Abstract
Seasonal freeze–thaw irrigation areas face challenges of soil salinization and water scarcity, requiring a deep understanding of soil freeze–thaw dynamics under the interaction between irrigation and groundwater. An in situ lysimeter experiment was conducted in the winters of 2020–2021 and 2023–2024 to investigate the effects of autumn irrigation (AI) timing (late AI conducted in late November and icing AI conducted in early December) and quota (0, 35, 135, 270 mm) on soil water, heat, and salt transport under varying groundwater levels in the Hetao Irrigation District, Northwest China. Results showed that AI had a strong short-term effect on the groundwater depth and there was a significant negative correlation between groundwater depth and air temperature on a monthly scale. The quota and air temperature during AI were the key factors in utilizing the “refrigerator effect”—where irrigation water pre-cooled by frozen layer accelerates soil freezing—to regulate soil water and salt transport under freeze–thaw cycles. The drastic reduction in AI water consumption lowered the groundwater level, highlighting air temperature as the dominant driver of soil dynamics. Thus, icing AI with low quota (35 mm) can optimize water use (water saving of 77% compared to the traditional quota of 150 mm) while maintaining soil moisture (an increase of 17.4% in water storage) and salinity control (a decrease of 41.6% in salt storage) in the root zone (0–40 cm) through the “refrigerator effect”, demonstrating its potential for sustainable irrigation in water-scarce cold regions.
1. Introduction
Seasonally frozen soils, covering vast arid and semi-arid regions such as Northwest China, are pivotal to agricultural production and ecosystem stability [1,2]. However, agricultural production in these regions relies heavily on irrigation, and improper irrigation management can result in persistent soil salinization, which is synergistically exacerbated by soil freeze–thaw cycles [3,4,5,6,7]. Autumn/winter irrigation (AI), a practice primarily employing flood irrigation in harvested croplands during late autumn to early winter, is widely adopted in arid regions like the Hetao Irrigation District (HID) [8]. AI effectively leaches excess soil salts, enhances soil moisture retention, regulates soil temperature, and is beneficial for spring sowing in the following year [9,10]. However, achieving these benefits requires substantial water inputs, with AI accounting for approximately 1/3 of HID’s annual irrigation water diversion [11,12]. Under the current circumstances of limited water availability, the efficient use of available water to address the soil salinity and its leaching effect is a major concern in these regions [13].
Based on the timing of AI, it can be divided into early AI (mid-September to mid-October) and late AI (mid-October to early November). Compared to late AI, the advantages of early AI lie not only in enhancing salt leaching but also in allowing the groundwater to fall below the critical levels, resulting in a predominate adoption of early AI in HID. Although extensive research has been conducted on the interactions among AI timing, irrigation quota, and groundwater level, as well as their effects on soil water, heat, and salt transport, most of the studies have primarily focused on early AI. For instance, Li et al. [14,15] proposed AI schemes (timing and quota) for soils with different degrees of salinization based on numerical simulation, e.g., for slight salinized soils, the quota is from 142 to 183 mm between 28 September and 23 October. The leaching of salt during AI is influenced not only by the irrigation quota but also by the groundwater level prior to AI [16]. The greater the amount of AI, the lower the soil salinity after irrigation; similarly, the lower the groundwater level before AI, the higher the salt leaching efficiency of AI [17,18]. In HID, the groundwater is strongly recharged by AI water, causing a rapid rise in the pre-freezing groundwater levels [19]. Groundwater can replenish the frozen soil, aggravating soil salinization, if the distance between the freezing front and the groundwater level is less than the corresponding soil’s capillary rise height [4,20]. Given the stricter regulation of the diversion allocation from the Yellow River to HID, decreasing the AI water is a possible way to conserve water resources, for example, the recent reductions in HID’s AI consumption from 13.06 × 109 (average value during 2014–2022) to 8.8 × 109 m3 (2023). However, due to increased water loss caused by longer evaporation exposure before soil freezing, the water amount for early AI is generally no less than 150 mm to satisfy the required soil moisture and salt conditions for the following spring sowing, implying that it is difficult to achieve further water savings by reducing the early AI quota.
Studies have shown that late AI is more effective in moisture retention but less effective in salt leaching. The decline of groundwater level caused by the application of water saving benefits the control of salinity, making late AI more suitable under the background of water saving. However, an excessive lowering of groundwater level may negatively impact crop productivity and the environment [21]. For example, depths greater than 2.0 m may result in water stress on vegetation due to reduced capillary rise in the Hetao Irrigation District [19]. This suggests that a regulation of groundwater levels during late AI is also required, yet such regulation becomes particularly challenging as freezing conditions impede drainage functionality. Tan et al. [22] and Guo et al. [23] proposed an icing AI method, which is implemented later than traditional late AI. This method can regulate the groundwater level by reallocating the irrigation water among surface (ice cover)/soil/groundwater and achieved good performance in soil moisture retention and salinity control. However, climate change and anthropogenic activities have introduced significant uncertainties into the spatiotemporal dynamics of groundwater level [24], which requires a deep understanding of the effect of icing AI on the water, heat, and salt transport in seasonally frozen soils under varying groundwater levels.
This study conducted an in situ lysimeter experiment at the Yonglian Experimental Station in the Hetao Irrigation District during the winters of 2020–2021 and 2023–2024. The dynamics of water, heat, and salt transport in soils under icing AI were monitored throughout the freeze–thaw period. The main objectives are (1) to investigate the effects of timing and quota of AI on the soil water, heat, and salt transport during freeze–thaw cycles under the same groundwater conditions; (2) to reveal the mechanisms underlying the influences of icing irrigation on the soil water, heat, and salt transport under varying groundwater level conditions. The findings are expected to enhance the mechanistic understanding of irrigation management under freeze–thaw cycles and provide sustainable AI practices in the Hetao Irrigation District.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and In Situ Experimental Setup
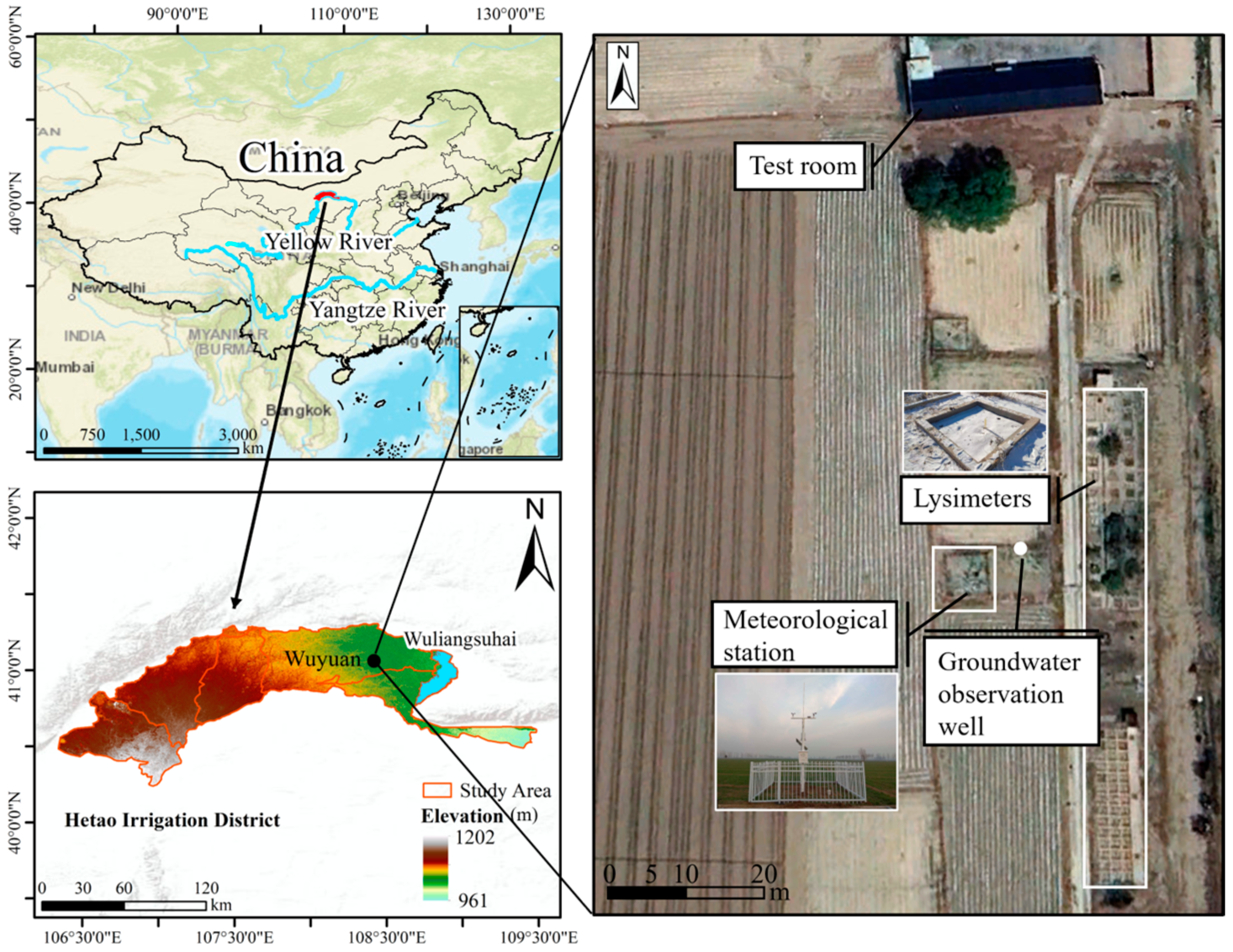
The Hetao Irrigation District, located in the upper reaches of the Yellow River (Figure 1), is one of the three largest irrigation districts of China, covering an area of 1.19 × 106 ha, of which 64.7% is irrigated land. The study area has an arid continental climate with an average annual precipitation of 136 mm, an average annual potential evaporation of 1938 mm, and an average annual temperature of 6.2 °C. The soil generally begins to freeze in the middle of November and does not thaw completely until late April or early May. The soil reaches its maximum frost depth (MFD) of approximately 1.1 m in mid-January. Autumn irrigation always starts in mid-September and lasts until early November, primarily adopting flood irrigation, with an irrigation quota of 220–270 mm (local field practice). The drilling results show that sandy/silty loam is the main soil texture, and the average depth of the groundwater table fluctuates between 1.4 and 2.2 m.
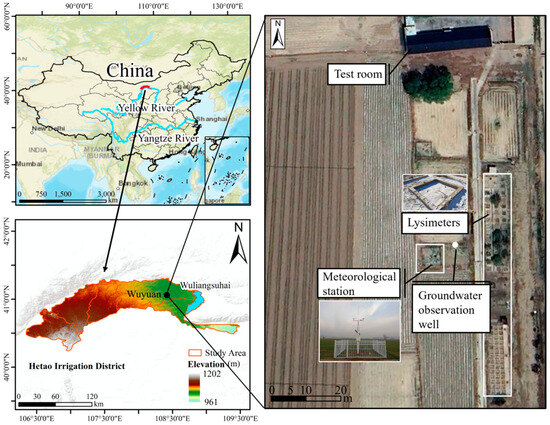
Figure 1.
Location of the Hetao Irrigation District and Yonglian experimental station.
The in situ experiment was conducted at the Yonglian experimental station, located in Yonglian Village, Wuyuan County, in the middle of the Hetao Irrigation District (41°08′06″ N, 108°06′18″ E) during the winters of 2020–2021 and 2023–2024 (Figure 1). Seven adjacent lysimeters (1.8 × 1.8 m) were selected and soil surface leveling was conducted in all lysimeters. The lysimeter is made of concrete, with an open bottom at a depth of 2.5 m. 1#, 2#, and 3# were flood-irrigated on 12 December 2020, and 12 December 2023, with 270, 135, and 35 mm of water, respectively (icing AI treatment). 4# was not irrigated (control), while 5#, 6#, and 7# were flood-irrigated on 24 November 2023, with 35, 135, and 270 mm of water, respectively (late AI treatment). The AI conducted in late November is classified as late AI within the traditional AI timeframe. However, AI carried out in early December occurs even later than late AI, often resulting in surface ice cover in the fields, therefore, defined here as icing AI. The quota of 270 mm was selected according to the local field practices. The quota of 135 mm represents the recommended values in previous studies [14] and 35 mm was primarily established to explore the potential for further water conservation. The irrigation water used in this study was pumped from mineralized groundwater (5 °C) according to the local brackish water irrigation practice because of practical difficulties in acquiring adequate pure water in winter. The electrical conductivity of the irrigation water was approximately 2 dS cm−1, which indicated an external salt input into the soil by irrigation. Meteorological data including air temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, air pressure, wind speed, and solar radiation were collected from a meteorological station at the experimental station. Monthly manual soil sampling was conducted using an electric drill at depths of 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60, 80, and 100 cm in lysimeters. The detailed sampling plan is shown in Table 1. The determination of the sampling depth is based on the studies of Li et al. [8] and Lu et al. [12], which were conducted in similar areas. To minimize perturbations, the sampling holes were backfilled after each sampling. The soil texture (Table A1), initial soil water, and salt content were determined through the sampling before irrigation. The total water content of the soil sample was measured using the oven-drying method (oven drying at 105 °C for 8 h). The electrical conductivity of the solution extracted from the soil water suspension (soil/water = 1:5) was measured using a DDS-307A conductivity meter (Shanghai Precision & Scientific Instrument Inc., Shanghai, China) to determine the soil salt content. The soil temperature was monitored hourly using a thermal sensor (WT0T1, Wangyunshan, Fuzhou, China) at the same depth as the moisture observations as well as the soil surface (0 cm). Groundwater depth was manually monitored once every 5 days through a well.

Table 1.
Meteorological data and observations in the experiment.
