Exploring the Ecological Climate Effects Based on Five Land Use Types: A Case Study of the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
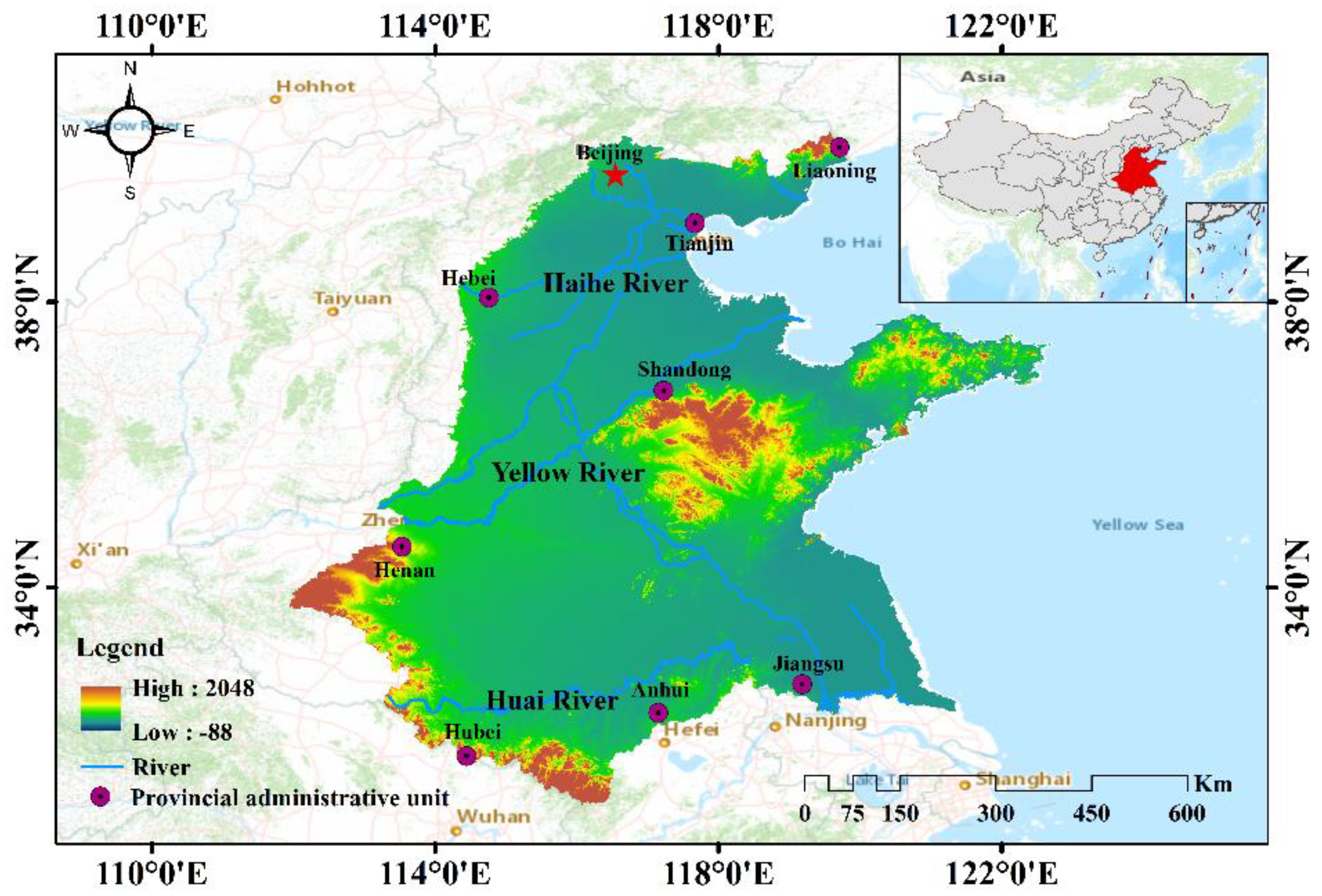
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resource
2.3. Research Methodology
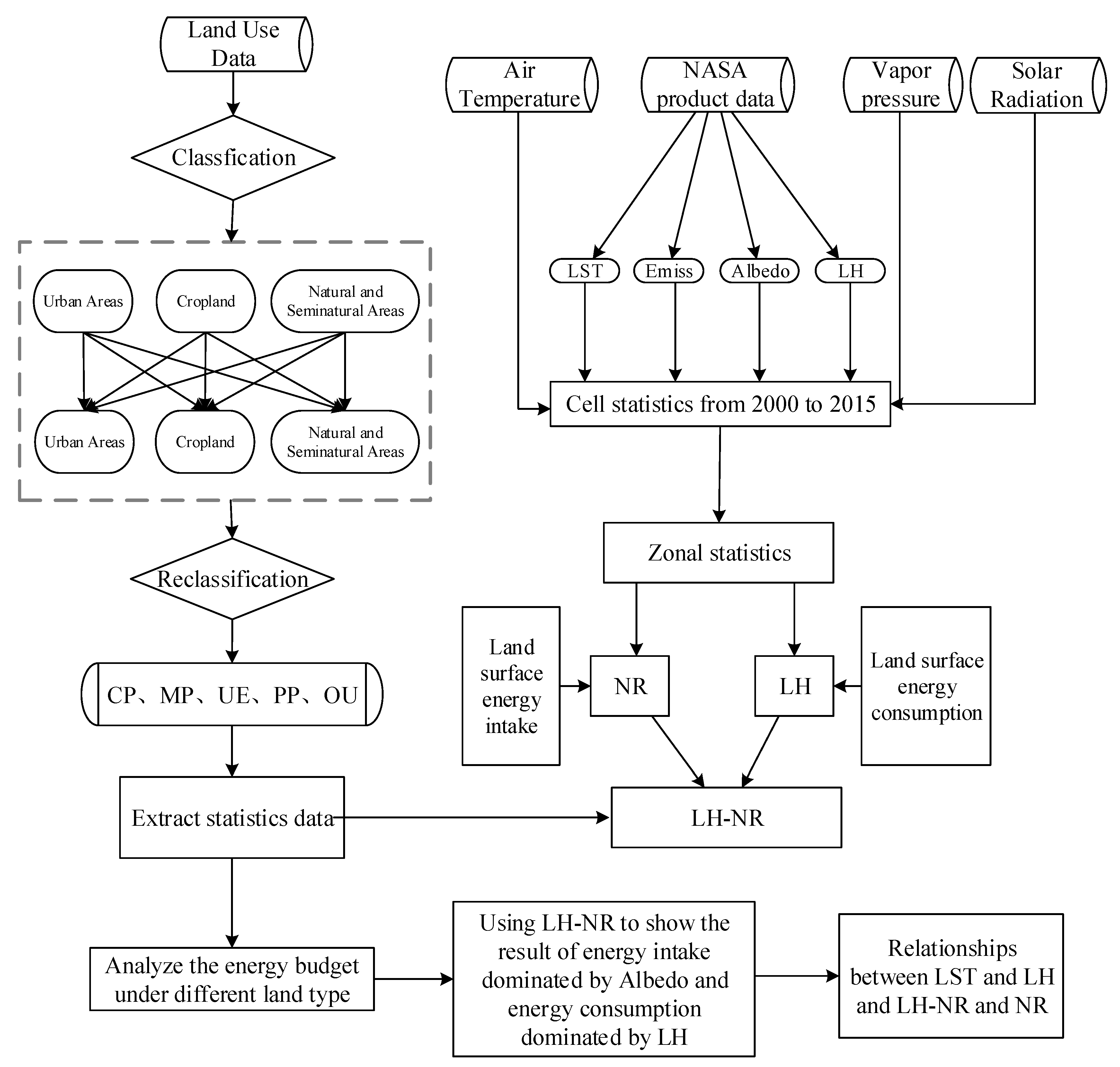
2.3.1. Land Use Reclassification
2.3.2. Calculation of Surface Energy Balance and Research Framework
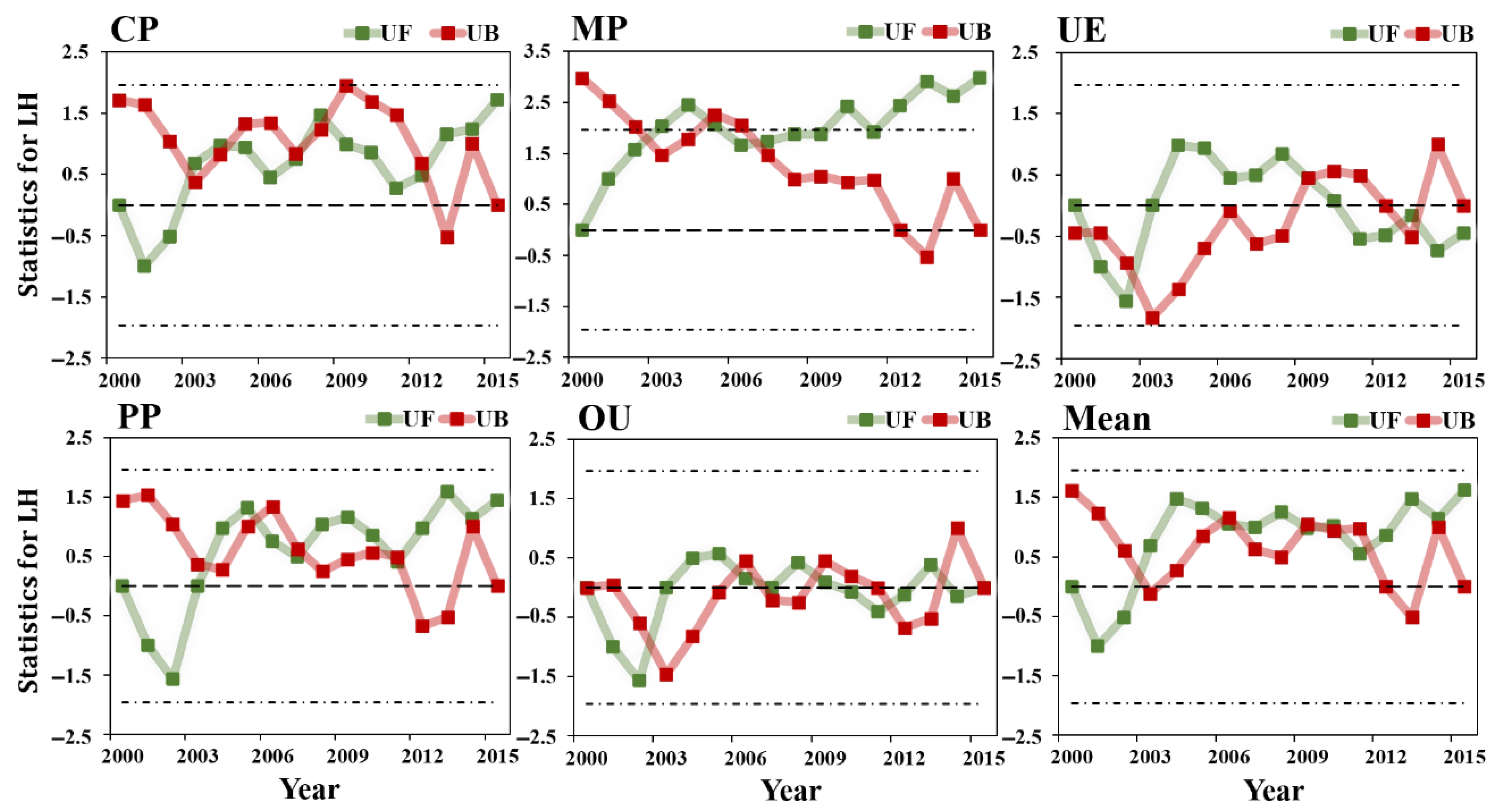
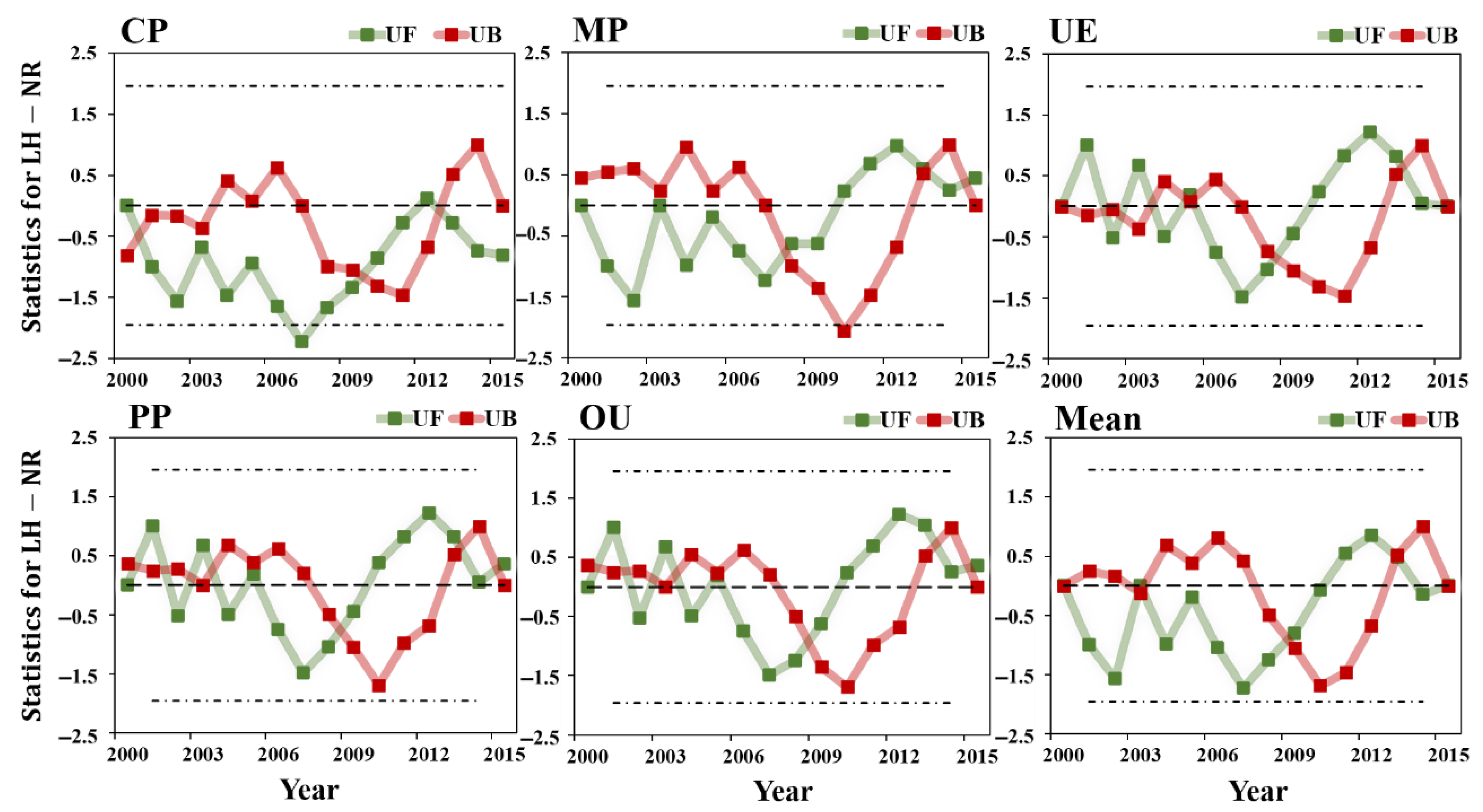
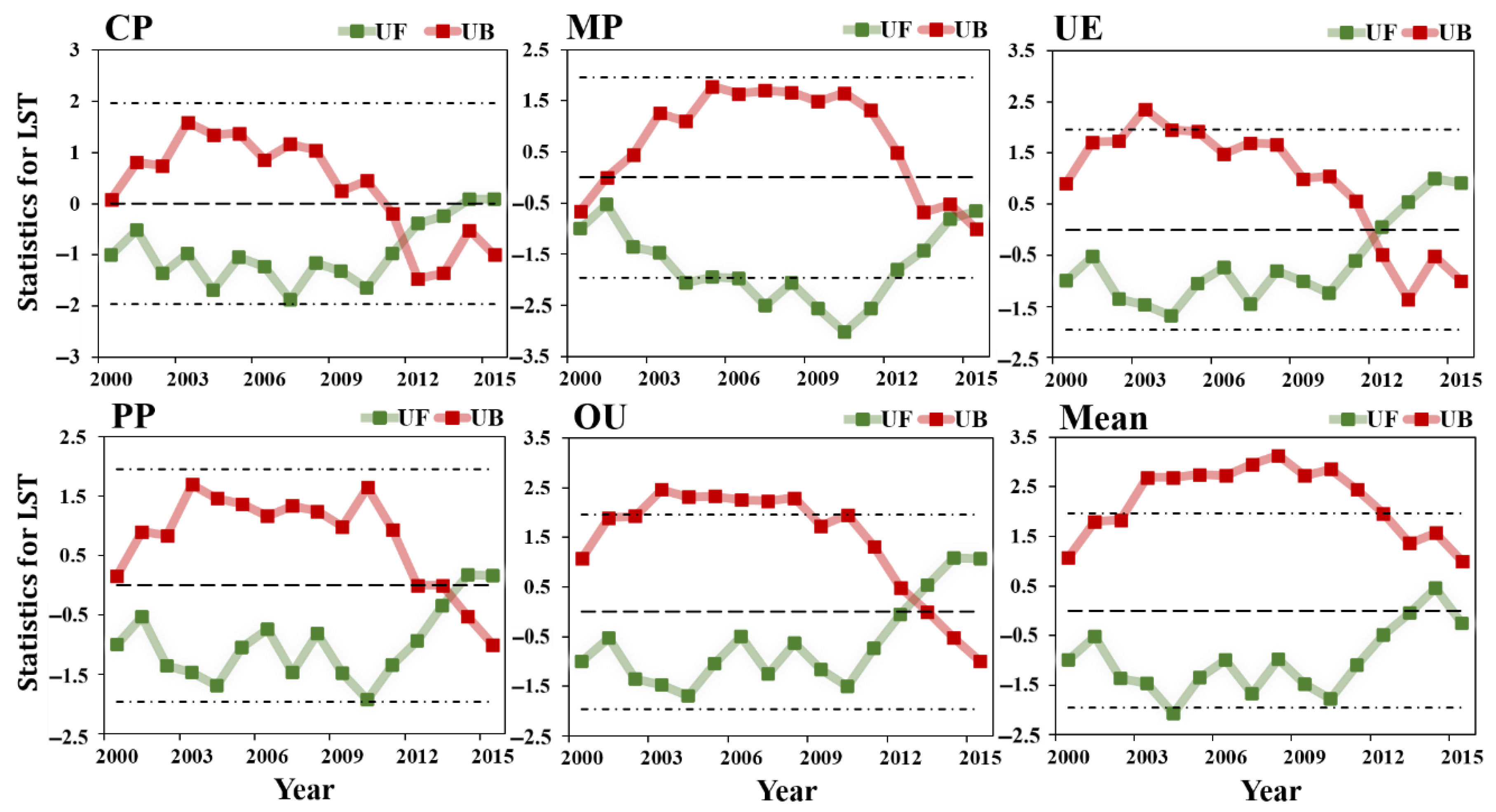
2.3.3. Nonparametric Mann-Kendall Trend Test
- (1)
- Suppose the time series X1, X2, …, Xn, represents the cumulative number of the ith sample Xi > Xj (1 j i), define the statistics:
- (2)
- The mean and variance of is:
- (3)
- Standardize :
3. Results
3.1. Changes of Surface Energy Intake
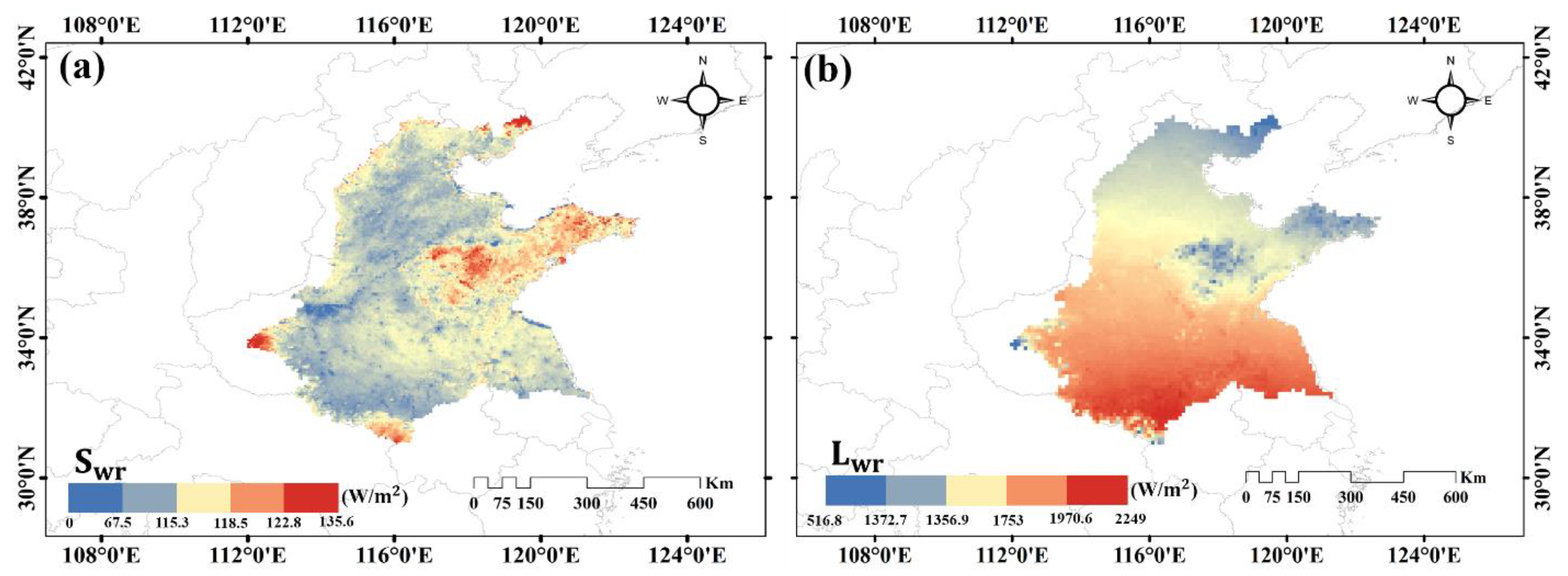
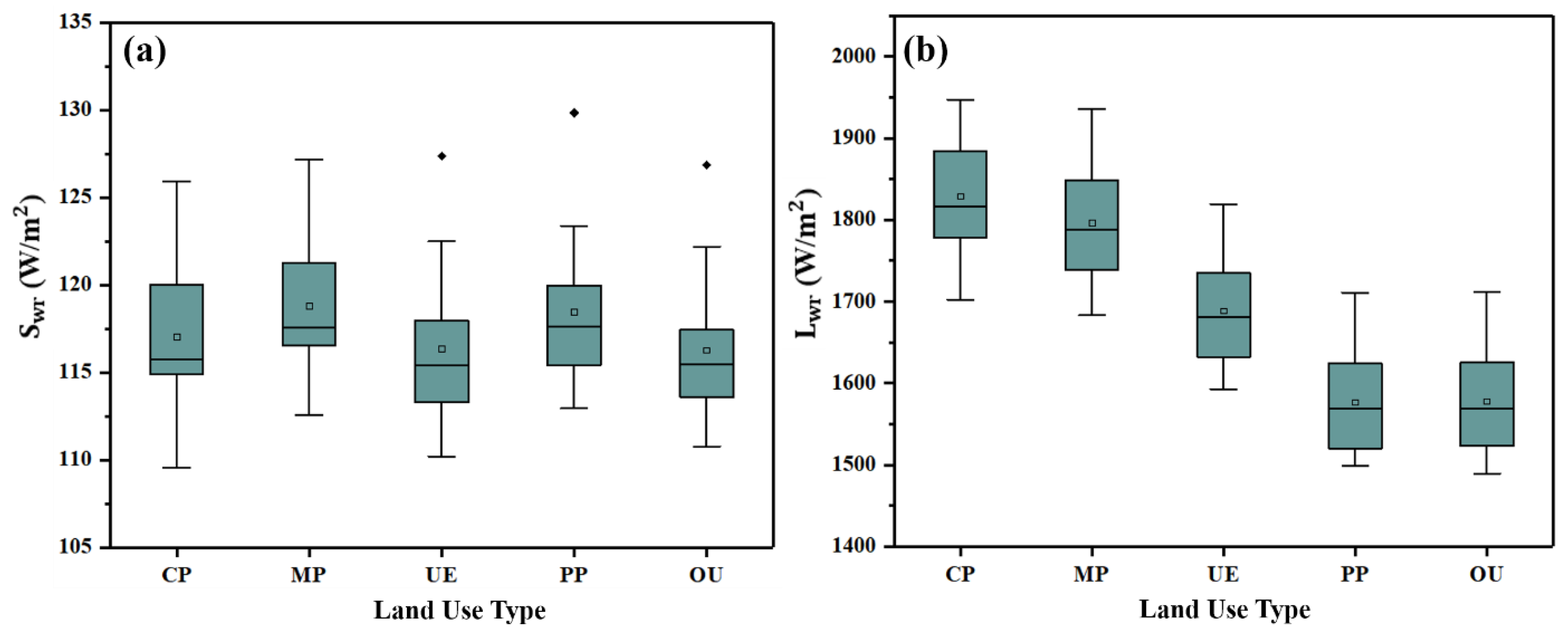
3.1.1. Net Shortwave and Longwave Radiation
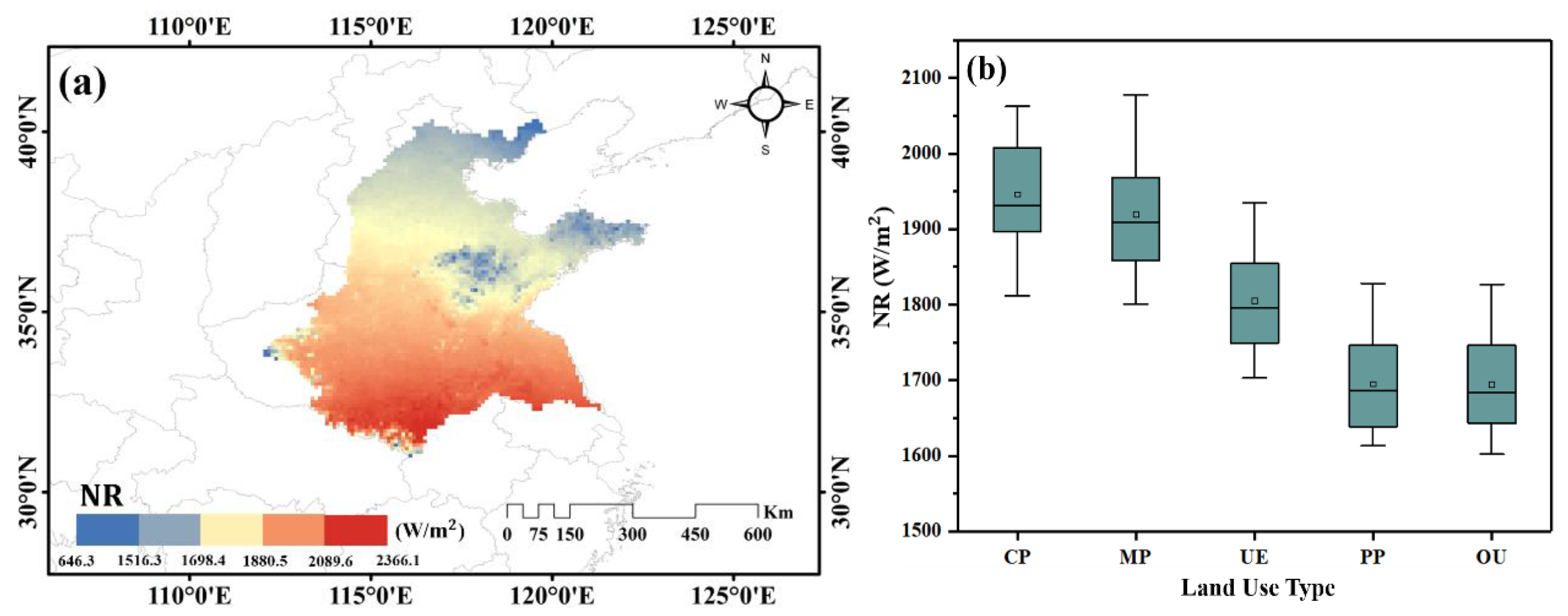
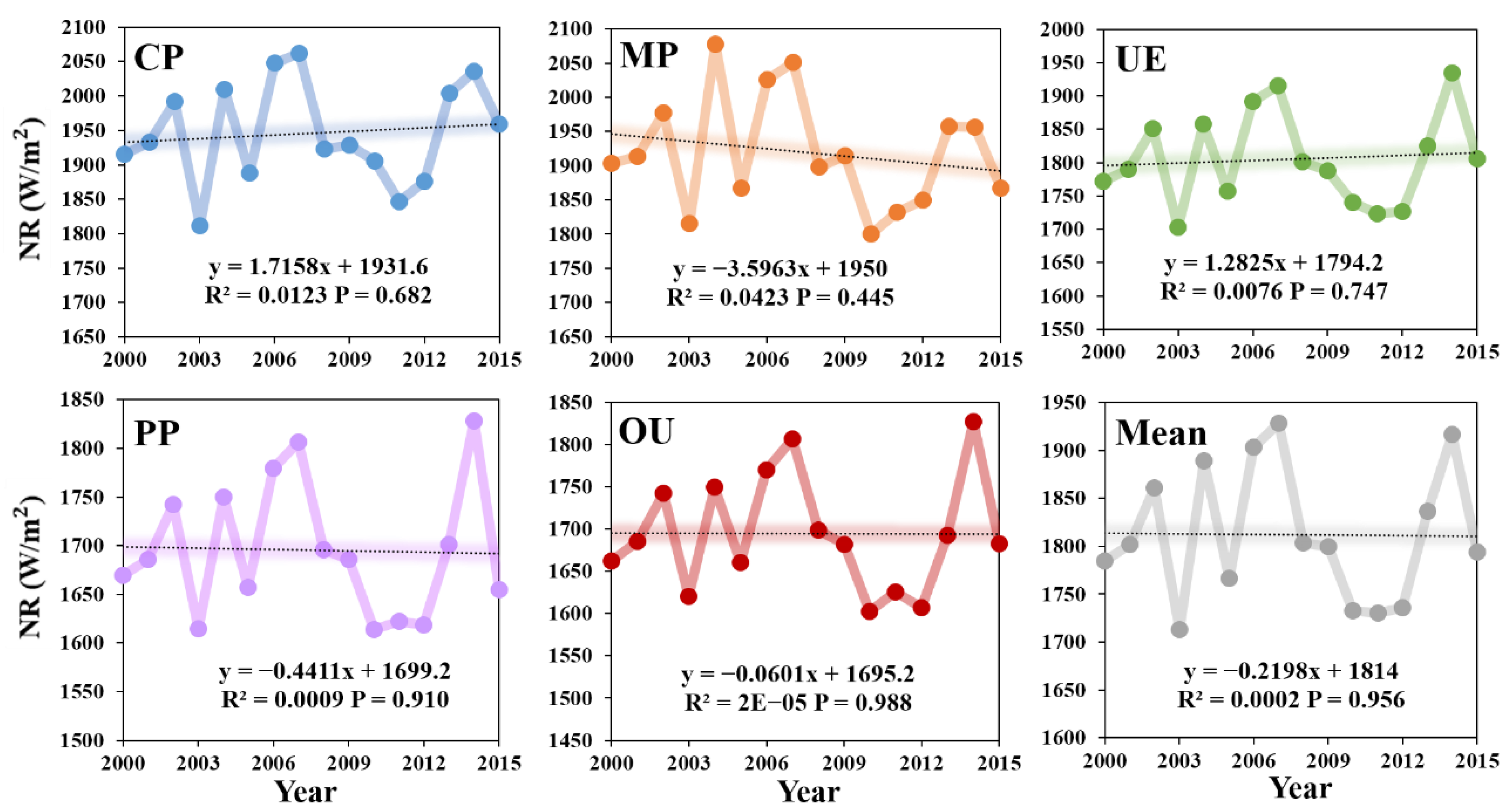
3.1.2. Changes of Net Radiation
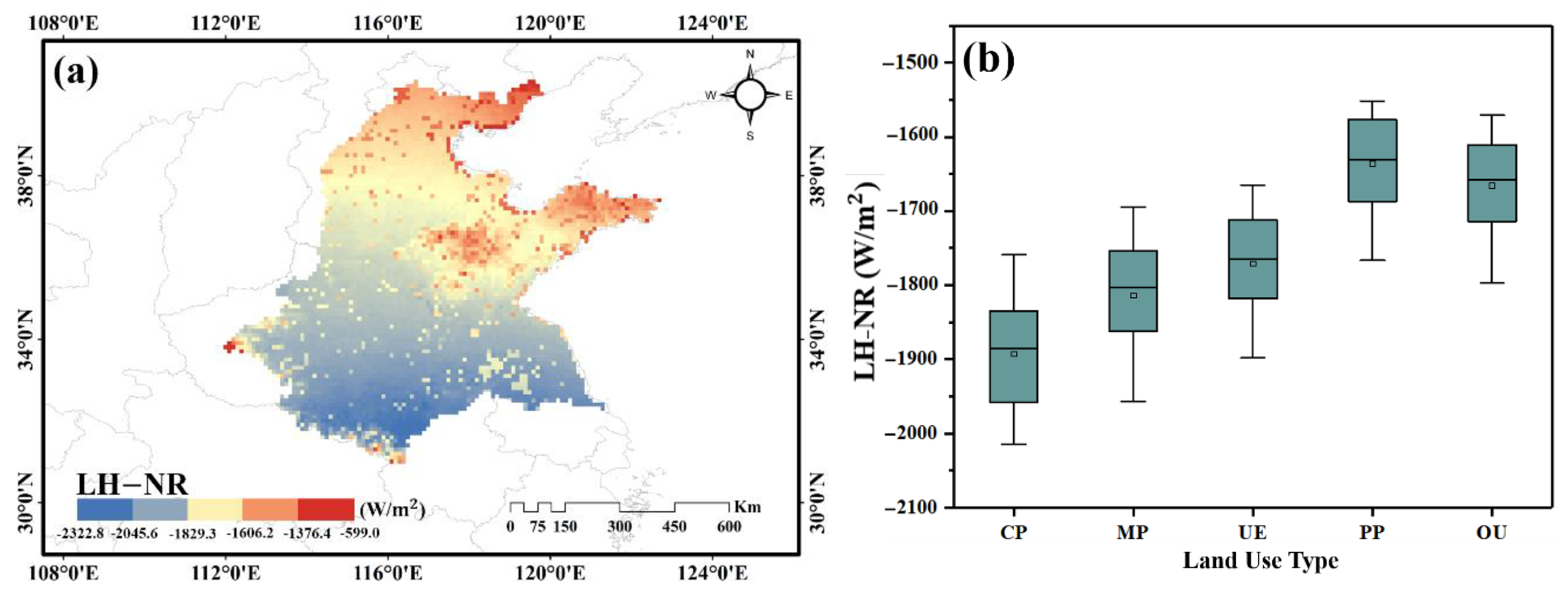
3.2. Analysis of Surface Energy Balance
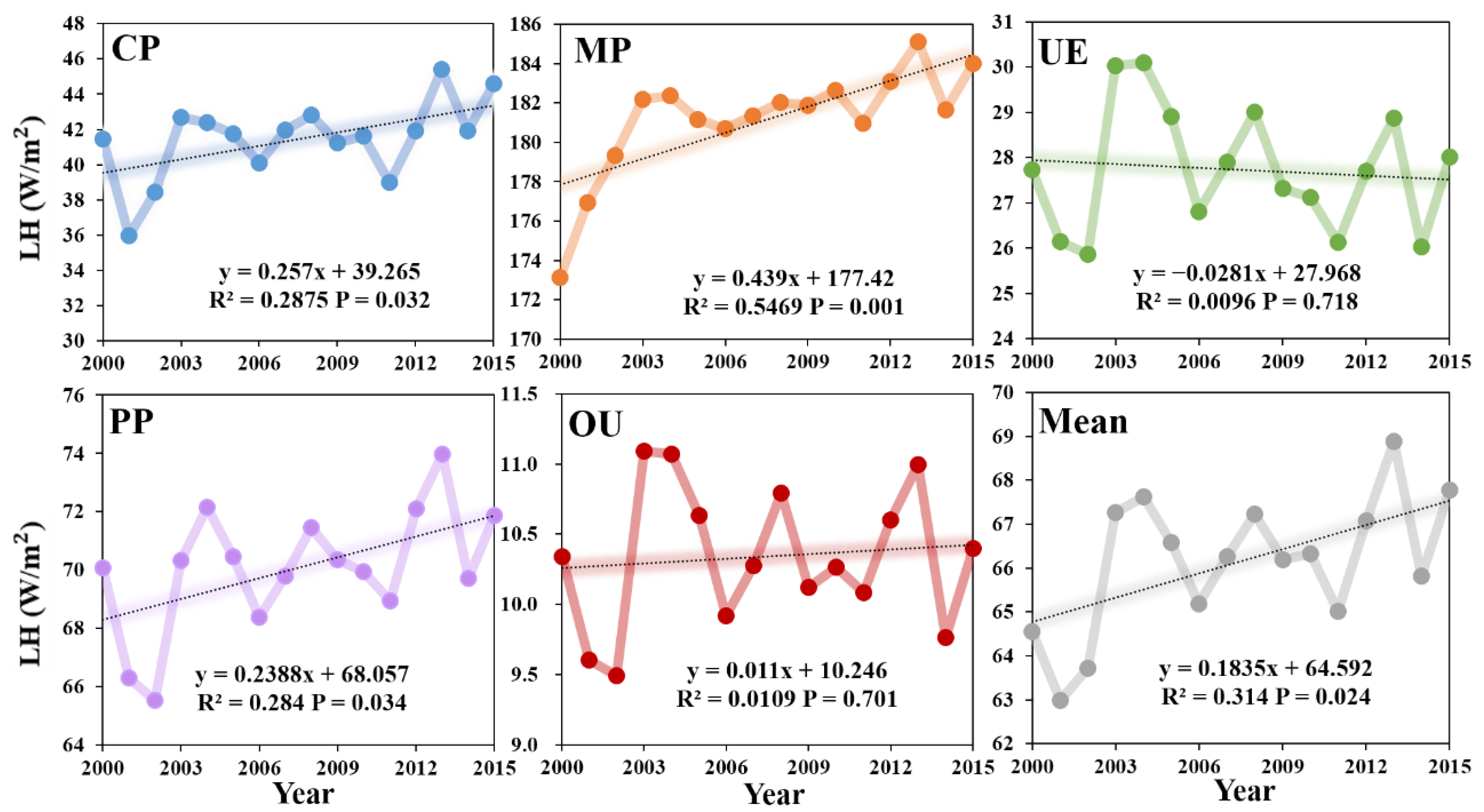
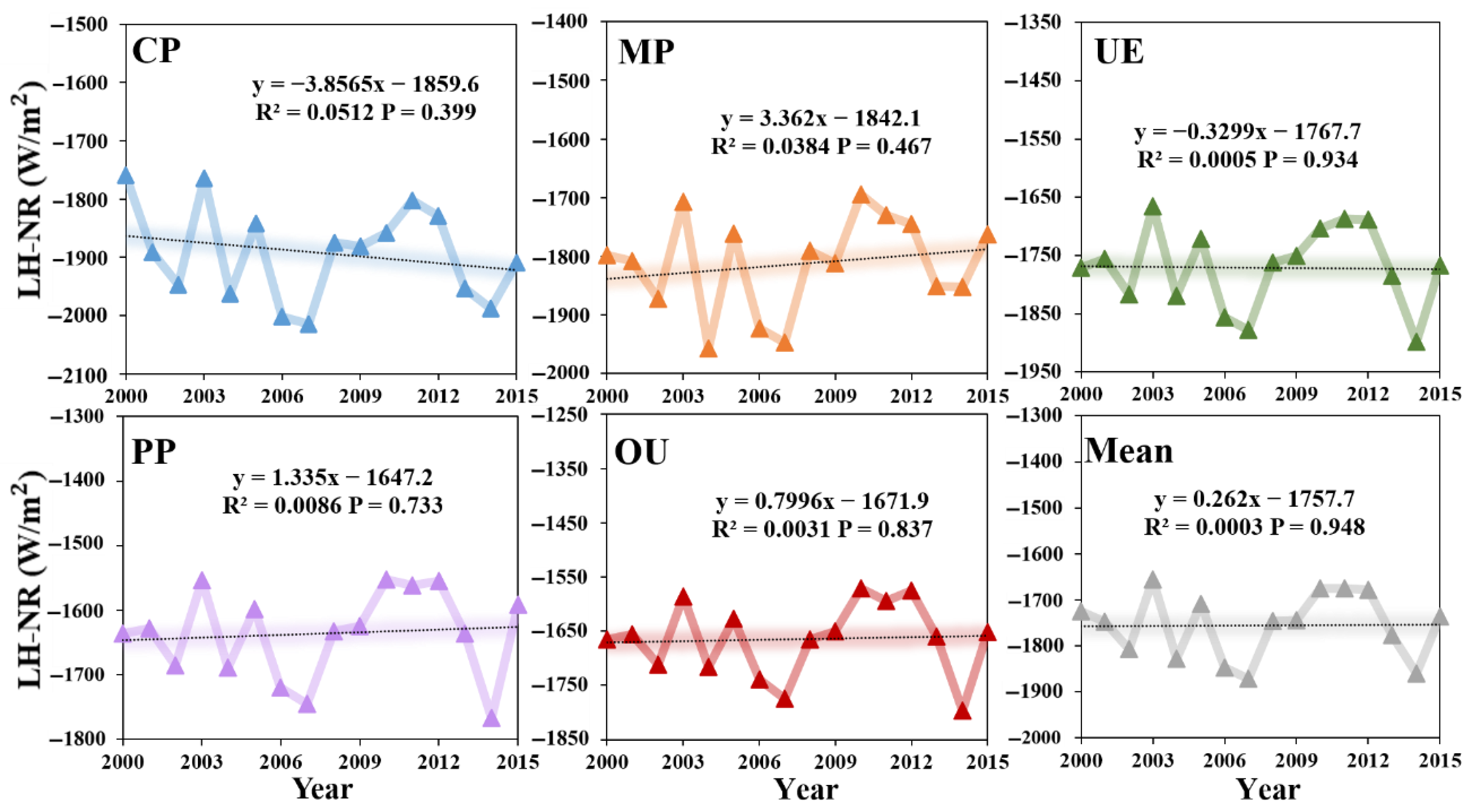
3.2.1. Changes in Surface Energy Consumption
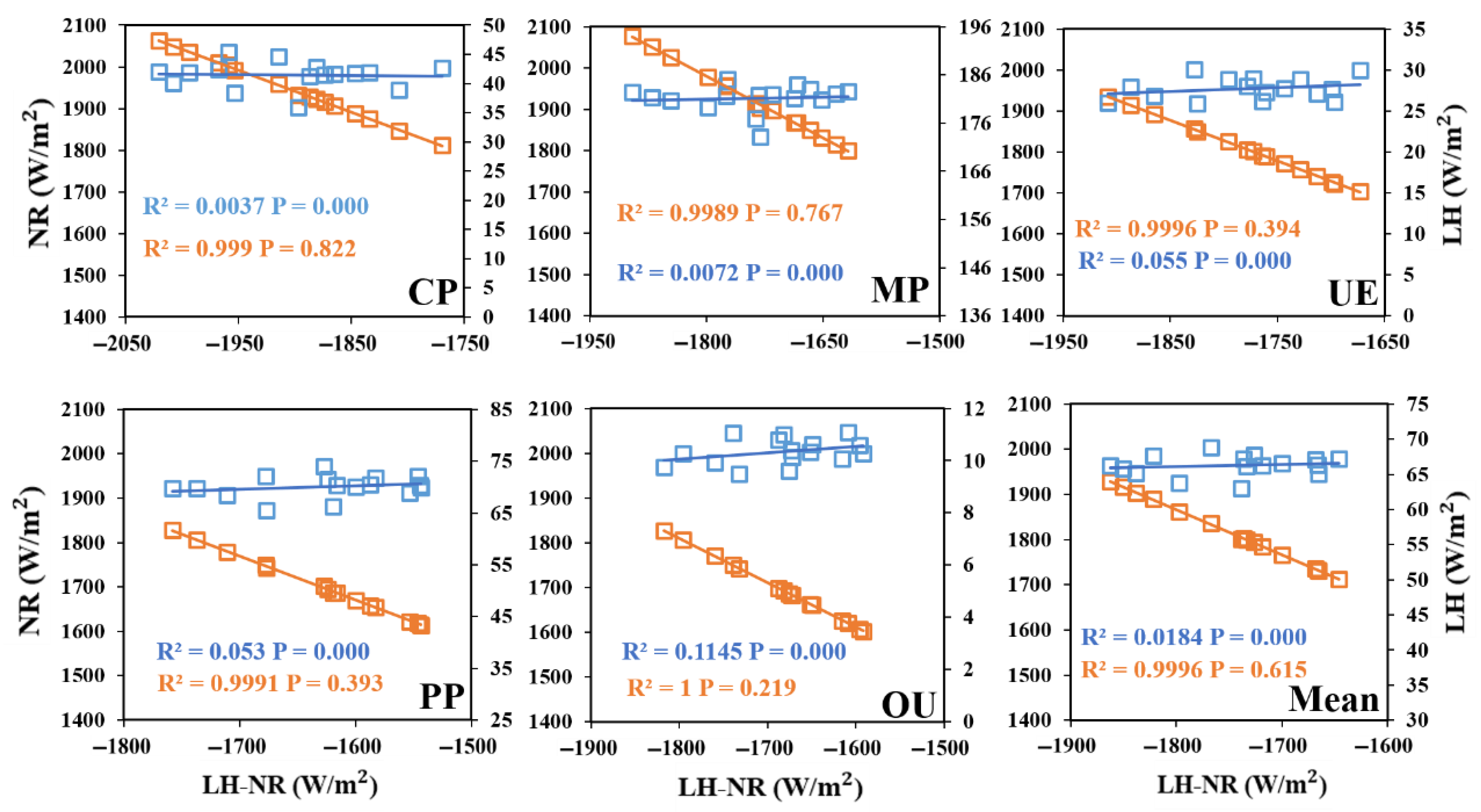
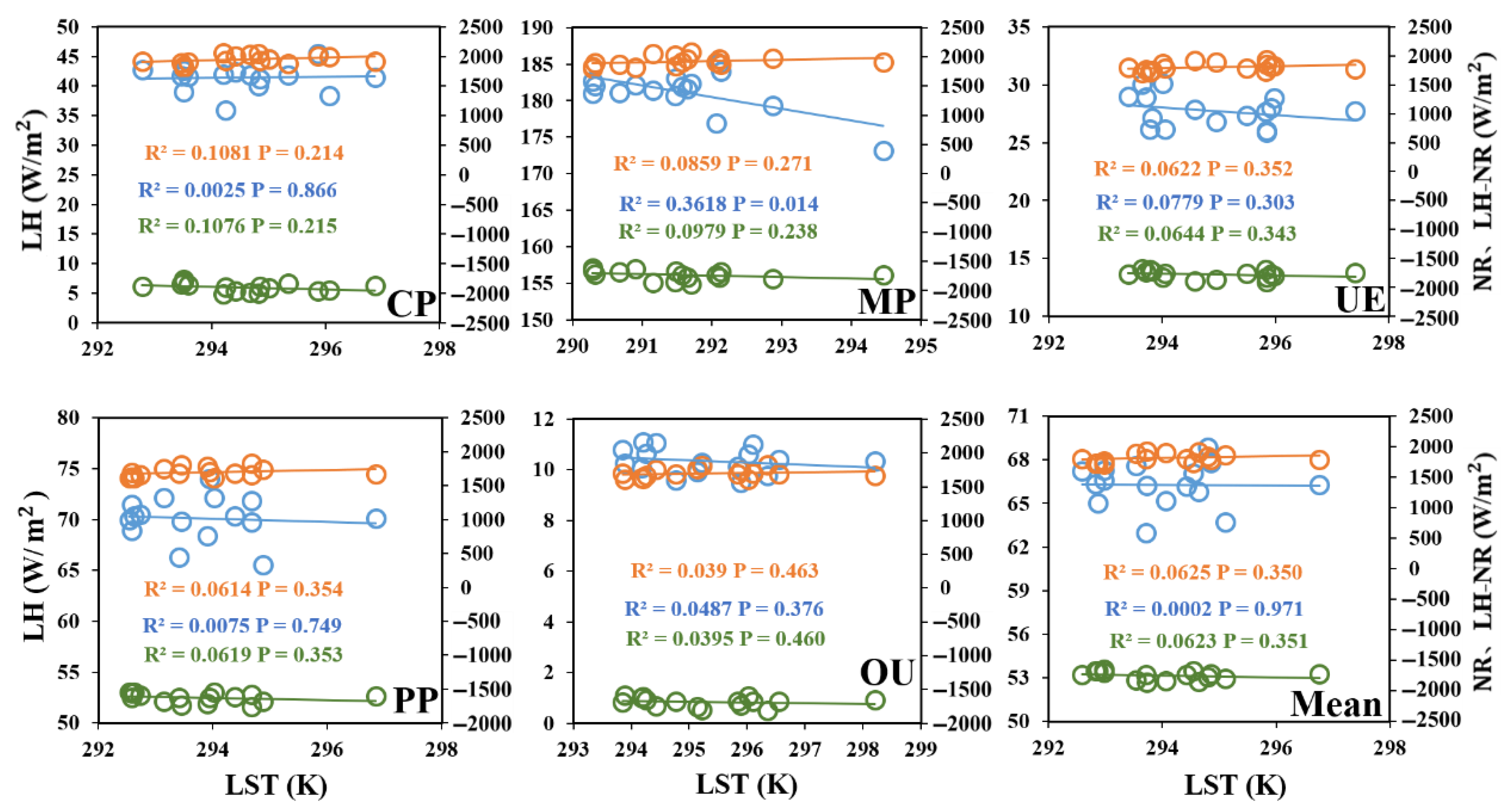
3.2.2. Comparison of Net Radiation and Latent Heat Fluxes
4. Discussion
5. Summary
- (1)
- From 2000 to 2015, the change trend of LH in five land use types was: MP > PP > CP > UE > OU. The NR values of UE and OU areas, which were greatly affected by human activities, were always lower than those of other land use types, and the NR values of CP and MP areas were much higher than those of UE, OU and PP areas. The NR values were generally on the rise, which was in line with the climate background of global warming.
- (2)
