A Review of the Sources, Monitoring, Detection, and Removal of Typical Olfactory Substances Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Analysis of Typical Taste and Odor Incidents
| T&O Outbreak | T&O Burst Time | Typical Substances Causing Odor | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Huangpu River, Shanghai, China | 1990s | GSM, 2-MIB | [20] |
| Yangcheng Lake, Suzhou, China | 1990s | 2-MIB | [21] |
| Derwent River, Australia | 2014–2017 | GSM, 2-MIB | [22] |
| Mediterranean River Tel | For the past few years | GSM | [23] |
| Paldang Reservoir, Korea | Summer 2012 | GSM | [24] |
| Bay of Quinte, Canada | - | GSM, 2-MIB | [25] |
| Taihu Lake, Wuxi, China | 2007 | Dimethyltrisulfide | [26] |
| Songhua River, Northeast China | For the past twenty years | - | [27] |
| Catalonia, Spain | 2015 | 3-(trifluoromethyl)phenol | [28] |
| Fortaleza, Brazil Lake Shinji, Japan | 2017 2007 | GSM, 2-MIB GSM | [29] [30] |
| China’s Luan River flows into Tianjin | 2015 | GSM | [31] |
| Barcelona, Spain Diamond Valley Lake, USA Wichita Falls, USA | 2002 2000–2004 2020 | Diacetyl GSM, 2-MIB GSM | [32] [33] [34] |
3. Sources of GSM and 2-MIB
4. GSM and 2-MIB Pre-Outbreak Monitoring
4.1. Monitoring of Algal Blooms
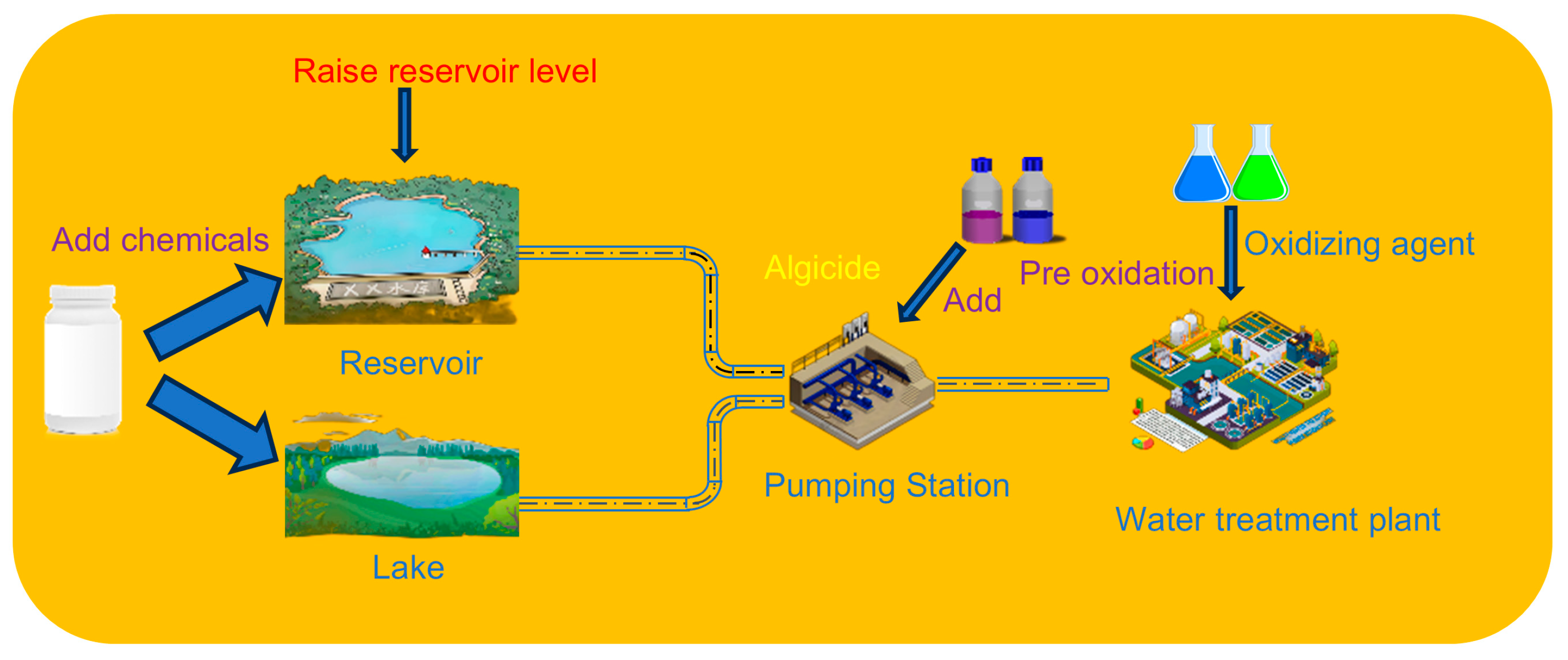
4.2. For the Treatment of Cyanobacteria in Water Sources
5. Detection and Analysis Methods
6. Removal of Olfactory Substances from Drinking Water
6.1. Traditional Methods of Removing Odors in Water Plants
6.1.1. Activated Carbon-Based Treatments
6.1.2. Biological Filtration in Biofilters with Biodegradable Geosmin and 2-MIB
6.1.3. Ozone Is a Common Removal Process in Water Treatment Plants
6.2. Advanced Oxidation Process
6.2.1. Hydroxyl Radicals
Fenton
Electrochemical Methods
Semiconductor Photocatalysis and Electrocatalysis
Nanobubbles
Plasma Technology
6.2.2. Chloride Radicals
6.2.3. Sulfate Radical
Ultraviolet Activation
Thermal Activation
Ultrasonic Activation
Electrochemical Activation
Transition Metal Activation
Carbon Material Activation
Joint Activation
6.3. Summary
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GSM | Geosmin |
| AOP | Advanced oxidation process |
| BAC | Biological activated carbon |
| BDD | Boron-doped diamond |
| BV | Bed volume |
| CBZ | Carbamazepine |
| DBPs | Disinfection by-products |
| EBCT | Empty-bed contact time |
| EO | Electrochemical oxidation |
| FPA | Flavor profile analysis |
| FRA | Flavor rating analysis |
| GC | Gas chromatography |
| IBMP | 2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine |
| IPMP | 3-methyl-4-isopropylphenol |
| MBs | Microbubbles |
| MC-LR | Microcystin-LR |
| NBs | Nanobubbles |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| OTC | Odor threshold concentration |
| PDS | Peroxydisulphate |
| PMS | Peroxymonosulphate |
| PS | Persulfate |
| qPCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| TBA | 2,4,6-tribromoanisole |
| TC | Tetracyline |
| TCA | 2,4,6-trichloroanisole |
| THMs | Trihalomethanes |
| 2-MIB | 2-methylisobomeol |
References
- Wang, C.; An, W.; Guo, Q.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Assessing the hidden social risk caused by odor in drinking water through population behavioral responses using economic burden. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Li, C.; Mao, X. An ignored and potential source of taste and odor (T&O) issues—Biofilms in drinking water distribution system (DWDS). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3537–3550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A.M.; Phetxumphou, K.; Gallagher, D.L. Systematic visualizing, and interpreting of consumer feedback for drinking water quality. Water Res. 2014, 66, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clercin, N.A.; Druschel, G.K.; Gray, M. Occurrences of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin –degrading bacteria in a eutrophic reservoir and the role of cell-bound versus dissolved fractions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, M.; Huang, X.; Shi, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y. Enhancement of thioethers removal by pre-oxidation-coagulation: Effects of background organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulou, M.; Evgenidou, E.; Lambropoulou, D.; Konstantinou, I. A review on advanced oxidation processes for the removal of taste and odor compounds from aqueous media. Water Res. 2014, 53, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Gallagher, D.L.; Byrd, J.; Yao, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Dietrich, A.M.; Yang, M. Pyrazines: A diverse class of earthy-musty odorants impacting drinking water quality and consumer satisfaction. Water Res. 2020, 182, 115971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xu, B.; Qi, F.; Kumirska, J. The occurrence of haloanisoles as an emerging odorant in municipal tap water of typical cities in China. Water Res. 2016, 98, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J. Studies on the degradation of trace phenol and indole odorants by chlorine and permanganate in drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-Y.; Lin, Y.-L.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Hu, C.-Y.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Z.-X.; Tang, Y.-L.; Xu, B.; Gao, N.-Y. The formation, analysis, and control of chlor(am)ination-derived odor problems: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Timermans, C.; Malfroot, B.; Dierendonck, C.; Mol, Z.; Pluym, T.; Waegenaar, F.; Arends, J.B.A.; Demeestere, K.; Walgraeve, C.; Boon, N.; et al. Pilot-scale drinking water distribution system to study water quality changes during transport. npj Clean Water 2023, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, W.F.; Horth, H.; Crane, R.; Ogden, T.; Arnott, M. Taste and odour threshold concentrations of potential potable water contaminants. Water Res. 1996, 30, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, I.; Mitsumori, T.; Kawakubo, S.; Saito, Y. Determination of Musty-Odor Compounds in Water by Gas ChromatographyÔÇôMass Spectrometry with a Needle-Type Sample-Preparation Device. Anal. Sci. 2014, 30, 979–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.T.; Park, Y.-G. Geosmin and 2-MIB Removal by Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Processes in the Republic of Korea. Water 2021, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Seyedahmad, H.; Niels, W.; Yannick, V.; Michael, C.; Hulle, S.V. Combining ozone with UV and H2O2 for the degradation of micropollutants from different origins: Lab-scale analysis and optimization. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3773–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Ellakany, H.F.; Abaza, S.S.; Geneedy, A.M.; Salem, H.M.; Taha, A.E.; Swelum, A.A.; Omer, F.A.; et al. Undesirable odour substances (geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol) in water environment: Sources, impacts and removal strategies. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, T.O.M.; Pinto, E.; Passos, L.S.; Dorr, F.; Vasconcelos, C.M.; Arpini, C.; Silva, M.O.; Pereira, T.M.; Coppo, G.C.; Merçon, J.; et al. Off-flavor detection in tilapia reared in cages in tropical lakes. Aquaculture 2022, 555, 738215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, S.; Marvin, C.; Brownlee, B.; Ridal, J.; Howell, T.; Rao, Y.R.; Charlton, M.; Watson, S.B. Off flavours in large waterbodies: Physics, chemistry and biology in synchrony. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Oil leak contaminates tap water: A view of drinking water security crisis in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4219–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Chen, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Insights into the Seasonal Olfactory Mechanism of Geosmin in Raw Water of Huangpu River. Toxics 2022, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Wang, Y.; Friese, K.; Zhang, L.; Han, C.; Kang, D.; Shen, Q. Spatial and Seasonal Distribution of 2-Methylisoborneol in a Large Eutrophic Shallow Lake, China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proemse, B.C.; Koolhof, I.; White, R.; Barmuta, L.A.; Coughanowr, C. Nutrient sources and loads in the River Derwent catchment, Tasmania. Australas. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, C.; Abril, M.; Bretxa, È.; Jutglar, M.; Ponsá, S.; Sellarès, N.; Vendrell-Puigmitjà, L.; Llenas, L.; Ordeix, M.; Proia, L. Driving Factors of Geosmin Appearance in a Mediterranean River Basin: The Ter River Case. Front Microbiol 2021, 12, 741750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Youn, S.-J.; Byeon, M.; Yu, S.-J. Occurrence of cyanobacteria, actinomycetes, and geosmin in drinking water reservoir in Korea: A case study from an algal bloom in 2012. Water Supply 2020, 20, 1862–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minns, C.K.; Moore, J.E.; Doka, S.E.; St. John, M.A. Temporal trends and spatial patterns in the temperature and oxygen regimes in the Bay of Quinte, Lake Ontario, 1972–2008. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2011, 14, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Burch, M.; Lin, T.-F. Taihu Lake Not to Blame for Wuxi’s Woes. Science 2008, 319, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Bai, S.; Lu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, L. Ecological risk assessment of eutrophication in Songhua Lake, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2007, 22, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.; Hernández, A.; Ventura, F.; Devesa, R.; Boleda, M.R. Identification of 3-(trifluoromethyl)phenol as the malodorous compound in a pollution incident in the water supply in Catalonia (N.E. Spain). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 16076–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, C.J.; Neto, J.C.; Barros, M.U.G.; Menezes, I.; Góis, A.; Santos, G. Consumer perception of water quality during an off-flavor event in Fortaleza-Brazil. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2019, 68, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godo, T.; Saki, Y.; Nojiri, Y.; Tsujitani, M.; Sugahara, S.; Hayashi, S.; Kamiya, H.; Ohtani, S.; Seike, Y. Geosmin-producing Species of Coelosphaerium (Synechococcales, Cyanobacteria) in Lake Shinji, Japan. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep41928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, F.; Yu, G.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, R. Geosmin production and polyphasic characterization of Oscillatoria limosa Agardh ex Gomont isolated from the open canal of a large drinking water system in Tianjin City, China. Harmful Algae 2017, 69, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matia, L.; Bernal, A.; Devesa, R.; Martín-Alonso, J. Managing an odour episode in Barcelona’s water supply: Strategies adopted, the causative agent (diacetyl) and determination of its organoleptic properties. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, W.D.; Izaguirre, G. Geosmin and MIB events in a new reservoir in southern California. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, H.; Reeder, S.; Southard, M. Monitoring Programs Are an Evolving Process: Detection of T&O in Filter Media. J. AWWA 2021, 113, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Dong, Y.; Su, M.; Dong, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M. Co-occurrence of odor-causing dioxanes and dioxolanes with bis(2-chloro-1-methylethyl) ether in Huangpu River source water and fates in O3-BAC process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 430, 128435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Guo, Q.; Sun, D.; Su, M.; An, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. Occurrence of swampy/septic odor and possible odorants in source and finished drinking water of major cities across China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Stuetz, R.M.; Hamilton, L.; Power, K.; Crosbie, N.D.; Tamburic, B. Management of biogenic taste and odour: From source water, through treatment processes and distribution systems, to consumers. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhaddada, R.; Nélieu, S.; Nasri, H.; Delarue, G.; Bouaïcha, N. High diversity of microcystins in a Microcystis bloom from an Algerian lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Sawade, E.; Newcombe, G. Biological treatment options for cyanobacteria metabolite removal—A review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1536–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, F.; Bhartia, S.; Mohseni, M.; Dorner, S.; Barbeau, B. Performance of vacuum UV (VUV) for the degradation of MC-LR, geosmin, and MIB from cyanobacteria-impacted waters. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 2048–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merel, S.; Walker, D.; Chicana, R.; Snyder, S.; Baurès, E.; Thomas, O. State of knowledge and concerns on cyanobacterial blooms and cyanotoxins. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelić, D.; Svirčev, Z.; Simeunović, J.; Vidović, M.; Trajković, I. Cyanotoxins: Characteristics, production and degradation routes in drinking water treatment with reference to the situation in Serbia. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 421–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Kong, F.; Zeng, Q.; Cao, H.; Qian, S.; Zhang, M. Seasonal variation of Microcystis in Lake Taihu and its relationships with environmental factors. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, X.; Wu, J.; Nan, J.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, C. Distribution, driving forces, and risk assessment of 2-MIB and its producer in a drinking water source-oriented shallow lake. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 71194–71208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Sorial, G.A. Treatment of taste and odor causing compounds 2-methyl isoborneol and geosmin in drinking water: A critical review. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Miao, H.; Shimada, M.; Utsumi, M.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Nishimura, O.; Asada, Y.; Fujimoto, N.; et al. Temperature affects growth, geosmin/2-methylisoborneol production, and gene expression in two cyanobacterial species. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 12017–12026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, X.; Pan, R. Algae-induced taste and odour problems at low temperatures and the cold stress response hypothesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 9079–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Ma, M.; Huang, T.; Li, H.; Ni, T.; Liu, X.; Ma, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Actinobacteria produce taste and odor in drinking water reservoir: Community composition dynamics, co-occurrence and inactivation models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, M.; Huang, T.; Miao, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, K.; Yang, W.; Ma, B. Spatial and temporal dynamics of actinobacteria in drinking water reservoirs: Novel insights into abundance, community structure, and co-existence model. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, K.; Huang, X.; Ma, B.; Li, N.; Sekar, R. Mixed-culture aerobic anoxygenic photosynthetic bacterial consortia reduce nitrate: Core species dynamics, co-interactions and assessment in raw water of reservoirs. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allgaier, M.; Grossart, H.-P. Diversity and Seasonal Dynamics of Actinobacteria Populations in Four Lakes in Northeastern Germany. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 3489–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, E.; Evans, C.; Dunstan, R.H.; Geary, P.; Cole, B. Distribution, abundance and activity of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol-producing Streptomyces in drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2018, 145, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitlin, B.; Watson, S.B. Actinomycetes in relation to taste and odour in drinking water: Myths, tenets and truths. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1741–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Bao, Z.; Deng, X.; Shen, H.; Liu, J.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. Thermal stratification controls taste and odour compounds by regulating the phytoplankton community in a large subtropical water source reservoir (Xin’anjiang Reservoir). J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; An, W.; Vogt, R.D.; Andersen, T.; Jia, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, M. MIB-producing cyanobacteria (Planktothrix sp.) in a drinking water reservoir: Distribution and odor producing potential. Water Res. 2015, 68, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Xu, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X. Effects of algae proliferation and density current on the vertical distribution of odor compounds in drinking water reservoirs in summer. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Jang, K.-S.; Xu, H.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Liu, M.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Rainstorm events shift the molecular composition and export of dissolved organic matter in a large drinking water reservoir in China: High frequency buoys and field observations. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, M.; Baker, L.; Sommerfeld, M. Seasonal occurrence and degradation of 2-methylisoborneol in water supply reservoirs. Water Res. 2005, 39, 4899–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuhtaram, H.; Kibuye, F.A.; Ajjampur, S.; Glover, C.M.; Hofmann, R.; Gaget, V.; Owen, C.; Wert, E.C.; Zamyadi, A. State of knowledge on early warning tools for cyanobacteria detection. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinet, J.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Sérodes, J.-B. Modelling geosmin concentrations in three sources of raw water in Quebec, Canada. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, I.; Qi, M.; Chen, J.; Sun, X.; Deng, X.; Niu, Y.; Xie, P. Development of Models for Predicting the Predominant Taste and Odor Compounds in Taihu Lake, China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51976. [Google Scholar]
- Dzialowski, A.R.; Smith, V.H.; Huggins, D.G.; deNoyelles, F.; Lim, N.-C.; Baker, D.S.; Beury, J.H. Development of predictive models for geosmin-related taste and odor in Kansas, USA, drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Lee, H.; An, K.-G. Predicting Taste and Odor Compounds in a Shallow Reservoir Using a Three–Dimensional Hydrodynamic Ecological Model. Water 2018, 10, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Arhonditsis, G.B.; Gao, J.; Chen, Q.; Peng, J. The magnitude and drivers of harmful algal blooms in China’s lakes and reservoirs: A national-scale characterization. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrose-Igho, G.; Seyoum, W.M.; Perry, W.L.; O’Reilly, C.M. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Water Quality Indicators in Small Lakes Using Sentinel-2 Satellite Data: Lake Bloomington and Evergreen Lake, Central Illinois, USA. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 637–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.M.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Darling, J.A.; Urquhart, E.A.; Johnston, J.M.; Ignatius, A.R.; Myer, M.H.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J.; Stumpf, R.P. Satellite monitoring of cyanobacterial harmful algal bloom frequency in recreational waters and drinking water sources. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-S.; Cho, I.-H.; Kim, H.-K.; Byun, J.-H.; Bae, M.-J.; Kim, B.-H. Prediction of Geosmin at Different Depths of Lake Using Machine Learning Techniques. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertone, E.; Burford, M.A.; Hamilton, D.P. Fluorescence probes for real-time remote cyanobacteria monitoring: A review of challenges and opportunities. Water Res. 2018, 141, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, S.; Hasegawa, E.; Yamaguchi, D.; Fujioka, T. The rapid counting method for 2-MIB-producing cyanobacteria (Pseudanabaena sp.) using fluorescence detection of phycocyanin pigments in algal cells. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 2561–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Huo, D.; Bi, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Yu, G. Using molecular detection for the diversity and occurrence of cyanobacteria and 2-methylisoborneol-producing cyanobacteria in an eutrophicated reservoir in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Fang, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Su, M.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Early warning of MIB episode based on gene abundance and expression in drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2023, 231, 119667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, E.S.; Krishna, A.; Emelko, M.B.; Müller, K.M. Sporadic diurnal fluctuations of cyanobacterial populations in oligotrophic temperate systems can prevent accurate characterization of change and risk in aquatic systems. Water Res. 2024, 252, 121199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, B.K.; Chislock, M.F.; Wilson, A.E. Eutrophication mediates a common off-flavor compound, 2-methylisoborneol, in a drinking water reservoir. Water Res. 2016, 92, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Pang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pei, H. Using sodium percarbonate to suppress vertically distributed filamentous cyanobacteria while maintaining the stability of microeukaryotic communities in drinking water reservoirs. Water Res. 2021, 197, 117111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Andersen, T.; Burch, M.; Jia, Z.; An, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Succession and interaction of surface and subsurface cyanobacterial blooms in oligotrophic/mesotrophic reservoirs: A case study in Miyun Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Jia, D.; Yu, J.; Vogt, R.D.; Wang, J.; An, W.; Yang, M. Reducing production of taste and odor by deep-living cyanobacteria in drinking water reservoirs by regulation of water level. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Su, M.; Liu, T.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Burch, M.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Light as a possible regulator of MIB-producing Planktothrix in source water reservoir, mechanism and in-situ verification. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.; Murri, A.; Mastitsky, S.; Yang, Z.; Foster, R.; Schweitzer, L. Geosmin reduction by algaecide application to drinking water: Field scale efficacy and mechanistic insights. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, P.; Fan, L.; Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A. A review of the use of sonication to control cyanobacterial blooms. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4319–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Pei, H. Moderate pre-ozonation coupled with a post-peroxone process remove filamentous cyanobacteria and 2-MIB efficiently: From bench to pilot-scale study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piezer, K.; Li, L.; Jeon, Y.; Kadudula, A.; Seo, Y. The Application of Potassium Permanganate to Treat Cyanobacteria-Laden Water: A Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, C.J.; Reeve, P.J.; Sawade, E.; Voldoire, C.F.; Newton, K.; Praptiwi, R.; Collingnon, L.; Dreyfus, J.; Hobson, P.; Gaget, V.; et al. Fate of cyanobacteria in drinking water treatment plant lagoon supernatant and sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, E.A.; Evans, C.A.; Geary, P.M.; Dunstan, R.H.; Cole, B. The role of Actinobacteria in taste and odour episodes involving geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in aquatic environments. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.-Aqua 2013, 62, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlingame, G.A.; Doty, R.L.; Dietrich, A.M. Humans as Sensors to Evaluate Drinking Water Taste and Odor: A Review. J. AWWA 2017, 109, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Q.; Su, M.; Liu, T.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y. Source-water odor during winter in the Yellow River area of China: Occurrence and diagnosis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, A.M.; Burlingame, G.A. A review: The challenge, consensus, and confusion of describing odors and tastes in drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 135061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahraei, S.K.; Salemi, A.; Schmidt, T.C. Sample preparation for determination of water taste and odor compounds: A review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 32, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, G.; Vegué, L.; Boleda, M.R.; Ventura, F. Simultaneous determination of the potential carcinogen 1,4-dioxane and malodorous alkyl-1,3-dioxanes and alkyl-1,3-dioxolanes in environmental waters by solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1487, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Lu, N.; Zhang, D. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the screening of potent swampy/septic odor-causing compounds in two drinking water sources in China. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 2458–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, S.; Gonçalves, C.; Cunha, E.; Guimarães, A.; Alpendurada, M.F. New developments in the analysis of fragrances and earthy–musty compounds in water by solid-phase microextraction (metal alloy fibre) coupled with gas chromatography–(tandem) mass spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 84, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guadayol, M.; Cortina, M.; Guadayol, J.M.; Caixach, J. Determination of dimethyl selenide and dimethyl sulphide compounds causing off-flavours in bottled mineral waters. Water Res. 2016, 92, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwins, H.; Stratton, H.; Teasdale, P.; Bauld, T. A fast stir bar sorptive extraction method for the analysis of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source and drinking water. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 55, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, T.; Chiang, P. Odorous compounds from a cyanobacterium in a water purification plant in Central Taiwan. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2522–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancho, B.; Ventura, F.; Galceran, M.; Diaz, A.; Ricart, S. Determination, synthesis and survey of iodinated trihalomethanes in water treatment processes. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3380–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, I.; Razak, N.A.; Mizuguchi, A.; Kawakubo, S.; Saito, Y.; Jinno, K. Needle-type extraction device for the purge and trap analysis of 23 volatile organic compounds in tap water. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1317, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Lao, Z.; Tan, J.; Yu, G.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y. Synthesis of CoNi-layered double hydroxide on graphene oxide as adsorbent and construction of detection method for taste and odor compounds in smelling water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, E.D.; Conway, S.C.; Miller, D.W.; Perschbacher, P.W. Determination of methylisoborneol in channel catfish pond water by solid phase extraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Water Res. 1996, 30, 2125–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, S.W.; Lea, J.M.; Zimba, P.V.; Grimm, C.C. Rapid analysis of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water using solid phase micro extraction procedures. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2140–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benanou, D.; Acobas, F.; de Roubin, M.R.; David, F.; Sandra, P. Analysis of off-flavors in the aquatic environment by stir bar sorptive extraction–thermal desorption–capillary GC/MS/olfactometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 376, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, R.L.; Haworth-Duff, A.; Young, I.S.; Myers, P.; Hampson, M.R.; Williams, J.; Maher, S. An automated micro solid phase extraction gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (muSPE-GC-MS) detection method for geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in drinking water. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardina, D.; Santamaria, A.; Alonso, M.L.; Bartolomé, L.; Alonso, R.M.; Maña, J.A.; Bilbao, E.; Lombraña, J.I.; Bartolome, M.; Hernando, L.M. HS-SPME-GC/MS Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Trihalomethanes, Geosmin, and 2-Methylisoborneol in Water Samples. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pochiraju, S.; Hoppe-Jones, C.; Adams, C.; Weinrich, L. Development and optimization of analytical methods for the detection of 18 taste and odor compounds in drinking water utilities. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Qu, X.; Huang, D.; Shi, Y.; Kong, C.; Wang, Y. Determination of earthy-musty odors in tap water by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry with silica solid-phase extraction. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.; Daurie, H.; Gagnon, G.A. Development and validation of an SPE-GC-MS/MS taste and odour method for analysis in surface water. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 94, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Lin, Q.; Sun, G. Automated ultratrace determination of musty odiferous compounds from environmental waters by online purge and trap (P&T) gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2018, 47, 278–291. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhao, L.; Fei, J.; Xuan, Z.; Huang, C.; Chen, X. Determination of Seven Odorants in Purified Water Among Worldwide Brands by HS-SPME Coupled to GC–MS. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuanjiang, L.; Li, G.; Liu, P.; Chen, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Ruan, D. Determination of 2-Methylisoborneol and Geosminin Water by Using Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction-Thermal Desorption Coupled with GC-MS. J. Water Chem. Technol. 2022, 44, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Li, F.; Xu, D.; Fu, M.-L. Comparison of two methods for the determination of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in algae samples by stable isotope dilution assay through purge-and-trap or headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with GC/MS. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parinet, J.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Serodes, J.; Proulx, F. Automated analysis of geosmin, 2-methyl-isoborneol, 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine, 2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine and 2,4,6-trichloroanisole in water by SPME-GC-ITDMS/MS. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2011, 91, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Jia, R.; Gao, B. Simultaneous analysis of five taste and odor compounds in surface water using solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2010, 6, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, N.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M. Simultaneous quantification of fifty-one odor-causing compounds in drinking water using gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortada, C.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Determination of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water and wine samples by ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liang, G.; Chen, J.; Qi, M.; Xie, P. Simultaneous determination of eight common odors in natural water body using automatic purge and trap coupled to gas chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3791–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bristow, R.L.; Young, I.S.; Pemberton, A.; Williams, J.; Maher, S. An extensive review of the extraction techniques and detection methods for the taste and odour compound geosmin (trans-1, 10-dimethyl-trans-9-decalol) in water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, P.; Shu, J.; Yang, B.; Huang, J. Rapid detection of taste and odor compounds in water using the newly invented chemi-ionization technique coupled with time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Yuan, H.; Yang, M. Identification of odorous compounds in reclaimed water using FPA combined with sensory GC-MS. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1600–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Yang, K.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Ren, L.; Yu, J. Electronic nose application for detecting different odorants in source water: Possibility and scenario. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.; Koo, J.-W.; Shin, Y.; Hwang, T.-M. Electronic tongue for the simple and rapid determination of taste and odor compounds in water. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Qiu, F.; Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Yu, J. Possibility for detecting 14 typical odorants occurring in drinking water by employing human odor-binding protein OBP2a. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyluoglu, M.; Kim, D.; Zaker, Y.; Karanfil, T. Removal mechanisms of geosmin and MIB by oxygen nanobubbles during water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 443, 136535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, S.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y. Variation and removal of 2-MIB in full-scale treatment plants with source water from Lake Tai, China. Water Res. 2019, 162, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, T.; Yang, B.; Ding, C. Implications for emergency response to the severe odor incident occurred in source water: Potential odorants and control strategy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 67022–67031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.; Newcombe, G.; Sztajnbok, P. The application of powdered activated carbon for mib and geosmin removal: Predicting pac doses in four raw waters. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1325–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lu, Q.; Hao, H.; Wei, Q.; Shi, B.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Evaluation of the treatability of various odor compounds by powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2019, 156, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Wang, Q.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Yang, M.; Yu, J. Algal organic matter impact on 2-methylisopropanol and geosmin adsorption by activated carbon: Variation with algae growth and decay, prediction by fluorescence surrogates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 320, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, A.; Fowler, G.D.; Graham, N.J. Insights into chemical regeneration of activated carbon for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chestnutt, T.E., Jr.; Bach, M.T.; Mazyck, D.W. Improvement of thermal reactivation of activated carbon for the removal of 2-methylisoborneol. Water Res. 2007, 41, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Hofmann, R. The effect of water temperature on the removal of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin by preloaded granular activated carbon. Water Res. 2020, 183, 116065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Ando, N.; Sasaki, H.; Matsushita, T.; Ohno, K. Branched pore kinetic model analysis of geosmin adsorption on super-powdered activated carbon. Water Res. 2009, 43, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, Y.; Nakao, S.; Sakamoto, A.; Taniguchi, T.; Pan, L.; Matsushita, T.; Shirasaki, N. Adsorption capacities of activated carbons for geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol vary with activated carbon particle size: Effects of adsorbent and adsorbate characteristics. Water Res. 2015, 85, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Gao, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, J. Process optimization and mechanism revealing of KMnO4 pre-oxidation coupled powdered activated carbon adsorption for 2-MIB removal. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-P.; Zang, P.; Li, Y.-M.; Bi, D.-S. TiO2-Powdered Activated Carbon (TiO2/PAC) for Removal and Photocatalytic Properties of 2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) in Water. Water 2021, 13, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamyadi, A.; Henderson, R.; Stuetz, R.; Hofmann, R.; Ho, L.; Newcombe, G. Fate of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in full-scale water treatment plants. Water Res. 2015, 83, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauderdale, C.V.; Aldrich, H.C.; Lindner, A.S. Isolation and characterization of a bacterium capable of removing taste- and odor-causing 2-methylisoborneol from water. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4135–4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaria, S.; Nir, S.; van Rijn, J. Combined adsorption and degradation of the off-flavor compound 2-methylisoborneol in sludge derived from a recirculating aquaculture system. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, R.W.; Sandusky, P. Biotransformations of 2-Methylisoborneol by Camphor-Degrading Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Zhou, B.; Shi, C.; Yu, L.; Zhang, C.; Gu, J. Biodegradation of 2-methylisoborneol by bacteria enriched from biological activated carbon. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Li, X.; Cui, Y.; Xu, L.; Huo, S.; Zou, B.; Qian, J.; Ma, A.; et al. Removal of Taste and Odor Compounds from Water: Methods, Mechanism and Prospects. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowall, B.; Hoefel, D.; Newcombe, G.; Saint, C.P.; Ho, L. Enhancing the biofiltration of geosmin by seeding sand filter columns with a consortium of geosmin-degrading bacteria. Water Res. 2009, 43, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Hoefel, D.; Bock, F.; Saint, C.P.; Newcombe, G. Biodegradation rates of 2-methylisoborneol (MIB) and geosmin through sand filters and in bioreactors. Chemosphere 2007, 66, 2210–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Hofmann, R. Adsorption and biodegradation of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin in drinking water granular activated carbon filters: A review and meta-analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, B.; Ding, C.; Wang, C.; Pan, M.; Ma, W.; Yu, J. Variation and mitigation of musty, septic, chemical, grassy, fishy odors and corresponding odorants in a full-scale drinking water treatment plant with advanced treatments. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbusinski, K.; Kalemba, K.; Kasperczyk, D.; Urbaniec, K.; Kozik, V. Biological methods for odor treatment—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 152, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, T.; Shao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Song, W.; Liang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, J. Biodegradation of 2-Methylisoborneol (2-MIB) by Single-Bacterium Isolations from Biological Filters in Drinking Water Treatment Plants. ACS ES&T Water 2023, 3, 3153–3160. [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Ziółek, M.; Nawrocki, J. Catalytic ozonation and methods of enhancing molecular ozone reactions in water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 639–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, X. Evaluating the Comparative Toxicity of DBP Mixtures from Different Disinfection Scenarios: A New Approach by Combining Freeze-Drying or Rotoevaporation with a Marine Polychaete Bioassay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10552–10561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Chen, Z.; Xu, B.; Xu, Z. Degradation of 2-methylisoborneol in drinking water by bauxite catalyzed ozonation. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.-Aqua 2008, 57, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, P.; Sun, D. Mechanism investigation of catalyzed ozonation of 2-methylisoborneol in drinking water over aluminum (hydroxyl) oxides: Role of surface hydroxyl group. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gallagher, D.L.; Dietrich, A.M.; Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, W.; Yu, J.; Yang, M. Data Analytics Determines Co-occurrence of Odorants in Raw Water and Evaluates Drinking Water Treatment Removal Strategies. Environ. Sci Technol 2021, 55, 16770–16782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yang, K.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Wen, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Xia, P.; Zhang, D. Simultaneous removal of multiple odorants from source water suffering from septic and musty odors: Verification in a full-scale water treatment plant with ozonation. Water Res. 2016, 100, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchet, A.; Laîné, J. Efficiency of membrane processes for taste and odor removal. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2005, 51, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wu, Q.; Shu, J.; Chen, C.; Tiraferri, A.; Liu, B. Efficient removal of organic matters and typical odor substances in rural drinking water using Ozone-BAC-UF combined system to meet new water quality standards in China. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 327, 124899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Qu, Q.; von Gunten, U.; Chen, C.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y. Comparison of methylisoborneol and geosmin abatement in surface water by conventional ozonation and an electro-peroxone process. Water Res. 2017, 108, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.; Burlingame, G.; Ikehata, K.; Furatian, L.; Suffet, I.H. The effect of pH on taste and odor production and control of drinking water. J. Water Supply: Res. Technol.-Aqua 2022, 71, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, D.; Hwang, T.-M.; Lee, Y. Oxidation kinetics of algal-derived taste and odor compounds during water treatment with ferrate(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capodaglio, A.G. Critical Perspective on Advanced Treatment Processes for Water and Wastewater: AOPs, ARPs, and AORPs. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbacher, A.; von Sonntag, J.; von Sonntag, C.; Schmidt, T.C. The •OH Radical Yield in the H2O2 + O3 (Peroxone) Reaction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9959–9964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutschera, K.; Börnick, H.; Worch, E. Photoinitiated oxidation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol by irradiation with 254 nm and 185 nm UV light. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2224–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-A.; Nam, H.-L.; Choi, J.-W.; Ha, J.; Lee, S.-H. Oxidation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol by the photo-Fenton process: Kinetics, degradation intermediates, and the removal of microcystin-LR and trihalomethane from Nak-Dong River water, South Korea. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; He, G.; Li, J. Pilot-scale and mechanistic study of the degradation of typical odors and organic compounds in drinking water by a combined UV/H2O2-BAC process. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, S.C.; Pangotra, D.; Vieira, L.; Csepei, L.-I.; Sieber, V.; Wang, L.; Ponce de León, C.; Walsh, F.C. Electrochemical synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from water and oxygen. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2019, 3, 442–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Deng, N.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Z.-T.; Fan, L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, X. On-site H2O2 electro-generation process combined with ultraviolet: A promising approach for odorous compounds purification in drinking water system. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Li, M.; Shimizu, K.; Utsumi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, C.; Gao, Y.; Sugiura, N. Electrochemical degradation of geosmin using electrode of Ti/IrO2–Pt. Desalination 2011, 265, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Z.; Deng, L.; Gao, N. Removal of 2-MIB and geosmin by electrogenerated persulfate: Performance, mechanism and pathways. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ma, Z.; Yang, X. Fundamentals of TiO2 Photocatalysis: Concepts, Mechanisms, and Challenges. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiou, T.; Triantis, T.M.; Kaloudis, T.; Papaconstantinou, E.; Hiskia, A. Photocatalytic degradation of water taste and odour compounds in the presence of polyoxometalates and TiO2: Intermediates and degradation pathways. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2014, 286, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, L. The destruction of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin using titanium dioxide photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 44, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pestana, C.J.; Robertson, P.K.J.; Edwards, C.; Wilhelm, W.; McKenzie, C.; Lawton, L.A. A continuous flow packed bed photocatalytic reactor for the destruction of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin utilising pelletised TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, P.K.J.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Lawton, L.A.; Bellu, E. A study of the kinetic solvent isotope effect on the destruction of microcystin-LR and geosmin using TiO2 photocatalysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2011, 108-109, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Li, F.; Zhao, M.; Xu, L.; Fang, S. A comparative study on photoelectrochemical performance of TiO2 photoanodes enhanced by different polyoxometalates. Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 30, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Wang, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, X.; Zhou, B. Effect of the wavelength on the pathways of 2-MIB and geosmin photocatalytic oxidation in the presence of Fe-N co-doped TiO2. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. TiO2-based catalysts for photothermal catalysis: Mechanisms, materials and applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 381, 135156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Principle and applications of microbubble and nanobubble technology for water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; O’shea, K.E. Ultrasonically induced degradation of 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2672–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Lo, S.-L. Advancing nanobubble technology for carbon-neutral water treatment and enhanced environmental sustainability. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.B.; Zou, J.J.; Dai, C.; Hu, J.; You, X.; Gao, M.-t.; Li, J.; Fu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Leong, K.H.; et al. Nanobubbles improve peroxymonosulfate-based advanced oxidation: High efficiency, low toxicity/cost, and novel collaborative mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, J.-O.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, H.-J.; Mok, Y.S. Decomposition of taste-and-odor compounds produced by cyanobacteria algae using atmospheric pressure plasma created inside a porous hydrophobic ceramic tube. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 247, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajouei, G.; Finklea, H.O.; Lin, L.-S. UV/chlorine advanced oxidation processes for degradation of contaminants in water and wastewater: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, M.J.; Hofmann, R.; Rcdsenfeldt, E.J. Low-pressure UV/Cl2 for advanced oxidation of taste and odor. J. AWWA 2012, 104, E58–E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Nam, S.-H.; Koo, J.-W.; Kim, E.; Hwang, T.-M. Comparative evaluation of 2-isopropyl-3-methoxypyrazine, 2-isobutyl-3-methoxypyrazine, and 2,4,6-trichloroanisole degradation by ultraviolet/chlorine and ultraviolet/hydrogen peroxide processes. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; El-Din, M.G.; Bolton, J.R. Assessment of the UV/Chlorine process as an advanced oxidation process. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Peng, F.; Yang, Z. Degradation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in water with UV/chlorine: Influencing factors, reactive species, and possible pathways. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, L.W.; Carter, K.E. Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Teng, Y.; Fan, M. Sulfate Radical and Its Application in Decontamination Technologies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 45, 1756–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, F.; Moradi, M. Application of peroxymonosulfate and its activation methods for degradation of environmental organic pollutants: Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 310, 41–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Shao, Y.; Gao, N.; Lu, X.; An, N.; Chu, W. Removal of β-cyclocitral by UV/persulfate and UV/chlorine process: Degradation kinetics and DBPs formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Jia, R.; Sun, S.; Feng, G.; Wang, M.; Sun, L.; Hou, L. Ultraviolet-mediated peroxymonosulfate diminution of earthy and musty compound trichloroanisole in water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, T.; Su, X.; Sun, P. Degradation of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in UV-based AOPs for photoreactors with reflective inner surfaces: Kinetics and transformation products. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Kuppers, S.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, N.; Zhang, D. Sulfate radical-based technology for the removal of 2-methylisoborneol and 2-methylisoborneol-producing algae in drinking water sources. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, N. Removal of carbamazepine from aqueous solution using sono-activated persulfate process. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2016, 29, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, D.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, A.; Yang, J.; Luo, L. Remediation of persistent organic pollutants in aqueous systems by electrochemical activation of persulfates: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, S.-Y.; Jiang, J.; Shen, Y.-M.; Song, Y.; Duan, J.-B.; Guo, Q. Enhanced peroxymonosulfate activation via complexed Mn(II): A novel non-radical oxidation mechanism involving manganese intermediates. Water Res. 2021, 193, 116856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ding, S.; Wang, P.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, H.; Chu, W. Simultaneous mitigation of disinfection by-product formation and odor compounds by peroxide/Fe(II)-based process: Combination of oxidation and coagulation. Water Res. 2021, 201, 117327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, B.; Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Ji, C.; Zhao, C.; Feng, L.; Feng, Y. Homogeneous/heterogeneous metal-catalyzed persulfate oxidation technology for organic pollutants elimination: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, T.Y.; Shin, W.S.; Hwang, I. Activation of Persulfate by Nanosized Zero-Valent Iron (NZVI): Mechanisms and Transformation Products of NZVI. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3625–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Xiao, S.; Zhong, H.; Yan, M.; Yang, X. Activation of persulfates by carbonaceous materials: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Metal-Free Carbocatalysis in Advanced Oxidation Reactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Si, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Luo, H.; Ren, N. B-doped graphitic porous biochar with enhanced surface affinity and electron transfer for efficient peroxydisulfate activation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 396, 125119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyekunle, D.T.; Zhou, X.; Shahzad, A.; Chen, Z. Review on carbonaceous materials as persulfate activators: Structure–performance relationship, mechanism and future perspectives on water treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 8012–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Yan, H.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Nian, Y. Activation of persulfate by blue algae biochar supported FeOX particles for tetracycline degradation: Performance and mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hansen, H.C.B.; Andersen, M.L.; Strobel, B.W.; Ma, H.; Dodge, N.; Jensen, P.E.; Lu, C.; Holm, P.E. Fast peroxydisulfate oxidation of the antibiotic norfloxacin catalyzed by cyanobacterial biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Du, X.; Jia, H.; Sun, H. P-doped biochar regulates nZVI nanocracks formation for superefficient persulfate activation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 130999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q. Simultaneous absorption of SO2 and NO from flue gas using ultrasound/Fe2+/heat coactivated persulfate system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 342, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Activated persulfate by the synergistic electro-activation and bimetals cathode (MBC@CF) leads to highly efficient degradation of tetracycline. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathne, H.N.P.; Angove, M.J.; Aryal, R.; Abuel-Naga, H.; Mainali, B. Removal of natural organic matter from source water: Review on coagulants, dual coagulation, alternative coagulants, and mechanisms. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Sillanpää, M. Removal of natural organic matter from drinking water by advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Analyte | Technology | Sample Volume | Extraction Phase | Recovery (%) | Detection Limit (ng/L) | Accuracy (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSM, 2-MIB | μSPE- GC/MS | 25 mL | C18 | 95.1–100.1% | GSM 2.0 2-MIB 4.3 | <7% | [102] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, THMs | HS-SPME- GC/MS | 5 mL | PDMS, CAR/PDMS, PDMS/DVB | 80–120% | GSM, 2-MIB 5–50 | <20% | [103] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 16 others | SPME-GC/MS/MS | 10 mL | DVB/CAR/PDMS | 70–120% | 2-MIB 17 GSM 5 | 2–20% | [104] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, IBMP, IPMP | LLE, SPE | 250 mL | Hexane and silica adsorption columns | 84.6–103% | 0.3–0.9 | 1.50–10.1% | [105] |
| GSM, 2-MIB | SPE-GC-MS/MS | 1 L | IRIS PLUS | 2-MIB > 90% GSM > 95% | 0.9–5.5 | GSM 8.5% 2-MIB 10.9% | [106] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 6 others | P&T+GC-MS | 25 mL | Nitrogen at 40 mL/min | 74.7–112.8% | MIB 0.3 GSM 0.2 | 2.6– 10.8% | [107] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 5 others | HS-SPME-GC-MS | 40 mL | DVB/CAR/PDMS | 2-MIB 84.1–119.0% GSM 87.7–95.9% | GSM 0.2 2-MIB 0.5 | GSM 7.0% 2-MIB 4.9% | [108] |
| GSM, 2-MIB | SBSE-TD-GC-MS | - | PDMS | 86–113% | 0.2 | <8% | [109] |
| GSM 2-MIB | SIDA-HS-SPME-GC/MS | - | PDMS/CAR/DVB | 81–121% | GSM 3.0 2-MIB 3.1 | GSM < 5.65% 2-MIB < 14.17% | [110] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 3 others | SPME-GC-ITDMS/MS | 15 mL | DVB/CAR/PDMS | 93–110% | <1.0 | 1–8% | [111] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 3 others | SPE-GC/MS | - | C18 | 93.5–108% | 0.5–1.5 | 1.58–7.31% | [112] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 49 others | LLE-GC-MS | 500 mL | - | 70–120% | 0.10–20.55 | <20% | [113] |
| GSM, 2-MIB | USAD-LLME | 12 mL | Tetrachloroethylene | 70–113% | GSM 2.0 2-MIB 9.0 | <11% | [114] |
| GSM, 2-MIB, and 6 others | PT-GC/MS | 25 mL | Nitrogen at 40 mL/min | 80.54–114.91% | <1.5 | 3.38– 8.59% | [115] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J. A Review of the Sources, Monitoring, Detection, and Removal of Typical Olfactory Substances Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol. Water 2025, 17, 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081236
Wang M, Xu Y, Xie Y, Yang L, Zhang J. A Review of the Sources, Monitoring, Detection, and Removal of Typical Olfactory Substances Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol. Water. 2025; 17(8):1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081236
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mingyang, Yufeng Xu, Yiping Xie, Liu Yang, and Jun Zhang. 2025. "A Review of the Sources, Monitoring, Detection, and Removal of Typical Olfactory Substances Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol" Water 17, no. 8: 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081236
APA StyleWang, M., Xu, Y., Xie, Y., Yang, L., & Zhang, J. (2025). A Review of the Sources, Monitoring, Detection, and Removal of Typical Olfactory Substances Geosmin and 2-Methylisoborneol. Water, 17(8), 1236. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081236






