Application of Agricultural Waste-Based Activated Carbon for Antibiotic Removal in Wastewaters: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characteristics, Sources, and Pathways Exposure, Detection, and Health Risk of Bisphenol A
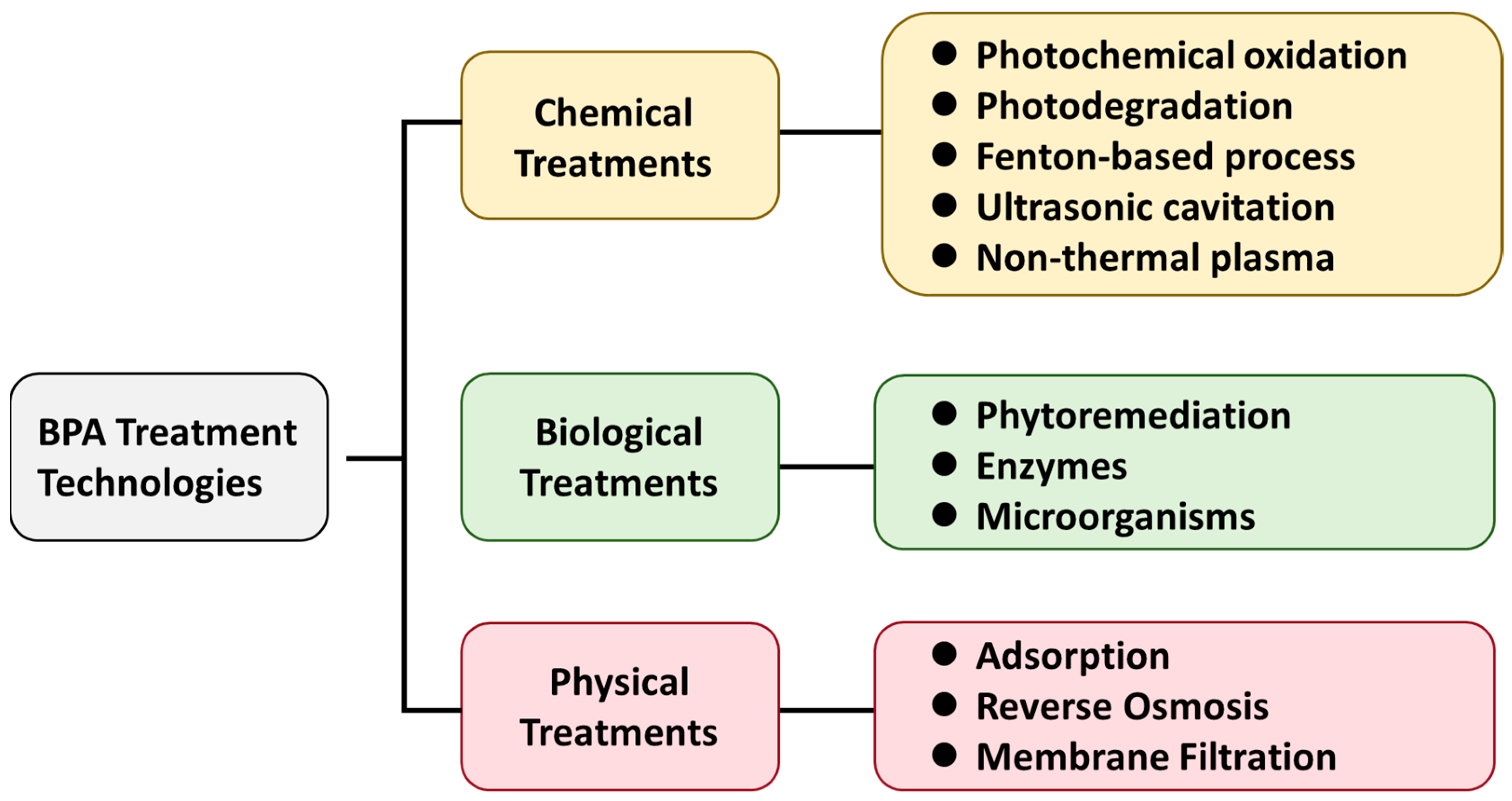
3. BPA Removal from Aquatic Environments
3.1. Chemical Treatment
3.2. Biological Treatment
3.3. Physical Treatment
4. Adsorption
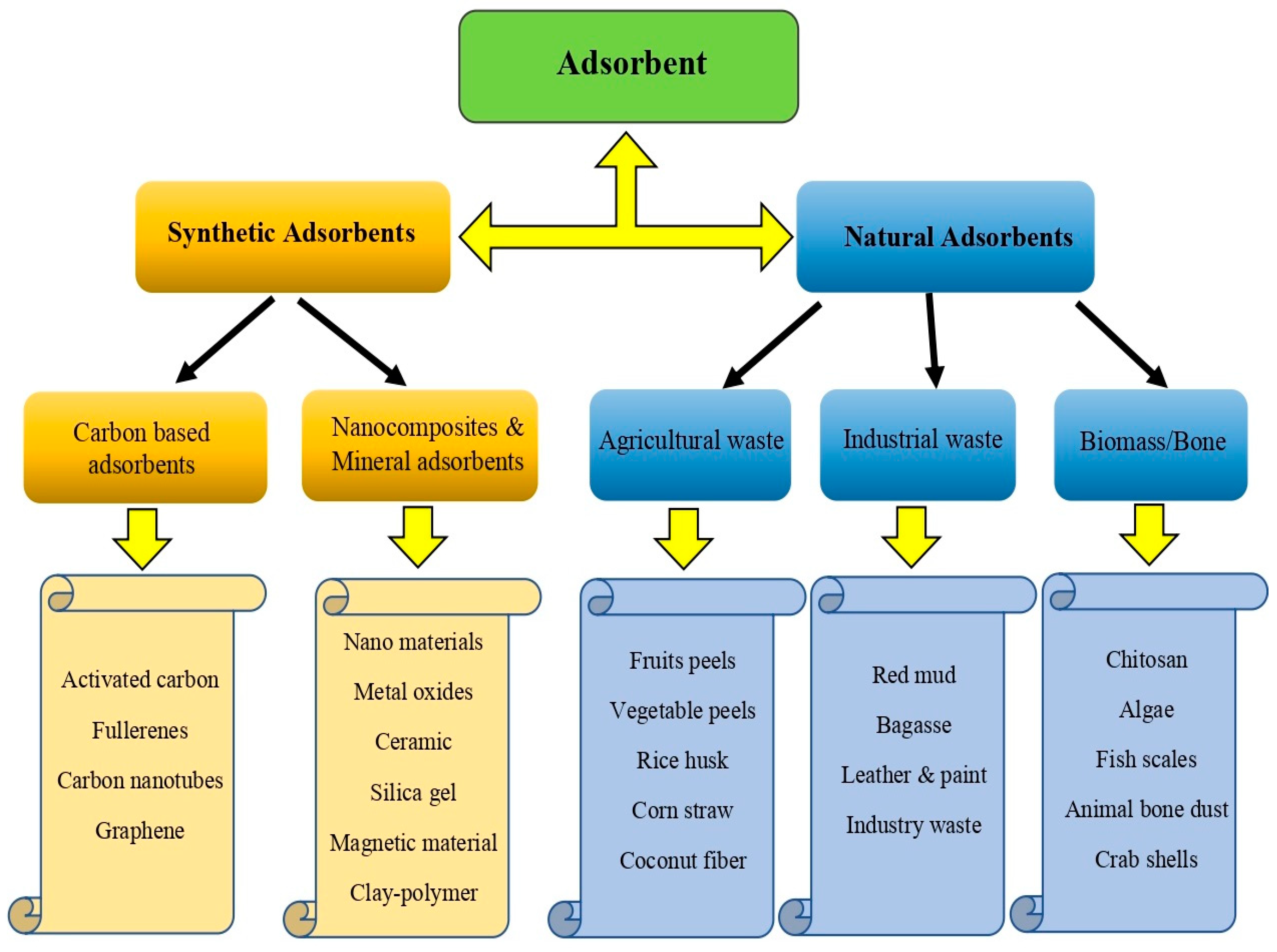
5. Removal of BPA from Aquatic Environments by Adsorbents
5.1. Natural Adsorbents
| Adsorbent | Surface Area (m2/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Peat | 1.02 | [169] |
| Sawdust | 0.72 | |
| Bagasse | 1.67 | |
| Rice husk | 0.24 |
5.2. Agricultural Waste Adsorbents
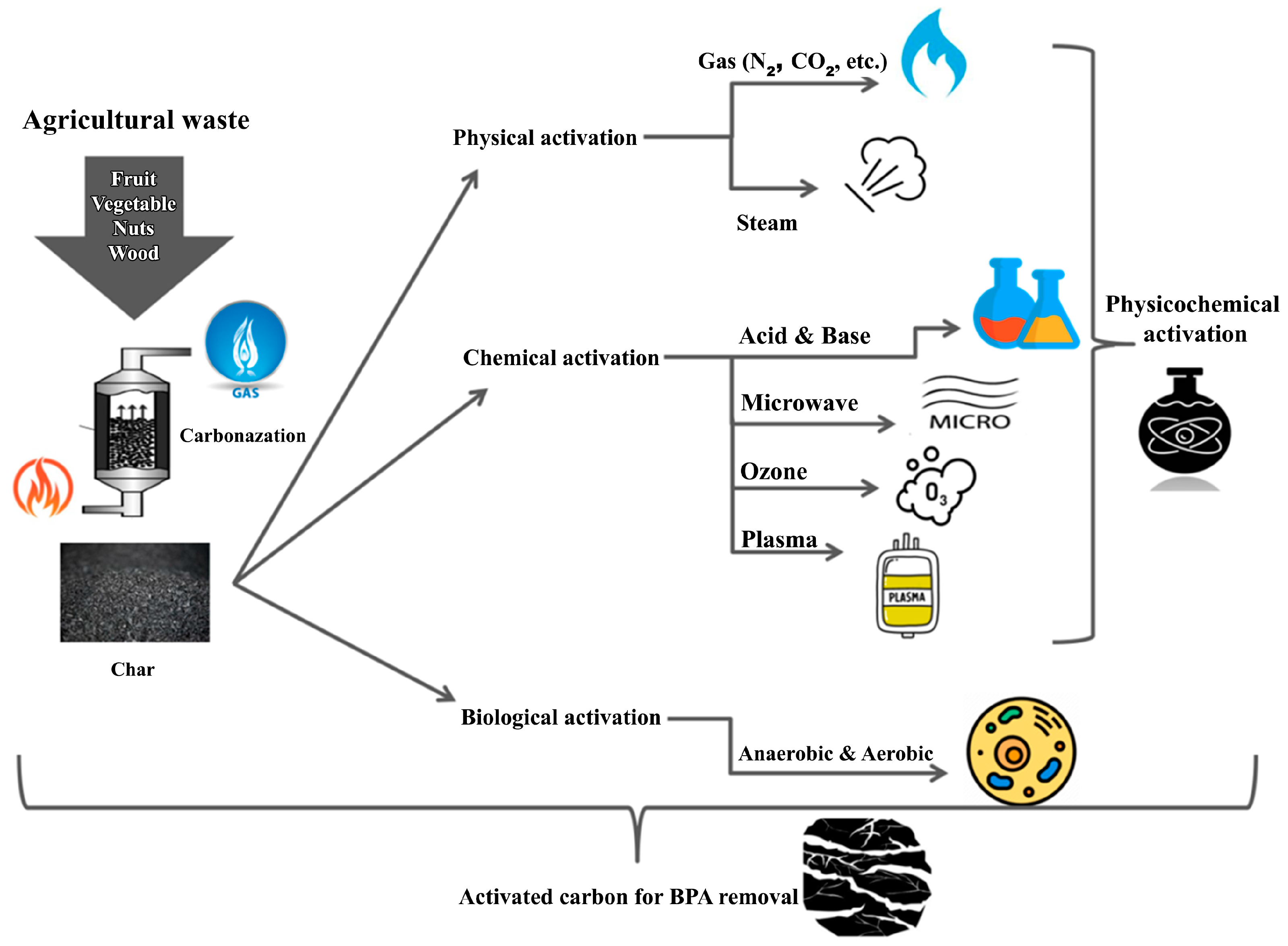
5.3. Activated Carbon (AC)
5.3.1. Physical Activation
5.3.2. Chemical Activation
Acid Activation
Alkaline Activation
Impregnation
Microwave Activation
Ozone Activation
Plasma Activation
5.3.3. Biological Activation
5.4. Integrated Technologies
6. Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mpatani, F.M.; Aryee, A.A.; Kani, A.N.; Guo, Q.; Dovi, E.; Qu, L.; Li, Z.; Han, R. Uptake of micropollutant-bisphenol A, methylene blue and neutral red onto a novel bagasse-β-cyclodextrin polymer by adsorption process. Chemosphere 2020, 259, 127439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, W.; Leng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Ding, H.; Zhou, J.; Cui, L. Review and Research Prospects on Additive Manufacturing Technology for Agricultural Manufacturing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, U.; Mostafa, M.G. Leather industrial effluent and environmental concerns: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, A.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, S.; Han, S.; Lin, Y. Acute and chronic toxicity of binary mixtures of bisphenol A and heavy metals. Toxics 2022, 10, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osae, R.; Essilfie, G.; Alolga, R.N.; Akaba, S.; Song, X.; Owusu-Ansah, P.; Zhou, C. Application of non-thermal pretreatment techniques on agricultural products prior to drying: A review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 2585–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Aguilar, A.; de León-Martínez, L.D.; Forgionny, A.; Acelas Soto, N.Y.; Mendoza, S.R.; Zárate-Guzmán, A.I. A systematic review on the current situation of emerging pollutants in Mexico: A perspective on policies, regulation, detection, and elimination in water and wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarink, D.; Franke, A.A.; White, K.K.; Wu, A.H.; Cheng, I.; Quon, B.; Le Marchand, L.; Wilkens, L.R.; Yu, H.; Merritt, M.A. BPA, parabens, and phthalates in relation to endometrial cancer risk: A case–control study nested in the multiethnic cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2021, 129, 057702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarny, K.; Szczukocki, D.; Krawczyk, B.; Zieliński, M.; Miękoś, E.; Gadzała-Kopciuch, R. The impact of estrogens on aquatic organisms and methods for their determination. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 909–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R. Application of electronic nose as a non-invasive technique for odor fingerprinting and detection of bacterial foodborne pathogens: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Lu, G.; Jiang, R.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y. Occurrence, toxicity and ecological risk of Bisphenol A analogues in aquatic environment—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Moreno, J.; Mora, A.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Mahlknecht, J. Groundwater contamination pathways of phthalates and bisphenol A: Origin, characteristics, transport, and fate—A review. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela, C.L.S.; Bassin, J.P.; Peixoto, R.S. Water contamination by endocrine disruptors: Impacts, microbiological aspects and trends for environmental protection. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharnikova, E.N.; Tchaikovskaya, O.N.; Solomonov, V.I.; Makarova, A.S. UV and pulsed electron beam radiation for effective bisphenol A degradation. Chemosphere 2024, 356, 141802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Liu, G.; Liu, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Du, K.; Jia, R.; Liu, Y.; Guo, J. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube catalytic membrane with peroxymonosulfate activation for the degradation of metronidazole and bisphenol A: Performance and mechanism comparison. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Tiwary, C.S.; Gupta, A.K. Visible light driven Z-scheme α-MnO2 (1D)/Bi7O9I3 (2D) heterojunction photocatalyst for efficient degradation of bisphenol A in water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ke, J.; Hu, C.; Lin, T.; Liang, J. Targeted degradation of Bisphenol A with peroxymonosulfate activated by nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on molecularly imprinted polymers. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Han, X.; Wang, R.; Zhu, K.; Han, R. Adsorption and catalytic degradation of bisphenol A and p-chlorophenol by magnetic carbon nanotubes. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, S.I.; Xi, Y.; Frost, R.L.; Ayoko, G.A. Environmental applications of inorganic–organic clays for recalcitrant organic pollutants removal: Bisphenol A. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 470, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmad, A.; Zango, Z.U.; Noh, T.U.; Usman, F.; Aldaghri, O.A.; Ibnaouf, K.H.; Shaharun, M.S. Response surface methodology and artificial neural network for prediction and validation of bisphenol a adsorption onto zeolite imidazole framework. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 21, 100925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoudinejad, M.; Rasoulzadeh, H.; Ghaderpoori, M. Magnetic chitosan nanocomposite: Fabrication, properties, and optimization for adsorptive removal of crystal violet from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Ding, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, D.; Dong, Z. Fabrication of modified-N-doped porous biochar and its enhanced adsorption of bisphenol-A: Critical contribution to π–π interactions by nitrogen doping. Surf. Interfaces 2024, 45, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altayan, M.M.; Tzoupanos, N.; Barjenbruch, M. Polymer based on beta-cyclodextrin for the removal of bisphenol A, methylene blue and lead(II): Preparation, characterization, and investigation of adsorption capacity. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 390, 122822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, Y.; Qiu, X.; Li, C.; Zhao, Y. Competitive adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and bisphenol A on magnetic biochar: Mechanism and site energy distribution. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhym, A.B.; Seilkhanova, G.A.; Mastai, Y. Physicochemical evaluation of the effect of natural zeolite modification with didodecyldimethylammonium bromide on the adsorption of Bisphenol-A and Propranolol Hydrochloride. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 318, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Ding, J.; Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Ding, L. Cellulose-incorporated imprinted materials with amphiphilic crosslinking structure for selective adsorption of bisphenol A. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 187, 115308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Boateng, L.K.; Flora, J.R.V.; Park, Y.-G.; Son, A.; Badawy, M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinyl estradiol by combined coagulation and adsorption using carbon nanomaterials and powdered activated carbon. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 107, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Gao, L.; Zhu, G.; Jiang, Y.; Rui, Y.; Zhang, P. Harnessing synergy: Integrating agricultural waste and nanomaterials for enhanced sustainability. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 123023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Ansar, R.; Jahan, Z.; Javaid, F.; Ahmad, R.; Anjum, H.; Ibrahim, M.; Bokhari, A. Thermochemical conversion of agricultural waste to hydrogen, methane, and biofuels: A review. Fuel 2023, 351, 128947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ding, F.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances in gelatine and chitosan complex material for practical food preservation application. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 6279–6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wu, S.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; He, J.; Siddique, K.H.M. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer derived from agricultural waste resources on soil properties and winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield in semi-humid drought-prone regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Chen, L.; Mustapha, A.T.; Yu, X.; Zhou, C.; Okonkwo, C.E. Natural and low-caloric rebaudioside A as a substitute for dietary sugars: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 615–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metyouy, K.; Benkirane, L.; Sánchez, M.E.; Cara-Jiménez, J.; Plakas, K.V.; Chafik, T. Valorization of agricultural olive waste as an activated carbon adsorbent for the remediation of water sources contaminated with pharmaceuticals. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 6, 100110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, O.A.; Hathout, A.S.; Abdel-Mobdy, Y.E.; Rashed, M.M.; Abdel Rahim, E.A.; Fouzy, A.S.M. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from agricultural wastes and their ability to remove chlorpyrifos from water. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.M.; Xu, Y.; Zareef, M.; Li, H.; Rong, Y.; Chen, Q. Recent advances of nanomaterial-based optical sensor for the detection of benzimidazole fungicides in food: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2851–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preethi, B.; Karmegam, N.; Manikandan, S.; Vickram, S.; Subbaiya, R.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Gomadurai, C.; Govarthanan, M. Nanotechnology-powered innovations for agricultural and food waste valorization: A critical appraisal in the context of circular economy implementation in developing nations. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 184, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainth, S.; Sharma, P.; Pandey, O.P. Green sorbents from agricultural wastes: A review of sustainable adsorption materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhair, S.; Zouari, N.; Ibrahim Ahmad Ibrahim, M.; Al-Ghouti, M.A. Efficacy of adsorption processes employing green nanoparticles for bisphenol A decontamination in water: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Anastopoulos, I. Adsorptive removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solution: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 885–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wang, J. Removal of bisphenol a from wastewater by adsorption and membrane separation: Performances and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahari, M.h.; Hadoudi, N.; Zaki, N.; Charki, A.; El Ouarghi, H.; Bayoussef, A.; Mansori, M.; El Barkany, S.; Salhi, A.; Amhamdi, H. Adsorption of bisphenol A (BPA) and pentachlorophenol (PCP) using a bentonite-chitosan composite: A study on removal efficiency. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 165, 112468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhlaei, R.; Babadi, A.A.; Sun, C.; Ariffin, N.M.; Khatib, A.; Selamat, J.; Xiaobo, Z. Application, challenges and future prospects of recent nondestructive techniques based on the electromagnetic spectrum in food quality and safety. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpatani, F.M.; Han, R.; Aryee, A.A.; Kani, A.N.; Li, Z.; Qu, L. Adsorption performance of modified agricultural waste materials for removal of emerging micro-contaminant bisphenol A: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.J.; Li, G.; Nazir, M.M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Siddique, K.H.; Iqbal, B.; Du, D. Harnessing soil carbon sequestration to address climate change challenges in agriculture. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 237, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.A.; Metz, L.; Yong, V.W. endocrine disrupting chemicals and immune responses: A focus on bisphenol-A and its potential mechanisms. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 53, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, R.O.; Yuan, S.; Hong, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, H. Irrigation, a productive tool for food security—A review. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2016, 66, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Liao, Q.; Xia, A.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Reungsang, A.; Liu, Z. Hydrothermal hydrolysis pretreatment of microalgae slurries in a continuous reactor under subcritical conditions for large-scale application. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenichel, P.; Chevalier, N.; Brucker-Davis, F. Bisphenol A: An endocrine and metabolic disruptor. Ann. Endocrinol. 2013, 74, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldini, M.; Marino, T.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Antioxidant Properties of Phenolic Compounds: H-Atom versus Electron Transfer Mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igor Otavio, M.; Cristine Vanz, B.; Maria Izabela, F.; Hector Alonzo Gomez, G.; Chung-Yen Oliver, C.; Giuseppina Pace Pereira, L. Phenolic Compounds: Functional Properties, Impact of Processing and Bioavailability. In Phenolic Compounds; Marcos, S.-H., Mariana, P.-T., Maria del Rosario, G.-M., Eds.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; p. Ch. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili Sadrabad, E.; Hashemi, S.A.; Nadjarzadeh, A.; Askari, E.; Akrami Mohajeri, F.; Ramroudi, F. Bisphenol A release from food and beverage containers—A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 3718–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: Food Exposure and Impact on Human Health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Hasan, H.; Muhamad, M.H.; Budi Kurniawan, S.; Buhari, J.; Husain Abuzeyad, O. Managing Bisphenol A Contamination: Advances in Removal Technologies and Future Prospects. Water 2023, 15, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnam, S.S.; Ghosh, R.C.; Mondal, S.; Mondal, M. Evaluation of subacute bisphenol—A toxicity on male reproductive system. Vet World 2015, 8, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutaki, D.; Paltoglou, G.; Vourdoumpa, A.; Charmandari, E. The Impact of Bisphenol A on Thyroid Function in Neonates and Children: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Nutrients 2021, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teppala, S.; Madhavan, S.; Shankar, A. Bisphenol A and Metabolic Syndrome: Results from NHANES. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 598180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Sun, L.; Du, Q. Securing Image Transmissions via Fountain Coding and Adaptive Resource Allocation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 83rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Nanjing, China, 15–18 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bernier, M.R.; Vandenberg, L.N. Handling of thermal paper: Implications for dermal exposure to bisphenol A and its alternatives. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolini, E.; Ferri, E.; Pitasi, A.L.; Montoya, A.; Di Giovanni, M.; Errani, E.; Girotti, S. Bisphenol A determination in baby bottles by chemiluminescence enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, lateral flow immunoassay and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Analyst 2014, 139, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ying, G.G.; Su, H.C.; Yang, X.B.; Wang, L. Simultaneous determination and assessment of 4-nonylphenol, bisphenol A and triclosan in tap water, bottled water and baby bottles. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, M. Novel polyphenol/graphene nanocomposite for solid-phase microextraction of bisphenol A and bisphenol B leached from plastic containers. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 321, 112599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Hu, Y.; Ali Buttar, N.; Mahmood, A. X-ray computed tomography for quality inspection of agricultural products: A review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerjian, L.; Alawadhi, N.; Nazer, K. Detection of bisphenol A in thermal paper receipts and assessment of human exposure: A case study from Sharjah, United Arab Emirates. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyvas, H.; Andra, S.S.; Charisiadis, P.; Karaolis, C.; Makris, K.C. Influence of household cleaning practices on the magnitude and variability of urinary monochlorinated bisphenol A. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.S.; Charisiadis, P.; Arora, M.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V.; Makris, K.C. Biomonitoring of human exposures to chlorinated derivatives and structural analogs of bisphenol A. Environ. Int. 2015, 85, 352–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.