- The in different land types of underlying surface showed a decreasing trend, with the OU, PP and UE regions showing a smaller trend than the CP and MP regions. The values of the five land-use types decreased with the increase in intensity of human activities, indicating that human activities weakened the positive trend of and increased the warming effect. The main energy regulation factors of surface temperature of different land use types were also different. With the increase in the intensity of human activities related to land use, the cooling effect of gradually increases.
- (3)
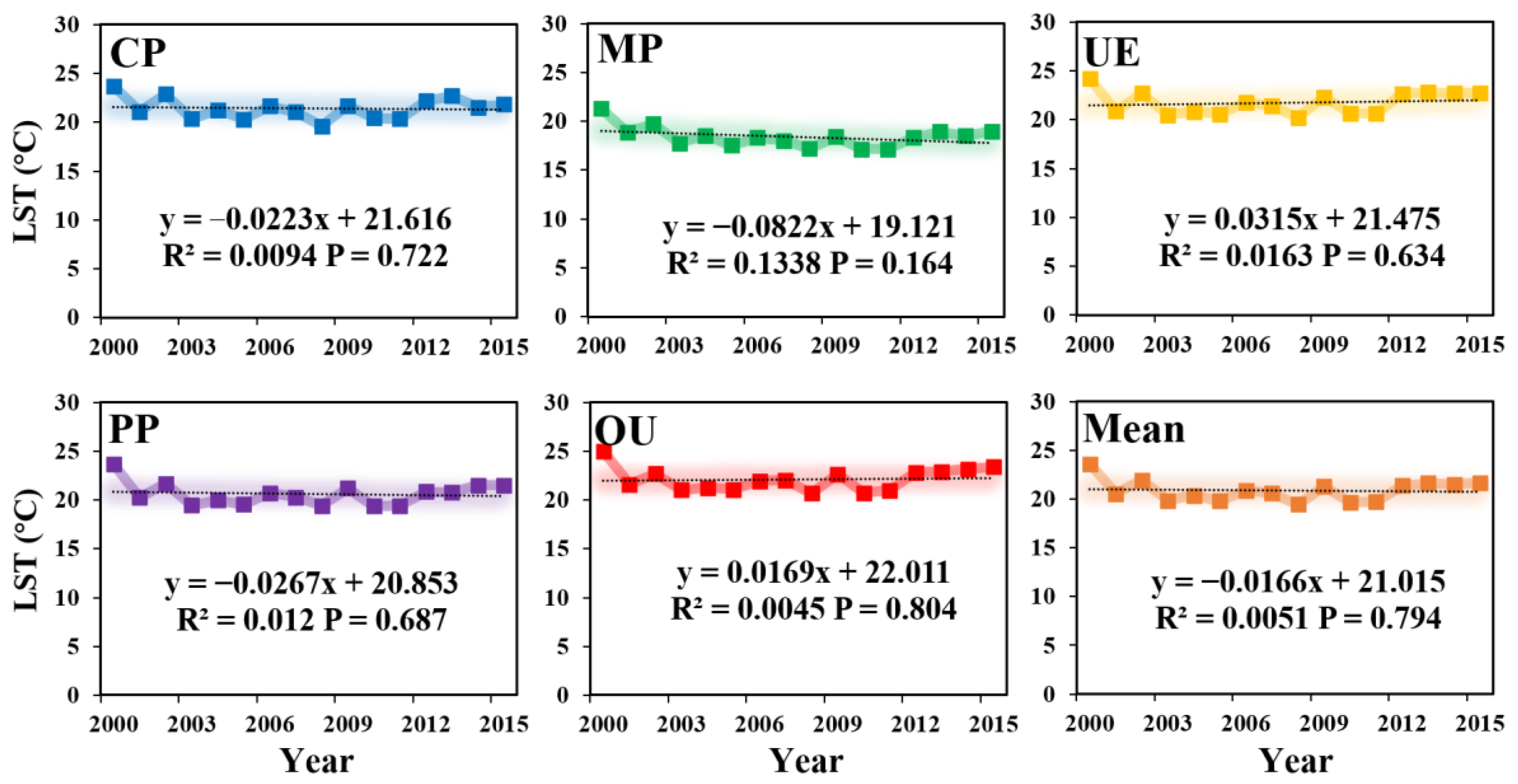
- The change trend of LST in five land use types was: OU > UE > CP > PP > MP. The values of LST in five land use types was higher in OU and UE, while the values of LST was lower in MP. MP refers to the area of mutual transformation between natural and seminatural pixel area and cropland, which is affected by certain human activities, indicating that land use change had a strong feedback effect on regional climate warming, which was conducive to controlling the rapid increase of land surface temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Lv, S.; Ao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Shang, L.; Ma, D. Characteristics of Radiation and Energy Budget over an Oasis under Different Synoptic and Irrigation Conditions in Summer. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2011, 33, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Huang, R. Comparison of Characteristics of Surface Radiation Energy Budget between Typical Arid Area and Plateau in Northwest my country. Clim. Environ. Res. 2006, 6, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, D.; Tang, W.; Cui, Y.; Lee, J. Exploring on the Eco-Climatic Effects of Land Use Changes in the Influence Area of the Yellow River Basin from 2000 to 2015. Land 2021, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhai, J.; Sun, C.