2.2. Methodologies
2.2.1. EEMD
An Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition (EEMD) method was introduced to quantify the relationship between groundwater and air temperature at different time scales. The EEMD was proposed by Wu and Huang [25], which decomposes the original signal into a series of intrinsic mode functions (IMFs) and a residual term based on the assumption that the signal consists of different intrinsic oscillatory modes. Each of these oscillatory modes is represented by an IMF with variable amplitude and frequency as a function of time. Each order IMF is defined by the following two conditions: (1) over its entire length, the number of extremes and the number of passing zeros must be equal or differ by at most 1; (2) at any point, the signal defined by the local maxima and the envelope defined by the local minima have a mean value of zero. The decomposed IMF components of each order highlight the local time scale characteristics of the data, and the residuals cannot contain a complete oscillation, which serves to reflect the overall trend of the signal. The procedure of EEMD is as follows [25]:
Add a white noise series to the original time series:
where ε(t) are independent Gaussian white noise.
Apply EEMD to decompose the noise-added time series:
where N is the number of final IMFs and is the residual.
Take the means of the corresponding IMFs as the final result:
2.2.2. Characteristics of Soil Water–Heat–Salt Dynamics
The soil frost depth is determined based on the 0 °C isotherm in the soil temperature profile; the freezing rate and thawing rate are subsequently calculated as follows:
where is the freezing and thawing rate soil at soil layer i (cm/day); is the thickness of soil layer i (cm); , are the time when soil layer i and I + 1 begin to freeze/thaw (day), respectively.
The soil temperature gradient is used to analyze the heat transfer process and can be computed as follows:
where is the temperature gradient (°C/cm). and denote soil depths (cm), > ; and represent the soil temperature (°C) at depths and , respectively. > 0 indicates that the heat transfers from deep to shallow soils; otherwise, the transfer occurs in the opposite direction.
The soil water storage from the surface to a depth of z is calculated as follows:
where is soil water storage (cm), and are the volumetric water content (cm3 cm−3) and thickness (cm) of the soil layer i, N represents the total number of soil layers within 0–z.
The salt storage is calculated as follows:
where is soil-salt storage (g cm−2), and are the salt content (g 100 g−1) and bulk density (g cm−3) of the soil layer i, respectively. Other terms are the same with above.
The mass balance equation was used to calculate the salt flux (QS: g 100 g−1 month−1):
where is the salt mass change in the soil layer of 0–z cm during the period . Using the monthly sampling data of the soil-salt profile, Equation (8) can be solved by assuming that QS0 is zero or equal to the external salt input from irrigation.
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was selected to evaluate the correlation between temperature/groundwater depth and soil water/salt storage:
where and represent the ith value and the mean of the variable X, respectively; and represent the ith value and the mean of the variable Y, respectively. The closer the absolute value is to 1, the stronger the correlation between the variables.
The water/salt content of freeze–thaw soil is jointly influenced by air temperature and groundwater depth. To investigate the effects of AT and GD and their interaction on the soil water and salt storage, we employed Two-way Analysis of Variance (Two-way ANOVA). The detailed steps and formulas are referred to the textbook of Seltman [26].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Air Temperature and Groundwater Dynamics During the Freezing–Thawing Period
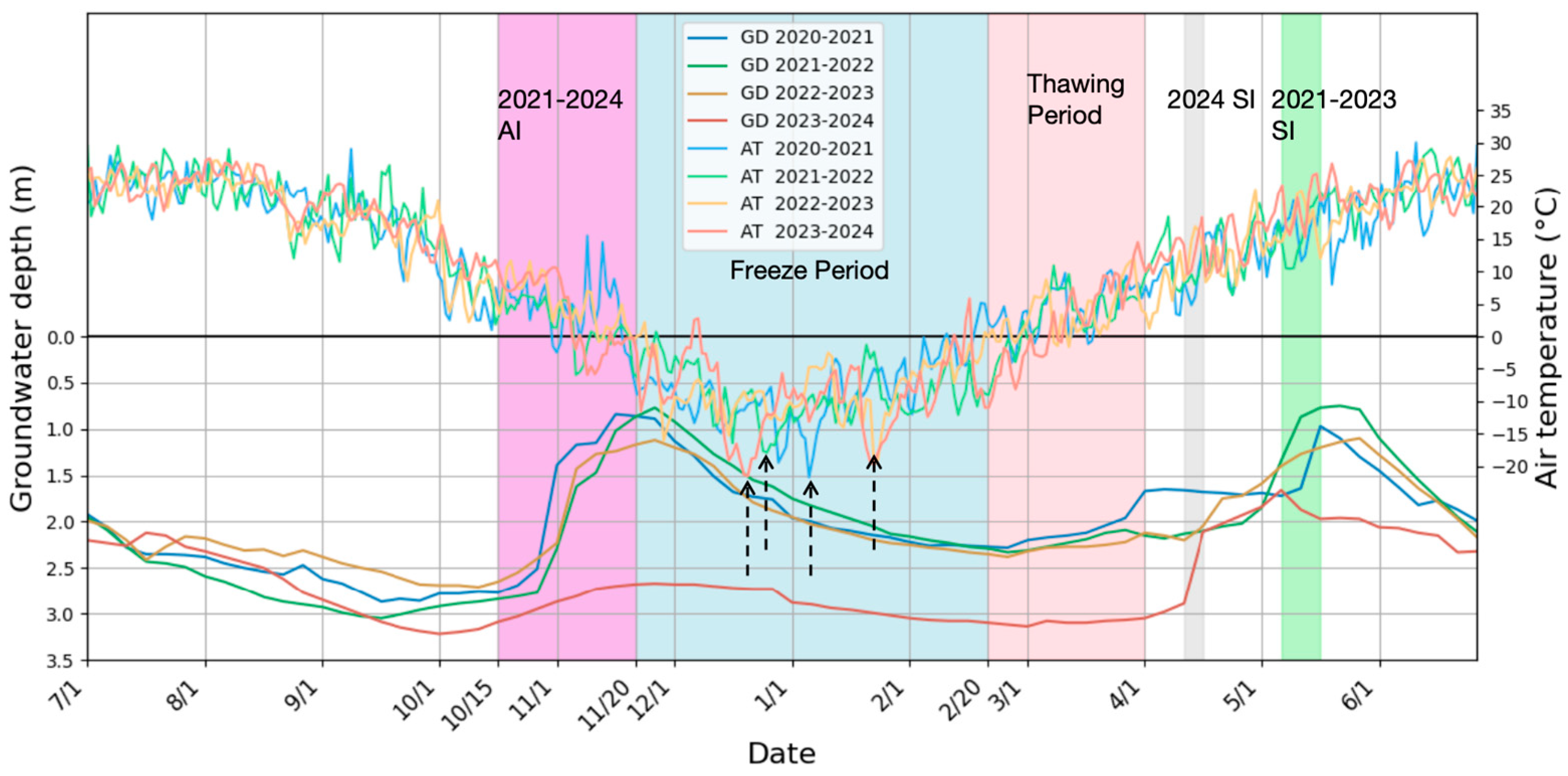
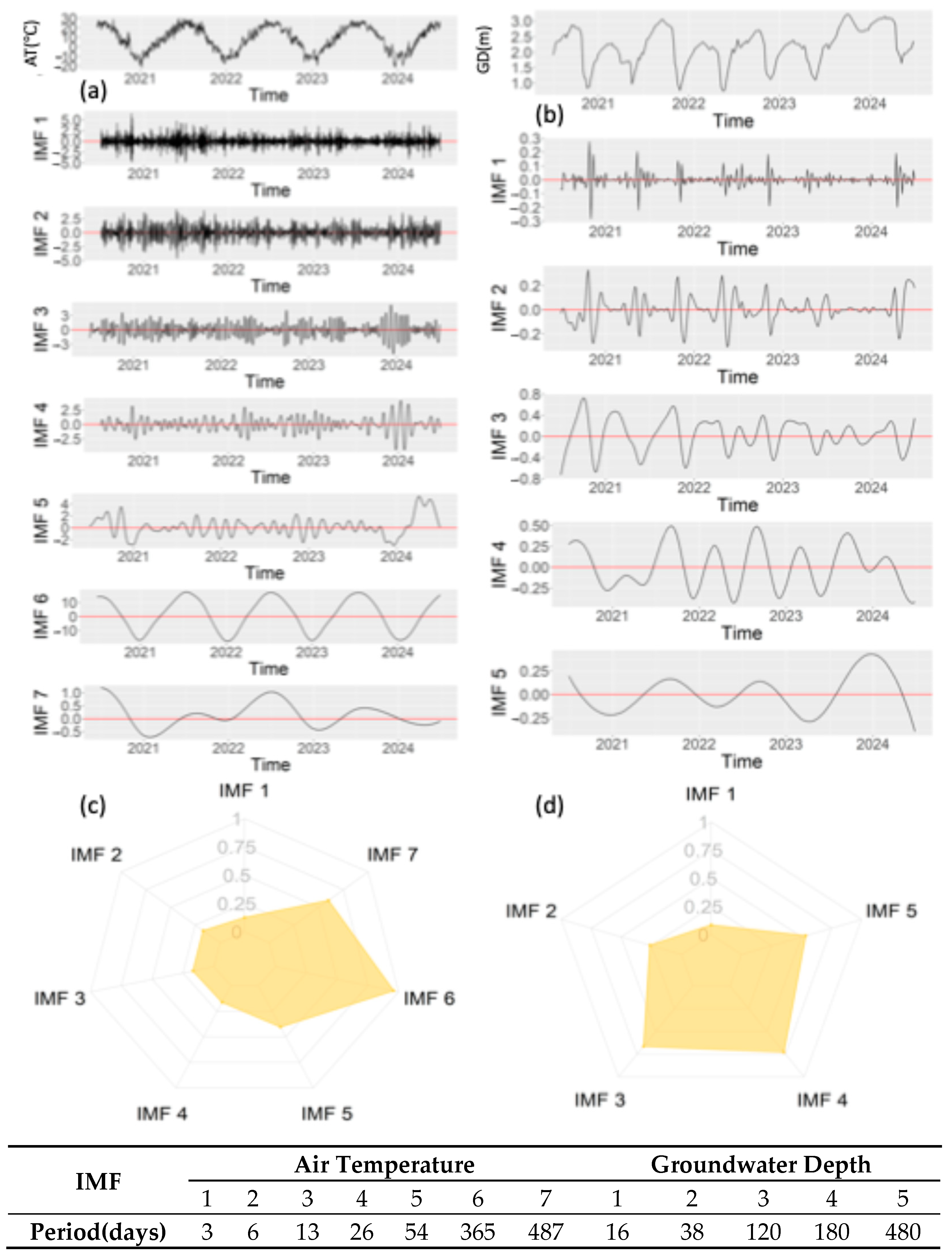
Figure 2 presents temporal variations in air temperature and groundwater depth from 2020 to 2024. While interannual differences existed for identical dates, consistent annual variation patterns were observed across years. The EEMD was employed to decompose both time series into IMFs with distinct temporal scales. Decomposition yielded seven IMFs for air temperature and five IMFs for groundwater depth (Figure 3).
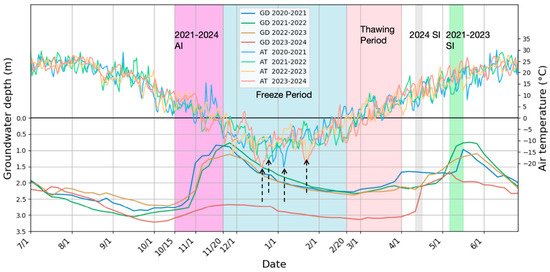
Figure 2.
Groundwater depth and air temperature dynamics from July 2020 to June 2024. The light blue and pink shaded area represents the multi-year average period of freezing and thawing, respectively. The purple shaded area represents the multi-year average period of intensive autumn irrigation, the grey shaded area represents the period of intensive spring irrigation in 2024, and the green shaded area represents the multi-year average period of intensive spring from 2021 to 2023. The dash arrows indicate the lowest values of air temperature.
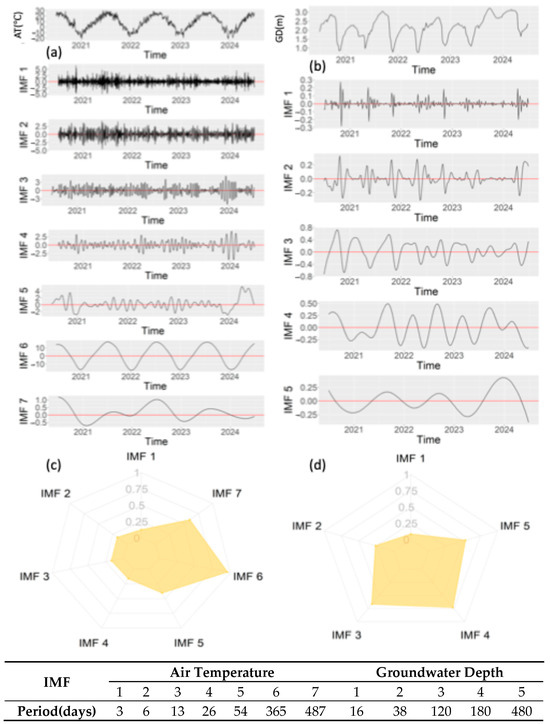
Figure 3.
(a) IMFs after EEMD decomposition of air temperature, and (b) IMFs after EEMD decomposition of groundwater depth; (c) the correlation between the IMFs after EEMD decomposition of air temperature and the original sequence; (d) the correlation between the IMFs after EEMD decomposition of groundwater depth and the original sequence.
Notably, the IMFs of air temperature demonstrated an inverse frequency–amplitude relationship, where higher frequency components exhibited lower amplitude magnitudes. For instance, IMF1 displayed a frequency of 1/6 day−1 with an amplitude of ±2.5 °C, while IMF6 exhibited a lower frequency (1/365 day−1) coupled with a larger amplitude (±10 °C). In contrast, groundwater depth IMFs showed no systematic frequency–amplitude correlation. This discrepancy arises from the different sampling resolutions between the air temperature (daily) and groundwater depth (five-day intervals). Consequently, primary temporal scales differed substantially between datasets—intra-weekly scales (IMFs 1–2) for air temperature versus semi-monthly scales (IMF1) for groundwater depth.
