Abstract
This study comprehensively explores the intricate hydrodynamic and geomorphological processes that affect the Sulina Channel and bar area. It employs advanced hydrodynamic, wave, and sediment transport models to simulate the influence of marine currents, waves, and shipping traffic on sediment transport and deposition patterns, providing valuable insights for maintaining navigable conditions in the Sulina Channel. It is shown that sediment deposition is highly dynamic, particularly in the Sulina bar area, where rapid sediment recolonization occurs within one to two months after dredging. The simulation indicates that vessels with drafts of 11.5 m cause notable erosion. In comparison, drafts of 7 m have a minimal impact on sediment transport, emphasizing the importance of managing vessel drafts to mitigate sediment disturbances. This research highlights and quantifies the siltation phenomenon from the Black Sea to the mouth of the Sulina Channel, effectively addressing the challenges posed by natural and anthropogenic factors to ensure the Channel’s sustainability and operational efficiency.
1. Introduction
Sediment transport in rivers and interaction between two different flow regimens (river–sea, for example) is an important study field due to the navigation safety and economic impact. In his article about sediment depositions in the British seas, Lebour [1] indicates that this subject is not new. However, the involved processes are highly dynamic and require modern solutions to assess and propose improvements. According to [2], the first theoretical attempt to calculate the sediment transport under waves and currents was carried out by Bijker [3] in 1967. Since then, multiple improvements to the approaches and methodologies have been proposed, the most recent involving the use of numerical models to solve hydraulic and sediment transport equations [2,4,5,6,7]. Due to the dynamic exchange involved, as the interaction between river flow, waves, and currents, sediment transport is a complicated problem from a computational viewpoint [8,9]. Vessel sediment resuspension has been studied in various contexts, such as the effects of the waves produced by the recreational boat passage [10,11] and the propeller impact on the riverbed sediment stability [12,13,14]. Research in various locations has tackled the impact of vessel traffic on potential sediment resuspension. The results have indicated that the sediment characteristics, the hydrodynamic changes produced by the vessel, and the vessel characteristics significantly influence this process.
Spoolder [15] investigated the return flow velocity produced by the propeller and performed a sensitivity analysis of the vessel velocity, width, and keel clearance. The results indicate that decreasing the values of the first two parameters and the rate of power efficiency will decrease the sediment transport. Other research [16,17] analyzed the impact of the wake waves on sediment resuspension, given the additional stress they exert on the protection infrastructure (such as dykes or jetties).
In Romania, the main studies in this research field concern the Sulina Channel, one of the Danube River’s branches. Budileanu [18] studied the Sulina bar‘s evolution, discussing the hydrological conditions, the sediment transport, and the human intervention in the area. Over time, a steady evolution of the bar has been observed, starting from 1876, when observations were made about the Sulina mouth area and sediment depositions.
Mateescu et al. [19] described the processes occurring at the Danube River mouth on the Sulina Channel, pointing out that the interaction between waves and currents produced by the freshwater discharge leads to longitudinal and riparian currents, with visible effects in short periods. Boșneagu et al. [20] analyzed the flow conditions using numerical modeling software and applied computational fluid dynamics theory. They addressed the flow transfer between the Danube and the Black Sea, at the mouth and longitudinally, along the jetties.
Bondar [21] made significant strides in modeling the sediment transport interactions around the Sulina mouth, showing the longitudinal evolution of the sediment deposition and erosion processes. Constantinescu et al. [22] analyzed the potential negative impacts of fluvial or coastal hazards and dike breaching on Sulina City. The two jetties constructed along the Sulina Channel impact the morphological conditions, splitting the area into two zones, north and south of the jetties. The most impacted zone is the northern one, where the jetties block sediment transport, leading to rapid sedimentation and the closing of the Musura Bay [23,24]. A sediment spit continues almost perpendicular to the two jetties. Răileanu et al. [25] and Ivan et al. [26] have focused on the effects of the wind and waves over the jetties and Sulina mouth area, highlighting the impact on the navigation conditions under heavy conditions.
We developed comprehensive hydrodynamic, wave, and sediment transport models to understand the impact of increasing the navigation depths on the Sulina bar, the hydromorphology, and the hydrodynamics of the Sulina Channel. They are designed to accurately simulate the complex hydrodynamic and geomorphological processes in the Sulina Channel and bar area. Our approach includes an analysis of marine currents, waves, and shipping traffic and their collective influence on the Sulina Channel fairway at the mouth of the Black Sea. We studied two predefined scenarios based on a representative vessel (predefined draught and characteristics) to determine the vessels’ impact on sediment transport.
This research has significant practical implications. It provides crucial insights into the environmental processes influencing navigation, including wave action, sediment deposition, and erosion. The results of our research ensure the background for the safe and efficient passage of vessels with varying draughts, thereby enhancing the overall navigability of the Sulina bar.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
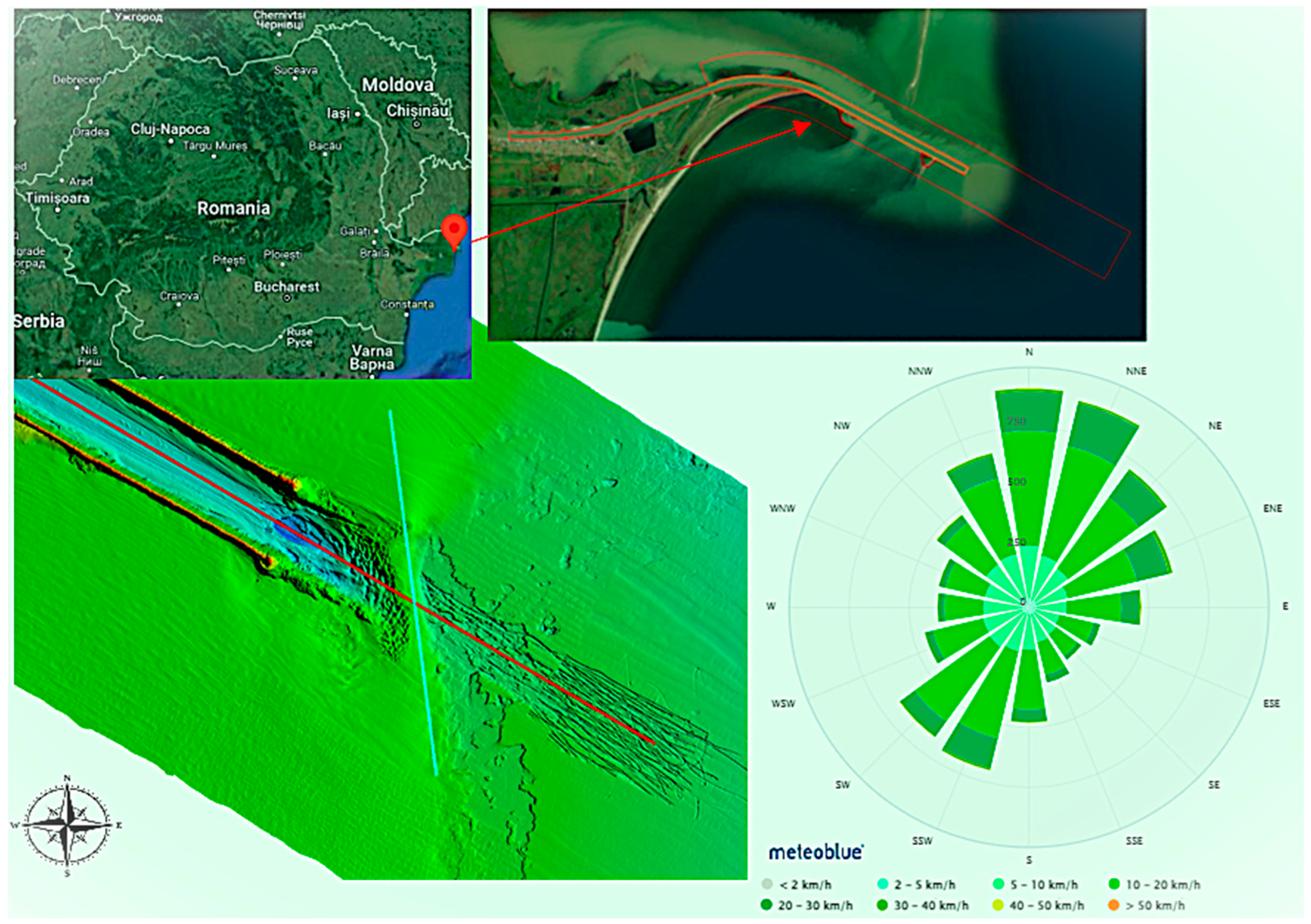
The Danube splits into three branches before it flows into the Black Sea. The Sulina branch is the middle navigable channel, with a length of approximately 60 km. The Sulina bar (Figure 1) is located at the mouth of the Sulina Channel and the Black Sea.
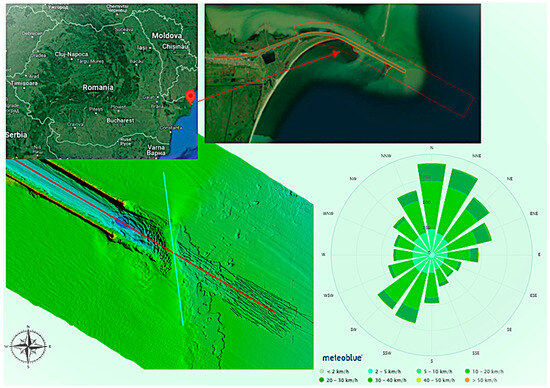
Figure 1.
A map of Romania (top left), the study area (top right), a bathymetric picture of a channel section (bottom left), and the wind rose (bottom right).
It represents a diked canal that allows smooth navigation from the Danube River branch into the sea. The dominant wave direction, from north-east, leads to the transport of the sediment southward, influencing coastal features. The jetties extend several kilometers from the original coastline, with shallow waters north of the breakwaters. A spit, formed by breaking waves, is growing southward due to longshore transport from the northeast. This growth may be stopped by water flowing between the spit and the northern jetty, potentially carrying sediment from the spit to the bar in front of the Channel’s mouth.
The climate in the area is continental with oceanic influences. The annual precipitation varies in the interval of 109–487 mm, with an average of about 260 mm and a coefficient of variation of about 30. In summer, the temperature is lower than in other zones of the Dobrogea Region to which the study belongs. The winters are cold due to the influence of the atmospheric masses that come from Russia [27,28,29,30,31,32,33].
As previous studies [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26] have shown, the Sulina bar area is significantly influenced by the transport of fine alluvial material along the Sulina Channel and by wind-induced currents and waves in the Black Sea. These processes result in a prominent accumulation zone for alluvial material near the mouth and submersible dams in the sea.
2.2. Data Series
This study utilized a comprehensive series of input data. This included a Digital Terrain Model (DTM) with a 1 × 1 m resolution derived from multibeam bathymetric measurements covering the entire riverbed and supplemented by topographic measurements of the defense dams. In the areas where these DTM sources were incomplete, DTMs from free sources were also incorporated.
Historical topo-bathymetric data consisted of raster files detailing the dynamics of the Sulina Channel bed and its mouth area in the Black Sea over nine years from 2014 to 2022. From 2014 to 2017, data were available only for the mouth area of the Sulina branch, with at least one measurement campaign per year. For 2018 and 2022, the minor riverbed was completely covered within the initially defined study area.
Hydrological data, such as flow rates and levels, were obtained from specific observations and measurements conducted within the project across 54 profiles. These data were used as boundary conditions and calibration information for the models. Additionally, data on the particle size distribution of riverbed sediments and solid flows were gathered from these profiles.
Information on the parental material within the riverbed perimeter and details of the riverbed substrate were collected through specific observations and measurements. This information was analyzed and processed to generate files for use in the models. A wave data string for the period 24 September 2020–29 July 2022, was recorded by a beacon, although the wave monitoring sensor was not operational for the entire period. Consequently, wave height data were available only for 24 September 2020–19 September 2021.
Data on marine currents from 1 February 2021 to 10 January 2023, were sourced from Copernicus. Wind data covering December 2008–January 2023 included the monthly frequency of wind directions and information on wind direction and speed in the Sulina branch area. Information was also gathered on a representative vessel.
Meteorological data recorded at the Sulina meteorological station from 1 January 2013 to 31 December 2022 were also used in this study. These data included multiannual monthly wind roses, average wind speed by direction, wind frequency by direction, wind frequency at different speed thresholds, maximum wind speed and its corresponding direction, and maximum gust wind speed.
Additional studies, documents, and scientific papers were also reviewed, including technical documentation on the existing port trestles for berthing sea and river vessels along the left bank of the Sulina Channel in the Commercial Port and vessel traffic data on the Sulina Channel from 2001 to 2022. Data from other sources, such as satellite imagery from Google Earth/Google Maps, and previous technical works and research studies conducted in the area or equivalent locations, were also consulted.
2.3. Methodology—Generalities
This study aims to assess the navigation conditions in the Sulina bar by developing and utilizing a series of advanced numerical models that that replicate the complex hydraulic and siltation phenomena.
Using the MIKE 21 FM software developed by the Danish Hydraulic Institute, the study examines the wave patterns in the Black Sea and sediment transport along the Sulina bar and coast and within the Sulina Canal, as well as the impact of vessel transit on sediment dynamics. The models provide insights into the environmental processes influencing navigation, including wave action, sediment deposition, and erosion, to ensure the safe and efficient passage of vessels with varying draughts.
