Integrating RUSLE Model with Cloud-Based Geospatial Analysis: A Google Earth Engine Approach for Soil Erosion Assessment in the Satluj Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials and Methods
2.2.1. RUSLE Thematic Maps Computation
2.2.2. Rainfall Erosivity (R) Factor
2.2.3. Soil Erodibility (K) Factor
2.2.4. Topographic (LS) Factor
2.2.5. Land Cover (C) Factor
2.2.6. Conservation Practice (P) Factor
2.2.7. Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
2.2.8. Slope
3. Results
3.1. Topographic (LS) Factor
3.2. Land Cover (C) Factor
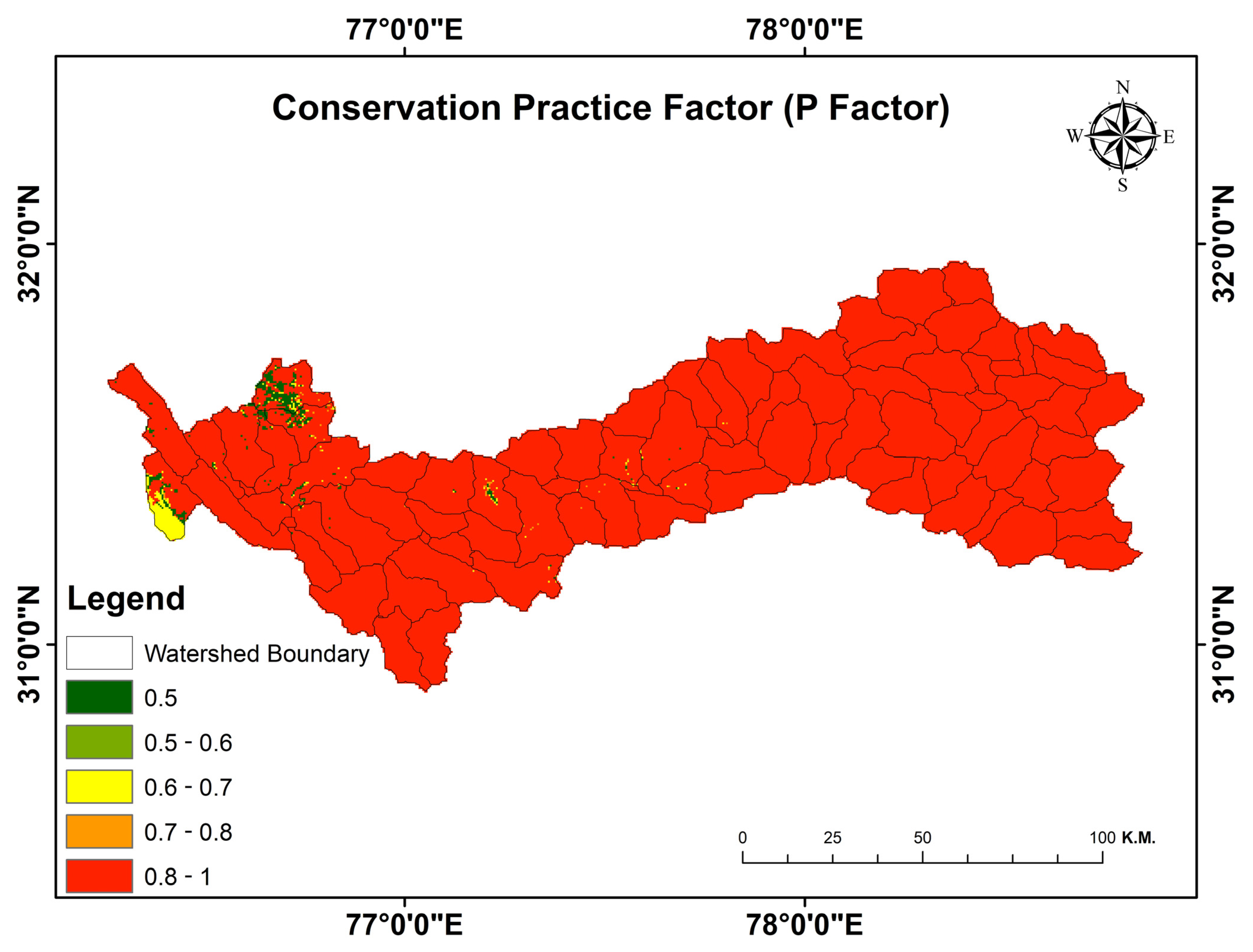
3.3. Conservation Practice (P) Factor
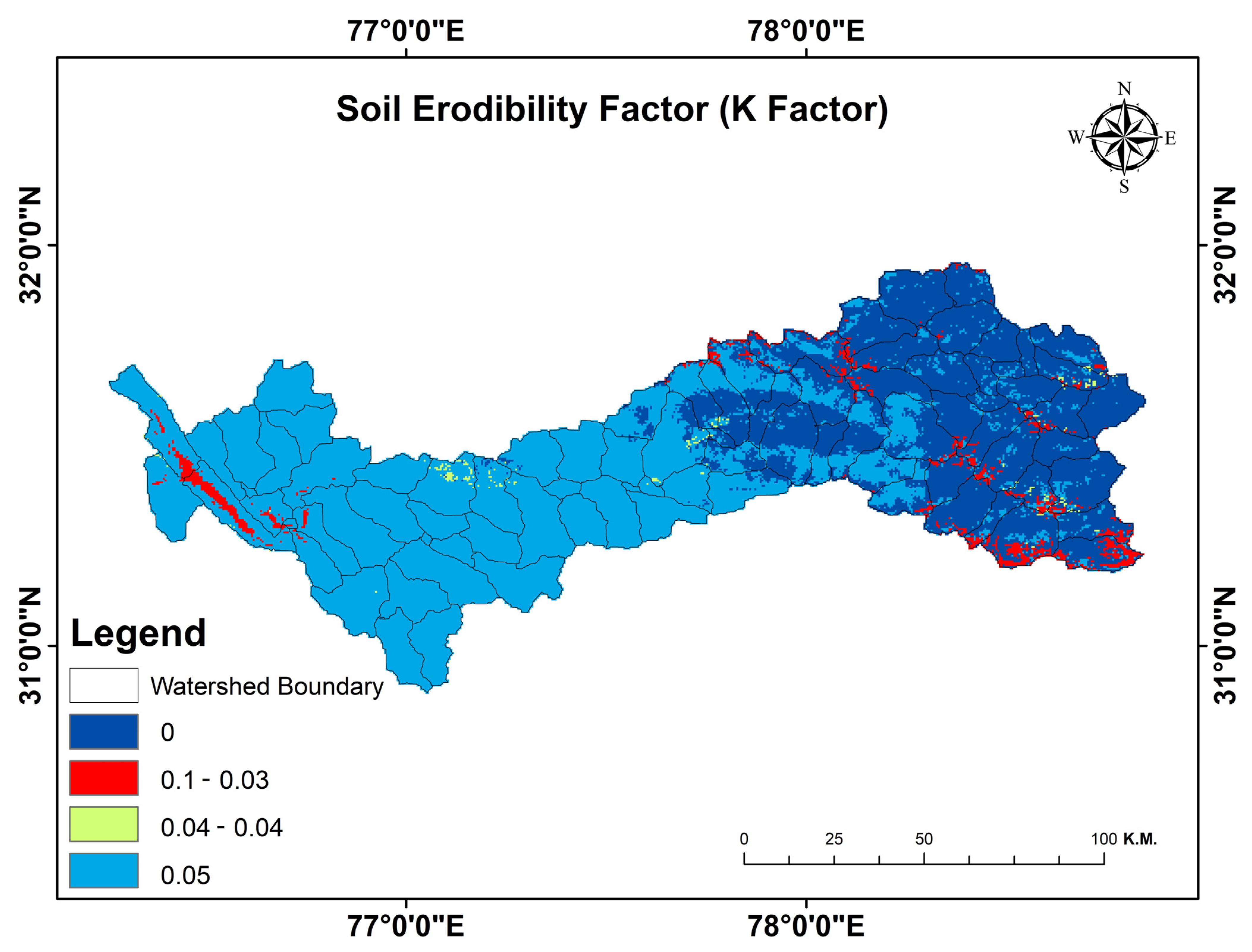
3.4. Soil Erodibility (K) Factor
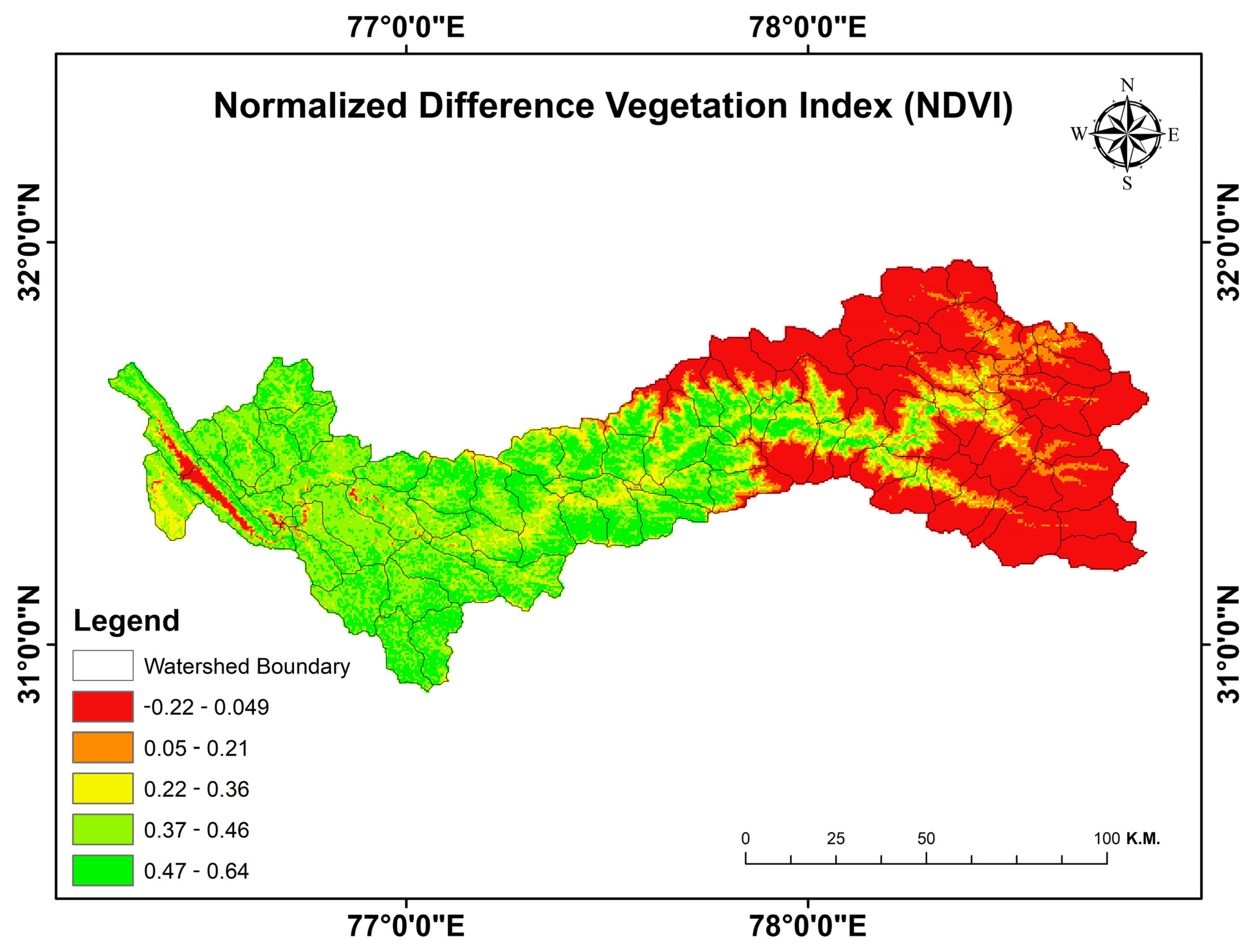
3.5. Analysis of NDVI
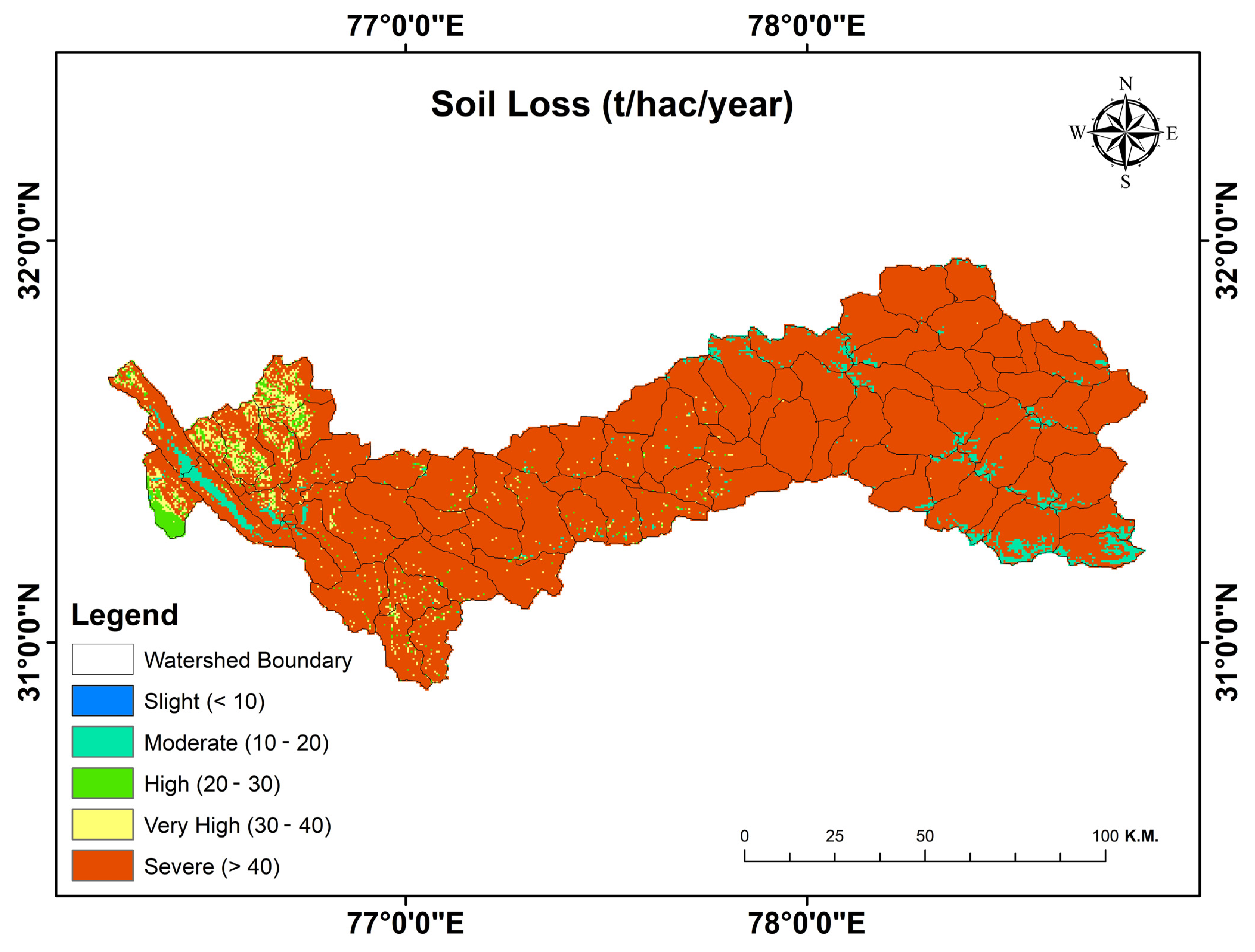
3.6. Soil Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allafta, H.; Opp, C. Soil Erosion Assessment Using the RUSLE Model, Remote Sensing, and GIS in the Shatt Al-Arab Basin (Iraq-Iran). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazbavi, Z.; Sadeghi, S.H.; Gholamalifard, M. Dynamic Analysis of Soil Erosion-Based Watershed Health. GES 2019, 12, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganasri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almouctar, M.A.S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Dossou, J.F. Soil Erosion Assessment Using the RUSLE Model and Geospatial Techniques (Remote Sensing and GIS) in South-Central Niger (Maradi Region). Water 2021, 13, 3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, X. Analysis of the Relationship between Soil Erosion Risk and Surplus Floodwater during Flood Season. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 1294–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Kaushal, A.; Yousuf, A.; Kaur, S.; Sharda, R.; Singh, S.P.; Gupta, O.; Sood, A. Prioritization of erosion susceptible watersheds using morphometric analysis and PCA approach: A case study of lower Sutlej River basin of Indian Punjab. Watershed Ecol. Environ. 2023, 5, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.D.; Goel, A.K.; Minhas, R.S. Water and Sediment Yields into the Sutlej River from the High Himalaya. Mt. Res. Dev. 1991, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Erosion: An Agricultural Production Challenge|Integrated Crop Management. Available online: https://crops.extension.iastate.edu/encyclopedia/soil-erosion-agricultural-production-challenge (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Chen, C.-N.; Tfwala, S.S.; Tsai, C.-H. Climate Change Impacts on Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield in a Watershed. Water 2020, 12, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezak, N.; Borrelli, P.; Mikoš, M.; Auflič, M.J.; Panagos, P. Towards multi-model soil erosion modelling: An evaluation of the erosion potential method (EPM) for global soil erosion assessments. CATENA 2024, 234, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargiri, S.A.; Samsampour, D. Principles of Soil Erosion Risk Modeling. In Soil Erosion—Risk Modeling and Management; Mahmood, S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.P.; Grant, K.T.; Bugna, G.C. A field method for soil erosion measurements in agricultural and natural lands. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 64, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Ahrends, H.; Habib-Ur-Rahman, M.; Gaiser, T. Modeling Approaches to Assess Soil Erosion by Water at the Field Scale with Special Emphasis on Heterogeneity of Soils and Crops. Land 2021, 10, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Bordoloi, R.; Thungon, L.T.; Paul, A.; Pandey, P.K.; Mishra, M.; Tripathi, O.P. An integrated approach of GIS, RUSLE and AHP to model soil erosion in West Kameng watershed, Arunachal Pradesh. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 129, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avand, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Mirchooli, F.; Kavian, A.; Tiefenbacher, J.P. A New Approach for Smart Soil Erosion Modeling: Integration of Empirical and Machine-Learning Models. Environ. Model. Assess. 2023, 28, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayet, N.; Pathak, K.; Chakrabarty, A.; Sahoo, S. Evaluation of soil loss estimation using the RUSLE model and SCS-CN method in hillslope mining areas. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 6, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhukar, A.; Hari, N.; Srivalli, R.; Neelima, T.L. Spatial Estimation of Soil Erosion Using RUSLE Model: A Case Study of Sangareddy Telangna State, India. IJPSS 2023, 35, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alewell, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Panagos, P. Using the USLE: Chances, challenges and limitations of soil erosion modelling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Universal Soil Loss Equation|Ontario.ca. Available online: http://www.ontario.ca/page/universal-soil-loss-equation (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Misra, K.G.; Yadav, R.R.; Misra, S. Satluj river flow variations since AD 1660 based on tree-ring network of Himalayan cedar from western Himalaya, India. Quat. Int. 2015, 371, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Yousuf, A.; Kaushal, A. Prioritization of watersheds for land and water management in lower Sutlej River Basin using geospatial technology. J. Nat. Resour. Conserv. Manag. 2023, 5, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.-H.; Lee, D.-H.; Chung, S.-R.; Jeong, G.-C. Effect of Rainfall Intensity, Soil Slope and Geology on Soil Erosion. J. Eng. Geol. 2014, 24, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zheng, F.; Wen, L.; Han, Y.; Hu, W. Impacts of rainfall intensity and slope gradient on rill erosion processes at loessial hillslope. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, R.; Kumar, U. Integrated Approach of Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and Geographical Information System (GIS) for Soil Loss Risk Assessment in Upper South Koel Basin, Jharkhand. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2012, 4, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, J.J.; Anijofor, S.C.; Obasa, P.; Avwevuruvwe, J.J. Effects of soil physical properties on erodibility and infiltration parameters of selected areas in Gidan Kwano. Nig. J. Technol. Res. 2017, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Bora, P.; Das, R. Estimation of slope length gradient (LS) factor for the sub-watershed areas of Juri River in Tripura. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Baartman, J.E.; Gai, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. An improved method for calculating slope length (λ) and the LS parameters of the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation for large watersheds. Geoderma 2017, 308, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsahin, E.; Duru, U.; Eroglu, I. Land Use and Land Cover Changes (LULCC), a Key to Understand Soil Erosion Intensities in the Maritsa Basin. Water 2018, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normalized Difference Vegetation Index—An Overview|ScienceDirect Topics. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/normalized-difference-vegetation-index (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Almagro, A.; Thomé, T.C.; Colman, C.B.; Pereira, R.B.; Junior, J.M.; Rodrigues, D.B.B.; Oliveira, P.T.S. Improving cover and management factor (C-factor) estimation using remote sensing approaches for tropical regions. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, D.P.; Silva, E.M.; Avanzi, J.C.; Muniz, J.A.; Ferreira, D.F.; Silva, M.L.N.; Acuña-Guzman, S.F.; Curi, N. RainfallErosivityFactor: An R package for rainfall erosivity (R-factor) determination. CATENA 2020, 189, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Asif, M.; Hirani, A.H.; Akram, M.N.; Goyal, A. Chapter 7—Modeling for Agricultural Sustainability: A Review. In Agricultural Sustainability; Bhullar, G.S., Bhullar, N.K., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, E.; Kebede, A.; Asfaw, S.; Feyissa, S. Optimizing soil erosion estimates of RUSLE model by analyzing land use/cover dynamics in upper Awash River Basin, Central