Environmental Monitoring of Pig Slurry Ponds Using Geochemical and Geoelectrical Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
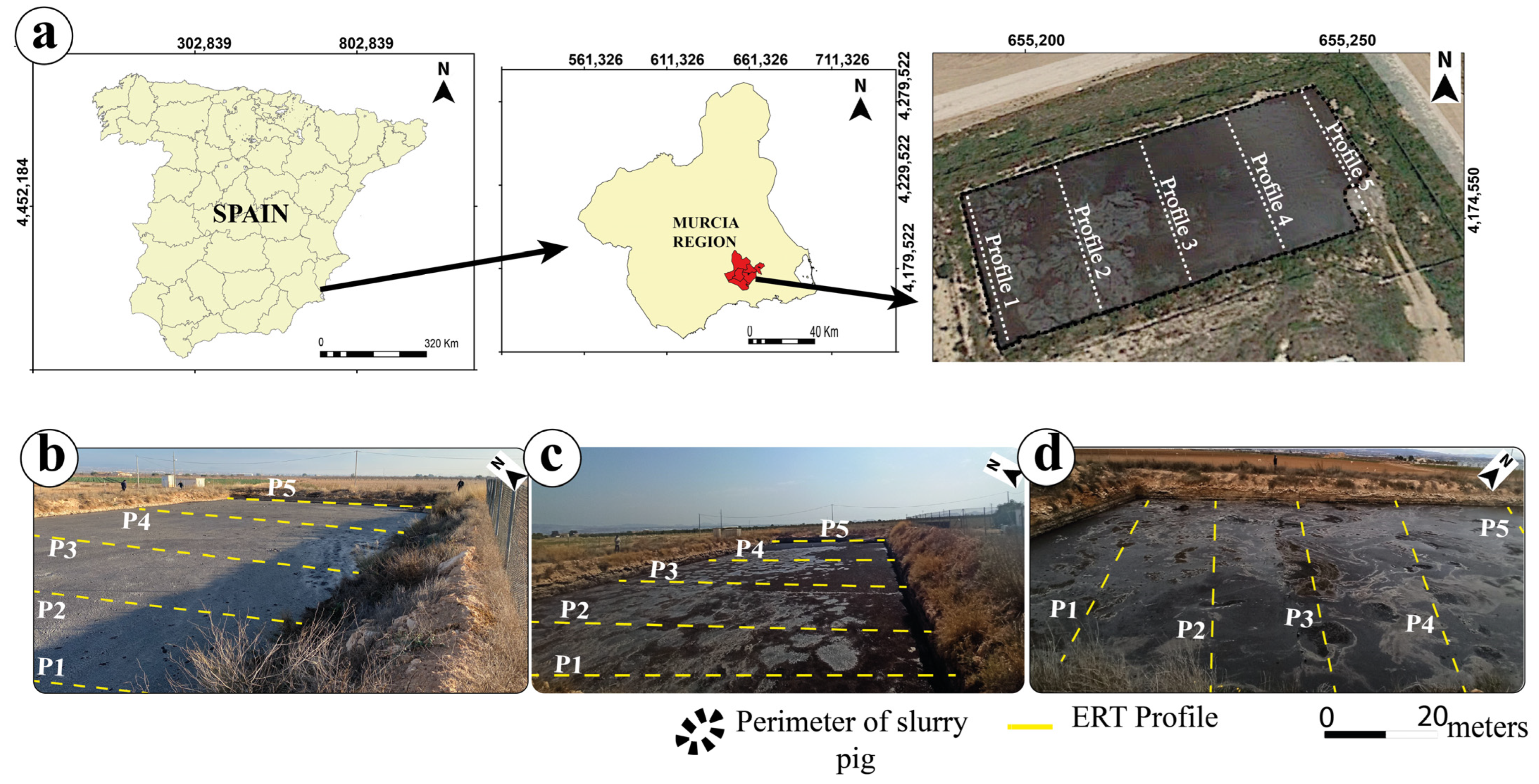
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Electrical Resistivity Tomography
2.3. Pig Slurry Sampling
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
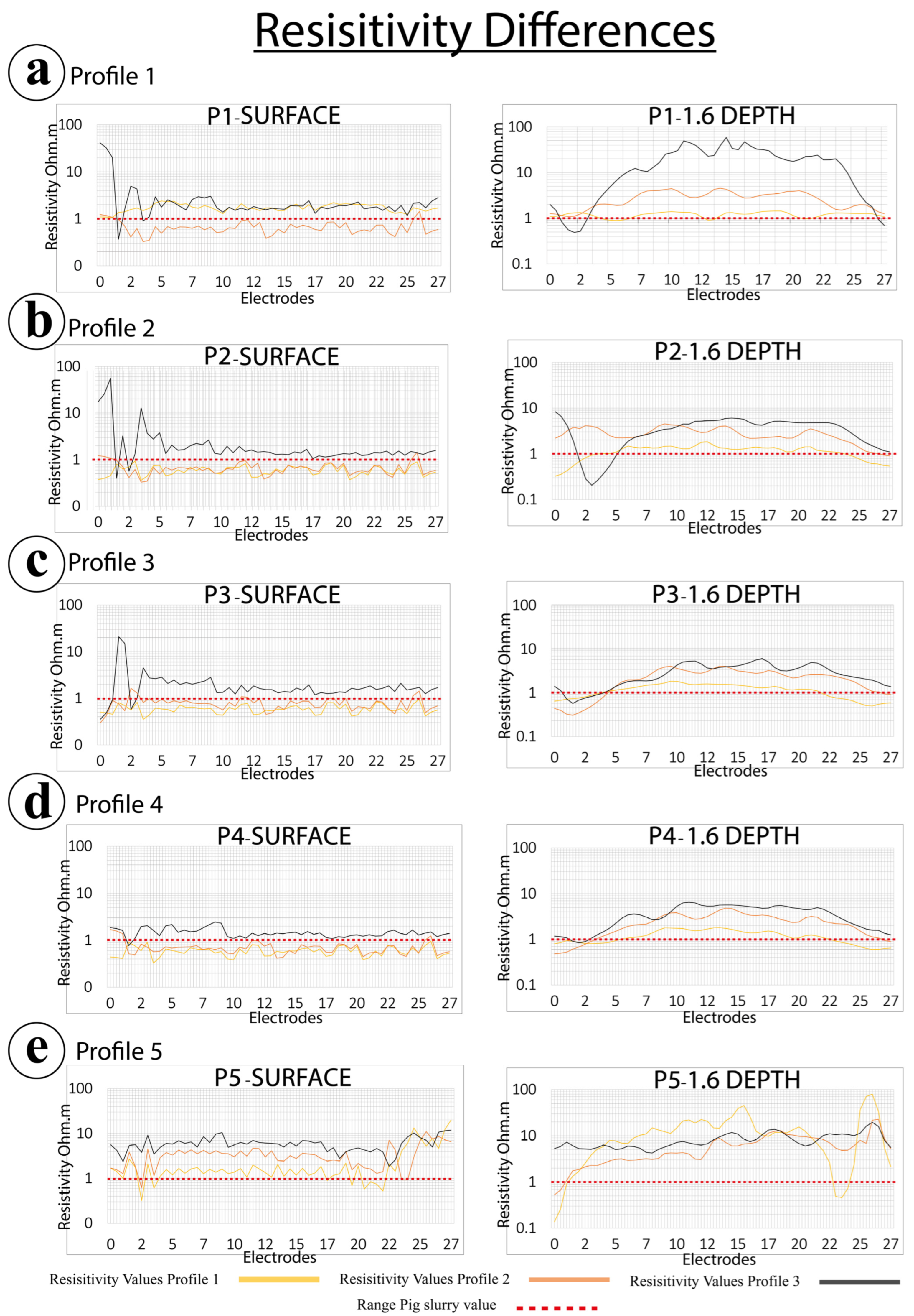
3.1. Electrical Resistivity Tomography of Pig Slurry
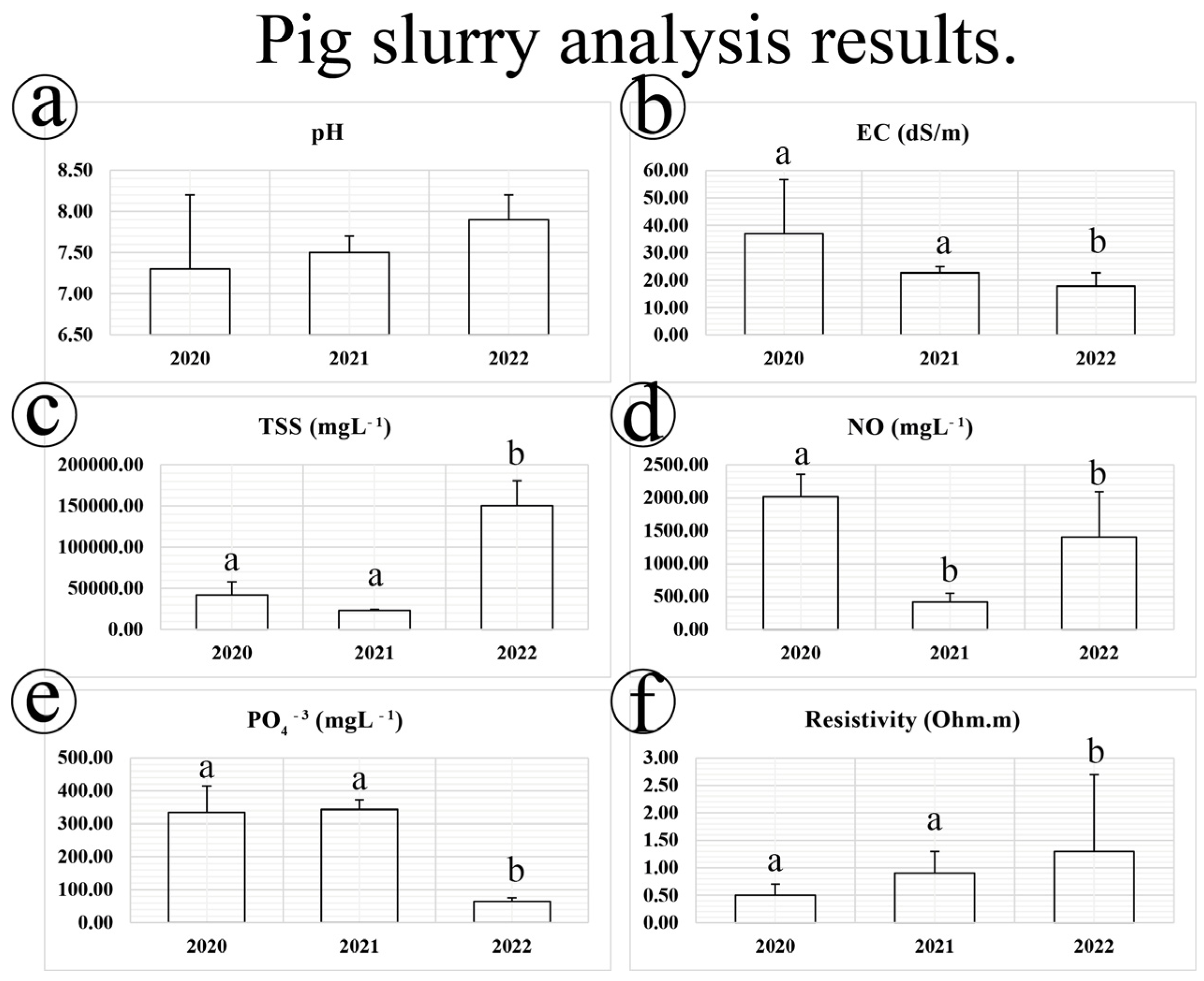
3.2. Pig Slurry Characterization and Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suresh, A.; Choi, H.L.; Oh, D.I.; Moon, O.K. Prediction of the nutrients value and biochemical characteristics of swine slurry by measurement of EC–Electrical conductivity. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4683–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Burton, C.H.; Sneath, R.W.; Farrent, J.W. A study of the potential contribution of sedimentation to aerobic treatment processes for pig slurry. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1995, 61, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venglovsky, J.; Sasakova, N.; Gregova, G.; Papajova, I.; Toth, F.; Szaboova, T. Devitalisation of pathogens in stored pig slurry and potential risk related to its application to agricultural soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21412–21419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministerio de Agricultura Pesca y Alimentación. El Sector de la Carne de Cerdo en Cifras: Principales Indicadores Económicos. In The Pig Sector in Numbers: Main Economic Indicators; Subdirección General de Producciones Ganaderas y Cinegéticas, Dirección General de Producciones y Mercados Agrarios: Madrid, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.; Jones, R. Work Package 1. The Contribution of Slurry Management Practices to Diffuse Pollution from Agriculture. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a7ca2dc40f0b6629523ad27/pb14045-slurry-management-storage-report-appendix.pdf#page=4 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Nrcs, U. Conservation Practice Standard Waste Storage Facility (Code 313). Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/ (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Real Decreto 306/2020, de 11 de febrero; Boletín Oficial del Estado: Madrid, Spain, 2019; Volume 2014, pp. 18987–19106.