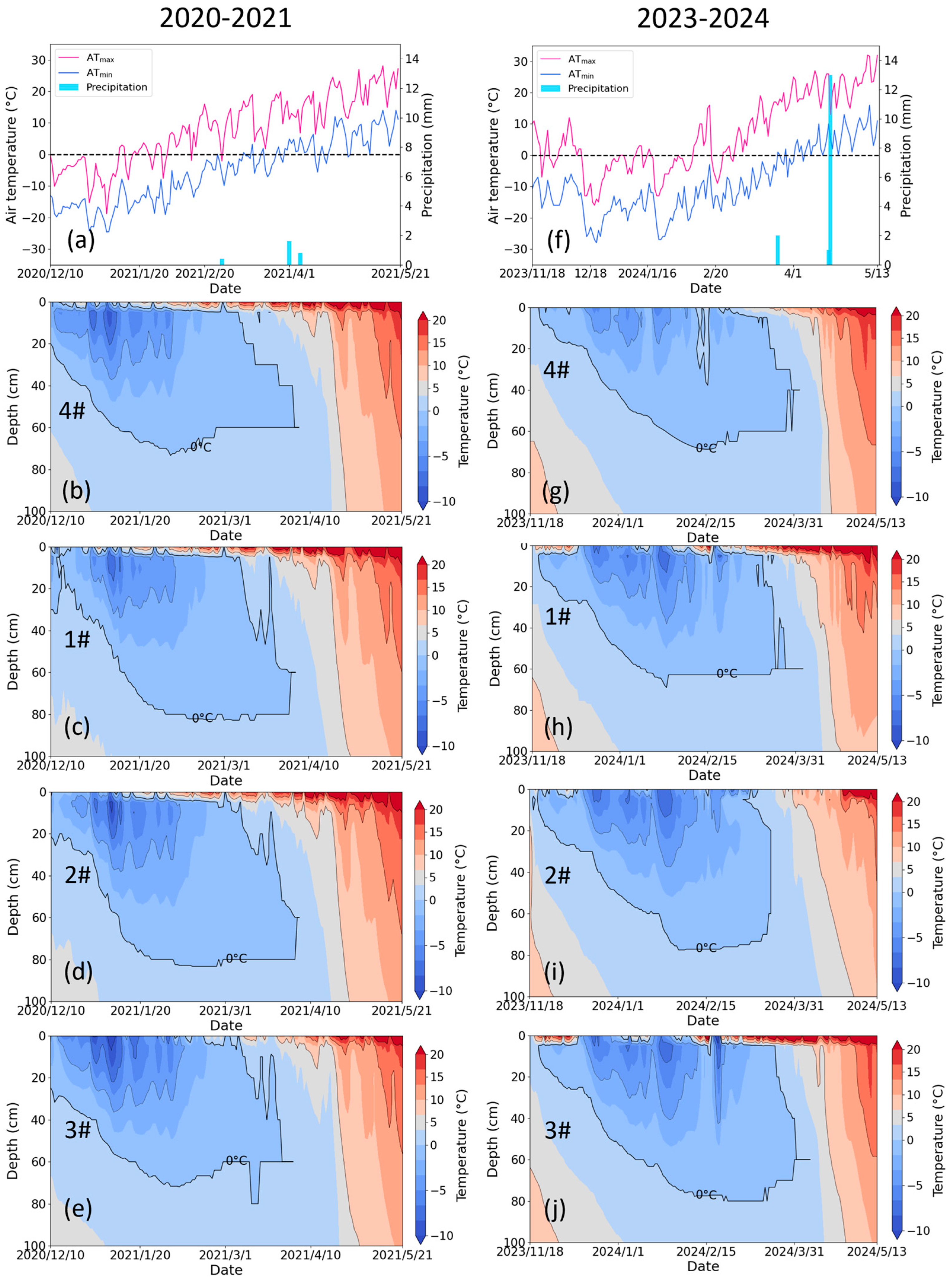
Representative IMFs were identified through maximum correlation analysis with the original time series (Figure 3c,d). For air temperature, IMF6 (annual scale) emerged as the representative IMF (r = 0.99), exhibiting a pronounced sinusoidal annual pattern. Conversely, groundwater dynamics were best characterized by IMF4 (r = 0.75), capturing seasonal variations comprising both short-term (weeks) and long-term (months) fluctuations, which is consistent with the study of Xu et al. [18]. Correlation analysis was performed between the IMFs of air temperature and IMFs of groundwater depth, revealing a strongly negative correlation between air temperature and groundwater depth IMFs at lower frequencies (long-term), contrasting with weak correlations at higher frequencies (short-term). In areas with shallow groundwater depths, groundwater is rapidly and strongly recharged by irrigation [18]. Hence, the short-term sharp increases in groundwater levels are mainly caused by irrigation events, such as AI beginning in mid-October and spring irrigation (SI) occurring in April and May (Figure 2). Moreover, the magnitude of the variation in groundwater depth depends on the amount of irrigation water. For instance, the average water consumption for AI from 2014 to 2022 was 13.06 × 109 m3, whereas in 2023, the water consumption for AI decreased to 8.8 × 109 m3. In 2021, the groundwater depth decreased from 2.77 m on 26 October to 0.77 m on 26 November. However, in 2023, the groundwater depth slightly decreased from 2.95 m on October 26 to 2.67 m on November 26, with the magnitude of variation decreasing by 86%. Due to the reduction in AI, SI started earlier in 2024, but the unchanged duration and quota led to a similar increase in groundwater levels as in previous years.
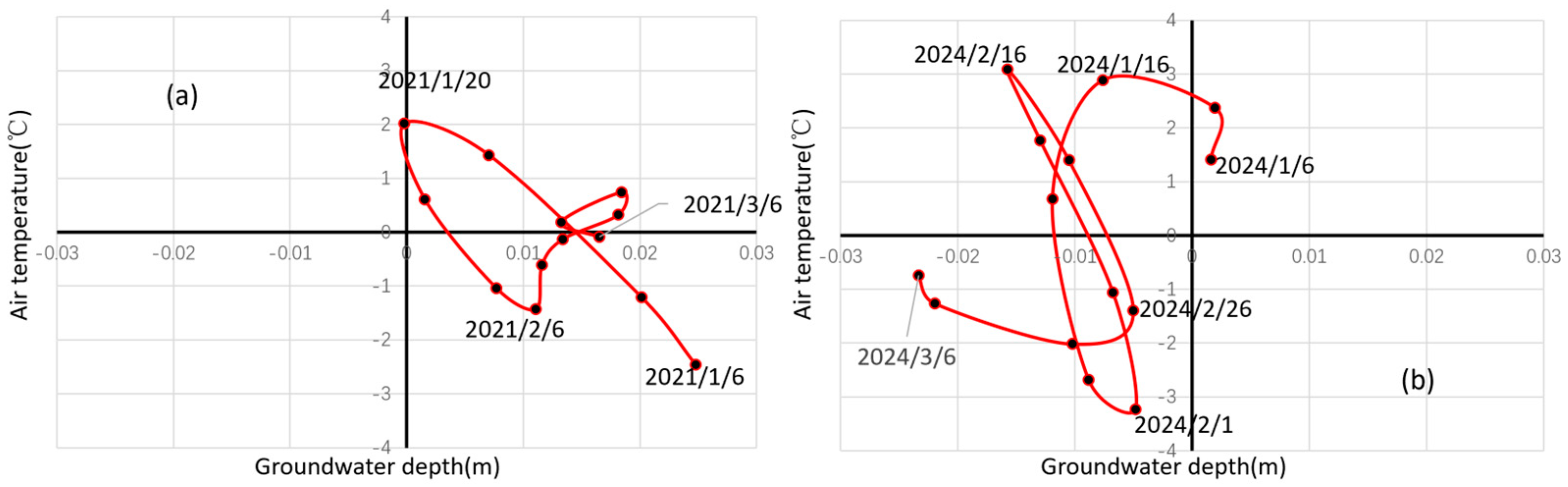
As shown in Figure 2, the air temperature reached its lowest value in early January (indicated by the dash arrows), serving as a critical hydrological transition point. Therefore, the experimental observation period can be divided into three stages: the early freezing stage (before the transition point), the stable freezing stage (from the transition point to the thawing stage), and the thawing stage. The EEMD results indicated that the long-term variation in groundwater depths was strongly negative with the air temperature across different periods. For example, during the early freezing stage, air temperature continuously decreases while groundwater depth gradually increases, showing a negative correlation. During the thawing stage, air temperature gradually increases while groundwater depth decreases, also exhibiting a negative correlation. However, the underlying mechanisms differed substantially. Groundwater declines (depth increases) during the early freezing stage derived from lateral groundwater drainage and vertical migration from unfrozen to frozen zones driven by the soil water potential gradient. During the stable freezing stage (6 January to 6 March), the IMF4 of air temperature and the IMF2 of groundwater depth were selected for the monthly scale relationship analysis. As shown in Figure 4, although there were significant fluctuations in air temperature, the groundwater level responded promptly through the exchange between groundwater and deep soil water. Comparative analysis of 2021 and 2024 data showed greater curve slopes and amplitudes in 2021 (Figure 4a,b), indicating stronger temperature–depth correlations under high groundwater levels. The substantial reduction in AI consumption in 2023 resulted in lower groundwater levels, making groundwater dynamics less influenced by air temperature. During thaw periods, increasing temperatures enhanced groundwater recharge through meltwater infiltration, reducing groundwater depth.
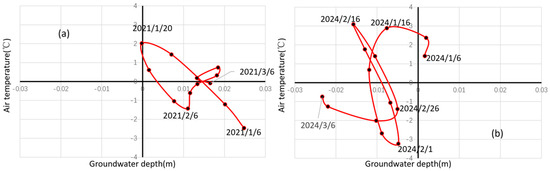
Figure 4.
Scatter plots of air temperature (IMF4) and groundwater depth (IMF2) in (a) 2021 and (b) 2024. The red line indicates the time series from 6 January to 6 March.