In the subsequent sections, we outline the methodology, discuss the integration of various data sources, and highlight the significant findings that enhance navigation depths while mitigating potential adverse effects on the surrounding marine and coastal environments. Figure 2 shows the chart flow of the analysis.
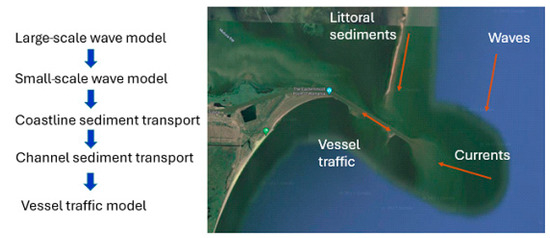
Figure 2.
The flowchart of the study.
- Large-scale wave model in the Black Sea area and Sulina Bar and small-scale wave model
A wave model was developed to estimate the general wave conditions impacting the infrastructure at the Sulina bar and surroundings. Due to the complexity of the processes in the Sulina Channel discharge area and the limited detailed data on the local wave regimen, it was necessary to extend the model to cover a larger area of the Black Sea. This broad model provides boundary conditions for a more focused wave model around the Sulina mouth.
The domain of the large-scale hydrodynamic model encompasses a significant portion of the Black Sea around the Sulina Channel, extending approximately 15 km from the Sulina branch into the Black Sea (Figure 3).
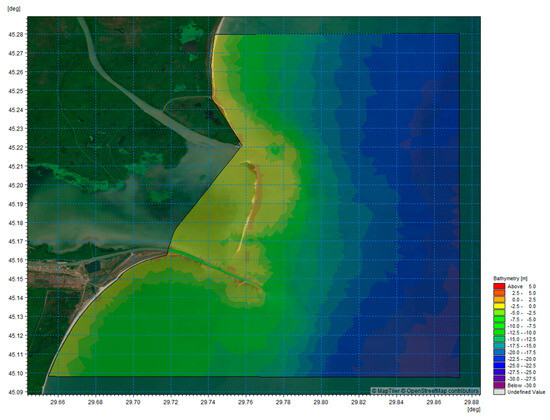
Figure 3.
The large-scale domain.
This domain was chosen to capture the interactions between large-scale wave and current patterns in the Black Sea and their influence on sediment transport and navigational conditions within the Sulina Channel. The model grid was generated using the MIKE 21 Flexible Mesh Spectral Wave (SW) model, ensuring a wide enough area to provide reliable boundary conditions for smaller-scale models focusing on the Sulina mouth and bar area.
The large-scale model was validated by comparing simulated wave height and period data against available wave measurements from offshore monitoring stations and satellite-derived wave data. The validation process covered both long-term simulations and extreme wave events. For wave heights, data from a beacon (available from September 2020 to September 2021) were utilized to calibrate the model, while for marine current data, we relied on the Copernicus Marine Service, which provided a reliable set of boundary conditions. Additionally, hindcast simulations of key historical storm events were compared to recorded observations, showing strong alignment between modeled and observed wave heights, current velocities, and directions, thus confirming the robustness of the large-scale model in representing offshore wave dynamics.
- Coastline sediment transport model
The Sulina Channel and bar area are influenced by various processes, particularly in the transition zone from river to marine environments. This zone experiences more pronounced sedimentation, primarily due to fine materials carried by the Danube and deposited at the bar due to current influences and density differences, as well as sands deposited by marine currents. The sediment transport model was designed to estimate the sediment intake along the shore, helping to determine the time required for recolonization after dredging activities.
- Channel sediment transport model
Like the coastal sediment transport model, a detailed model of fine sediment flow and transport within the Sulina Channel was created. This model simulates the transport, erosion, and deposition of fine sediments, particularly at the discharge area into the sea, where depths decrease from an average of −11 m to about −7 m. The model aids in estimating the quantities of sediments moving from the Channel to the mouth, ensuring timely dredging to maintain the minimum depth required for vessels with draughts of 11 or 11.5 m. Additionally, by monitoring sediment transport dynamics, the model assists in planning field interventions to maintain the continuous fairway.
- Vessel traffic model
To ensure navigable conditions for vessels with draughts higher than currently practiced, a model was developed to assess the impact of vessel transit on sediment resuspension and redeposition within the Channel and bar. This model integrates the hydrodynamic and fine sediment transport models, incorporating data on vessel routes, speeds, draughts, propulsion coefficients, and travel direction (upstream or downstream). This comprehensive approach allows for an accurate assessment of how vessel transit affects sediment dynamics, aiding in maintaining navigable depths.
It is important to note that the study took into account the currents from both the river and the marine sides when developing hydrodynamic and sediment transport models. The freshwater discharge from the Danube River interacts with the marine currents of the Black Sea, creating a complex hydrodynamic environment.
The model incorporated the river discharge from the Sulina branch as an upstream boundary condition based on the average value measured during the bathymetry survey. The MIKE 21 FM hydrodynamic module simulated the downstream flow of the Danube into the Black Sea, considering variations in discharge rates. The study particularly analyzed the impact of the river discharge on sediment transport and siltation in the Sulina bar, identifying areas of high sediment deposition in the transition zone between the river and the sea.
For marine currents, we used boundary conditions from the Copernicus Marine Service database, covering the period from February 2021 to January 2023. These currents were introduced at the seaward boundaries of the model to simulate large-scale water movement in the Black Sea. We paid particular attention to the interaction between these marine currents and wave action in the Sulina mouth area. The combined effect of longshore currents driven primarily by northeast winds and marine currents was crucial for accurately representing sediment transport along the coast and in the channel. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of wave-driven currents on the stability of protective jetties and the navigation fairway through sensitivity analysis.
3. Case Study
3.1. Large-Scale Wave Model in the Black Sea Area and Sulina Bar and Small-Scale Wave Model
To characterize the wave climate at the river mouth with respect to extreme waves, a two-step approach was employed:
- a.
- A wave simulation model for the Black Sea was used to determine the local offshore wave climate.
- b.
- A local wave model was developed to (i) propagate extreme wave conditions towards the river mouth and (ii) determine the local wave conditions necessary for calculating littoral sediment transport.
Note that the effect of currents (both offshore and riverine current) is disregarded in the analysis presented in 3.1.
3.1.1. Offshore Wave Climate Characterization
The wave model developed for the Black Sea, specifically for the area adjacent to the Sulina Channel and bar, was simulated over 10 years. The purpose was to identify a representative year to be used in simulating the impact of waves on flow conditions in the Sulina bar area (local wave model) and to extract information on the external forces acting on the existing dike infrastructure of the Sulina Channel into the Black Sea for further use in other potential stability analyses.
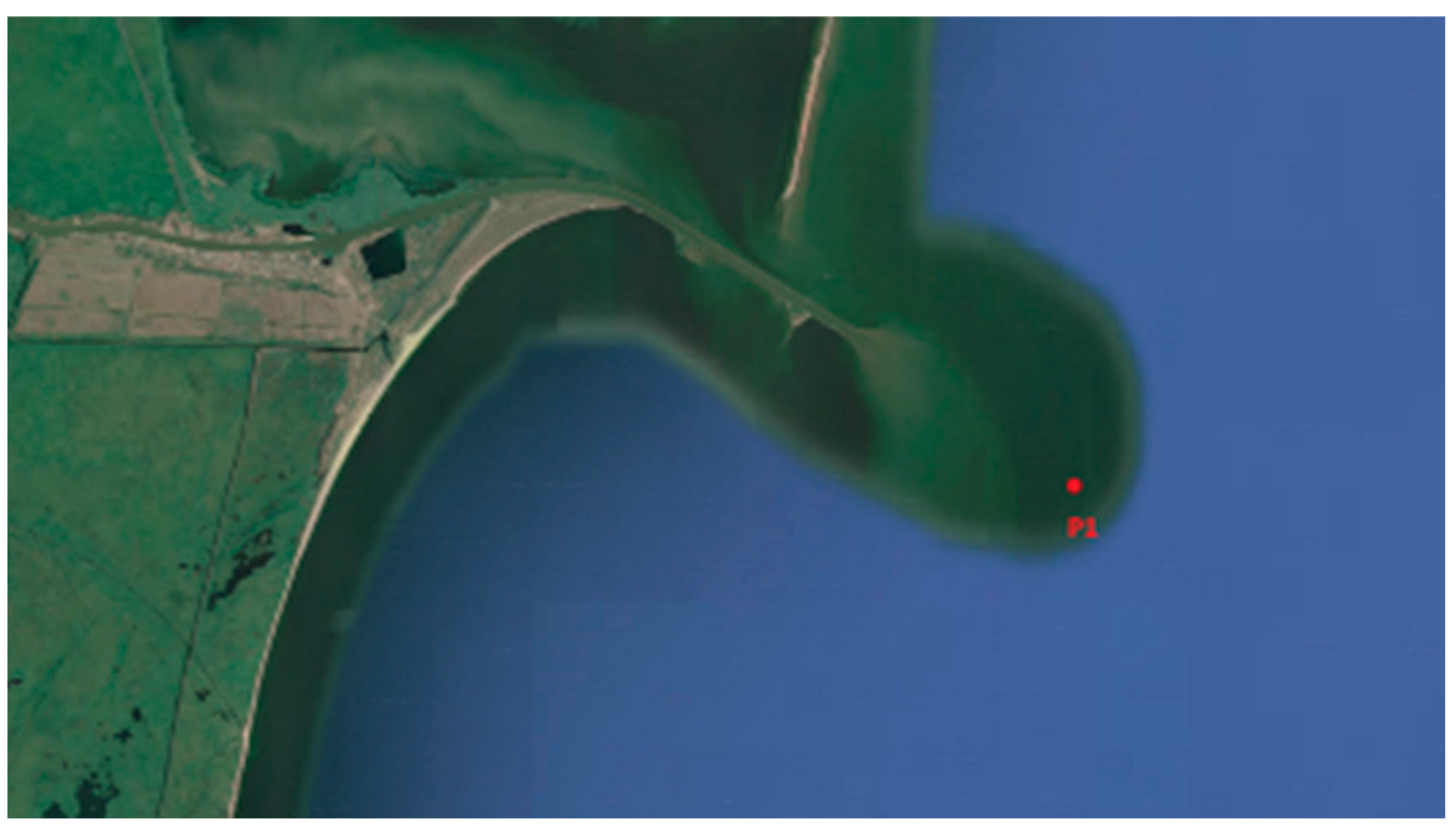
To investigate the wave conditions near the Sulina Channel mouth, a directional extreme value analysis (EVA) of significant wave heights and associated return periods was performed at point P1, located in the Black Sea, near the Sulina Channel (Figure 4). The EVA utilized wave data from the spectral wave model (Metocean Data) developed by DHI for the Black Sea, covering the period from 31 December 1979 to 31 December 2020.
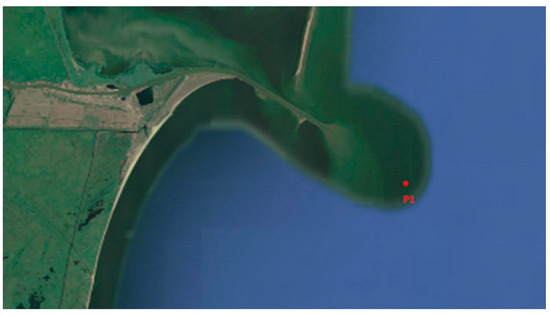
Figure 4.
The position of the point (P1) where the wave analysis was developed.
The wave rose at P1 (Figure 5(left)) is a significant source of information, providing insights into significant wave heights (Hm0) and mean wave directions (MWD). It is accompanied by the current rose, presented in Figure 5(right)) which gives indications about the current directions and intensity.
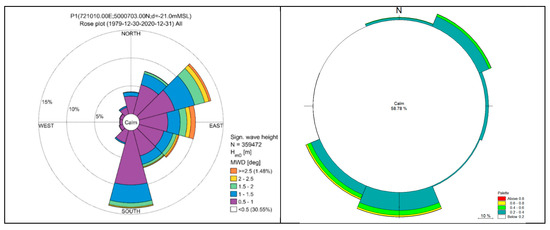
Figure 5.
The wave rose at P1, showing the significant waves’ height and the mean wave direction (left) and the current rose at P1 (right).
The main wave direction is between 0° N and 180° N, with the highest waves predominantly from 60° N–120° N sector. The information provided by the wave rose is presented in Table 1. Figure 6 shows the wave heights (Hm0) for the relevant MWDs from 0°N to 180°N in 30° intervals and for the ominidirectional directions. Among the various distribution functions tested, the two-parameter Weibull distribution (fitted using the least squares methods and a threshold value corresponding to the average annual peak (λ = 1)) provided the best model for wave height data over the 41 years for which wave information is available.

Table 1.
Mean wave direction and frequency of occurrence.
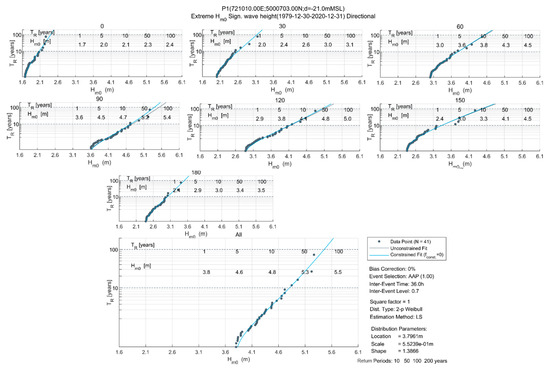
Figure 6.
