The Impact of the Construction of Large Reservoirs on the Cultural Landscape: A Case Study of the Shimen Reservoir, Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Did the construction of the Shimen Reservoir have any real effect on the residents of the original community?
- How can the old and large-scale government dormitories be renovated and adapted for reuse by the community?
- In the face of climate change, how can the reservoir strike a balance between the tourism industry and the maintenance of the natural environment?
2. Literature Review
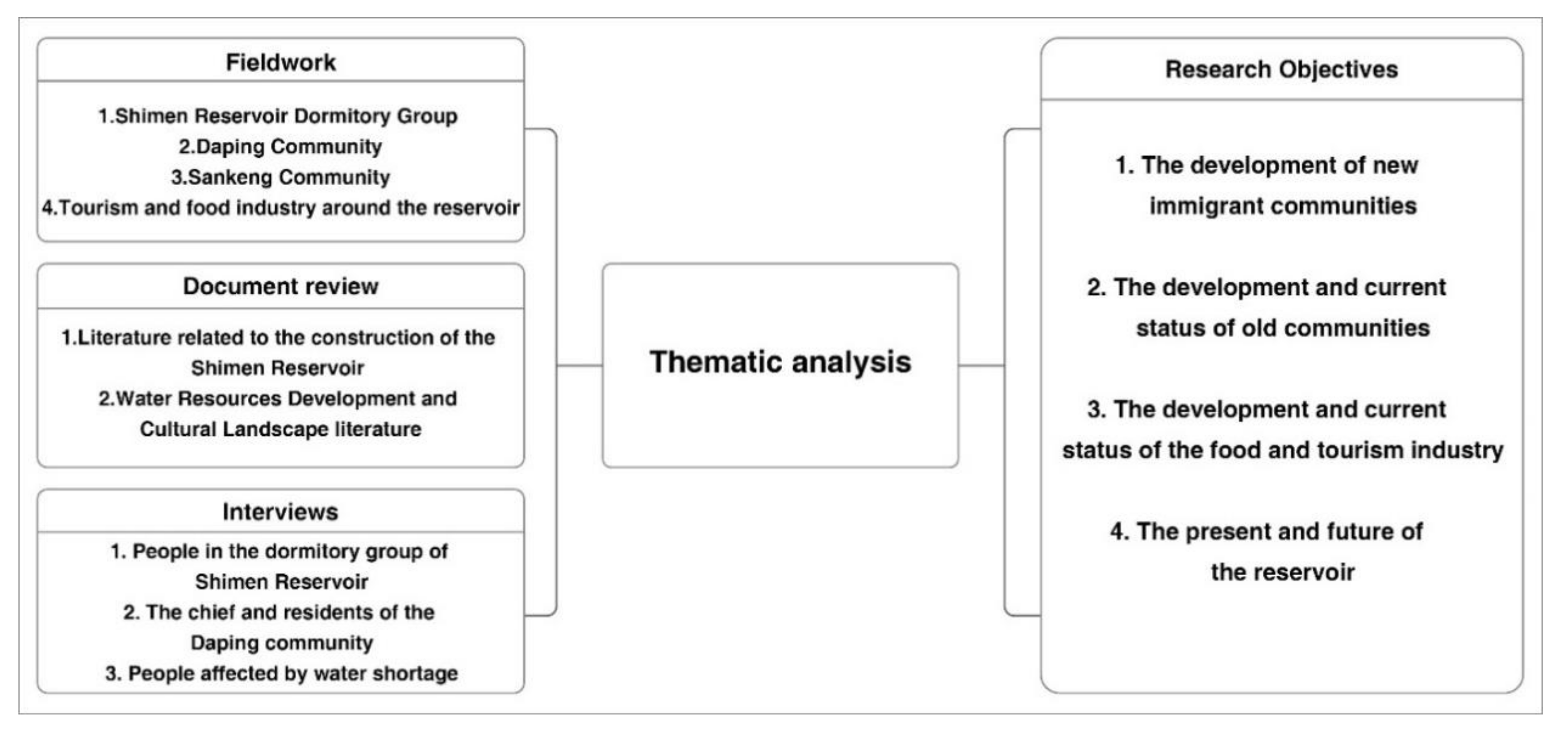
3. Methods
3.1. Fieldwork
- Sankeng Community.
- Shiyifen Northern Region Water Resources Office and Shimen Reservoir dormitory group.