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Ning, J.; Zhao, G.S. Biogeophysical Forcing of Land-Use Changes on Local Temperatures across Different Climate Regimes in China. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 7053–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Wu, Y.; Yu, M.; Shi, Z.; Yin, X.; Song, Y.; Sun, K. Contributions of vegetation restoration and climate change to spatiotemporal variation in the energy budget in the loess plateau of china. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazame, R.; Tanrvermis, H.; Kapusuz, Y.E. Land management and sustainable use of land resources in the case of Burkina Faso. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, X.; Deng, Q.; Li, D.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Cui, Y. Spatial Association of Urbanization in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Kuang, W. Modeling the radiation balance of different urban underlying surfaces. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; He, F.; Wang, Z. Application of MODIS BRDF/Albedo data in temperature simulation in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2011, 66, 356–366. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Hou, M.; Yan, X. Analysis on the Characteristics of Vegetation Changes in Northern China at the Beginning of the 21st Century. Clim. Environ. Res. 2013, 2, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhai, J. Comparison of the influence of land surface cover changes on the surface albedo in four countries. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 24, 917–932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Meng, P. Estimation of kilometer-scale heat fluxes over a hilly area in Northern China using an optical-microwave scintillometer. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 244, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Roujean, J.; Cao, B.; Du, Y.; Li, H.; Gamet, P.; Fang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q. Modeling the directional anisotropy of fine-scale TIR emissions over tree and crop canopies based on UAV measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, Z.; Ren, T.; Wang, W. Within-city spatial and temporal heterogeneity of air temperature and its relationship with land surface temperature. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 206, 103979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, N.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Run, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, G.; Dong, J. Human Activities Enhance Radiation Forcing through Surface Albedo Associated with Vegetation in Beijing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moges, D.M.; Bhat, H.G. An insight into land use/cover changes and their impacts in Rib watershed, North-western highland Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3317–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Qian, J. Research progress on the thermal environment of the urban surfaces. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1134–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Cai, M.; Yang, S.; Sergio, A.S. Air temperature feedback and its contribution to global warming. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2018, 61, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Michael, M.E.; Li, N.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, G.; Dong, J. Land Cover Change Intensifies Actual and Potential Radiative Forcing through CO2 in South and Southeast Asia from 1992 to 2015. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Han, Z.; Zhang, Q. The Impact of Land Use Change on Surface Temperature in the Semi-arid Area of Northern China at the Beginning of the 21st Century. Clim. Environ. Res. 2016, 21, 65–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Mysterud, A.; Ottersen, G.; Hurrell, J.W.; Chan, K.; Lima, M. Ecological Effects of Climate Fluctuations. Science 2002, 297, 1292–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Run, Y.; Chubwa, O.G.; et al. Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2020, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benali, A.; Carvalho, A.C.; Nunes, J.P.; Carvalhais, N.; Santos, A. Estimating air surface temperature in Portugal using MODIS LST data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Yu, D.; Sun, Y.; He, R.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Research Progress on the Quantitative Relationship between Land-Use/Land-CoverChange and Climate Change. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 880–890. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Li, X.; Bai, J.; Cui, B. Tracking three decades of land use and land cover transformation trajectories in Chinese large river deltas. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Long, H. Land use transitions and their dynamic mechanism: The case of the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, S.; Han, Y.; Yu, W.; Cao, Y.; Cai, W.; Yang, P.; Wu, W.; Yu, Q. Spatio-temporal differences and factors influencing intensive cropland use in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1626–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chi, Q.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Liu, D.; Tang, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Ye, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Quantifying the Contribution of LUCC to Surface Energy Budget: A Case Study of Four Typical Cities in the Yellow River Basin in China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeta, S.J.; Payal, M. Assessment of seasonal climate transference and regional influential linkages to land cover–Investigation in a river basin. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2020, 199, 105209. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Gamal, S.E.A.; Mohamed, E.E. Impact of climate change on rainfall variability in the Blue Nile basin. Alex Eng. J. 2021, 61, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, Z.; Sun, P. Spatiotemporal variations and extreme value analysis of significant wave height in the South China Sea based on 71-year long ERA5 wave reanalysis. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 113, 102750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric Tests against Trend. Econometrica 2013, 3, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, A.; Berna, A. Spatial variability of long-term trends of significant wave heights in the Black Sea. Appl. Ocean Res. 2018, 79, 20–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xue, X.; Niu, J.; Wang, Y. Remote Sensing Retrieval Analysis of Surface Heat Flux in Nanjing Area. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2016, 25, 636–646. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, S.; Maity, S.; Singh, K.S.; Nayak, H.P.; Dutta, S. Influence of the Changes in Land-Use and Land Cover on Temperature over Northern and North-Eastern India. Land 2021, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, K.; Jiao, Z.; Ruan, X.; Wang, Y. Migration of heavy metals in the soil-grape system and potential health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Meng, H.; Song, H.; Zheng, H. Progress in Dust Modelling, Global Dust Budgets, and Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics. Land 2022, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, S.; Wang, L.; Chi, Q.; Zhu, M.; Tang, W.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Ye, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Research on the Planning of an Urban Ventilation Corridor Based on the Urban Underlying Surface Taking Kaifeng City as an Example. Land 2022, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier, H.; Raúl, G.; Esteban, J.; Marcelo, N. Surface albedo raise in the South American Chaco: Combined effects of deforestation and agricultural changes. Agr. Forest Meteorol. 