The distribution of Hm0 for directional 30° and omnidirectional ranges at P1.
The directional and omnidirectional extreme values of wave heights for return periods (TR) of 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 years are detailed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Extreme wave heights (Hm0) for 30° intervals and directions for return periods of 1, 5, 10, 50, and 100 years at P1.
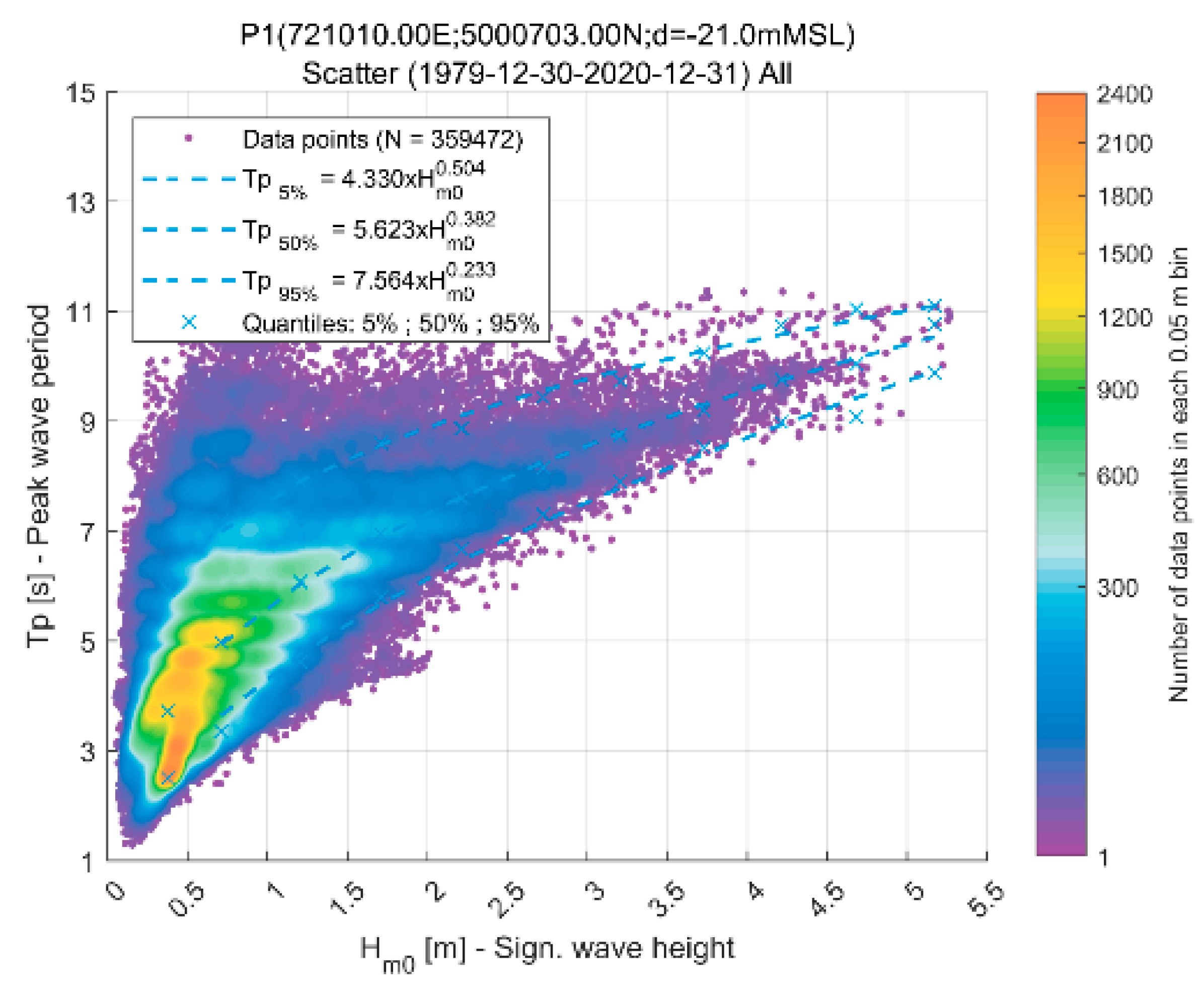
The peak wave periods (Tp) associated with extreme waves are derived from the graph shown in Figure 7, highlighting the functional relationship between Hm0 and Tp for all waves (omnidirectional). The matching coefficients are given in Table 3. These values were used as boundary conditions for spectral wave simulations propagating waves from offshore to the Channel mouth.
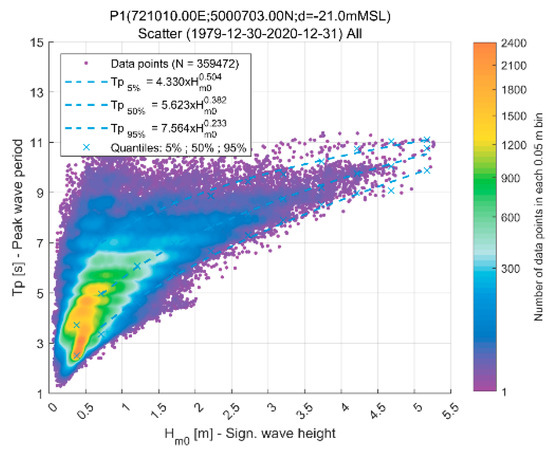
Figure 7.
The significant wave height (Hm0) and peak wave period (Tp) at P1.

Table 3.
Matching coefficients (Tp = a Hm0 b) at P1.
To simulate the extreme wave conditions in the Sulina Canal area, a local wave model was developed using Mike 21 Flexible Mesh Spectral (Danish Hydraulic Institute).
The full spectral formulation is based on the wave action conservation equation, presented in [34,35], where the direction–frequency wave action spectrum serves as the dependent variable.
3.1.2. Local Wave Climate Characterization
Specific wave events were simulated using a local wave model to provide extreme wave conditions in the Sulina Channel area for stability analysis. Additionally, a 10-year simulation of spectral waves (from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2020) was conducted to establish a database to assist in calculating littoral sediment transport processes.
The model is based on the topographic and bathymetric data provided within the project, as well as data from open sources, as detailed in the input data chapter. The computational mesh consists of 7043 elements, with the smallest element area being approximately 3600 m2 and the largest 550,000 m2.
For specific wave events, Hm0, Tp, and MWD were determined based on the statistical analyses described in previous sections. For the 10-year simulation, data were extracted from the spectral wave model developed for the Black Sea.
3.1.3. Loads Acting on Protection Dikes
To accurately compute the loads on the protective dikes, it was necessary to simulate local wave conditions using the above described 2D model for a series of selected events (local wave climate characterization). The wave heights were extracted from the simulation results and subsequently applied in the stability computations. The wave model was simulated over an extended period to identify representative wave conditions in the bar area that could affect the dikes. Detailed information regarding the current structure of the dike, including its design and verification criteria, was not available. Therefore, the analysis was conducted based on the relevant literature and expertise.
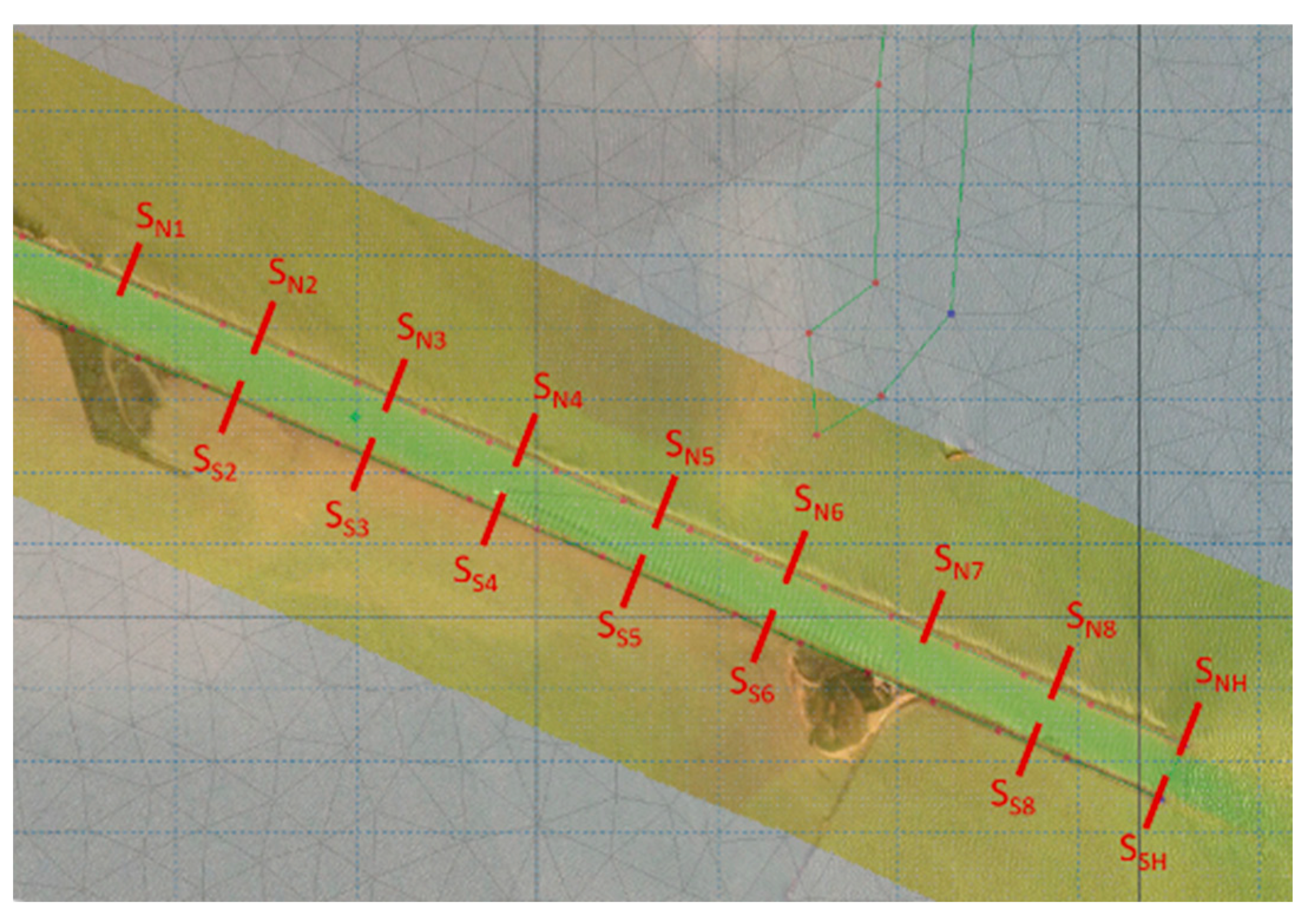
Due to the uncertainty regarding the probability associated with the design and verification standards of the protective works and the size of the rocks used during construction, it was reasonable to use, for calculations, events with a 1% return period. The wave heights were extracted from the simulation results. The boundary conditions were used in the dikes stability analysis by comparing design values for unit weights for the dike rocks with known weights. In the calculations, a series of dike sections on the northern structure (SN) and the southern structure (SS) of the Sulina Channel were considered, as shown in Figure 8.
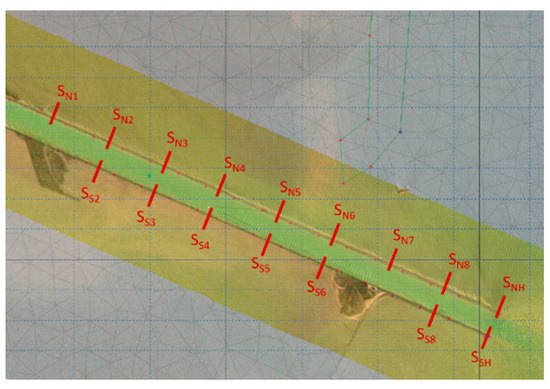
Figure 8.
Sections selected for calculating loads on north and south dikes.
Sections were selected at the beginning of the dikes into the sea and upstream, ensuring that a variety of wave heights and cross-sectional characteristics were captured. The two sections at the sea entrance (dike heads) are designated as SNH (north) and SSH (south). The analysis of the dike sections utilized the available LIDAR data, which included the most recent and detailed measurements from the project’s survey campaign (2023) providing crucial information on the actual dikes’ dimensions and slopes. The SS1 to SS6 sections (located on the southern dike) have recorded water levels lower than the terrain elevation and, therefore, were not considered in the calculation of wind-generated wave loads on the southern side.
The Hudson equations [36,37] were used to estimate the minimum unit weight required for the dike’s surface layer, assuming minimal damage due to wave action for different dike sections. The overtopping height and overflow across the dike were calculated according to Eurotop [38]. The physical or geometric parameters related to the waves characteristics that were included in the calculations are:
- H [m]—Wave height, which is the height of the wave from crest to trough,
- T [s]—Wave period, which represents the time it takes for two consecutive wave crests to pass a fixed point,
- Direction (°)—Wave direction, which is the angle of wave propagation relative to true north,
- β [°]*—A parameter related to the wave incidence angle relative to the dike structure,
- L [m]—Wavelength, which is the distance between two consecutive wave crests.
