Phytoplankton Composition During the Ice-Free Period of Lakes on Horseshoe Island (Antarctica) by Metagenomic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
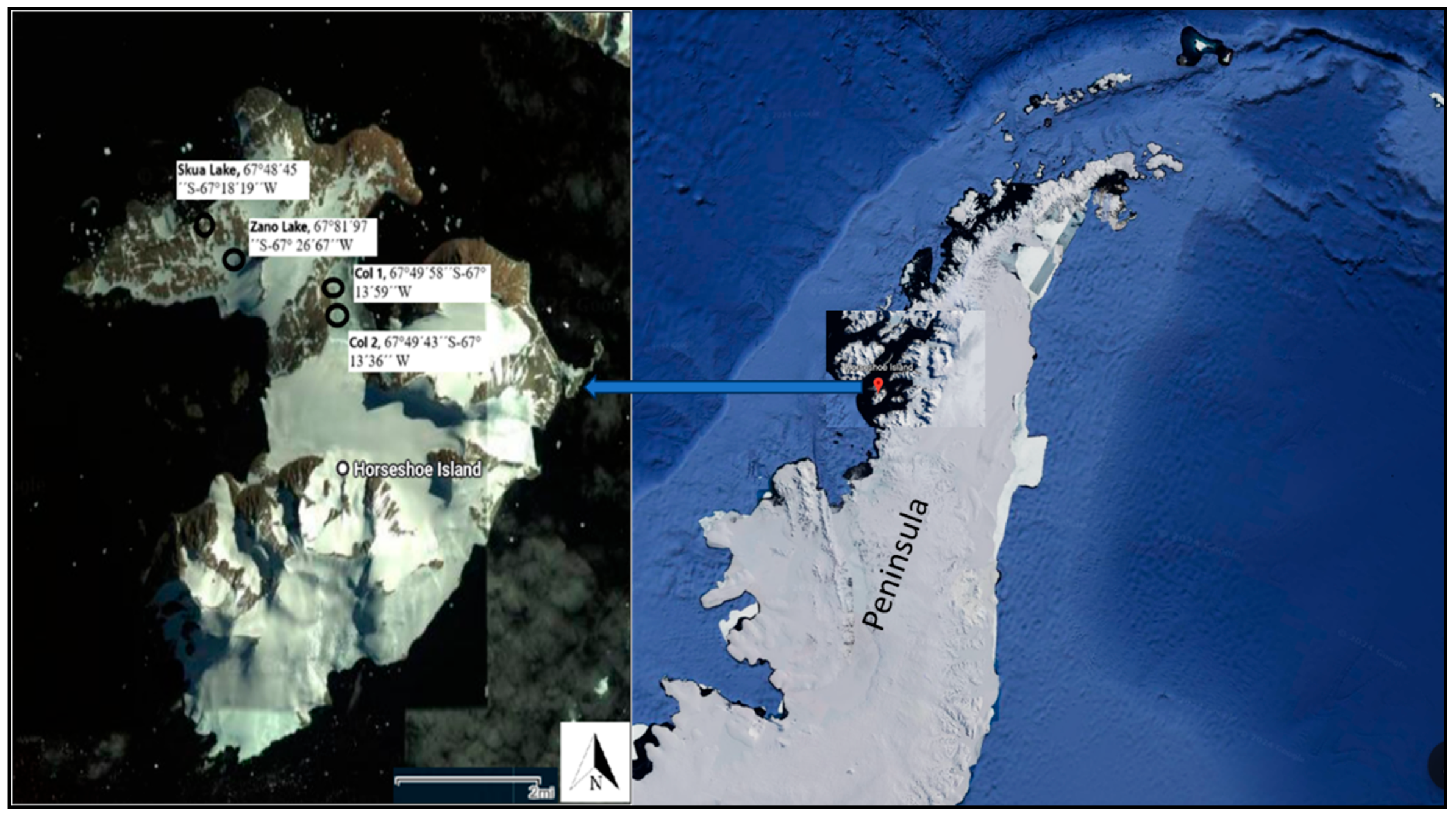
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Methods and Preservation
2.3. Amplification of Barcoding Regions, Processing, and Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wetzel, R.G. Limnology; W.B. Sounders Company: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U. The periodicity of phytoplankton in Lake Constance (Bodensee) in comparison to other deep lakes of central Europe. Hydrobiologia 1986, 138, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Rinaldi, S.; Huisman, J.; Weissing, F.J. Why plankton communities have no equilibrium: Solutions to the paradox. Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunmark, S. Zur soziologie des süsswasserplanktons. Eine methodisch ökologische studie. Folia Limnol. Skand 1945, 3, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard, G. Hidrobiological studies on some Danish ponds and lakes. Part II: The quotient hypothesis and some little known plankton organisms. K Dan Vidensk Selsk Biol. Skr. 1949, 7, 1–293. [Google Scholar]
- Lepistö, L.; Rosenström, U. The most typical phytoplankton taxa in four types of boreal lakes. Hydrobiologia 1998, 369/370, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Schleifer, K.H. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cells without cultivation. Microbiol. Rev. 1995, 59, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, I.; Saunders, J.; Pickup, R. Microbial Evolution, Diversity, and Ecology: A Decade of Ribosomal RNA Analysis of Uncultivated Microorganisms. Microb. Ecol. 1998, 35, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, P.; Rodríguez-Valera, F.; Pedrós-Alió, C.; Moreira, D. Unexpected diversity of small eukaryotes in deep-sea Antarctic plankton. Nature 2001, 409, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.; López-García, P. “Missing” protists: A molecular prospective. Biodivers. Conserv. 2007, 17, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.C. Flexibility and Specificity in Coral-Algal Symbiosis: Diversity, Ecology, and Biogeography of Symbiodinium. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2003, 34, 661–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Metagenomics for studying unculturable microorganisms: Cutting the Gordian knot. Genome Biol. 2005, 6, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, E.; Ünal, E. Environmental DNA (eDNA); Nobel Akademic Press: Ankara, Türkiye, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.S.; Clarke, A.; Cockell, C.S.; Convey, P.; Detrich, H.W.; Fraser, K.P.P.; Johnston, I.A.; Methe, B.A.; Murray, A.E.; Peck, L.S.; et al. Antarctic genomics. Comp. Funct. Genom. 2004, 5, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, L.S.; Clark, M.S.; Clarke, A.; Cockell, C.S.; Convey, P.; Detrich, H.W.; Fraser, K.P.P.; Johnston, I.A.; Methe, B.A.; Murray, A.E.; et al. Genomics: Applications to Antarctic ecosystems. Polar Biol. 2004, 28, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, T.B.; Krüger, K.; Fuchs, B.M.; Teeling, H.; Amann, R.I. Candidatus Prosiliicoccus vernus, a spring phytoplankton bloom associated member of the Flavobacteriaceae. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 42, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieb, A.; Bowers, R.M.; Oggerin, M.; Goudeau, D.; Lee, J.; Malmstrom, R.R.; Woyke, T.; Fuchs, B.M. A pipeline for targeted metagenomics of environmental bacteria. Microbiome 2020, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, K.; Morimoto, D.; Nishimura, Y.; Ogata, H.; Yoshida, T. In silico Prediction of Virus-Host Interactions for Marine Bacteroidetes with the Use of Metagenome-Assembled Genomes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobev, A.; Dupouy, M.; Carradec, Q.; Delmont, T.O.; Annamalé, A.; Wincker, P.; Pelletier, E. Transcriptome reconstruction and functional analysis of eukaryotic marine plankton communities via high-throughput metagenomics and metatranscriptomics. Genome Res. 2020, 30, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; He, X.; He, L.; Ao, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, A.; et al. Metagenome and analysis of metabolic potential of the microbial community in pit mud used for Chinese strong-flavor liquor production. Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.; Barry, K.; Daum, C.; Eloe-Fadrosh, E.; Roux, S.; Schmidt, K.; Tringe, S.G.; Valentin, K.U.; Varghese, N.; Salamov, A.; et al. Metagenome-assembled genomes of phytoplankton microbiomes from the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans. Microbiome 2022, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unrein, F.; Izaguirre, I.; Massana, R.; Balagué, V.; Gasol, J. Nanoplankton assemblages in maritime Antarctic lakes: Characterisation and molecular fingerprinting comparison. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2005, 40, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Ramachandran, A.; Khawasik, O.; Beisner, B.E.; Rautio, M.; Huot, Y.; Walsh, D.A. Microbial life under ice: Metagenome diversity and in situ activity of Verrucomicrobia in seasonally ice-covered Lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2568–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.M.; Uria, A.R.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; Milbredt, D.; van Pée, K.-H.; Piel, J.; Goss, R.J.M. An Unusual Flavin-Dependent Halogenase from the Metagenome of the Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei WA. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogin, M.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Huber, J.A.; Welch, D.M.; Huse, S.M.; Neal, P.R.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12115–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taib, N.; Mangot, J.-F.; Domaizon, I.; Bronner, G.; Debroas, D. Phylogenetic Affiliation of SSU rRNA Genes Generated by Massively Parallel Sequencing: New Insights into the Freshwater Protist Diversity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vick-Majors, T.J.; Priscu, J.C.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Modular community structure suggests metabolic plasticity during the transition to polar night in ice-covered Antarctic lakes. ISME J. 2013, 8, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logares, R.; Tesson, S.V.; Canbäck, B.; Pontarp, M.; Hedlund, K.; Rengefors, K. Contrasting prevalence of selection and drift in the community structuring of bacteria and microbial eukaryotes. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieu, B.; Lara, Y.; Pessi, I.S.; Wilmotte, A.; Tytgat, B.; Sweetlove, M.; Pinseel, E.; Verleyen, E.; Vyverman, W.; Van der Vijver, B.; et al. Climate Change and Antarctic Microbial Diversity’CCAMBIO; Final Report; British Antarctic Survey: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Influence of Environmental Drivers and Potential Interactions on the Distribution of Microbial Communities from Three Permanently Stratified Antarctic Lakes. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochera, C.; Camacho, A. Limnology and Aquatic Microbial Ecology of Byers Peninsula: A Main Freshwater Biodiversity Hotspot in Maritime Antarctica. Diversity 2019, 11, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, C. Geomorphology of Horseshoe Island, Marguerite Bay, Antarctica. J. Maps 2019, 16, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yirmibeşoğlu, S.; Oktar, Ö.; Özsoy, B. Review of Scientific Research Conducted in Horseshoe Island Where Potential Place for Turkish Antarctic Base. Int. J. Environ. Geoinformat. 2022, 9, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruesse, E.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. SINA: Accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 2016, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, D.; Siebert, C.; Polerecky, L.; Munwes, Y.Y.; Lott, C.; Häusler, S.; Bižić-Ionescu, M.; Quast, C.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O.; et al. Microbial and Chemical Characterization of Underwater Fresh Water Springs in the Dead Sea. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, A.; Raio, F.; Martins, T.P.; Ribeiro, H.; Sousa, A.G.G.; Séneca, J.; Baptista, M.S.; Lee, C.K.; Cary, S.C.; Ramos, V.; et al. Actinobacteria and Cyanobacteria Diversity in Terrestrial Antarctic Microenvironments Evaluated by Culture-Dependent and Independent Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijs, S.; Op De Beeck, M.; Beckers, B.; Truyens, S.; Stevens, V.; Van Hamme, J.D.; Weyens, N.; Vangronsveld, J. Comparative evaluation of four bacteria-specific primer pairs for 16S rRNA gene surveys. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, A.R.; Presting, G.G. Universal primers amplify a 23S rDNA plastid marker in eukaryotic algae and cyanobacteria. J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino, M.R.; Lara, E.; Fernández, L.D.; Balagué, V.; Singer, D.; Seppey, C.C.W.; Massana, R.; Izaguirre, I. Microbial eukaryote communities exhibit robust biogeographical patterns along a gradient of Patagonian and Antarctic lakes. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5249–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kezlya, E.; Tseplik, N.; Kulikovskiy, M. Genetic Markers for Metabarcoding of Freshwater Microalgae: Review. Biology 2023, 12, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, R.; Mäusbacher, R.; Müller, J. Holocene diatom flora and stratigraphy from sediment cores of two Antarctic lakes (King George Island). J. Paleolimnol. 1990, 3, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, S.A.; McKnight, D.M.; Stoermer, E.F.; Doran, P.T. Diatoms in sediments of perennially ice-covered Lake Hoare, and implications for interpreting lake history in the McMurdo Dry Valleys of Antarctica. J. Paleolimnol. 1996, 17, 403–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbe, K.; Verleyen, E.; Hodgson, D.; Vanhoutte, K.; Vyverman, W. Benthic diatom flora of freshwater and saline lakes in the Larsemann Hills and Rauer Islands, East Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2003, 15, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizotte, M.P. Phytoplankton and primary production. In Polar Lakes and Rivers: Limnology of Arctic and Antarctic Aquatic Ecosystems; Laybourn-Parry, J., Vincent, W.F., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 157–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bielewicz, S.; Bell, E.; Kong, W.; Friedberg, I.; Priscu, J.C.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Protist diversity in a permanently ice-covered Antarctic Lake during the polar night transition. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Ream, D.C.; Priscu, J.C.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Diversity and Expression of RubisCO Genes in a Perennially Ice-Covered Antarctic Lake during the Polar Night Transition. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4358–4366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, W.; Romancova, I.; Prášil, O.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. An integrated study of photochemical function and expression of a key photochemical gene (psbA) in photosynthetic communities of Lake Bonney (McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 89, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhi, J.M.; Teufel, A.G.; Kong, W.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Diversity and spatial distribution of autotrophic communities within and between ice-covered Antarctic lakes (McMurdo Dry Valleys). Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre, I.; Allende, L.; Schiaffino, M.R. Phytoplankton in Antarctic lakes: Biodiversity and main ecological features. Hydrobiologia 2020, 848, 177–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinocur, A.; Unrein, F. Typology of lentic water bodies at Potter Peninsula (King George Island, Antarctica) based on physical-chemical characteristics and phytoplankton communities. Polar Biol. 2000, 23, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwell, S.; Kalra, I.; Li, W.; McKnight, D.M.; Priscu, J.C.; Morgan-Kiss, R.M. Antarctic lake phytoplankton and bacteria from near-surface waters exhibit high sensitivity to climate-driven disturbance. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 6017–6032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, S.O.; Shtarkman, Y.M.; Koçer, Z.A.; Edgar, R.; Veerapaneni, R.; D’Elia, T. Ecology of Subglacial Lake Vostok (Antarctica), Based on Metagenomic/Metatranscriptomic Analyses of Accretion Ice. Biology 2013, 2, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.A.; Hodgson, D.A.; Bentley, M.J.; Verleyen, E.; Leng, M.J.; Roberts, S.J. Limnology of Two Antarctic Epishelf Lakes and their Potential to Record Periods of Ice Shelf Loss. J. Paleolimnol. 2006, 35, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J. The diversity, distribution and ecology of diatoms from Antarctic inland waters. Biodivers. Conserv. 1996, 5, 1433–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesada, A.; Vincent, W.F. Cyanobacteria in the cryosphere: Snow, ice and extreme cold. In Ecology of Cyanobacteria II: Their Diversity in Space and Time; Whitton, B.A., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 387–399. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, W.F. Evolutionary origins of Antarctic microbiota: Invasion, selection and endemism. Antarct. Sci. 2000, 12, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Lovejoy, C.; Vincent, W.F. Global distribution of cyanobacterial ecotypes in the cold biosphere. ISME J. 2009, 4, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verleyen, E.; Sabbe, K.; Hodgson, D.A.; Grubisic, S.; Taton, A.; Cousin, S.; Wilmotte, A.; De Wever, A.; Van der Gucht, K.; Vyverman, W. Structuring effects of climate-related environmental factors on Antarctic microbial mat communities. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessi, I.S.; Maalouf, P.D.C.; Laughinghouse, H.D.; Baurain, D.; Wilmotte, A. On the use of high-throughput sequencing for the study of cyanobacterial diversity in Antarctic aquatic mats. J. Phycol. 2016, 52, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalff, J. Limnology; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Velichko, N.; Smirnova, S.; Averina, S.; Pinevich, A. A survey of Antarctic cyanobacteria. Hydrobiologia 2021, 848, 2627–2652. [Google Scholar]



| Primer Set | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CYA359F/CYA781R | 5′-GGGGAATYTTCCGCAATGGG-3′ | 5′-GACTACWGGGGTATCTAATCCCWTT-3′ | [41] |
| 799F/1191R | 5′-AACMGGATTAGATACCCKG-3′ | 5′-ACGTCATCCCCACCTTCC-3′ | [42] |
| p23SrV_f1/p23SrV_r1 | 5′-GGACAGAAAGACCCTATGAA-3′ | 5′-TCAGCCTGTTATCCCTAGAG-3′ | [43] |
| Euk1f/Euk516r | 5′-CTGGTTGATCCTGCCAG-3′ | 5′-ACCAGACTTGCCCTCC-3′ | [44] |
| 18S_V9_F1/18S_V9_R | 5′-TTGTACACACCGCCCTCGC-3′ | 5′-CCTTCYGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3′ | [45] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakıoğlu, Ö.; Karadayı, M.; Topal, M.F.; Demir, N.; Karadayı, G.; Güllüce, M. Phytoplankton Composition During the Ice-Free Period of Lakes on Horseshoe Island (Antarctica) by Metagenomic Analysis. Water 2025, 17, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070975
Fakıoğlu Ö, Karadayı M, Topal MF, Demir N, Karadayı G, Güllüce M. Phytoplankton Composition During the Ice-Free Period of Lakes on Horseshoe Island (Antarctica) by Metagenomic Analysis. Water. 2025; 17(7):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070975
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakıoğlu, Özden, Mehmet Karadayı, Muhammet Furkan Topal, Nilsun Demir, Gökçe Karadayı, and Medine Güllüce. 2025. "Phytoplankton Composition During the Ice-Free Period of Lakes on Horseshoe Island (Antarctica) by Metagenomic Analysis" Water 17, no. 7: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070975
APA StyleFakıoğlu, Ö., Karadayı, M., Topal, M. F., Demir, N., Karadayı, G., & Güllüce, M. (2025). Phytoplankton Composition During the Ice-Free Period of Lakes on Horseshoe Island (Antarctica) by Metagenomic Analysis. Water, 17(7), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070975