- Council Directive 91/676/EEC of 12 December 1991 Concerning the Protection of Waters against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/ALL/?uri=celex%3A31991L0676 (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Díez López, J.A.; Hernáiz, P.J.; Muñoz, M.J.; Torre, A.; Vallejo, A. Impact of pig slurry on soil properties, water salinization, nitrate leaching and crop yield in a four-year experiment in Central Spain. Soil Use Manag. 2004, 20, 444–450. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, L.; Tanunchai, B.; Glaser, B. Antibiotics residues in pig slurry and manure and its environmental contamination potential. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcalá, F.J.; Paz, M.C.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Santos, F.M. Integrated Geophysical Methods for Shallow Aquifers Characterization and Modelling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Crespo, T.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; De Ignacio-San José, C.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Lillo, J.; Faz, A. Geoenvironmental characterization of riverbeds affected by mine tailings in the Mazarrón district (Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2012, 119, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzoli, L.; Giampaolo, V.; De Martino, G.; Perciante, F.; Lapenna, V.; Rizzo, E. ERT and GPR prospecting applied to unsaturated and subwater analogue archaeological site in a full scale laboratory. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaiwa, D.A.; Ikponmwen, M.O. Application of 2D and 3D Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) in Predicting Soil Erodibility in Oredide Village, Auchi in Etsako West LGA of Edo State, Southern Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2021, 25, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Song, X.; Wu, Y.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Fingerprinting Organochlorine Groundwater Plumes Based on Non-Invasive ERT Technology at a Chemical Plant. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondo Medhus, A.; Klynkby, L. Engineering Geophysics, 1st ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2022; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Farzamian, M.; Santos, F.A.M.; Khalil, M.A. Application of EM38 and ERT methods in estimation of saturated hydraulic conductivity in unsaturated soil. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 112, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.K. Near-Surface Geophysics; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2005; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rosales, R.M.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Faz, A.; Bech, J. Study of subsoil in former petrol stations in SE of Spain: Physicochemical characterization and hydrocarbon contamination assessment. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 147, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Z. Categorical modeling on electrical anomaly of room-and-pillar coal mine fires and application for field electrical resistivity tomography. J. Appl. Geophys. 2017, 136, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeh, C.C.; Maike, S.M. Using vertical electrical sounding and 2D resistivity tomography to investigate Osogbo central waste dumpsite, Osun State, Nigeria. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2023, 18, 25–37. [Google Scholar]
- Arifin, M.H.; Kayode, J.S.; Ismail MK, I.; Abdullah, A.M.; Embrandiri, A.; Nazer NS, M.; Azmi, A. Environmental hazard assessment of industrial and municipal waste materials with the applications of RES2-D method and 3-D Oasis Montaj modeling: A case study at Kepong, Kuala Lumpur, Peninsula Malaysia. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiang, F.B.; Emujakporue, G.O.; Nwosu, L.I. Leachate delineation and aquifer vulnerability assessment using geo-electric imaging in a major dumpsite around Calabar Flank, Southern Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.K.; Pelinson, N.S.; Bastianon, D.; Saraiva, F.A.; Wendland, E. Using Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) to assess the effectiveness of capping in old unlined landfills. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2023, 180, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini MS, I.; Hasan, M.; Zolkepli, M.F. Urban landfills investigation for leachate assessment using electrical resistivity imaging in Johor, Malaysia. Environ. Chall. 2022, 6, 100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udosen, N.I. Geo-electrical modeling of leachate contamination at a major waste disposal site in south-eastern Nigeria. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa-Camacho, X.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Gabarrón, M.; Faz, Á. Delimiting pig slurry affected subsurface areas by combining geophysical and geochemical techniques. Water 2022, 14, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capa-Camacho, X.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Martínez-Segura, M.; Gabarrón, M.; Faz, Á. Electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and geochemical analysis dataset to delimit subsurface affected areas by livestock pig slurry ponds. Data Brief 2022, 45, 108684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Pagín, P.; Faz, A.; Aracil, E. The use of 2D electrical tomography to assess pollution in slurry ponds of the Murcia region, SE Spain. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 7, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pagán, P.; Cano, Á.F.; Ramos da Silva, G.R.; Olivares, A.B. 2-D electrical resistivity imaging to assess slurry pond subsoil pollution in the southeastern region of Murcia, Spain. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2010, 15, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabarrón, M.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Bueso, M.C.; Martínez-Martínez, S.; Faz, Á.; Acosta, J.A. Electrical resistivity tomography as a support tool for physicochemical properties assessment of near-surface waste materials in a mining tailing pond (El Gorguel, SE Spain). Minerals 2020, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Nover, D.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yen, H.; He, B. Assessment of extrinsic and intrinsic influences on water quality variation in subtropical agricultural multipond systems. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Pagan, P.; Gomez-Ortiz, D.; Martin-Crespo, T.; Martin-Velazquez, S.; Martinez-Segura, M. Electrical resistivity imaging applied to tailings ponds: An overview. Mine Water Environ. 2021, 40, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Pagán, P. “Aplicación de diferentes técnicas no destructivas de prospección geofísica a problemas relacionados con contaminación ambiental producidas por diferentes actividades antrópicas en la Región de Murcia.” (2006).
