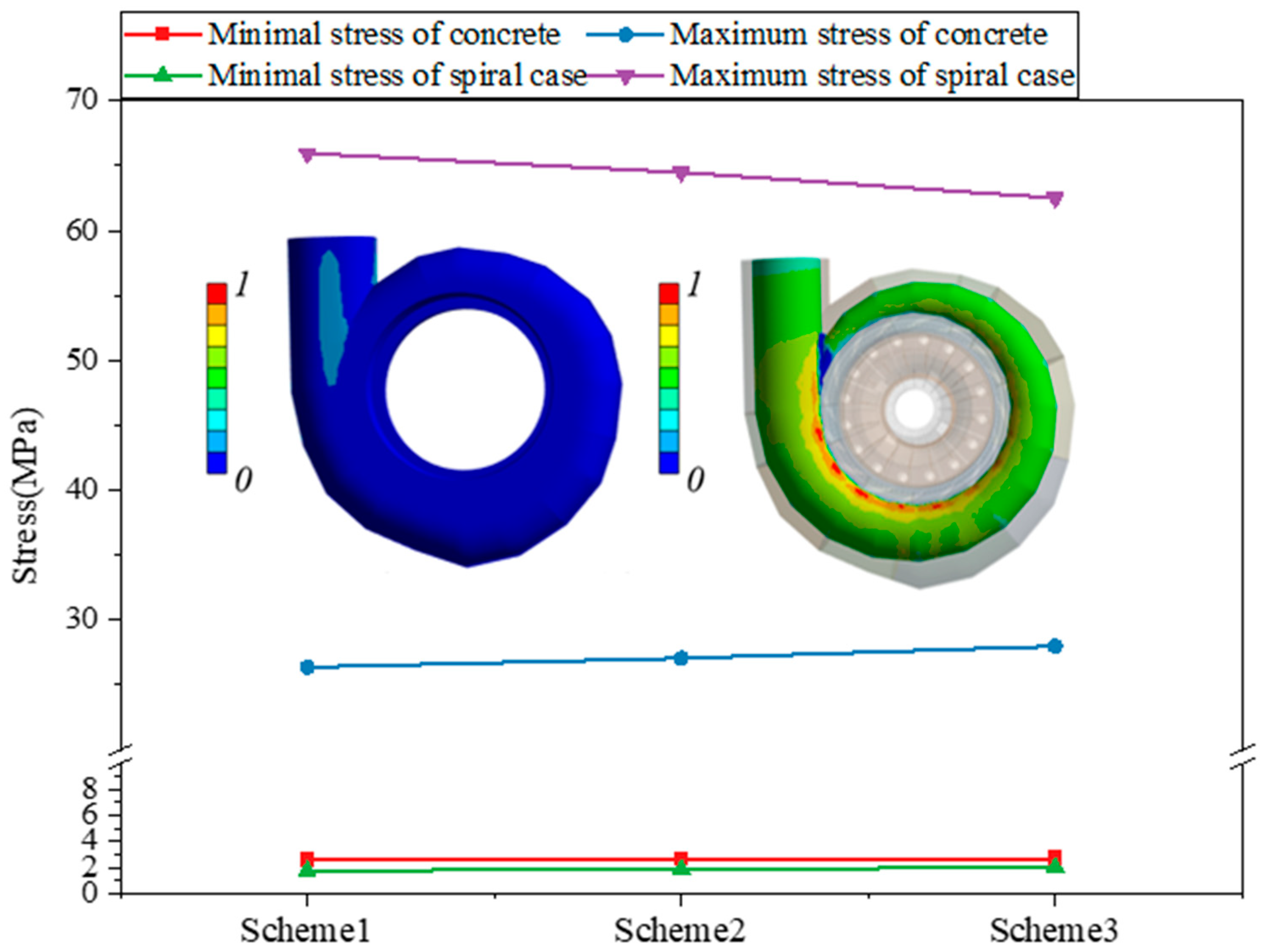
- With the increase in tensile strength and elastic modulus, the point analysis of the inner surface of concrete shows that the compression of concrete decreases, and the increase of deformation in the Z direction leads to the increase in tensile stress.
- 4.