- h/L [-]—Ratio of water depth (h) to wavelength (L)
- H/h [-]—Ratio of wave height (H) to water depth (h).
Wave breaking was considered for horizontal beds with H/h = 0.78 and for sloped beds with H/h = 0.55.
The required weight for tetrapod elements was also calculated to provide context for the necessary weights to withstand wave loads for a 100-year return period.
3.2. Coastline Sediment Transport Model
The sediment transport models along the coast and within the Sulina Channel and bar area were employed to estimate the dynamics of sediment deposition. This model includes solid discharges from the channel, influenced by currents and waves, and marine sediments deposited in the bar area due to changes in the flow regime.
A one-dimensional model (LITDRIFT), developed by DHI, was used to investigate the temporal and spatial variation of sediment transport along the northern coast of the Sulina Channel. It focuses on littoral evolution and excludes the two-dimensional processes already addressed by other models. LITDRIFT is an integrated modeling system that simulates non-cohesive sediment transport along quasi-stationary coastal lines using an “n-line” approach, combining a robust deterministic sediment transport model with the ability to simulate a wide range of wave and current scenarios, employing methods such as the integrated momentum approach [39], the Engelund and Fredsoe model [40] for bedload transport, and the vertical diffusion equation for suspended sediments [41] to evaluate coastal currents and sediment transport for applications like coastal works impact assessment and beach development optimization.
The inputs in the model are the wave climate, coastal profile data, sediment characteristics, and water levels.
The LITDRIFT calculations were based on a 10-year wave climate simulation (2011–2020). Three profiles were used to model the coastal zone between the Chilia branch and the Sulina Channel. The results were presented as net and gross transport capacities along these profiles and their distribution along the coastline.
3.2.1. The Wave Climate
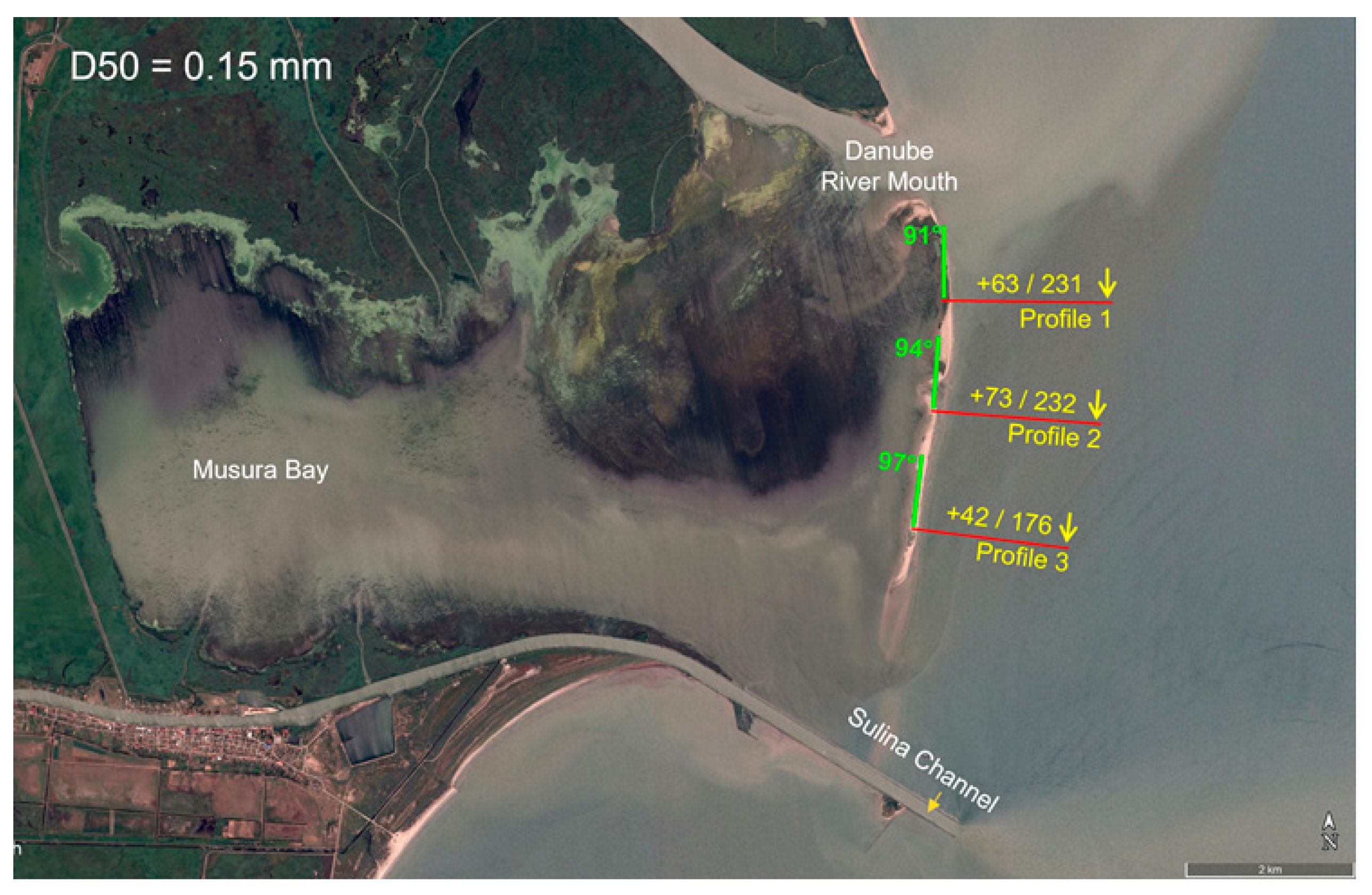
The wave climate is the primary factor driving sediment movement. Wave data were extracted from the hydraulic model, which provided time series of transformed waves (height, period, and direction) at the seaward ends of the profiles. These locations (Figure 9), with water depths of approximately −8 m relative to mean sea level (MSL), were chosen to avoid the wave breaking and closure zones, ensuring the model captured a full range of conditions. Predominant wave directions were identified as NE-E.

Figure 9.
The locations of the coastal profiles (red lines) and the associated wave climates represented as wave roses. Satellite image from Google Earth Pro, dated 11 July 2017.
3.2.2. Coastal Profiles
For the given wave conditions, the shape of coastal profiles determines the wave breaking zone and its magnitude. The profiles were derived from bathymetric data with an 80 × 100 m resolution, primarily based on GEBCO Gridded Bathymetric Datasets, and refined with higher-resolution local data. It is noted that the resolution may not fully capture the beach slope and sand dune (Figure 10). Beach slopes were manually adjusted using satellite imagery to reflect field conditions accurately. The profiles extended perpendicularly from the shore to a depth of −8 m MSL.
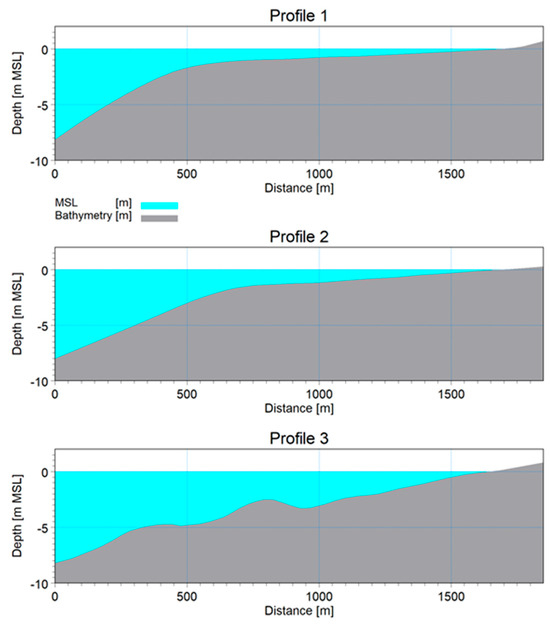
Figure 10.
Cross-sectional profiles extracted along the sand dune north of the Sulina Channel.
3.2.3. Water Level
The variation in water levels within the study area is minimal, and the tidal range is negligible. Therefore, a constant mean sea level was assumed for the simulations, as the wave-induced variations were deemed more significant.
3.2.4. Sediment Characteristics
The model incorporated two median particle sizes (d50) of 0.15 mm and 0.2 mm, with associated settling velocities of 0.0183 m/s and 0.0267 m/s. A roughness coefficient of 0.0037 m and 0.005 m was applied to account for coastal changes in the simulations.
3.3. Channel Sediment Transport
To simulate water flow and sediment transport in the downstream sector of the Sulina branch, we developed a two-dimensional model that operated continuously on a distance of 11 km from Sulina to the discharge point into the Black Sea. The model used is Mike 21 Flexible Mesh of Danish Hydraulic Institute from Denmark with Mud Transport (MT) module. The hydrodynamic system is based on the Navier–Stokes equations, encompassing the mass continuity equation, the momentum continuity equation, and variations in temperature, salinity, and density, as well as incorporating a turbulence model, while computational equations underlying the MT module are based on those described in [42]. For enhanced accuracy and model stability, the calculation range was extended approximately 19 km northward, encompassing the Musura Gulf, and around 19 km eastward and 24 km southward into the Black Sea.
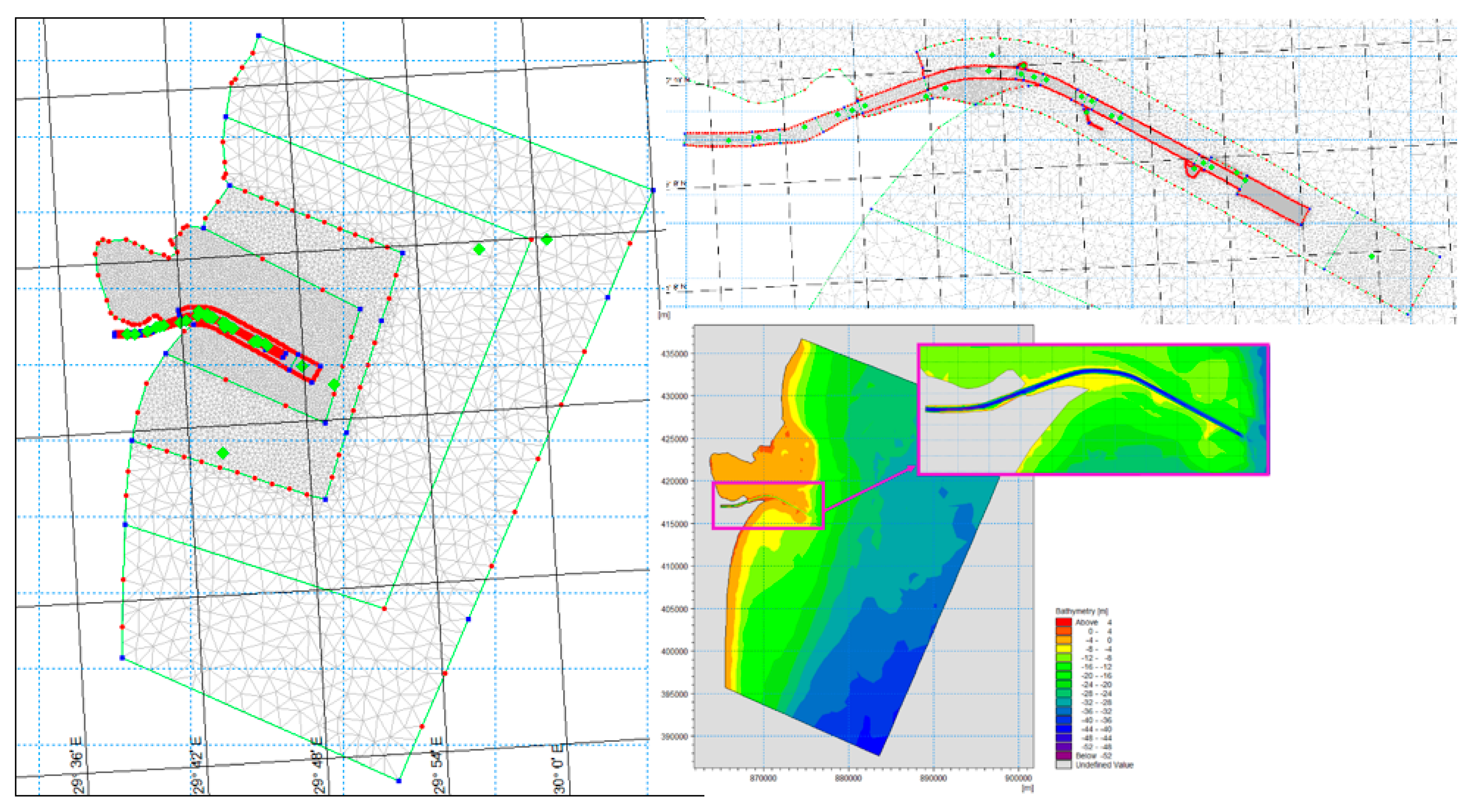
The study area (Figure 3) was defined after the analysis of topo-bathymetric data, superimposed on maps and orthophotos. This zone, covering 1077 km2, includes all relevant features: the minor bed of the Sulina branch, defense dams, the locality, and the extension into the Black Sea.