- Daping Community.
- The Erping area (the dormitory has been demolished).
- Nanyuan Park (former Shimen Reservoir Construction Quarry and later Asian Paradise).
3.2. Document Review
3.3. Interviews
- Residents living in the Shimen Project area.
- Those who have been involved in activities and organizations in the local community for a long time.
- Residents whose lives have been affected by changes in the reservoir (water outages).
- Whether the government’s planning and renovation in response to the community development has exerted the necessary influence.
- The nature of the changes in the community during the construction of the reservoir and the current situation.
- Whether the community has been renovated and planned as in the Shimen Urban Planning Area.
- How do we view the current tourism industry and the future development of the reservoir?
- Whether the siltation of the reservoir has affected the life of Taoyuan when it is facing a major water outage.
- From the perspective of cultural landscape development, how do we balance community development and economic benefits?
- Whether the government has made positive contributions to the development of the cultural landscape.
- IV1, a local teacher who used to live in the Dam Engineering Office dormitory and later moved to the Stone Authority dormitory.
- IV2, an owner of a live fish restaurant, who had moved out of Stonegate Canyon as an indigenous person and came back to the reservoir to run a live fish restaurant.
- IV3, an engineer who lives in Taixi and is unable to live normally because of the water cut-off in the reservoir.
- IV4, a housewife living in Bade, Taoyuan, whose life was affected by the reservoir’s water failure.
- IV5, a local chief whose ancestors have been cultivating the local land temple and who is familiar with the local development and construction process of the reservoir.