-y.; Aizawa, T.; Ookubo, S. Products of Aqueous Chlorination of Bisphenol A and Their Estrogenic Activity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 1980–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, A.; Lacroix, M.; Olea-Serrano, F.; Laios, I.; Leclercq, G.; Olea, N. Estrogenic effect of a series of bisphenol analogues on gene and protein expression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 82, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, H.; Ma, J.; Sayama, K.; Terao, Y.; Zhu, B.T.; Shimoi, K. In vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of chlorinated derivatives of bisphenol A. Toxicology 2005, 207, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, J.-i.; Saito, K.; Goto, J.; Dakeyama, F.; Matsuo, M.; Nishihara, T. New Screening Methods for Chemicals with Hormonal Activities Using Interaction of Nuclear Hormone Receptor with Coactivator. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1999, 154, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hou, J. A critical review of presence, removal and potential impacts of endocrine disruptors bisphenol A. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 254, 109275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahigian, J.M.; Zuo, Y. Occurrence, endocrine-related bioeffects and fate of bisphenol A chemical degradation intermediates and impurities: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 207, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Prakash, J.; Swati; Singh, S.P. Effect of Bisphenol A on human health and its degradation by microorganisms: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro-González, N.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; López-Mahía, P.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Trends in analytical methodologies for the determination of alkylphenols and bisphenol A in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 962, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. Recent trends and applications of cellulose nanocrystals in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.-P.; Liu, Z.-H.; Yin, H.; Dang, Z.; Wu, P.-X.; Zhu, N.-W.; Lin, Z. Bisphenol A concentrations in human urine, human intakes across six continents, and annual trends of average intakes in adult and child populations worldwide: A thorough literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Duan, W.; Shi, Y.; Chang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S. Sensitive detection of bisphenol A in drinking water and river water using an upconversion nanoparticles-based fluorescence immunoassay in combination with magnetic separation. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5313–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, P.; Zou, M.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Z.; et al. Measurement of trace bisphenol A in drinking water with combination of immunochromatographic detection technology and SERS method. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 267, 120519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.P. Determination of bisphenol A in barreled drinking water by a SPE-LC-MS method. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard Subst. Environ. Eng. 2020, 55, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Kang, F.S.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R.S. High-Performance enrichment and sensitive analysis of bisphenol and its analogues in water and milk using a novel Ni-Based cationic Metal-Organic framework. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodur, S.; Erarpat, S.; Dalgıç Bozyiğit, G.; Selali Chormey, D.; Öz, E.; Özdoğan, N.; Bakırdere, S. A sensitive determination method for trace bisphenol A in bottled water and wastewater samples: Binary solvent liquid phase microextraction-quadrupole isotope dilution-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhua, S.; Zhen, L.; Feng, D. Determination of bisphenol A in effluent water of analogue MBR wastewater treatment system using high-performance liquid chromatography. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2011, 15, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Miao, M.; Herrinton, L.J.; Wu, C.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Z.; Li, D.K. Bisphenol A levels in blood and urine in a Chinese population and the personal factors affecting the levels. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Wong, L.Y.; Reidy, J.A.; Needham, L.L. Exposure of the U.S. population to bisphenol A and 4-tertiary-octylphenol: 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, G.D.; Yang, C.Z.; Stoner, M.A. Estrogenic chemicals often leach from BPA-free plastic products that are replacements for BPA-containing polycarbonate products. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catenza, C.J.; Farooq, A.; Shubear, N.S.; Donkor, K.K. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health implications of bisphenol analogues. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshamy, A.I.; Mohamed, T.A.; Essa, A.F.; Abd-El Gawad, A.M.; Alqahtani, A.S.; Shahat, A.A.; Yoneyama, T.; Farrag, A.R.H.; Noji, M.; El-Seedi, H.R. Recent advances in Kaempferia phytochemistry and biological activity: A comprehensive review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, N.N.; Lau, H.L.; Suhaimi, N.A.A.; Shahri, N.N.M.; Verinda, S.B.; Nur, M.; Lim, J.-W.; Usman, A. Recent Advances in Advanced Oxidation Processes for Degrading Pharmaceuticals in Wastewater—A Review. Catalysts 2024, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ren, W.; Ma, T.; Ren, N.; Wang, S.; Duan, X. Transformative Removal of Aqueous Micropollutants into Polymeric Products by Advanced Oxidation Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 4844–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, K.O.; Brandão, F.; átia Mendes, C.; Carvalho, M.G.V.S.; Mazierski, P.; Zaleska-Medynska, A.; Gomes, J.; Martins, R.C.; Domingues, E. Olive mill waste bio-based catalyst application in advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment. Catal. Today 2024, 432, 114618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusvuran, E.; Yildirim, D. Degradation of bisphenol A by ozonation and determination of degradation intermediates by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subagio, D.P.; Srinivasan, M.; Lim, M.; Lim, T.-T. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol-A by nitrogen-doped TiO2 hollow sphere in a vis-LED photoreactor. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2010, 95, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandarkhaeva, M.; Batoeva, A.; Sizykh, M.; Aseev, D.; Garkusheva, N. Photo-Fenton-like degradation of bisphenol A by persulfate and solar irradiation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, S.A.; Farzadkia, M.; Esrafili, A.; Kalantari, R.R.; Jafari, A.J.; Kermani, M.; Gholami, M. Bisphenol A removal from aqueous solutions using novel UV/persulfate/H(2)O(2)/Cu system: Optimization and modelling with central composite design and response surface methodology. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2016, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutseyekwa, M.E.; Doğan, Ş.; Pirgalıoğlu, S. Ozonation for the removal of bisphenol A. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2764–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khataee, A.R.; Mirzajani, O. UV/peroxydisulfate oxidation of C. I. Basic Blue 3: Modeling of key factors by artificial neural network. Desalination 2010, 251, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.J.; Wang, Y.J.; Chu, J.; Kawasaki, S.; Tang, C.S.; Cheng, L.; Du, Y.J.; Shashank, B.S.; Singh, D.N.; Han, X.L. Bio-mediated soil improvement: An introspection into processes, materials, characterization and applications. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 68–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, V.; Bingham, J.-P.; Kan, E. Heterogeneous Fenton degradation of bisphenol A by carbon nanotube-supported Fe3O4. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 133, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.M.; Raman, A.A.A.; Asghar, A. A review on approaches for addressing the limitations of Fenton oxidation for recalcitrant wastewater treatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 126, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diya’uddeen, B.H.; AR, A.A.; Daud, W.W. On the limitation of Fenton oxidation operational parameters: A review. Int. J. Chem. React. Eng. 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the biological and chemical treatment technologies for emerging contaminant removal from wastewater: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balest, L.; Lopez, A.; Mascolo, G.; Di Iaconi, C. Removal of endocrine disrupter compounds from municipal wastewater using an aerobic granular biomass reactor. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 41, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwaw, E.; Tchabo, W.; Ma, Y.; Apaliya, M.T.; Sackey, A.S.; Mintah, B.K.; Farooq, M.; Ma, S. Effect of storage on quality attributes of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice subjected to combined pulsed light and ultrasonic pasteurization treatment. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuhiro, K.; Ike, M.; Furukawa, K.; Fujita, M.; Jin, C. Chemical and Biological Influence of Hazardous Substances and Obstacle Organisms to Aquatic Environment and Their Control. Biodegradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) by River Water Microcosms. J. Jpn. Soc. Water Environ. 1996, 19, 878–884. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, G.-G.; Kookana, R.S.; Dillon, P. Sorption and degradation of selected five endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquifer material. Water Res. 2003, 37, 3785–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, P.B.; Chou, C.-S.; Gentempo, J.J. Degradation of bisphenol A in natural waters. Chemosphere 1987, 16, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Kitamura, H.; Miyata, N.; Iwahori, K. Biodegradation of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Aerobic and Anaerobic Sludges. Nihon Mizushori Seibutsu Gakkaishi 2005, 41, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, W.; Luo, M.; Wang, B.; Qu, W.; He, R.; Owusu, J.; Li, Y. Effects and mechanism of ultrasound pretreatment on rapeseed protein enzymolysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, J.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Otu, P.N.Y. Heat and/or ultrasound pretreatments motivated enzymolysis of corn gluten meal: Hydrolysis kinetics and protein structure. LWT 2017, 77, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, F.; Cui, F.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, J. Improved postharvest quality and respiratory activity of straw mushroom (Volvariella volvacea) with ultrasound treatment and controlled relative humidity. Sci. Hortic. 2017, 225, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyamud, B.; Thiravetyan, P.; Gadd, G.M.; Panyapinyopol, B.; Inthorn, D. Bisphenol A removal from a plastic industry wastewater by Dracaena sanderiana endophytic bacteria and Bacillus cereus NI. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Khan, Q.M.; Sessitsch, A. Endophytic bacteria: Prospects and applications for the phytoremediation of organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yagoub, A.E.; Ma, H.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X. Effects of tri-frequency ultrasound-ethanol pretreatment combined with infrared convection drying on the quality properties and drying characteristics of scallion stalk. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2809–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Apaliya, M.T.; Mahunu, G.K.; Chen, L.; Li, W. Control of ochratoxin A-producing fungi in grape berry by microbial antagonists: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Khir, R.; Pan, Z.; Wood, D.; Mahoney, N.E.; El-Mashad, H.; Wu, B.; Ma, H.; Liu, X. Simultaneous decontamination and drying of rough rice using combined pulsed light and holding treatment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2874–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdualrahman, M.A.Y.; Ma, H.; Zhou, C.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Hu, J.; Yang, X. Thermal and single frequency counter-current ultrasound pretreatments of sodium caseinate: Enzymolysis kinetics and thermodynamics, amino acids composition, molecular weight distribution and antioxidant peptides. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4861–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ike, M.; Chen, M.Y.; Danzl, E.; Sei, K.; Fujita, M. Biodegradation of a variety of bisphenols under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-T.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, Z.-W.; Chen, Z.-L.; Ma, H.; Yan, J.-K. Effects of ultrasound modification at different frequency modes on physicochemical, structural, functional, and biological properties of citrus pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayek, N.M.; Xiao, J.; Farag, M.A. A multifunctional study of naturally occurring pyrazines in biological systems; formation mechanisms, metabolism, food applications and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 5322–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H.; Li, S.; Yagoub, A.E.A.; Abdualrahman, M.A. Proteomics analyses and morphological structure of Bacillus subtilis inactivated by pulsed magnetic field. Food Biophys. 2016, 11, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press-Kristensen, K.; Lindblom, E.; Schmidt, J.E.; Henze, M. Examining the biodegradation of endocrine disrupting bisphenol A and nonylphenol in WWTPs. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Feng, M.; Chitrakar, B.; Cheng, J.; Wei, B.; Wang, B.; Zhou, C.; Ma, H. Multi-frequency power thermosonication treatments of clear strawberry juice: Impact on color, bioactive compounds, flavor volatiles, microbial and polyphenol oxidase inactivation. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zhen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Cao, J.; Liu, Y. Ultra-High Hydrostatic Pressure Pretreatment on White Que Zui Tea: Chemical Constituents, Antioxidant, Cytoprotective, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Foods 2023, 12, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Yi, J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Du, M. Effects of ethanol pretreatment on osteogenic activity and off-flavors in blue mussel (Mytilus edulis L.) enzymatic hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2023, 167, 112701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwaw, E.; Osae, R.; Apaliya, M.T.; Alolga, R.N.; Sackey, A.S.; Yongkun, M.; Tchabo, W.; Obikyembi, V. Effect of optimized pulsed light treatment conditions on microbiological safety, phytochemical and sensory properties of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Bułkowska, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Bernat, K.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Removal of bisphenol A (BPA) from biologically treated wastewater by microfiltration and nanofiltration. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shao, J.; Duan, Y.; Geng, F.; Jin, W.; Zhang, H.; Peng, D.; Deng, Q. Insights into digestibility, biological activity, and peptide profiling of flaxseed protein isolates treated by ultrasound coupled with alkali cycling. Food Res. Int. 2024, 190, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mahoney, N.E.; Pan, Z.; Khir, R.; Wu, B.; Ma, H.; Zhao, L. Effectiveness of pulsed light treatment for degradation and detoxification of aflatoxin B1 and B2 in rough rice and rice bran. Food Control 2016, 59, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ding, X.; Dai, C.; Ma, H. Changes in the structure and dissociation of soybean protein isolate induced by ultrasound-assisted acid pretreatment. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharan, P.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Kaushal, I. Multifunctional CNT supported metal doped MnO2 composite for adsorptive removal of anionic dye and thiourea sensing. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 221, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovani, S.; Santos, J.J.; Guilhen, S.N.; Corio, P.; Fungaro, D.A. Fast, efficient and clean adsorption of bisphenol-A using renewable mesoporous silica nanoparticles from sugarcane waste ash. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 27706–27712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y. Mechanism of bisphenol A removal by a submerged membrane bioreactor in the treatment of synthetic municipal sewage: Staged analyses. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 12364–12374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, C.G.; Moreira, M.H.; Silva, V.; Santos, H.G.; Bila, D.M.; Fonseca, F.V. Treatment of Bisphenol A (BPA) in water using UV/H(2)O(2) and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes: Assessment of estrogenic activity and membrane adsorption. Water Sci. Technol. 2019, 80, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wei, J. Treatment of phenolic wastewater by combined UF and NF/RO processes. Desalination 2015, 355, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Chatzisymeon, E.; Chidichimo, F.; Beneduci, A.; Chidichimo, G. Removal of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals from Water: Adsorption of Bisphenol-A by Biobased Hydrophobic Functionalized Cellulose. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K. Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I. New generation adsorbents for water treatment. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5073–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P.W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; et al. The adverse health effects of bisphenol A and related toxicity mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezvani-Ghalhari, M.; Nabizadeh, R.; Sani, M.A.; Sanaei, D.; Bashardoust, P.; McClements, D.J.; Nasseri, S.; Mahvi, A.H. Adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions using cellulose-based adsorbents prepared by sol-gel method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, F.; Khoshmardan, M.E.; Sanaei, D.; Ghalhari, M.R.; Sharifan, H.; Inglezakis, V.J.; Arcibar-Orozco, J.A.; Shaikh, W.A.; Khan, E.; Biswas, J.K. Adsorptive removal of anthracene from water by biochar derived amphiphilic carbon dots decorated with chitosan. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghalhari, M.R.; Sanaei, D.; Nabizadeh, R.; Mahvi, A.H. Cellulose-based hydrogel beads derived from wastepapers: Application for organic dye adsorption. Cellulose 2023, 30, 9669–9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Qu, L.; Han, R. Fabrication of zirconium (IV)-loaded chitosan/Fe3O4/graphene oxide for efficient removal of alizarin red from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 248, 116792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Gao, D.-W.; Pan, H.; Hao, L.; Wang, P. Equilibrium and kinetics of aniline adsorption onto crosslinked sawdust-cyclodextrin polymers. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 40071–40077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna; Bagotia, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Kumar, S. A review on modified sugarcane bagasse biosorbent for removal of dyes. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Wang, L.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zou, J.-J. Rational design, synthesis, adsorption principles and applications of metal oxide adsorbents: A review. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 4790–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; You, S.-J.; Chao, H.-P. Fast and efficient adsorption of methylene green 5 on activated carbon prepared from new chemical activation method. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 188, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Bian, L.; Jiang, F. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of CTAB-modified SiO(2) for removal of bisphenol A. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; He, F.; Fu, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Wang, W. Long non-coding RNA HOXA-AS2 promotes the migration, invasion and stemness of bladder cancer via regulating miR-125b/Smad2 axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 375, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nairi, B.M.; Vishnu, D.; Kumar, A.; Al Salmi, M.; Al Yaqoobi, S.; Al-Saadi, M.A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Biochar Activated Carbon for Oil Spills Removal. Johns. Matthey Technol. Rev. 2024, 68, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingamdinne, L.P.; Angaru, G.K.R.; Pal, C.A.; Koduru, J.R.; Karri, R.R.; Mubarak, N.M.; Chang, Y.-Y. Insights into kinetics, thermodynamics, and mechanisms of chemically activated sunflower stem biochar for removal of phenol and bisphenol-A from wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Ro, K.; Guo, M.; Novak, J.; Mashayekhi, H.; Xing, B. Sorption of bisphenol A, 17α-ethinyl estradiol and phenanthrene on thermally and hydrothermally produced biochars. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 5757–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, N.; Nawaz, A.; Chandel, K.S.; Devnarayan, D.; Gupta, L.; Singh, S.; Khan, M.S.; Lee, M.; Sharma, A.K. A cohesive effort to assess the suitability and disparity of carbon nanotubes for water treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 124832–124853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Lara, M.A.; Calero, M.; Ronda, A.; Iáñez-Rodríguez, I.; Escudero, C. Adsorptive Behavior of an Activated Carbon for Bisphenol A Removal in Single and Binary (Bisphenol A—Heavy Metal) Solutions. Water 2020, 12, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhan, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, S.; Pang, R.; Xie, B. Removal of emerging contaminants (bisphenol A and antibiotics) from kitchen wastewater by alkali-modified biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Sun, Z.; Park, Y.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L. Removal of bisphenol A from wastewater by Ca-montmorillonite modified with selected surfactants. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T.; Hsu, H.-C.; Su, T.-Y.; Lin, K.-Y.; Lin, C.-M. Adsorption characteristics of bisphenol-A in aqueous solutions onto hydrophobic zeolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 299, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libbrecht, W.; Vandaele, K.; De Buysser, K.; Verberckmoes, A.; Thybaut, J.W.; Poelman, H.; De Clercq, J.; Van Der Voort, P. Tuning the pore geometry of ordered mesoporous carbons for enhanced adsorption of bisphenol-A. Materials 2015, 8, 1652–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hu, W.; Pan, J.; Zhou, H.; Guan, W.; Wang, X.; Dai, J.; Xu, L. Selective adsorption and separation of BPA from aqueous solution using novel molecularly imprinted polymers based on kaolinite/Fe3O4 composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y. Adsorption of bisphenol A from water by surfactant-modified zeolite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 348, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Qin, Q. Adsorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solution onto activated carbons with different modification treatments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Li, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, X. Synthesis of recyclable powdered activated carbon with temperature responsive polymer for bisphenol A removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, P.K.; Gan, L.; Liu, M.; Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, D.; Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Rao, N.N. One-pot assembly of silica@two polymeric shells for synthesis of hollow carbon porous nanospheres: Adsorption of bisphenol A. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Gao, N.; Li, R.; Deng, Y. Desorption of bisphenol-A (BPA) and regeneration of BPA-spent granular activated carbon using ultrasonic irradiation and organic solvent extraction. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 54, 3106–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, B.; Choo, K.-H.; Choi, S.-J. Selective adsorption of bisphenol A by organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous silicas. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 138, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ren, D.; Xia, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J. Photocatalytic degradation of Bisphenol A (BPA) using immobilized TiO2 and UV illumination in a horizontal circulating bed photocatalytic reactor (HCBPR). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Kondo, F. Bisphenol A Degradation by Bacteria Isolated from River Water. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2002, 43, 0265–0269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Shimazaki, R.; Kashiwada, A.; Matsuda, K.; Yamada, K. Use of chitosan for removal of bisphenol a from aqueous solutions through quinone oxidation by polyphenol oxidase. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.H.; Ghadermazi, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sadighara, P.; Jahed-Khaniki, G.; Heibati, B.; McKay, G. Adsorptive removal of endocrine disrupting bisphenol A from aqueous solution using chitosan. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2647–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadoudi, N.; Amhamdi, H.; Ahari, M.H. Sorption of bisphenol A from aqueous solutions using natural adsorbents: Isotherm, kinetic and effect of temperature. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 314, 07003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, P.; Lu, J. Application of natural biosorbent and modified peat for bisphenol a removal from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hameed, B.H.; Ok, Y.S.; Omirou, M. A review on waste-derived adsorbents from sugar industry for pollutant removal in water and wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praspaliauskas, M.; Pedišius, N.; Čepauskienė, D.; Valantinavičius, M. Study of chemical composition of agricultural residues from various agro-mass types. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 10, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokula, B.E.; Dada, A.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Obayomi, K.S.; Bello, O.S.; Pal, U. Agro-waste based adsorbents as sustainable materials for effective adsorption of Bisphenol A from the environment: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Ling, C.; Fu, L.; Xue, Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C. N-doped porous bowl-like carbon with superhigh external surface area for ultrafast degradation of bisphenol A: Key role of site exposure degree. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, N.; Jin, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, H.; Wu, M.; Pan, B. The role of ash content on bisphenol A sorption to biochars derived from different agricultural wastes. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Le Velly, M.; Rhind, S.M.; Kyle, C.E.; Hough, R.L.; Duff, E.I.; McKenzie, C. A study on temporal trends and estimates of fate of Bisphenol A in agricultural soils after sewage sludge amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Su, Y.; Du, C. Adsorbent biochar derived from corn stalk core for highly efficient removal of bisphenol A. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 74916–74927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katibi, K.K.; Yunos, K.F.; Man, H.C.; Aris, A.Z.; Mohd Nor, M.Z.; Azis, R.S. An insight into a sustainable removal of bisphenol a from aqueous solution by novel palm kernel shell magnetically induced biochar: Synthesis, characterization, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Polymers 2021, 13, 3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Xu, L.; Qu, J.; Graham, N. Investigation of pre-coagulation and powder activate carbon adsorption on ultrafiltration membrane fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 459, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benstoem, F.; Nahrstedt, A.; Boehler, M.; Knopp, G.; Montag, D.; Siegrist, H.; Pinnekamp, J. Performance of granular activated carbon to remove micropollutants from municipal wastewater—A meta-analysis of pilot- and large-scale studies. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakić, V.; Rac, V.; Krmar, M.; Otman, O.; Auroux, A. The adsorption of pharmaceutically active compounds from aqueous solutions onto activated carbons. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 282, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Aarts, A.; Shang, R.; Heijman, B.; Rietveld, L. Integrating powdered activated carbon into wastewater tertiary filter for micro-pollutant removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Deshayes, S.; Zedek, S.; Cren-Olivé, C.; Cartiser, N.; Eudes, V.; Bressy, A.; Caupos, E.; et al. Study of a large scale powdered activated carbon pilot: Removals of a wide range of emerging and priority micropollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Res. 2015, 72, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M.; Ferro-García, M.Á.; Prados-Joya, G.; Ocampo-Pérez, R. Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 1268–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalova, L.; Knappe, D.R.; Lehnberg, K.; Kazner, C.; Hollender, J. Removal of highly polar micropollutants from wastewater by powdered activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 3607–3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailler, R.; Gasperi, J.; Coquet, Y.; Derome, C.; Buleté, A.; Vulliet, E.; Bressy, A.; Varrault, G.; Chebbo, G.; Rocher, V. Removal of emerging micropollutants from wastewater by activated carbon adsorption: Experimental study of different activated carbons and factors influencing the adsorption of micropollutants in wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1102–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Guo, W.; Ngo, H.H.; Nghiem, L.D.; Hai, F.I.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Wang, X.C. A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 619–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhl, A.S.; Zietzschmann, F.; Hilbrandt, I.; Meinel, F.; Altmann, J.; Sperlich, A.; Jekel, M. Targeted testing of activated carbons for advanced wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 257, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-W.; Jo, B.-I.; Yoon, Y.; Zoh, K.-D. Occurrence and removal of selected micropollutants in a water treatment plant. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, C.W.; Park, J.K. Removal efficiencies of endocrine disrupting chemicals by coagulation/flocculation, ozonation, powdered/granular activated carbon adsorption, and chlorination. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 23, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zietzschmann, F.; Stützer, C.; Jekel, M. Granular activated carbon adsorption of organic micro-pollutants in drinking water and treated wastewater—Aligning breakthrough curves and capacities. Water Res. 2016, 92, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J.; Zietzschmann, F.; Geiling, E.-L.; Ruhl, A.S.; Sperlich, A.; Jekel, M. Impacts of coagulation on the adsorption of organic micropollutants onto powdered activated carbon in treated domestic wastewater. Chemosphere 2015, 125, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J.; Ruhl, A.S.; Zietzschmann, F.; Jekel, M. Direct comparison of ozonation and adsorption onto powdered activated carbon for micropollutant removal in advanced wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2014, 55, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbardella, L.; Comas, J.; Fenu, A.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Weemaes, M. Advanced biological activated carbon filter for removing pharmaceutically active compounds from treated wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Aa, L.T.J.; Kolpa, R.J.; Rietveld, L.C.; van Dijk, J.C. Improved removal of pesticides in biological granular activated carbon filters by pre-oxidation of natural organic matter. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. -Aqua 2012, 61, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.R.; Vinitnantharat, S. Competitive Removal of Phenol and 2,4-Dichlorophenol in Biological Activated Carbon System. Environ. Technol. 2000, 21, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounis, M.; Sanz-Santos, E.; Fakhfakh, F.; Younes, M.K.; Hadrich, B.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Larriba, M.; García, J. Optimisation of Adsorption Removal of Bisphenol A Using Sludge-Based Activated Carbons: Application of Response Surface Methodology with a Box–Behnken Design. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xing, B. Adsorption site identification and regulation to guide design of N-doped porous carbon-based materials for efficient and selective removal of bisphenol a. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 486, 150150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrakchi, F.; Fazeli Zafar, F.; Wei, M.; Yuan, C.; Cao, B.; Wang, S. N-doped mesoporous H3PO4–pyrocarbon from seaweed and melamine for batch adsorption of the endocrine disruptor bisphenol A. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganathan, K.K.; Faizal, A.N.M.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Ali, A. Adsorptive removal of Bisphenol a from aqueous solution using activated carbon from coffee residue. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazid, H.; Bouzid, T.; El Himri, M.; Regti, A.; El Haddad, M. Bisphenol A (BPA) remediation using walnut shell as activated carbon employing experimental design for parameter optimization and theoretical study to establish the adsorption mechanism. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.C.F.; Antero, R.V.P.; de Oliveira, S.B.; Ojala, S.A.; Scalize, P.S. Activated carbon produced from waste coffee grounds for an effective removal of bisphenol-A in aqueous medium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 24850–24862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, F.F.; Barati, B.; Rasoulzadeh, H.; Sheikhmohammadi, A.; Wang, S.; Chen, H. Adsorption kinetics analysis and optimization of Bisphenol A onto magnetic activated carbon with shrimp shell based precursor. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 166, 106604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussalah, C.; Kaouah, F.; Boumaza, S.; Trari, M. Highly efficient removal of the bisphenol A from aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from cores of nuts of Sapindus mukorossi. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 18869–18885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamarehie, B.; Tizabi, S.M.S.; Heydari, R.; Jafari, A.; Ghaderpoori, M.; Karami, M.A.; Ghaderpoury, A. Data on the bisphenol A adsorption from aqueous solutions on PAC and MgO~PAC crystals. Data Brief 2018, 21, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grich, A.; Bouzid, T.; Naboulsi, A.; Regti, A.; El Himri, M.; El Haddad, M. Synthesis and optimization of activated carbon from Doum (Chamaerops humilis) fiber via pyrolysis-assisted H3PO4 activation for removal of bisphenol A and α-Naphthol. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 145, 111061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Abreu, A.B.; Álvarez-Torrellas, S.; Águeda, V.I.; Larriba, M.; Delgado, J.A.; Calvo, P.A.; García, J. Enhanced removal of the endocrine disruptor compound Bisphenol A by adsorption onto green-carbon materials. Effect of real effluents on the adsorption process. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noufel, K.; Djebri, N.; Boukhalfa, N.; Boutahala, M.; Dakhouche, A. Removal of bisphenol A and trichlorophenol from aqueous solutions by adsorption with organically modified bentonite, activated carbon composites: A comparative study in single and binary systems. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarinejad, Z.; Dehghani, M.H.; Heidari, M.; Javedan, G.; Ali, I.; Sillanpää, M. Methods for preparation and activation of activated carbon: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, A.U.; Vithanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Seo, D.-C.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S. Steam activation of biochars facilitates kinetics and pH-resilience of sulfamethazine sorption. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhen, S.N.; Rovani, S.; Araujo, L.G.d.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Mašek, O. Uranium removal from aqueous solution using macauba endocarp-derived biochar: Effect of physical activation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yue, Q.; Gao, B.; Li, A. Insight into activated carbon from different kinds of chemical activating agents: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, H. Nitrogen enriched biochar modified by high temperature CO2–ammonia treatment: Characterization and adsorption of CO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 257, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiral, H.; Demiral, İ.; Karabacakoğlu, B.; Tümsek, F. Production of activated carbon from olive bagasse by physical activation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burhenne, L.; Aicher, T. Benzene removal over a fixed bed of wood char: The effect of pyrolysis temperature and activation with CO2 on the char reactivity. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 127, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.-W.; Cho, S.-H.; Song, H.; Kwon, E.E. Carbon dioxide assisted sustainability enhancement of pyrolysis of waste biomass: A case study with spent coffee ground. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ro, K.S.; Chen, J. Physically (CO2) activated hydrochars from hickory and peanut hull: Preparation, characterization, and sorption of methylene blue, lead, copper, and cadmium. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 24906–24911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; He, T.; Wu, J. Corn stalks char from fast pyrolysis as precursor material for preparation of activated carbon in fluidized bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Din, M.I.; Ashraf, S.; Intisar, A. Comparative study of different activation treatments for the preparation of activated carbon: A mini-review. Sci. Prog. 2017, 100, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamar, M.; Désarmot, G.; Fagebaume, O.; Hitmi, R.; Pinsonc, J.; Savéant, J.M. Modification of carbon fiber surfaces by electrochemical reduction of aryl diazonium salts: Application to carbon epoxy composites. Carbon 1997, 35, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.R.; Freire, C.; de Castro, B.; Freitas, M.M.A.; Figueiredo, J.L. Anchoring of a nickel(II) Schiff base complex onto activated carbon mediated by cyanuric chloride. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2001, 46, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otake, Y.; Jenkins, R.G. Characterization of oxygen-containing surface complexes created on a microporous carbon by air and nitric acid treatment. Carbon 1993, 31, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.B.; Martínez-Alonso, A.; Leon y Leon, C.A.; Tascón, J.M.D. Modification of the surface properties of an activated carbon by oxygen plasma treatment. Fuel 1998, 77, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, O.V.; Krasnova, T.A.; Semenova, S.A. Effect of modification of granulated activated carbons with ozone on their properties. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2011, 84, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Goyal, M.; Bansal, R.C. Adsorption of chromium by activated carbon from aqueous solution. Carbon 1999, 37, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.K.; Kim, Y.M.; Woo, S.H.; Park, J.M. Removal of cadmium using acid-treated activated carbon in the presence of nonionic and/or anionic surfactants. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 99, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-García, P. Activated carbon from lignocellulosics precursors: A review of the synthesis methods, characterization techniques and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1393–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurewicz, K.; Babeł, K.; Źiółkowski, A.; Wachowska, H. Ammoxidation of active carbons for improvement of supercapacitor characteristics. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1491–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.J.J.; van Bekkum, H. XPS of nitrogen-containing functional groups on activated carbon. Carbon 1995, 33, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymundo-Piñero, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Linares-Solano, A. The role of different nitrogen functional groups on the removal of SO2 from flue gases by N-doped activated carbon powders and fibres. Carbon 2003, 41, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, G.G.; Samaras, P.; Sakellaropoulos, G.P. Effect of activated carbons modification on porosity, surface structure and phenol adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henning, K.D.; Schäfer, S. Impregnated activated carbon for environmental protection. Gas Sep. Purif. 1993, 7, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanaga, S.; Hiwara, A.; Yasuda, H. Preparation and high bacteriostatic action of the activated carbons possessing ultrafine silver particles. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2002, 3, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeddou, A.R.; Chergui, S.; Chergui, A.; Halet, F.; Hamza, A.; Nadjemi, B.; Ould-Dris, A.; Belkouch, J. Removal of cyanide in aqueous solution by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in presence of copper-impregnated activated carbon. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 788–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchomgui-Kamga, E.; Alonzo, V.; Nanseu-Njiki, C.P.; Audebrand, N.; Ngameni, E.; Darchen, A. Preparation and characterization of charcoals that contain dispersed aluminum oxide as adsorbents for removal of fluoride from drinking water. Carbon 2010, 48, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan Jr, R.L.; Reed, B.E. Modeling As (V) removal by a iron oxide impregnated activated carbon using the surface complexation approach. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheib, S.A.; Karanfil, T.; Cheng, W. Tailoring activated carbons for enhanced removal of natural organic matter from natural waters. Carbon 2004, 42, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorishi, S.B.; Keeney, R.M.; Serre, S.D.; Gullett, B.K.; Jozewicz, W.S. Development of a Cl-impregnated activated carbon for entrained-flow capture of elemental mercury. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 4454–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Lin, W.; Ying, W.-c. Preparation of iron-impregnated granular activated carbon for arsenic removal from drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhoum, N.; Monser, L. Removal of cyanide from aqueous solution using impregnated activated carbon. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2002, 41, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehdashti, A.; Khavanin, A.; Rezaee, A.; Assilian, H.; Motalebi, M. Application of microwave irradiation for the treatment of adsorbed volatile organic compounds on granular activated carbon. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2011, 8, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Shu, Y.; Li, F.; Peng, G. Bimetallic catalysts as electrocatalytic cathode materials for the oxygen reduction reaction in microbial fuel cell: A review. Green Energy Environ. 