- Alshuwaikhat, H.M.; Abubakar, I. An integrated approach to achieving campus sustainability: Assessment of the current campus environmental management practices. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BORM-s-2021-90328 Decreto-Ley 5/2021, de 27 de Agosto, de Modificación de la Ley 3/2020, de 27 de Julio, de Recuperación y Protección del Mar Menor. Available online: https://www.boe.es/buscar/doc.php?id=BORM-s-2021-90328 (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Boletín Oficial de la Región de Murcia. Publicación Número 8097 del BORM Número 298 de 27/12/2019. Available online: https://www.borm.es/services/anuncio/ano/2019/numero/8097/pdf?id=782214 (accessed on 21 November 2023).
- Fuente Álamo de Murcia Climate: Temperature Fuente Álamo de Murcia & Weather by Month. Available online: https://en.climate-data.org/europe/spain/region-de-murcia/fuente-alamo-de-murcia-31093/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Marín Lechado, C.; Roldán García, F.J.; Pineda Velasco, A.; Martinez Zubieta, P.; Rodero Pérez, J.; Diaz Pinto, G. Mapa Geológico Continuo de España1:50 000 Zonas Internas de las Cordilleras Béticas (Zona, -2.2.1.0.). in, G.E.O.D.E. Mapa Geológico Digital Continuo de España. [En Linea]. 2008. Available online: https://info.igme.es/cartografiadigital/geologica/geodezona.aspx?ld=Z1800 (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Romero Díaz, A.; Belmonte Serrato, F.; Hernández Bastida, J.A. El Campo de Cartagena una visión global. Recorridos por el Campo de Cartagena. Control de la degradación y uso sostenible del suelo; Instituto Mediterráneo del Agua: Murcia, Spain, 2011; pp. 17–48. [Google Scholar]
- Everett, M.E. Near-Surface Applied Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega, M.; Osella, A.; Lascano, E. Joint inversion of Wenner and dipole–dipole data to study a gasoline-contaminated soil. J. Appl. Geophys. 2003, 54, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I. (AGI) Advanced Geosciences,” Instruction Manual for EarthImager 2D Version 2.4.0 Resistivity and IP Inversion Software”, no. 512, p. 139, 2009. Available online: https://geophysicalequipmentrental.com/files/2020/01/EarthImager2DManual.pdf. (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- APHA; AWWA; WEF. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; p. 1360. [Google Scholar]
- Hoegger, R. Training Papers Nitrogen Determination According to Kjeldahl; Büchi Labortechnik AG: Flawil, Switzerland, 1998; Volume 1, p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- González Martínez, A. Problemática Medioambiental de los Distintos Tipos de Explotaciones Ganaderas; 1995. Available online: https://helvia.uco.es/bitstream/handle/10396/3831/08-1995-04.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Popovic, O.; Hjorth, M.; Stoumann Jensen, L. Phosphorus, copper, and zinc in solid and liquid fractions from full-scale and laboratory-separated pig slurry. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, N.; Elaoud, A.; Gabtni, H.; Trabelsi, I.; Khalfallah, K.K. Agricultural soil characterization using 2D electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) after direct and intermittent digestate application. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, G.; Pilawski, T.; Dzaomuho-Lenieregue, P.; Hiligsmann, S.; Delvigne, F.; Thonart, P.; Hermans, T. Gravimetric water distribution assessment from geoelectrical methods (ERT and EMI) in municipal solid waste landfill. Waste Manag. 2016, 55, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichet, V.; Grisey, E.; Aleya, L. Spatial characterization of leachate plume using electrical resistivity tomography in a landfill composed of old and new cells (Belfort, France). Eng. Geol. 2016, 211, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, J.; Martínez, J.; Hidalgo, M.C.; Mendoza, R.; Sandoval, S. Assessment of tailings ponds by a combination of electrical (ERT and IP) and hydrochemical techniques (Linares, southern Spain). Mine Water Environ. 2021, 40, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusim, A.S.; Abdullah, N.E.; Hashim, H.; Kutty, S.B. Effects of salt content on measurement of soil resistivity. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 7th International Power Engineering and Optimization Conference (PEOCO), Langkawi, Malaysia, 3–4 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Fan, L.; Deng, Y. Effect of salt concentrations on the electrical resistivity of cement-treated soils. In GeoCongress 2012: State of the Art and Practice in Geotechnical Engineering; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2012; pp. 1016–1025. [Google Scholar]
