The Removal of Acidic Drugs from Domestic Wastewater Using an Innovative System of Constructed Wetlands/Stabilization Ponds in Series
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wastewater Sampling Study Zone
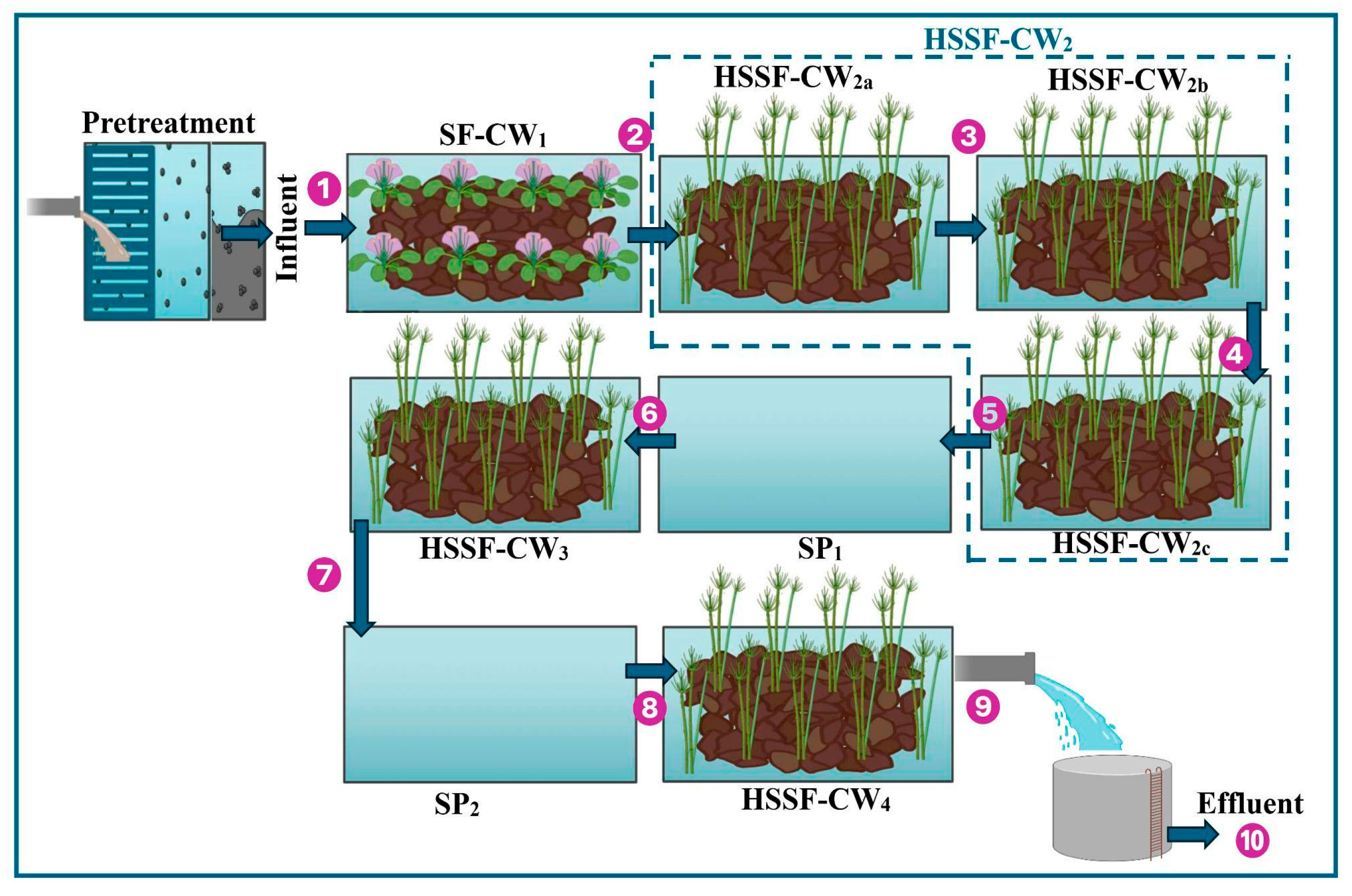
2.2. Wastewater Treatment System
2.3. Analytical and Instrumental Methods
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Sample Conditioning
2.3.3. Water Quality Characterization
2.3.4. Acidic-Drug Quantification
2.3.5. Database Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Behavior
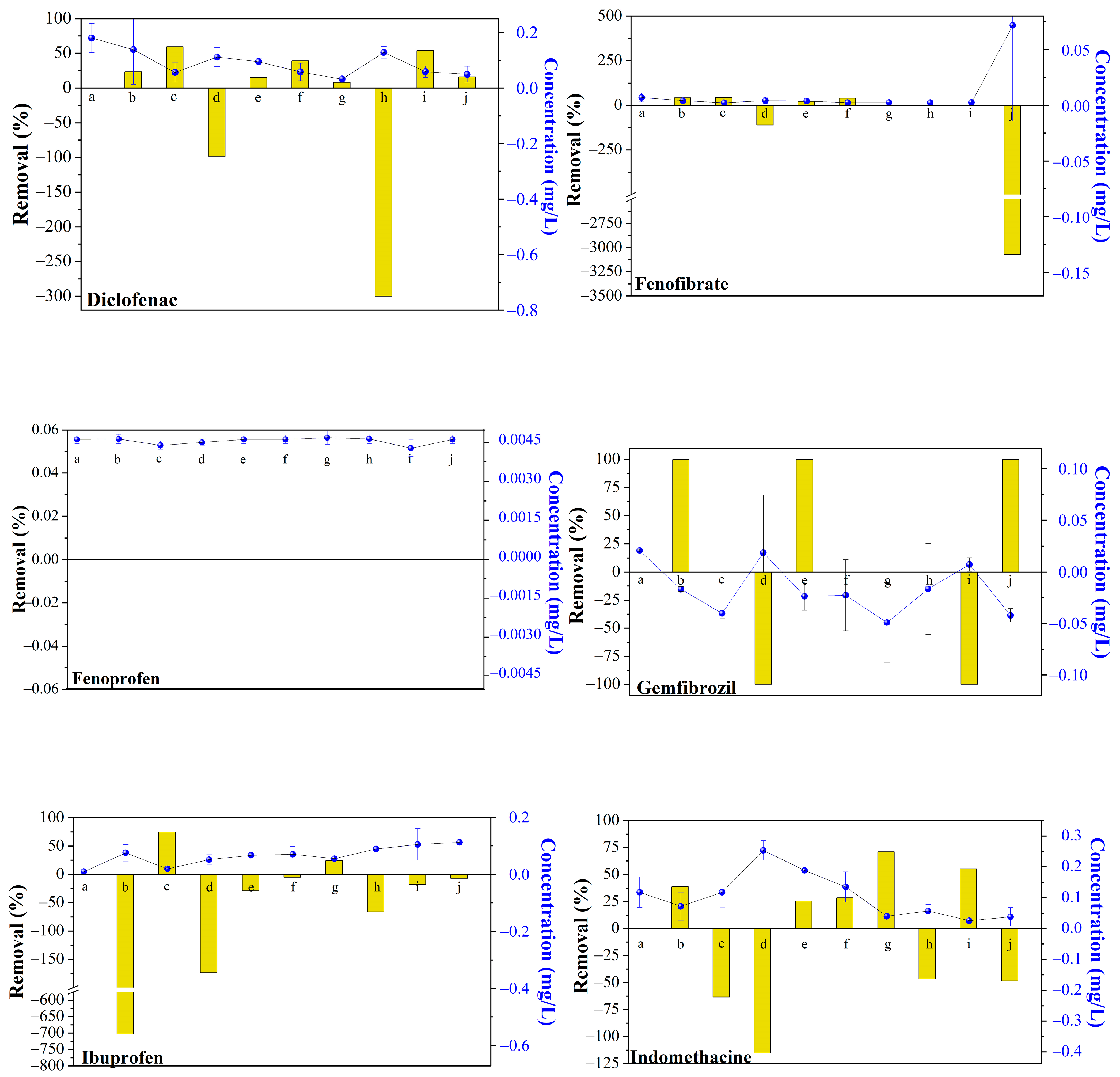
3.2. AD Removal Performance
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dvořáková Březinova, T.; Vymazal, J.; Koželuh, M.; Kule, L. Occurrence and Removal of Ibuprofen and Its Metabolites in Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands Treating Municipal Wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, P.; Kim, M.; Shah, A.; Alaee, M.; Smyth, S.A. Occurrence and Fate of Antibiotic, Analgesic/Anti-Inflammatory, and Antifungal Compounds in Five Wastewater Treatment Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473–474, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Gin, K.Y.-H.; Lin, A.Y.-C.; Reinhard, M. Impacts of Emerging Organic Contaminants on Freshwater Resources: Review of Recent Occurrences, Sources, Fate and Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 6062–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamur, J.M. Analytical techniques in pharmaceutical pollution of the world’s rivers: A review. ChemChemTech 2024, 67, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiraju, R.; Nair, H.; Chintagunta, P. Diffusion of New Pharmaceutical Drugs in Developing and Developed Nations. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2004, 21, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achag, B.; Mouhanni, H.; Bendou, A. Improving the Performance of Waste Stabilization Ponds in an Arid Climate. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2021, 12, 3634–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, H.; Fai, C.M.; binti Bahruddin, A.S.; Dinesh, A.A.A. Effect of Temperature on Nutrient Removal Efficiency of Water Hyacinth for Phytoremediation Treatment. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, H.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Ngo, H.H.; Liang, S.; Lu, S.; Wu, W. Effect of Photosynthetically Elevated PH on Performance of Surface Flow-Constructed Wetland Planted with Phragmites Australis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 15524–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerra-Herrera, M.; Honda, L.; Richter, P. Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography—Time-of-Flight High Resolution Mass Spectrometry to Quantify Acidic Drugs in Wastewater. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1423, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jing, R.; Feng, X.; Dai, Y.; Tao, R.; Vymazal, J.; Cai, N.; Yang, Y. Removal of Acidic Pharmaceuticals by Small-Scale Constructed Wetlands Using Different Design Configurations. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieno, N.; Sillanpää, M. Fate of Diclofenac in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant—A Review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. A Review on Removing Pharmaceutical Contaminants from Wastewater by Constructed Wetlands: Design, Performance and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 908–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flippin, J.L.; Huggett, D.; Foran, C.M. Changes in the Timing of Reproduction Following Chronic Exposure to Ibuprofen in Japanese Medaka, Oryzias Latipes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 81, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.N.; Kim, H.N.; Park, K.S.; Lee, S.