Abstract
There are various methods for environmental organic pollutant degradation and removal, among which ultraviolet/persulfate has drawn significant attention due to its excellent oxidizing properties, high maneuverability, and less formation of by-products. To comprehensively assess the development of ultraviolet/persulfate, a bibliometric analysis was conducted based on relevant literature indexed by Web of Science from 2002 to 2024. The findings revealed a growing number of publications, with China, Iran, and the United States being the top three countries with the highest total number of publications. Robust regional collaborations were evident. Additionally, Chinese and American scholars presented more significant activity in this field, and their publications exhibited higher quality. Furthermore, the current research hotspots, as indicated by keywords, primarily focused on the degradation mechanism of ultraviolet/persulfate and the reaction kinetic model simulation. Bibliometric results underscored that ultraviolet/persulfate, as an effective and environmentally friendly disinfection technology, possessed substantial potential for controlling diverse environmental pollutants, such as antibiotics, dyes, natural organic substances, heavy metals, microorganisms, and so on. Future research might concentrate on developing new catalytic composites and optimization of the photoactivation system. The practical application still needs to be investigated due to the complexity of the water matrix. The revival of microorganisms and the variation of toxicity should be considered further.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of the global economy and the continuous advancement of industrialization, severe environmental burden has become a thorny problem worldwide [1,2]. Traditional environmental contaminants, emerging contaminants (ECs), and trace organic pollutants (TOPs) [3], such as bacteria, dyes, antibiotics, personal care products (PPCPs), perfluoroalkyl acids (PFAAs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and so on, have significant adverse effects on the environment and human health [4]. Traditional biochemical treatments are insufficient to remove ECs and TOPs, resulting in the secondary effluent failure to meet current water quality standards, and further advanced treatments are of great necessity. To make up for the limitations of traditional water and wastewater treatment, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have been widely employed due to better performance for pollutant removal and higher selectivity, stability, and safety [5]. AOPs could effectively oxidize organic pollutants and inactivate viruses, bacteria, and other microorganisms [6]. Moreover, AOPs might generate less disinfection by-products during the reactions. Thus, AOPs might be a good choice for not only meeting more stringent water quality standards but also protecting human health and reducing environmental burden.
Activation of persulfate (PS) is one of the most widely used advanced oxidation technologies. The activated persulfate could generate sulfate radical (SO4−·) and hydroxyl radical (·OH), which possess much stronger oxidizability than unactivated persulfate and can realize the oxidation and even mineralization of organic pollutants at room temperature. There are two types of persulfates: peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and peroxydisulfate (PDS). PMS possesses an asymmetric structure and is easily activated by electron transfer. PDS is not easily activated due to its molecular symmetry, but the activated PDS would produce more SO4−· resulting in a higher oxidation ability than that of PMS in general. Both PMS and PDS are cheap, stable, and easily available. Therefore, persulfate, as a highly effective oxidant, has excellent advantages in environmental pollution control.
Most traditional activation methods for PS require additional chemicals, which might bring potential adverse effects and production. In addition, with the introduction of Standards for drinking water quality (GB 5749-2022), Water reuse guidelines-Benefits evaluation of reclaimed water use (GB/T 42247-2022) in China, and the promulgation of Environmental management systems by the United Nations (ISO 14002-2:2023), the public have become more concerned about water safety. UV-activated persulfate (UV/PS) technology has received extensive attention recently because of less chemical addition. Much research has demonstrated the significant degradation effect of UV/PS on both traditional and emerging pollutants, and TOPs [7], and this technology presents strong application potential for the removal of toxic and harmful organic pollutants in the environment.
Bibliometrics is a measurement method that helps to analyze the published literature quantitatively and systemically. It is capable of evaluating the development of research status and predicting the future trend in a particular field [8] based on various characteristics of academic publications, such as the number of the literature and their citations, the number of authors (individuals or collectively as a group), and so on [9]. This paper focused on the application of UV/PS technology. Therefore, bibliometrics was applied in the study to summarize the development and research interests of UV/PS technology based on Web of Science (WOS) data from January 2002 to April 2024. CiteSpace was used to visually analyze and present the cooperative network, research topics and trends, aiming to deeply explore and analyze the research development in the field of UV/PS and provide helpful information for researchers in this field.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
In order to improve the representativeness and credibility of the collected literature data, all the data were obtained from the WOS core collection. The WOS data retrieval conditions were: [Topic = (UV AND persulfate) OR (UV AND PDS) OR (UV AND PS) AND (AOPs AND UV)]. The literature type was “Research Article” and they were written in English. The screening conditions for research directions were set as “Chemistry, Engineering, Environmental Sciences Ecology, Water Resources, Science Technology Other Topics, Public Environmental Occupational Health, Biotechnology Applied Microbiology” and so on based on search conditions in WOS. The publication period was from January 2002 to April 2024. A total of 2898 papers were retrieved under this search condition, and 835 valid papers were obtained by manually excluding the irrelevant literature. All documents were downloaded in TXT format files, and the number of data files was prefixed with “download_”as the file name.
2.2. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
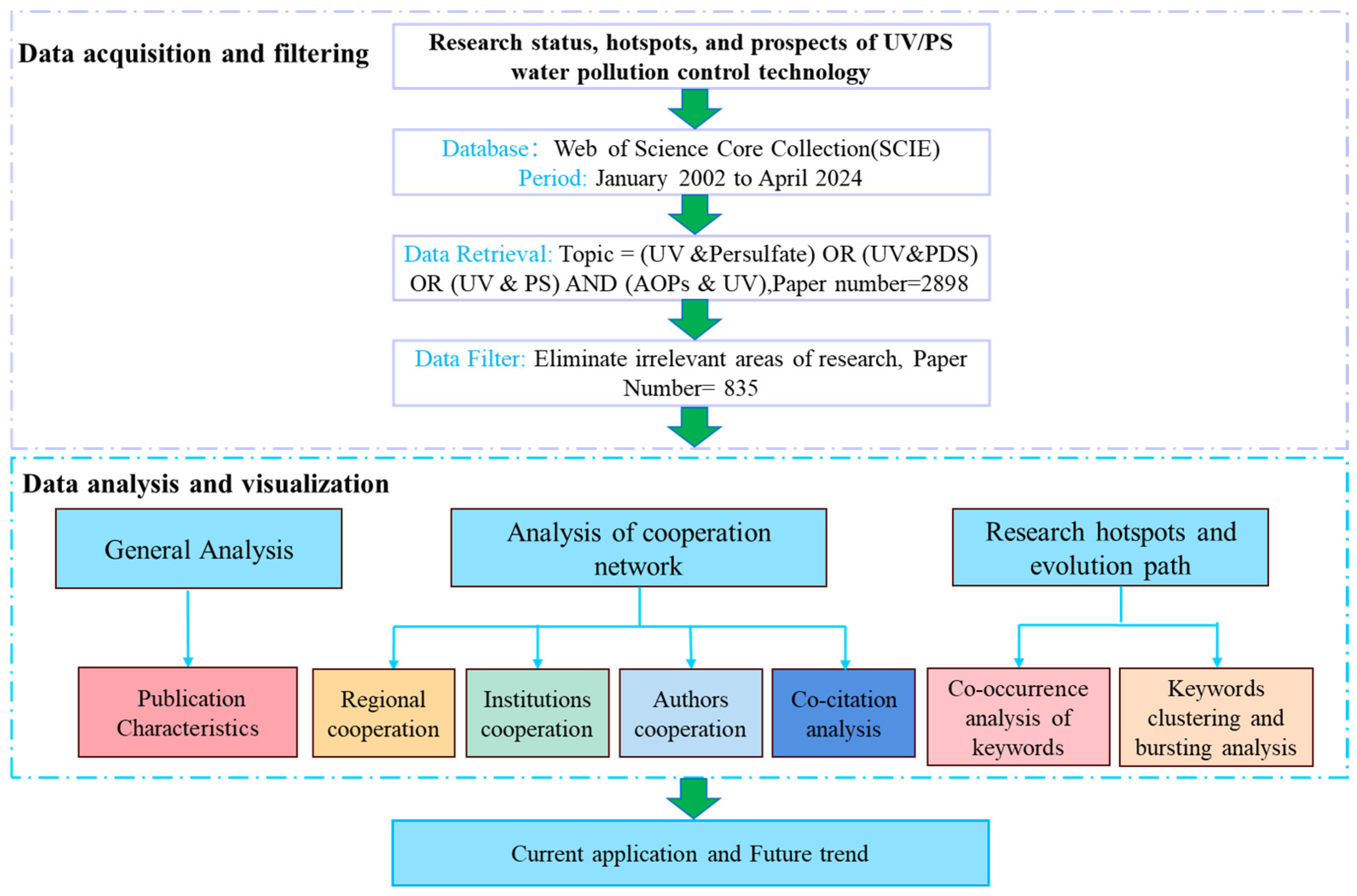
CiteSpace was applied for visual analysis, with the time slicing set to 2002–2024 in 1-year increments. Four folders, “input”, “output”, “data”, and “project”, were established, respectively. Node types selected included institution, region, author, keywords, and reference. Data analysis was conducted using Microsoft Excel 2019, and related graphics were produced by Origin 2021 and R (version 4.3.3) with the ggplot2 toolkit. The flow chart of this bibliometric analysis is shown in Figure 1.
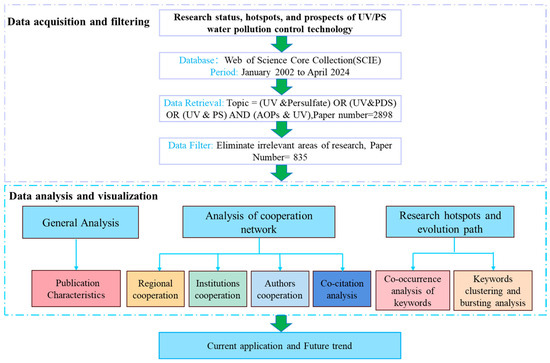
Figure 1.
Flow chart of bibliometric analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Publication Characteristics
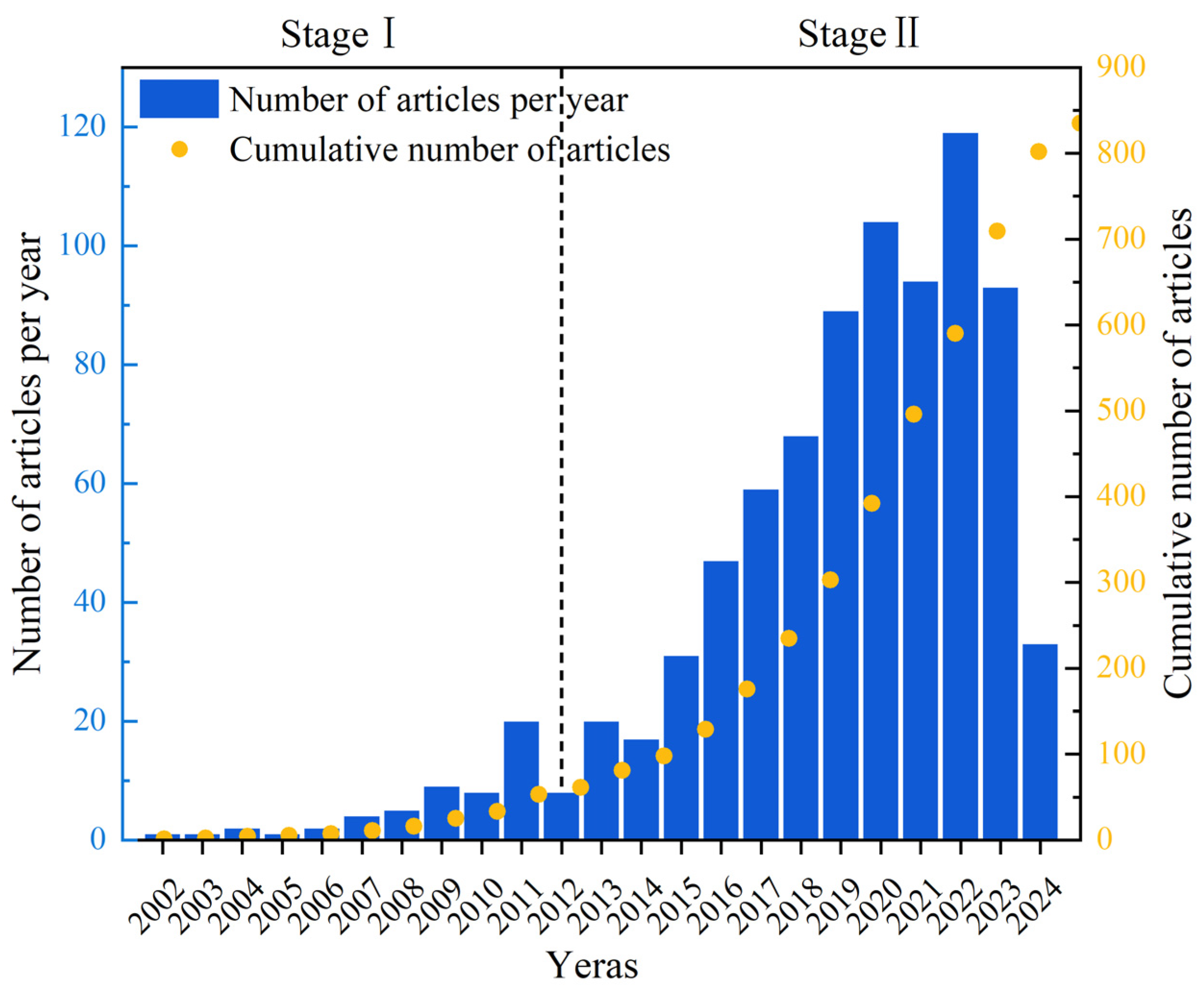
The annual number of published papers is an important criterion for evaluating the development of related research. In order to understand the development history, current situation, and future trends of UV/PS, the number of research articles issued by the WOS database was assessed year by year, as shown in Figure 2. It could be seen that the number of papers published from 2002 to 2024 is increasing yearly. In general, the development history focusing on UV/PS could be divided into two stages. The first phase was a slow development phase, from 2002 to 2012 with 61 publications. Then, a rapid development stage appeared, and the number of publications has increased rapidly with a total of 774 articles published during that time. The rapid increase in annual publications after 2012 might be closely related to the update of international policy. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality (4th edition) issued by WHO in July 2011 provided an authoritative basis for more restrictive international water safety standards [10]. The number of publications has increased year by year since then and reached the highest in 2022, reflecting the policies’ guidance for the rapid progress of science and technology. Researchers showed much more enthusiasm, and their research confidence has become more and more sufficient.
