Horizon Scan of Transboundary Concerns Impacting Snow Leopard Landscapes in Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
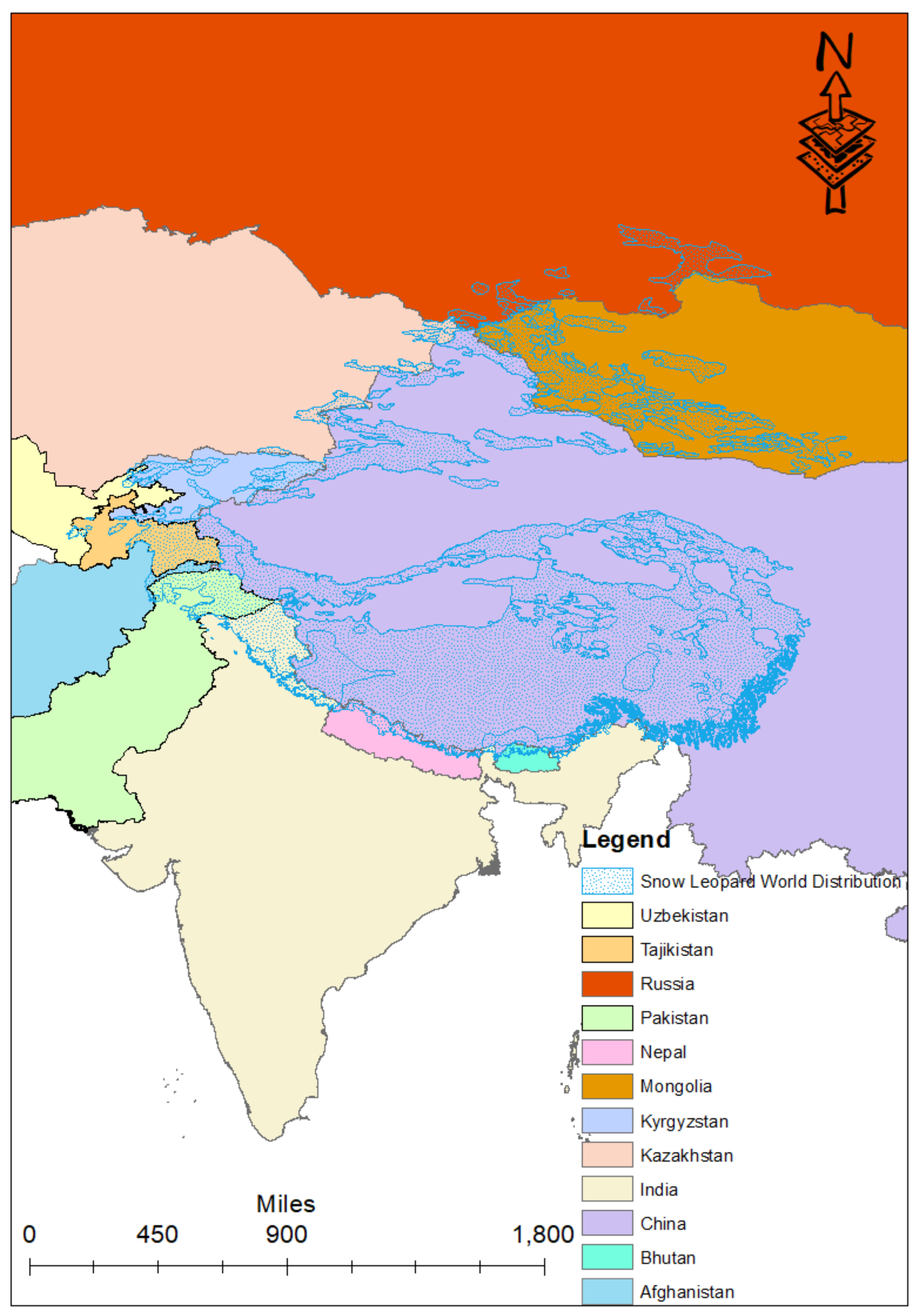
2. Transboundary Vulnerability Factors at the Global Snow Leopard Landscape Level
2.1. Political Factors
2.1.1. Habitat Fragmentation through Border Fencing
2.1.2. Non-Uniform Conservation Policies
2.2. Social Factors
2.2.1. Human–Snow Leopard Conflict
2.2.2. Increasing Human Population
2.3. Ecological Factors
2.3.1. Climate Change
2.3.2. Land Use and Land Cover Changes
2.4. Economic Factors
2.4.1. Habitat Fragmentation through Trade Corridors
2.4.2. Unsustainable Tourism in the Snow Leopard Landscape
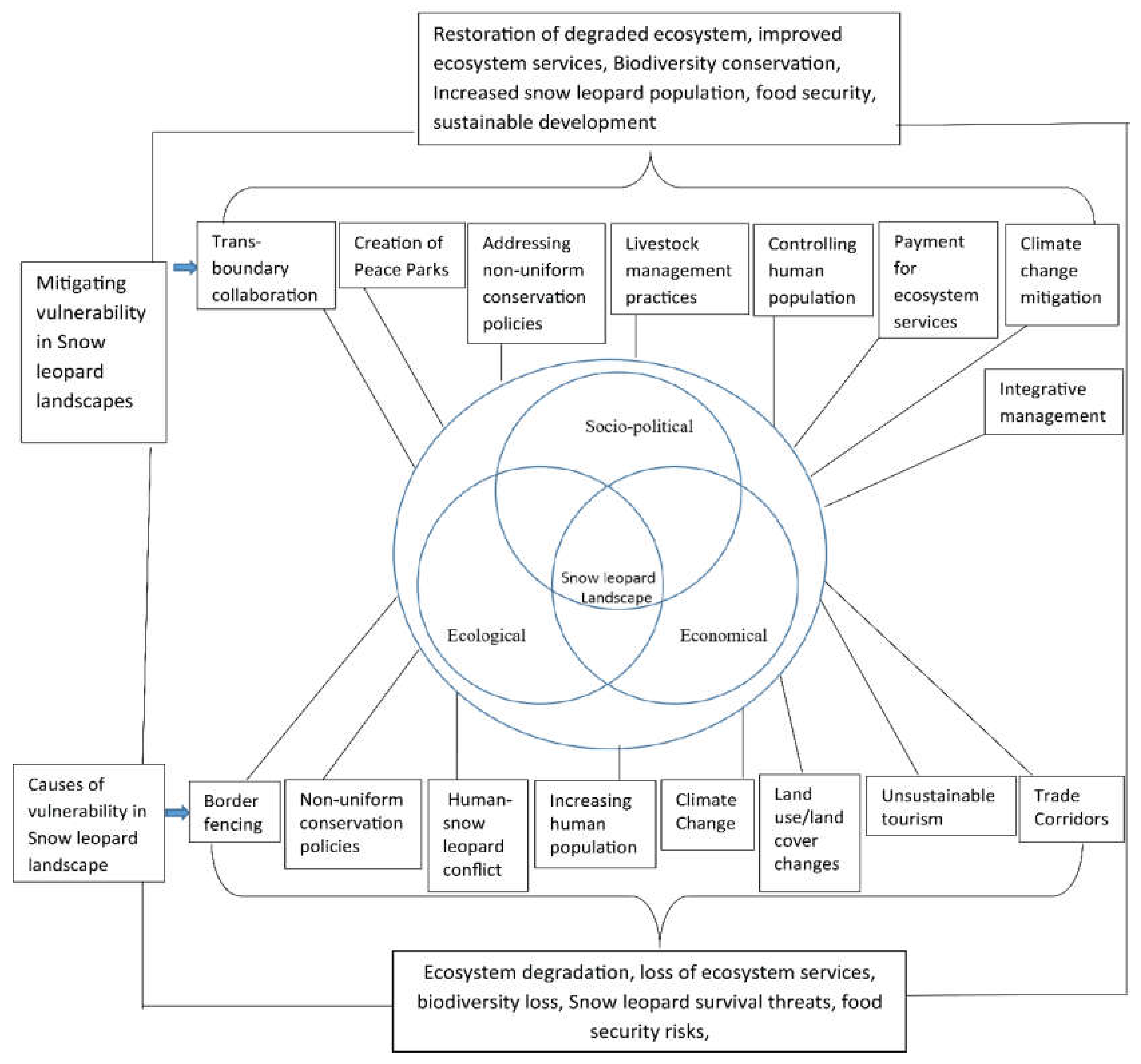
3. Implications of Snow Leopard Landscape Degradation
3.1. Political Implications
3.1.1. Implications Arising from Political Boundaries
3.1.2. Implications Arising from Non-Uniform Conservation Policies
3.2. Ecological Implications
3.2.1. Environmental Degradation
3.2.2. Implication of Climate Change
3.3. Social Implications
3.3.1. Human–Snow Leopard Conflict
3.3.2. Increasing Human Population
3.4. Economic Implications
3.4.1. Habitat Fragmentation through Trade Corridors
3.4.2. Unsustainable Tourism in the Snow Leopard Landscape
4. Possible Pathways to Handle Snow Leopard Transboundary Conservation Issues
4.1. Handling Political Boundaries Related Issues
4.1.1. Transboundary Collaboration (Regional Cooperation)
4.1.2. Creation of Peace Parks
4.1.3. Addressing Non-Uniform Conservation Policies
4.2. Handling Social Issues
4.2.1. Improving Livestock Management Practices
4.2.2. Controlling Human Population Growth
4.2.3. Payment for Ecosystem Services
4.3. Handling Ecological Issues
4.3.1. Climate Change Mitigation (Climate-Smart Technologies and Nature-Based Solutions)
4.3.2. Integrative Management of Transboundary Conservation Landscape
4.4. Handling Economic Issues
4.4.1. Environment-Friendly Trade Corridors in the Snow Leopard Landscape
4.4.2. Sustainable Tourism
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashid, W.; Shi, J.; Rahim, I.U.; Sultan, H.; Dong, S.; Ahmad, L. Research trends and management options in human-snow leopard conflict. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 242, 108413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.B.; Jackson, R.; Nadeem, M.S.; Janečka, J.E.; Hussain, S.; Beg, M.A.; Muhammad, G.; Qayyum, M. Food habits of the snow leopard Panthera uncia (Schreber, 1775) in Baltistan, Northern Pakistan. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2011, 57, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunquist, F.; Sunquist, M. The Wild Cat Book; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 2014; p. 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Brunton, D.; Ji, W.; Karmacharya, D.; McCarthy, T.; Bencini, R.; Raubenheimer, D. Multipronged strategy including genetic analysis for assessing conservation options for the snow leopard in the central Himalaya. J. Mammal. 2014, 95, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.S.; Cheng, Z.C.; Kun, S.; Riordan, P. A spotlight on snow leopard conservation in China. Integr. Zool. 2016, 11, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.S.; Cusack, J.J.; Pengju, C.; Kun, S.; Riordan, P. Conservation of snow leopards: Spill-over benefits for other carnivores? Oryx 2016, 50, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, T.M.; Fuller, T.K.; Munkhtsog, B. Movements and activities of snow leopards in Southwestern Mongolia. Biol. Conserv. 2005, 124, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, P.; Cushman, S.A.; Mallon, D.; Shi, K.; Hughes, J. Predicting global population connectivity and targeting conservation action for snow leopard across its range. Ecography 2016, 38, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Schaller, G.B.; McCarthy, T.M.; Wang, D.; Jiagong, Z.; Cai, P.; Basang, L.; Lu, Z. A Communal Sign Post of Snow Leopards (Panthera uncia) and Other Species on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Int. J. Biodivers. 2013, 2013, 370905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.K.; Bhatnagar, Y.V.; Mishra, C. Does livestock benefit or harm snow leopards? Biol. Conserv. 2015, 190, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mccarthy, T.M.; Wang, H.; Weckworth, B.V.; Schaller, G.B.; Mishra, C.; Lu, Z.; Beissinger, S.R. Climate refugia of snow leopards in High Asia. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 203, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Sharma, R.K.; Bhatnagar, Y.V. Change in snow leopard predation on livestock after revival of wild prey in the Trans-Himalaya. Wildl. Biol 2020, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bitabarova, A.G. Unpacking Sino-Central Asian engagement along the New Silk Road: A case study of Kazakhstan. J. Contemp. East Asia Stud. 2019, 7, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrington, J.D.; Tsering, D. Human-snow leopard conflict in the Chang Tang region of Tibet, China. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 237, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Tokman, D.; Córdoba-Aguilar, A.; Dáttilo, W.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Sánchez-Guillén, R.A.; Villalobos, F. Insect responses to heat: Physiological mechanisms, evolution and ecological implications in a warming world. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, M.; Songster, E.E. Studying the snow leopard: Reconceptualizing conservation across the China–India border. Br. J. Hist. Sci. 2016, 1, 169–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Weckworth, B.V.; McCarthy, T.M.; Liang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xing, R.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Jackson, R.; et al. Defining priorities for global snow leopard conservation landscapes. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 241, 108387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, H.C.; Lechner, A.M.; Walton, G.W.; Chan, F.K.S.; Cheshmehzangi, A.; Tan-Mullins, M.; Chan, H.K.; Sternberg, T.; Campos-Arceiz, A. Environmental Impacts of Infrastructure Development under the Belt and Road Initiative. Environments 2019, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cumming, G.S.; Peterson, G.D. Unifying Research on Social–Ecological Resilience and Collapse. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2017, 32, 695–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauerburg, R.A.M.; Diekmann, R.; Blanz, B.; Gee, K.; Held, H.; Kannen, A.; Möllmann, C.; Probst, W.N.; Rambo, H.; Cormier, R.; et al. Socio-ecological vulnerability to tipping points: A review of empirical approaches and their use for marine management. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penjor, U.; Wangdi, S.; Tandin, T.; Macdonald, D.W. Vulnerability of mammal communities to the combined impacts of anthropic land-use and climate change in the Himalayan conservation landscape of Bhutan. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.; Sinisalo, A.; Nüsser, M.; Garrard, R.; Eriksson, M. Contributions of the cryosphere to mountain communities in the Hindu Kush Himalaya: A review. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trouwborst, A.; Blackmore, A. Hot Dogs, Hungry Bears, and Wolves Running Out of Mountain—International Wildlife Law and the Effects of Climate Change on Large Carnivores. J. Int. Wildl. Law Policy 2020, 23, 212–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, J.L.; Wikramanayake, E.; Shrestha, R.; Areendran, G.; Gyeltshen, K.; Maheshwari, A.; Mazumdar, S.; Naidoo, R.; Thapa, G.J.; Thapa, K. Conservation and climate change: Assessing the vulnerability of snow leopard habitat to treeline shift in the Himalaya. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 150, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.H.; Schutgens, M.; Leader-Williams, N. What factors best explain attitudes to snow leopards in the Nepal Himalayas? PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, R.M.; Wangchuk, R. A Community-Based Approach to Mitigating Livestock Depredation by Snow Leopards. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2004, 9, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, P.S.; Takpa, J.; Parsons, M.H. Factors contributing to a striking shift in human–wildlife dynamics in Hemis National Park, India: 22 years of reported snowleopard depredation. Oryx 2017, 53, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laterra, P.; Barral, P.; Carmona, A.; Nahuelhual, L. Focusing Conservation Efforts on Ecosystem Service Supply May Increase Vulnerability of Socio-Ecological Systems. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goursi, U.H.; Anwar, M.; Bosso, L.; Nawaz, M.A.; Kabir, M. Spatial distribution of the threatened Asiatic black bear in northern Pakistan. Ursus 2021, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrouet, L.M.; Machado, J.; Villegas-Palacio, C. Vulnerability of socio-ecological systems: A conceptual Framework. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yong, D.L.; Choi, C.-Y.; Gibson, L. Transboundary Frontiers: An Emerging Priority for Biodiversity Conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2020, 35, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddiki, S. Border fencing in India: Between colonial legacy and changing security challenges. Int. J. Arts Sci. 2016, 7, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, A.M. Political borders should not hamper wildlife. Nature 2014, 508, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leki; Thinley, P.; Rajaratnam, R.; Shrestha, R. Establishing baseline estimates of blue sheep (Pseudois nayaur) abundance and density to sustain populations of the vulnerable snow leopard (Panthera uncia) in Western Bhutan. Wildl. Res. 2018, 45, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Ma, M.; Yang, W.; Blank, D.; Wu, Y.; Mccarthy, T.; Munkhtsog, B. Winter habitat use of snow leopards in Tomur National Nature Reserve of Xinjiang, Northwest China. J. Arid. Land 2012, 4, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitkalova, A.V.; Feng, L.; Rybin, A.N.; Gerber, B.D.; Miquelle, D.G.; Wang, T.; Yang, H.; Shevtsova, E.I.; Aramilev, V.V.; Ge, J. Transboundary cooperation improves endangered species monitoring and conservation actions: A case study of the global population of Amur leopards. Conserv. Lett. 2018, 11, e12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janecka, J.E.; Yu-guang, Z.; Di-qiang, L.; Munkhtsog, B.; Bayaraa, M.; Galsandorj, N.; Wangchuk, T.R.; Karmacharya, D.; McCarthy, T.; Li, J.; et al. Range-Wide Snow Leopard Phylogeography Supports Three Subspecies. J. Hered. 2017, 108, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherp, A. Cost of non-uniform climate policies. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2021, 11, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvin, K.; Clarke, L.; Krey, V.; Blanford, G.; Jiang, K.; Kainuma, M.; Kriegler, E.; Luderer, G.; Shukla, P.R. The role ofAsia in mitigating climate change: Results from the Asia modeling exercise. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, S251–S260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachel, S.M.; Mccarthy, K.P.; Mccarthy, T.M.; Oshurmamadov, N. Investigating the potential impact of trophy hunting of wild ungulates on snow leopard Panthera uncia conservation in Tajikistan. Oryx 2017, 51, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khatoon, R.; Hussain, I.; Anwar, M.; Nawaz, M.A. Diet selection of snow leopard (Panthera uncia) in Chitral, Pakistan. Turk. J. Zool. 2017, 41, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, T.; Hussain, S.; Mohammad, G.; Jackson, R.; Janecka, J.E.; Michel, S. Reconciling Sustainable Development of Mountain Communities With Large Carnivore Conservation. Mt. Res. Dev. 2012, 32, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Awan, S.; Khan, B.; Abbas, S.; Ali, A. A review of behavioural ecology and conservation of large predators inhabiting the Central Karakoram National Park (CKNP). J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2014, 5, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.; Bayrakcismith, R.; Tumursukh, L.; Johansson, O.; Sevger, P.; McCarthy, T.; Mishra, C. Vigorous dynamics underlie a stable population of the endangered snow leopard Panthera uncia in Tost Mountains, South Gobi, Mongolia. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.Z.; Khan, B.; Awan, M.S.; Begum, F. Livestock depredation by large predators and its implications for conservation and livelihoods in the Karakoram Mountains of Pakistan. Oryx 2017, 52, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, K.R.; Bhatnagar, Y.V.; Redpath, S.; Mishra, C. People, predators and perceptions: Patterns of livestock depredation by snow leopards and wolves. J. Appl. Ecol. 2013, 50, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, A.; Brunton, D.; Ji, W.; Barraclough, R.K.; Raubenheimer, D. Human–carnivore conflict: Ecological and economical sustainability of predation on livestock by snow leopard and other carnivores in the Himalaya. Sustain. Sci. 2014, 9, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashari, M.; Sills, E.; Peterson, M.N.; Cubbage, F. Hunting in Afghanistan: Variation in motivations across species. Oryx 2017, 52, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Xiao, L.; Lu, Z. Challenges of snow leopard conservation in China. Sci. China (Life Sci.) 2016, 59, 637–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangay, T.; Vernes, K. Human-wildlife conflict in the Kingdom of Bhutan: Patterns of livestock predation by large mammalian carnivores. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Gao, Y.; Lee, A.T.L.; Cering, L.; Shi, K.; Clark, S.G. Human-carnivore coexistence in Qomolangma (Mt. Everest) Nature Reserve, China: Patterns and compensation. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 197, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgail, T.; Fox, J.L.; Bhatnagar, Y.V. Carnivore-Caused Livestock Mortality in Trans-Himalaya. Environ. Manage. 2007, 39, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetri, M.; Odden, M.; Devineau, O.; Wegge, P. Patterns of livestock depredation by snow leopards and other large carnivores in the Central Himalayas, Nepal. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simms, A.; Moheb, Z.; Salahudin; Ali, H.; Ali, I.; Wood, T. Saving threatened species in Afghanistan: Snow leopards in the Wakhan Corridor. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2011, 68, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esipov, A.; Bykova, E.; Protas, Y.; Aromov, B. Central Asia: Uzbekistan. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity of the World: Conservation from Genes to Landscapes; McCarthy, T., Mallon, D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiddorj, T.N.; Alexander, J.S.; Samelius, G. Livestock depredation by large carnivores in the South Gobi, Mongolia. Wildl. Res. 2018, 45, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltsyn, M.; Poyarkov, A.; Spitsyn, S.; Kuksin, A.; Istomov, S.; Gibbs, J.P.; Jackson, R.M.; Castner, J.; Kozlova, S.; Karnaukhov, A.; et al. Northern Range: Russia. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity Of The World: Conservation From Genes To Landscapes; McCarthy, T.M., Mallon, D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardillo, M.; Purvis, A.; Sechrest, W.; Gittleman, J.L.; Bielby, J.; Mace, G.M. Human Population Density and Extinction Risk in the World’s Carnivores. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Shoemaker, S.P. A look at food security in China. npj Sci. Food 2018, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, R.K.; Mohanty, S.K.; Mishra, U.S. Population Trends, Distribution and Prospects in the Districts of India. In The Demographic and Development Divide in India: A District-Level Analyses; Mohanty, S.K., Mishra, U.S., Chauhan, R.K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 17–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S. Global warming and export competitiveness of agriculture sector: Evidence from heterogeneous econometric analysis of Pakistan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, G.W. A review of the relationships between human population density and biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2007, 82, 607–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.S.; Gopalaswamy, A.M.; Shi, K.; Hughes, J.; Riordan, P. Patterns of Snow Leopard Site Use in an Increasingly Human-Dominated Landscape. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmeyer, K.R.; Shaw, M.R.; Mackenzie, J.B.; Cameron, D.R. Landscape-scale indicators of biodiversity’s vulnerability to climate change. Ecosphere 2011, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Yu, X.; Yu, C.; Tayibazhaer, A.; Xu, F.; Skidmore, A.K.; Wang, T. Impacts of future climate and land cover changes on threatened mammals in the semi-arid Chinese Altai Mountains. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrington, J.D.; Li, J. Climate Change Impacts on Snow Leopard Range. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity of the World: Conservation from Genes to Landscapes; McCarthy, T.M., Mallon, D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–222. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2021 The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–223. [Google Scholar]
- Asad, F.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, E.; Muhammad, S.; Farhan, S.B.; Hussain, I.; Wazir, M.A.; Ahmed, M.; Esper, J. Are Karakoram temperatures out of phase compared to hemispheric trends? Clim. Dyn. 2017, 48, 3381–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spies, M. Mixed manifestations of climate change in high mountains: Insights from a farming community in northern Pakistan. Clim. Dev. 2020, 12, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, K.; Yanagawa, A.; Sasaki, T.; Rao, M.P.; Kanae, S. Socio-ecological Interactions in a Changing Climate: A Review of the Mongolian Pastoral System. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorg, A.; Bolch, T.; Stoffel, M.; Solomina, O.; Beniston, M. Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokorin, A.O. Assessment Report Climate Change and Its Impact on Ecosystems, Population and Economy of the Russian Portion of the Altai-Sayan Ecoregion; WWF Russia: Moscow, Russia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Talipova, E.; Shrestha, S.; Alimkulov, S.; Nyssanbayeva, A.; Tursunova, A.; Isakan, G. Influence of climate change and anthropogenic factors on the Ile River basin streamflow, Kazakhstan. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchenko, S.S.; Gorbunov, A.P.; Romanovsky, V.E. Permafrost warming in the Tien shan Mountains, Central Asia. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2007, 56, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholmatjanov, B.M.; Sulaymonova, N.N.; Petrov, Y.V.; Khujanazarov, T.; Abdikulov, F.I.; Tanaka, K. Analysis of Temperature Change in Uzbekistan and the Regional Atmospheric Circulation of Middle Asia during 1961–2016. Climate 2020, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, I.; Kassam, K.-A.; Senftl, T.; Zandler, H.; Samimi, C. Measurements meet human observations: Integrating distinctive ways of knowing in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan to assess local climate change. Clim. Chang. 2021, 165, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, B. Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 1729–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Qin, D.; Kang, S.; Qin, X. Characteristics and changes in air temperature and glacier’s response on the north slope of Mt. Qomolangma (Mt. Everest). Arct. Antarct. Alp. Res. 2011, 43, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adnan, M.; Nabi, G.; Kang, S.; Zhang, G.; Adnan, R.M.; Anjum, M.N.; Iqbal, M.; Ali, A.F. Snowmelt Runoff Modelling under Projected Climate Change Patterns in the Gilgit River Basin of Northern Pakistan. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2017, 26, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabin, T.P.; Krishnan, R.; Vellore, R.; Priya, P.; Borgaonkar, H.P.; Singh, B.B.; Sagar, A. Climate Change Over the Himalayas. In Assessment of Climate Change Over the Indian Region; Krishnan, R., Sanjay, J., Gnanaseelan, C., Mujumdar, M., Kulkarni, A., Chakraborty, S., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2020; pp. 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.B.; Wake, C.P.; Mayewski, P.A.; Dibb, J.E. Maximum temperature trends in the Himalaya and its vicinity: An analysis based on temperature records from Nepal for the period 1971–1994. J. Clim. 1999, 12, 2775–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khurshid, M.; Nafees, M.; Rahim, I.u.; Rashid, W. Impacts of Agriculture Land use Changes on Mobile Pastoral System in Naran Valley of Western Himalayan Northern Pakistan. Sarhad J. Agric. 2016, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Robeson, S.M.; Thapa, P.; Saikia, A. Land-use/land-cover change and forest fragmentation in the Jigme Dorji National Park, Bhutan. Phys. Geogr. 2016, 38, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Graf, H.-F. Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: A review. Clim. Chang. 2009, 94, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Zamanian, K.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Zarebanadkouki, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Degradation of Tibetan grasslands: Consequences for carbon and nutrient cycles. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilani, H.; Shrestha, H.L.; Murthy, M.S.R.; Phuntso, P.; Pradhan, S.; Bajracharya, B.; Shrestha, B. Decadal land cover change dynamics in Bhutan. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 148, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dame, J.; Schmidt, S.; Müller, J.; Nüsser, M. Urbanisation and socio-ecological challenges in high mountain towns: Insights from Leh (Ladakh), India. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 189, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhou, W. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of Precipitation and Its Relationship with Land Use/Cover Change on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Land 2021, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, P.; Huafu, J.; Khan, M.A.; Rashid, W.; Khan, S. Modification of Land Use/Land Cover and Its Impact on Groundwater in Peshawar City, Pakistan. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2022, 50, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsi, M.; Malaviya, S.; Oinam, G.; Joshi, P.K. A landscape approach for quantifying land-use and land-cover change (1976–2006) in middle Himalaya. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2010, 10, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, M.; Kim, K.; Joshi, C. Temporal mapping of deforestation and forest degradation in Nepal: Applications to forest conservation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 256, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.S.; Saranya, K.R.L. Earth observation data for assessment of nationwide land cover and long-term deforestation in Afghanistan. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2017, 155, 115–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, W.; Shi, J.; Rahim, I.U.; Qasim, M.; Baloch, M.N.; Bohnett, E.; Yang, F.; Khan, I.; Ahmad, B. Modelling Potential Distribution of Snow Leopards in Pamir, Northern Pakistan: Implications for Human–Snow Leopard Conflicts. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Tao, S.; Pueppke, S.G.; Espolov, T.E.; Beksultanov, M.; Chen, X.; Cai, X. Changes in land use/land cover and net primary productivity in the transboundary Ili-Balkhash basin of Central Asia, 1995–2015. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duulatov, E.; Xi, C.; Kurban, A.; Ndayisaba, B.; Monoldorova, A. Detecting Land Use/Land Cover change using Landsat Imagery: Jumgal District, Kyrgyzstan. Int. J. Geoinform. 2016, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breckle, S.-W.; Wuchere, W. Vegetation of the Pamir (Tajikistan): Land use and desertification problems. In Land Use Change and Mountain Biodiversity; Spehn, E.M., Liberman, M., Körner, C., Eds.; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis Group): Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 225–238. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Gang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Odeh, I.; Qi, J. Comparative assessment of grassland degradation dynamics in response to climate variation and human activities in China, Mongolia, Pakistan and Uzbekistan from 2000 to 2013. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 135, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiyama, A.; Takeuchi, W.; Shimada, S. Detection of Grassland Degradation Using MODIS Data in Mongolia. J. Arid. Land Stud. 2014, 24, 175–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg, T.; Tsolmon, R.; Middleton, N.; Thomas, D. Tracking desertification on the Mongolian steppe through NDVI and field-survey data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanova, E. Land use/cover change in Russia within the context of global challenges. Rom. J. Geogr. 2012, 56, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, L.S.; Campos-Arceiz, A.; Sloan, S.; Hughes, A.C.; Tiang, D.C.F.; Li, B.V.; Lechner, A.M. The scale of biodiversity impacts of the Belt and Road Initiative in Southeast Asia. Biol. Conserv. 2020, 248, 108691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Drivers of Land Use and Land Cover Change in the China-Mongolia-Russia Economic Corridor. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 2527–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naboureh, A.; Bian, J.; Lei, G.; Li, A. A review of land use/land cover change mapping in the China-Central Asia-West Asia economic corridor countries. Big Earth Data 2021, 5, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, A.H.; Li, W.; Hassan, M.; Nabi, G.; Mabey, P.T.; Islam, M.M.; Rashid, W.; Ujjan, S.A.; Memon, K.H. Biodiversity Governance and Management in Pakistan: A Way Forward Through the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2021, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-X.; Li, S.