- IV6, a local resident who has lived in the community around the reservoir since childhood and is involved in local affairs.
- Reservoir Newcomers and Dormitory Clusters.
- The Current State of the Old Stone Gate Neighborhood—Daping Community.
- The Current State of the Old Stone Gate Neighborhood—Sankeng Community.
- The current situation of the sightseeing and amusement areas.
- The live fish tourism industry.
4. Results
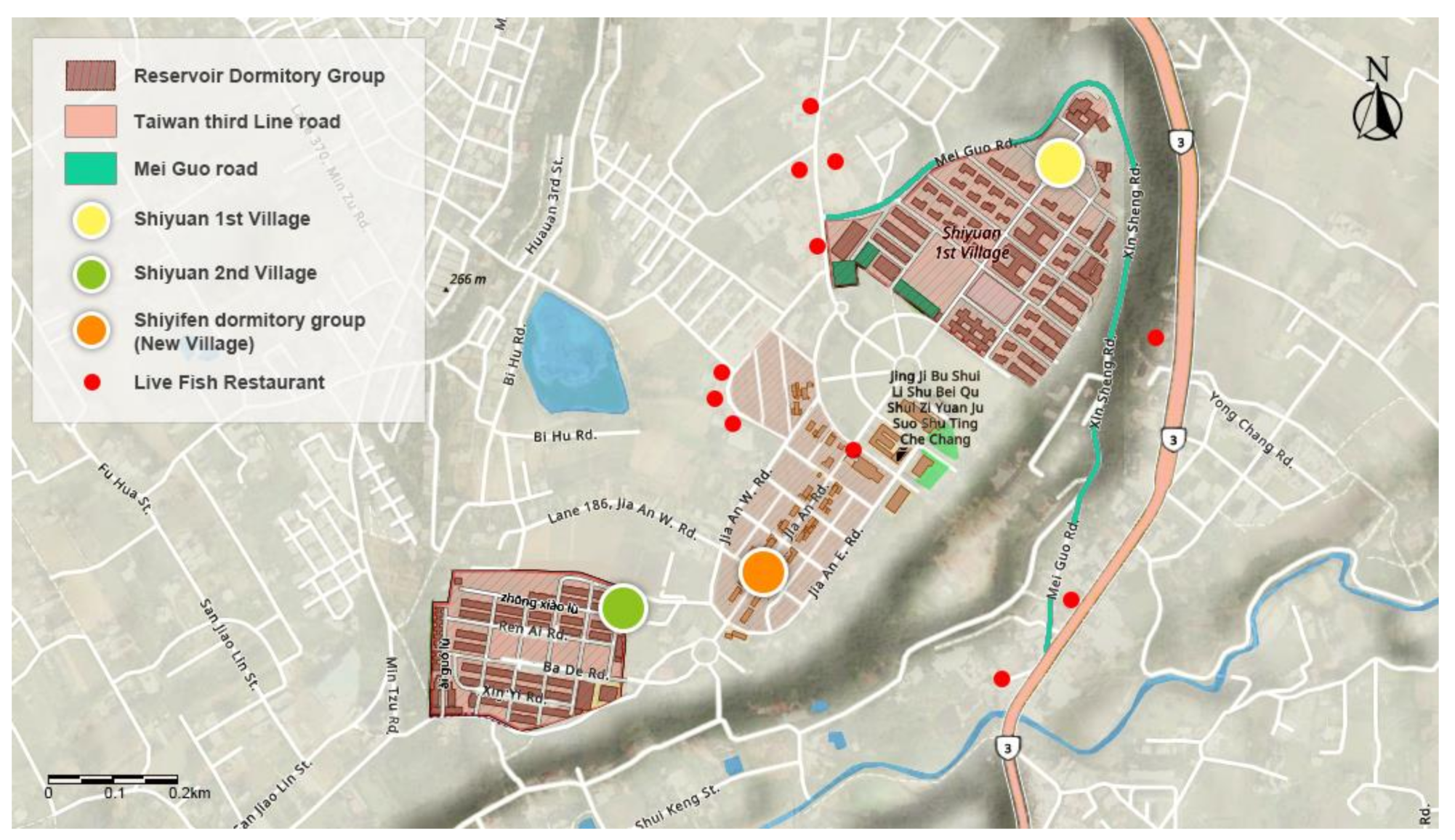
4.1. Reservoir Newcomers and Dormitory Clusters
- American consultants.
- Employees of the Shimen Reservoir Construction Committee (Northern Region Water Resources Office).
- Workers building the reservoir.
- Residents who have started commercial activities depending on the reservoir.
4.2. The Current State of the Old Stone Gate Neighborhood—Daping Community
4.3. The Current State of the Old Stone Gate Neighborhood—Sankeng Community
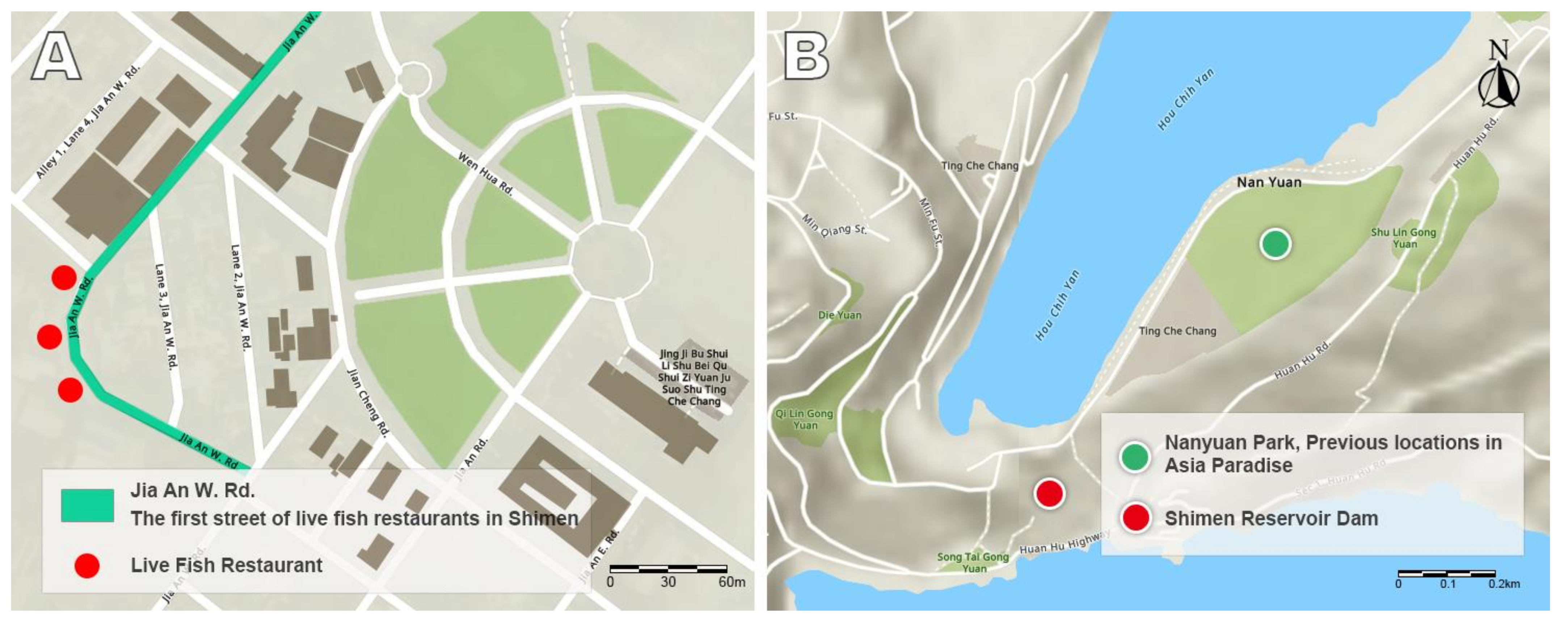
4.4. Current Situation of Sightseeing and Amusement Areas
4.5. Live Fish Tourism Industry
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- After the reservoir was built, the change in lifestyle, including the newly established dormitory clusters, has created a new type of community where community residents come together to reach a consensus and pursue better development. However, it has dramatically affected the original old streets and villages. Due to the constraints of urban planning, road planning, and other factors, the old streets could not develop and gradually declined. Only Sankeng has developed its unique tourism model, which continues to attract visitors.