Based on the analyzed and vectorized data, a bathymetry file specific to MIKE 21 FM software was created by constructing a network of finite elements (mesh) (Figure 11), with various dimensions tailored to each area of interest:
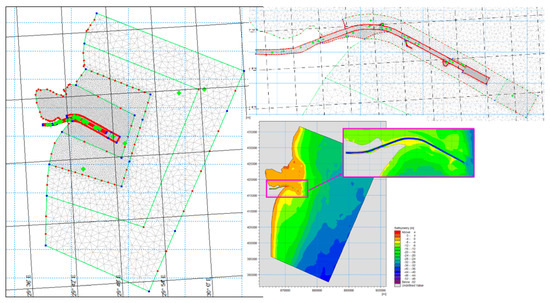
Figure 11.
The finite elements mesh (left and top right); Bathymetry file used in hydrodynamic model (right down).
- In the minor riverbed, quadrilateral elements were used with sizes varying from 90 × 30 m to 90 × 10 m along the Channel. Locally, triangular elements with a maximum size of 50 m2 were utilized in the upstream area. For the Danube River–Sulina Branch mouth area, a triangular mesh with elements sized at 55 m2 was employed.
- For the rest of the domain, triangular elements were generated with surfaces ranging from 500 m2 to 75,000 m2, and the element size progressively increased from the land towards the Black Sea coast.
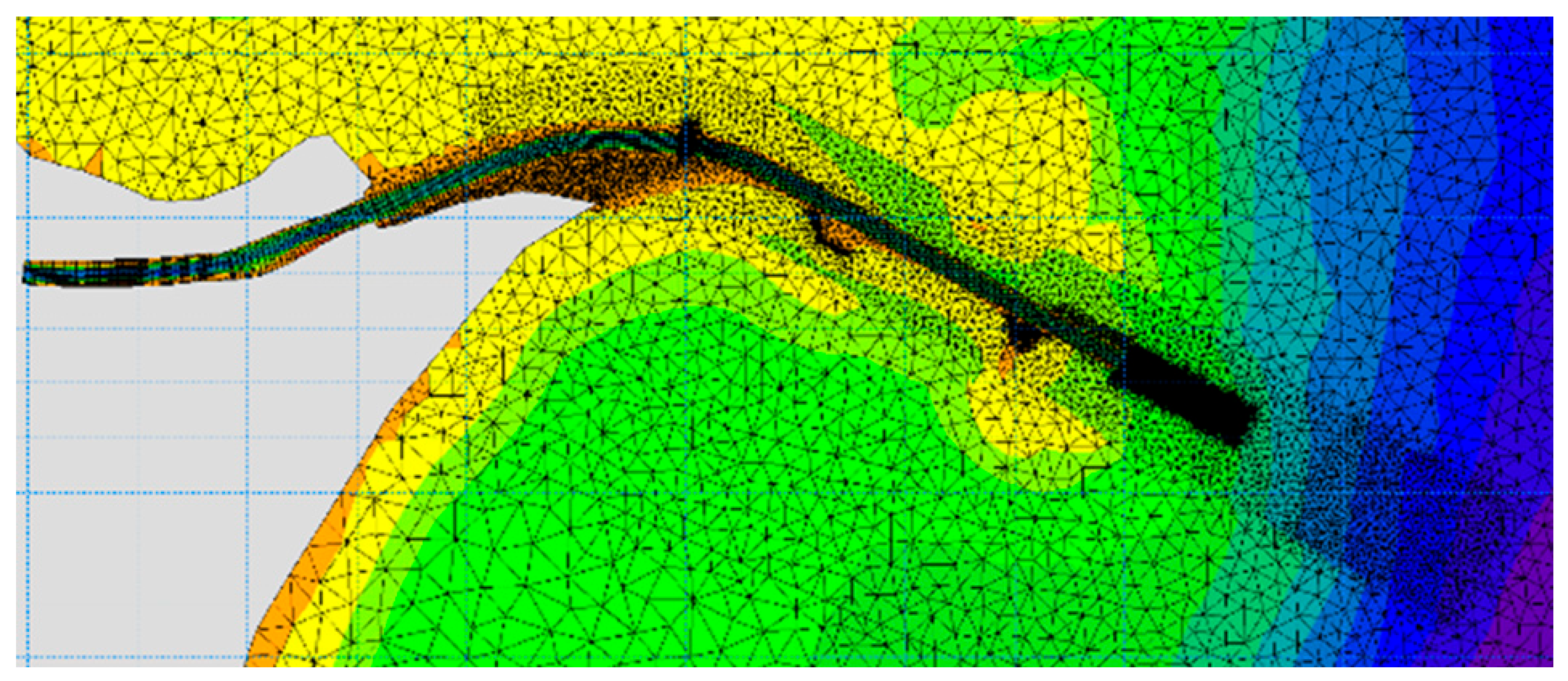
To find an optimal solution, it was essential to determine the appropriate number of finite elements that would accurately describe the areas of interest while avoiding stability and convergence issues and optimize the computational time. Based on the requirement for precision and taking into account previous experience, a finite element network consisting of 37,925 elements was established. Figure 12 displays the mesh details, allowing for an observation of the elements’ density.
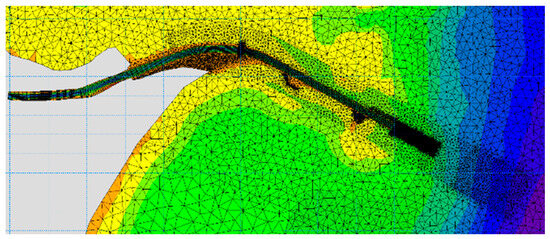
Figure 12.
Detail of the network of finite elements (mesh).
The two-dimensional hydrodynamic model integrated the information below:
- Turbulent viscosity;
- The Manning Roughness Coefficient [43], n, crucial for the hydrodynamics of a watercourse, which was determined based on the following information:
- o
- The type and size of materials composing the bed and banks of the riverbed;
- o
- The shape of the riverbed.
To assess the vegetation and land use in the major riverbed, the roughness coefficients were selected according to recommendations from specialized literature [44]. This selection was further refined through analysis of available aerial photography charts. Using the available land use data, the CLC (Corine Land Cover 2018) file was processed and improved, assigning values to each type of use:
- The values assigned to n were between 0.023 and 0.027 in the minor bed of the Sulina Channel;
- The Manning coefficient was set to 0.014 in the Black Sea area;
- The Manning coefficient ranged from 0.050 to 0.085 in the major riverbed.
Based on experience from previous studies and sensitivity analyses, an average wind speed of 5 m/s and a direction of 55 degrees were used. Hydrological data (flow and levels) from project measurement campaigns were also included, with an upstream flow value of 1410 m3/s and variable boundary level conditions for the northern and southern areas, the beach, and the Black Sea.
The model integrates two-dimensional sediment transport processes, addressing sedimentary flow and morphology changes through erosion or accumulation. Measurements were processed to determine particle size distribution and bed stratification, enabling precise simulation of sediment resuspension dynamics.
The Engelund & Hansen model [45] was selected for sand transport, with the following sediment properties: porosity—0.4, relative density—2.65, and particle diameter based on field data, including a grain size of 0.15/0.2 mm for the Black Sea area. Roughness coefficients from the hydrodynamic model were applied.
For mud transport, cohesive material transport was calculated based on flow conditions, with additional data for three layers of parental material and erosion and density parameters set according to field sampling information. Wave regime data, with average values for height (1.0 m), period (3 s), and direction (55 degrees), were also incorporated.
Several fairway depth scenarios (8–12 m) were analyzed to simulate sediment transport. The “Fairway −12 m” scenario was used as a baseline, representing an extreme but informative hypothesis. The model was validated by comparing hydrodynamic results with field measurements, showing accurate reproduction of flow phenomena.
3.4. Vessel Traffic Model
The model was further developed to analyze the dynamics of the fairway under the influence of currents, waves, and naval traffic by incorporating elements that account for the location and direction of ship movement, such as route, draught, propeller diameter, speed, propulsion coefficient, and propeller RPM. It also considers the tangential forces produced by the ship propellers, comparing them with the threshold force needed to resuspend sediments, which helps in identifying areas of erosion and deposition.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Results of the Large-Scale Wave Model in the Black Sea Area and Sulina Bar and Small-Scale Wave Model
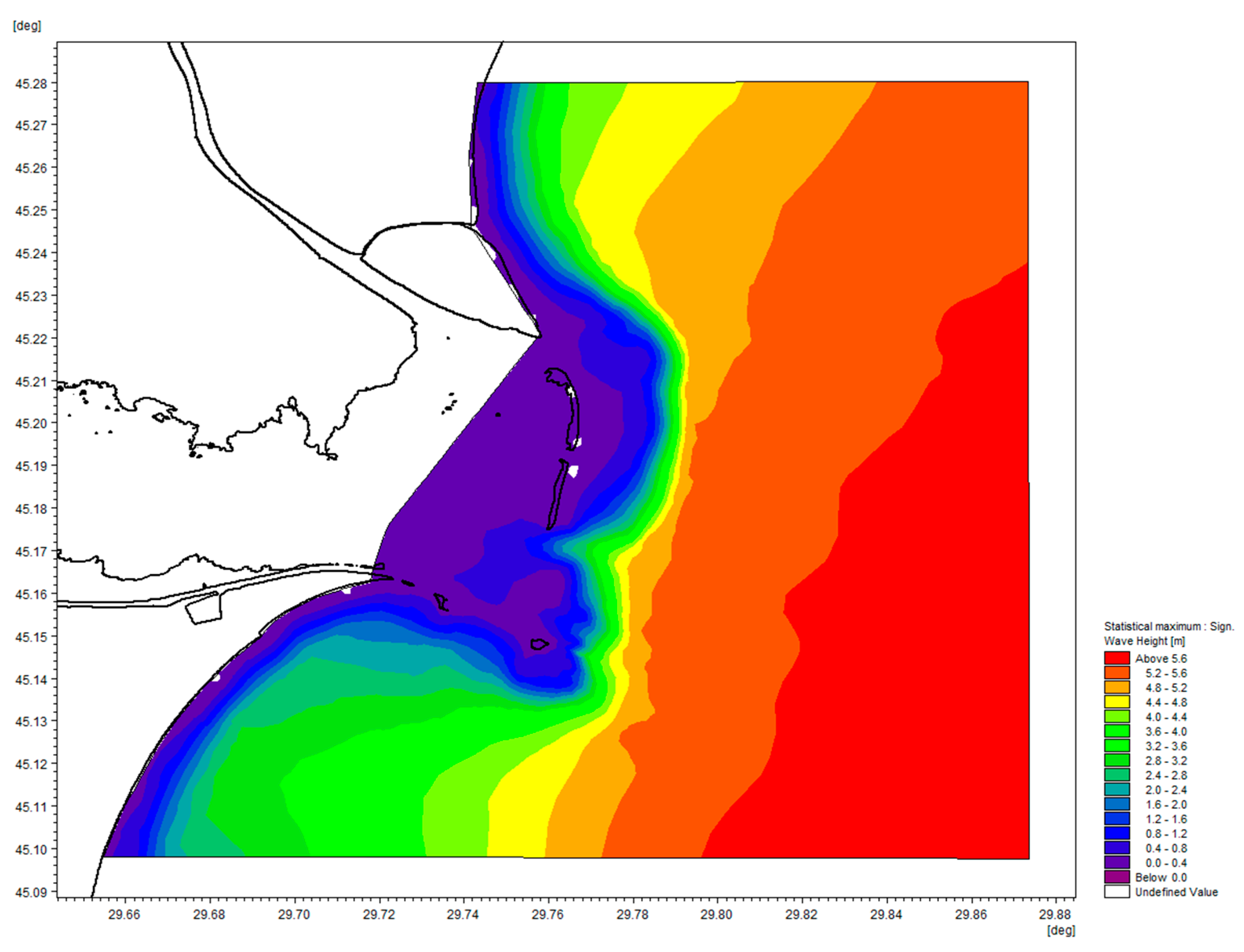
The MIKE 21 SW non-stationary simulation was conducted over 10 years from 1 January 2011 to 31 December 2020. For example, the maximum values of wave heights can be seen in Figure 13.
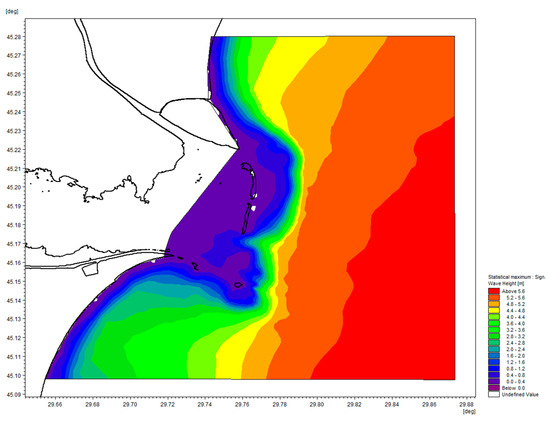
Figure 13.
The maximum value of the significant wave height (Hm0) for a 10-year simulation.
The maximum wave heights for a 100-year return period were determined using the results from the MIKE 21 SW model. Table 4 presents the wave characteristics at the selected sections.

Table 4.
Wave properties at the selected sections.