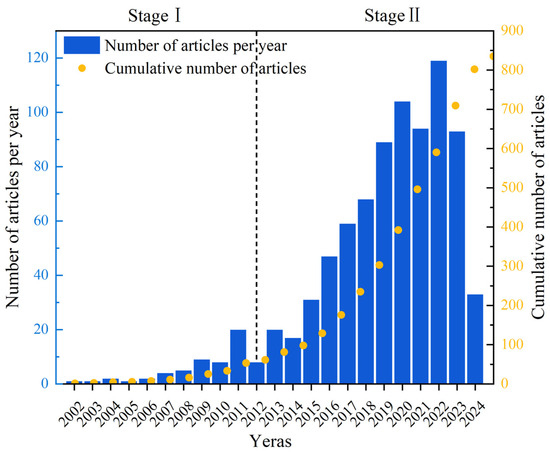
Figure 2.
Number of publications on UV/PS per year from 2002 to 2024.
Figure 3 shows a statistical chart of the top ten subject areas or research directions according to the numbers of publications on UV/PS applications based on the WOS search conditions. The number of articles published in the subject area is indicated. It could be seen that UV/PS technology has been applied more frequently in the fields of Environmental Sciences Ecology (100 articles), Engineering (82 articles), Water Resources (66 articles), and Chemistry (62 articles). It could be seen that the application of UV/PS is wide-ranging. Unexpectedly, to facilitate the application of UV/PS, a lot of researchers also estimated the economic cost or cost-effectiveness of UV/PS (referring to Business Economics in Figure 3, 31 articles).

Figure 3.
Number of publications on UV/PS in the top ten subject areas.
UV/PS could be widely applied for pollutant removal in environmental governance. During the COVID-19 pandemic and post-epidemic period, potential risks have been presented to the ecological environment and human health resulting from the frequent and excessive use of disinfectants. With the introduction of the Standards for Driving Water Quality (GB 5749-2022) and Standard Test Method for Drinking Water (GB/T 5750-2023) in China in recent years, the use of disinfectants and the supervision of disinfection by-products are becoming more and more strict [11]. It might predict that green disinfection technology based on UV/PS would draw extensive attention in the next few years.
3.2. Analysis of Cooperation Network
Through the analysis of the cooperation network, the communication trajectory of scientific research activities could be obtained, including the communication within or between different countries, regions, institutions and scientific research groups, and so on.
3.2.1. Research Contributions from Different Countries and Regions
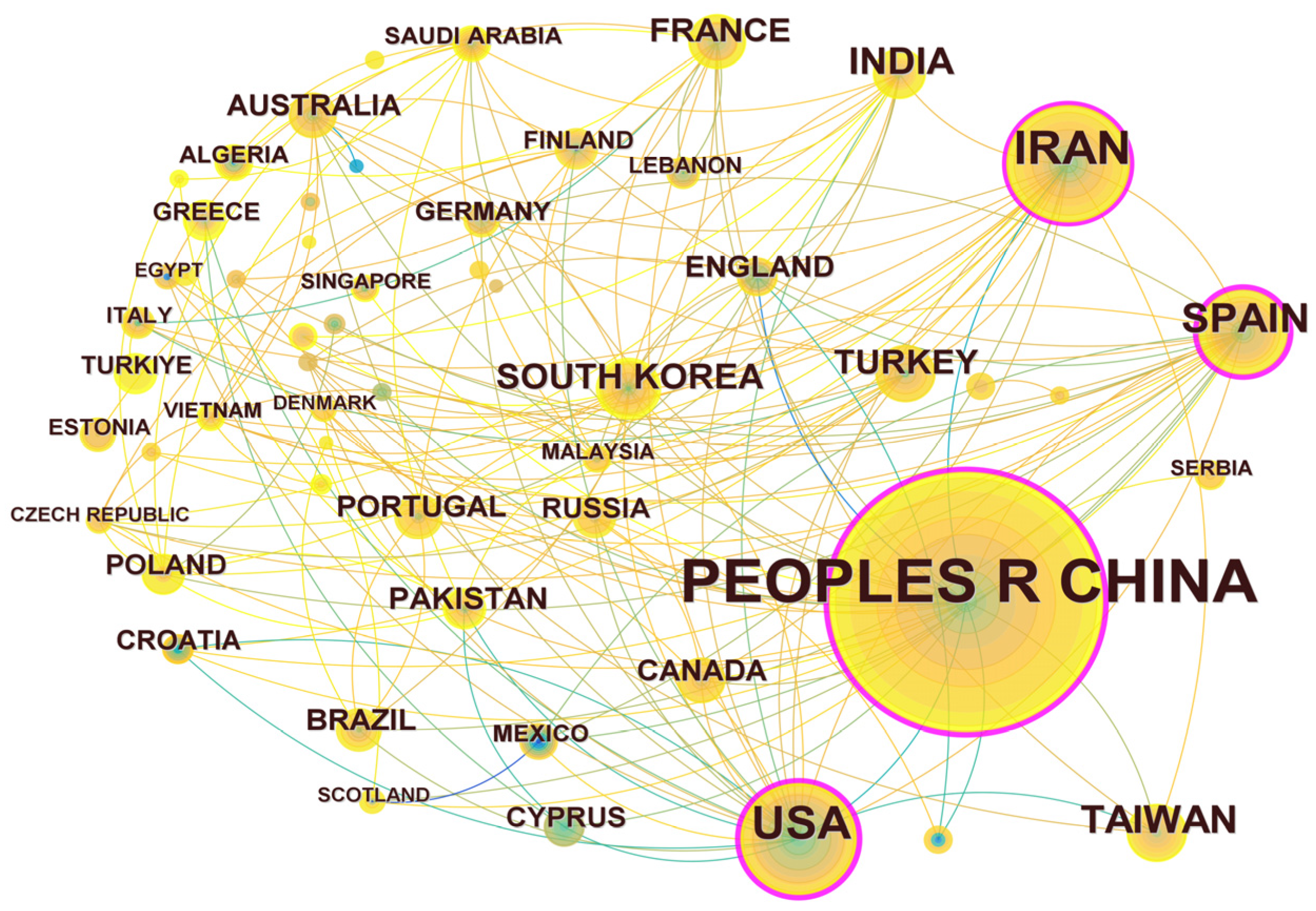
Through the statistical analysis of research articles published by different countries and regions, the scientific investment and academic influence of the country or region in certain research fields could be obtained. The results are shown in Figure 4. There are 57 nodes and 174 connections in the regional cooperation network diagram, indicating that a total of 57 countries or regions have published articles in the field of UV/PS. The statistics of the number of publications are shown in Table 1. The top five are China (408 articles), Iran (97 articles), the United States (87 articles), Spain (53 articles), and Chinese Taiwan (39 articles), among which China is the leading country in this field. From the perspective of the number of citations, articles published by China were cited the most, indicating that Chinese research achievements have been highly recognized and Chinese researchers are in a leading position in this field. The number of articles published by the United States were cited the second most. The research on UV/PS in the United States began earlier, and the related research achievements also have a great influence. The cooperation network diagram shows that there is certain cooperation between countries, while the nodes represented by China, Spain, the United States, and Iran are in the purple outer ring, with an intermediary centrality of 0.37, 0.27, 0.23, 0.16, and 0.10, respectively. Whether from the number of publications or intermediary centrality, these four countries had frequent and close international cooperation in this field with other regions, and they all made great efforts on UV/PS.
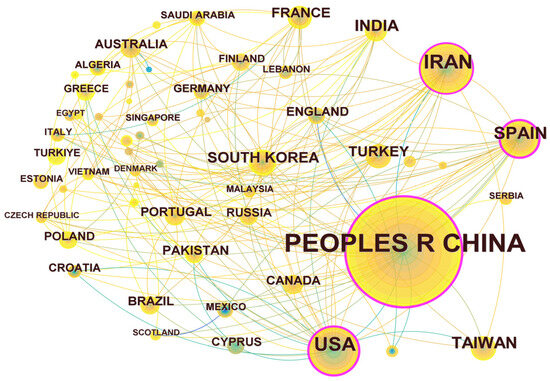
Figure 4.
Network map of national and regional cooperation focusing on UV/PS.

Table 1.
Statistics on the number of national and regional publications and citations in the field of UV/PS.
3.2.2. Research Contributions from Different Institutions
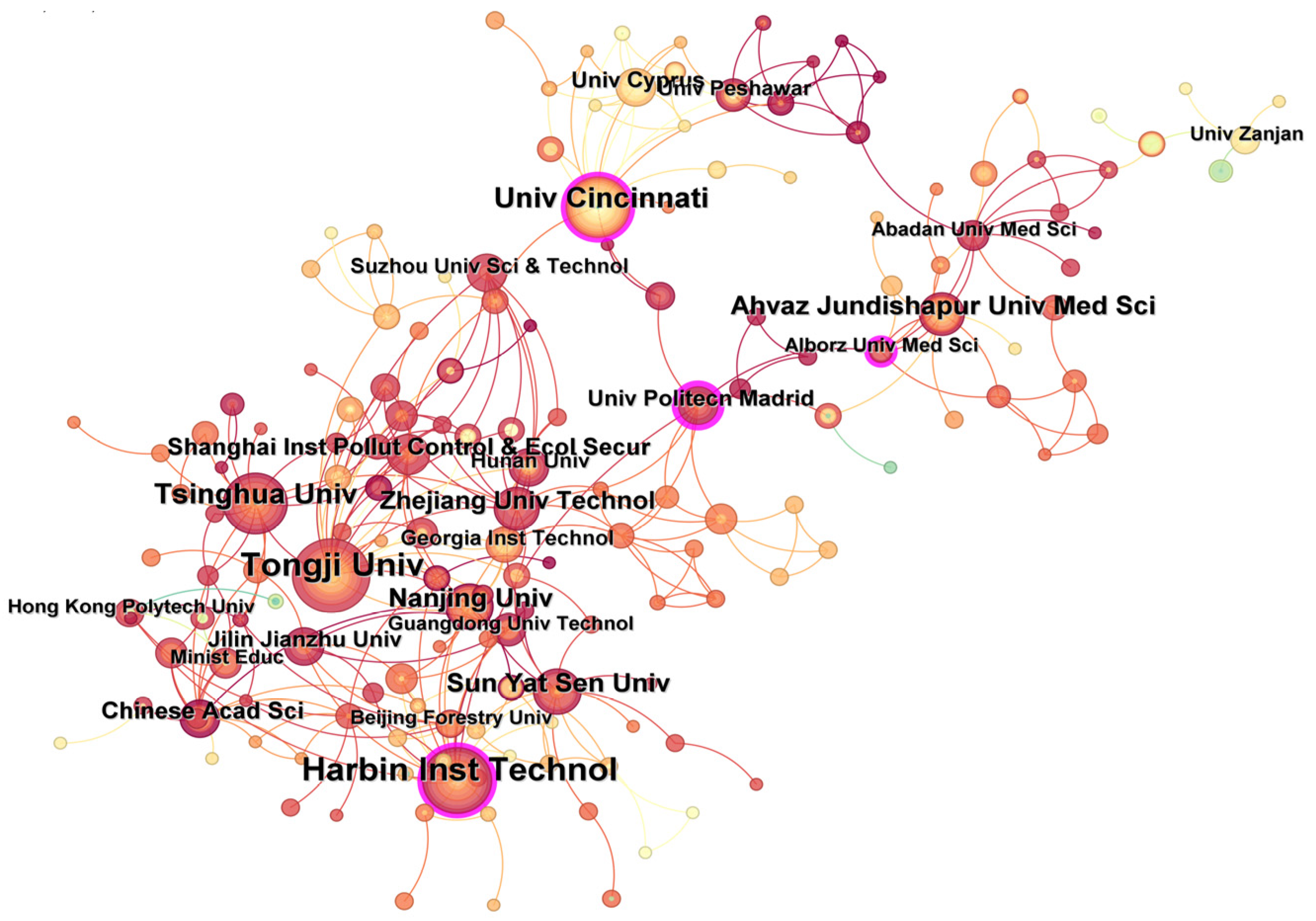
Analysis of contributions from different research institutions could reveal the achievements and cooperation relationships of institutions in certain fields [12]. Figure 5 shows the collaboration map of institutions. According to statistics, 317 research institutions published literature focusing on UV/PS from 2002 to 2024, with a network density of 0.0078. Among all institutions, Tongji University (46 articles), Harbin Institute of Technology (40 articles), University of Cincinnati (24 articles), and Tsinghua University (24 articles) are the top five institutions with the highest number of research articles published in this field. However, the network density value is relatively low, indicating that the cooperation between domestic and foreign institutions is more dispersed, and the cooperation seems to be more regional. The cooperation network is mainly centered on the Harbin Institute of Technology, Tongji University, the University of Cincinnati, Alberts Medical University of Iran, and the Technical University of Madrid. A close cooperative relationship exists between universities and institutions in the geographically close area. The intermediary centrality of the number of papers published by the Technical University of Madrid and Harbin Institute of Technology are the top two, indicating that these two institutions conducted relatively close cooperation and communication with other institutions. The researchers from these two institutions are the main force in this field and provide academic contributions of major significance to the field. To promote technological development, institutional cooperation, especially for academic exchanges, should be encouraged and conducted.