- With the reservoir’s completion, the natural landscape has changed, and tourism development has changed the surrounding food culture. Still, only the tourism industry, which has a symbiotic relationship with the reservoir, can drive local economic growth and become an essential resource for the local economy.
- The impact of climate change on the function of the reservoir, in the face of reduced rainfall and the COVID-19 epidemic, not only affects the water supply and power generation, but also has a significant impact on the tourism industry of the reservoir, which seriously affects the lives and incomes of residents.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, P. Concept of Region in Geography and the Discourses on the Eastern Taiwan Studies. J. East. Taiwan Stud. 2000, 5, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.D. Landscape Diversity and Landscape Conservation. Sci. Dev. 2009, 7, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.C.; Lee, S.H.; Hou, J.S. The Revitalization of Degrading Cultural Landscape the Spatial Signification of Historical Railway of Tai-An Village. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 61, 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. Operational Guidelines for the Implementation of the World Heritage Convention; UNESCO World Heritage Center: Paris, France, 2019; Volume 1, p. 83. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.C. Spatial Analysis of Urban Landscape Change in Kaohsiung. Ocean. Cult. J. 2008, 4, 195–223. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.W. Hong Kong Style 2 Destroy Hong Kong; Zuni Icosahedron: Hong Kong, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H. Dialectics in Multitude an Exploration Into/Beyond Henri Lefebvre’s Conceptual Triad of Production of Space. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 55, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, S.M. Space and Capitalist Society. Lunching Cult. Studies Lingnan 2008, 10, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre, H.; Nicholson-Smith, D., Translators; The Production of Space; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1991; pp. 38–52.
