Abstract
The sustainable development of arid regions is significantly constrained by the availability of water resources, which play a crucial role in this context. It is necessary to deeply investigate and analyze the hydrochemical characteristics and major ion sources. This study, which was based on data from 183 water samples collected from the Jinghe River Basin, provided a comprehensive analysis of the river water hydrochemistry. The results show that the average TDSs (total dissolved solids) was measured at 49.8 mg·L−1. HCO3− (82.4%) and Ca2+ (77.1%) were the ions present in the highest abundances. The river water was classified as the HCO3−-Ca2+ hydrochemical type. The Gibbs diagrams indicated that the ion composition was primarily influenced by rock weathering. Additionally, the Na-normalized molar ratio diagrams suggested that the chemical composition was primarily governed by the weathering and dissolution of silicate rocks, while the carbonate rock dissolution played a lesser role. This study demonstrates a critical aspect of water resources quality evaluation, which is of great significance for the sustainable development, utilization and environmental protection of regional water resources.
1. Introduction
In modern society, water resources have a significant impact on the development of agriculture, industry and even human society [1,2]. Lake water constitutes a significant component of the water resources in arid regions, where it helps to maintain the balance of the regional ecosystem. These lakes are key to sustainable social development and ecological environment protection [3,4,5]. There are a large number of saline lakes in the arid and semi-arid western region of China, where freshwater lakes constitute only a minor fraction of the total. For example, freshwater reserves account for just 16.6% and 3.2% of the total lake water in the Tibetan Plateau and the Mongolia–Xinjiang Plateau, respectively [6]. Hence, saline lakes occupy a significant position in the water cycle in these regions, where water resources are extremely limited [7,8]. Water is considered the most valuable natural resource in Northwestern China, particularly in Xinjiang.
Lakes in arid zones are particularly affected by human activities. Large-scale land and water resource development has led to the significant interception of surface and groundwater in the middle reaches of river basins, which drastically reduces the water flow to terminal lakes in Northwest China [9,10]. The arid climate, which is marked by limited precipitation and strong evaporation, further accelerates the reduction in lake runoff. As a result, many lakes have shrunk, become saline or dried up entirely [11,12,13,14]. The shrinking or disappearance of the terminal lakes in fragile ecosystems poses a severe threat to these environments located in arid regions and the fragile ecosystems within them [6,15,16].
Studies showed that the lakes in northwest China experienced rapid shrinkage and intensified salinization in recent decades due to unreasonable factors in the utilization of water resources, as well as the combined effects of climate change and human activities. These factors have weakened the adjustment function of lakes to the regional ecological environment and have degraded the ecological environment of lakes and surrounding areas [17]. Significant changes have occurred in the regional eco-hydrological processes due to alterations in climate and human activities [18,19]. These changes may result in severe water shortages in arid areas and can cause irreversible environmental impacts on ecosystems [20,21]. Hydrochemical changes in the upper watershed have impacted the surface water chemistry, which, in turn, has affected the water resource availability and the quality of the surrounding ecosystem. In the Ebinur Lake Basin, these ecological and environmental issues have raised concerns over water resource availability and quality. With the national implementation of the Western Development Strategy, balancing the use of regional water resources with lake and environmental protection has become a pressing issue [8].
The ionic composition and chemical characteristics of natural water bodies are a reflection of long-term interactions with the surrounding environment during the water cycle. The transformation process of different water bodies is accompanied by the exchange of solutes in water. Therefore, the chemical composition of natural water serves as a record of the history of water formation and migration. Rivers, as an active and very important part of the global water cycle, play a crucial role in the geochemical cycling of elements [22,23]. The chemical composition of river water largely indicates the environmental quality of the water body and reflects the regional environmental characteristics, as well as the distribution and migration of elements [24,25]. Its hydrochemical content and distribution characteristics can reflect the influence of atmospheric precipitation, rock differentiation, human activities and other factors in the region, which provide indirect judgements on the source, migration and transformation of materials in the river water, as well as the relationship with regional natural conditions [26]. The study of the regional water chemistry constitutes a core component of water resources quality evaluation and holds immense significance for the development, utilization and environmental protection of regional water resources. Analyzing the characteristics and controlling factors of the chemical ion composition in river water is of great significance for deeply comprehending the recharge relationship between surface water and groundwater, as well as identifying the sources of river water at the catchment scale [27,28].
The Ebinur Lake, which is situated in northern Xinjiang, China, is the terminal lake of the Ebinur Lake Basin. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological security of the watershed, as well as the ecological environment protection of Xinjiang [29]. Over the past 50 years, the large-scale human exploitation of land and water resources, particularly through river irrigation in the mid-lower reaches, has severed many rivers’ surface water connections to the Ebinur Lake. Therefore, only the surface water of the Bortala River and Jinghe River can flow into the Ebinur Lake at present. The area of the Ebinur Lake has shrunk from 1200 km2 in the 1950s to approximately 500 km2 today due to the drastic reduction in the water volume [30,31]. As the lake has shrunk, large areas of saline–alkali sand and dust has been exposed, which causes severe sandstorm hazards that threaten the Eurasian Continental Bridge and Wuyi Road. Desertification has caused major environmental disasters, which result in wind and sand erosion that affect the economic zones on the northern slopes of the Tianshan Mountains and the Hexi Corridor. These issues directly impact the long-term development of the northern Tianshan Economic Belt and the safe operation of the New Eurasian Continental Bridge [32,33]. This study primarily focused on investigating the hydrochemical characteristics of the main ions and the influencing factors in the surface water of the Jinghe River within the Ebinur Lake Basin. Attempts were made to explore the causes of water chemistry by providing a scientific foundation for the watershed water resources evaluation, management and ecological environment. The objective of this study was to provide improvements to the knowledge and comprehension of the hydrochemical characteristics and factors that affect the runoff into inland lakes in arid areas. This study aimed to provide the scientific foundation for the prevention and control of salinization, desertification, salt dust storms and other environmental challenges in arid areas. Conducting fundamental research on surface water chemistry and its influencing factors in the Ebinur Lake Basin is essential for understanding the water chemistry and evaluating the water resource availability in the region.
In summary, this study focused on analyzing the water quality and hydrochemical characteristics of the Jinghe River Basin, which is located in the Ebinur Lake Basin, Xinjiang, China. This study evaluated different water sources in the region, including the river water, glacier meltwater and snow water, and investigated the physicochemical properties and ion concentrations of these water bodies to understand the factors that control the water chemistry in the area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