2017, 232, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Yue, D.; Guo, J.; Chao, Z.; Meng, X. Assessing the impact of land conversion and management measures on the net primary productivity in the Bailong River Basin, in China. Catena 2021, 207, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, X.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, J. Spatial analysis of land-use management for gully land consolidation on the Loess Plateau in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadahisa, K.; Huang, W. Land use management recommendations for reducing the risk of downstream flooding based on a land use change analysis and the concept of ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 287, 112341. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, S.; Wang, L.C.; Lin, A.W.; Yu, D.Q.; Yuan, M.X.; Li, C.A. Distinguishing the impacts of climate change and anthropogenic factors on vegetation dynamics in the Yangtze River Basin. China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 108, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Ponce, A.; Corona-Núñez, R.O.; Nava, L.F.; Estrada, F.; Calderón-Bustamante, O.; Martínez-Meyer, E.; Carabias, J.; Larralde-Corona, A.H.; Barrios, M.; Pardo-Villegas, P.D. Impacts of land management and climate change in a developing and socioenvironmental challenging transboundary region. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Items | Time Resolution | Spatial Resolution | Data Resource |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albedo | daily | 500 m | MCD43A3 |
| Temperature (LST) | daily | 1 Km | MOD11A1 |
| Latent heat flux (LH) | 8 daily | 500 m | MOD16A2 |