- Chen, H.T. The Establishment and Operation of Irrigation Business in the Period of Taiwan under Japanese Occupation: Exemplified by the Irrigation of Chia-nan System. Fu Jen Hist. J. 2001, 12, 117–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, L.Y. From Canal to Reservoir: Construction and Land Use of Shimen Reservoir. Taoyuan J. Hist. 2016, 1, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, L.W. Study on the History of Land Development of Shimen Reservoir-The Beginning of the Construction of the Dam. Ecol. Taiwan 2004, 3, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, B.Y. Wei da Taiwan de Mei Yuan (1949–1957): V.S. de Beausset’s Order of Brilliant Star; Lin Bingyan: Taipei, Taiwan, 2004. [Google Scholar]
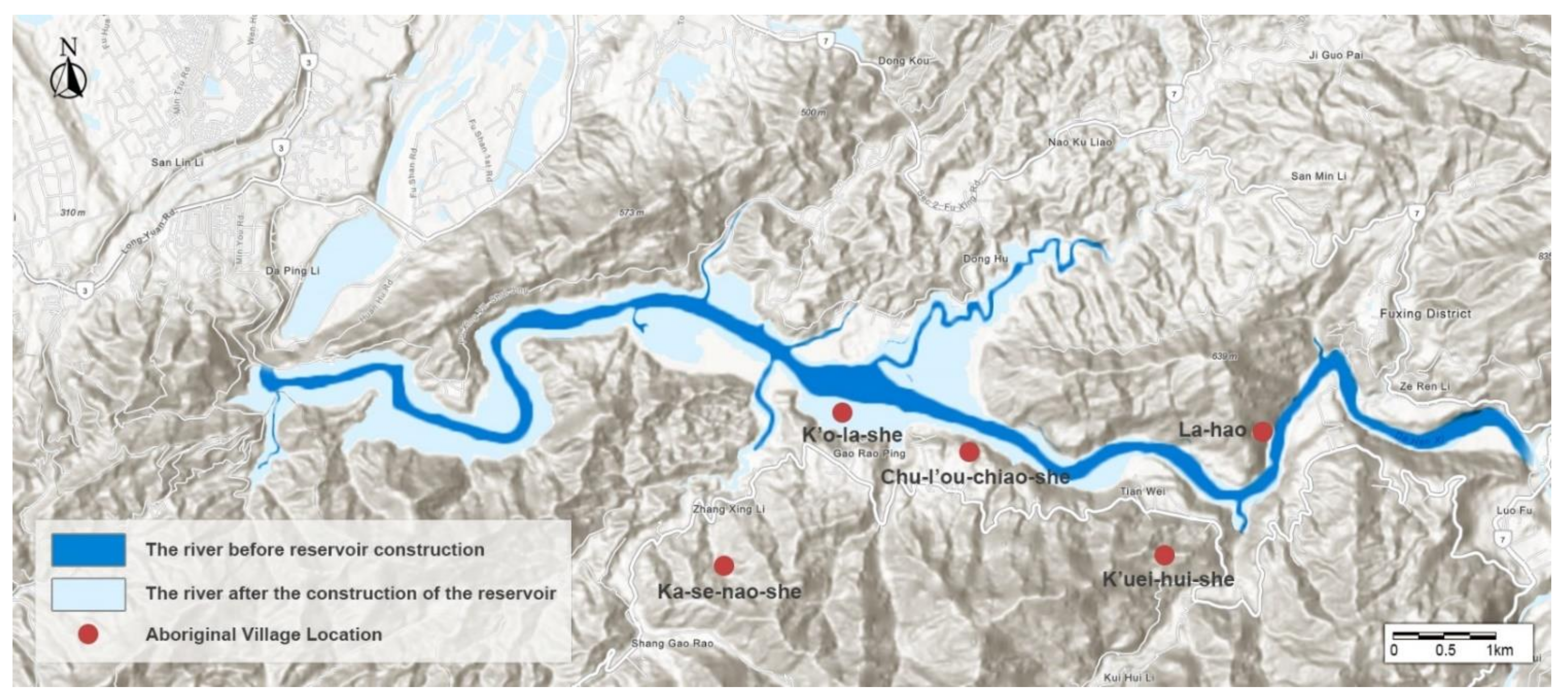
- Sun, C.T.; Yen, A.C. An Investigation of Watershed Management and Land Ethics-A Case of Indigenous Communities on Upstream Shimen Reservoir Catchments Area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2004, 66, 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shimen Reservoir Construction Committee. Shimen Reservoir Construction History; Shimen Reservoir Construction Committee: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, Y.N.; Shiau, J.T. Impacts of Optimal and Fuzzified Rule Curves on Water Deficits for Nanhua Reservoir. J. Taiwan Agric. Eng. 2017, 63, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, J.H.; Yu, T.Y. Taiwan’s Strategy for Efficient Use of Water Resources. CTCI Found. 2014, 5. Available online: https://www.ctci.org.tw/8838/publication/10798/15815/ (accessed on 30 August 2021).