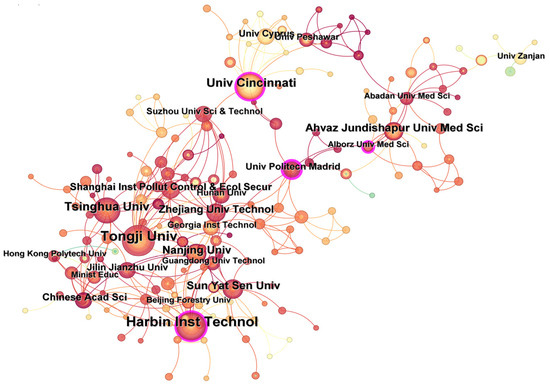
Figure 5.
Number of publications and cooperation relationships regarding UV/PS from different institutions.
3.2.3. Research Contributions from Different Authors
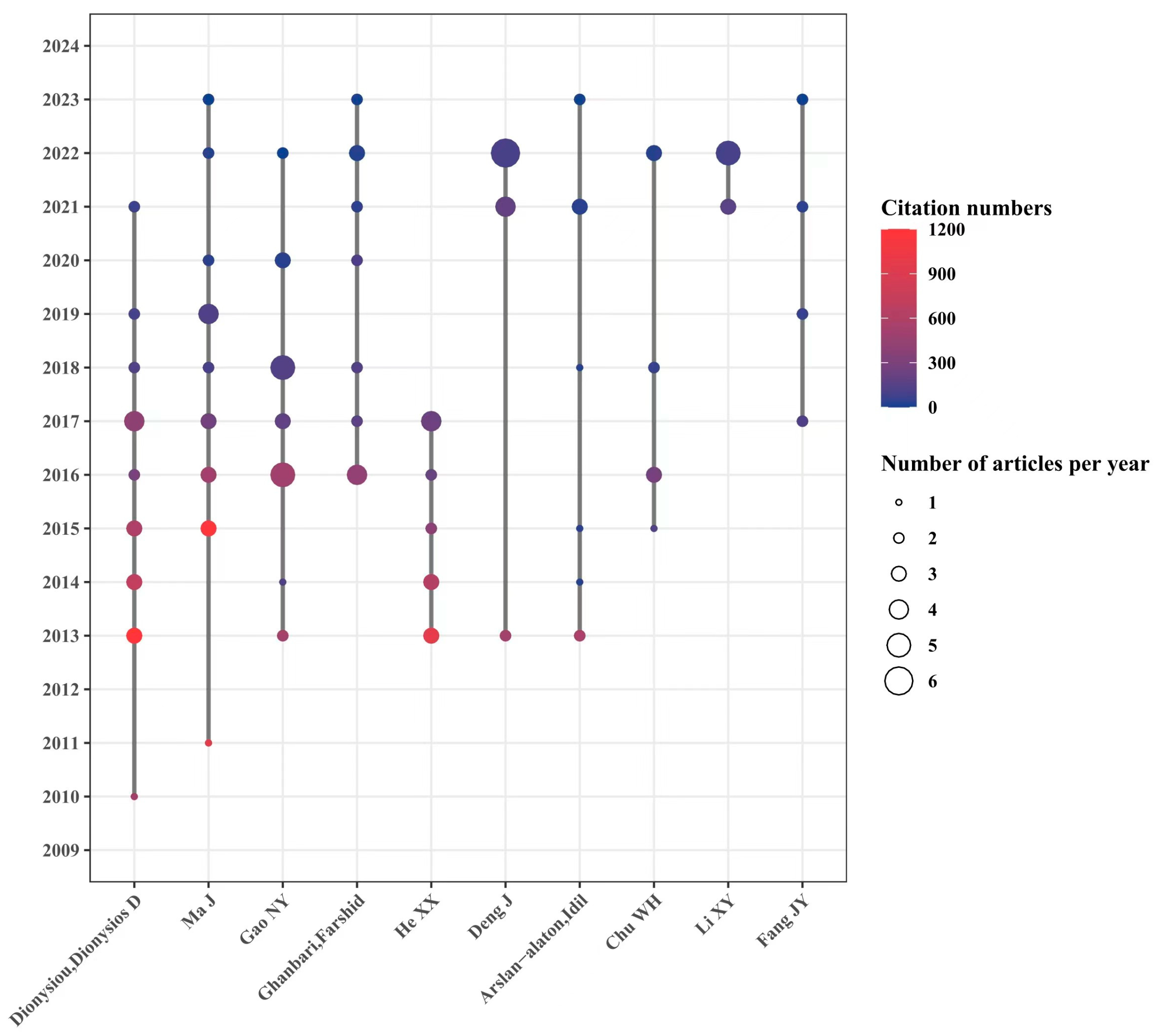
Figure 6 shows the cooperative relationship, the number, and the quality of published papers based on the authors. A total of 540 authors are involved in this field, among which Professor Ma Jun from the Harbin Institute of Technology in China and Professor Dionysiou Dionysios from the University of Cincinnati in the United States might be the most prominent contributors in the field. Three authors have published more than 20 articles: Professor Dionysiou Dionysios D from the University of Cincinnati (22 articles), Professor Ma Jun from the Harbin Institute of Technology (22 articles), and Professor Gao Naiyun from Tongji University (21 articles). Independent research groups are led by these three authors, among which Prof. Dionysiou Dionysios D published articles that were cited the most, with 4035 times. The total citations of articles supervised by Professor Ma Jun and Professor Gao Naiyun were 3187 and 1515 times, respectively. As for a single article, the article focusing on the effect of pH value on the degradation of refractory organic matter in UV/PMS systems [12] conducted by Professor Ma Jun’s group is the most cited article and has been cited as many as 979 times, suggesting good guidance and inspiration for later scholars. The research on UV/PS drew wide attention and made great improvement in the last 10 years, and 7 of the top 10 authors are Chinese scholars, indicating the fruitful research achievements and high research enthusiasm from Chinese scholars in the field of UV/PS. It also showed huge research progress and worldwide academic influence made by Chinese scholars. However, there seems to be a relatively fixed cooperative relationship between the institutions, groups, and the scientific researchers. It might be seen that the articles are usually organized by certain groups with frequent cooperation. Therefore, strengthening communication between researchers from different regions and institutions would help promote in-depth research in UV/PS and accelerate its application in various fields besides environmental governance.
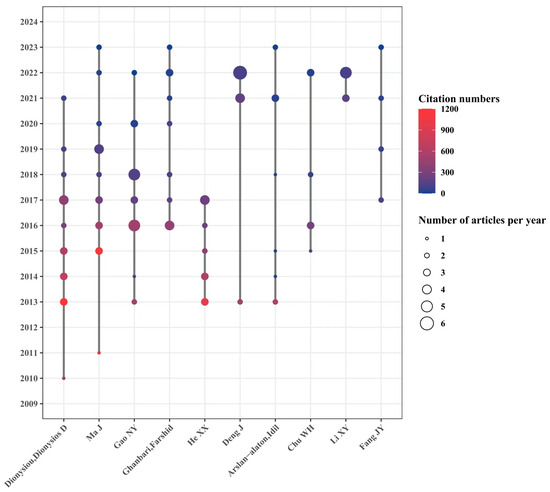
Figure 6.
Timeline of authors focusing on UV/PS.
3.2.4. Co-Citation Analysis
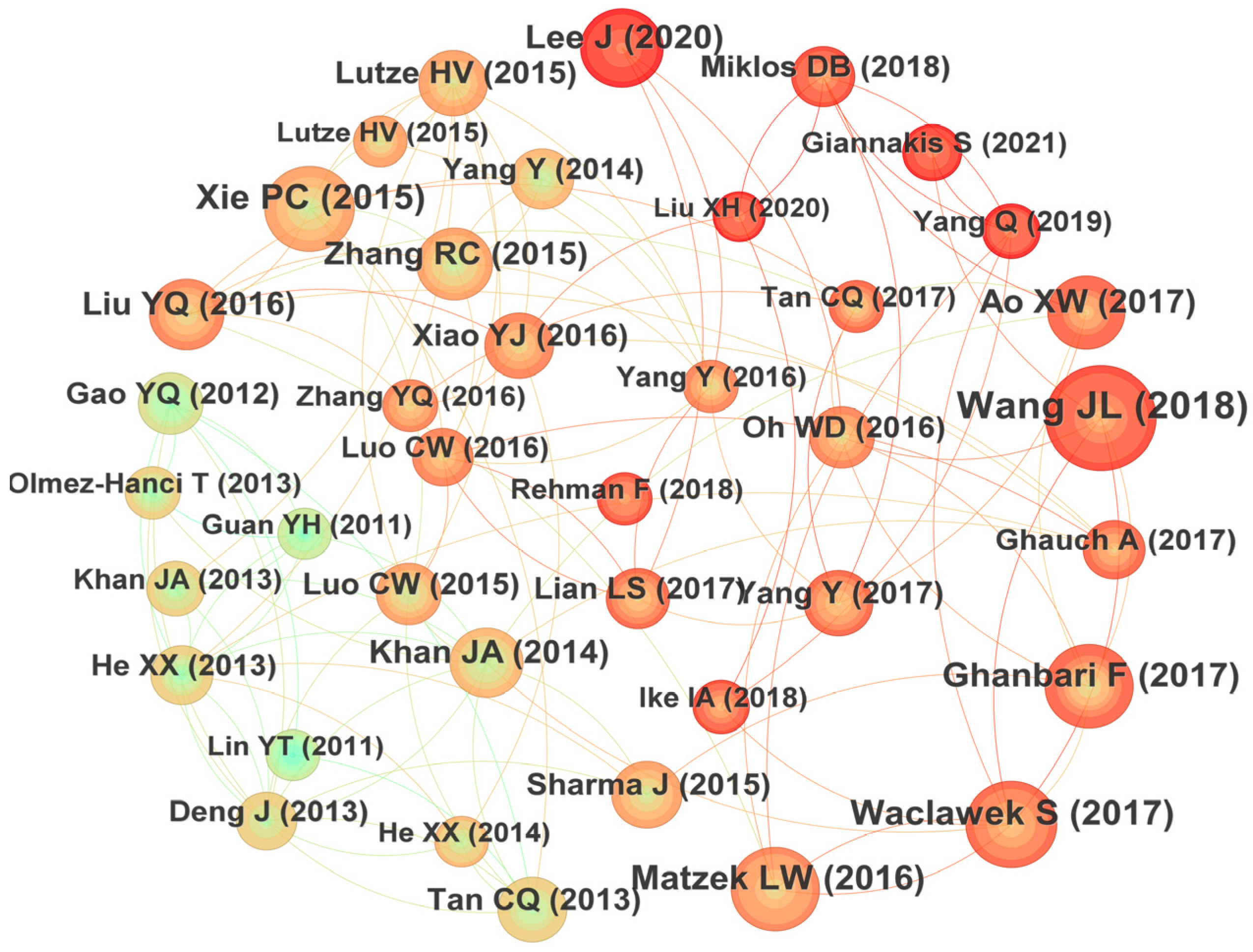
Co-citation refers to the fact that two or more papers are cited simultaneously by one or more papers, and the cited papers constitute a co-citation relationship. It would reflect the knowledge structure of certain research fields and is an important index to measure the academic influence of the cited papers. The relationships of those most co-cited papers in the field of UV/PS are plotted in Figure 7 [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47]. It could be seen that the author with the highest number of co-citations is Wang JL (2018) with a total of 65 citations, followed by Waclawek S (2017) with 74 citations, and Xie PC (2015) with 72 citations in the third place. The specific information of the highly co-cited papers is summarized in Table 2. The research team led by Prof. Wang JL of Tsinghua University studied the catalytic activation of persulfate by metals [46] or visible light [47] to degrade traditional organic pollutants and ECs [48]. Their research made great efforts on the modification of the advanced oxidation technology. The research, supervised by Prof. Xie PC, focused on the degradation of emerging pollutants and disinfection by-products by UV-activated chlorine [49] and UV-activated persulfate [50]. Their findings provide a new insight for future investigations. The articles of these highly cited authors mainly focused on the removal effect of different types of pollutants, the modification of the research methods, and the exploration of the mechanism, which constitutes the basic framework of UV/PS technology.