3.2. The Effects of AI on Soil Freezing–Thawing Dynamics
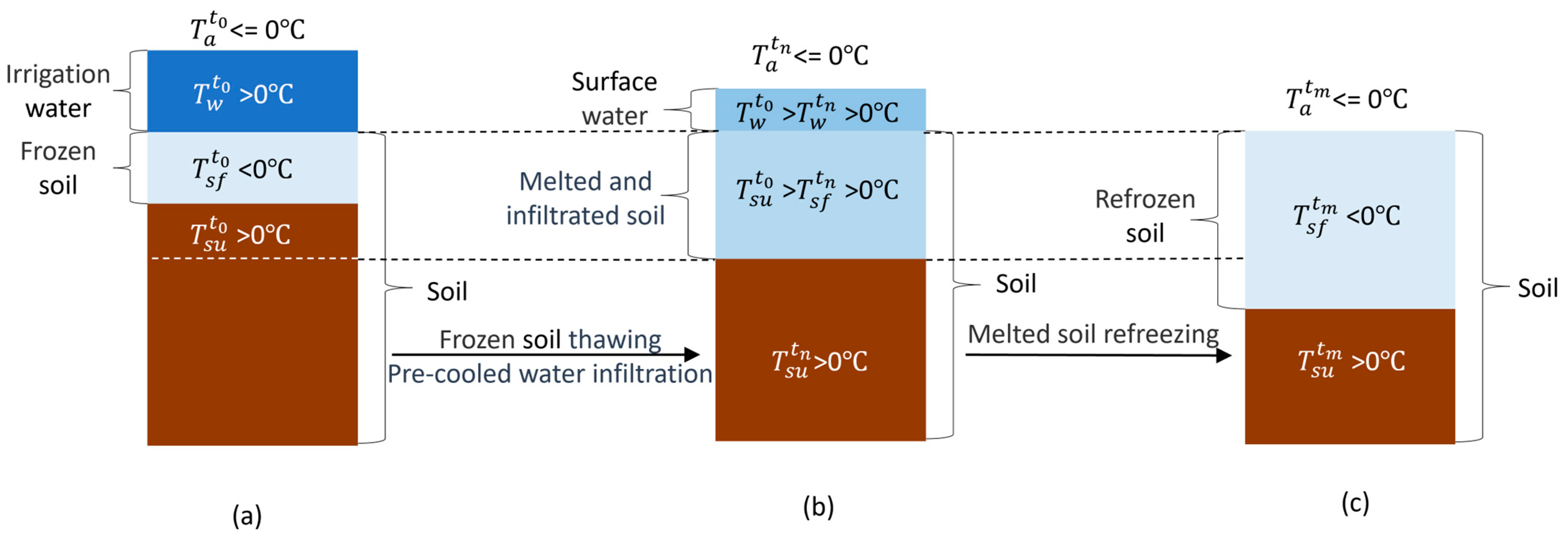
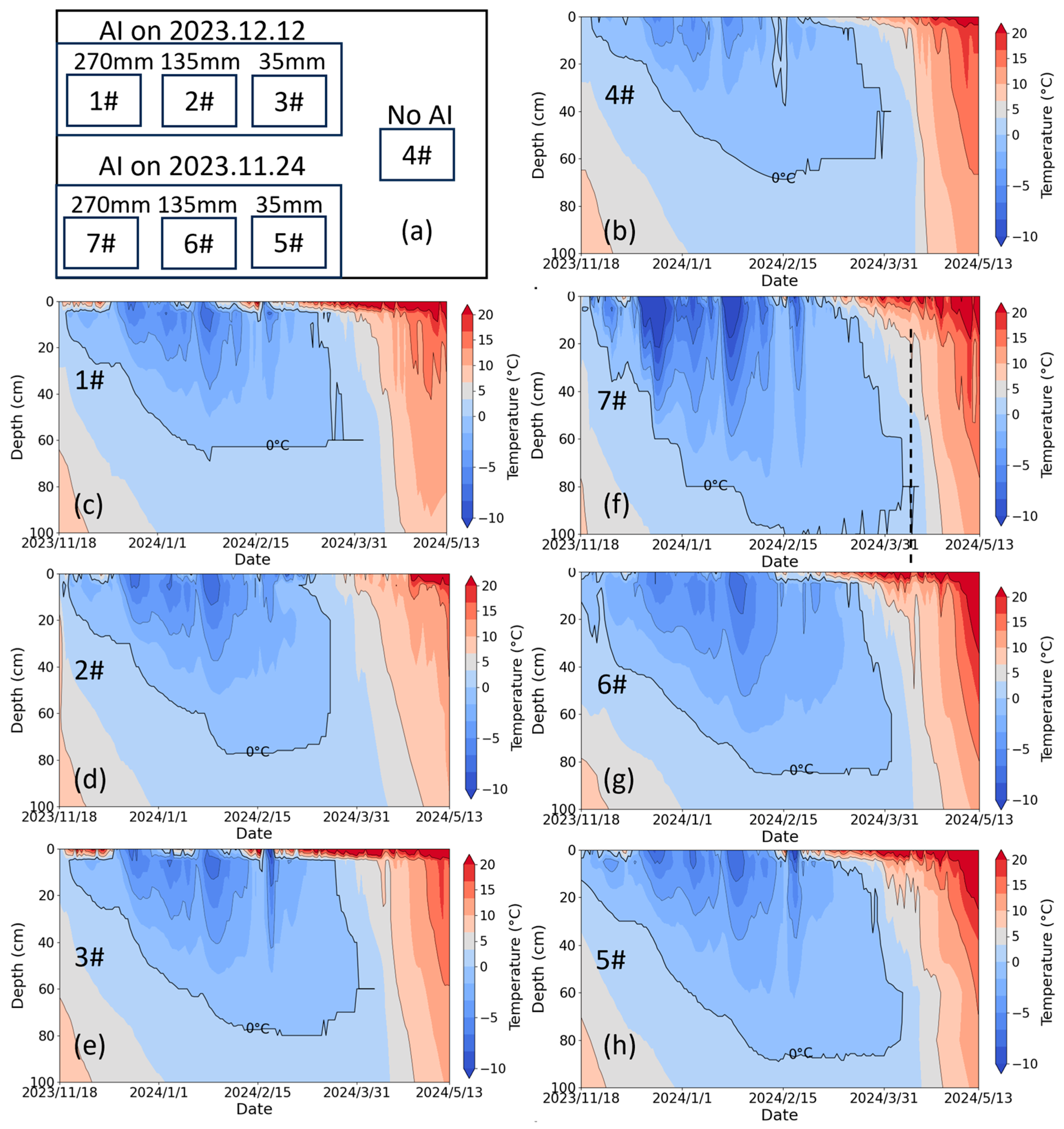
The AI exerted significant impacts on soil frost dynamics during the freeze–thaw cycle in 2023–2024. For convenience, 0 °C is considered the freezing point to determine whether the soil is frozen and, consequently, to decide the frost depth. Figure 6 revealed distinct MFD patterns that the ranking followed 7# > 5# > 6# > 4# for late AI, whereas icing AI exhibited 3# > 2# > 1# = 4#. This indicated that although irrigation at both timings increased the MFD compared to the non-irrigated control, the relationship between the MFD and irrigation quota exhibited opposite patterns for the two irrigation timings. A positive correlation emerged between irrigation quota and MFD for late AI. Regardless of late AI and icing AI, the soil was already frozen to a certain depth (about 10–20 cm) before irrigation. During the irrigating–thawing process, the heat of the irrigation water is consumed by the latent heat of phase transition in frozen layers, leading to cool irrigation water (defined as the “refrigerator effect” by Guo et al. [14]) (Figure 5). When the irrigation is sufficient to fully penetrate the frozen layer, the cooled irrigation water infiltrates into deeper soil layers, resulting in a deeper and more uniformly distributed low-temperature profile [14]. With the upward transfer of heat, these low-temperature soils are prone to cooling down to 0 °C, thereby being identified as a frozen layer. Therefore, sufficient irrigation can result in a deeper frost depth, e.g., 7# had a deeper frost depth than 5#, indicating that irrigation quota is a key factor in utilizing the “refrigerator effect” to regulate the dynamics of soil water and salt during freeze–thaw cycles. Notably, late AI consistently produced greater frost depths than icing AI at equivalent water quotas. For instance, the MFD in 7# (late AI) exceeded 100 cm, while it reached 68 cm in 1# (icing AI). The relationship between MFD and irrigation quota under icing AI in 2020–2021 was consistent with that under late AI in 2023–2024 (Figure 6b–e vs. Figure 11b–e) but differed from that under icing AI in 2023–2024 (Figure 11). The temperatures at 17:00 on 12 December 2020 (icing irrigation), 24 November 2023 (late irrigation), and 12 December 2023 (icing irrigation), were −8 °C, −3 °C, and 0 °C, respectively. Although the late AI occurred earlier than the icing AI in 2023–2024, the air temperature during irrigation was lower. The lower temperatures during the icing AI in 2020–2021 and the late AI in 2023–2024 enhanced the “refrigerator effect”, resulting in a consistent relationship between the MFD and irrigation quota in both cases. For icing AI in 2023–2024, the sudden rise in air temperature facilitated easier infiltration of irrigation water, weakening the “refrigerator effect”, thereby a distinct relationship between MFD and irrigation quota was observed. This inconsistency indicates that air temperature when irrigating is another key factor in utilizing the “refrigerator effect” to regulate the dynamics of soil water and salt during freeze–thaw cycles.
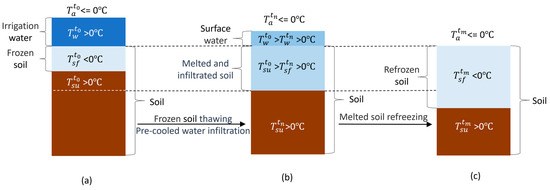
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the “refrigerator effect”: (a) before irrigation; (b) frozen soil thawing after irrigation; (c) soil refreezing after irrigation. T represents temperature, the subscripts a, w, sf, and su represent air, water, frozen soil, and unfrozen soil, respectively. The superscripts t0, tn, and tm represent different times, and m > n > 0.