- Igbal, M.Z.; Krothe, N.C. Infiltration mechanisms related to agricultural waste transport through the soil mantle to karst aquifers of southern Indiana, USA. J. Hydrol. 1995, 164, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukas, V.; Neudert, L.; Novák, J.; Kren, J. Estimation of Soil Physico-chemical Properties by On-the-go Measurement of Soil Electrical Conductivity. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2018, 83, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, S.O.; Lind, A.M.; Sommer, S.G. Nitrogen, and organic matter losses during storage of cattle and pig manure. J. Agric. Sci. 1998, 130, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helene LP, I.; Moreira, C.A.; Bovi, R.C. Identification of leachate infiltration and its flow pathway in landfill by means of electrical resistivity tomography (ERT). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanief, A. Phosphorus Fractions in Biosolids, Biosolid-Amended Soils, Runoffs, and Its Impact on Primary Productivity in Aquatic Ecosystems. Master’s Thesis, Ryerson University, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, P.; Schwark LV, U.S.; Horn, H.; Saravia, F. Nutrient recovery and ammonia-water production by MF-vacuum evaporation treatment of pig manure. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, L.; Massé, D.I.; Beaudette, V.; Muir, M. Size distribution and composition of particles in raw and anaerobically digested swine manure. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.L.; Hjorth, M.; Keiding, K. Characterization of pig slurry with reference to flocculation and separation. Water Res. 2009, 43, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.; Hjorth, M.; Jensen, L.S.; Magid, J. Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus distribution in particle size–fractionated separated pig and cattle slurry. J. Environ. Qual. 2011, 40, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FOG, K. The effect of added nitrogen on the rate of decomposition of organic matter. Biol. Rev. 1988, 63, 433–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, T.; Dzakpasu, M.; Li, X. Nutrient dynamics and retention in a vegetated drainage ditch receiving nutrient-rich sewage at low temperatures. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140268. [Google Scholar]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Capa-Camacho, X.; Martínez-Pagán, P.; Acosta, J.A.; Martínez-Segura, M.A.; Vásconez-Maza, M.; Faz, Á. Environmental Monitoring of Pig Slurry Ponds Using Geochemical and Geoelectrical Techniques. Water 2024, 16, 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071016
Capa-Camacho X, Martínez-Pagán P, Acosta JA, Martínez-Segura MA, Vásconez-Maza M, Faz Á. Environmental Monitoring of Pig Slurry Ponds Using Geochemical and Geoelectrical Techniques. Water. 2024; 16(7):1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071016
Chicago/Turabian StyleCapa-Camacho, Ximena, Pedro Martínez-Pagán, José A. Acosta, Marcos A. Martínez-Segura, Marco Vásconez-Maza, and Ángel Faz. 2024. "Environmental Monitoring of Pig Slurry Ponds Using Geochemical and Geoelectrical Techniques" Water 16, no. 7: 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071016
APA StyleCapa-Camacho, X., Martínez-Pagán, P., Acosta, J. A., Martínez-Segura, M. A., Vásconez-Maza, M., & Faz, Á. (2024). Environmental Monitoring of Pig Slurry Ponds Using Geochemical and Geoelectrical Techniques. Water, 16(7), 1016. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16071016