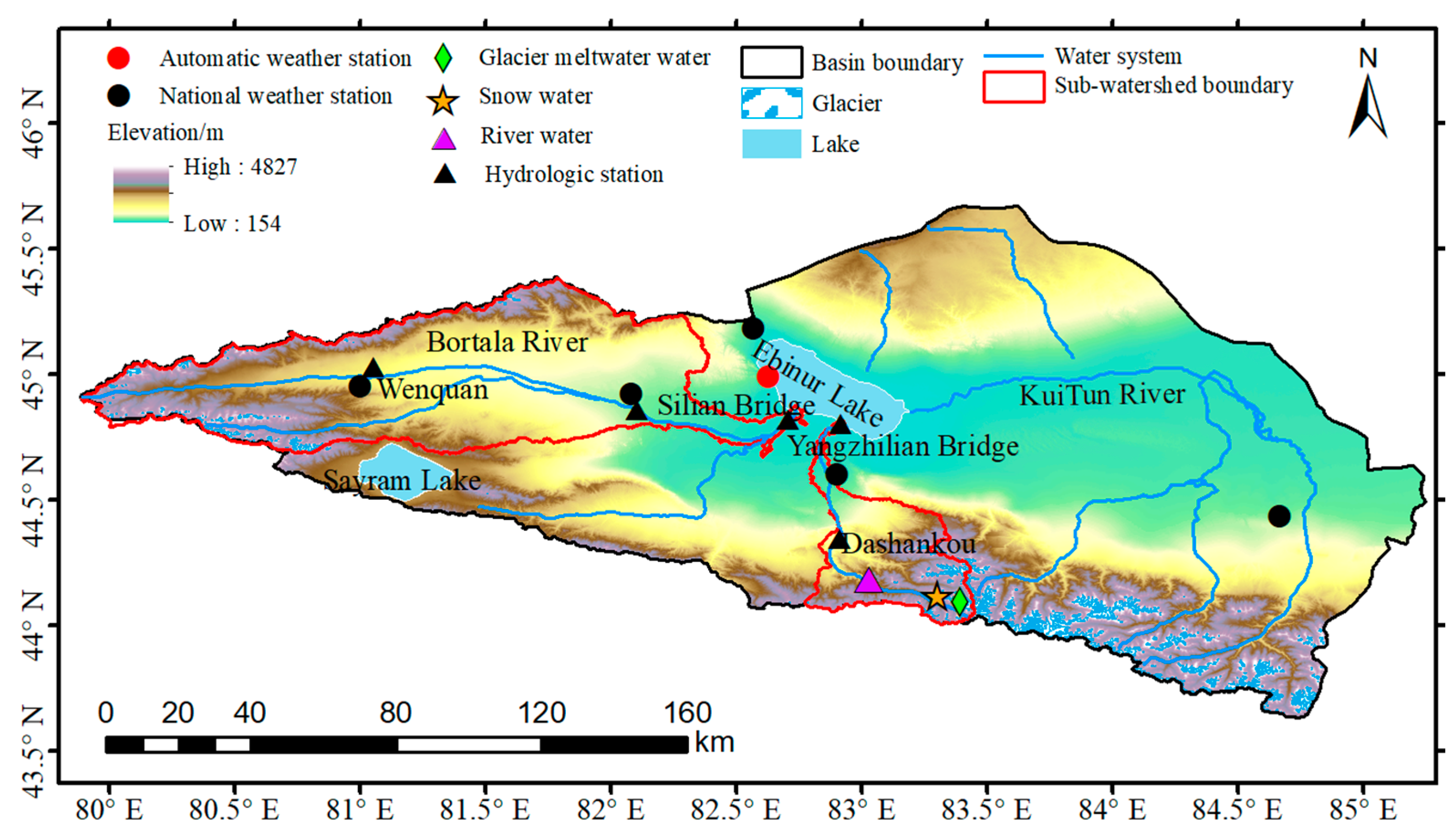
The Ebinur Lake Basin (43°38′–45°52′ N, 79°53′–85°02′ E) is located in the Bortala Mongol Autonomous Prefecture, Xinjiang Province, China (Figure 1). It is encircled by mountains to the north, south and west, and connected with the Junggar Basin to the east, with an altitude of 154 to 4827 m [33]. The study area has a temperate continental drought climate regime, with a mean annual temperature of 8.0 °C, mean annual precipitation of 89.9 to 169.7 mm and mean annual evaporation of 1569 to 3421 mm. The Ebinur Lake Basin is drained by several main rivers, including the Bortala River, the Jinghe River, the Kuitun River and the Aksu River. The Ebinur Lake stands out as the largest saltwater lake in Xinjiang, where it covers an area of 542 km2. During the last 20 years, the area of farmland irrigation in the alluvial plain of each river has been continuously expanding, and the utilization of water and soil resources has been increasing, in which the Kuitun River with the largest water volume and the longest process has been completely cut off. The Aksu River is also depleted due to evaporation, infiltration and irrigation during the flow to the Ebinur Lake. At present, the Ebinur Lake is only recharged by the Bortala River and the Jinghe River, with drainage areas of 11,376 km2 and 2150 km2, respectively. The Jinghe River, which is one of the rivers entering the lake, was selected for this study. Because of the cooperation with the hydrological station, the temporal continuity of the samples could be guaranteed. Different water samples were collected from the Jinghe River Basin (43°35′–45°93′ N, 81°08′–83°06′ E). The overall length of the river is 114 km, where it flows into the Ebinur Lake from south to north, with an average annual runoff of 4.76 × 108 m3. The average annual temperature is 7.3 °C and the average annual precipitation is 91 mm.
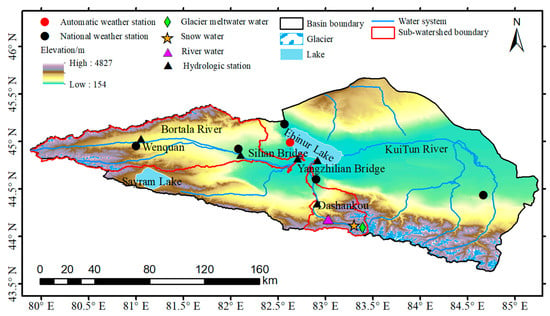
Figure 1.
The river water, snow water and glacier meltwater sample sites in the Jinghe River Basin.
2.2. Collection and Analyses of Samples
A total of 183 samples of different water bodies were collected from June to August 2020 from the mainstream of the Jing River. This included 157 river water samples, 12 glacial meltwater samples and 14 snow water samples. The locations of the sampling points, along with their related information, are displayed in Figure 1. Samples of stream water were taken from live, naturally flowing water. The polyethylene bottles were rinsed three times with sample water before each collection and then packed into polyethylene containers. River water samples were collected approximately three times a week along the mainstream channel known as the Jing River. This sampling frequency ensured that the samples were comprehensive and representative in time. Each sampling included three periods of the day, that is, 8:00 a.m., 2:00 p.m. and 8:00 p.m. The snow samples were collected with fresh snow that had fallen on the surface and was used to represent the water chemistry of the snowfall. Snow samples were collected by first removing the contaminated portion of the fresh snow surface, then the portion away from the surface was collected while wearing disposable polyethylene gloves at all times. Glacier meltwater and snow sampling were conducted once a week because of restricted access. All water samples were immediately sealed after the collection and transported to the State Key Laboratory of Cryosphere Science at the Northwest Institute of Ecological and Environmental Resources, Chinese Academy of Sciences, where they were cryopreserved until the analytical processing.
For the purpose of the major element analyses, all samples underwent filtration through a 0.45 μm Millipore membrane. Hydrochemical characteristic values, such as the total dissolved solids (TDSs), electrical conductivity (EC), pH and major ion concentrations, were analyzed for all the samples. The TDSs and EC were determined by a conductivity meter model DDSJ-308A with an error of ±0.5%. The pH was measured by a Raycom PHS-3E pH meter with an accuracy of ±0.01. The cationic concentrations (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ and K+) and the anion concentrations (Cl−, SO42−, NO3−) were analyzed using a DX-600 and ICS-2500 ion chromatograph from the Dionex company (Sunnyvale, CA, USA), respectively. The data result for each sample represented the average of two consecutive measurements. The analytical precision was less than 1%, and the detection limit for all major ions was less than 0.1 mg L−1. The concentration of CO32− was inversely proportional to the concentration of H+, which could be neglected when the pH was less than 8.3. The concentration of HCO3− was calculated by ionic equilibrium, i.e., the total cation charge was equal to the total anion charge of the solute in water. The correlation analysis between the measured and calculated TDS values revealed a correlation coefficient of 0.86, which successfully achieved significance at the 0.01 level in the test, which indicates that the data quality was relatively reliable.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Various Water Types
The water quality and environmental properties of the river water are demonstrated by its chemical characteristics [34,35]. The water temperature, TDSs, pH, EC, and concentrations of major ions in the river water, glacier meltwater, and snow water were measured, and all of these indicator values represented the basic hydrochemical properties and characteristics of different bodies of water. The physicochemical parameters (TDSs, EC, pH and T) and the major ion concentrations of the investigated different water samples are presented in Table 1. The TDSs of the river water varied from 20.8 to 60.1 mg·L−1, with an average of 49.8 mg·L−1. The mean of the TDSs for glacier meltwater and snow water were 19.6 and 13.7 mg·L−1, respectively. The TDSs of different water bodies in descending order were river water, glacier meltwater and snow water. The EC of the river water varied from 39.5 μs·cm−1 to 117.8 μs·cm−1, with an average of 94.3 μs·cm−1. The average EC for the glacier meltwater and snow water were 37.3 μs·cm−1 and 26.1 μs·cm−1, respectively. The pH values of the river water ranged between 7.1 and 8.2, with an average of 7.7. The mean pH values for the glacier meltwater and snow water were 7.8 and 7.2, respectively. Therefore, we can see that the different water bodies in the study area were weakly alkaline.

Table 1.
Hydrochemical characteristic values of river water, glacier meltwater and snow water from June to August 2020 in Jinghe River Basin.
3.2. Hydrochemical Composition and Types of Different Water
The average concentrations of the cations Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ and K+ in the river water were 17.40 mg·L−1, 2.29 mg·L−1, 1.41 mg·L−1 and 1.39 mg·L−1, respectively, and they decreased in this order. The average concentrations of the anions HCO3−, SO42−, NO3− and Cl− in the river water were 22.63 mg·L−1, 3.34 mg·L−1, 0.96 mg·L−1 and 0.34 mg·L−1, and decreased in turn. The orders of the cation and anion concentrations in the glacial meltwater were the same as those in the river water and the ion concentration was smaller than that in river water. The average concentrations of Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ and K+ in the glacier meltwater were 5.40 mg·L−1, 1.15 mg·L−1, 0.44 mg·L−1 and 0.99 mg·L−1, respectively. The average concentrations of HCO3−, SO42−, NO3− and Cl− in the glacial meltwater were 9.64 mg·L−1, 0.97 mg·L−1, 0.75 mg·L−1 and 0.27 mg·L−1, respectively. The orders of the cation and anion concentrations in the snow water were the same as those in the river water and glacier meltwater and the ion concentration was the smallest among the three different water bodies. The average concentrations of Ca2+, Na+, Mg2+ and K+ in the snow water were 1.40 mg·L−1, 1.27 mg·L−1, 0.11 mg·L−1 and 0.32 mg·L−1, respectively. The average concentrations of HCO3−, SO42−, NO3− and Cl− in the snow water were 9.06 mg·L−1, 0.51 mg·L−1, 0.62 mg·L−1 and 0.43 mg·L−1, respectively.