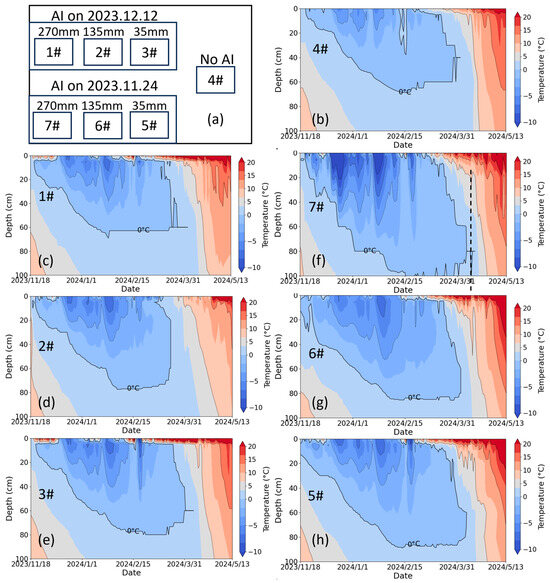
Figure 6.
(a) The schematic diagram of the experimental treatments, (b–h) the soil temperature profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, 3#, 7#, 6#, and 5#, respectively, during the period from November 2023 to May 2024. 4# represents the control plot with no irrigation. 1#–3# represent the icing AI (irrigated on 12 December 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively. 7#–5# represent the late AI (irrigated on 24 November 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively.
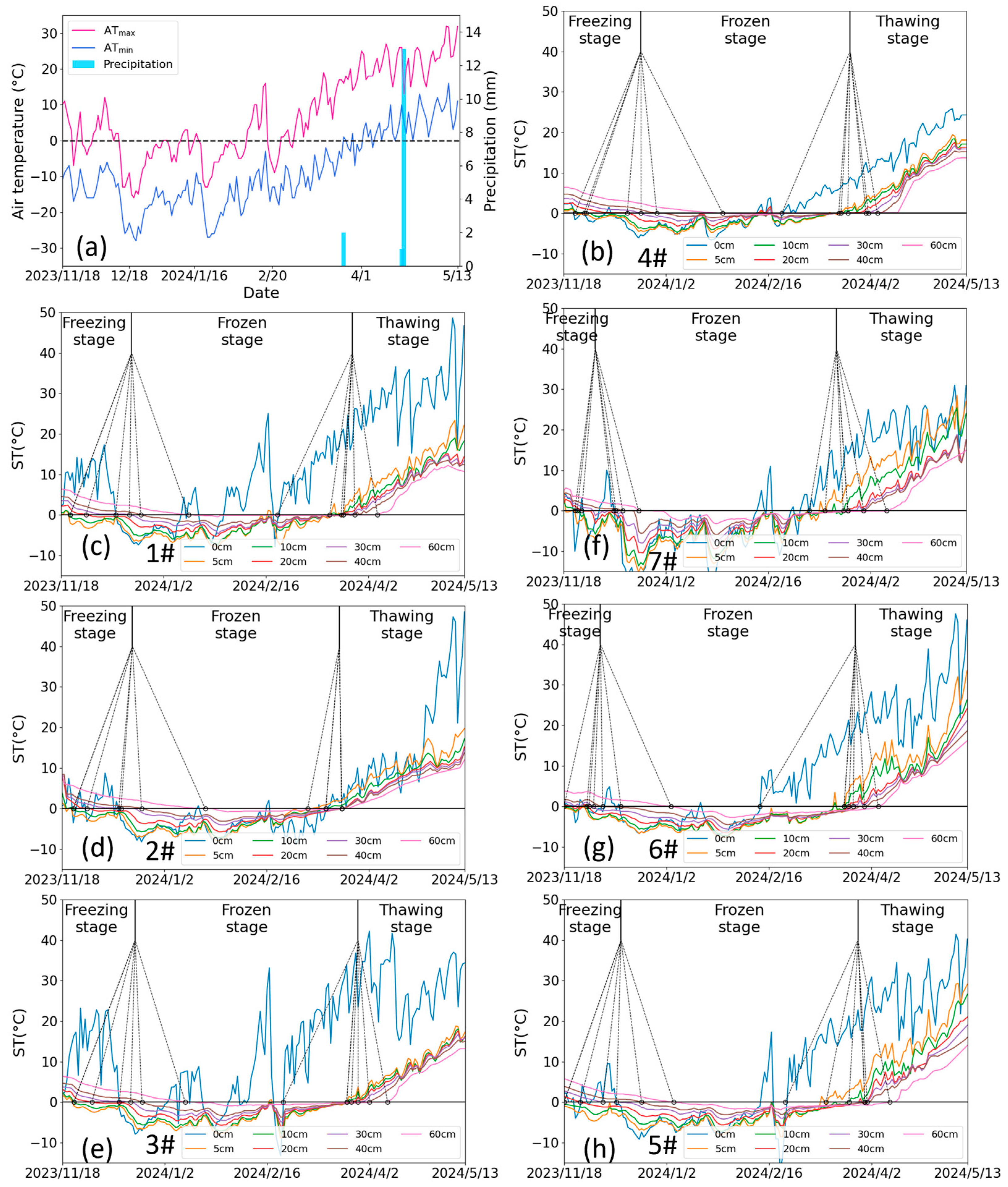
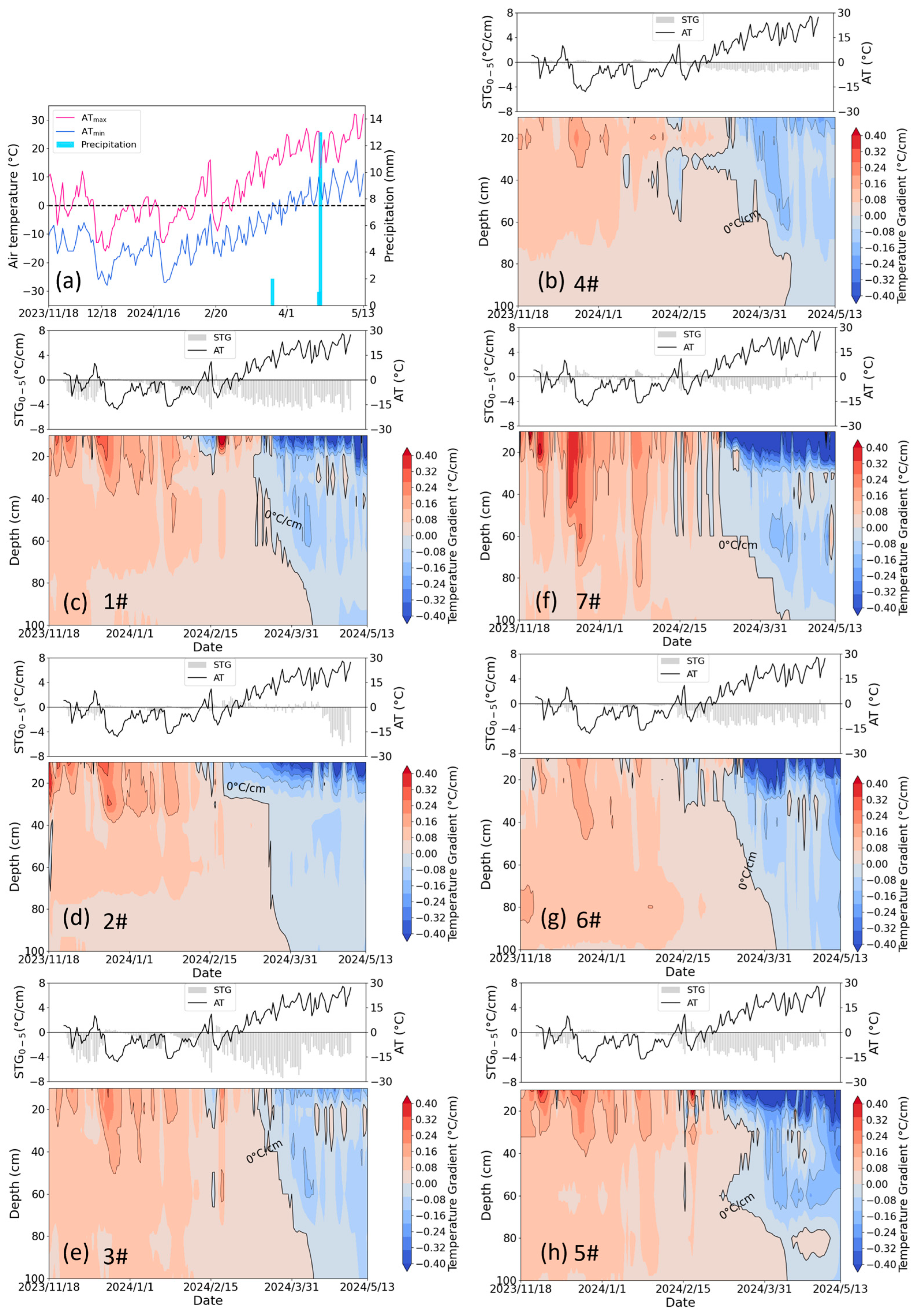
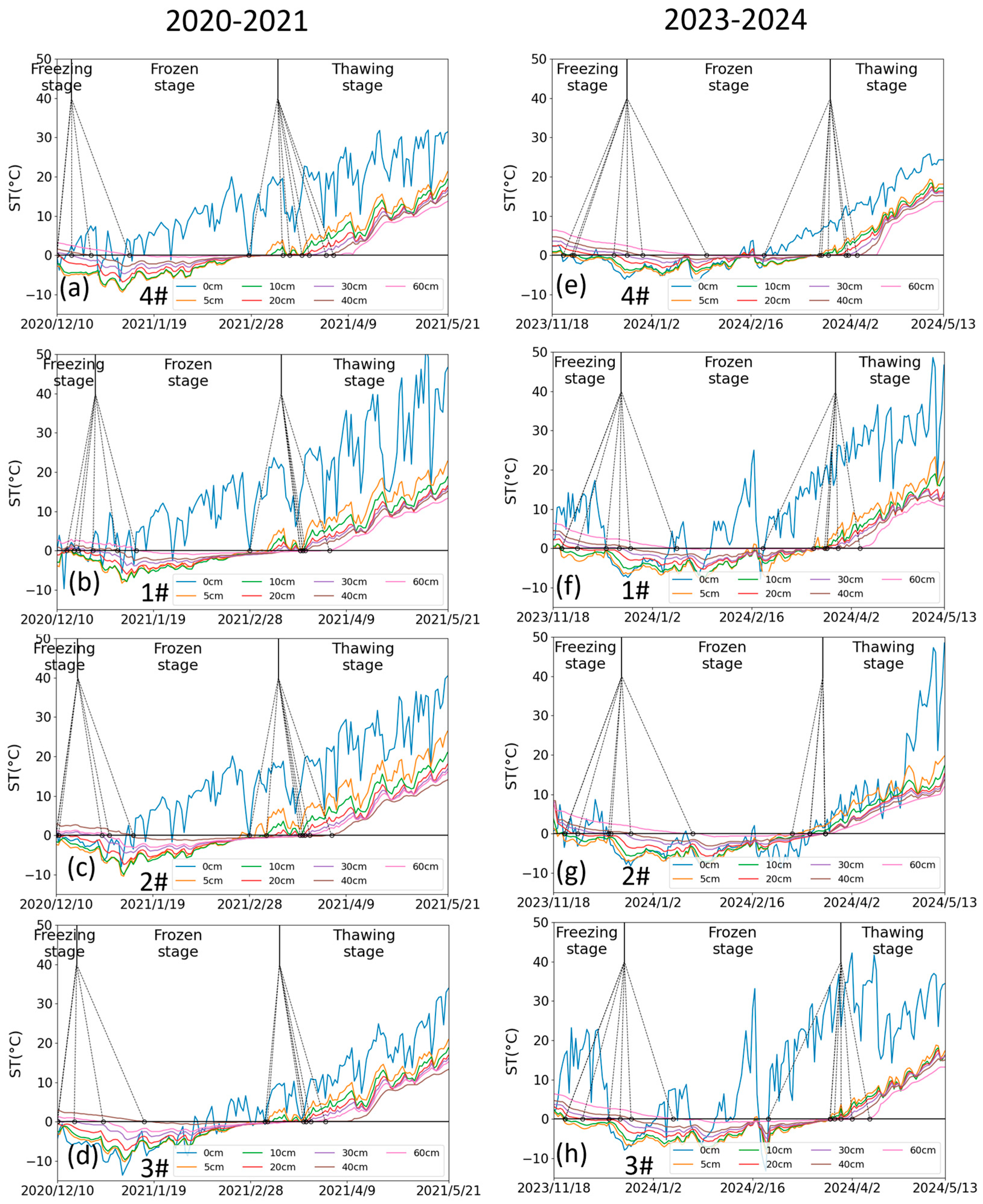
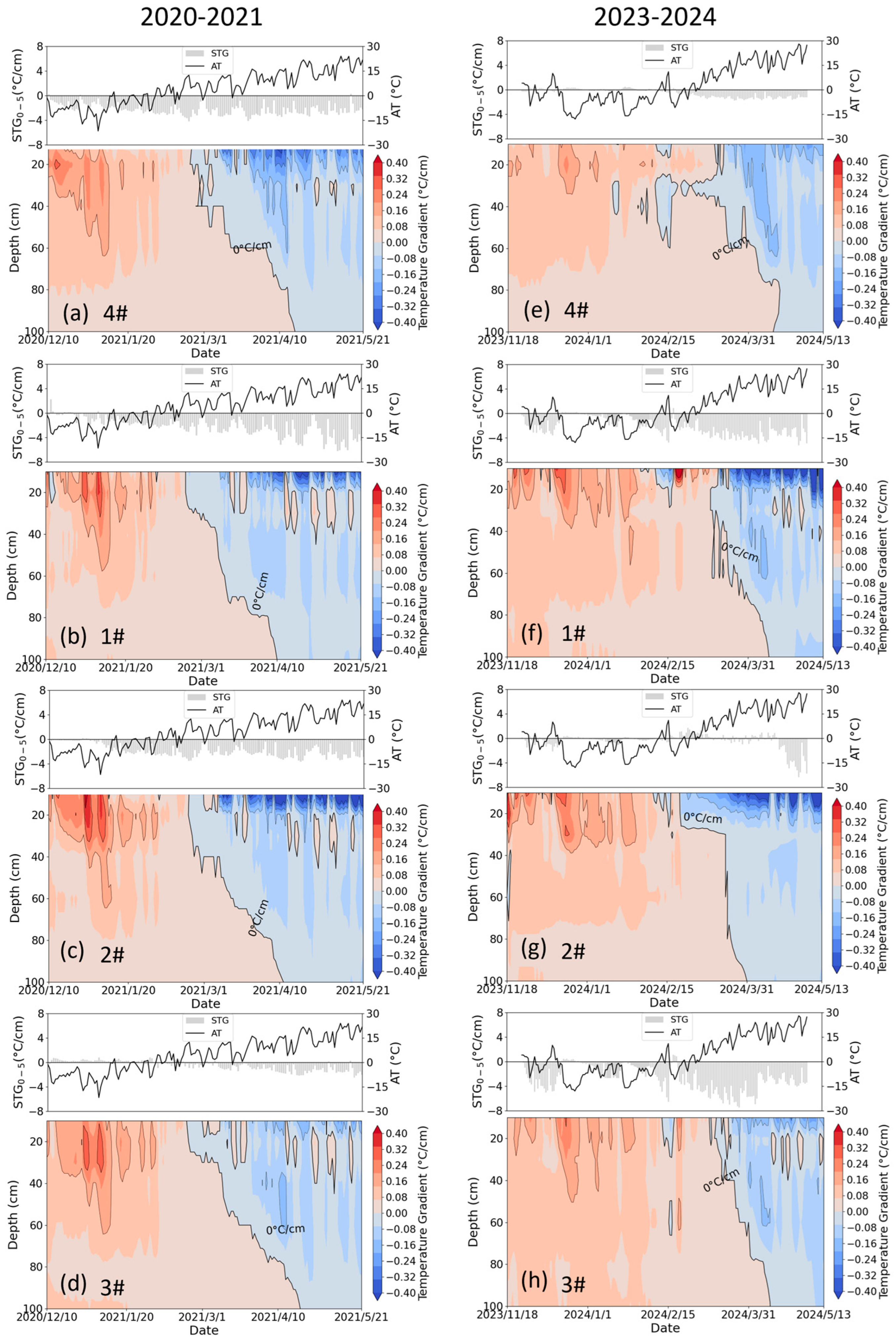
Freeze–thaw temporal dynamics showed clear depth-dependent patterns (Figure 7). The response of soil temperature to air temperature decreased exponentially with depth, creating depth-dependent phase transitions. Shallow layers (0–20 cm) exhibited earlier freezing onsets (26 November 2023 ± 4.16 days) and prolonged frozen durations (115 ± 4.96 days) compared to deeper soils (>20 cm) that froze on 25 December 2023 ± 11.78 days with a duration of 95 ± 10.32 days, as quantified in Table 2. This vertical thermal decoupling arises from differential heat transfer mechanisms—rapid conductive/convective exchange in the surface layers compared to delayed conductive transfer in the subsoil. The characteristic temperature gradient distribution (steep upper profile transitioning to gradual lower gradients) shown in Figure 8 further confirms this depth-dependent thermal behavior.
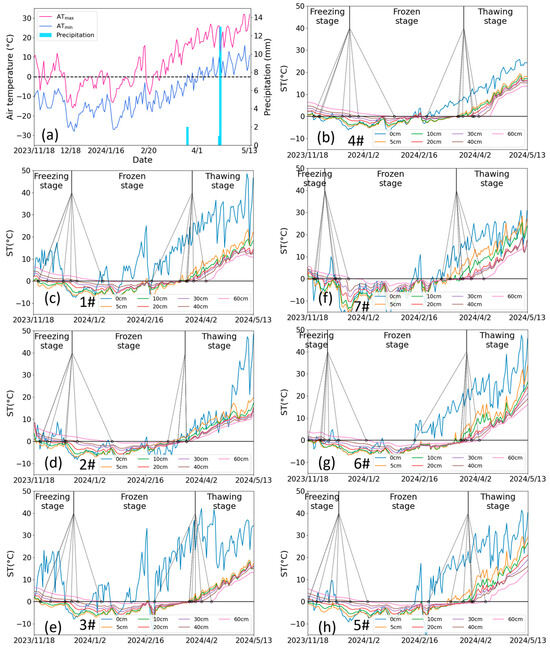
Figure 7.
(a) The daily air temperature and precipitation, and (b–h) the time series of soil temperature at the depths of 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, 60 cm and freeze–thaw stage division in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, 3#, 7#, 6#, and 5#, respectively, during the period from November 2023 to May 2024. 4# represents the control lysimeter with no irrigation. 1#–3# represent the icing AI (irrigated on 12 December 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively. 7#–5# represent the late AI (irrigated on 24 November 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively.

Table 2.
Time points and rates of freezing and thawing at different depths in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period from November 2023 to May 2024, and in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period from December 2020 to May 2021.
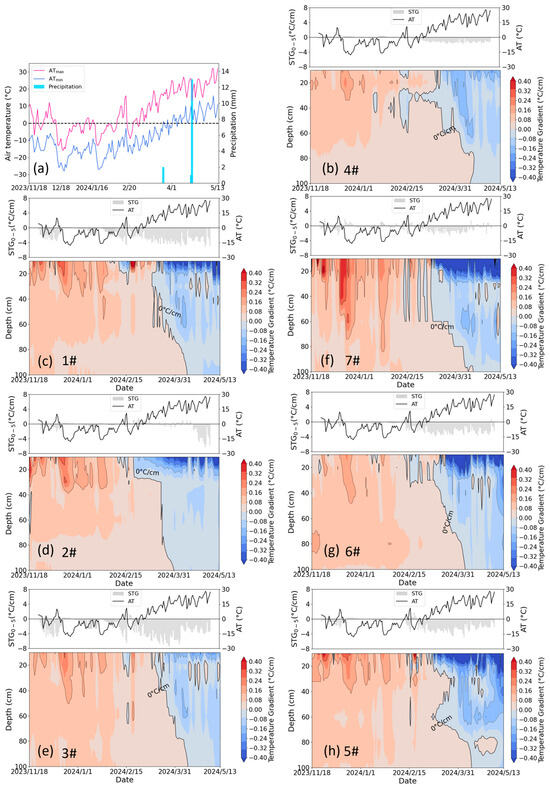
Figure 8.
(a) The daily air temperature and precipitation, and (b–h) the soil temperature gradient (STG) profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, 3#, 7#, 6#, and 5#, respectively, during the period from November 2023 to May 2024. 4# represents the control lysimeter with no irrigation. 1#–3# represent the icing AI (irrigated on 12 December 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively. 7#−5# represent the late AI (irrigated on 24 November 2023) treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively. The positive value indicates that the heat transfers from deep to shallow soils; otherwise, the transfer occurs in the opposite direction.