-K.; Gu, M.B. Analysis of the Effects Diclofenac Has on Japanese Medaka (Oryzias Latipes) Using Real-Time PCR. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Lee, S.; Ha, N.; Kho, Y.; Park, K.; Kim, P.; Ahn, B.; Kim, S.; Choi, K. Effects of Gemfibrozil on Sex Hormones and Reproduction Related Performances of Oryzias Latipes Following Long-Term (155 d) and Short-Term (21 d) Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakada, N.; Tanishima, T.; Shinohara, H.; Kiri, K.; Takada, H. Pharmaceutical Chemicals and Endocrine Disrupters in Municipal Wastewater in Tokyo and Their Removal during Activated Sludge Treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipma, J.; Osuna, B.; Collado, N.; Monclús, H.; Ferrero, G.; Comas, J.; Rodriguez-Roda, I. Comparison of Removal of Pharmaceuticals in MBR and Activated Sludge Systems. Desalination 2010, 250, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Coy, A.M.; Martínez-Pachón, D.; Boix, C.; Rincón, R.J.; Castillo, N.; Arias-Marín, L.P.; Manrique-Losada, L.; Torres-Palma, R.; Moncayo-Lasso, A.; Hernández, F. An Investigation into the Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Colombian Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.Q.; Gersberg, R.M.; Hua, T.; Zhu, J.; Tuan, N.A.; Tan, S.K. Pharmaceutical Removal in Tropical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands at Varying Hydraulic Loading Rates. Chemosphere 2012, 87, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.-M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhou, X.-F.; Duan, Y.-P.; Liu, S.-G. Selective Removal of Acidic Pharmaceuticals from Contaminated Lake Water Using Multi-Templates Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 211–212, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Xu, J. Progress in the Biological and Chemical Treatment Technologies for Emerging Contaminant Removal from Wastewater: A Critical Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 274–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Preparation, Modification and Environmental Application of Biochar: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 227, 1002–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.A.; Túa, L.; Rueda, A.; Montaño, B.; Rodríguez, M.; Prats, D. Monitoring and Analysis of the Energy Cost of an MBR. Desalination 2010, 250, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Performance Comparison of Different Types of Constructed Wetlands for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Their Transformation Products: A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 14342–14364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Ray, S. Sustainable wastewater management: Exploring nature-based treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 15, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Samal, K.; Dash, R.R. Waste Stabilization Pond (WSP) for Wastewater Treatment: A Review on Factors, Modelling and Cost Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, C.I.; Kapsi, M.G.; Konstas, P.S.G.; Trantopoulos, E.P.; Boti, V.I.; Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. Assessment of Multiclass Pharmaceutical Active Compounds (PhACs) in Hospital WWTP Influent and Effluent Samples by UHPLC-Orbitrap MS: Temporal Variation, Removals and Environmental Risk Assessment. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; Masih, I.; van Hullebusch, E.D. Pharmaceuticals’ Removal by Constructed Wetlands: A Critical Evaluation and Meta-Analysis on Performance, Risk Reduction, and Role of Physicochemical Properties on Removal Mechanisms. J. Water Health 2020, 18, 253–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruchlik, Y.; Linge, K.; Joll, C. Removal of Organic Micropollutants in Waste Stabilisation Ponds: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 206, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Liang, S.; Fan, J.; Liu, H. A Review on the Sustainability of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment: Design and Operation. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Matamoros, V.; Fontàs, C.; Salvadó, V. The Ability of Biologically Based Wastewater Treatment Systems to Remove Emerging Organic Contaminants—A Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 11708–11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; Sellamuthu, B.; Ouarda, Y.; Drogui, P.; Tyagi, R.D.; Buelna, G. Review on Fate and Mechanism of Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants from Wastewater Using Biological Approach. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rühmland, S.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A.; Barjenbruch, M. Fate of Pharmaceuticals in a Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland and Two Ponds. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 80, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gersberg, R.M.; Ng, W.J.; Tan, S.K. Removal of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Aquatic Plant-Based Systems: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 184, 620–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama Aziz, K.H.; Mustafa, F.S.; Hassan, M.A.; Omer, K.M.; Hama, S. Biochar as Green Adsorbents for Pharmaceutical Pollution in Aquatic Environments: A Review. Desalination 2024, 583, 117725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakarmi, K.J.; Daneshvar, E.; Eshaq, G.; Puro, L.; Maiti, A.; Nidheesh, P.V.; Wang, H.; Bhatnagar, A. Synthesis of Biochar from Iron-Free and Iron-Containing Microalgal Biomass for the Removal of Pharmaceuticals from Water. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hethnawi, A.; Alnajjar, M.; Manasrah, A.D.; Hassan, A.; Vitale, G.; Jeong, R.; Nassar, N.N. Metformin Removal from Water Using Fixed-Bed Column of Silica-Alumina Composite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 597, 124814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, S.; Shafi, T.; Dubey, B.K.; Chowdhury, S. Biochar-Mediated Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Aqueous Matrices via Adsorption. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2023, 5, 37–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdová, H.; Brázová, V.; Kwoczynski, Z.; Snow, J.; Trögl, J.; Kříženecká, S. Miscanthus x Giganteus Biochar: Effective Adsorption of Pharmaceuticals from Model Solution and Hospital Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 460, 142545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriam, C.A.; Milton, B.A.; Del Castillo Daynet, S.; Eulalia, V.M.; Omar, R.B. Phytoremediation of Five Pharmaceutical Products Registered as Emerging Contaminants in an Aqueous Medium Using the Species Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes). Bionatura 2023, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Licht, A.; Carranza-Lopez, L.; De la Parra-Guerra, A.C.; Acevedo-Barrios, R. Unlocking the Potential of Eichhornia Crassipes for Wastewater Treatment: Phytoremediation of Aquatic Pollutants, a Strategy for Advancing Sustainable Development Goal-06 Clean Water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 43561–43582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, S.P.; Londoño, Y.A.; Gutiérrez, F.R.; Peñuela, G.A. Evaluación de Humedales Artificiales de Flujo Subsuperficial En La Remoción de Diferentes Concentraciones de Ibuprofeno Empleando Cyperus Papyrus. Tecnol. Y Cienc. Del Agua 2017, 8, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijosa-Valsero, M.; Matamoros, V.; Martín-Villacorta, J.; Bécares, E.; Bayona, J.M. Assessment of Full-Scale Natural Systems for the Removal of PPCPs from Wastewater in Small Communities. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secretaría del Medio Ambiente, R.N. y P. NOM-003-SEMARNAT-1997. Available online: https://www.conagua.gob.mx/conagua07/publicaciones/publicaciones/sgaa-15-13.pdf (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Kumawat, M.; Sharma, P.; Pal, N.; James, M.M.; Verma, V.; Tiwari, R.R.; Shubham, S.; Sarma, D.K.; Kumar, M. Occurrence and Seasonal Disparity of Emerging Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in a Drinking Water Supply System and Associated Health Risk. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.H.; Wallace, S.D. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group, Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; ISBN 9781566705264. [Google Scholar]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Wastewater Sampling; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sacher, F.; Thomas Lange, F.; Brauch, H.-J.; Blankenhorn, I. Pharmaceuticals in Groundwaters Analytical Methods and Results of a Monitoring Program In Baden-Wurttemberg, Germany. J Chromatogr A 2001, 938, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA-AWWA-WEF. Standard Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Diclofenac. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3033 (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Matamoros, V.; Nguyen, L.X.; Arias, C.A.; Salvadó, V.; Brix, H. Evaluation of Aquatic Plants for Removing Polar Microcontaminants: A Microcosm Experiment. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan-Roblero, J.; Cruz-Maya, J.A. Ibuprofen: Toxicology and Biodegradation of an Emerging Contaminant. Molecules 2023, 28, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambuludi, S.L.; Panizza, M.; Oturan, N.; Özcan, A.; Oturan, M.A. Kinetic Behavior of Anti-Inflammatory Drug Ibuprofen in Aqueous Medium during Its Degradation by Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2381–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Fenoprofen. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Fenoprofen (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Liu, F.; Nielsen, A.H.; Vollertsen, J. Sorption and Degradation Potential of Pharmaceuticals in Sediments from a Stormwater Retention Pond. Water 2019, 11, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.M. Elimination of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5811–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Bambague, E.M.; Madera-Parra, C.A.; Ortiz-Escobar, A.C.; Morales-Acosta, P.A.; Peña-Salamanca, E.J.; Machuca-Martínez, F. High-Rate Algal Pond for Removal of Pharmaceutical Compounds from Urban Domestic Wastewater under Tropical Conditions. Case Study: Santiago de Cali, Colombia. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center of Biotechnology Information Indomethacin. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3715#section=LogP (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- National Center of Biotechnology Information Fenofibrate. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3339#section=Environmental-Abiotic-Degradation (accessed on 11 April 2025).