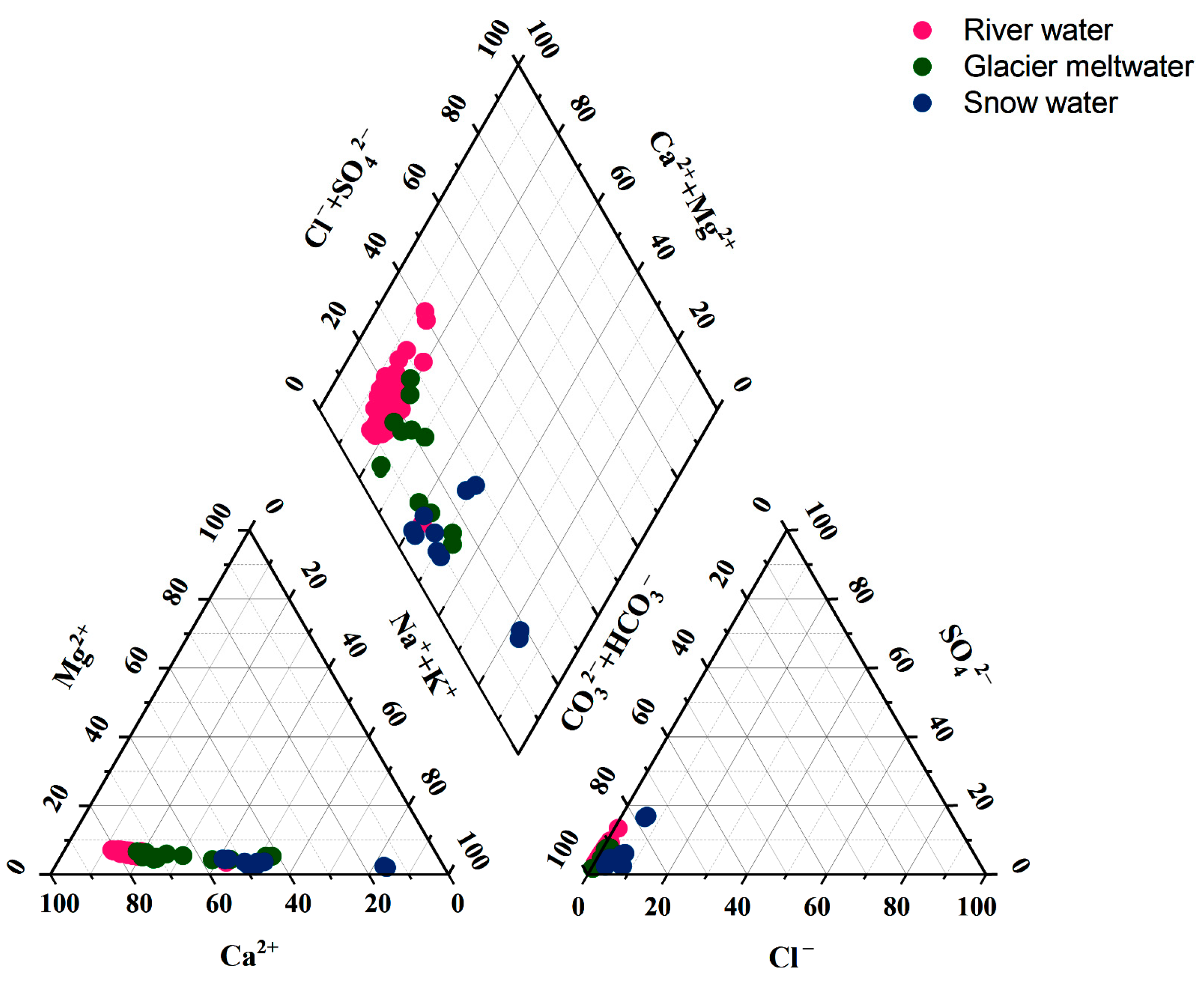
In order to determine the characteristics of the hydrochemical composition, this study used the Piper trilinear plot to determine its hydrochemical type. The milligram equivalents of the major cations and anions were calculated so that ions with milligram equivalents greater than 25% were involved in the classification of the water type [36]. As exhibited in Figure 2, the anions of the river water, glacial meltwater and snow water were close to the HCO3− endmembers. Therefore, HCO3− was the principal anion in all the water samples. There was a difference in the distribution of cations in different water types. The cations in the river water were skewed toward the Ca2+ endmembers, with an equivalent concentration of 77.1% of the mean value of total cations. Therefore, the hydrochemical type of the river water was HCO3−-Ca2+. Anion and cation triangles can represent the relative abundance and distribution characteristics of major ions in the solute load of river water, thus revealing the relative contribution of different rock weathering to the total solute composition of the river water. When the anionic component is mostly located on the HCO3− side and the cationic component is mostly located on the Ca2+ side, this indicates that it is mainly affected by carbonate rock weathering [37,38,39]. This result is consistent with that obtained from the Gibbs model below. The glacial meltwater samples tended to be biased toward the Na+ + K+ axis, with Ca2+ and Na+ + K+ accounting for 63.49% and 31.21% of the total cations. The hydrochemistry type of the glacier meltwater was HCO3−-Ca2+·Na+·K+. The cations of snow water samples were skewed toward the Na+ + K+ endmembers, with Na+ + K+ and Ca2+ accounting for 53.91% and 42.71% of the total cations. The hydrochemistry type of the snow water was HCO3−-Na+·K+·Ca2+.
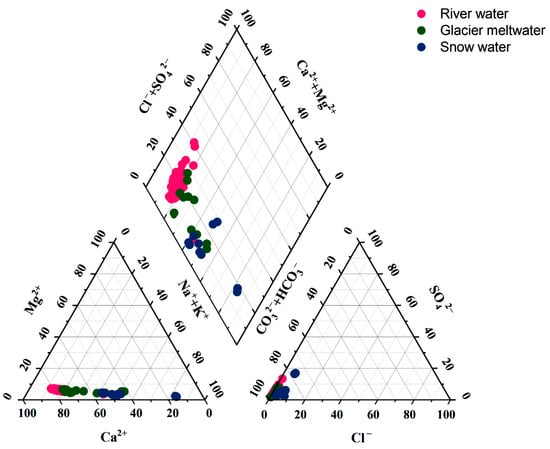
Figure 2.
Piper diagram of anions and cations in river water, glacier meltwater and snow water of Jinghe River Basin.