- The concrete cracking is easy to occur at the tongue, and the local reinforcement can be arranged to strengthen the tensile strength of the concrete and increase the stability of the plant structure.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trivedi, C.; Gandhi, B.; Michel, C.J. Effect of transients on Francis turbine runner life: A review. J. Hydraul. Res. 2013, 51, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, S.; Gong, R.; Wang, H.; Luo, X. Cavitation effects on pressure fluctuation in pump-turbine hump region. J. Energy Storage 2022, 47, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, Z.; Wei, X. Dynamic instability of a pump-turbine in load rejection transient process. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 1765–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Yao, Z.; Zhu, B.; Wang, F. Study on pressure fluctuation and rotating stall characteristics in the vaneless space of a pump-turbine in pump mode. J. Energy Storage 2024, 94, 112385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, Y.; Kan, K.; Rossi, M. Numerical investigation of hydraulic instability of pump-turbines in fast pump-to-turbine transition. J. Energy Storage 2024, 96, 112731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Rossi, M.; Xu, L.; Chen, H. The vortex dynamics characteristics in a pump-turbine: A rigid vorticity analysis while varying guide vane openings in turbine mode. Energy 2024, 289, 130086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Binama, M. Entropy Production Evaluation within a Prototype Pump-Turbine Operated in Pump Mode for a Wide Range of Flow Conditions. Processes 2022, 10, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.T.; Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.X. Spatial distribution of rigid vorticity in pump turbine under turbine mode with different heads. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2707, 012058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.T.; Kan, K.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.X. Spatial distribution of rigid vorticity in pump-turbine under turbine mode with different guide vane openings. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2752, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Cavazzini, G.; Santolin, A.; Nascimben, F. Enhancing operational stability of a reversible pump-turbine through blade lean design. J. Energy Storage 2024, 92, 112218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Cavazzini, G.; Santolin, A. Effect of the von Karman Shedding Frequency on the Hydrodynamics of a Francis Turbine Operating at Nominal Load. Int. J. Turbomach. Propuls. Power 2023, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Siviero, M.; Cavazzini, G.; Santolin, A. Application of the 3D Inverse Design Method in Reversible Pump Turbines and Francis Turbines. Water 2023, 15, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, G.; Cavazzini, G.; Santolin, A. Three-dimensional evolution of the flow unsteadiness in the S-shape of pump-turbines and its correlation with the runner geometry. J. Energy Storage 2023, 57, 106176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H. Propagation characteristics analysis of high-frequency vibration in pumped storage power station based on a 1D fluid-solid coupling model. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Xiao, T.; Liu, D.; Ye, F.; Xiong, D. The offshore prefabrication and semi-wet towing of a bucket foundation for offshore wind turbines. Ocean Eng. 2023, 285, 115354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, K.; Cheng, Y. Evaluating the pressure fluctuations during load rejection of two pump-turbines in a prototype pumped-storage system by using 1D-3D coupled simulation. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui, K.; Zorn, M.; Ségoufin, C.; André, F.; Kerner, J.; Riedelbauch, S. Dynamic stress prediction for a Pump-Turbine in Low-Load Conditions: Experimental validation and phenomenological analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2024, 162, 108428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y. Dynamic progressive collapse response of 3D monolithic precast concrete frame structures considering slab effects. Structures 2024, 60, 105928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W. Behaviour of concrete-filled circular steel tubular K-joints in wind turbine towers. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 218, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Guo, T. Multiple factors-based damage level assessment method of concrete structures based on evidential reasoning and particle swarm optimization. Eng. Struct. 2024, 316, 118626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Du, S. Kernel extreme learning machine and finite element method fusion fire damage prediction of concrete structures. Structures 2024, 68, 107172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Guo, T. Mechanism-driven and data-driven fusion prediction of seismic damage evolution of concrete structures based on cooperative multi-particle swarm optimization. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Li, Y.; Guo, T. A particle swarm optimization and prior knowledge fusion seismic damage prediction of concrete structures. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 157, 111552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.-Y.; Zhou, X.-H.; Ren, W.; Wang, Y.-H.; Luo, W. Research on hexagonal concrete-filled steel tubular transition pieces for wind turbine hybrid towers under axial compression. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 200, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.-Y.; Zhou, X.-H.; Ren, W.; Wang, Y.-H.; Li, R.-F. Axial compressive behavior of concrete-filled double skin steel tubular columns with different stiffening constructions for wind turbine towers. Structures 2024, 63, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, J.; Mankar, A.; Kramhøft, C.; Sørensen, J.D. Probabilistic calibration of fatigue safety factors for offshore wind turbine concrete structures. Eng. Struct. 2020, 222, 111090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, J.; Kramhøft, C.; Sørensen, J.D.; Zorzi, G. Fatigue reliability of large monopiles for offshore wind turbines. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 134, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, J.; Bachynski, E.E. Design and fatigue analysis of monopile foundations to support the DTU 10 MW offshore wind turbine. Energy Procedia 2017, 137, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, J.; Kramhøft, C.; Mankar, A.; Sørensen, J.D. Uncertainty Modeling and Fatigue Reliability Assessment of Offshore Wind Turbine Concrete Structures. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2019, 29, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liang, A.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, B. Impact of rotor–stator axial spacing on the gas–liquid–solid flow characteristics of a multiphase rotodynamic pump based on the Euler multi-fluid model. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 063314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surkutwar, Y.; Sandu, C.; Untaroiu, C. Review of modeling methods of compressed snow-tire interaction. J. Terramech. 2023, 105, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
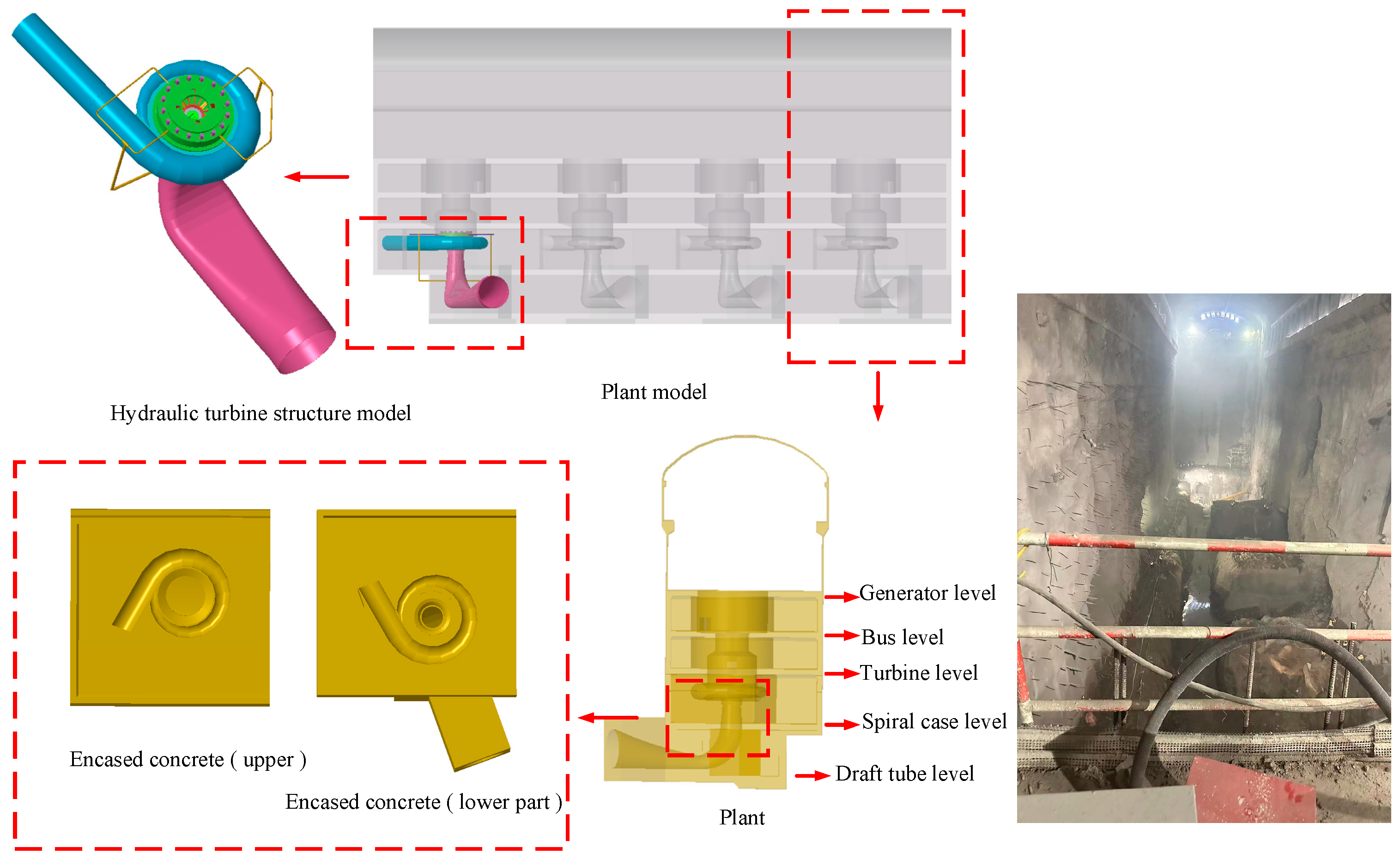
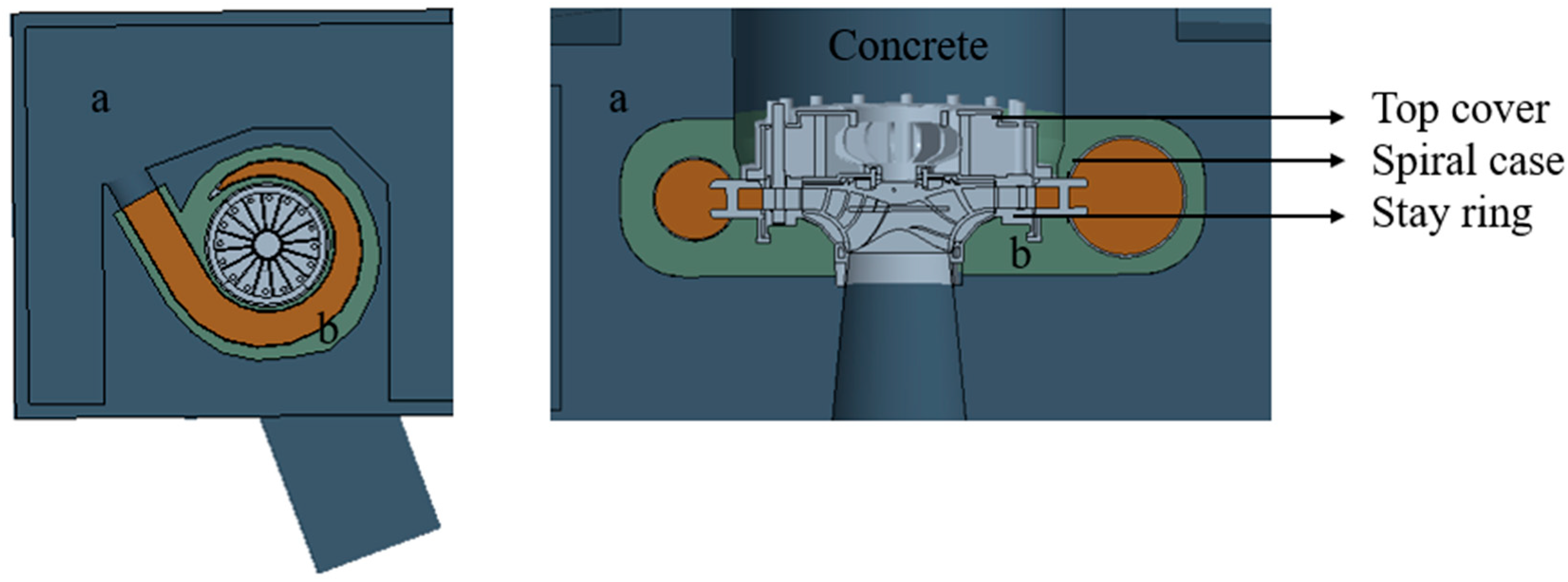




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated flow rate, m3/s | 105.8 |
| Rated head, m | 326 |
| Rated speed, rpm | 333.3 |
| Rated output of the turbine, MW | 306 |
| Diameter of the high-pressure side of the runner, m | 4.81 |
| Number of stay vanes, piece | 15 |
| Number of active guide vanes, piece | 16 |
| Number of runner blades (long + short), piece | 5 + 5 |
| Material | Density /(kg/m3) | Strength Limit /MPa |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete | 2690 | 3.2 |
| Spiral case (HD610F) | 610 |
| Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | Fstk | Es | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 19 | 22 | 30 | 9.11 | 30,370 |
| Scheme 2 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 13.20 | 32,190 |
| Scheme 3 | 42 | 52 | 62 | 16.19 | 34,812 |
| Deformation—X (mm) | Deformation—Y (mm) | Deformation—Z (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | 0.13143 | 0.030971 | 0.01294 |
| Scheme 2 | 0.12509 | 0.029697 | 0.013171 |
| Scheme 3 | 0.1169 | 0.028042 | 0.013387 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Dong, H.; Sun, C.; Wang, Z. Stability Study and Strengthening Strategy of Spiral Case-Encased Concrete Structure of Pumped Storage Power Station. Water 2024, 16, 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182687
Zhao Y, Li X, Lu Y, Dong H, Sun C, Wang Z. Stability Study and Strengthening Strategy of Spiral Case-Encased Concrete Structure of Pumped Storage Power Station. Water. 2024; 16(18):2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182687
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yun, Xiji Li, Yonggang Lu, Haiyang Dong, Chuanzhen Sun, and Zhengwei Wang. 2024. "Stability Study and Strengthening Strategy of Spiral Case-Encased Concrete Structure of Pumped Storage Power Station" Water 16, no. 18: 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182687
APA StyleZhao, Y., Li, X., Lu, Y., Dong, H., Sun, C., & Wang, Z. (2024). Stability Study and Strengthening Strategy of Spiral Case-Encased Concrete Structure of Pumped Storage Power Station. Water, 16(18), 2687. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16182687