- Li, Y.J. Water Resources Management in Response to Climate Change. Econ. Outlook Bimon. 2013, 147, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Water Resources Agency. Statistical Report on Water Storage Facility Operation in Taiwan; Water Resources Agency: Taichung, Taiwan, 2008; Volume 98, p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.C. Cultural Landscape and Community Development. Sci. Dev. 2009, 439, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Wittfogel, K.A. Oriental Despotism: A Comparative Study of Total Power; Yale University Press: New Haven, CN, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak, B. The Sociology of Irrigation: Two Taiwanese villages. In Economic Organization in Chinese Society; Willnott, W.E., Ed.; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1972; pp. 193–213. [Google Scholar]
- Drakou, E.G.; Kallimanis, A.S.; Sgardelis, S.P.; Pantis, J.D. Landscape structure and habitat composition in reservoirs, lakes, and rivers. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2008, 24, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, D.M.; McCully, P.; Pringle, C.M. Global-Scale Environmental Effects of Hydrological Alterations: Introduction. BioScience 2000, 50, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popp, A.; Hoagland, D.K. Changes in benthic community composition in response to reservoir aging. Hydrobiologia 1995, 306, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havel, J.E.; Lee, C.E.; Vander Zanden, J.M. Do Reservoirs Facilitate Invasions into Landscapes? BioScience 2005, 55, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daus, M.; Koberger, K.; Gnutzmann, N.; Hertrich, T.; Glaser, R. Transferring Water While Transforming Landscape: New Societal Implications, Perceptions and Challenges of Management in the Reservoir System Franconian Lake District. Water 2019, 11, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bär, S. Ganzheitliches Tourismus-Marketing. In Die Gestaltung Regionaler Kooperationsbeziehungen; Deutscher Universitäts-Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-8350-0275-3. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.P. A Study of the Transformation of Cultural Landscape with the Viewpoint of Irrigation Constructions by the Example of Taoyuan County throughout the Century (1900–2000). J. Archit. 2013, 85, 77–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.C. Rural Social Relations from the Development of Taiwan’s Farmland Water Resources in the Qing Dynasty. Taiwan Hist. 1985, 36, 107–150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.H. The Development of Irrigation and the Change of Spatial Organization in Tao-Yuan Tableland. Dep. Geogr. NTNU 1979, 5, 49–77. Available online: http://rportal.lib.ntnu.edu.tw/handle/20.500.12235/23667 (accessed on 21 October 2020).
- Zhao, D.; Xiao, M.; Huang, C.; Liang, Y.; An, Z. Landscape Dynamics Improved Recreation Service of the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, J.; Luo, S.; Yang, Y.; Qin, P.; Qi, P.; Li, Q. Spatiotemporal Evolution and the Influencing Factors of Tourism-Based Social-Ecological System Vulnerability in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossel, H. Indictors for Sustainable Development. Theory, Method, Applications; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Yin, M.H.; Yang, X.Z.; Yao, Z.Z. Spatio-temporal evolution and impact mechanism of socio-ecological system vulnerability in poor mountainous tourist destinations: Taking dabie mountain area as example. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1663–1679. Available online: http://rwdl.xisu.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12325.shtml (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Huang, C.; Huang, X.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Teng, M.; Wang, P. Land use/cover change in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China: Reconciling the land use conflicts between development and protection. CATENA 2019, 175, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. A Review on the Adaptability of Tourism and Social-Ecosystem. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 2018, 11, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.K.; Lin, B.H.; Ji, S.Y. Assessment of man-made and natural rehabilitation of the collapsed land in the catchment area of Shimen Reservoir after Typhoon Avery. Sinotech Eng. 2014, 124, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.T. An Investigation of Human-Land Relationship and Social-Ecological Systems Resilience-A Case on Upstream Shimen Reservoir Catchments Area. Land Issues Res. Q. 2021, 32, 1–64. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11296/cc2jvv (accessed on 15 September 2021).