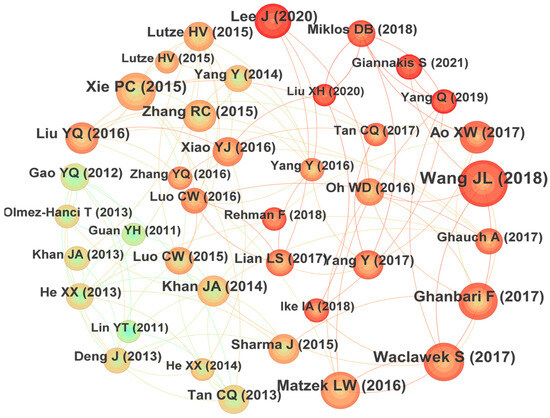
Figure 7.
Co-citation graph focusing on UV/PS. The relationships of those most co-cited papers in the field of UV/PS are plotted in Figure 7 [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47].

Table 2.
Highly cited papers focusing on UV/PS.
3.3. Research Hotspots and Evolution Path
Keyword co-occurrence, clustering, and burst terms analysis could help investigators better identify research hotspots and trends in various fields and give academic support.
3.3.1. Co-Occurrence Analysis of Keywords
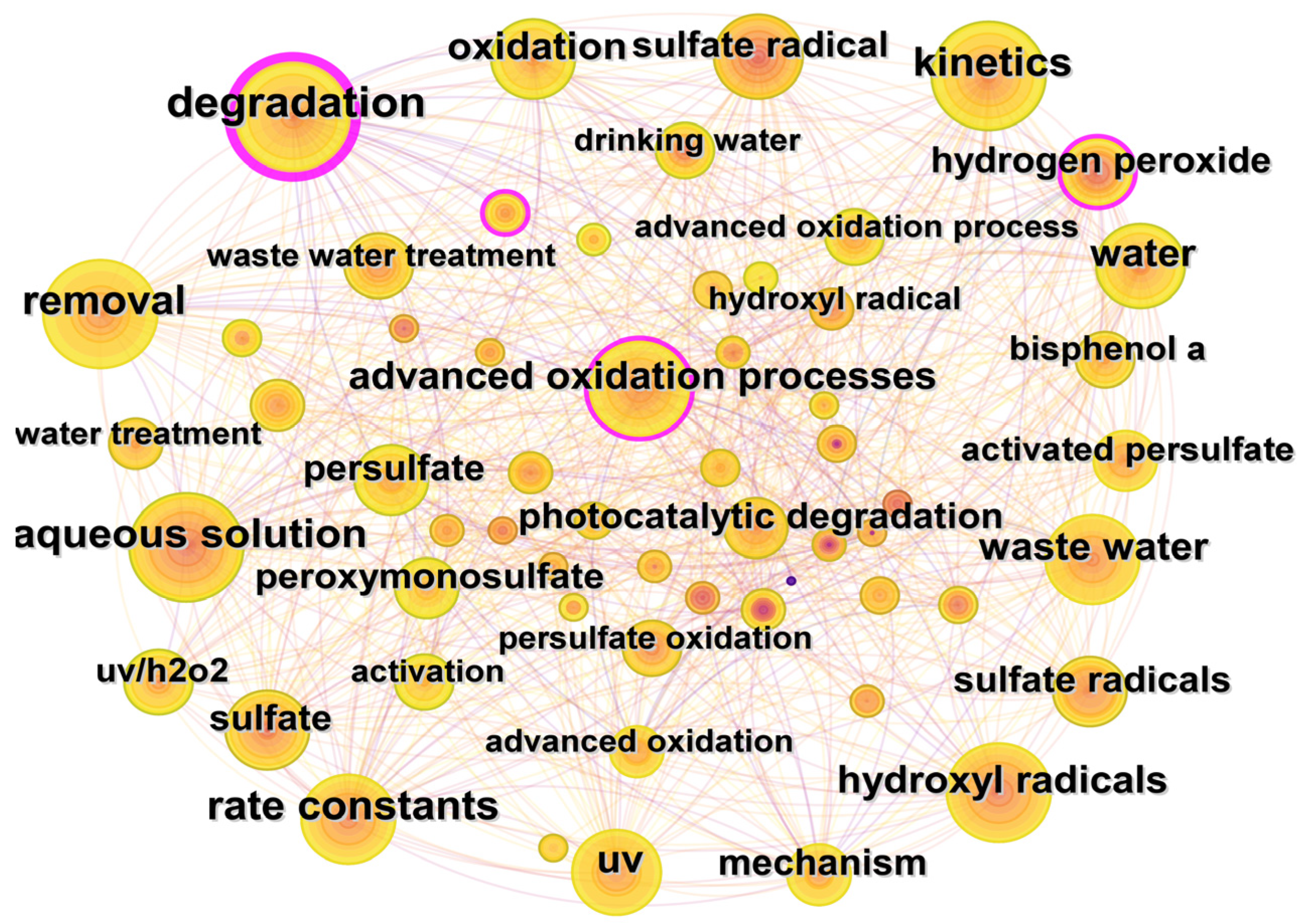
Co-occurrence analysis of keywords could help to reveal the research hotspots and development trends in certain fields. The keywords co-occurrence map of the WOS database is shown in Figure 8. The most frequently used keywords are degradation (270 times), removal (216 times), kinetics (215 times), aqueous solution (211 times), and rate constants (204 times). The keywords could be divided into the following three categories according to their research purposes.
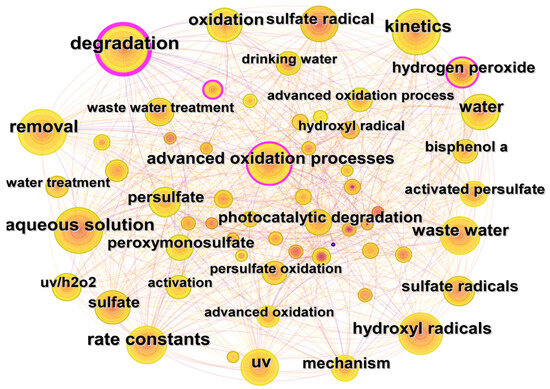
Figure 8.
Keywords collaboration network for UV/PS in Web of Science.
(1) Degradation mechanism: “hydroxyl radicals”, “sulfate radicals”, “UV”, and “Persulfate” are the typical keywords. Studies on UV/PS suggest that pollutants might be mainly degraded in two ways: UV direct photolysis and PS activation. As for the direct photolysis, energy input by UV could directly degrade pollutants by destroying certain chemical bonds. Zhang et al. compared the degradation of sulfamethoxazole (SMX) and trimethoprim by UV, UV/PS, and UV/H2O2, respectively. It was found that a higher contribution rate and a better degradation effect by UV alone was obtained [16]. The direct photolysis rate of pollutants varies significantly due to their molar absorption coefficient and quantum yield. On the other hand, UV radiation could activate PS to generate SO4−· and ·OH, indirectly contributing to the degradation of pollutants. The experiments of PDS or PMS alone without UV activation showed that the removal rate of organic pollutants is almost negligible, but UV activation could accelerate 80–100% of pollutant removal [54]. No matter the direct or indirect effect of UV, it mainly depends on the specific structure of the pollutants.
(2) Reaction kinetics: “kinetics” and “rate constants” are the representative keywords. The order and model of kinetic reaction are commonly used to describe the rate of the reactions. The simulation of degradation models is frequently obtained by comparing the accuracy and similarity of calculation of different established formulations. Feng et al. used different models, such as Chick–Watson, Collins–Selleck, Hom, and Biphasic, to simulate the inactivation rate of E. coli under UV irradiation. The experimental results show that the Biphasic model could well reflect the kinetic changes of E.coli inactivation under the experimental conditions [55].
(3) The applications: the typical keywords are often expressed as “bisphenol a” and other “dyes”, “drinking water”, “wastewater”, and other environmental media containing various organic pollutants and pathogenic microorganisms [51]. At present, activated persulfate advanced oxidation technologies are often used in the degradation and removal of antibiotics [26], pesticides [56], dyes [37], and other traditional and emerging pollutants and TOPs in water, and it also has huge potential in the soil organic pollution remediation [57].
The current research regarding UV/PS mainly focuses on the exploration of the mechanism, the free radical and non-free radical reaction pathways, the factors that influence the degradation process, and the kinetic simulation expression. Moreover, the research interests have gradually shifted from the degradation of certain single pollutants to the removal of co-existing pollutants which could reflect the true environmental pollution.
3.3.2. Keywords Clustering and Bursting Analysis
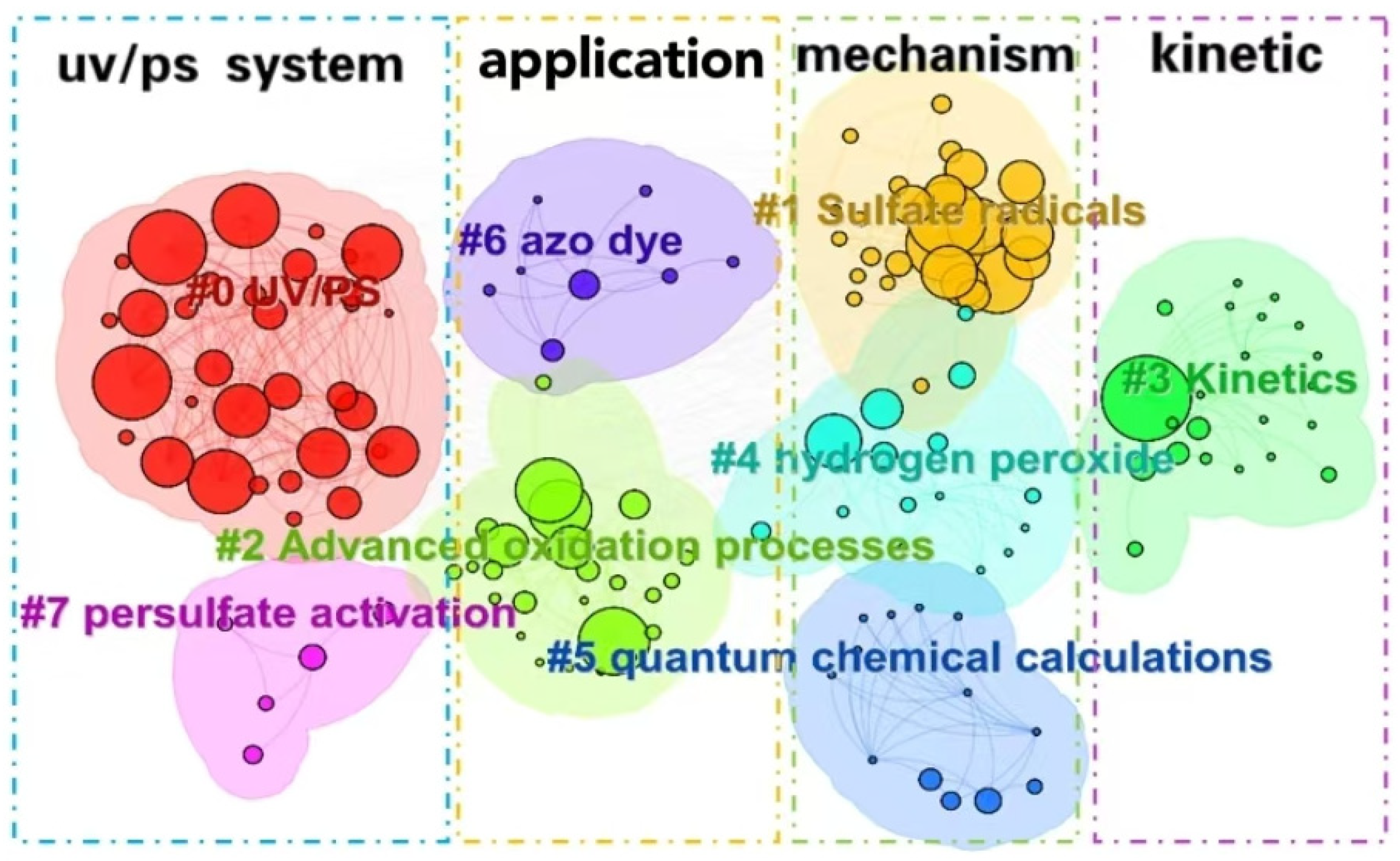
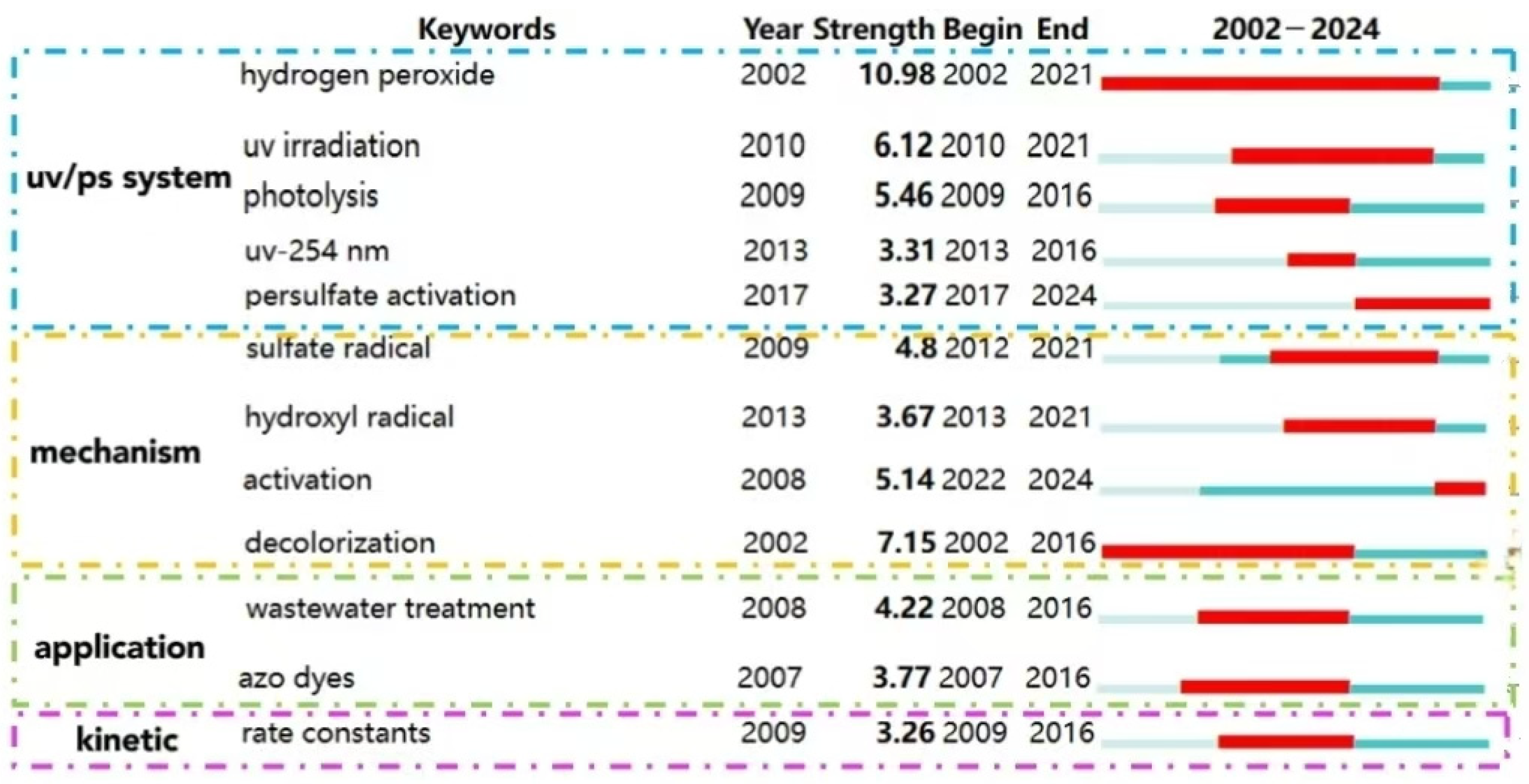
The cluster analysis of keywords (as shown in Figure 9) and bursting keywords information (as shown in Figure 10) in WOS are summarized. The keywords could be divided into four categories as follows: UV/PS system, mechanism, pollutants, and kinetics.