3.3. Temporal Variation Characteristic of Major Ions
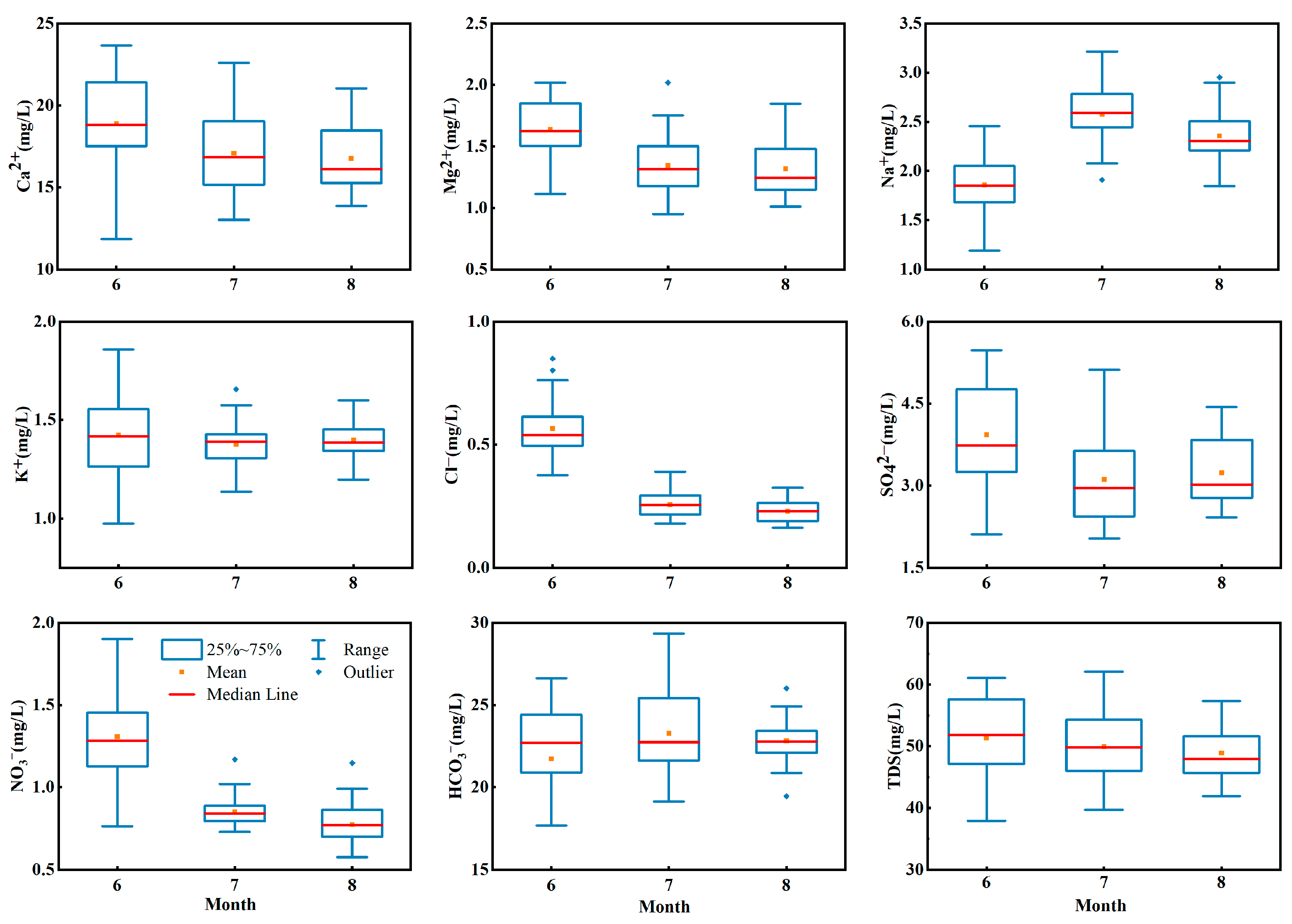
The temporal variation in the ionic concentrations and TDSs in the stream water are shown in the box plot in Figure 3. The concentration of Ca2+ varied from 23.67 mg·L−1 to 11.84 mg·L−1 in summer. The mean concentration of Ca2+ decreased gradually from June to August in summer. The mean concentration of Ca2+ was 18.88 mg·L−1 in June, which was 1.13 times that in August. The median concentration of Ca2+ showed the same trend and decreased in summer. For example, the median concentration of Ca2+ was 18.81 mg·L−1 in June, which was 1.16 times that in August. The averages and medians of Mg2+, Cl−, NO3− and TDSs showed the same trends as that of Ca2+. The concentration of Cl− varied from 1.0 mg·L−1 to 0.16 mg·L−1 in summer. The average Cl− concentrations in June, July and August were 0.57 mg·L−1, 0.26 mg·L−1 and 0.22 mg·L−1, respectively. The median concentration of Cl− in June was 0.53 mg·L−1, which was 2.11 times and 2.34 times higher than that in July and August, respectively. It can be seen that the average and median concentrations of Cl− decreased gradually from June to August. The average and median concentrations of Na+ and HCO3− increased first and then decreased, which were different from the variation trend of the ions mentioned above. Taking Na+ as an example, the average concentration in June was 1.86 mg·L−1, which increased to 2.60 mg·L−1 in July and then decreased to 2.32 mg·L−1 in August. Meanwhile, K+ and SO42− showed trends of decreasing first and then increasing. For example, the mean concentration of SO42− was 3.93 mg·L−1 in June, which decreased to 3.12 mg·L−1 in July and then increased to 3.24 mg·L−1 in August. The changes in the ion concentrations were related to the runoff changes, and they also had a connection to the alterations in the recharge rate of glacial meltwater, groundwater and precipitation to runoff at different times.
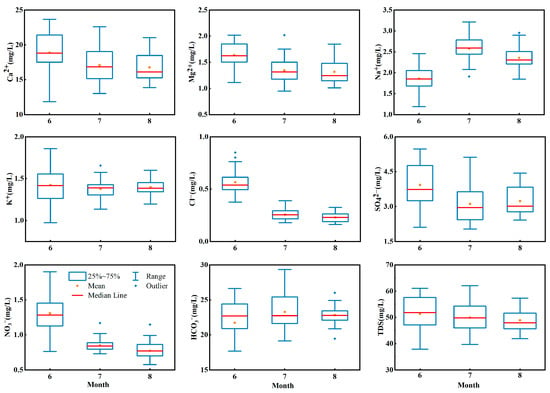
Figure 3.
Temporal variations in major ion concentrations and TDSs in river water of Jinghe River Basin.
3.4. Correlation and PCA Analysis of Major Ions
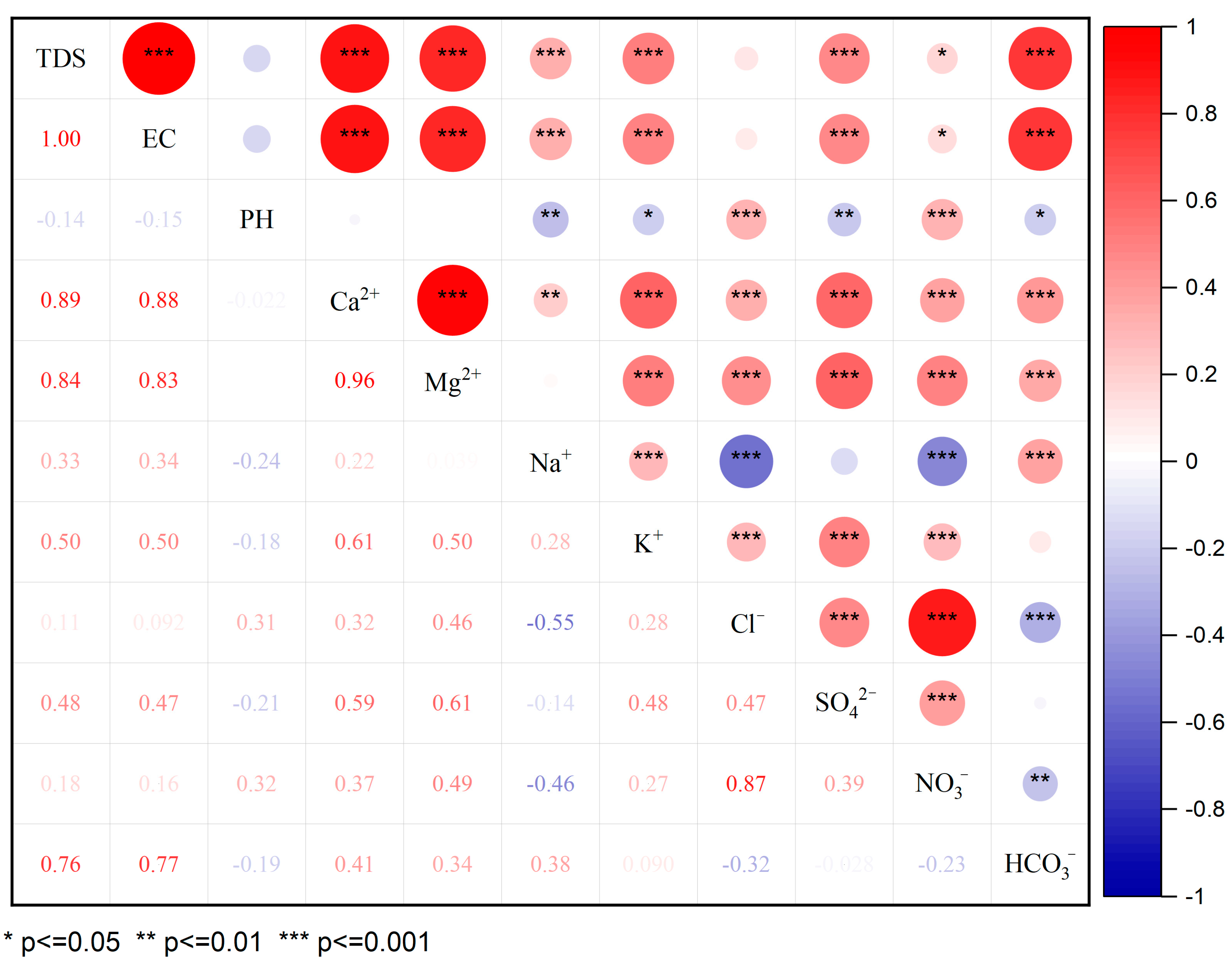
The results of the Pearson correlation analysis are presented in Figure 4. The results show that the TDSs were significantly correlated with Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ and HCO3−, and the coefficients were all greater than 0.5, which indicates that these ions were the main factors that caused the changes in the TDSs. SO42− had a significant correlation with Ca2+ and Mg2+. It was also strongly correlated with other ions, such as K+ and Cl−. The high correlations between SO42− and the anthropogenic input ions K+ and Cl− suggest that they may have originated from the same source. SO42− originates from human activities and the dissolution of sulfide oxidation, such as pyrite. Figure 4 shows that the correlation between NO3− and Cl− was as high as 0.87. Cl− is widely present in the natural environment, which derives from domestic sewage, human and animal waste, industrial waste and other man-made pollution sources. It also includes natural sources, such as mineral deposits and seawater intrusion. The ratio of nitrate to chloride ion concentrations is often applied to determine the source of NO3−. This method is divided into three cases. A high concentration of Cl− and a low ratio of nitrate to chloride ion concentration means that the NO3− in the water comes from feces and domestic sewage. A low concentration of Cl− and a high ratio of nitrate to the chloride ion concentration means that the NO3− in the water was affected by agricultural activities. A low concentration of Cl− and a low ratio of nitrate to the chloride ion concentration means that the NO3− in the water was derived from the soil. Based on the observed values of the samples, nitrate ions in most water samples were affected by agricultural activities, and a few samples had nitrate ions that originated from nitrogen in the soil [40].