| Emissivity | daily | 1 Km | MOD11A1 |
| Land Use Change from 2000 to 2015 | Unchanged Land Types from 2000 to 2015 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Categories | Percentage | Categories | Percentage |
| cropland to urban areas | 2.73% | urban areas | 2.23% |
| natural and seminatural areas to urban areas | 3.47% | cropland | 63.74% |
| natural and seminatural areas to cropland | 0.06% | natural and seminatural areas | 27.70% |
| cropland to natural and seminatural areas | 0.07% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Liu, D.; Tang, W.; Chi, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, S. Exploring the Ecological Climate Effects Based on Five Land Use Types: A Case Study of the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin in China. Land 2022, 11, 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020265
Zhu M, Liu D, Tang W, Chi Q, Zhao X, Xu S, Ye S, Wang Y, Cui Y, Zhou S. Exploring the Ecological Climate Effects Based on Five Land Use Types: A Case Study of the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin in China. Land. 2022; 11(2):265. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020265
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Mengyao, Dandan Liu, Weichao Tang, Qian Chi, Xiao Zhao, Siqi Xu, Siyu Ye, Yaobin Wang, Yaoping Cui, and Shenghui Zhou. 2022. "Exploring the Ecological Climate Effects Based on Five Land Use Types: A Case Study of the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin in China" Land 11, no. 2: 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020265
APA StyleZhu, M., Liu, D., Tang, W., Chi, Q., Zhao, X., Xu, S., Ye, S., Wang, Y., Cui, Y., & Zhou, S. (2022). Exploring the Ecological Climate Effects Based on Five Land Use Types: A Case Study of the Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin in China. Land, 11(2), 265. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020265