- Merino-Solís, M.L.; Villegas, E.; de Anda, J.; López-López, A. The Effect of the Hydraulic Retention Time on the Performance of an Ecological Wastewater Treatment System: An Anaerobic Filter with a Constructed Wetland. Water 2015, 7, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbi, B.P.; Moodley, B.; Birungi, G.; Ndungu, P.G. Detection and Quantification of Acidic Drug Residues in South African Surface Water Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Method 1694: Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Water, Soil, Sediment, and Biosolids by HPLC/MS/MS; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lashkarizadeh, M.; Munz, G.; Oleszkiewicz, J.A. Impacts of Variable PH on Stability and Nutrient Removal Efficiency of Aerobic Granular Sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 73, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, M.; Lee, B. Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 62, 421–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, S.L.; van Haandel, A. Transformation of Waste Stabilization Ponds: Reengineering of an Obsolete Sewage Treatment System. Water 2021, 13, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ávila, F.; Patiño-Chávez, J.; Zhinín-Chimbo, F.; Donoso-Moscoso, S.; Flores del Pino, L.; Avilés-Añazco, A. Performance of Phragmites Australis and Cyperus Papyrus in the Treatment of Municipal Wastewater by Vertical Flow Subsurface Constructed Wetlands. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2019, 7, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Removal of Enteric Bacteria in Constructed Treatment Wetlands with Emergent Macrophytes: A Review. Proc. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Toxic/Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2005, 40, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.; Gupta, A.K.; Ghosal, P.S.; Majumder, A. A Review on Performance of Constructed Wetlands in Tropical and Cold Climate: Insights of Mechanism, Role of Influencing Factors, and System Modification in Low Temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Q.W.; Yan, B.X.; Liang, Y.X.; Yu, X.F.; Gerchman, Y.; Cheng, X.W. Influence of Vegetation Type and Temperature on the Performance of Constructed Wetlands for Nutrient Removal. Water Sci. Technol. 2018, 77, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohórquez, E.; Paredes, D.; Arias, C.A. Vertical Flow-Constructed Wetlands for Domestic Wastewater Treatment under Tropical Conditions: Effect of Different Design and Operational Parameters. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Xiong, J.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Sohail, I.; He, Z. A Constructed Wetland System with Aquatic Macrophytes for Cleaning Contaminated Runoff/Storm Water from Urban Area in Florida. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, H.; Masih, I. The Performance of the Intensified Constructed Wetlands for Organic Matter and Nitrogen Removal: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morató, J.; Codony, F.; Sánchez, O.; Pérez, L.M.; García, J.; Mas, J. Key Design Factors Affecting Microbial Community Composition and Pathogenic Organism Removal in Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevopoulos, S.; Smeets, P. Quantifying the Log Reduction of Pathogenic Microorganisms by Constructed Wetlands: A Review. Proceedings 2020, 48, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, A.E.; Hernãndez, M.E.; Bayona, J.M.; Morales, L.; Ruiz, P. Removal of Selected Organic Pollutants and Coliforms in Pilot Constructed Wetlands in Southeastern Mexico. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2011, 91, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, M.; Patil, M.D.; Wani, S.P. Potency of Constructed Wetlands for Deportation of Pathogens Index from Rural, Urban and Industrial Wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, L.; Canobbio, S.; Fornaroli, R.; Cabrini, R.; Marazzi, F.; Mezzanotte, V. COD, Nutrient Removal and Disinfection Efficiency of a Combined Subsurface and Surface Flow Constructed Wetland: A Case Study. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2016, 18, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, N.; Marzo, A.; Randazzo, C.; Caggia, C.; Toscano, A.; Cirelli, G.L. Constructed Wetlands Combined with Disinfection Systems for Removal of Urban Wastewater Contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 656, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Patrolecco, L.; Ademollo, N.; Tolomei, A.; Barra Caracciolo, A. Degradation of Gemfibrozil and Naproxen in a River Water Ecosystem. Microchem. J. 2013, 107, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Ncube, S. Occurrence and Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs in South African Aquatic Environment: What Is Known and the Missing Information? Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbhele, Z.E.; Ncube, S.; Madikizela, L.M. Synthesis of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Its Application in Selective Extraction of Fenoprofen from Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 36724–36735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, C.F.; Lange, L.C.; Amaral, M.C.S. Occurrence, Fate and Removal of Pharmaceutically Active Compounds (PhACs) in Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants—A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrolecco, L.; Capri, S.; Ademollo, N. Occurrence of Selected Pharmaceuticals in the Principal Sewage Treatment Plants in Rome (Italy) and in the Receiving Surface Waters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5864–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, D.; Cimetiere, N.; Giraudet, S.; Tan, R.; Wolbert, D.; Le Cloirec, P. Adsorption-Desorption of Organic Micropollutants by Powdered Activated Carbon and Coagulant in Drinking Water Treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Kühnert, M.; Gläser, R.; Schulze, A. Photocatalytic Degradation and Toxicity Evaluation of Diclofenac by Nanotubular Titanium Dioxide-PES Membrane in a Static and Continuous Setup. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 16340–16348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcieszyńska, D.; Łagoda, K.; Guzik, U. Diclofenac Biodegradation by Microorganisms and with Immobilised Systems—A Review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simazaki, D.; Kubota, R.; Suzuki, T.; Akiba, M.; Nishimura, T.; Kunikane, S. Occurrence of Selected Pharmaceuticals at Drinking Water Purification Plants in Japan and Implications for Human Health. Water Res. 2015, 76, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Stumpf, M.; Mueller, J.; Haberer, K.; Wilken, R.-D.; Servos, M. Behavior and Occurrence of Estrogens in Municipal Sewage Treatment Plants I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 1999, 225, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Pedescoll, A.; Matamoros, V.; Bayona, J.M.; García, J. Capacity of a Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetland System for the Removal of Emerging Pollutants: An Injection Experiment. Chemosphere 2010, 81, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Dvořáková Březinová, T.; Koželuh, M.; Kule, L. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals in Four Full-Scale Constructed Wetlands in the Czech Republic—The First Year of Monitoring. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and Removal of Pharmaceuticals, Hormones, Personal Care Products, and Endocrine Disrupters in a Full-Scale Water Reclamation Plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1503–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, R.; Sachan, S.G.; Sachan, A. Environmental and Human Exposure to Antimicrobial Agent Triclosan: A Review. In In vitro Plant Breeding towards Novel Agronomic Traits; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 237–261. [Google Scholar]