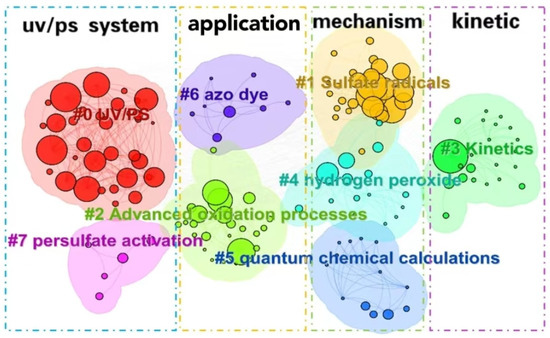
Figure 9.
Clustering analysis of keywords in the UV/PS field.
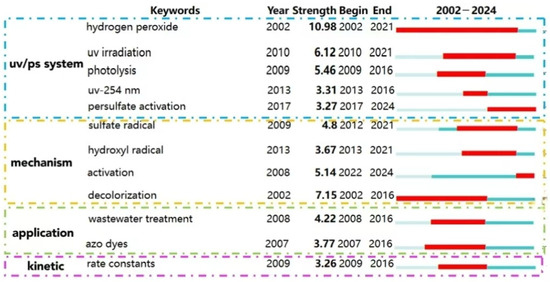
Figure 10.
Keyword bursting map of UV/PS technology in WOS.
(1) Optimization of UV/PS
Clusters 0# UV/PS and 7# persulfate activation are the main bodies for these kinds of research. The burst keyword “UV/PS system” also indicates the system optimization. Due to the strong oxidation property, persulfate has shown great advantages in efficiently degrading organic pollutants in water [58]. Traditional activation methods include heating, ultrasonic, transition metal, and ultraviolet irradiation [59]. Luo et al. [39] investigated the removal of 2,4,6-trichloroanisole using persulfate activated by UV254 and found that SO4−· played a more dominant role than ·OH in the degradation process. Significant progresses have been made in photoactivated PS technology based on UV, visible light, or sunlight irradiation [35,60]. Currently, optimization of the UV/PS system draws a lot of research interest. There are two aspects for the UV/PS system optimization. One is the choice of different UV wavelengths. Due to the high free radical yield, the processes based on the KrCl excimer lamp (UV222-AOPs) have attracted wide attention in water and wastewater treatment. Some studies have applied UV222/PS to degrade antibiotics such as florfenicol and ciprofloxacin [61], pesticides, endocrine-disrupting compounds [62], etc. A good removal efficiency was achieved. Verma et al. found that for the degradation of anatoxin-a, UV260 could activate PMS more effectively than UV270, resulting in up to 98.6% degradation rate under the condition of [PMS]/[anatoxin-a] = 100:1. The process would be inhibited by the presence of carbonate and bicarbonate ions; meanwhile, the presence of humic acids (HA) with a certain concentration range would enhance the degradation of anatoxin-a through the photosensitization effect [63]. That means the choice of different wavelengths would directly impact the effect of pollutant removal. Vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) is also used to activate persulfate, alone or combined with other activation methods. VUV/PS was applied to remove the total odor substances (2-methylisoborneol and geosmin) in water. At a PS concentration of 0.5 mmol/L, the VUV/PS process increased the removal of 2-MIB and GSM by 76% and 74%, respectively, compared to VUV alone or PS alone. The degradation of 2-MIB and GSM would be enhanced with the increase in the PS concentration and VUV intensity within a certain range, but inhibited by HCO3− and humic acid [64]. UV/VUV/PS was suggested to be superior to degrade dye methylene blue (MB) regarding organic pollutant removal efficiency and water treatment cost. It was indicated that MB degradation could be fitted well with pseudo-first-order kinetics in all the PS, UV254, VUV/UV254, UV254/PS, and VUV/UV254/PS processes, and reach the highest reaction rate at 327.6 m2 einstein−1 in the UV/VUV/PS system, while the degradation would be significantly affected by pH and the introduction of HA, HCO3−, Cl−, etc., would inhibit MB degradation [65]. Thus, the selection and combination of different UV wavelengths would be of great potential to improve the efficiency of UV/PS.
(2) Application and development of UV/PS
The keywords classified as clusters 6# azo dye and 2# AOPs are mainly focusing on the application of UV/PS, as well as the bursting keywords “wastewater treatment” and “azo dye.” Dyes, antibiotics, PPCPs, microorganisms, and other organic pollutants in the water body have a great impact on the water environment. Therefore, AOPs (2# advanced oxidation processes) are widely used in water pollution control. Tan et al. [21] used UV, UV/H2O2, and UV/PS to degrade antipyrine in water. UV/PS showed the highest degradation efficiency and is regarded as a priority technology for controlling emerging pollutants such as PPCP. Clustering analysis suggested that researchers not only focused on the removal effect of traditional environmental pollutants by UV/PS, but also extended their interests to the degradation of disinfection products, by-products, and some other ECs and TOPs, indicating the potential of UV/PS as a green disinfectant.
(3) Degradation mechanism of UV/PS
Clusters 1# sulfate radicals, 4# hydrogen peroxide, and 5# quantum chemical calculations, represented the research on the reactive species in the UV/PS process. Khan et al. [15] used UV/PS to degrade atrazine and found that the reactive free radicals produced in AOP were more effective in removing the side alkyl groups of atrazine. The chemical properties of PMS and PDS are shown in Table 3. As mentioned above, under UV irradiation, the O-O bond in S2O82− (mainly for PDS) is broken to generate two SO4−·, while the O-O bond in HSO5− (mainly for PMS) would generate one SO4−· and one ·OH (Equations (1) and (2)) [39]. Due to the oxidability of SO4−· being stronger than that of ·OH, PDS presents a higher oxidability. However, when acting with water solution, H2O could utilize UV light to generate electron transfer resulting in the activation of PDS or PMS (Equations (3)–(5)) [66]. Moreover, the generated SO4−· could also react with H2O and OH− to form ·OH (Equations (6) and (7)) [39].

Table 3.
Basic features of PMS and PDS.
Along with the degradation caused by free radicals, the non-radical pathway in persulfate advanced oxidation processes has recently gained attention due to its advantages of high selectivity and resistance to interference. The researchers investigated the degradation effect of ciprofloxacin by UV/PDS. It was found that O2−· could be converted into singlet oxygen (1O2) by reacting with H2O or H+, and 1O2 was identified as the dominant active species during the degradation process [67]. When PMS activated by the Bimetallic Ni/Fe Atom Cluster Catalysts was used to remove phenol, it was also found that the non-free radical pathway was dominant in the degradation, indicating 1O2 and electron transfer promoted the efficient degradation of phenol in wastewater [68]. It could be seen that non-free radicals also play an important role in the UV/PS oxidization process. However, further studies are still needed due to the diverse and complex mechanisms. Therefore, research focusing on the reaction mechanism would still be one of the hotspots.
(4) Kinetics simulation of UV/PS
The cluster3# kinetics and the burst keyword “rate constants” represent the research concentrated on the reaction kinetics, which would be directly helpful to understanding the degradation efficiency. Lu et al. found that UV/PS could significantly promote the degradation of sulfadimethoxine, and the degradation rate constant is four times and twenty times higher than that of the single UV and single PS, respectively, and the degradation rate constant increases with the increase in UV intensity and PS dosage, while the degradation decline was observed with the existence of some background inorganic anions [69].
4. Discussion
4.1. Current Application
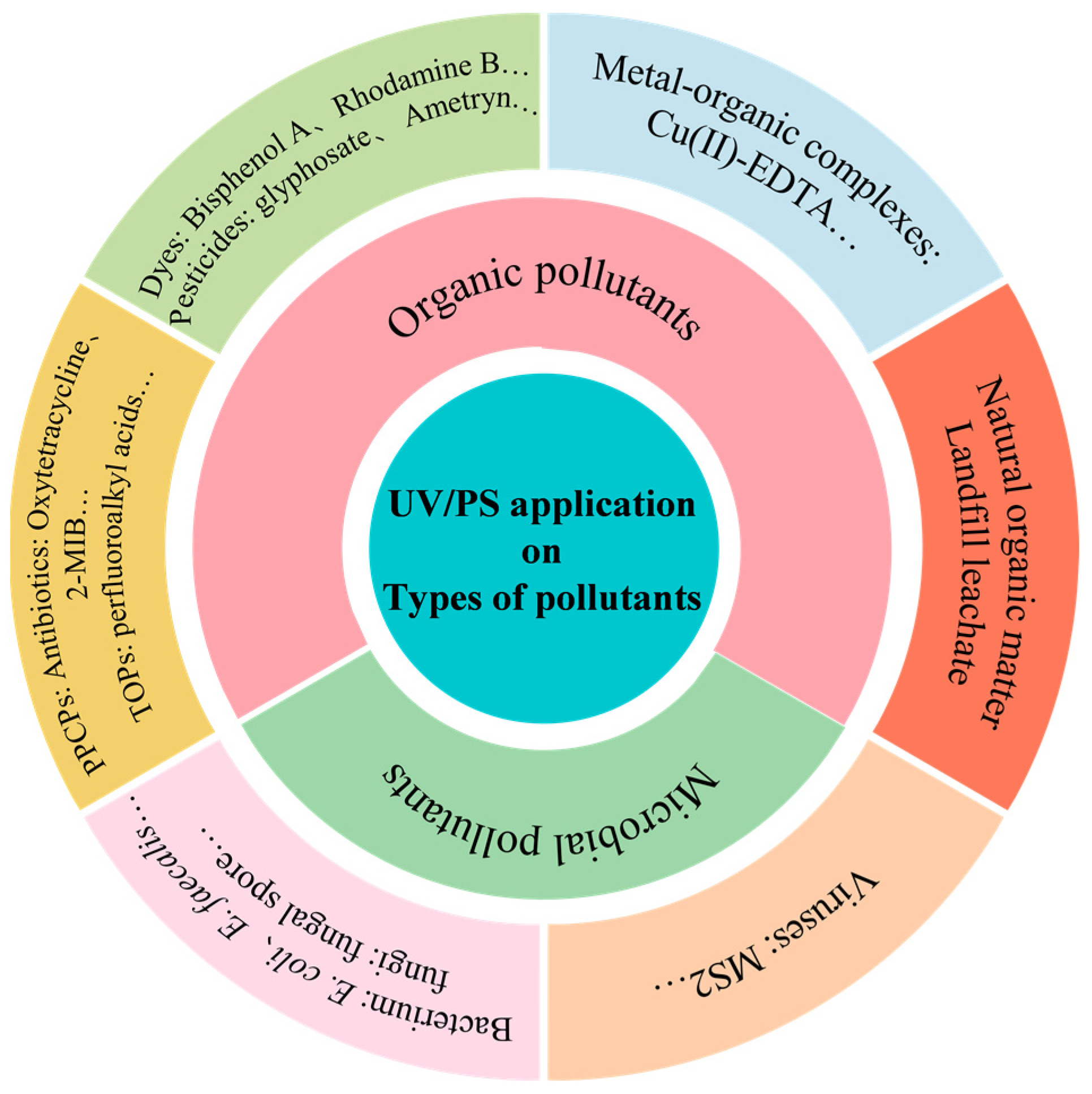
There is a huge potential for UV/PS application in environment remediation. UV/PS has been mainly applied for organic and microbial pollutants removal, which are shown in Figure 11. Table 4 lists some typical cases of various pollutants removal by UV/PS technology to further understand the effect and mechanism of UV/PS technology. Here, three typical types of pollutants were introduced.