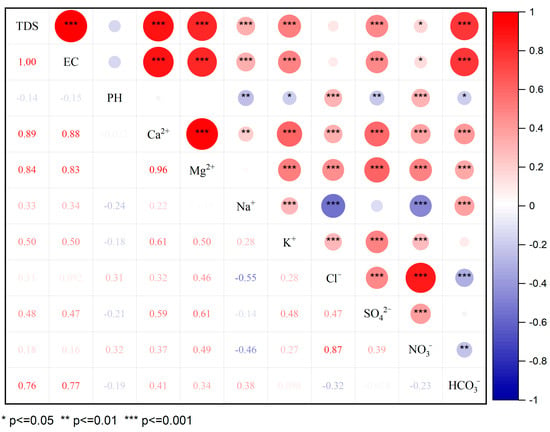
Figure 4.
Spearman’s correlations for the major ions in the river water of Jinghe River Basin and other parameters.
The principal component analysis (PCA) method can simplify multiple ion concentration variables in a water body into a few principal components that reflect the main characteristics of the original ion concentrations while reducing the data dimensionality for subsequent analysis [41,42]. This study carried out a PCA to identify the sources of the major ions in the Jing River Basin (Table 2). For the Jing River, three principal components with eigenvalues above 1 were reserved, which could explain 82.58% of the total variance. PC1, with the most variance (45.75%) in the hydrochemical characteristic, was affected by the positive loadings of Ca2+ (0.69), Na+ (0.51) and SO42− (0.52). In PC2, there were strong positive loading values in the river water from K+ (0.58) and Mg2+ (0.51). HCO3− (0.66) held a high loading in PC3, where it explained 10.61% of the variance.

Table 2.
Principal component analysis (PCA) of water quality parameters in river water.
3.5. Sources and Controlling Factors of the Major Ions
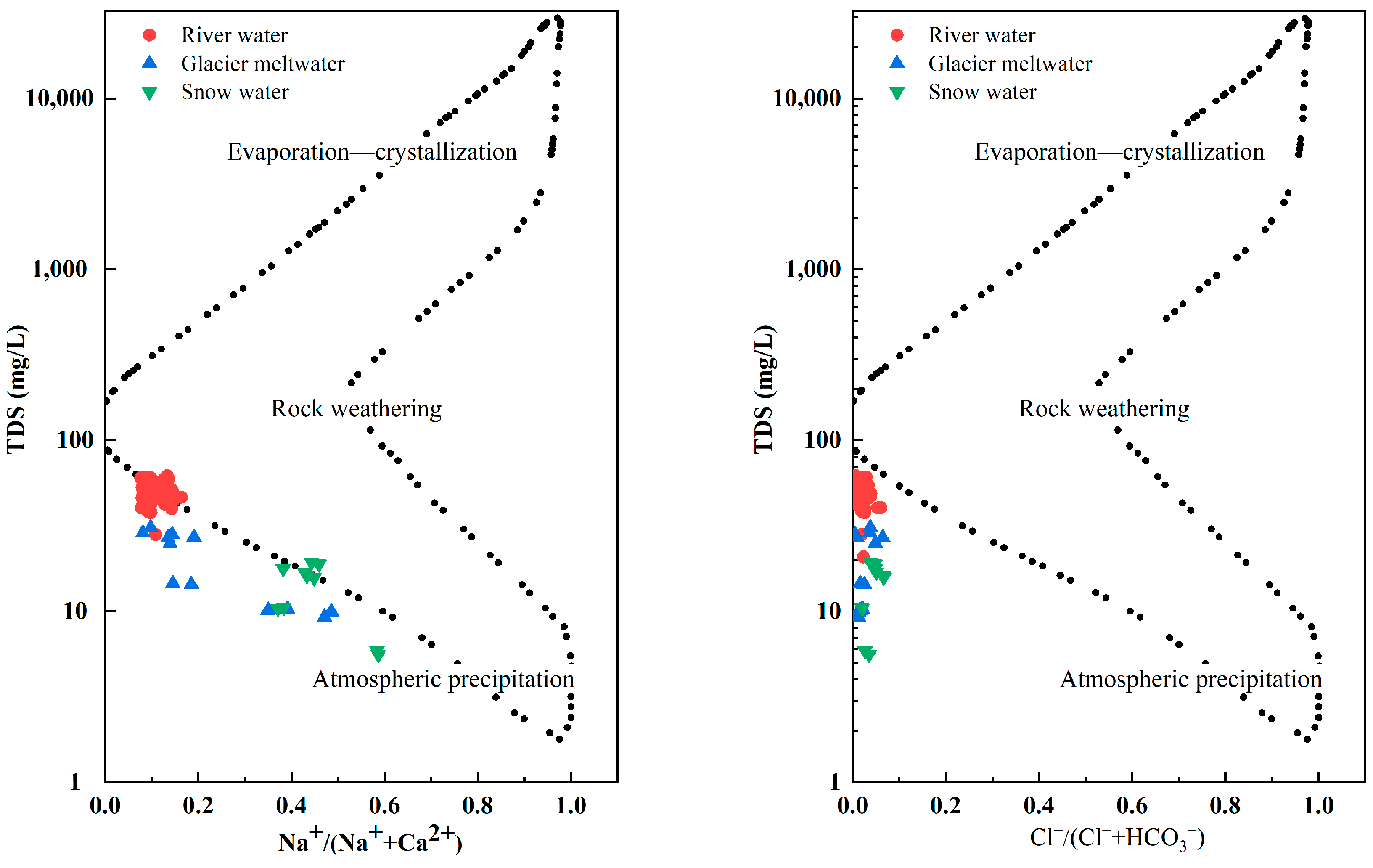
Gibbs diagrams are an important means of qualitatively determining the effects of regional rocks, atmospheric precipitation and evaporation–crystallization on river water chemistry. The Gibbs diagram was employed for a qualitative analysis of the origins of the chemical components in the water, in which the vertical coordinates represent total dissolved solids in the river water in logarithmic values and the horizontal coordinates represent the ratio of Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) or Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) in arithmetic values [43]. The water chemistry data of the river water described in this paper is plotted on a Gibbs diagram (Figure 5). The fact that the hydrochemical composition of the river water samples in the study area all fell within the Gibbs distribution model suggests a minimal impact from human activities on the river water in this region. The figure exhibits that the data points of the river water samples in the study area fell in the middle and were skewed to the left of the distribution model. Most of the river water samples had TDS values in the range of 10~100 mg·L−1. The averages of the Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) ratios were 0.12 and 0.02, respectively. The significant distance between the hydrochemical data of the river water samples and both the evaporation crystallization zone and the atmospheric precipitation zone suggests that the hydrochemical composition of the river water samples in the study area were primarily influenced by rock weathering. The average Cl−/Na+ ratio was 1.16, which slightly exceeded the world average seawater ratio of Cl−/Na+ = 1.15. This indicates that the sea salt carried by the atmospheric circulation had a certain influence on the ion composition of the river water in the Ebinur Lake Basin, which was also the reason for the slightly higher content of Na+ and Cl− in the river water samples in the research area. Furthermore, the ratios of Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) of the snow water were 0.45 and 0.04. The ratios of Na+/(Na+ + Ca2+) and Cl−/(Cl− + HCO3−) of the glacier meltwater were 0.23 and 0.03. This shows that the snow water and glacier meltwater were controlled by rock weathering and atmospheric precipitation.