Ethiopia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2257363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Anees, S.A.; Rehman, A.; Pan, S.; Tariq, A.; Zubair, M.; Liu, Q.; Rabbi, F.; Khan, K.A.; Luo, M. Exploring spatiotemporal dynamics of NDVI and climate-driven responses in ecosystems: Insights for sustainable management and climate resilience. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Sustainability 2015, 7, 5875–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainability|Free Full-Text|Restoring Soil Quality to Mitigate Soil Degradation. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/7/5/5875 (accessed on 18 March 2024).
- Flanagan, D.C.; Ii, J.C.A.; Nieber, J.L.; Misra, D.; Kyle, R. Douglas-Mankin. Advances in Soil Erosion Research: Processes, Measurement, and Modeling. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalise, D.; Kumar, L.; Kristiansen, P. Land Degradation by Soil Erosion in Nepal: A Review. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Sur, K.; Al-Ansari, N.; Arya, P.K.; Verma, V.; Malik, A. GIS integrated RUSLE model-based soil loss estimation and watershed prioritization for land and water conservation aspects. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1136243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Class Name | Area in Hectare |
|---|---|
| Shrubland | 5487.32 |
| Grassland | 266,070.68 |
| Cropland | 25,520.39 |
| Built-up | 6037.37 |
| Bare/sparse vegetation | 244,650.11 |
| Snow and ice | 55,688.06 |
| Permanent water bodies | 15,695.61 |
| Herbaceous wetland | 299.98 |
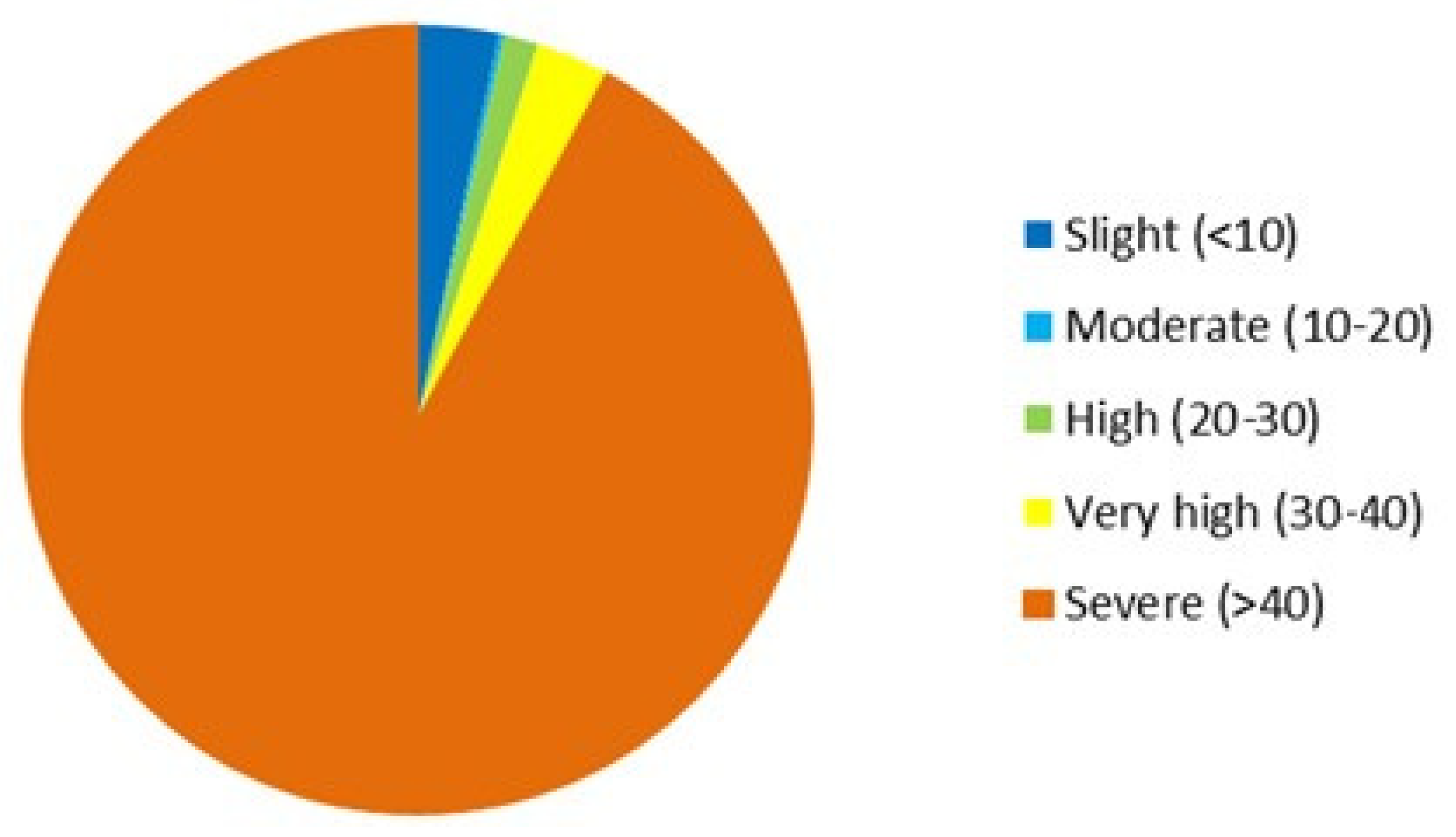
| Sr. No. | Class | Area (ha) | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Slight | 1980 | 3.3 |