Irrigation management significantly altered freeze–thaw chronology across lysimeters (Figure 7 and Table 2). Compared to the non-irrigated control, AI-treated soils demonstrated earlier freezing onset and extended frozen duration. For example, the soil at a depth of 20 cm froze on 16 December 2023 with a frozen duration of 97 days in 4#, while it froze on 1 December 2023 with a duration of 114 days in 3#, and on 25 November 2023 with a duration of 125 days in 5#. Irrigation not only introduces additional heat but also increases the soil’s heat capacity, which theoretically would delay soil freezing [27]. However, the “refrigerator effect” accelerates the soil freezing, which is also supported by the fact that the freezing rate in irrigated soil is higher than that in the control group (4#). Due to air temperature fluctuations, the shallow soil without irrigation undergoes multi-day scale freeze–thaw cycles, whereas the irrigated shallow soil, once frozen, is more resistant to thawing, giving the impression that irrigated soil freezes earlier. Under icing AI, the water amount had little impact on the timing of soil freezing but significantly affected the frozen duration, with a quota of 35 mm resulting in the longest duration. Under late AI, the more water applied, the later the upper soil layers froze and the earlier the lower soil layers froze; the frozen duration of the upper soil layers increased, while that of the lower soil layers decreased. Substantial irrigation introduces external heat and induces ice cover formation over the soil surface, delaying the freezing of the upper soil layers, but allows cool irrigation water to infiltrate into deeper soil layers, thereby accelerating deep soil freezing. However, this mechanism does not hold under icing AI, as the sudden rise in temperature during this period prevents irrigation water from forming ice cover, leading to full infiltration into the soil [28]. Consequently, similar water distribution in the shallow soil results in comparable freezing timing. Regarding thawing, the soil with no and low irrigation (3# and 5#) exhibited a distinct pattern of thawing from both ends inward, whereas other irrigation treatments showed a concentrated and rapid top-down thawing process within the depth of 0–40 cm, which benefits soil desalinization (Figure 10).
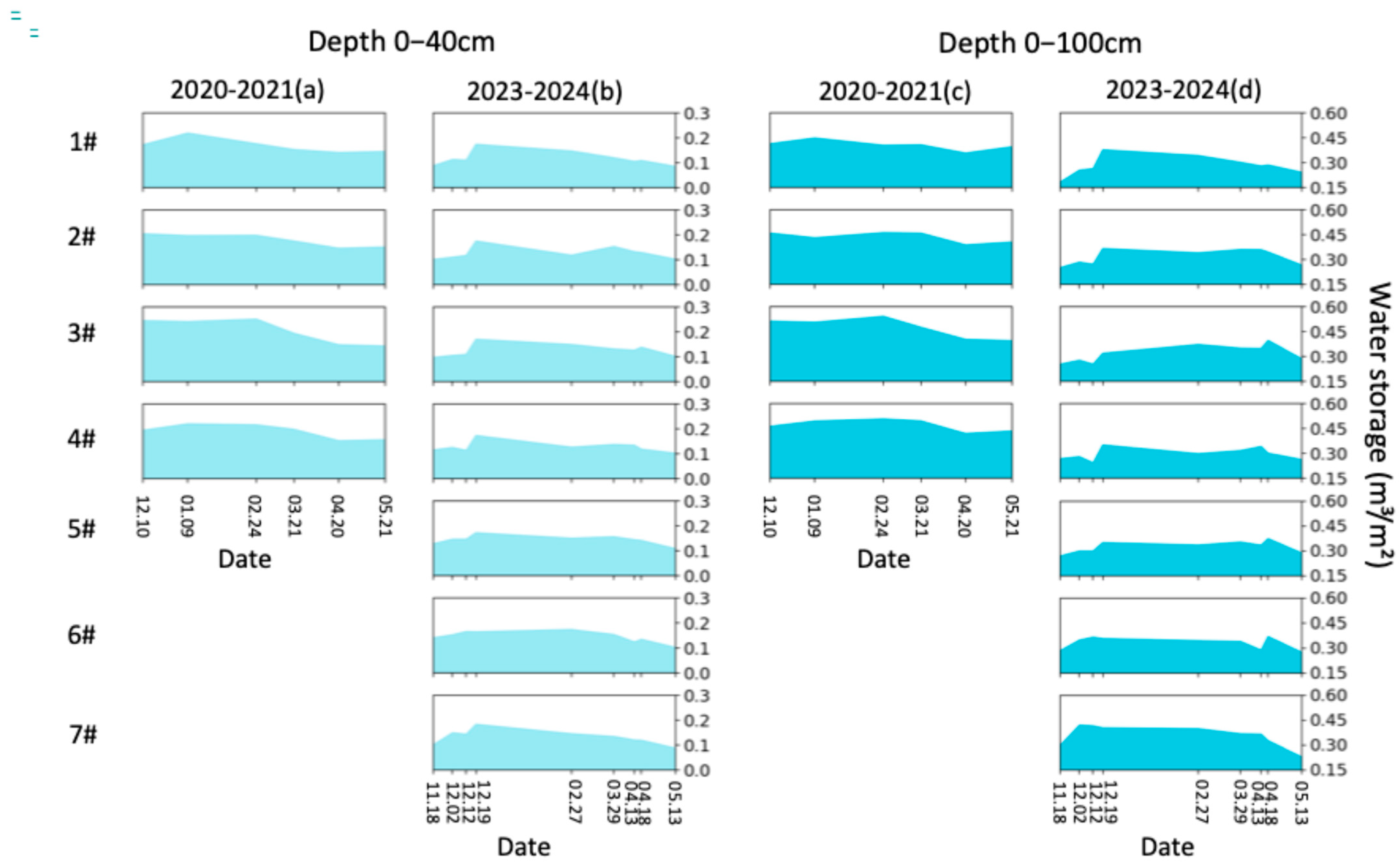
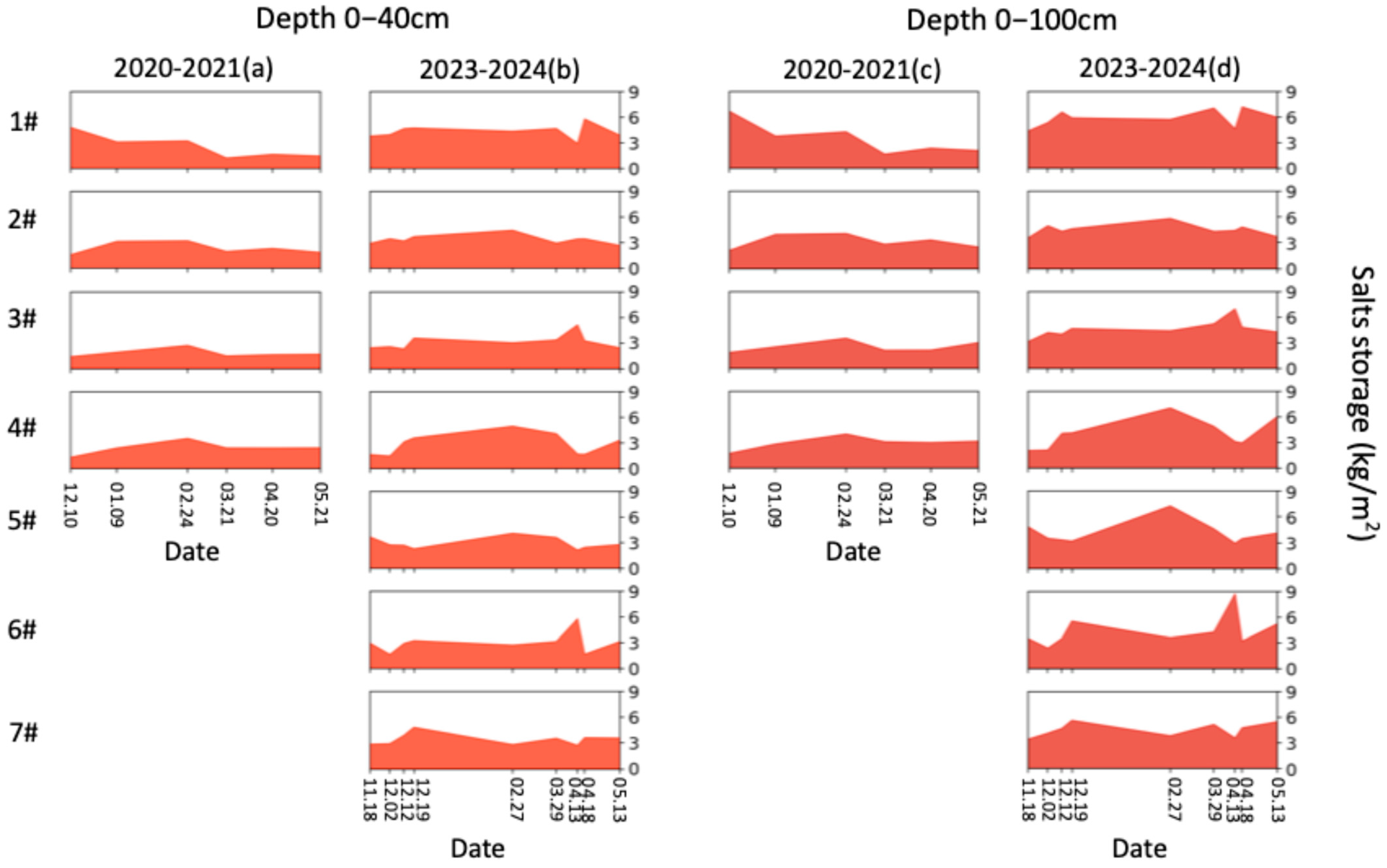
The sharp increases in water storage and decreases in salt storage on 18 April 2024 are caused by spring irrigation (Figure 9 and Figure 10). To eliminate the effects of spring irrigation, we used data up to 13 April 2024 to analyze the dynamics of soil water and salt. From the perspective of soil water availability in the cultivated horizon (0–40 cm), the final ranking is 5# > 4# > 2# > 3# > 6# > 7# > 1#, while the final ranking of salt storage is 4# < 5# < 7# < 1# < 2# < 3# < 6# (Figure 9 and Figure 10). Both 4# and 5# performed well in retaining soil moisture and controlling salinization, with 4# (no irrigation) being more water-saving. However, compared to the initial water and salt storage, 4# showed an increase of 20 mm (17.4%) in water storage and an increase of 0.04 kg m–2 (2.5%) in salt storage, whereas 5# also showed a 20 mm increase (15.6%) in water storage but a reduction of 1.53 kg m–2 (41.6%) in salt storage. Under the low groundwater level conditions of 2024, the treatment without irrigation effectively maintained salt balance and kept salinity levels consistent with those prior to AI. However, considering the salt accumulation during the crop growth period [29,30], no irrigation would struggle to achieve desalinization if the salt content before AI is high, which could hinder sustainable agricultural production. As shown in Table 3, the salt leaching effect of AI varies with the groundwater levels and irrigation scheme. Under low groundwater levels (2023–2024), icing AI shows poor salt leaching during the freezing period but performs well during the thawing period. Conversely, under high groundwater levels (2020–2021), icing AI demonstrates good salt leaching during the freezing period but poor performance during the thawing period. For low groundwater levels, the thawing-period salt leaching of icing AI under both 270 mm and 135 mm surpasses that of late AI. However, late AI with 35 mm achieves better salt leaching during the thawing period than icing AI.
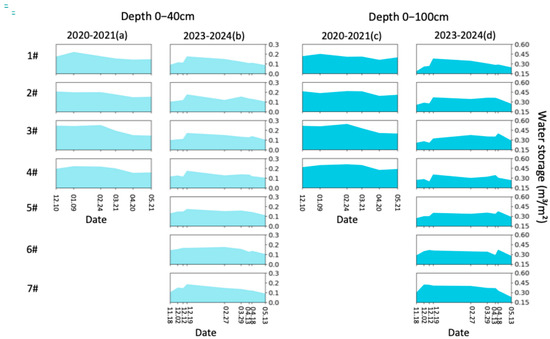
Figure 9.
(a) The water storage of 0–40 cm in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period of December 2020 to May 2021; (b) the water storage of 0–40 cm in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period of November 2023 to May 2024; (c) the water storage of 0–100 cm in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period of December 2020 to May 2021; (d) the water storage of 0–100 cm in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period of November 2023 to May 2024.
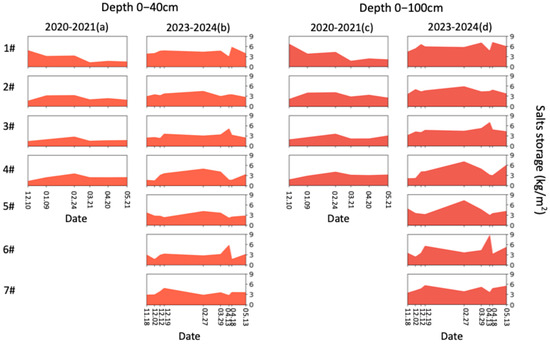
Figure 10.
(a) The salt storage of 0–40 cm in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period of December 2020 to May 2021; (b) the salt storage of 0–40 cm in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period of November 2023 to May 2024; (c) the salt storage of 0–100 cm in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period of December 2020 to May 2021; (d) the salt storage of 0–100 cm in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period of November 2023 to May 2024.

Table 3.
The salt flux (QS: g 100 g−1 month−1) of freezing and thawing at different depths in lysimeters 1#–7# during the period from November 2023 to May 2024, and in lysimeters 1#–4# during the period from December 2020 to May 2021.
From the analysis of temperature dynamics above, it can be inferred that the “refrigerator effect” may accelerate freezing under low air temperatures for a low quota irrigation, resulting in more irrigation water being retained and less salt accumulation in the frozen layer during the early freezing period. During the thawing period, the irrigation water retained in the frozen layers tends to thaw rapidly, potentially contributing to desalination. Therefore, our study suggests that late AI of 35 mm can achieve the goals of water-saving, soil moisture retention, and salinization control.
3.3. Contribution of Groundwater to the Soil Freezing–Thawing Dynamics Under AI
As shown in Figure 11, the relationship between MFD and irrigation amount was opposite in 2020–2021 and 2023–2024. As mentioned above, the “refrigerator effect” is less pronounced due to the sudden rise in air temperature during this period in 2023, allowing irrigation water to fully infiltrate into the soil and greater percolation losses. Consequently, the insufficiently cooled irrigation water hindered the advancement of the freezing front. Thus, the more water irrigated, the lower frost depth reached in 2023 (Figure 11h–j). Figure 12 and Table 2 demonstrate that for the control group without irrigation (4#), the soil at 40 cm froze and thawed earlier in 2020–2021 compared to 2023–2024; whereas the soil at 60 cm froze earlier and thawed later in 2020–2021 compared to 2023–2024, leading to a longer frozen duration. As shown in Figure 12a,e, the 40 cm soil temperature responded to fluctuations in air temperature, while the 60 cm soil temperature was less affected by air temperature. Meteorological data indicate that the average maximum air temperature in December 2020 was −5 °C, compared to −3 °C in December 2023, with the average minimum air temperature being consistent at −15 °C. The lower air temperature in December 2020 caused the upper soil layer to freeze earlier and the same mechanism caused the upper soil layer to thaw earlier in March 2021. It can be seen in Figure 2 that there is a significant difference in groundwater levels between the two years. The higher groundwater level during 2020–2021 resulted in more frequent heat exchange between groundwater and soil during the thawing period, as the low-temperature groundwater (9 °C) prolonged the frozen duration of the deeper soil layers. In addition to air temperature and groundwater level, irrigation management also significantly altered freeze–thaw chronology across lysimeters (Figure 12 and Table 2). In 2020–2021, irrigation delayed soil freezing, accelerated soil thawing, and reduced the frozen duration in comparison to the control. In 2023–2024, irrigation accelerated soil freezing and thawing, and prolonged the frozen duration, in comparison to the control.