2023, 8, 1043–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monser, L.; Adhoum, N. Modified activated carbon for the removal of copper, zinc, chromium and cyanide from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2002, 26, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.J.; Wei, L.B.; Zhao, P.C.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Qin, Y.B. Study on Preparation of Activated Carbon from Corncob Furfural Residue with ZnCl2 by Microwave Irradiation. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 152–153, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, K.Y.; Hameed, B.H. Microwave assisted preparation of activated carbon from pomelo skin for the removal of anionic and cationic dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaror, C.A. Enhanced oxidation of toxic effluents using simultaneous ozonation and activated carbon treatment. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 1997, 70, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M. Ozonation of 1,3,6-naphthalenetrisulphonic acid catalysed by activated carbon in aqueous phase. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2002, 39, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M. The role of dispersive and electrostatic interactions in the aqueous phase adsorption of naphthalenesulphonic acids on ozone-treated activated carbons. Carbon 2002, 40, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Hong, S.H.; Paek, K.-H.; Ju, W.-T. Adsorbability enhancement of activated carbon by dielectric barrier discharge plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2277–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Kim, B.-J. Influence of oxygen plasma treatment on hydrogen chloride removal of activated carbon fibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazak, O.; Eker, Y.R.; Bingol, H.; Tor, A. Novel preparation of activated carbon by cold oxygen plasma treatment combined with pyrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 325, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Mishra, I.; Kumar, V. Degradation and mineralization of Bisphenol A (BPA) in aqueous solution using advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2 and UV/S2O82− oxidation systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 156, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, P.-K.; Lee, C.-H.; Kwon, H.-H.; Lee, S. A novel hybrid system for the removal of endocrine disrupting chemicals: Nanofiltration and homogeneous catalytic oxidation. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 312, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellana, G.; Loffredo, E. Simultaneous removal of endocrine disruptors from a wastewater using white rot fungi and various adsorbents. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X.; Ng, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.D. Removal of bisphenol A via a hybrid process combining oxidation on β-MnO2 nanowires with microfiltration. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 392, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Index | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H16O2 | |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid | |
| Physical property | Molecular weight | 228.29 g/mol |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 | |
| Flash Point | 227 °C | |
| Volatility | Non-volatile | |
| Odor | Mild phenolic odor | |
| Vapor Pressure | 4.0 × 10−8 mmHg at 25 °C | |
| Boiling Point | 220 °C at 4 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 153–156 °C | |
| Solubility in water | 300 mg/L at 25 °C | |
| Chemical Structure |  | |
| Chemical property | Partition Coefficient (LogP) | 3.32 |
| Dissociation Constants | pKa = 9.6 | |
| Chemical Classes | Endocrine Disruptors | |
| Structural Features | Two phenolic rings linked by isopropylidene bridge (propane bridge) | |
| Functional Groups | Phenolic hydroxyl groups (–OH) | |
| Chemical Class | Phenolic compound, Endocrine disruptor | |
| Reactivity | Reactive with strong bases, acids, oxidizers | |
| Stability | Stable under normal conditions; susceptible to oxidative degradation |
| Procedure | Matrix | Detection Limit | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| fluorescence immunoassay | Unfiltered water | 0.02 μg L | [75] |
| Surface Enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) | water | 0.1pg/mL | [76] |
| LC-MS | drinking water | 7.0 ng/L | [77] |
| HPLC-diode array detection (DAD) | water and milk | 0.07–0.16 ng/mL | [78] |
| GC-MS | bottled water and wastewater | 0.30 ng/g | [79] |
| HPLC | pretreatment of effluent | 10.5/μg/L | [80] |
| HPLC | urine | 0.12 ng/mL | [81] |
| HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) | urine | 0.4 ng/mL | [82] |
| Adsorbent | Surface Area (m2/g) | Micropore Volume | Mesopore Volume | (Total) Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Pore Size/Diameter (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Ca-montmorillonite | 75.725 | – | – | 0.126 | 6.649 | [154] |
| Hydrophobic Zeolite | 504.5 ± 4.8 | – | – | 0.317 ± 0.006 | – | [155] |
| Powdered AC (PAC) | 1027 | – | – | 0.50 | <3 | |
| CMK-3 | 1420 | – | – | 1.14 | 4.0 | [156] |
| Soft templated carbon | 476 | – | – | 0.49 | 7.0 | |
| Kaolinite/Fe3O4 | 7.62 | – | – | 0.029 | 15.04 | [157] |
| Kaolinite/Fe3O4 | 65.15 | – | – | 0.207 | 12.70 | |
| Magnetic molecular polymers | 142.90 | – | – | 0.158 | 4.41 | |
| MNIPs | 150.80 | – | – | 0.177 | 4.68 | |
| Ca–Mt | 54.44 | – | – | 0.139 | 10.19 | [18] |
| Al–Mt | 228.64 | – | – | 0.197 | 3.533 | |
| Zeolite synthesized from coal fly ash | 91.50 | – | – | – | – | [158] |
| W20 | 1777 | – | – | – | – | [159] |
| W20N | 1760 | – | – | – | – | |
| PAC | 1326 | – | 0.9017 | 3.710 | – | [160] |
| PAC-PNIPAM(1) | 603 | – | 0.4665 | 3.835 | – | |
| PAC-PNIPAM(2) | 313 | – | 0.2387 | 3.711 | – | |
| Silica@carbon | 259 | – | – | 0.7 | – | [161] |
| Hollow carbon porous nanospheres | 477 | – | – | 1.1 | – | |
| Granular AC | 896 | – | – | – | – | [162] |
| Modified peat | 0.66 | – | – | – | – | |
| Hydrophobic mesoporous material | 1030 | 0.09 | – | 0.98 | 2.54 | [163] |
| Organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous material | 750 | 0.42 | – | 0.48 | 0.96 | |
| Powdered AC | 1780 | 0.59 | – | 1.59 | – |
| Adsorbents | Qmax (mg/g) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Sludge-Based ACs | 285.8 | [196] |
| Activated sunflower stem biochar | 365.81 | [149] |
| N-doped porous carbon-based | 462.5 | [197] |
| Activated seaweed pyrocarbon with a melamine (TSWP–M) | 270.5 | [198] |
| AC from coffee residue | 105 | [199] |
| Walnut shell AC (AC-Ws) | 238.63 | [200] |
| AC produced from waste coffee grounds | 123.22 | [201] |
| AC with shrimp shell-based precursor | 207.77 | [202] |
| AC derived from cores of nuts of Sapindus mukorossi (CNSM–ACH) | 216.99 | [203] |
| Powder AC (PAC) with manganese oxide (MgO) | 9.200 | [204] |
| Doum (Chamaerops humilis) fiber | 56.11 | [205] |
| Commercial AC (F400) | 407.00 | [206] |
| AC from Kraft lignin | 220.000 | |
| Carbon xerogel | 78.000 | |
| Calcium alginate/organo-activated bentonite | 252.900 | [207] |
| Calcium alginate/AC | 419.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zafar, F.F.; Barati, B.; Sanaei, D.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Ahmadi, E.; Ansari, M.; Ghalhari, M.R.; Rasoulzadeh, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Application of Agricultural Waste-Based Activated Carbon for Antibiotic Removal in Wastewaters: A Comprehensive Review. Water 2025, 17, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081190
Zafar FF, Barati B, Sanaei D, Yousefzadeh S, Ahmadi E, Ansari M, Ghalhari MR, Rasoulzadeh H, Zheng X, Wang S, et al. Application of Agricultural Waste-Based Activated Carbon for Antibiotic Removal in Wastewaters: A Comprehensive Review. Water. 2025; 17(8):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081190
Chicago/Turabian StyleZafar, Fatemeh Fazeli, Bahram Barati, Daryoush Sanaei, Samira Yousefzadeh, Ehsan Ahmadi, Mohsen Ansari, Mohammad Rezvani Ghalhari, Hassan Rasoulzadeh, Xiaolong Zheng, Shuang Wang, and et al. 2025. "Application of Agricultural Waste-Based Activated Carbon for Antibiotic Removal in Wastewaters: A Comprehensive Review" Water 17, no. 8: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081190
APA StyleZafar, F. F., Barati, B., Sanaei, D., Yousefzadeh, S., Ahmadi, E., Ansari, M., Ghalhari, M. R., Rasoulzadeh, H., Zheng, X., Wang, S., & Chen, H. (2025). Application of Agricultural Waste-Based Activated Carbon for Antibiotic Removal in Wastewaters: A Comprehensive Review. Water, 17(8), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081190