- Casado-Arzuaga, I.; Onaindia, M.; Madariaga, I.; Verburg, P.H. Mapping recreation and aesthetic value of ecosystems in the Bilbao Metropolitan Greenbelt (northern Spain) to support landscape planning. Landsc. Ecol. 2014, 29, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleo-Torres, A.; Gurley, K.; Pinelli, J.-P.; Baradaranshoraka, M.; Zhao, M.; Suppasri, A.; Peng, X. Vulnerability of Florida residential structures to hurricane induced coastal flood. Eng. Struct. 2020, 220, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Gardner, T.A.; Bennett, E.M.; Balvanera, P.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.; Daw, T.; Folke, C.; Hill, R.; Hughes, T.P.; et al. Advancing Sustainability through Mainstreaming a Social-Ecological Systems Perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 14, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, F. Henri Lefebvre’s Theory of the Production of Space and the Critical Theory of Communication. Commun. Theory 2019, 29, 129–150. [Google Scholar]
- Georgousis, E.; Savelidi, M.; Savelides, S.; Holokolos, M.-V.; Drinia, H. Teaching Geoheritage Values: Implementation and Thematic Analysis Evaluation of a Synchronous Online Educational Approach. Heritage 2021, 4, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, P.H. Comparison of data analysis of different qualitative research methods. In The Heteroglossia of Qualitative Research Methods; Zhou, P., Yang, H., Eds.; Institute of Sociology Nanhua University: Chiayi, Taiwan, 2007; pp. 127–149. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.P. The People’s Story of Mobility: A Study of the Migration due to the Construction of Reservoir in Taoyuan County. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 64, 67–96. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.M.; Yu, H.T.; Su, C.; Huang, Y.Y. Basic Research of the Effects of US Aid on Shimen Water Reservoir Engineering Techniques. In National Science Council Result Report; Project Number: NSC 100-2221-E-033-076; National Science Council: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.C. Water, Power and Mobilities: A Discussion of Fen Space Transformation of Shi-I-Fen Community due to the Construction of the Shi-Men Reservoir; Graduate School of Interior Design, Chung Yuan University: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2008; pp. 1–229. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, P.M. Research on community brand reengineering a study of Longtan Shiyifen. In Proceedings of the LSHI 2018: International Conference of Cultural Heritage and Design Innovation, Taoyuan, Taiwan, 25–27 October 2018; pp. 191–201. [Google Scholar]
- CHEN, S.R. The “Shiyifen Tourism and Cultural Park” is Now Open! Experience the Charm of the Family Village Where “Our Times”. Available online: https://udn.com/news/story/7206/4040881 (accessed on 15 March 2021).
- Shiyifen Cultural and Creative Platforms Construction and Counseling Project-“Revitalizing the old Shiyifen dormitory complex and shaping a new base for Taoyuan culture and creativity”. Available online: https://tour.tycg.gov.tw/zh-tw/majorproject/hightlight/10 (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Huang, C.L. Taoyuan County Historic Building “DaPing Bridge” Research and Restoration and Reuse Project; Cultural Affairs Bureau of Taoyuan County Government: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.L. Research and Restoration Project of “Longtan Township Sankeng Village Weng House” (Chuan Sheng Xin Ji Shop), a Historical Building in Taoyuan County; Cultural Affairs Bureau of Taoyuan County Government: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hakka, T.V. Exploring the Starting Point of Taiwan Taiwan Third line and Reproducing the Elegance of Erduantan Ferry Berth. Hakka TV. 2017. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ct2tI9aD2gM (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- CommonWealth Magazine Humanities Publishing Featured Author Group. Romantic Taiwan’s Third-Line Spiritual Footprints; CommonWealth Magazine & Hakka Committee: Taipei, Taiwan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.G. Travelogue of Shimen Reservoir. Educ. Mon. 1969, 22, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Minsheng Daily. Taoyuan County accelerated the development of local tourism business and held a joint meeting of committee members yesterday and approved a number of important proposals. In Taoyuan County Accelerated the Development of Local Tourism Business and Held a Joint Meeting of Committee Members Yesterday and Approved a Number of Important Proposals; Minsheng Daily: Taipei, Taiwan, 1971; p. 9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.S. The six phases of Taiwan’s four-year economic construction plan and the development of the tourism industry. Econ. Dly. News 1973, 6, 14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lai, B.H.; Wu, C.S. Shimen Reservoir and its Catchment Management Project. RDEC Bimon. 2008, 32, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.P. Rescue The Next Drop of Water, Our Island. 2011. Available online: https://ourisland.pts.org.tw/content/234 (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Ho, H.C.; Lin, B.S.; Chi, S.Y.; Chung, C.R.; Chiu, S.Y. Spatio-temporal Analysis for Landslide Change and Remediation Efficiency in Shih-Men Reservoir Watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. Technol. 