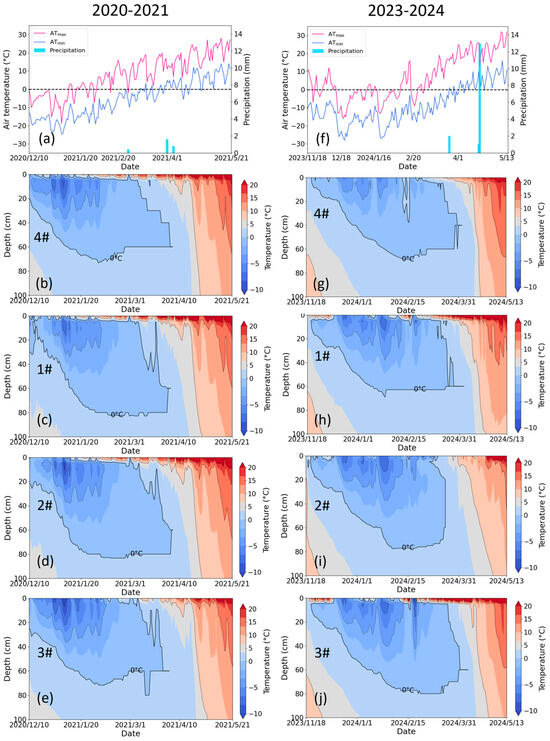
Figure 11.
(a) The daily air temperature and precipitation during the period of December 2020 to May 2021, (b–e) the soil temperature profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of December 2020 to May 2021. (f) The daily air temperature and precipitation during the period of November 2023 to May 2024, (g–j) the soil temperature profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of November 2023 to May 2024. 4# represents the control lysimeter with no irrigation. 1#–3# represent the treatment lysimeters with irrigation of 270 mm, 135 mm, and 35 mm, respectively.
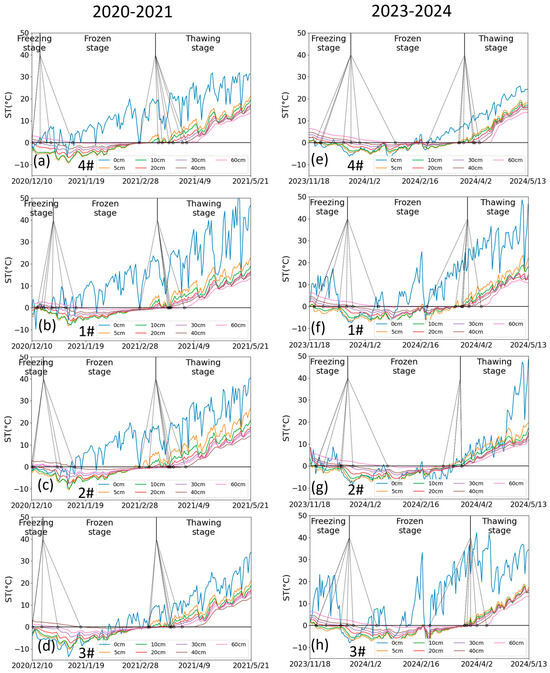
Figure 12.
(a–d) The soil temperature at different depths in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of December 2020 to May 2021. (e–h) The soil temperature at different depths in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of November 2023 to May 2024.
As shown in Figure 9, in 2020–2021, the water storages of 0–40 cm soil layers in the four lysimeters were similar (about 150 mm) on 20 April 2021. However, compared to the initial water storages on 10 December 2020, lysimeters 2#–4# showed increases of 12.9%, 15.3%, and 18.8%, respectively, while lysimeter 1# experienced a decrease of 4.7%. In 2023–2024, the water storages in lysimeters 1#–4# were 105, 132, 126, and 134 mm, respectively, on 13 April 2024. Compared to the initial water storages on 12 December 2023, these values decreased by 18.1%, 28.8%, 39.5%, and 21.4%, respectively. As shown in Figure 10, in 2020–2021, the salt storages of 0–40 cm soil layers in lysimeters 1#–4# were 1.68, 2.37, 1.63, and 2.40 kg m−2, respectively, on 20 April 2021. However, compared to the initial salt storages on 10 December 2020, lysimeters 2#–4# showed increases of 46%, 17%, and 84%, respectively, while lysimeter 1# experienced a decrease of 65%. In 2023–2024, the salt storages in lysimeters 1#–4# were 2.94, 3.48, 5.11, and 1.68 kg m−2, respectively, on 13 April 2024. Compared to the initial salt storages on 12 December 2023, lysimeters 1# and 4# showed decreases of 38% and 46%, respectively, while lysimeters 2# and 3# experienced an increase of 8% and 166%, respectively. To achieve the goals of water conservation, soil moisture retention, and salinity control synchronously, the optimal quota for icing AI was 35 mm (3#) in 2020–2021, while no irrigation (4#) was the optimal strategy in 2023–2024. This discrepancy in icing AI strategy between different years is attributed to the impacts of air temperature and groundwater level on soil freezing–thawing dynamics.
Figure 13a–d reveal the insulation effects of the ice cover derived from icing AI, where the soil surface temperature gradient in the control group was negative, while in irrigation treatments, it remained at zero during the presence of the ice cover. However, this phenomenon was not evident in 2023–2024 (Figure 13e–h), as the sudden rise in air temperature during the irrigation period prevented the formation of ice cover. Compared to the control group, irrigation increased the surface temperature gradient during both the freezing and thawing periods, intensifying the heat exchange between the soil and the atmosphere, thereby accelerating soil freezing and/or thawing.
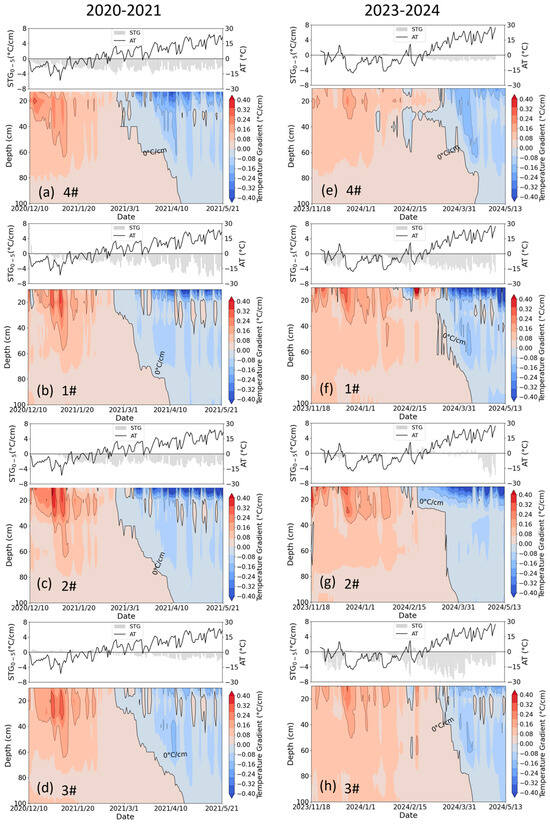
Figure 13.
(a–d) The soil temperature gradient (STG) profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of December 2020 to May 2021. (e–h) The soil temperature gradient (STG) profile in lysimeters 4#, 1#, 2#, and 3#, respectively, during the period of November 2023 to May 2024. The positive value indicates that the heat transfers from deep to shallow soils; otherwise, the transfer occurs in the opposite direction.
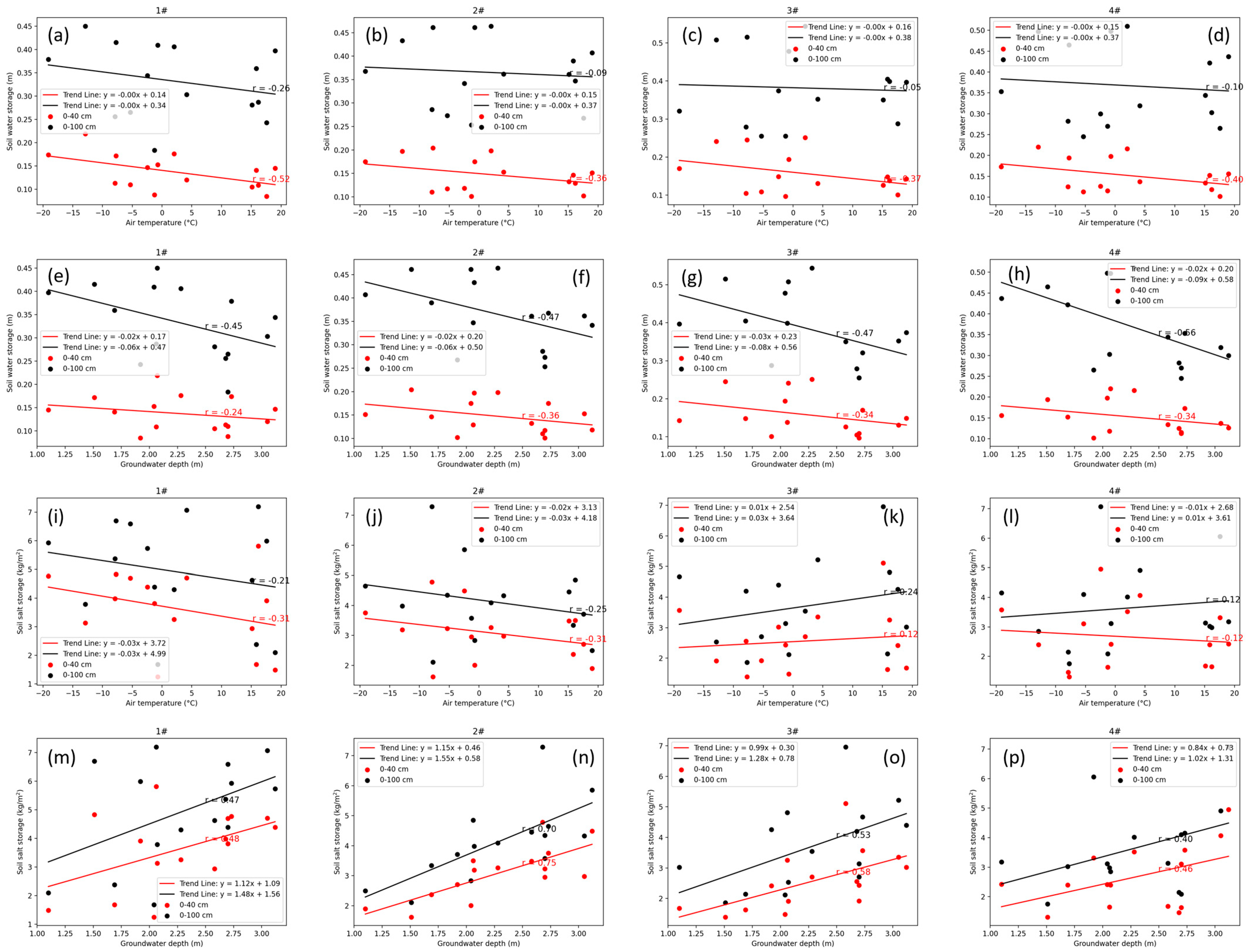
As shown in Figure 14a–d, soil water storage exhibited a negative correlation with air temperature, and this relationship was independent of irrigation amounts. This finding is consistent with previous studies, which suggest that rapid freezing due to low air temperature can effectively preserve soil moisture. Higher water storage is expected under a high irrigation quota; however, increased irrigation prolongs the freezing process, leading to greater water losses by deep percolation losses. Moreover, soil water storage was negatively correlated with groundwater depth, with a stronger correlation observed in the 0–100 cm soil layer compared to the 0–40 cm layer (Figure 14e–h). This indicates that the groundwater moves upward to supply the soil water storage under shallow groundwater depth conditions. Notably, this exchange exhibits no significant relationship with irrigation water amounts, as the irrigation is insufficient to alter the groundwater table significantly in the experiment.
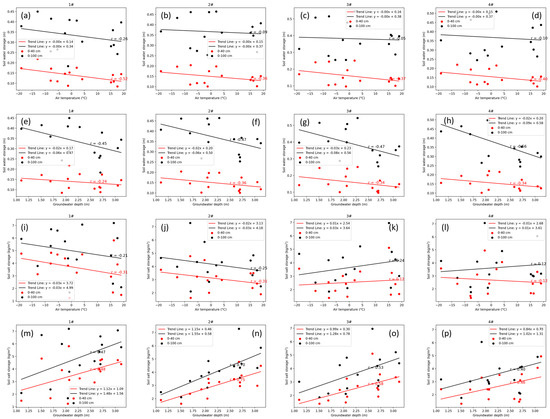
Figure 14.
(a–d) The correlations between the air temperature and soil water storage in lysimeters 1#–4#, respectively. (e–h) The correlations between the groundwater depth and soil water storage in lysimeters 1#–4#, respectively. (i–l) The correlations between the air temperature and soil-salt storage in lysimeters 1#–4#, respectively. (m–p) The correlations between the groundwater depth and soil-salt storage in lysimeters 1#–4#, respectively.