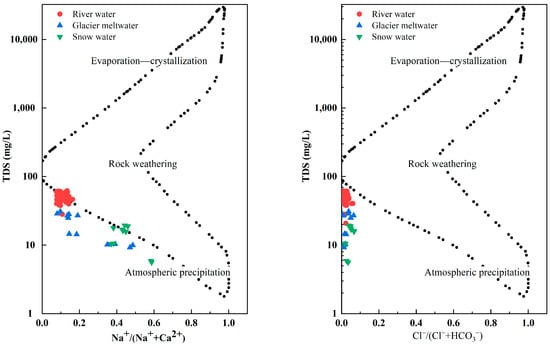
Figure 5.
Gibbs plots of river water, snow water and glacier meltwater in Jinghe River Basin.
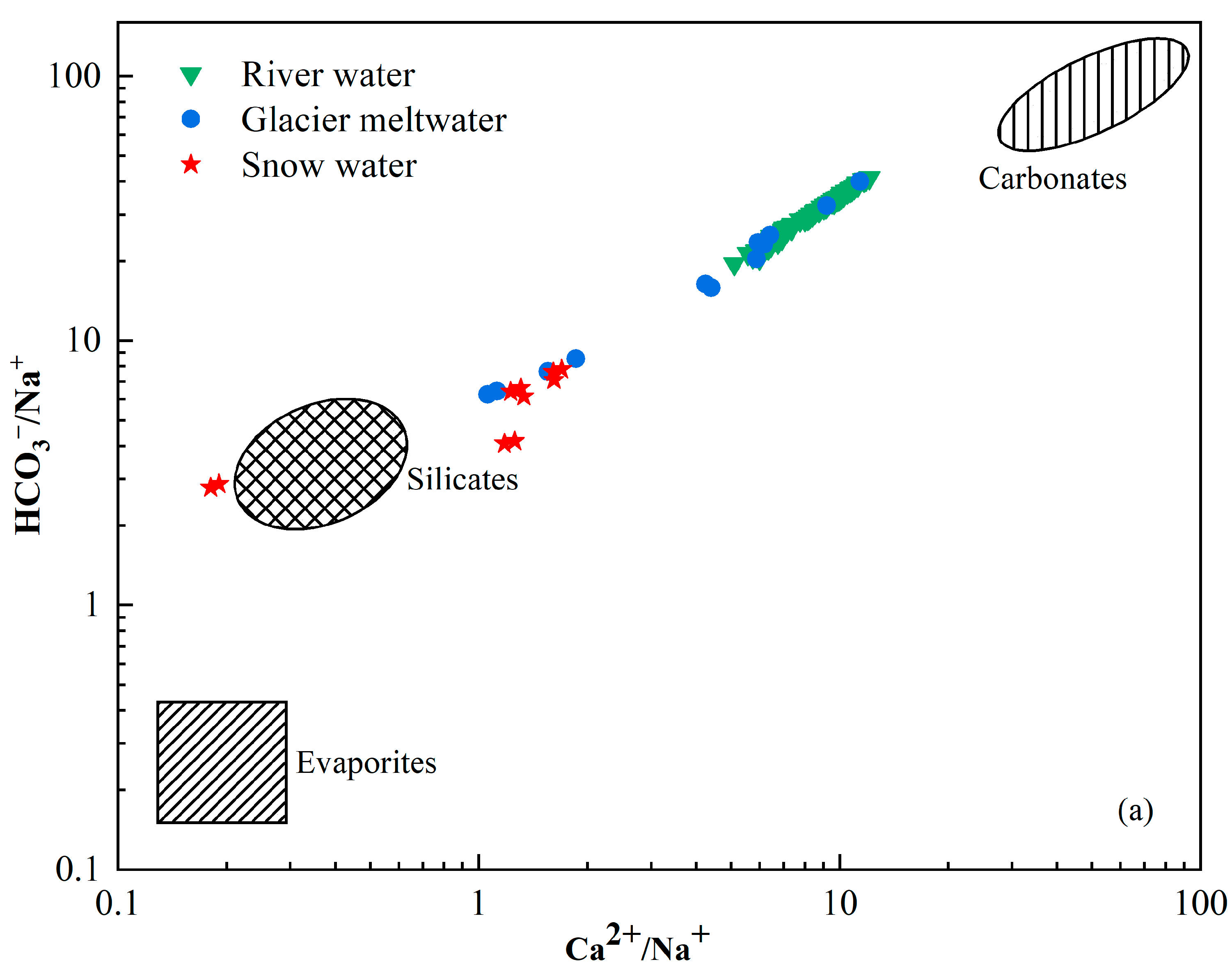
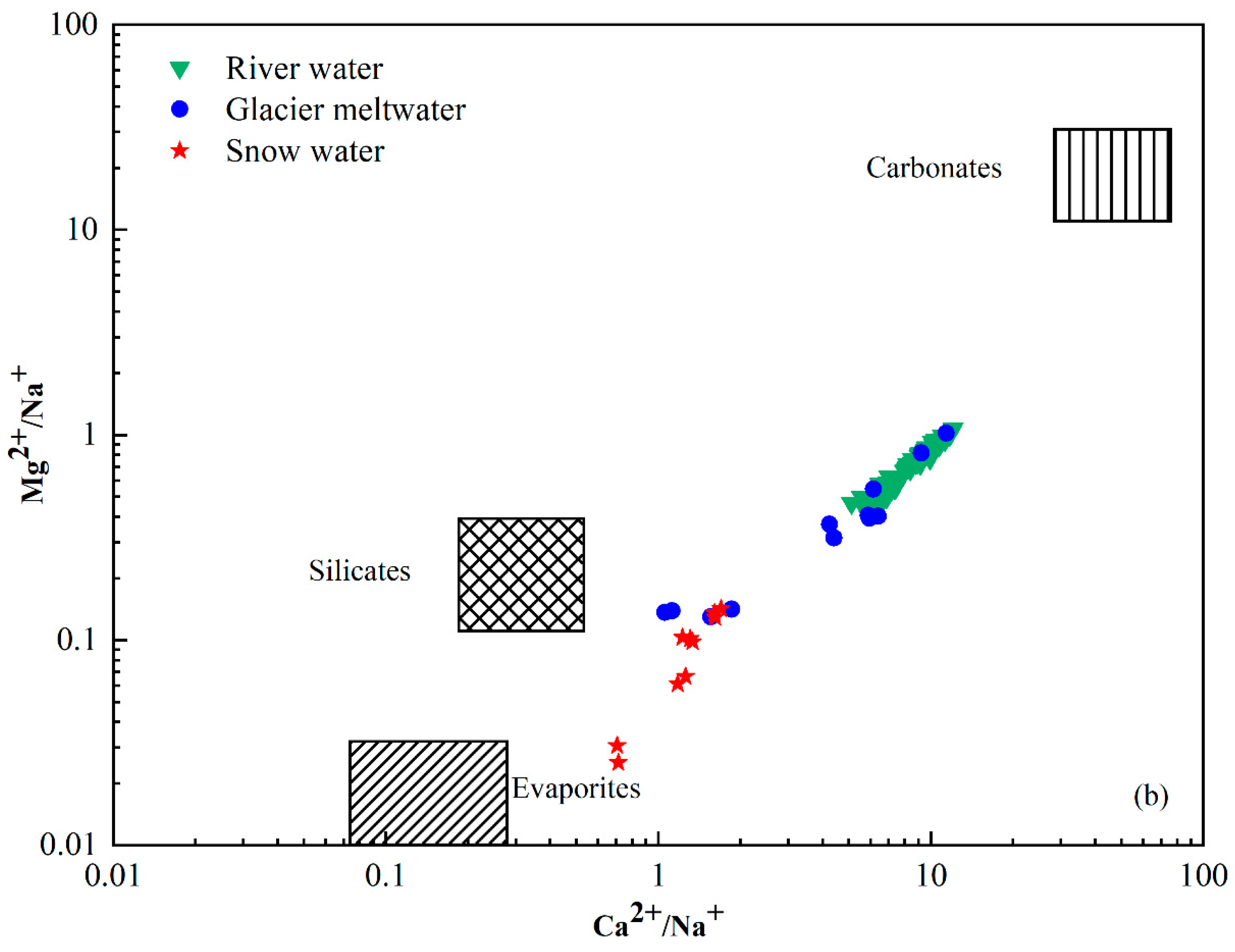
The chemical composition of river water is primarily regulated by the chemistry of its possible sources, which include atmospheric deposition, the weathering of bedrocks and their relative contributions to the solutes [44,45]. The Na-normalized molar ratio is used to analyze the influence of rock weathering and dissolution on water samples. Figure 6 is a mixing graph of Ca2+/Na+ vs. Mg2+/Na+ with evaporite, silicate and carbonate endmembers and a plot of the catchment rocks and river chemistry [46,47]. The molar concentration ratios of Ca2+/Na+ and Mg2+/Na+ produced by silicate weathering were 0.35 ± 0.15 and 0.24 ± 0.12, respectively. The molar concentration ratios of Ca2+/Na+ and Mg2+/Na+ produced by carbonate weathering were 50 ± 0.12 and 20 ± 8 and by evaporites was 0.17 ± 0.09 and 0.02 ± 0.01. All the river water samples were plotted between the silicate and carbonate endmembers with higher Ca2+/Na+ and Mg2+/Na+ compared with snow water and glacier meltwater samples. The mean value of the catchment fell near the silicate end member. This indicates that the primary controlling factor was the weathering and dissolution of silicate rocks, whereas the dissolution of carbonate rocks had a relatively minor impact on the various water bodies within the study area. Furthermore, the positive correlation investigated between Na-normalized Ca2+ and Mg2+ (Figure 6) suggests that Ca2+ and Mg2+ in the catchment could be derived from silicate minerals.