The computed values for the minimum unit weight required for the surface layer, overtopping height, and overflow across the dike are presented in Table 5, where KD is a stability coefficient, W is the weight, and Q is the overflow over the crest.

Table 5.
Estimated minimum weight of rocks along with overtopping height (Ru2%) and the overflow over the crest (Q).
The unit weights of the surface layer components are reasonable along most of the dike length, matching the known values of the stones forming the dike structure. For the sections at the heads, these weights reach high values, justified by greater depths and stronger wave impacts on these sections, which are the most exposed to the wave climate. Given that the dike’s entire structure and the constituent rocks’ weight are only partially known, it is impossible to conclude definitively on the stability of the protective structure’s elements. However, the dikes’ stability was assessed by considering them as a cohesive mass influenced by hydrostatic and hydrodynamic pressures from wave action. The computation shows that the overtopping height Ru2% is lower than the freeboard for all sections, and the overflow over the crest (Q) is negligible.
4.2. Results of the Coastline Sediment Transport Model
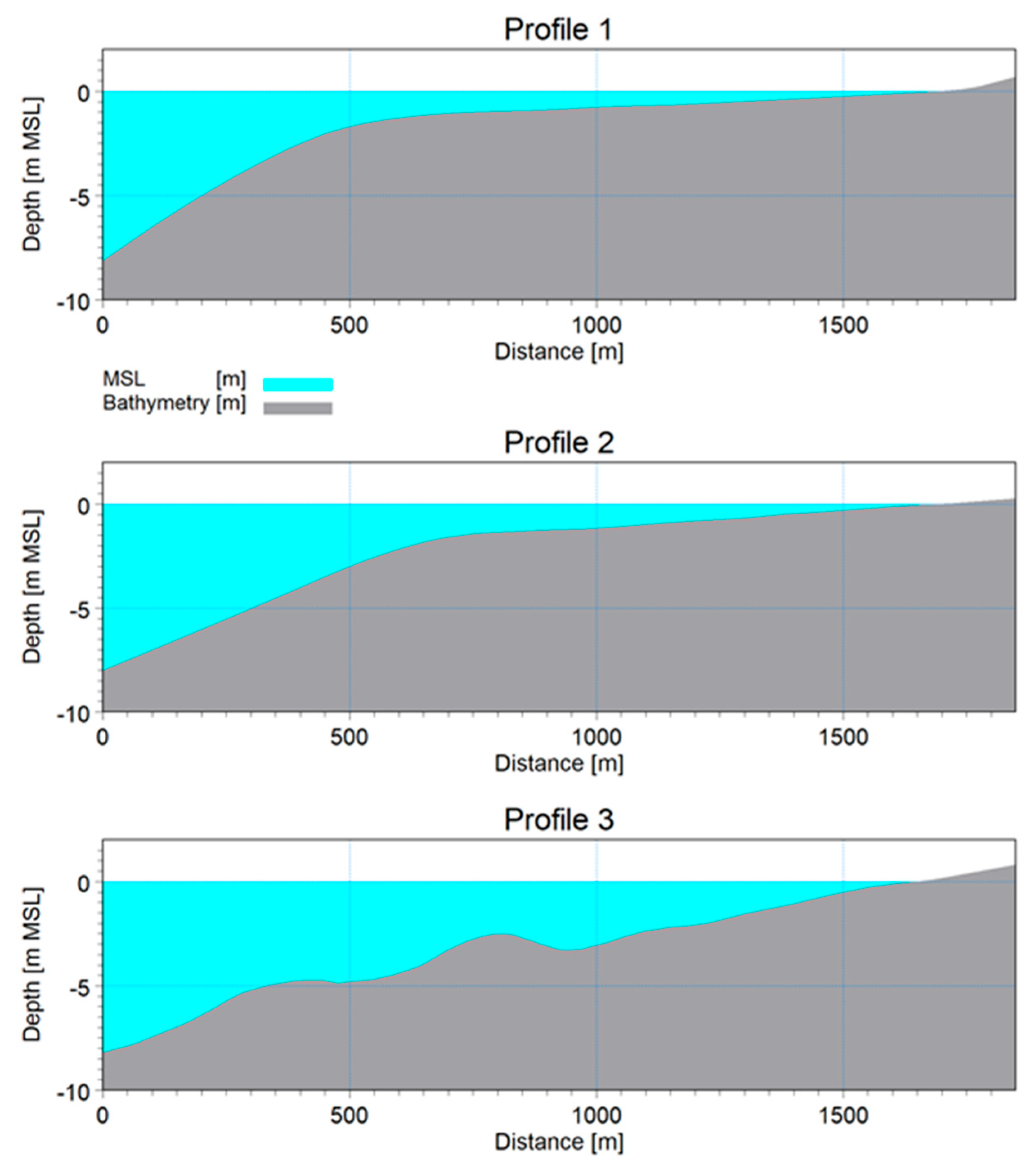
A modeling scenario was implemented to analyze sediment transport dynamics between the Chilia Branch and the Sulina Channel, corresponding to a median particle diameter of 0.15 m. The 10-year time series of littoral sediment transport, illustrated in Figure 14, focuses on Profile 2 for 0.15 mm.
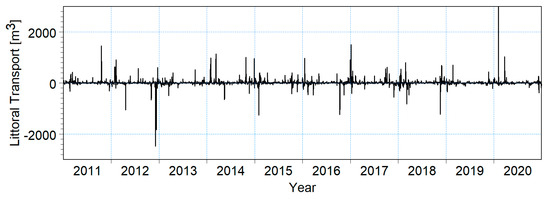
Figure 14.
Time series of estimated littoral transport (m3) over 10-years for Profile 2, with a beach orientation of 94° and a sand particle size of 0.15 mm. Negative values indicate transport towards the north, whereas positive values indicate transport towards the south.
These time series highlight seasonal and interannual variations in sediment transport, most occurring during winter. Notably, negative values indicate sediment transport from south to north, while positive values indicate transport from north towards the Sulina Channel and bar. Similar sediment transport trends are observed in Profiles 1 and 3.
The distribution of modeled sediment transport along the cross-sectional profiles is presented in Figure 15. The charts display the bathymetric elevation (relative to mean sea level) on the left Y-axis and transport rates on the right Y-axis, including annual net and gross transport rates from north to south and from south to north.
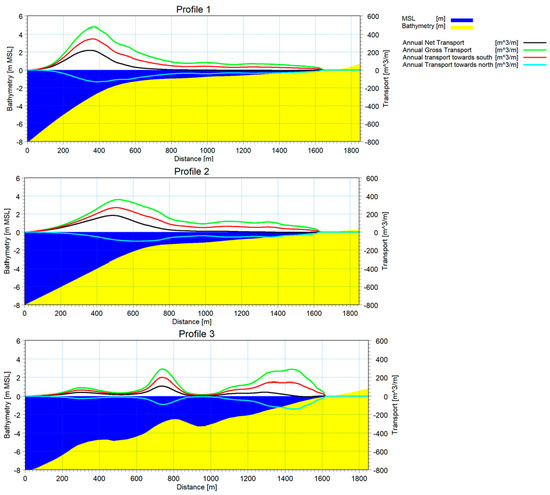
Figure 15.
The distribution of littoral transport across three profiles for sediment sizes with a median diameter (D50) of 0.15 mm.
Remember that Net Transport is defined as the difference between the transport in both directions. In contrast, Gross Transport refers to the sum of transport in both directions, considering movement from the Sulina Channel towards Chilia and vice versa.
The resulting distribution indicates that sediment transport is mainly concentrated along the slope of the beach and sand dune (as observed in Profile 3) and around the beach where waves break, generating littoral currents and, consequently, sediment transport.
For sediments with a median diameter (D50) of 0.15 mm, the net transport capacities (the difference between transport capacities in both directions, N-S and S-N) across the three modeled profiles range from approximately 40,000 m3/year to 70,000 m3/year. The predominant direction of transport for all three profiles is from north to south towards the Sulina Channel. The annual gross transport capacities range from 150,000 m3/year to 230,000 m3/year.
Considering the limitations in data availability, net sediment transport along the coast north of the Sulina Channel is estimated to range between 30,000 m3/year and 70,000 m3/year towards the river mouth. Consequently, an intensive deposition process is expected in the river mouth area. However, sedimentation and annual sediment transport are likely to increase due to additional sediment input from the Danube, which also deposits in the Sulina bar area.
Figure 16 shows the results of the sediment transport model along the coast. The measurement unit is 1000 m3/year. The net transport (left number) and gross transport (right number) are shown in yellow, along with the transport direction. The profile orientation relative to the beach is shown in green.
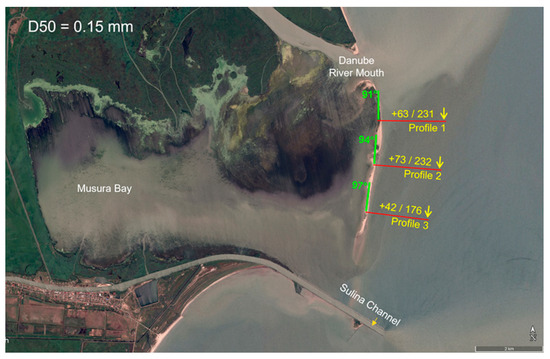
Figure 16.
Forecasted littoral transport capacities for 0.15 mm sediments.
4.3. Results of the Channel Sediment Transport Model
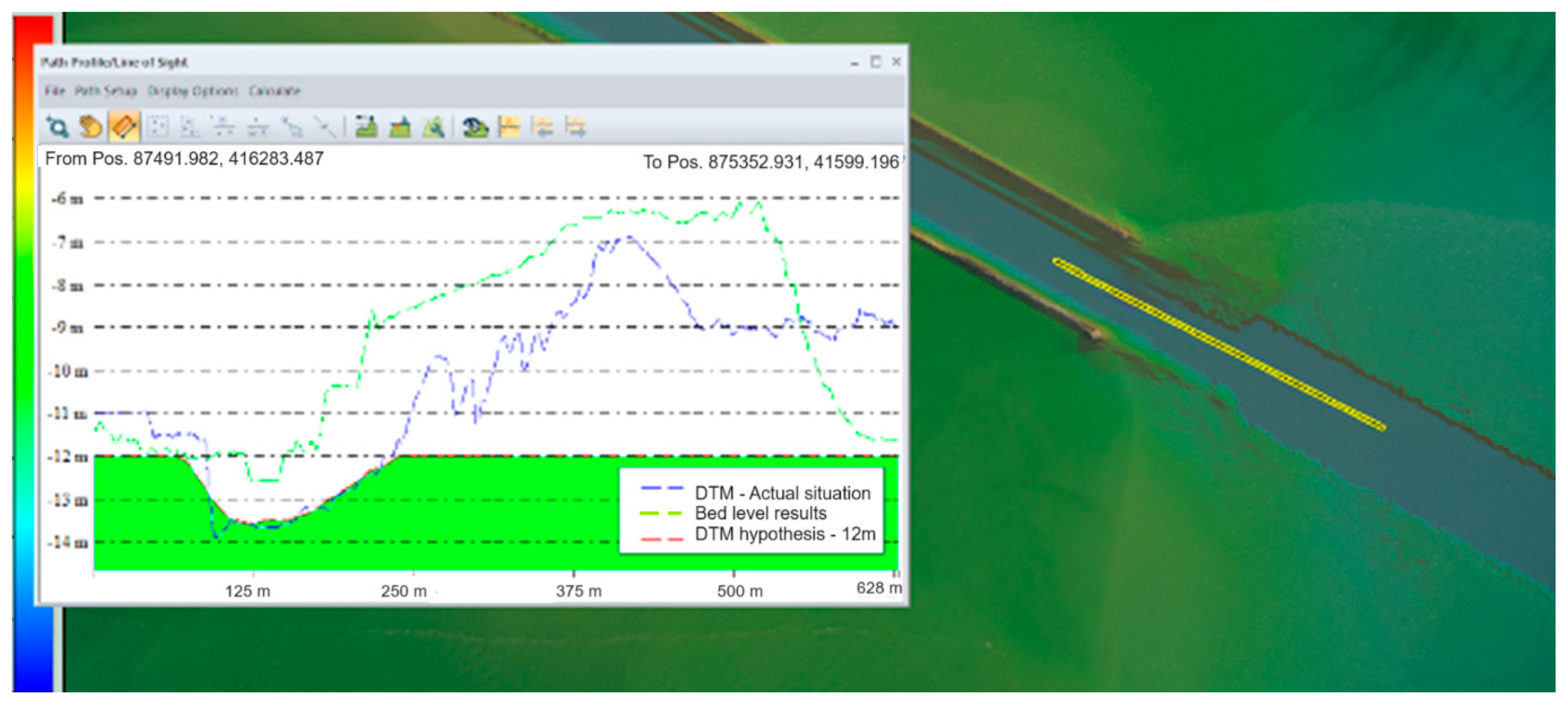
The results show sediment deposition in the Sulina Channel’s discharge area into the Black Sea. A representative image shows bed elevation changes from −12.0 m to about −7.3 m. The sediment deposition dynamics were analyzed in various scenarios, with estimates for required maintenance volumes. Figure 17 shows, in the longitudinal profile through the bar, the differences between the results obtained from the modeling (green line), the topo-bathymetric data obtained in the project campaign (blue line), and the processed file in which the fairway level has been established as −12 m (red line).