In contrast, salt storage was positively correlated with groundwater depth (Figure 14m–p), indicating that lower groundwater levels were associated with higher salt storage. This finding deviates from previous studies, which suggest that shallow groundwater depth accelerates soil salinization [4]. In this study, the groundwater depth was primarily observed during the freeze–thaw period rather than the onset of freezing. It gradually increased throughout the freezing process prior to the thawing period, corresponding to the process of salt accumulation. During the thawing period, as soil water from melting infiltrates the soil, it simultaneously leaches salts (reducing salt storage) and raises the groundwater table. Therefore, a positive relationship was observed between salt storage and groundwater depth. The results of the ANOVA indicate that only the relationship between air temperature and soil water and salt storage was significant, whereas the groundwater table has no significant effect (Table 4). Additionally, the impact of air temperature on water storage is more significant in the 0–100 cm soil layer than in the 0–40 cm layer; in contrast, the impact of air temperature on salt storage is more significant in the 0–40 cm layer than in the 0–100 cm layer. However, this conclusion requires further validation through continuous observations.

Table 4.
The results of the two-way ANOVA for quantifying the effect of groundwater depth (GD) and air temperature (AT) on soil water and salt storage.
4. Conclusions
This study elucidates the mechanisms of AI on soil water–heat–salt dynamics in seasonally frozen soils under varying groundwater levels. The key findings are as follows:
- (1)
- The air temperature and groundwater dynamics are characterized by annual and seasonal variations, respectively. Air temperature and groundwater depth exhibit a strong negative correlation on a long-term scale, while the correlation is relatively weak on a short-term scale. Moreover, the correlation, whether long-term or short-term, weakens as the groundwater level decreases.
- (2)
- The quota and air temperature during AI were the key factors in utilizing the “refrigerator effect”—where irrigation water pre-cooled by a frozen layer accelerates soil freezing—to regulate soil water and salt transport under freeze–thaw cycles.
- (3)
- Late AI with a quota of 35 mm achieved optimal water savings (significantly lower than the recommended quotas for early AI) while maintaining soil moisture (an increase of 17.4% in water storage) and reducing salinity (a decrease of 41.6% in salt storage) in the root zone (0–40 cm) through the “refrigerator effect”.
- (4)
- The lower the groundwater level and air temperature, the more pronounced the “refrigerator effect”, which enhances the water-saving, soil moisture retention, and salinity control benefits of icing AI.
These findings suggest that, under the constraints of water-saving policies and the resulting continuous decline in groundwater levels, limited irrigation under low air temperatures (late- or short-term drop in air temperature) provides a promising water-saving autumn irrigation strategy, aligning water-saving goals with soil health in water-scarce regions like the Hetao Irrigation District. Further studies should explore long-term impacts of icing AI on crop productivity and regional hydrology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.T.; methodology, X.T.; investigation, Z.Y.; resources, A.C. and Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Y.; writing—review and editing, X.T.; visualization, Z.Y. and Y.Z.; supervision, W.Z.; funding acquisition, X.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, grant number 2022SCU12113; and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51909175.
Data Availability Statement
Data is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Autumn Multidisciplinary |
| AT | Air temperature |
| GD | Groundwater depth |
| MFD | Maximum frost depth |
| STG | Soil temperature gradient |
Appendix A

Table A1.
The basic physical properties of soils in lysimeters.
Table A1.
The basic physical properties of soils in lysimeters.
| Lysimeter | Soil Layer (cm) | Bulk Density (kg m−3) | Particle Size Distribution (%) | Texture | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Silt | Clay | ||||
| 1# | 0–5 | 1368.3 | 28.43 | 65.50 | 6.07 | Silt loam |
| 5–10 | 1390.3 | 30.78 | 64.17 | 5.05 | Silt loam | |
| 10–20 | 1340.3 | 32.72 | 62.70 | 4.58 | Silt loam | |
| 20–30 | 1514.3 | 32.43 | 63.49 | 4.08 | Silt loam | |
| 30–40 | 1548.3 | 26.07 | 68.74 | 5.19 | Silt loam | |
| 40–60 | 1313.3 | 28.66 | 67.83 | 3.51 | Silt loam | |
| 60–80 | 1496.3 | 36.48 | 60.50 | 3.02 | Silt loam | |
| 80–100 | 1484.3 | 58.79 | 39.33 | 1.88 | Sandy loam | |
| 2# | 0–5 | 1518.3 | 23.33 | 70.22 | 6.45 | Silt loam |
| 5–10 | 1410.3 | 27.30 | 67.32 | 5.38 | Silt loam | |
| 10–20 | 1458.3 | 25.69 | 68.39 | 5.92 | Silt loam | |
| 20–30 | 1488.3 | 25.07 | 69.23 | 5.70 | Silt loam | |
| 30–40 | 1558.3 | 30.74 | 64.63 | 4.63 | Silt loam | |
| 40–60 | 1514.3 | 23.89 | 70.16 | 5.95 | Silt loam | |
| 60–80 | 1487.3 | 20.75 | 73.52 | 5.73 | Silt loam | |
| 80–100 | 1551.3 | 32.13 | 63.37 | 4.50 | Silt loam | |
| 3# | 0–5 | 1436.3 | 21.29 | 72.68 | 6.03 | Silt loam |
| 5–10 | 1436.3 | 21.14 | 72.36 | 6.50 | Silt loam | |
| 10–20 | 1406.3 | 20.16 | 73.48 | 6.36 | Silt loam | |
| 20–30 | 1523.3 | 19.27 | 74.18 | 6.55 | Silt loam | |
| 30–40 | 1599.3 | 21.02 | 72.56 | 6.42 | Silt loam | |
| 40–60 | 1592.6 | 21.15 | 73.06 | 5.79 | Silt loam | |
| 60–80 | 1619.3 | 19.29 | 75.06 | 5.65 | Silt loam | |
| 80–100 | 1467.3 | 35.54 | 60.80 | 3.66 | Sandy loam | |
| 4# | 0–5 | 1411.3 | 28.08 | 66.93 | 4.99 | Silt loam |
| 5–10 | 1449.3 | 28.47 | 66.82 | 4.71 | Silt loam | |
| 10–20 | 1446.3 | 31.10 | 64.69 | 4.16 | Silt loam | |
| 20–30 | 1499.3 | 23.24 | 71.47 | 5.29 | Silt loam | |
| 30–40 | 1469.3 | 16.80 | 76.68 | 6.46 | Silt loam | |
| 40–60 | 1419.3 | 13.67 | 81.71 | 4.62 | Silt loam | |
| 60–80 | 1502.3 | 26.80 | 69.65 | 3.45 | Silt loam | |
| 80–100 | 1455.3 | 57.40 | 40.83 | 1.83 | Sandy loam | |
| 5# | 0–5 | 1479.3 | 0.12 | 96.84 | 3.04 | Silt |
| 5–10 | 1471.3 | 0.14 | 97.15 | 2.71 | Silt | |
| 10–20 | 1497.3 | 0.00 | 95.89 | 4.11 | Silt | |
| 20–30 | 1327.3 | 0.00 | 97.03 | 2.97 | Silt | |
| 30–40 | 1482.3 | 0.00 | 95.62 | 4.38 | Silt | |
| 40–60 | 1456.3 | 0.00 | 96.41 | 3.59 | Silt | |
| 60–80 | 1434.3 | 0.20 | 97.93 | 1.87 | Silt | |
| 80–100 | 1441.3 | 0.23 | 98.14 | 1.63 | Silt | |
| 6# | 0–5 | 1453.3 | 0.12 | 96.97 | 2.91 | Silt |
| 5–10 | 1496.3 | 0.12 | 96.67 | 3.21 | Silt | |
| 10–20 | 1425.3 | 0.14 | 97.02 | 2.84 | Silt | |
| 20–30 | 1439.8 | 0.00 | 96.77 | 3.23 | Silt | |
| 30–40 | 1454.3 | 0.00 | 96.79 | 3.21 | Silt | |
| 40–60 | 1422.3 | 0.00 | 96.78 | 3.22 | Silt | |
| 60–80 | 1435.3 | 0.25 | 97.70 | 2.05 | Silt | |
| 80–100 | 1525.3 | 0.27 | 97.08 | 2.65 | Silt | |
| 7# | 0–5 | 1410.3 | 2.41 | 97.42 | 0.17 | Silt |
| 5–10 | 1380.3 | 3.08 | 96.92 | 0.00 | Silt | |
| 10–20 | 1434.3 | 3.13 | 96.87 | 0.00 | Silt | |
| 20–30 | 1494.3 | 2.82 | 97.18 | 0.00 | Silt | |
| 30–40 | 1411.3 | 2.18 | 97.70 | 0.12 | Silt | |
| 40–60 | 1406.3 | 1.68 | 98.20 | 0.12 | Silt | |
| 60–80 | 1403.3 | 1.71 | 98.29 | 0.00 | Silt | |
| 80–100 | 1473.3 | 2.22 | 97.78 | 0.00 | Silt | |
References
- Singh, P.K.; Chudasama, H. Pathways for Climate Change Adaptations in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Ayantobo, O.O.; Li, H.; Song, L. Assessing the Impact of Seasonal Freezing and Thawing on the Soil Microbial Quality in Arid Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 161029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The Threat of Soil Salinity: A European Scale Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Huang, J.; Jansson, P.-E.; Zhang, W. Simulation of Dynamical Interactions between Soil Freezing/Thawing and Salinization for Improving Water Management in Cold/Arid Agricultural Region. Geoderma 2019, 338, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, S. Mechanism of Freeze–Thaw Action in the Process of Soil Salinization in Northeast China. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, H. Investigating the Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical Behavior of Loess Subjected to Freeze–Thaw Cycles. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 6305–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, M.; You, Z.; Li, S.; Bai, R. Study on the Coupling Mechanism of Water-Heat-Vapor-Salt-Mechanics in Unsaturated Freezing Sulfate Saline Soil. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 169, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, H.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Akae, T.; Wang, C. Simulation of Freezing and Thawing Soils in Inner Mongolia Hetao Irrigation District, China. Geoderma 2012, 173–174, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.-Z.; Wang, X.-K.; Feng, Z.-W. Soil N and Salinity Leaching after the Autumn Irrigation and Its Impact on Groundwater in Hetao Irrigation District, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 71, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G. Predicting Agroecosystem Responses to Identify Appropriate Water-Saving Management in Arid Irrigated Regions with Shallow Groundwater: Realization on a Regional Scale. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 247, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Huo, Z.; Bai, Y.; Feng, S.; Huang, G.; Shi, H.; Qu, Z. Soil Salt and Groundwater Change in Flood Irrigation Field and Uncultivated Land: A Case Study Based on 4-Year Field Observations. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, R.; Shi, H.; Liang, J.; Miao, Q.; Fan, L. Successive Simulations of Soil Water-Heat-Salt Transport in One Whole Year of Agriculture after Different Mulching Treatments and Autumn Irrigation. Geoderma 2019, 344, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Shang, S.; Rahman, K.U.; Xia, Y.; Ren, D. A Semi-Distributed Drainage Model for Monthly Drainage Water and Salinity Simulation in a Large Irrigation District in Arid Region. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, H.; Flerchinger, G.N.; Zou, C.; Li, Z. Modeling the Effect of Antecedent Soil Water Storage on Water and Heat Status in Seasonally Freezing and Thawing Agricultural Soils. Geoderma 2013, 206, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Flerchinger, G.N. Scheme of Water Saving Irrigation in Autumn Based on SHAW Model in Inner Mongolia Hetao Irrigation District. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. (Trans. CSAE) 2010, 26, 31–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, N.; Li, J.; Huang, G. Effect of Autumn Irrigation on Salt Leaching under Subsurface Drainage in an Arid Irrigation District. Water 2023, 15, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Z. Development and Application of a Monthly Water and Salt Balance Model for Seasonally Frozen Agricultural and Non-Agricultural Areas with Shallow Groundwater Table. CATENA 2024, 235, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Liu, M.; Paredes, P.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z.; Lei, H.; Pereira, L.S. Salts Dynamics in Maize Irrigation in the Hetao Plateau Using Static Water Table Lysimeters and HYDRUS-1D with Focus on the Autumn Leaching Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 283, 108306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huang, G.; Qu, Z.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing the Groundwater Dynamics and Impacts of Water Saving in the Hetao Irrigation District, Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 98, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Jansson, P.-E. Experimental Study on Evaporation from Seasonally Frozen Soils under Various Water, Solute and Groundwater Conditions in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, D.; Huang, G. Long-Term Regional Groundwater Responses and Their Ecological Impacts under Agricultural Water Saving in an Arid Irrigation District, Upper Yellow River Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 288, 108493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, M.; Huang, J.; Tan, B.; Li, L. Effects of Ice Cover on Soil Water, Heat, and Solute Movement: An Experimental Study. Geoderma 2021, 403, 115209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Tan, X.; He, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, J.; Zhuang, W.; Liu, C. Transport of Heat, Water, and Salts in Freeze–Thaw Soils under Flood Irrigation: Experiment and Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2025, 652, 132688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibek, J.; Allen, D.M. Modeled Impacts of Predicted Climate Change on Recharge and Groundwater Levels. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltman, H. Chapter 11: Two-Way ANOVA; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Xue, J.; Chen, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, H. Evaluating Spatial and Temporal Variations of Soil Water, Heat, and Salt under Autumn Irrigation in the Hetao Irrigation District Based on Distributed SHAW Model. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 293, 108707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Kito, T.; Dun, S.; Wu, J.Q.; Greer, R.C.; Flury, M. Water Infiltration into a Frozen Soil with Simultaneous Melting of the Frozen Layer. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12, vzj2011.0188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Shi, H.; Li, R.; Miao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yu, D.; Zhou, L.; Wang, B. Effects of Controlled Drainage on the Content Change and Migration of Moisture, Nutrients, and Salts in Soil and the Yield of Oilseed Sunflower in the Hetao Irrigation District. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Wei, B.; Xu, X.; Engel, B.; Li, G.; Huang, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Huang, G. Analyzing Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Soil Salinity in Arid Irrigated Agro-Ecosystems Using Integrated Approaches. Geoderma 2019, 356, 113935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).