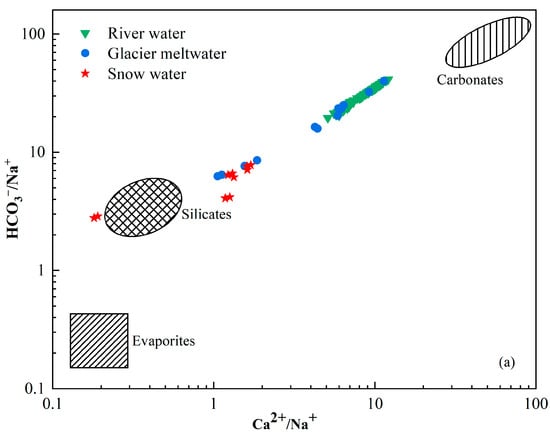
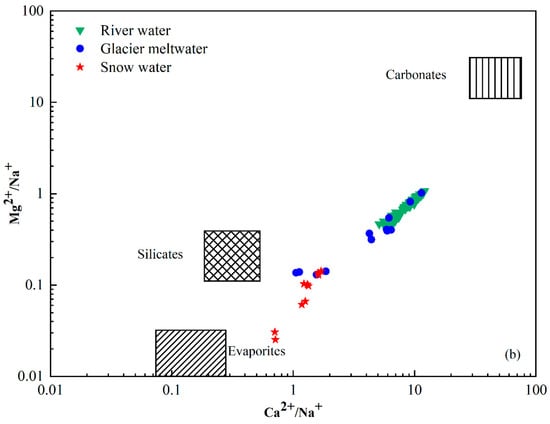
Figure 6.
Mixing diagrams of (a) Ca2+/Na+ vs. HCO3−/Na+ and (b) Ca2+/Na+ vs. Mg2+/Na+ ratios of river water in Jinghe River Basin.
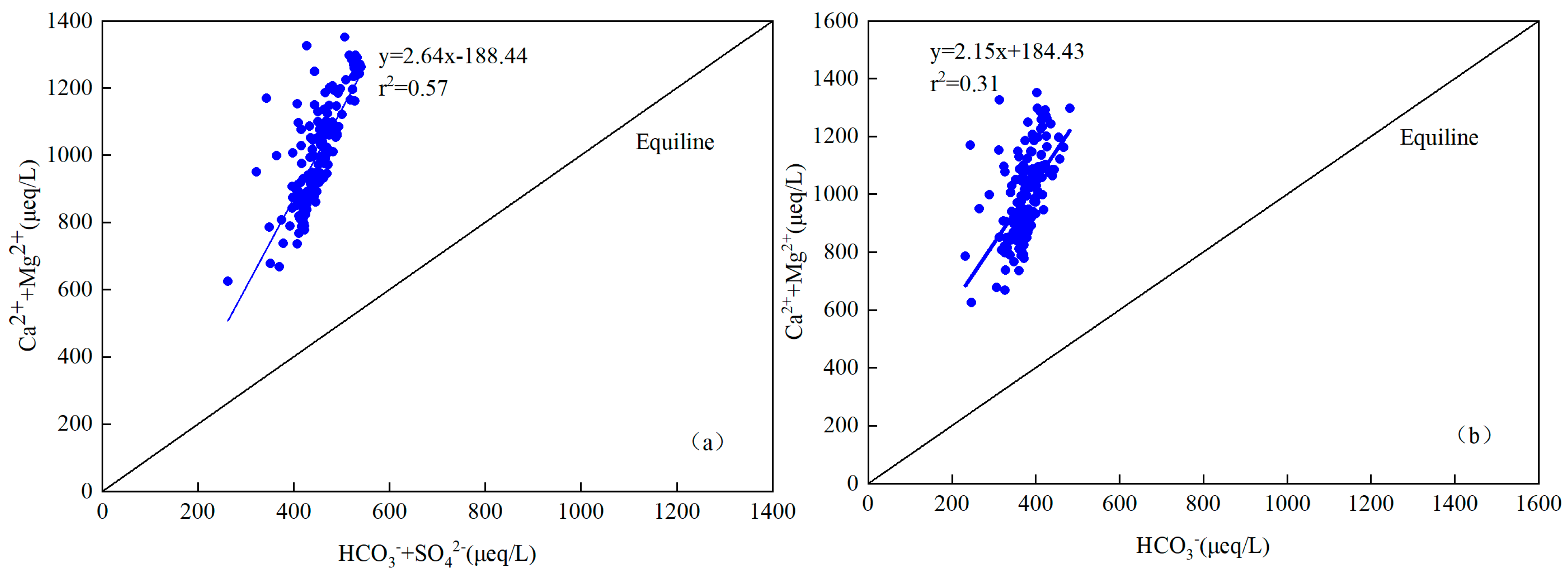
The scatter plot of major ions (normal concentration, μeq/L) were used to recognize the main sources and chemical characteristics in the Jinghe River Basin. The scatter plot of Mg2+ + Ca2+ versus HCO3− (in μeq/L) of the river water lay around the equiline with r2 equaling 0.31, which indicates that the source of these ions in the river water of Jing River was from the weathering of carbonate rocks (Figure 7b). This result is inconsistent with the result of Li et al. [39]. The scatter plot of Mg2+ + Ca2+ versus HCO3−+ SO42− (in μeq/L) of the river water lies around the equiline with r2 equaling 0.57 (Figure 7a). The excess of Ca2+ + Mg2+ over HCO3− in river water further explained the contribution of carbonate weathering to river waters. Similar findings were observed in the Heihe River, Yamuna River and the Brahmaputra River [48,49,50,51].
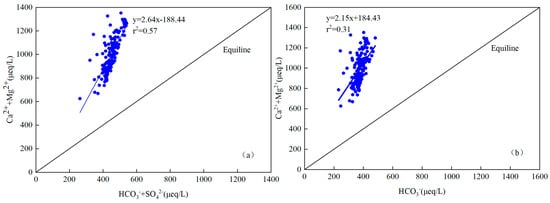
Figure 7.
Scatter plot of HCO3− vs. Ca2+ + Mg2+ (a) and HCO3− + SO42− vs. Ca2+ + Mg2+ (b) for all river water samples in Jinghe River Basin.
4. Conclusions
The analysis of the chemical composition of river water in the Ebinur Lake Basin revealed key features of its hydrochemistry and the factors that controlled these properties. This study examined 183 water samples and found that the TDSs in the river water ranged from 20.8 mg·L−1 to 60.1 mg·L−1, with an average of 49.8 mg·L−1. The mean of the TDSs for the glacier meltwater and snow water were 19.6 mg·L−1 and 13.7 mg·L−1, respectively. The absolute dominant anion was HCO3− and the main cation was Ca2+ in the river water. Therefore, the river water exhibited a hydrochemical type of HCO3−-Ca2+. The glacier meltwater and snow water exhibited slightly different compositions, with hydrochemical types of HCO3−-Ca2+·Na+·K+ and HCO3−-Na+·K+·Ca2+, respectively. The correlation analysis highlighted that the TDSs where significantly influenced by the presence of Ca2+, Mg2+, K+ and HCO3−, as indicated by correlation coefficients above 0.5. This suggests that these ions were major contributors to changes in the TDS levels. Gibbs plots indicate that river water in the basin was primarily influenced by rock weathering rather than evaporation or atmospheric precipitation. Meanwhile, the snow water and glacier meltwater were controlled by both rock weathering and atmospheric precipitation. The river water’s chemical composition was most closely aligned with the weathering of silicate rocks. The Na-normalized molar ratios further confirmed that the river water chemistry was primarily controlled by the weathering and dissolution of silicate rocks, with a minor contribution from the dissolution of carbonate rocks. This analysis provides insight into the geochemical processes governing river water chemistry in the Ebinur Lake Basin, with a particular emphasis on the role of silicate weathering over carbonate dissolution.
Author Contributions
Methodology, J.Z.; validation, Q.L.; formal analysis, R.Y.; investigation, C.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, F.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (22JR5RA549, 22JR5RA547, 24JRRA537) and the Education Science and Technology Innovation Project of Gansu Province (2021QB-118).