2012, 7, 174–188. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.Y. Shimen tourism is frustrated, industry players criticize the authorities for not supporting. Econ. Dly. News 1994, 14. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H. Shimen Reservoir is famous for eating live fish. Econ. Dly. News 2001, 43, 29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.C. Key Success Factors of Shimen Fresh Fish Restaurant; Chung Yuan Christian University: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2018; pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, K.F.; Yang, Z.H.; Cheng, K.L.; Fan, W.T. Water and epidemic situation burned at both ends, Shimen Reservoir closed. United Daily News. Available online: https://udn.com/news/story/7324/5465078 (accessed on 20 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Chen, H.T. From Ponds to Irrigations: The Evolution of the Water Resources in Taoyuan Plateau. Dong Hwa J. Humanist. Stud. 2003, 5, 183–207. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y. The historical transition of the dispute of water conservancy in the irrigated area of Hòu Cun Zùn (1763–1945). Baisha J. GeoHistory 2012, 14, 65–169. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, T.C.; Cheng, F.L.; Pei, C.Y. Importance-Performance Analysis: Application of the Satisfaction of Visitors Dining at Shimen Fresh Fish Restaurants. J. Manag. Pract. Princ. 2008, 2, 89–104. [Google Scholar]
- Szivas, E. The Development of Wine Tourism in Hungary. Int. J. Wine Mark. 1999, 11, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvín, P.; Vizina, A.; Nesládková, M.; Blöcher, J.; Makovcová, M.; Moravec, V.; Hanel, M. Minimum Residual Flows for Catchments in the Czech Republic. Water 2021, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahseen, S.; Karney, B.W. Reviewing and critiquing published approaches to the sustainability assessment of hydropower. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vano, J.A.; Miller, K.; Dettinger, M.D.; Cifelli, R.; Curtis, D.; Dufour, A.; Olsen, J.R.; Wilson, A.M. Hydroclimatic extremes as challenges for the water management community: Lessons from oroville dam and hurricane harvey. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2019, 100, S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, S.; Hawkins, D. ‘NOT a Drill’: 188,000 Evacuated, Emergency Declared, as Calif’s Massive Oroville Dam Threatens Floods. Washington Post. 13 February 2017. Available online: https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2017/02/13/not-a-drill-thousands-evacuated-in-calif-as-oroville-dam-threatens-to-flood/ (accessed on 26 October 2021).
- Lin, C.Y.; Lin, C.R.; Jeng, J.H.; Liu, C.W. Reasons for Sediment Disaster Caused by Typhoon Aere on Shimen Reservoir Watershed. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 2006, 37-4, 327–336. [Google Scholar]
- Sýs, V.; Fošumpaur, P.; Kašpar, T. The Impact of Climate Change on the Reliability of Water Resources. Climate 2021, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ke, C.J.; Hsu, T.Y. A Study on the Flood Risk Maps to Cultural Assets-Taking New Taipei City as an Example. J. Archit. 2014, 88, 175–191. [Google Scholar]
- News Center. Because It Does Not even Come from the Typhoon! It Is the First Time in 56 Years That No Typhoon Has Hit Taiwan. 2020. Available online: https://tw.appledaily.com/life/20201013/B5V4TVY7OND43HGFLZUTNW55XQ/ (accessed on 20 April 2021). (In Chinese).
- Song, J.; Sciubba, M.; Kam, J. Risk and Impact Assessment of Dams in the Contiguous United States Using the 2018 National Inventory of Dams Database. Water 2021, 13, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Basic Data of the Interviewees | Age | Gender | Identity | Residence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 58 | Male | Teacher | Longtan |
| B | 60 | Male | Resident of Daping Neighborhood | Longtan |
| C | 55 | Male | Resident of Daping Neighborhood | Longtan |
| D | 42 | Male | Engineer | Dasi |
| E | 70 | Female | Retired housewife | Bade |
| F | 50 | Male | Live fish shop owner | Longtan |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-Z.; Chou, R.-J. The Impact of the Construction of Large Reservoirs on the Cultural Landscape: A Case Study of the Shimen Reservoir, Taiwan. Land 2021, 10, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111161
Chen L-Y, Hsieh W-Z, Chou R-J. The Impact of the Construction of Large Reservoirs on the Cultural Landscape: A Case Study of the Shimen Reservoir, Taiwan. Land. 2021; 10(11):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111161
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Li-Yu, Wen-Zhe Hsieh, and Rung-Jiun Chou. 2021. "The Impact of the Construction of Large Reservoirs on the Cultural Landscape: A Case Study of the Shimen Reservoir, Taiwan" Land 10, no. 11: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111161
APA StyleChen, L.-Y., Hsieh, W.-Z., & Chou, R.-J. (2021). The Impact of the Construction of Large Reservoirs on the Cultural Landscape: A Case Study of the Shimen Reservoir, Taiwan. Land, 10(11), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111161