| 2 | Moderate | 120 | 0.2 |
| 3 | High | 840 | 1.4 |
| 4 | Very high | 1800 | 3 |
| 5 | Severe | 55,200 | 92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sud, A.; Sajan, B.; Kanga, S.; Singh, S.K.; Singh, S.; Durin, B.; Kumar, P.; Meraj, G.; Sahariah, D.; Debnath, J.; et al. Integrating RUSLE Model with Cloud-Based Geospatial Analysis: A Google Earth Engine Approach for Soil Erosion Assessment in the Satluj Watershed. Water 2024, 16, 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081073
Sud A, Sajan B, Kanga S, Singh SK, Singh S, Durin B, Kumar P, Meraj G, Sahariah D, Debnath J, et al. Integrating RUSLE Model with Cloud-Based Geospatial Analysis: A Google Earth Engine Approach for Soil Erosion Assessment in the Satluj Watershed. Water. 2024; 16(8):1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081073
Chicago/Turabian StyleSud, Anshul, Bhartendu Sajan, Shruti Kanga, Suraj Kumar Singh, Saurabh Singh, Bojan Durin, Pankaj Kumar, Gowhar Meraj, Dhrubajyoti Sahariah, Jatan Debnath, and et al. 2024. "Integrating RUSLE Model with Cloud-Based Geospatial Analysis: A Google Earth Engine Approach for Soil Erosion Assessment in the Satluj Watershed" Water 16, no. 8: 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081073
APA StyleSud, A., Sajan, B., Kanga, S., Singh, S. K., Singh, S., Durin, B., Kumar, P., Meraj, G., Sahariah, D., Debnath, J., & Chand, K. (2024). Integrating RUSLE Model with Cloud-Based Geospatial Analysis: A Google Earth Engine Approach for Soil Erosion Assessment in the Satluj Watershed. Water, 16(8), 1073. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16081073