Data Availability Statement
Datasets analyzed during the present study are accessible from the current author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Karthe, D.; Chalov, S.; Borchardt, D. Water resources and their management in central Asia in the early twenty-first century: Status, challenges and future prospects. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modaresi, R.A.; Kreitler, J.; Abatzoglou, J.T.; Fallon, K.; Roche, K.R.; Sadegh, M. Anthropogenic stressors compound climate impacts on inland lake dynamics: The case of Hamun Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, O.; Shree, B.; Emmanuel, G.; Olusegun, S.T. Impact of climate change on the water resurces, Lake Powell, United States. Am. J. Water Resour. 2023, 3, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Recent lake area changes in central Asia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y. Ecological benefits of the emergency stream water feeding to the lower reaches of Tarim River, Xin Jiang. Arid Land Geogr. 2002, 25, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhtiar, F.; Tobia, L.; Davoud, O.; Samira, P. Health effects of shrinking hyper-saline lakes: Spatiotemporal modeling of the Lake Urmia drought on the local population, case study of the Shabestar County. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1622. [Google Scholar]
- Maria, D.P.A.; Eleonora, C.; Ines, E.; Andres, B.; Daniel, A. Hydrochemistry, isotopes studies and salt formation in saline lakes of arid regions: Extra-Andean Patagonia, Argentina. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 816, 151529. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Yao, T.; Shum, C.K.; Yi, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, H.; Feng, W.; Bolch, T.; Wang, L.; Ali, B.; et al. Lake volume and groundwater storage variations in Tibetan Plateau’s endorheic basin. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5550–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.; Jiang, B.; Bohn, T.; Lee, K.; Lettenmaier, D.; Ma, D.; Ouyang, Z. Lake and wetland ecosystem services measuring water storage and local climate regulation. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 3197–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshime, D.W.; Haile, A.T.; Absi, R.; Ledésert, B. Impact of Water Resource Development Plan on Water Abstraction and Water Balance of Lake Ziway, Ethiopia. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.; Guo, B.; Kuang, H.; Yang, H.; Ma, M. Lake area changes and their influence on factors in arid and semi-arid regions along the Silk Road. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Wang, X.; Veroustraete, F.; Dong, L. Change in area of Ebinur Lake during the 1998–2005 period. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 5523–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, S.M.; Voss, C.I.; Walvoord, M.A.; Minsley, B.J.; Rover, J. Linkages between lake shrinkage/expansion and sublacustrine permafrost distribution determined from remote sensing of interior Alaska, USA. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.K.; Paul, D. Linkages between land cover change, lake shrinkage, and sublacustrine influence determined from remote sensing of select Rift Valley Lakes in Kenya. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136022. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, S.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, Y.; Zhu, N. Stable isotope evidence for identifying the recharge mechanisms of precipitation, surface water, and groundwater in the Ebinur Lake basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hao, X.; Shen, Y. Hydrology and water resources variation and its response to regional climate change in Xinjiang. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, H.; Kang, S. Impacts of climate change on the discharge and glacier mass balance of the different glacierized watersheds in the Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yang, F.; Yang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Chi, Y.; Yang, G. Identification of potential impacts of climate change and anthropogenic activities on streamflow alterations in the Tarim River Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Q.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T.; Marold, U. Impacts and implications of major changes caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour Manag. 2012, 26, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, G.; Liang, J.; Guo, S.; Huang, L.; Wu, H.; Hua, S. Quantitative assessment of the contribution of climate variability and human activity to streamflow alteration in Dongting Lake, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Hydrochemistry of inland rivers in the north Tibetan Plateau constraints and weathering rate estimation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mors, R.; Gomez, F.; Astini, R.; Mlewski, E.; Gerard, E. Physico-chemical and biological controls in a travertine system in the high Andes of northwestern Argentina. Sediment. Geol. 2022, 439, 106214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Zheng, L. Combining hydrochemistry and hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes to reveal the influence of human activities on surface water quality in Chaohu Lake Basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupam, S.; Gyana, R.T.; Aswin, T.P.; Anirban, M. Major ion chemistry of two cratonic rivers in the tropics: Weathering rates and their controlling factors. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14035. [Google Scholar]
- Modie, L.; Kenabatho, P.; Stephens, M.; Mosekiemang, T. Investigating groundwater and surface water interactions using stable isotopes and hydrochemistry in the Notwane River Catchment, South East Botswana. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 40, 101014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, S. Streamflow generation in semi-arid, glacier-covered, montane catchments in the upper Shule River, Qilian Mountains, northeastern Tibetan plateau. Hydrol. Process. 2021, 35, e14276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Dong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, M. Hydrological processes and water quality in arid regions of Central Asia: Insights from stable isotopes and hydrochemistry of precipitation, river water, and groundwater. Hydrogeol. J. 2023, 32, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Che, Y.; Chen, F.; Qiang, F. Contribution of recycled moisture to precipitation in oases of arid central Asia: A stable isotope approach. Water Resour. Res. 2016, 52, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, F. Glacier shrinkage in the Ebinur Lake basin, Tien Shan, China, during the past 40 years. J. Glaciol. 2014, 60, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Li, G.; Liang, J.; Yu, D.; Aishan, T.; Liu, J. Dynamic detection of water surface area of Ebinur Lake using multi-source satellite data (Landsat and Sentinel-1A) and its responses to changing environment. Catena 2019, 177, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, J.; Wu, P.; Tan, J.; Huang, S.; Teng, D.; Chen, W. Assessing arid inland lake watershed area and vegetation response to multiple temporal scales of drought across the Ebinur Lake watershed. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, A.; Mu, G.; Zhang, Y. Reasonable water surface estimation and effect monitoring for controlling wind erosion of dry lake bottom in Ebinur Lake. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzin, T.; Mahmoud, A.W.; Sidra, I.; Mika, S. Major ion chemistry of the Teesta River in Sikkim Himalaya, India: Chemical weathering and assessment of water quality. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2019, 24, 100612. [Google Scholar]
- Khadka, U.R.; Ramanathan, A.L. Major ion composition and seasonal variation in the lesser himalayan lake: Case of begnas lake of the pokhara valley, Nepal. Arabian. J. Geosci. 2012, 6, 4191–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of wateranalyses. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Gabet, E.J.; Edelman, R.; Langner, H. Hydrological controls on chemical weathering rates at the soil-bedrock interface. Geology 2006, 34, 1065–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M.; Gjessing, E.T.; Vogt, R.D. Water quality in the Tibetan Plateau: Major ions and trace elements in the headwaters of four major Asian rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ji, H. Chemical weathering and the role of sulfuric and nitric acids in carbonate weathering: Isotopes (13C, 15N, 34S, and18O) and chemical constraints. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1288–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.D.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.W.; Zhang, X.L. Seasonal variation of the isotope and hydrochemical characteristics of the main lake rivers in Lake Ebinur, Xinjiang. J. Lake Sci. 2018, 30, 1707–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guo, H. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Ion Source Analysis of the Yarlung Tsangpo River Basin. Water 2023, 15, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; An, Y. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Risk Assessment of Tongzi River, Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Water 2023, 15, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, R. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 1970, 170, 1088–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurumurthy, G.P.; Balakrishna, K.; Tripti, M.; Riotte, J.; Audry, S.; Braun, J.J.; Shankar, H.U. Sources of major ions and processes affecting the geochemical and isotopic signatures of subsurface waters along a tropical river, Southwestern, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Q.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Sun, J.L. Hydrochemical Characteristics of Surface Water and Groundwater in Oasis Edge in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2022, 42, 1818–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Gaillardet, J.; Dupr′e, B.; Louvat, P.; Allegre, C. Global silicate weathering and CO2 consumption rates deduced from the chemistry of large rivers. Chem. Geol. 1999, 159, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadakkeveedu, N.A.; Kumar, A.; Dsouza, N.; Keshava, B.; Harikripa, N.U.; Neloy, K. Major ion chemistry and silicate weathering rate of a small Western Ghats river, Sharavati, southwestern India. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 136, 105182. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwakarma, C.A.; Sen, R.; Singh, N.; Singh, P.; Rena, V.; Rina, K.; Mukherjee, S. Geochemical Characterization and Controlling Factors of Chemical Composition of Spring Water in a Part of Eastern Himalaya. J. Geol. Soc. India 2018, 92, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, T.; Krishnaswami, S.; Sarin, M. Major ion chemistry in the headwaters of the Yamuna river system. Geochim. Cosmochim. 2002, 66, 3397–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Sillanpää, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wahed, M.S.M.A.; Kang, S. Water chemistry of the headwaters of the Yangtze River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 6443–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Dreybrodt, W.; Liu, H. Atmospheric CO2 sink: Silicate weathering or carbonate weathering? Appl. Geochem. 2011, 26, S292–S294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).