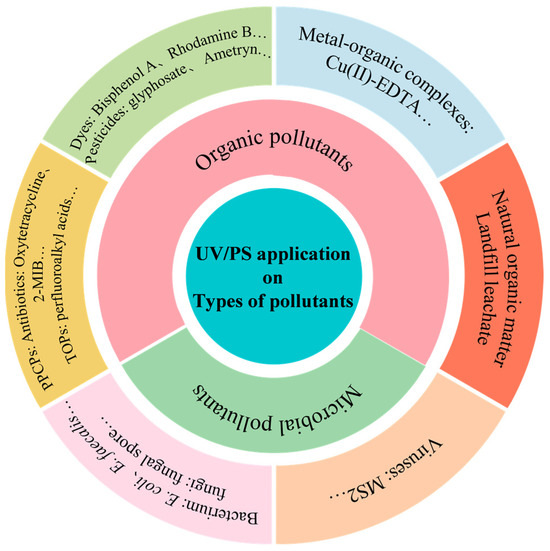
Figure 11.
Pollutant categories in UV/PS application.
(1) Natural organic matter
Natural organic matter (NOM) are important components in a water environment. The fluctuation of their composition and concentration would result in various interactions in biogeochemical cycles [70]. The UV/PS technology has shown significant effectiveness in NOM removal. Alayande et al. [71] used UV/PMS to mineralize the transparent exopolymer particles (TEPs), and a removal rate exceeding 44% only within 180 min was achieved. Under UV irradiation, SO4−· and ·OH generated by UV/PMS would attack the unsaturated bonds and aromatic structures in TEPs. Tian et al. [72] investigated the removal efficiency of NOM by UV, PDS, and UV/PS, with removal rates of 35%, 15%, and 91%, respectively. The radicals produced by UV/PS would primarily target the unsaturated NOM fraction, followed by the refractory fraction, resulting in the destruction of unsaturated bonds and aromatic structures. It would suggest that the main mechanism of NOM removal by UV/PS involves the generation of free radicals to break down the unsaturated bonds and aromatic structures. The degradation efficiency of UV/PS technology is not high for certain natural organic compounds due to the complex environmental pollution. For example, the existence of bromide ions would inhibit the degradation of some organic micropollutants by the UV/PS, and the degradation rate might be reduced by almost 89.5%. This indicates that the degradation efficiency of UV/PS technology would be affected by some other components co-existing in the reaction system [73]. Thus, there might be a relatively wide range for the degradation efficiency of NOM by UV/PS, and the specific degradation efficiency depends on a variety of factors, including the reaction conditions, the characteristics of NOM, other components in the reaction system, and so on.
(2) Antibiotics
In recent years, antibiotics have been widely used in medical treatment, animal husbandry, and aquaculture. The consequent antimicrobial resistance and antibiotic resistance genes pose serious threats to the environment and public health [74]. UV/PS exhibits excellent ability to effectively degrade insoluble pollutants such as antibiotics in water [28]. Ao et al. [75] used medium-pressure ultraviolet (MPUV), PMS, and MPUV/PMS to degrade tetracycline (TTC) in water. The results showed that the removal rates of TTC were 14%, 17%, and 82% for MPUV, PMS, and MPUV/PMS, respectively. Hydroxylation, demethylation, and decarboxylation effects were observed in the process. Furthermore, ·OH attacking the double bond in TTC played a leading role in the degradation; meanwhile, MPUV was indicated to directly destroy the ketone/enol bond. In addition, Ghauch et al. [26] studied the chloramphenicol (CAP) degradation by UV/PS in water. Both SO4−· and ·OH are crucial for CAP degradation. The UV/PS system could significantly improve the degradation and mineralization efficiency compared with the single UV system. Another investigation showed that the degradation of the antiepileptic drug oxcarbazepine (OXC) by UV/PS was more efficient than UV or PS alone [76]. The removal rate of antibiotics might be in the range of 70–100%. The specific degradation efficiency is also influenced by a variety of factors, including the type and concentration of antibiotic, the pH of the reaction system, and the type of catalyst used, and so on. With the global consensus on antibiotic pollution and the implementation of the WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) antibiotic book (2023), the WHO Guidance on wastewater and solid waste management for manufacturing of antibiotics (2024), and WHO bacterial priority pathogens list (2024), UV/PS would still play a huge role in antibiotic removal.
(3) Microorganisms
Microorganisms could not be completely removed by traditional water and wastewater treatment processes, thus resulting in a huge potential health risk to human beings. It is of great necessity to inactivate microorganisms, especially pathogens in water by efficient and safe water treatment technologies. A phage MS2 inactivation experiment showed that a 4.39 log inactivation rate could be achieved for only 4 min by UV/PS treatment, which was 1.44 log higher than that of the single UV treatment [77]. Guerra-Rodriguez et al. [78] studied the inactivation effect of E. faecalis in distilled water, salt water, and simulated wastewater by UV/PMS and UV/H2O2. The results showed that under the UV/PMS system, the bacteria could be completely inactivated with less dose of chemicals, less energy input, and shorter reaction time. The inactivation mechanisms of microorganisms by UV/PS are suspected as the following three aspects: First, free radicals, such as ·OH and SO4−·, could lead to bacterial inactivation. Free radicals generated in the outside of cells possess strong oxidizing abilities, which could first oxidize lipids and proteins in the cell membrane to cause cell structure damage with intracellular substances leakage, and then those intracellular substances might be attacked resulting in the final bacterial death [79]. The second one might be the direct and indirect destruction of endogenous processes caused by UV radiation, which would result in excessive pressure on cells, so that the reactive oxygen species might penetrate the cell membrane and react with the cytoplasm, leading to oxidative stress much more beyond the tolerance of cells. Thirdly, persulfate might directly oxidize and then penetrate the cell wall and cell membrane, which would promote the reaction between PS and the metals that already existed in the cells [80], and result in cell death. The inactivation efficiency for free-living bacteria by UV/PS could reach more than 90%, but the application of UV/PS to inactivate biofilm is rarely investigated and the repair effect of microorganisms also needs to be further studied.

Table 4.
Research on UV/PS application for different kinds of pollutants.
Table 4.
Research on UV/PS application for different kinds of pollutants.
| Contaminants | Light Wavelength and Intensity | Concentration of Pollutant | Concentration of PS | Reaction Water Body | Active Species | Removal Rate | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type I Organic pollutant | anti- biotic | chloram- phenicol (CAP) | 253.6 nm 2.43 mW/cm2 | 31 μM | 0.25 mM | river water (RW) filtered (FWW) non-filtered (NFWW) | ·OH, SO4− | NFWW 86.9% FWW 87.3% RW 50% | [26] |
| oxytetracycline (OTC) | 254 nm 0.1 mW/cm2 | 10 μM | 1 mM | simulative water | ·OH, SO4− | 97% | [14] | ||
| florfenicol (FLO) | 254 nm 398 μW/cm2 | 20 μM | 2 mM | ultrapure water | ·OH, SO4− | UV 24.9% PS 0% UV/PS 98.4% | [81] | ||
| dye | orange II | 254 nm 0.73 mW/cm2 | 20 mg/L | 1 mM | ultrapure water | ·OH, SO4−· | 56.3% | [82] | |
| methylene blue (MB) | 185 nm 2.59 × 10−5 einstein m−2 s−1 254 nm 5.31 × 10−4 einstein m−2 s−1 | 10 μM | 0.5 mM | filtered water surface water secondary wastewater effluent | ·OH, SO4−· | Compared with UV/PS, the pseudo-first- order kinetic k of VUV/UV/PS increases | [65] | ||
| natural organic matter | HA | 254 nm 0.25 mW/cm2 | 2 mg/L | 0.5 mM | DI water NaCl solution synthetic seawater | ·OH, SO4−· | DI water100% NaCl solution 78% synthetic seawater 58% | [83] | |
| UV254/DOC | 254 nm 1.53 mW/cm2 | 5.41–7.55 mg/L 0.098–0.122 mg/L | 0.6 mM/0.6 mM | surface water | ·OH, SO4−· | UV254 91% DOC 58% | [72] | ||
| Type I Inorganic pollutant (metal complexes) | Cu(II)-EDTA | 254 nm 0.25 mW/cm2 | 0.3 mM | [84]0/[Cu(II)-EDTA]0 = 60 mM | simulative water | ·OH, SO4−· | about 90% | [85] | |
| Type II Micro- organism | bacteria | macrolides- resistant bacteria (MRB) sulfonamides-resistant bacteria (SRB) tetracyclines- resistant bacteria (TRB) quinolones- resistant bacteria (QRB) | 254 nm 400 μW/cm2 | 8, 512, 16, 32 mg/L | 1 mmol/L | secondary effluent | ·OH, SO4−· | MRB 96.6% SRB 94.7% TRB 98.0% QRB 99.9% | [86] |
| virus | bacterio- phage (MS2) | 253.7 nm 160 μW/cm2 | 106 PFU/mL | 0.3 mmol/L | ultrapure water | ·OH, SO4−· | 4.39 lg can be removed in 4 min | [77] | |
| fungal or spore | Penicillium Aspergillus niger Trichoderma harzianum | 265 nm, 280 nm, 265 & 280 nm 0.215, 0.214, 0.185 mW/cm2 | 2–4 × 106 CFU/mL | 1 mM | fungal spore suspensions | ·OH, SO4−· | The membrane damage and permeability of the three fungi were accelerated, and the level of photoactiva- tion was reduced | [87] | |
4.2. Future Trend
A large number of studies have shown that there is a great potential for UV/PS in environmental remediation.
(1) From the perspective of the light source system, the ultraviolet light-emitting diode (UV-LED) would be a better alternative light source for UV irradiation due to its low operating cost and excellent sustainability. Studies have shown that the removal rate of humic acid by UV-LED/chlorine is higher than that of traditional UV/chlorine [88]. UV-LED provides some unique functions. For example, UV-LED could emit various radiation wavelengths; meanwhile, periodic high-frequency illumination would occur. Periodic high-frequency illumination could trigger pulse irradiation. Studies have shown that pulse irradiation could help to reach a significantly higher degradation efficiency than that of continuous irradiation [89]. However, the pulsed UV-LED/PS method is affected by the duty cycle, pulse period, and so on [90]. Therefore, pulsed irradiation of UV-LED might be a potential research hotspot. Besides UV activation, visible light activation of PS (Vis/PS) might be more energy-saving and more efficient in removing pollutants. However, due to the insufficient visible light absorption and the electron-hole complexation, Vis/PS usually needs to be mediated by photoresponsive catalytic materials to regulate the optical properties and the activation rate of PS [91,92]. The enhancement of pollutant degradation was suggested due to the synergistic effect between photocatalysis and persulfate activation [60]. Therefore, visible photocatalytic activation should also be further investigated.