- Matamoros, V.; García, J.; Bayona, J.M. Behavior of Selected Pharmaceuticals in Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands: A Pilot-Scale Study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5449–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Zhou, T.; Lian, J.; Li, Y.; Zou, H. Organic Acid Responses in Root Exudates of Wetland Plant Due to the Stress of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnarova, L.; Halesova, T.; Tomesova, D.; Vaclavikova, M.; Bosakova, Z. Monitoring Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Healthcare Effluent Wastewater Samples and the Effectiveness of Drug Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using the UHPLC-MS/MS Method. Molecules 2024, 29, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Trade Name | Function | Molecular Structure (g/mol) | pka | Log Know | Log Koc | Chemical Structure | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diclofenac | Analgesic/anti-inflammatory | C14H11Cl2NO2 | 4.2 | 4.02 | 2.91 |  | [50,51] |
| 296.1 | |||||||
| Ibuprofen | Analgesic/anti-inflammatory | C8H10N4O2 | 4.9 | 3.71 | 3.5 | 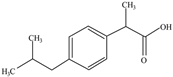 | [52,53] |
| 206.3 | |||||||
| Gemfibrozil | Lipid regulator | C15H22O3 | 4.8 | 4.77 | 2.63 | 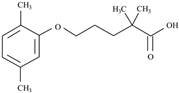 | [53] |
| 250.3 | |||||||
| Fenoprofen | Anti-inflammatory | C15H14O3 | 4.5 | 4.05 | - | 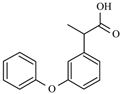 | [54] |
| 242.3 | |||||||
| Naproxen | Analgesic/anti-inflammatory | C14H14O3 | 4.2 | 3.18 | 2.54 | 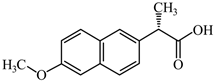 | [55,56] |
| 230.3 | |||||||
| Indomethacin | Analgesic/anti-inflammatory | C19H16ClNO4 | 4.5 | 4.27 | 3.15 |  | [57,58] |
| 357.8 | |||||||
| Fenofibrate | Lipid regulator and metabolite | C20H21ClO4 | - | 5.19 | 3.58 |  | [59,60] |
| 360.8 |
| Parameter | Symbol | Units | Raw | Treated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen potential | pH | - | 7.3–7.6 | 7.9–8.1 |
| Temperature | T | °C | 23.0–26.0 | 20.0–23.0 |
| Electrical conductivity | EC | µS/cm | 1338.0–1623.00 | 244.0–1158.0 |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand | BOD5 | mg/L | 141.0–257.0 | 1.0–9.0 |
| Suspended Solid Total | SST | mg/L | 74–107.0 | 8.0 |
| Total Nitrogen | TN | mg/L | 84.6 | 18.0 |
| Total Phosphorous | TP | mg/L | 45.0–47.0 | 3.0–5.0 |
| Oils and fats | O&F | mg/L | 10.0–10.5 | 9.1–9.5 |
| Total Coliforms | TC | NMP/100 mL | 1.5 × 107–1.5 × 107 | 2.0–5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallegos-Castro, E.; Almeida-Naranjo, C.E.; Rivas, A.; Figueroa, N.; Montellano, L.; Villamar-Ayala, C.A. The Removal of Acidic Drugs from Domestic Wastewater Using an Innovative System of Constructed Wetlands/Stabilization Ponds in Series. Water 2025, 17, 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081192
Gallegos-Castro E, Almeida-Naranjo CE, Rivas A, Figueroa N, Montellano L, Villamar-Ayala CA. The Removal of Acidic Drugs from Domestic Wastewater Using an Innovative System of Constructed Wetlands/Stabilization Ponds in Series. Water. 2025; 17(8):1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081192
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallegos-Castro, Elvia, Cristina E. Almeida-Naranjo, Armando Rivas, Nancy Figueroa, Leticia Montellano, and Cristina Alejandra Villamar-Ayala. 2025. "The Removal of Acidic Drugs from Domestic Wastewater Using an Innovative System of Constructed Wetlands/Stabilization Ponds in Series" Water 17, no. 8: 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081192
APA StyleGallegos-Castro, E., Almeida-Naranjo, C. E., Rivas, A., Figueroa, N., Montellano, L., & Villamar-Ayala, C. A. (2025). The Removal of Acidic Drugs from Domestic Wastewater Using an Innovative System of Constructed Wetlands/Stabilization Ponds in Series. Water, 17(8), 1192. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081192