-Y. The analysis of the impact of the Belt and Road initiative on the green development of participating countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.M.; Chan, F.; Campos-Arceiz, A. Biodiversity conservation should be a core value of China’s Belt and Road Initiative. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, W.; Shi, J.; Rahim, I.u.; Dong, S.; Sultan, H. Issues and Opportunities Associated with Trophy Hunting and Tourism in Khunjerab National Park, Northern Pakistan. Animals 2020, 10, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S. The status of the snow leopard in Pakistan and its conflict with local farmers. Oryx 2003, 37, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A. A Siachen Peace Park: The Solution to a Half-Century of International Conflict? Mt. Res. Dev. 2002, 22, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xu, H.; Ahmed, W. Resolving strategic conflict for environmental conservation of glacial ecosystem: An attitudinal conflict resolution approach. Int. J. Glob. Warm. 2019, 18, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.E.; Gamble, R.; Roche, G.; Gawne, L. International relations and the Himalaya: Connecting ecologies, cultures and geopolitics. Aust. J. Int. Aff. 2021, 75, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, K.M.; Fiorella, K.J.; Gregory, G.H.; Kurz, D.J.; Seto, K.L.; Withey, L.S.; Brashares, J.S. War and wildlife: Linking armed conflict to conservation. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbach-Hertig, W.; Gleeson, T. Regional strategies for the accelerating global problem of groundwater depletion. Nat. Geosci. 2012, 5, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meadowcroft, J. Politics and scale: Some implications for environmental governance. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 61, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, E.G.; Elmhagen, B.; Glen, A.S.; Letnic, M.; Ludwig, G.; McDonald, R.A. Ecosystem restoration with teeth: What role for predators? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilman, E.A.; Wilman, E.N. Modeling outcomes of approaches to sustained human and snow leopard coexistence. Conserv. Biol. 2015, 30, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, R.; Redpath, S.; Mishra, C. The value of ecosystem services in the high altitude Spiti Valley, Indian Trans-Himalaya. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namgail, T.; Majumder, B.; Dadul, J. Himalayan Homestays: Fostering Human-Snow Leopard Coexistence. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity Of The World: Conservation From Genes To Landscapes; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutgens, M.G.; Hanson, J.H.; Baral, N.; Ale, S.B. Visitors’ willingness to pay for snow leopard Panthera uncia conservation in the Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal. Oryx 2018, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foggin, J.M. Depopulating the Tibetan Grasslands. Mt. Res. Dev. 2008, 28, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zakharenka, A.; Sharma, K.; Kochorov, C.; Rutherford, B.; Varma, K.; Seth, A.; Kushlin, A.; Lumpkin, S.; Seidensticker, J.; Laporte, B.; et al. The global snow leopard and ecosystem protection program. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity of the World: Conservation from Genes to Landscapes; McCarthy, T., Mallon, D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augugliaro, C.; Christe, P.; Janchivlamdan, C.; Baymanday, H.; Zimmermann, F. Patterns of human interaction with snow leopard and co-predators in the Mongolian western Altai: Current issues and perspectives. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 24, e01378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y. Effect of Degradation Intensity on Grassland Ecosystem Services in the Alpine Region of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abhijitha, C.S.; Areendran, G.; Raj, K.; Bhat, P.; Sahana, M. Habitat linkages for Asian elephants in Central Indian landscape. In Habitat, Ecology and Ekistics. Advances in Asian Human-Environmental Research; Rukhsana, Haldar, A., Alam, A., Satpati, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, E.W.; Mallon, D.; McCarthy, T.; Zahler, P.; Fisher, K. Global strategies for Snow Leopard conservation: A synthesis. In SNOW LEOPARDS, Biodiversity of the World: Conservation from Genes to Landscapes, 1st ed.; McCarthy, T., Mallon, D., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2016; pp. 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 127.Murali, R.; Lkhagvajav, P.; Saeed, U.; Kizi, V.A.; Jumabay-Uulu, K.; Nawaz, M.A.; Bhatnagar, Y.V.; Sharma, K.; Mishra, C. Valuation of Ecosystem Services in Snow Leopard Landscapes of Asia; Nature Conservation Foundation: Mysuru, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Atwood, T.B.; Valentine, S.A.; Hammill, E.; McCauley, D.J.; Madin, E.M.P.; Beard, K.H.; Pearse, W.D. Herbivores at the highest risk of extinction among mammals, birds, and reptiles. Sci. Adv. 2020, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, H.S.; McCauley, D.J.; Galetti, M.; Dirzo, R. Patterns, Causes, and Consequences of Anthropocene Defaunation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2016, 47, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirt, M.R.; Barnes, A.D.; Gentile, A.; Pollock, L.J.; Rosenbaum, B.; Thuiller, W.; Tucker, M.A.; Brose, U. Environmental and anthropogenic constraints on animal space use drive extinction risk worldwide. Ecol. Lett. 2021, 24, 2576–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Merenlender, A.M. Landscapes that work for biodiversity and people. Science 2018, 362, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, Ö.; Rauset, G.R.; Samelius, G.; McCarthy, T.; Andrén, H.; Tumursukh, L.; Mishra, C. Land sharing is essential for snow leopard conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2016, 203, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R. Fostering community-based stewardship of wildlife in Central Asia: Transforming Snow Leopards from pests into valued assets. In Rangeland Stewardship in Central Asia: Balancing Improved Livelihoods, Biodiversity Conservation and Land Protection; Squires, V., Ed.; SpringerLink: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foggin, J.M.; Lechner, A.M.; Emslie-Smith, M.; Hughes, A.C.; Sternberg, T.; Dossani, R. Belt and Road Initiative in Central Asia: Anticipating socioecological challenges from large-scale infrastructure in a global biodiversity hotspot. Conserv. Lett. 2021, 14, e12819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, J.H.; Schutgens, M.; Baral, N. What explains tourists’ support for snow leopard conservation in the Annapurna Conservation Area, Nepal? Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2019, 24, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Chen, P.; Damerell, P.; Youkui, W.; Hughes, J.; Shi, K.; Riordan, P. Human wildlife conflict involving large carnivores in Qilianshan, China and the minimal paw-print of snow leopards. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 187, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Mishra, C. Living with large carnivores: Predation on livestock by the snow leopard (Uncia uncia). J. Zool. 2006, 268, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, F.; D’Amico, M.; Barrientos, R. No Planet for Apes? Assessing Global Priority Areas and Species Affected by Linear Infrastructures. Int. J. Primatol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, K.; Ahmad, T.; Khan, M.A. Use, exploitation and prospects for conservation: People and plant biodiversity of Naltar Valley, northwestern Karakorums, Pakistan. Biodivers. Conserv. 2002, 11, 715–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Kindlmann, P. Implications of landscape genetics and connectivity of snow leopard in the Nepalese Himalayas for its conservation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhadinia, M.S.; Maheshwari, A.; Nawaz, M.A.; Ambarlı, H.; Gritsina, M.A.; Koshkin, M.A.; Rosen, T.; Hinsley, A.; Macdonald, D.W. Belt and Road Initiative may create new supplies for illegal wildlife trade in large carnivores. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmail, N.; Wintle, B.C.; Sas-Rolfes, M.T.; Athanas, A.; Beale, C.M.; Bending, Z.; Dai, R.; Fabinyi, M.; Gluszek, S.; Haenlein, C.; et al. Emerging illegal wildlife trade issues: A global horizon scan. Conserv. Lett. 2020, 13, e12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, K.L. The side effects of mass tourism: The voices of Bali islanders. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2019, 25, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorpas, A.A.; Voukkali, I.; Pedreño, J.N. Tourist area metabolism and its potential to change through a Proposed Strategic Plan in the framework of Sustainable Development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3609–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akis, A. The effects of mass tourism: A case study from Manavgat (Antalya—Turkey). Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 19, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rico, A.; Martínez-Blanco, J.; Montlleó, M.; Rodríguez, G.; Tavares, N.; Arias, A.; Oliver-Solà, J. Carbon footprint of tourism in Barcelona. Tour. Manag. 2019, 70, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.; Newman, S.P.; Stead, S.M. Community perceptions link environmental decline to reduced support for tourism development in small island states: A case study in the Turks and Caicos Islands. Mar. Policy 2019, 108, 103671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantinato, E. The impact of (mass) tourism on coastal dune pollination networks. Biol. Conserv. 2019, 236, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soboleva, E.; Krivokhizh, S. Chinese initiatives in Central Asia: Claim for regional leadership? Eurasian Geogr. Econ. 2021, 62, 634–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Shao, G.; Guo, X. An indicator framework for assessing cooperative cross-border conservation in the Karakoram-Himalayan region. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Chettri, N.; Yang, Y.; Lodhi, M.S.; Htun, N.Z.; Sharma, E. Integrating geospatial tools and species for conservation planning in a data-poor region of the Far Eastern Himalayas. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2020, 4, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, J.-D. China’s Role in Establishing and Building the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO). J. Contemp. China 2010, 19, 855–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembayev, Z. Implementing the Silk Road Economic Belt: From the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation to the Silk Road Union? Asia Eur. J. 2018, 16, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.S.; Ahmed, S.; Bhatnagar, S. Conflict or Cooperation? India and Pakistan in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation. Pac. Focus 2019, 34, 5–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garlick, J. The Regional Impacts of China’s Belt and Road Initiative. J. Curr. Chin. Aff. 2020, 49, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. The Siachen peace park proposal: Moving from concept to reality. Environment 2008, 50, 43. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, A. Ease conflict in Asia with snow leopard peace parks. Science 2020, 367, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, O.E.; Duguma, L.A.; Minang, P.A. Operationalizing the integrated landscape approach in practice. Ecol. Soc. 2015, 20, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, K.; Ichikawa, K.; Elmqvist, T. Satoyama landscape as social-ecological system: Historical changes and future perspective. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2016, 19, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, L.; Meyer, W.S. Future landscapes: Managing within complexity. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Franco, G.; Alvarado-Macancela, N.; Quinchuela, T.G.; Carrión-Mero, P. Participatory socio-ecological system: ManglaraltoSanta Elena, Ecuador. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2018, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reed, J.; Vianen, J.V.; Deakin, E.L.; Barlow, J.; Sunderland, T. Integrated landscape approaches to managing social and environmental issues in the tropics: Learning from the past to guide the future. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2016, 22, 2540–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Tylianakis, J.M.; Rand, T.A.; Didham, R.K.; Fahrig, L.; Batary, P.; Bengtsson, J.; Clough, Y.; Crist, T.O.; Dormann, C.F.; et al. Landscape moderation of biodiversity patterns and processes—Eight hypotheses. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 661–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisshuhn, P. Indexing the vulnerability of biotopes to landscape changes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, J.; Sunderland, T.; Ghazoul, J.; Pfund, J.-L.; Sheil, D.; Meijaard, E.; Venter, M.; Boedhihartono, A.K.; Day, M.; Garcia, C.; et al. Ten principles for a landscape approach to reconciling agriculture, conservation, and other competing land uses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, 8349–8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johansson, Ö.; McCarthy, T.; Samelius, G.; Andrén, H.; Tumursukh, L.; Mishra, C. Snow leopard predation in a livestock dominated landscape in Mongolia. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 184, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.; Wangchuk, R. Linking Snow Leopard Conservation and People-Wildlife Conflict Resolution:: Grassroots Measures to Protect the Endangered Snow Leopard from Herder Retribution. Endanger. Species Update 2001, 18, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.S.; Agvaantseren, B.; Gongor, E.; Mijiddorj, T.N.; Piaopiao, T.; Redpath, S.; Young, J.; Mishra, C. Assessing the Effectiveness of a Community-based Livestock Insurance Program. Environ. Manag. 2021, 68, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crist, E.; Mora, C.; Engelman, R. The interaction of human population, food production, and biodiversity protection. Science 2017, 356, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Smith, S.R.; Fowler, G.; Velis, C.; Kumar, S.J.; Arya, S.; Rena; Kumar, R.; Cheeseman, C. Challenges and opportunities associated with waste management in India. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradshaw, C.J.A.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Beattie, A.; Ceballos, G.; Crist, E.; Diamond, J.; Dirzo, R.; Ehrlich, A.H.; Harte, J.; Harte, M.E.; et al. Underestimating the Challenges of Avoiding a Ghastly Future. Front. Conserv. Sci. 2021, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shao, Q.; Liu, J.; Lu, Q. Improving ecological conservation and restoration through payment for ecosystem services in Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriagada, R.; Villaseñor, A.; Rubiano, E.; Cotacachi, D.; Morrison, J. Analysing the impacts of PES programmes beyond economic rationale: Perceptions of ecosystem services provision associated to the Mexican case. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczan, D.; Pfaff, A.; Rodriguez, L.; Shapiro-Garza, E. Increasing the impact of collective incentives in payments for ecosystem services. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2017, 86, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waylen, K.A.; Martin-Ortega, J. Surveying views on Payments for Ecosystem Services: Implications for environmental management and research. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Fu, B. Comparison between tourists’ and inhabitants’ willingness to pay for nature in the Tibetan Plateau. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badola, R.; Ahmed, T.; Gill, A.K.; Dobriyal, P.; Das, G.C.; Badola, S.; Hussain, S.A. An incentive-based mitigation strategy to encourage coexistence of large mammals and humans along the foothills of Indian Western Himalayas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; Ren, W.; Coyne, M.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Tao, B.; Hui, D.; Yang, J.; Matocha, C. Responses of soil carbon sequestration to climate-smart agriculture practices: A meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 2591–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri-Chhetri, A.; Pant, A.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Vasireddy, V.V.; Yadav, A. Stakeholders prioritization of climate-smart agriculture interventions: Evaluation of a framework. Agr. Syst. 2019, 174, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhogyel, N.; Kumar, L.; Bajgai, Y. Consequences of Climate Change Impacts and Incidences of Extreme Weather Events in Relation to Crop Production in Bhutan. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, R.; Ghafoor, A.; Xuehao, B.; Wei, Z. Fostering sustainable agriculture: Do institutional factors impact the adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices among new entry organic farmers in Pakistan? J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, R.; Bhatta, L.D.; Udas, E.; Agrawal, N.K.; Joshi, K.D.; Panday, D. Climate-smart practices for improvement of crop yields in mid-hills of Nepal. Cogent Food Agric. 2019, 5, 1631026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.R.P.-J.; Molinos, J.G.; Okuda, A.; Johnstone, J.; Atsumi, K.; Futamura, R.; Williams, M.A.; Matsuoka, Y.; Uchida, J.; Kumikawa, S.; et al. Predators mitigate the destabilising effects of heatwaves on multitrophic stream communities. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, E. Top predators provide insurance against climate change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 479–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow Leopard Trust. Transboundary Cooperation for Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Conservation; Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Programme: Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan, 2021; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bawa, K.S.; Koh, L.P.; Lee, T.M.; Liu, J.; Ramakrishnan, P.S.; Yu, D.W.; Zhang, Y.-p.; Raven, P.H. China, India, and the Environment. Science 2010, 327, 1457–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, Y. The dynamic links between CO2 emissions, energy consumption and economic development in the countries along “the Belt and Road”. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ren, S.; Yan, G.; Hao, Y. Does China’s outward direct investment improve green total factor productivity in the “Belt and Road” countries? Evidence from dynamic threshold panel model analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 275, 111295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuiyun, C.; Chazhong, G. Green development assessment for countries along the belt and road. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, T.M.; Akçakaya, H.R.; Burgess, N.D.; Butchart, S.H.M.; Hilton-Taylor, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Juffe-Bignoli, D.; Kingston, N.; MacSharry, B.; Parr, M.; et al. Analysing biodiversity and conservation knowledge products to support regional environmental assessments. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheshmehzangi, A.; Xie, L.; Tan-Mullins, M. Pioneering a Green Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) alignment between China and other members: Mapping BRI’s sustainability plan. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 3, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickman, A.; Packer, C.; Johnson, P.J.; Macdonald, D.W. A sideways look at conservation and consistency in tourism policy. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 32, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, S.d.C.; Rockett, G.C.; Portz, L.C.; Filho, J.R.d.S. Beach landscape management as a sustainable tourism resource in Fernando de Noronha Island (Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, C.; Gallagher, A.J.; Barnett, A.; Brunnschweiler, J.; Shiffman, D.S.; Hammerschlag, N. Conservation potential of apex predator tourism. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 215, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannelli, K.; Hampton, M.P.; Namgail, T.; Black, S.A. Community participation in ecotourism and its effect on local perceptions of snow leopard (Panthera uncia) conservation. Hum. Dimens. Wildl. 2019, 24, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pătru-Stupariu, I.; Hossu, C.A.; Grădinaru, S.R.; Nita, A.; Stupariu, M.-S.; Huzui-Stoiculescu, A.; Gavrilidis, A.-A. A Review of Changes in Mountain Land Use and Ecosystem Services: From Theory to Practice. Land 2020, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pătru-Stupariu, I.; Nita, A.; Mustăţea, M.; Huzui-Stoiculescu, A.; Fürst, C. Using social network methodological approach to better understand human-wildlife interactions. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, V.D.; Pop, M.I.; Rozylowicz, L. Trophy hunting undermines public trust. Science 2021, 372, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| No. | Global Snow Leopard Range | Country | Type of Livestock Predated by Snow Leopard | No. of Livestock Depredated | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Himalaya Range (HIMLY) | Bhutan | Yaks, Horses, Cattle, Sheep, | 32 | 2003–2005 | [50] |
| 2 | China | Yaks, Cattle–Yak hybrid, Cows, Sheep and Goats | 5877 | 2011–2013 | [51] | |
| 3 | India | Horse, Yaks, Goat, Sheep, others | 112 | 2003 | [52] | |
| 4 | Nepal | Horses, Yak, Yak–Cow hybrid, Cows, Goats, Sheep | 362 | 2014 | [53] | |
| 5 | Karakorum and Hindukush (KK/HK) | Afghanistan | Yaks, Horses, Cattle, Sheep, Goats | 378 | 2007–2008 | [54] |
| 6 | Pakistan | Yak, Yak–Cow hybrid, Cows, Goats, Sheep | 223 | 2013 | [45] | |
| 7 | Commonwealth of Independent States and Western China (CISWC) | Kazakhstan | --None-- | ---- | ----- | ----- |
| 8 | Kyrgyzstan | --None-- | ---- | ----- | ----- | |
| 9 | Tajikistan | --None-- | ---- | ----- | ----- | |
| 10 | Uzbekistan | Horses, Sheep, and Goats | 82 | 2004 | [55] | |
| 11 | Northern Range (NRANG) | Mongolia | Horses, Sheep, Goats | 740 | 2010 | [56] |
| 12 | Russia | Sheep and Goats | 233 | 2000–2003 | [57] |
| Location | Period | Warming Rate | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global Mean Surface Temperature | 1951–2012 | 0.12 °C/decade | [67] [68] |
| Altai Sayan Ecoregion (Russia) | 1976–2008 | 0.58 °C/decade | [73] |
| Almaty (Kazakhstan) | 1974–2015 | 0.52 °C/decade | [74] |
| Naryn (Kyrgyzstan) | 1930–1989 | 0.32 °C/decade | [75] |
| Oygaing, (Uzbekistan) | 1961–2016 | 0.25 °C/decade | [76] |
| Pamir mountains (Tajikistan) | 1979–2018 | 0.32 °C/decade | [77] |
| Tibetan Plateau (China) | 1955–1996 | 0.16 °C/decade | [78] |
| Dingri, Tibetan Plateau (China) | 1959–2007 | 0.62 °C/decade | [79] |
| Gilgit (Pakistan) | 1986–2010 | 0.39 °C/decade | [80] |
| Hindukush Himalaya region (Parts of Afghanistan, Pakistan, Tajikistan, China, India, Nepal, Bhutan) | 1951–2014 | 0.20 °C/decade | [81] |
| Trans-Himalaya Region (Nepal) | 1977–1994 | 0.90 °C/decade | [82] |
| No. | Global Snow Leopard Range | Country/ Location | Type of Land Use/Landcover Changes | Period | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Himalaya Range (HIMLY) | Bhutan | Increase in forest cover | 1990–2010 | [87] |
| 2 | Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China | Grassland decreased Unused land increased | 1980–2018 | [89] | |
| 3 | Central Himalayas, (India) | Increasing deforestation, Forest fragmentation | 1976–2006 | [91] | |
| 4 | Nepal | Deforestation Forest degradation | 1976–2001 | [92] | |
| 5 | Karakorum and Hindukush (KK/HK) | Afghanistan | Deforestation, Forest fragmentation | 1976–2014 | [93] |
| 6 | Pakistan | Built-up area increased Cropland increased | 2008–2018 2000–2020 | [94] | |
| 7 | Commonwealth of Independent States and Western China (CISWC) | Kazakhstan | Vegetation cover decreased Built-up area increased | 1995–2015 | [95] |
| 8 | Kyrgyzstan | Forest decreased Barren land increased Agriculture increased | 1996–2014 | [96] | |
| 9 | Pamir mountains (Tajikistan) | Deforestation Desertification | -- | [97] | |
| 10 | Uzbekistan | Grassland degradation | 1991–2010 | [98] | |
| 11 | Northern Range (NRANG) | Mongolia | Grassland degradation | 2000–2006 1998–2006 | [99] [100] |
| 12 | Altai region (Russia) | Land degradation | -- | [101] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sultan, H.; Rashid, W.; Shi, J.; Rahim, I.u.; Nafees, M.; Bohnett, E.; Rashid, S.; Khan, M.T.; Shah, I.A.; Han, H.; et al. Horizon Scan of Transboundary Concerns Impacting Snow Leopard Landscapes in Asia. Land 2022, 11, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020248
Sultan H, Rashid W, Shi J, Rahim Iu, Nafees M, Bohnett E, Rashid S, Khan MT, Shah IA, Han H, et al. Horizon Scan of Transboundary Concerns Impacting Snow Leopard Landscapes in Asia. Land. 2022; 11(2):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020248
Chicago/Turabian StyleSultan, Hameeda, Wajid Rashid, Jianbin Shi, Inam ur Rahim, Mohammad Nafees, Eve Bohnett, Sajid Rashid, Muhammad Tariq Khan, Izaz Ali Shah, Heesup Han, and et al. 2022. "Horizon Scan of Transboundary Concerns Impacting Snow Leopard Landscapes in Asia" Land 11, no. 2: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020248
APA StyleSultan, H., Rashid, W., Shi, J., Rahim, I. u., Nafees, M., Bohnett, E., Rashid, S., Khan, M. T., Shah, I. A., Han, H., & Ariza-Montes, A. (2022). Horizon Scan of Transboundary Concerns Impacting Snow Leopard Landscapes in Asia. Land, 11(2), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020248