(2) The choice of different wavelengths also significantly affects the pollutant’s degradation. For example, by comparing the degradation efficiency from the wavelength 255 to 365 nm generated by UV-LED, the highest degradation efficiency of ciprofloxacin was found at 280 nm [93]. VUV has also emerged as a compelling candidate for its high efficiency and environmental friendliness. It was demonstrated that 185 nm VUV irradiation is capable of generating ROS in situ, resulting in a superior performance in the degradation of organic pollutants [94]. Studies have shown that the PS activation rate by 185 nm VUV and the pollutant’s removal rate were much higher than those of 254 nm, and it was suggested that 185 nm UV might promote the formation of ·OH. However, the mechanism still needs to be explored [95]. One study compared the removal rate of bioleachate by UV254/PS and UV365/PS, respectively. The results showed that the UV365/PS system was more effective [54]. In addition to what has been mentioned above, the combination of different wavelengths might be another research trend. The VUV/UV/PS process was indicated superior to the UV/PS process regarding organic pollutant removal efficiency and water treatment cost [65]. The exploration of pulse irradiation, the combination of multi-wavelength UV, and the potential synergistic effects for simultaneous removal of various pollutants in water still need to be investigated.
(3) The synthesis and modification of carriers such as bimetallic catalysts [96], magnetic nanocomposites [97,98], and nitrogen-doped carbonaceous materials [99] are also of great importance to optimize persulfate advanced oxidation technology [100]. Lee et al. [101] used UV/PS and UV/PS/Cu2+ to assess the degradation effect of non-oxidizing bactericides and fungicides. The results indicated that UV/PS/Cu2+ could increase the degradation efficiency by 4.4–22.2%. It would be seen that the combination of metal-based materials and UV/PS technology has a more significant removal effect on certain pollutants. Therefore, the current research and development of UV/PS should focus on the effective activation of persulfate to continuously produce various active species to achieve a better degradation effect of environmental pollutants.
(4) Regarding the oxidant selection, PMS and PDS showed different characteristics in degrading pollutants through UV activation. By comparison of the degradation of imidacloprid by UV/PMS and UV/PDS, different k-values were obtained under the same reaction time, oxidant, and UV dose, with 0.057/min for UV/PDS and 0.041/min for UV/PMS respectively. Meanwhile, the removal rate for UV/PDS was also higher [102]. Similar results were found when comparing the removal rate of pollutants in textile wastewater [103]. However, UV/PMS was sometimes indicated to be more effective than UV/PDS, e.g., the degradation efficiency of SMX by UV/PMS is slightly higher than that of UV/PDS, and the effect of pH might be one potential reason [17]. Therefore, researchers should rationally select the oxidant with careful consideration in the future.
(5) As for complex water bodies application, UV activation of persulfate is affected by various factors, including the concentration of oxidant, pH, inorganic anions, organic substances, actual UV light intensity, and reaction time [104]. In the present studies, natural water bodies are rarely applied, and the experimental condition was frequently set up to simulate the natural water samples which might focus on just a few kinds of pollutants. The subsequent studies should focus on the actual water bodies, such as rivers, lakes, reclaimed water seawater, and so on, to investigate the interference effects of natural water matrix such as humic acid, inorganic anions, as well as some other reactive species generated in the engineering practice. In addition, photoreactivation and dark repair of microorganisms and some resistant types of cells such as viable but nonculturable cells (VBNC) and persisters should also be considered. The risk assessment of biotoxicity and ecotoxicity needs to be comprehensively investigated as well.
5. Conclusions
Based on the bibliometric analysis, UV/PS has been suggested as an effective and environmentally friendly disinfection technology for controlling diverse environmental pollutants. The following conclusions could be drawn:
(1) UV/PS has been attracting the attention of researchers since its invention. Researchers in China, Iran, and the United States made a great contribution to the field of UV/PS, and the research interests are still growing.
(2) The research teams led by Prof. Ma Jun, Prof. Gao Naiyun, and Prof. Dionysiou Dionysiou D showed widespread and profound academic influence for later research. The research article supervised by Prof. Wang JL at Tsinghua University was cited the most, which provides a good insight for the related researchers.
(3) The research in the field of UV/PS mainly focused on the reaction mechanism and kinetics simulation. Moreover, UV/PS, indicated as an effective technology, could be applied for the degradation of traditional pollutants, ECs, and TOPs in various scenarios.
(4) The improvement of the light source system, the combination of multi-wavelengths, the development of reusable and efficient catalysts, and the selection of suitable oxidants might become the hotspots for future research on UV/PS.
(5) To promote the application of UV/PS, the influencing factors (inorganic anions, etc.) in the practical water matrix and some other active species (active chlorine species, etc.), especially generated during the practical engineering application should be focused on. The revival of certain microorganisms, the induce of VBNC and persister cells might be further investigated. Moreover, the potential toxicity risk needs to be assessed.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Z.J.; modeling, H.W.; formal analysis, H.W.; data analysis, H.W. and W.S.; data curation, H.W., R.L. and H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W. and Z.J.; writing—review and editing, Z.J.; visualization, H.W.; supervision, Z.J.; funding acquisition, Z.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52000127), the Science and Technology Project of Xi’an (22GXFW0018) and (2017071CG/RC034(SXSF002)), the China Scholarship Council (201906875037), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2017JQ5074).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
AOPs: advanced oxidation process; AWaRe, Access, Watch, Reserve; CAP, chloramphenicol; ECs, emerging contaminants; GSM, geosmin; ·OH, hydroxyl radical; HA, humic acids; 2-MB, 2-methylisoborneol; MB, methylene blue; MPUV, medium pressure ultraviolet; NOM, natural organic matter; OXC, oxcarbazepine; PPCPs, personal care products; PFAAs, perfluoroalkyl acids; PCBs, polychlorinated biphenyls; PS, persulfate; PMS, peroxymonosulfate; PDS, peroxydisulfate; SMX, sulfamethoxazole; SO4−·, sulfate radical; 1O2, singlet oxygen; TEPs, transparent exopolymer particles; TTC, tetracycline; TOPs, trace organic pollutants; UV/PS, UV-activated persulfate; UV-LED, ultraviolet light-emitting diode; Vis/PS, visible light/PS; VBNC, viable but nonculturable cells; VUV, vacuum ultraviolet; WOS, Web of Science.
References
- Zhao, F.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Does industrial agglomeration and environmental pollution have a spatial spillover effect?: Taking panel data of resource-based cities in China as an example. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 76829–76841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Chen, L.H.; Ye, M.L.; Su, W.S.; Lei, C.; Jin, X.J.; Lu, Y.S. U(VI) removal on polymer adsorbents: Recent development and future challenges. In Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, H.; Hu, J.; Rui, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, N. Drivers of change behind the spatial distribution and fate of typical trace organic pollutants in fresh waste leachate across China. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Lichtfouse, E.; Liu, G.; Balaram, V.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; Lu, Z.; Stock, F.; Carmona, E.; Teixeira, M.R.; Picos-Corrales, L.A.; et al. Worldwide cases of water pollution by emerging contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 2311–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Khalil, Z.; Baalbaki, A.; Bejjani, A.; Ghauch, A. MIL88-A as a mediator for the degradation of sulfamethoxazole in PS systems: Implication of solar irradiation for process improvement. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2022, 1, 797–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, F.; Yi, L.; Dieketseng, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, G. Free radicals removing extracellular polymeric substances to enhance the degradation of intracellular antibiotic resistance genes in multi-resistant Pseudomonas Putida by UV/H2O2 and UV/peroxydisulfate disinfection processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Xiang, J.L.; Wang, J.J.; Du, H.S.; Wang, T.T.; Huo, Z.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Liu, M.; Du, Y. Ultraviolet-based synergistic processes for wastewater disinfection: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liang, G.; Alex, J.; Zhang, T.; Ma, C. Research Progress of Energy Utilization of Agricultural Waste in China: Bibliometric Analysis by Citespace. Sustainability 2020, 12, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.; Ahmed, S.; Mubushar, M.; Gulzar, A. Global Research on Ethical Leadership: A Bibliometric Investigation and Knowledge Mapping. J. Chin. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2023, 14, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, L. Interpretation of the Guidelines for drinking-water quality (fourth edition) issued by World Health Organization. Water Wastewater Eng. 2012, 38, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pandian, A.M.K.; Rajamehala, M.; Singh, M.V.P.; Sarojini, G.; Rajamohan, N. Potential risks and approaches to reduce the toxicity of disinfection by-product—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Ma, J.; Li, X.C.; Fang, J.Y.; Chen, L.W. Influence of pH on the Formation of Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radicals in the UV/Peroxymonosulfate System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Gunten, U.v.; Kim, J.H. Persulfate-Based Advanced Oxidation: Critical Assessment of Opportunities and Roadblocks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3064–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Q.; He, X.X.; Fu, Y.S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Kinetics and mechanism investigation on the destruction of oxytetracycline by UV-254 nm activation of persulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 305, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.A.; He, X.; Shah, N.S.; Khan, H.M.; Hapeshi, E.; Fatta-Kassinos, D.; Dionysiou, D.D. Kinetic and mechanism investigation on the photochemical degradation of atrazine with activated H2O2, S2O82− and HSO5−. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.C.; Sun, P.Z.; Boyer, T.H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, C.H. Degradation of Pharmaceuticals and Metabolite in Synthetic Human Urine by UV, UV/H2O2, and UV/PDS. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3056–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.W.; Liu, W.J. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by medium pressure UV and oxidants: Peroxymonosulfate, persulfate, and hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Bircher, S.; Rapp, I.; Kerlin, N.; Bakkour, R.; Geisler, M.; Von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. Degradation of Chlorotriazine Pesticides by Sulfate Radicals and the Influence of Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Mishra, I.M.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Kumar, V. Oxidative removal of Bisphenol A by UV-C/peroxymonosulfate (PMS): Kinetics, influence of co-existing chemicals and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 276, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.J.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, W.; Lim, K.Y.; Webster, R.D.; Lim, T.T. Comparative evaluation of iodoacids removal by UV/persulfate and UV/H2O2 processes. Water Res. 2016, 102, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Gao, N.Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Sui, M.H.; Deng, J.; Zhou, S.Q. Degradation of antipyrine by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/PS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 260, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.Q.; Gao, N.Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Ma, Y. Ultraviolet (UV) light-activated persulfate oxidation of sulfamethazine in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 195, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.W.; Ma, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Song, Y.; Yang, Y.; Guan, Y.H.; Wu, D.J. Simulation and comparative study on the oxidation kinetics of atrazine by UV/H2O2, UV/HSO5 and UV/S2O82-. Water Res. 2015, 80, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.L.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, G.Q.; Cao, Y.; Liu, W.L.; Li, J.; Pang, S.Y.; Kong, X.J.; et al. Degradation of sulfamethoxazole by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate (PDS): Formation of oxidation products and effect of bicarbonate. Water Res. 2017, 118, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.S.; Yao, B.L.; Hou, S.D.; Fang, J.Y.; Yan, S.W.; Song, W.H. Kinetic Study of Hydroxyl and Sulfate Radical-Mediated Oxidation of Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2954–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghauch, A.; Baalbaki, A.; Amasha, M.; El Asmar, R.; Tantawi, O. Contribution of persulfate in UV-254 nm activated systems for complete degradation of chloramphenicol antibiotic in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 317, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; de la Cruz, A.A.; Dionysiou, D.D. Destruction of cyanobacterial toxin cylindrospermopsin by hydroxyl radicals and sulfate radicals using UV-254 nm activation of hydrogen peroxide, persulfate and peroxymonosulfate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2013, 251, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Huebner, U. Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment-A critical review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.D.; Dong, Z.; Lim, T.T. Generation of sulfate radical through heterogeneous catalysis for organic contaminants removal: Current development, challenges and prospects. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2016, 194, 169–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, S.; Lin, K.Y.A.; Ghanbari, F. A review of the recent advances on the treatment of industrial wastewaters by Sulfate Radical-based Advanced Oxidation Processes (SR-AOPs). Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Shao, Y.S.; Gao, N.Y.; Xia, S.J.; Tan, C.Q.; Zhou, S.Q.; Hu, X.H. Degradation of the antiepileptic drug carbamazepine upon different UV-based advanced oxidation processes in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 222, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.A.; He, X.X.; Khan, H.M.; Shah, N.S.; Dionysiou, D.D. Oxidative degradation of atrazine in aqueous solution by UV/H2O2/Fe2+, UV/S2O82−/Fe2+ and UV/HSO5−/Fe2+ processes: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 218, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Xiao, Y.J.; Chang, V.W.C.; Lim, T.T. Kinetic and mechanistic investigation of azathioprine degradation in water by UV, UV/H2O2 and UV/persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ike, I.A.; Linden, K.G.; Orbell, J.D.; Duke, M. Critical review of the science and sustainability of persulphate advanced oxidation processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, Y.H.; Chen, F.; Yao, F.B.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.N.; Yi, K.X.; Hou, L.H.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.B. Recent advances in photo-activated sulfate radical-advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for refractory organic pollutants removal in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 122149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Liang, C.J.; Chen, J.H. Feasibility study of ultraviolet activated persulfate oxidation of phenol. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Sayed, M.; Khan, J.A.; Shah, N.S.; Khan, H.M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Oxidative removal of brilliant green by UV/S2O82-, UV/HSO5- and UV/H2O2 processes in aqueous media: A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Comparison of Halide Impacts on the Efficiency of Contaminant Degradation by Sulfate and Hydroxyl Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.W.; Jiang, J.; Ma, J.; Pang, S.Y.; Liu, Y.Z.; Song, Y.; Guan, C.T.; Li, J.; Jin, Y.X.; Wu, D.J. Oxidation of the odorous compound 2,4,6-trichloroanisole by UV activated persulfate: Kinetics, products, and pathways. Water Res. 2016, 96, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; de la Cruz, A.A.; O’Shea, K.E.; Dionysiou, D.D. Kinetics and mechanisms of cylindrospermopsin destruction by sulfate radical-based advanced oxidation processes. Water Res. 2014, 63, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutze, H.V.; Kerlin, N.; Schmidt, T.C. Sulfate radical-based water treatment in presence of chloride: Formation of chlorate, inter-conversion of sulfate radicals into hydroxyl radicals and influence of bicarbonate. Water Res. 2015, 72, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmez-Hanci, T.; Arslan-Alaton, I. Comparison of sulfate and hydroxyl radical based advanced oxidation of phenol. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 224, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, G.D.; Guo, X.C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, T.T.; Xi, B.D. Degradation difference of ofloxacin and levofloxacin by UV/H2O2 and UV/PS (persulfate): Efficiency, factors and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 385, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.Q.; Fu, D.F.; Gao, N.Y.; Qin, Q.D.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, H.M. Kinetic degradation of chloramphenicol in water by UV/persulfate system. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2017, 332, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Pignatello, J.J.; Ma, J.; Mitch, W.A. Effect of matrix components on UV/H2O2 and UV/S2O82− advanced oxidation processes for trace organic degradation in reverse osmosis brines from municipal wastewater reuse facilities. Water Res. 2016, 89, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.L. Iron and sulfur co-doped graphite carbon nitride (FeOy/S-g-C3N4) for activating peroxymonosulfate to enhance sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, T.C.; Wang, J.L. Photocatalytic selective oxidation of ammonium to dinitrogen by FeOx-MgO activated persulfate under solar-light irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Ma, J.; Liu, W.; Zou, J.; Yue, S.; Li, X.; Wiesner, M.R.; Fang, J. Removal of 2-MIB and geosmin using UV/persulfate: Contributions of hydroxyl and sulfate radicals. Water Res. 2015, 69, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Xie, P.; Wang, Z.; Ding, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wiesner, M.R. Comparative study on the pretreatment of algae-laden water by UV/persulfate, UV/chlorine, and UV/H2O2: Variation of characteristics and alleviation of ultrafiltration membrane fouling. Water Res. 2019, 158, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waclawek, S.; Lutze, H.V.; Grubel, K.; Padil, V.V.T.; Cernik, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. Chemistry of persulfates in water and wastewater treatment: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, M.; Dionysiou, D.D. What is the role of light in persulfate-based advanced oxidation for water treatment? Water Res. 2021, 189, 116627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.N.; Xu, D.Y.; Dong, Y.L.; Zhnag, L.; Wang, P.F.; Ren, Z.J. Kinetic Model and Influencing Factors of UV Disinfection. Water Purif. Technol. 2020, 39, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Derbalah, A.; Sakugawa, H. Sulfate Radical-Based Advanced Oxidation Technology to Remove Pesticides From Water A Review of the Most Recent Technologies. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2024, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Z.; Cang, L. Progress of Chemical Oxidation Mechanism of Peroxymonosulfate and Its Application in Remediation of Organic Contaminated Soil. Soil 2022, 54, 653–666. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, X.; Duan, X.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zhao, X. Remediation of environmentally persistent organic pollutants (POPs) by persulfates oxidation system (PS): A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 160818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.V.; Divyapriya, G.; Titchou, F.E.; Hamdani, M. Treatment of textile wastewater by sulfate radical based advanced oxidation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarpour, H.; Padervand, M.; Soltanieh, M.; Vossoughi, M. Enhanced decolorization of rhodamine B solution through simultaneous photocatalysis and persulfate activation over Fe/C3N4 photocatalyst. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 153, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Liu, Y.Y.; Feng, M.B.; Yu, X.; Wang, L. Degradation mechanisms of antibiotics in UV222/H2O2 and UV222/ persulfate systems: Dual roles of inorganic anions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shang, C. Far-UVC Photolysis of Peroxydisulfate for Micropollutant Degradation in Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6030–6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Nakamura, S.; Sillanpaa, M. Application of UV-C LED activated PMS for the degradation of anatoxin-a. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shi, L.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Tang, X. Removal of Odorants in Drinking Water Using VUV/Persulfate. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2018, 39, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, D.; Li, W.T.; Lv, J.R.; Qiang, Z.M.; Li, M.K. Methylene blue degradation by the VUV/UV/persulfate process: Effect of pH on the roles of photolysis and oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 121855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, X.R.; Yang, X. Treating disinfection byproducts with UV or solar irradiation and in UV advanced oxidation processes: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; He, R.; Liu, S. Insights into the radical and nonradical oxidation degradation of ciprofloxacin in peroxodisulfate activation by ultraviolet light. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Han, D. Bimetallic Ni/Fe Atom Cluster Catalysts Enhance Non-free Radical Degradation of Organic Pollutant Phenol. Catal. Lett. 2024, 154, 2182–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ding, P.; Lyu, Z.; Xu, G.; Peng, M.; Du, E.; Zheng, L. Degradation kinetics and mechanism of SDM by UV/PS process in water. Environ. Pollut. Control 2022, 44, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Sillanpaa, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Matilainen, A. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of natural organic matter from drinking water sources: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 208, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, A.B.; Yun, E.T.; Silva, F.; Hong, S. Mechanistic insights into the potential applicability of a sulfate-based advanced oxidation process for the control of transparent exopolymer particles in membrane-based desalination. Desalination 2022, 522, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Y.; Wu, C.W.; Yu, H.R.; Gao, S.S.; Li, G.B.; Cui, F.Y.; Qu, F.S. Applying ultraviolet/persulfate (UV/PS) pre-oxidation for controlling ultrafiltration membrane fouling by natural organic matter (NOM) in surface water. Water Res. 2018, 132, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q. Effect of Bromine Ion on Kinetics of Degradation of Organic Micropollutants in Ultraviolet/Persulfate Oxidation System. Master Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.G.; Maqbool, F.; Hu, Y. Removal of antibiotics pollutants in wastewater by UV-based advanced oxidation processes: Influence of water matrix components, processes optimization and application: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, X.W.; Sun, W.J.; Li, S.M.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Lu, Z.D. Degradation of tetracycline by medium pressure UV-activated peroxymonosulfate process: Influencing factors, degradation pathways, and toxicity evaluation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.J.; Zhou, S.Q.; Shi, Z.; Deng, L.; Li, G.C.; Yi, Q.H.; Gao, N.Y. Degradation of oxcarbazepine by UV-activated persulfate oxidation: Kinetics, mechanisms, and pathways. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 2848–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.M.; Yang, H.M.; Wang, Z. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Bacteriophage MS2 Inactivation in Water by UV Activated Sodium Persulfate. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 4807–4814. [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Rodriguez, S.; Rodriguez, E.; Moreno-Andres, J.; Rodriguez-Chueca, J. Effect of the water matrix and reactor configuration on Enterococcus sp. inactivation by UV-A activated PMS or H2O2. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Liu, K.; Bai, L.; Minakata, D.; Seo, Y.; Goktas, R.K.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Tang, C.J.; Wei, Z.; Spinney, R. Inactivation of pathogenic microorganisms by sulfate radical: Present and future. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruti, I.; Oller, I.; Inmaculada Polo-Lopez, M. Direct oxidation of peroxymonosulfate under natural solar radiation: Accelerating the simultaneous removal of organic contaminants and pathogens from water. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Galvis, E.A.; Ferraro, F.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Degradation of highly consumed fluoroquinolones, penicillins and cephalosporins in distilled water and simulated hospital wastewater by UV254 and UV254/persulfate processes. Water Res. 2017, 122, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Tong, Y.; Liu, Z.Z.; Huang, L.Z.; Yuan, J.P.; Xue, Y.W.; Fang, Z. Enhanced degradation of Orange II using a novel UV/persulfate/sulfite system. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayande, A.B.; Hong, S. Ultraviolet light-activated peroxymonosulfate (UV/PMS) system for humic acid mineralization: Effects of ionic matrix and feasible application in seawater reverse osmosis desalination*. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anipsitakis, G.P.; Dionysiou, D.D. Transition metal/UV-based advanced oxidation technologies for water decontamination. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2004, 54, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shan, C.; Xie, B.H.; Liu, Y.; Pan, B.C. Decomplexation of Cu(II)-EDTA by UV/persulfate and UV/H2O2: Efficiency and mechanism. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2017, 200, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.S.; Wu, J.W.; Dong, L.L.; Liu, B.F.; Xing, D.F.; Yang, S.S.; Wu, X.K.; Wang, Q.; Fan, J.N.; Feng, L.P.; et al. Removal of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater effluent by UV-activated persulfate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.Q.; Cao, R.H.; Wen, G.; Xu, X.Q.; Xia, Y.C.; Wu, G.H.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, H.N.; Lin, Y.Z.; et al. Efficacy of UV-LED based advanced disinfection processes in the inactivation of waterborne fungal spores: Kinetics, photoreactivation, mechanism and energy requirements. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Xu, B.; Xia, Y.C.; Hu, C.Y.; Zhang, T.Y.; Cao, T.C.; Pan, Y.; Gao, N.Y. A comparison of dissolved organic matter transformation in low pressure ultraviolet (LPUV) and ultraviolet light-emitting diode (UV-LED)/chlorine processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 702, 134942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarian, M.R.; Ganjkhanloo, M.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Hosseini, S.A. Energy-efficient removal of acid red 14 by UV-LED/persulfate advanced oxidation process: Pulsed irradiation, duty cycle, reaction kinetics, and energy consumption. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 127, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimiri, I.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Dorraji, M.S.S.; Eskandarian, M.R. Study of controlled pulsed illumination (CPI) efficiency in the homogeneous UV-LED/S2O82- process for the removal of organic dye from contaminated water. Results Eng. 2024, 21, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, P.; Ke, T.; Li, W. Heterogeneous activation of persulfate for Rhodamine B degradation with 3D flower sphere-like BiOI/Fe3O4 microspheres under visible light irradiation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bai, X.; Shi, J.; Du, X.; Xu, L.; Jin, P. Quasi-full-visible-light absorption by D35-TiO2g-C3N4 for synergistic persulfate activation towards efficient photodegradation of micropollutants. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2019, 256, 117759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.S.; Ye, J.S.; Ma, S.L.; Wei, C.H.; Gao, N.Y.; He, J.Z. Degradation of ciprofloxacin by UV and UV/H2O2 via multiple-wavelength ultraviolet light-emitting diodes: Effectiveness, intermediates and antibacterial activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, F. Chemical-free vacuum ultraviolet irradiation as ultrafiltration membrane pretreatment technique: Performance, mechanisms and DBPs formation. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Westerhoff, P.; Zheng, M.X.; Wu, M.Y.; Yang, Y.; Chiu, C.A. UV-activated persulfate oxidation and regeneration of NOM-Saturated granular activated carbon. Water Res. 2015, 73, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, G.; Yang, F. Kinetics research on bimetallic CoMnO_x/UV catalyzed persulfate for the degradation of AO7. Ind. Water Treat. 2018, 38, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandarian, M.R.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Fazli, M.; Ghalamchi, L.; Choi, H. Synergistic decomposition of imidacloprid by TiO2-Fe3O4 nanocomposite conjugated with persulfate in a photovoltaic-powered UV-LED photoreactor. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Gao, Y.; Hu, R.; Li, G.; Yu, X. Degradation of Methyl Orange in Aqueous Solution via Magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4 Conjugated with Persulfate. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.F.; Lin, Q.T.; He, W.J.; Fu, H.Y.; Huang, Z.F.; Wang, Y.P.; Wu, L.B. Study on the nonradical pathways of nitrogen-doped biochar activating persulfate for tetracycline degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.T.; Jin, X.L. Research Progress of Bismuth-Based Bimetallic Oxides in Advanced Oxidation of Persulfate; Journal of Tianjin Polytechnic University: Tianjin, China, 2023; pp. 483–495. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, M.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Du, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Huang, N.; Xu, Z.B.; Wu, Q.Y.; Ye, B. Enhancement effect among a UV, persulfate, and copper (UV/PS/Cu2+) system on the degradation of nonoxidizing biocide: The kinetics, radical species, and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Rao, P.; Li, G.; Dong, L.; Zhang, X.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Chu, W.; Xu, B.; An, N.; et al. Degradation of imidacloprid by UV-activated persulfate and peroxymonosulfate processes: Kinetics, impact of key factors and degradation pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifci, D.I.; Sensoy, O.; Gunes, E.; Gunes, Y. Treatment of a textile wastewater using sulfate and hydroxyl radicals based oxidation under the UV light: A Comparision between UV/H2O2, UV/PS and UV/PMS. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2023, 22, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calaixo, M.R.C.; Ribeirinho-Soares, S.; Madeira, L.M.; Nunes, O.C.; Rodrigues, C.S.D. Catalyst-free persulfate activation by UV/visible radiation for secondary urban wastewater disinfection. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).