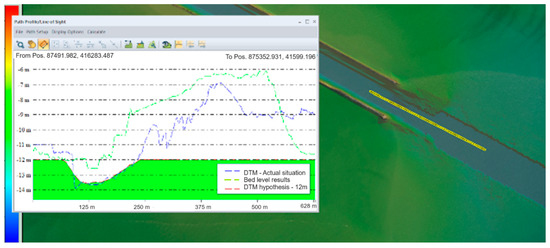
Figure 17.
Comparison between modeling result and DTM in the current situation—longitudinal profile.
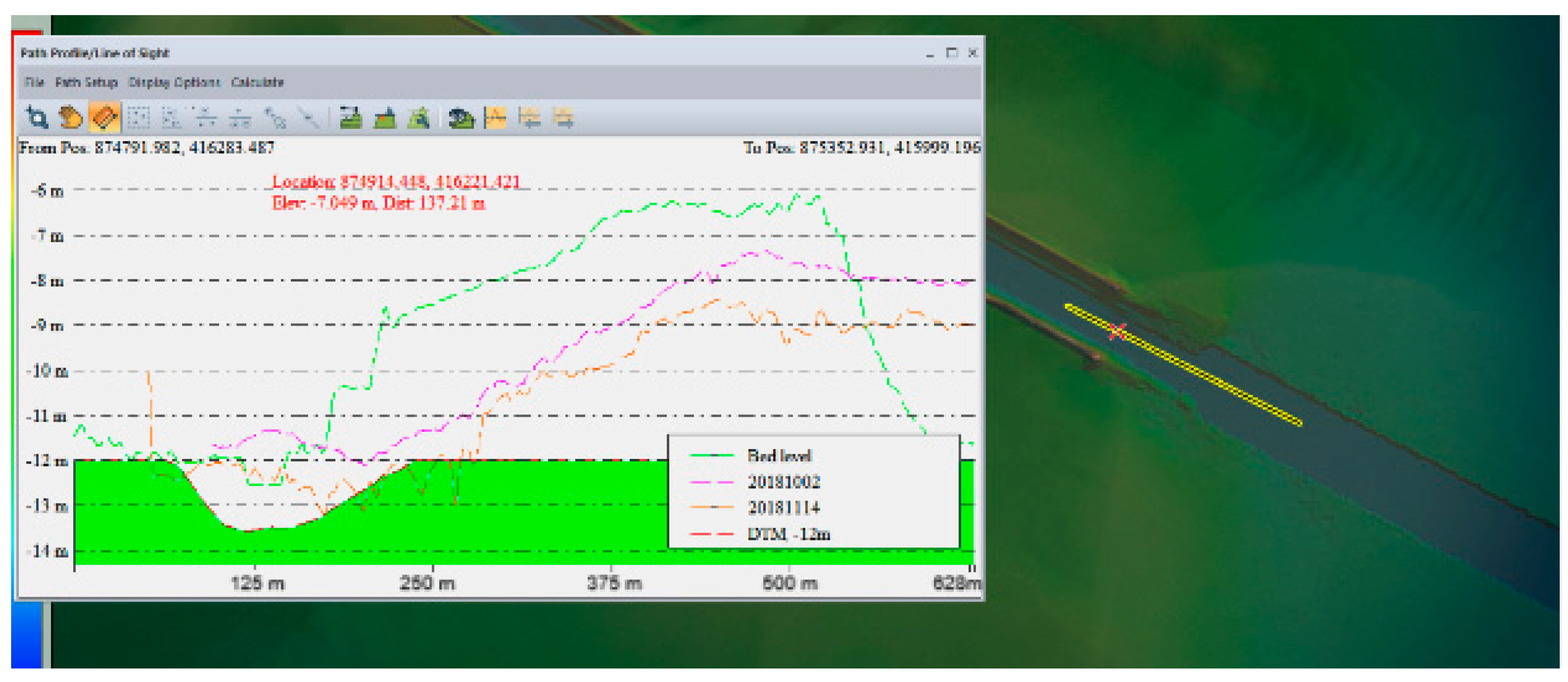
All available historical data have been used for a proper comparison with the results from the coupled hydrodynamic-sediment transport model. The historical data were acquired during various monitoring surveys done in 2018, 2022, and 2022 by the Lower Danube Administration specialists. The comparison has pointed out a dynamic phenomenon of sediment deposition in the river channel around the river mouth area. The deposition is slightly uneven, both transversally and longitudinally, but happens continuously.
Figure 18 depicts the comparison between the simulated deposition (green line) and the measured deposition bar.
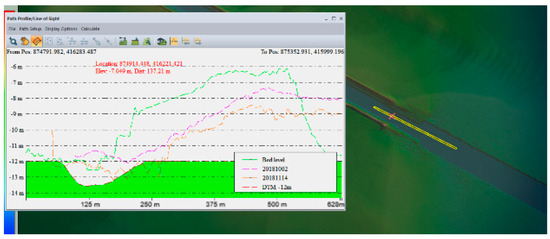
Figure 18.
Comparison between the simulated scenario and historical measurements.
4.4. Results of Vessel Traffic Model
Simulations conducted over a week, with approximately 150 vessels of 11.5 m draught moving at 2.5 m/s, revealed that ships cause additional erosion along their routes, particularly in the upper layer of less consolidated clay. This erosion process stabilizes after 3–5 passages, with the more consolidated second layer experiencing less erosion. Scenarios involving tugboat-assisted vessels showed similar trends, with slightly higher erosion at the fairway’s edges.
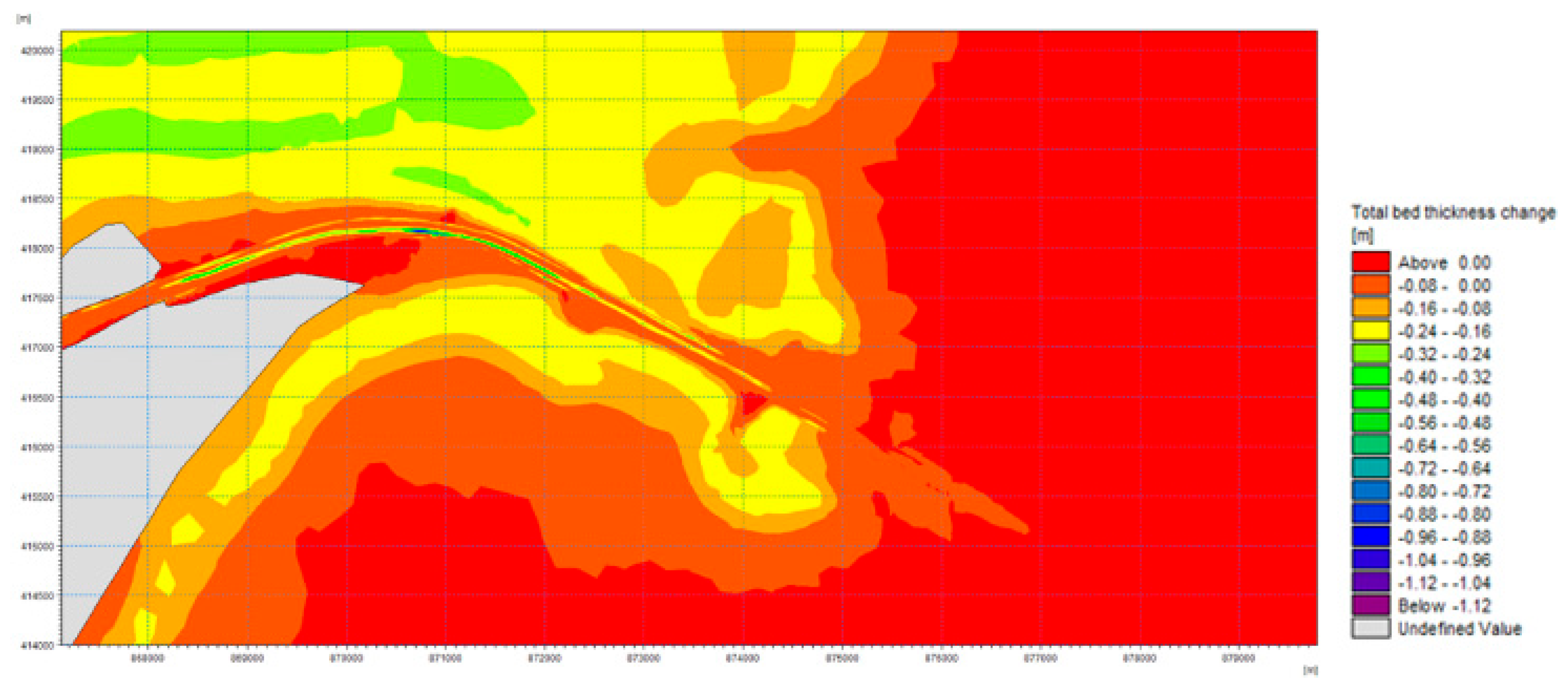
The model results indicate that a vessel with a draught of 11.5 m transiting the new navigable channel generates additional erosion due to the currents produced by the propellers. The results show that this additional erosion generally occurs within a 30–50 cm range, with only a few areas where these values are exceeded (Figure 19).
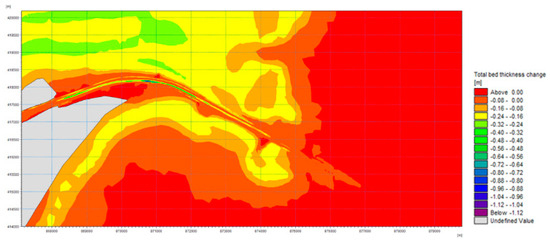
Figure 19.
Riverbed erosion due to propellers.
For ships with a draught of 7 m, propeller effect on sediment transport is minimal.
It is crucial to note that the erosion caused by vessels is primarily concentrated along the ships’ route. This means that vessels do not impact the dikes if they adhere to the defined channel route. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that ships remain as close as possible to the channel’s center, thereby avoiding additional tangential stress on the dike bottoms.
4.5. Discussion
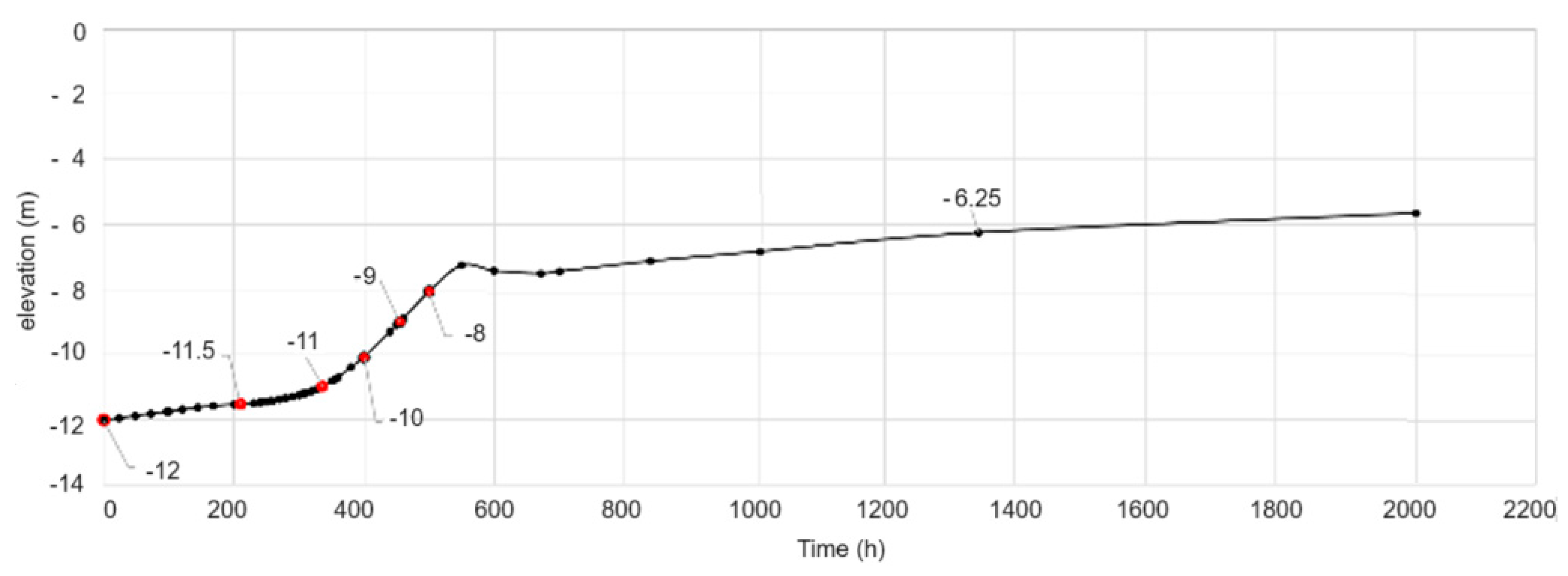
Regarding the sediments recolonization, the results show that the Sulina Channel mouth area is highly dynamic. The particles resedimentation occurs quite rapidly, with the water depth varying from −12 m to the stability depth of around −7 m in one to two months. Figure 20 presents the riverbed evolution in time in a representative area of the bar. Remark that about 800 h after dredging, the depth to the riverbed is above −7 m.
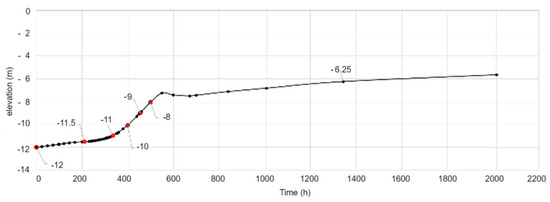
Figure 20.
Evolution of the seabed level in the Sulina Channel’s mouth area.
This recolonization happens mainly in places with a sudden transition between the Danube’s fluvial flow regime and the Black Sea’s marine current regime because sand particles from the Black Sea are deposited rapidly. The obtained results match the observations regarding the deposition area and deposited quantity and the development of a sand dune from north to south directly through the Sulina bar.
The dikes’ stability analysis has shown that the longitudinal dike along the Sulina canal is stable and not influenced by external conditions in terms of the lateral pressure applied by the hydrodynamic wave forces and potential erosion or rock displacement caused by waves overtopping.
In this study, an additional scenario considered the vessel propulsion, where the vessel would not be self-propelled but rather assisted by tugboats, which would have much smaller draughts than the cargo vessel. The same route and travel speed have been proposed as for the self-propelled vessel. This scenario was mainly simulated to assess if the tugboats would induce any scouring in the protection dikes. The simulation results showed that the tugboats would not have a scouring impact on the dikes’ bottom, thus not threatening the dike stability. Also, considering the smaller draught values, the tugboat propellers are not powerful enough to cause any significant material resuspension.
The study brings significant insight into the integrated dynamics of various forcings (waves, currents, winds, river discharge, mud transport, sediment transport, and vessel traffic) that act on the Sulina Channel’s mouth area and bar.
The novelty of the study is represented by:
- Proposing various models for assessing the individual and combined effects of the processes that impact the navigability in the Sulina Channel;
- Designing a vessel traffic model to evaluate the impact of the increased vessel traffic (that takes into account the increase in vessel sizes) on the sediment resuspension;
- Evaluating the potential sediments’ redeposition in the Sulina bar area;
- Evaluating the dredging period to maintain the navigability on the canal. This is especially important during wintertime when the bar could suffer significant re-sedimentation due to storms and increased sediment transport.
5. Conclusions
The study brings significant insight into the complex dynamics occurring in the Sulina Channel mouth area accounting for the combined effects of natural forces and anthropogenic activities. Its novelty consists of presenting an integrated approach that aims to obtain the necessary input to fully assess the area in terms of interactions between waves, currents, river flows, and sediment transport and the impact of vessels’ navigation on sediment resuspension in the Sulina Channel.
Through advanced hydrodynamic, wave, and sediment transport models, the following key conclusions have been drawn.
- The transition zone between the Danube River and the Black Sea experiences significant sedimentation, primarily due to the fine materials carried by river discharge and sand deposited by marine currents. This finding is crucial for planning regular maintenance dredging and the associated costs for maintaining the navigability in the Channel.
- The vessels’ transit contributes to additional erosion along predefined routes, with propeller-induced currents causing significant sediment resuspension. Erosion stabilizes after multiple vessel passages, primarily affecting the less consolidated upper sediment layers.
- The developed wave model successfully estimated the wave conditions impacting the Sulina Channel and its infrastructure, providing essential data for understanding the coastal sediment transport processes.
- Extreme wave height analyses revealed significant wave directions predominantly between 60° N and 120° N. Therefore, it is necessary to consider these directions in future coastal management plans.
- Stability analyses of the dikes along the Sulina Channel demonstrate that the existing structures can withstand extreme hydrodynamic forces, with calculated wave-induced pressures confirming the dikes’ resilience. Longitudinal dikes were stable against both lateral hydrodynamic pressures and potential erosion or rock displacement caused by wave overtopping, ensuring the continued protection of the Sulina Channel.
The findings underscore the importance of an integrated approach in managing navigable waterways, ensuring operational efficiency and environmental sustainability.
To enhance the accuracy of future studies, it is recommended that more detailed field measurements be acquired, particularly regarding wave and current conditions in the Black Sea. Further investigations should include the impact of wake waves on dike erosion processes and sensitivity analyses of different vessel characteristics to refine the understanding of their effects on sediment transport.
Overall, this study presents significant insights into the complex dynamics at the Sulina Channel mouth, offering valuable information that could significantly shape the future of the sustainable management and maintenance of this critical navigational route.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.I.C. and M.V.S.; methodology, M.I.C. and M.V.S.; software, M.V.S. and D.S.; validation, M.I.C., A.B. and C.Ș.D.; formal analysis, R.S., A.B. and C.Ș.D.; investigation A.M. and R.S.; resources, M.V.S.; data curation, A.M. and R.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.I.C. and A.B.; writing—review and editing, A.B. and C.Ș.D.; visualization, D.S.; supervision, A.B.; project administration, M.I.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lebour, G. 1. On the deposits now forming in British seas. Proc. Geolog. Assoc. 1875, 4, 158–164. Available online: https://eurekamag.com/research/080/857/080857833.php (accessed on 19 July 2024). [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sediment Transport under Waves and Currents. 1985. Available online: https://eprints.hrwallingford.com/66/1/SR22.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Bijker, E.W. Some Considerations about Scales for Coastal Models with Moveable Beds; Delft Hydraulics Laboratory Publisher: Delft, The Netherlands, 1967; Volume 50, Available online: https://repository.tudelft.nl/record/uuid:cdf2f061-3fe6-4361-a0e7-636fc69c9eca (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Slingerland, R.L. Numerical models and simulation of sediment transport and deposition. In Sedimentology. Encyclopedia of Earth Science; Finkl, C.H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 775–783. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.G.; Yu, C.; Ding, Y. Numerical Simulation of Sediment Transport in Unsteady Open Channel Flow. Water 2023, 15, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerihun, Y.T. Numerical Modeling of Sediment Transport and Bed Evolution in Nonuniform Open-Channel Flows. Arch. Hydro-Eng. Environ. Mech. 2024, 71, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmakova, M. Sediment Transport in River Flows: New Approaches and Formulas. In Modeling of Sediment Transport; Pasquali, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/81410 (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Popescu, C.; Bărbulescu, A. On the Flash Flood Susceptibility and Accessibility in the Vărbilău Catchment (Romania). Rom. J. Phys. 2022, 67, 811. [Google Scholar]
- Crăciun, A.; Costache, R.; Bărbulescu, A.; Pal, S.C.; Costache, I.; Dumitriu, C.Ș. Modern Techniques for Flood Susceptibility Estimation across the Deltaic Region (Danube Delta) from the Black Sea’s Romanian Sector. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parchure, T.M.; Davis, J.E.; McAdory, R.T. Modeling fine sediment resuspension due to vessel passage. Proc. Mar. Sci. 2007, 8, 449–464. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, M.; Sriram, V.; Murali, K. Investigation of ship-induced hydrodynamics and sediment resuspension in a restricted water-way. Appl. Ocean Resear. 2024, 142, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoschek, O.; Precht, E.; Larsen, O.; Jain, M.; Yde, L.; Ohle, N.; Strotmann, T. Sediment Resuspension and Seabed Scour Induced by Ship-Propeller Wash. Available online: https://www.dhigroup.com/upload/publications/coastsea/Stoschek_2014.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Guarnieri, A.; Saremi, S.; Pedroncini, A.; Jensen, J.H.; Torretta, S.; Vaccari, M.; Vincenzi, C. Effects of marine traffic on sediment erosion and accumulation in ports: A new model-based methodology. Ocean Sci. 2021, 17, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srše, J.; Perkovič, M.; Grm, A. Sediment Resuspension Distribution Modelling Using a Ship Handling Simulation along with the MIKE 3 Application. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoolder, B. Influence of Inland Shipping on Sediment Transport in the Waal River. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2023. Available online: https://essay.utwente.nl/97135/ (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Ji, S.C.; Ouahsine, A.; Smaoui, H.; Sergent, P.; Jing, G.Q. Impacts of ship movement on the sediment transport in shipping channel. J. Hydrodyn. Ser. B 2014, 26, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConchie, J.A.; Toleman, I.E.J. Boat wakes as a cause of riverbank erosion: A case study from the Waikato River. J. Hydrol. 2003, 42, 163–179. [Google Scholar]
- Budileanu, M. Evolution of Sulina Mouth Bar (Danube River) Evolution of Sulina Mouth Bar (Danube River). Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309427460_Evolution_of_Sulina_mouth_bar_Danube_river (accessed on 23 July 2024).
- Mateescu, R.; Ivan, A.; Omer, I.; Butunoiu, D.; Niculescu, D. Aspects of the coastal hydro-geomorphological processes at the Danube river mouths. Ann. Univ. Dunarea De Jos Galati Fascicle II Math. Phys. Theor. Mech. 2013, 2, 316–322. [Google Scholar]
- Boșneagu, R.; Scurtu, I.C.; Popov, P.; Mateescu, R.; Dumitrache, L.; Mihailov, M.E. Hydraulics numerical simulations using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method for the mouth of Sulina channel. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2019, 20, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Bondar, C. On a mathematical model of simulating the hydraulic process of bars’ formation at the Danube River mouths. Sci. Ann. “Danube Delta” Instit. 2018, 23, 3–12. Available online: https://www.ddniscientificannals.ro/images//23_01.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Constantinescu, A.C.; Pindic, P.; Bănescu, A.; Anore, C. Flooding Hazard and Risk Maps for Localities along Sulina and Sf. Gheorghe branches. Sci. Ann. Danube Delta Instit. 2019, 24, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- Stănică, A.; Dan, S.; Ungureanu, V.G. Coastal changes at the Sulina mouth of the Danube River as a result of human activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2007, 55, 555–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrache, L.; Popov, P. The Port of Sulina. Eastern European Seagate—Past and Present. Available online: https://tulcealibrary.ro/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/The-Port-of-Sulina-Past-and-Present-Dumitrache-L.-Popov-P..pdf (accessed on 8 August 2024).
- Răileanu, A.B.; Rusu, L.; Marcu, A.; Rusu, E. The Expected Dynamics for the Extreme Wind and Wave Conditions at the Mouths of the Danube River in Connection with the Navigation Hazards. Inventions 2024, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, A.S.; Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, E. Influence of the interactions between waves and currents on the navigation at the entrance of the Danube Delta. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2012, 13, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Bărbulescu, A.; Dumitriu, C.S.; Dragomir, F. Detecting Aberrant Values and Their Influence on the Time Series Forecast. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Mauritius, Mauritius, 7–8 October 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărbulescu, A.; Dumitriu, C.S.; Maftei, C. On the Probable Maximum Precipitation Method. Rom. J. Phys. 2022, 67, 801. [Google Scholar]
- Bărbulescu, A.; Maftei, C.E. Evaluating the Probable Maximum Precipitation. Case study from the Dobrogea region, Romania. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2023, 75, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirosca, G.; Mihailov, M.E.; Tomescu-Chivu, M.I.; Chirosca, A.V. Enhanced Machine Learning Model For Meteo-Oceanographic Time-Series Prediction. Rom. J. Phys. 2022, 67, 815. [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, M. Climatic Risk Phenomena in Dobrogea; Editura Universitara: Bucharest, Romania, 2010. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Lungu, M. Dobrogea Climate Resources; Editura Universitara: Bucharest, Romania, 2010. (In Romanian) [Google Scholar]
- Nitu, O.A.; Ivan, E.S.; Nitu, D.S. Climate change and its impact on water consumption in the main agricultural crops of the Romanian Plain and Dobrogea. Sci. Papers. Ser. A Agron. 2023, 66, 474–478. [Google Scholar]
- Komen, G.J.; Cavaleri, L.; Donelan, M.; Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S.; Janssen, P.A.E.M. Dynamics and Modelling of Ocean Waves; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Young, I.R. Wind Generated Ocean Waves; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Coastal Engineering Manual Part VI: Design of Coastal Project Elements, US Army Corps of Engineers. 2002. Available online: https://www.publications.usace.army.mil/Portals/76/Publications/EngineerManuals/EM_1110-2-1100_Part-06.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Shore Protection Manual, Part II, USACE, US Army Corps of Engineers. 1984. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/37917948/SHORE_PROTECTION_MANUAL (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- EurOtop. Manual on Wave Overtopping of Sea Defence and Related Structures. Available online: http://www.overtopping-manual.com/ (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Fredsoe, J. Turbulent Boundary Layer in Wave-current Motion. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 100, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelund, F.; Fredsoe, J. A sediment Transport Model for Straight Alluvial Channels. Nord. Hydrol. 1976, 7, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredsoe, J.; Anderse, O.A.; Silberg, S. Distribution of Suspended Sediment in Large Waves. J. Waterw. Port C Div. 1985, 111, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.J.; Hayter, E.J.; Parker, W.R.; Krone, R.B.; Teeter, A.M. Cohesive Sediment Transport. I: Process Description. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1989, 115, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, R. On the flow of water in open channels and pipes. chez Trans. Inst. Civ. Eng. Irel. 1891, 20, 161–207. [Google Scholar]
- Manning’s n (Roughness Coefficient) for HEC-RAS 2D Modeling. 2021. Available online: https://rashms.com/blog/mannings-n-roughness-coefficient-for-hec-ras-2d-modeling/ (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Engelund, F.; Hansen, E. A Monograph on Sediment Transport in Alluvial Stream; Teknisk Forlag: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1967. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).