Abstract
Improving water utilization efficiency can effectively alleviate the contradiction between water shortage and water demand in the process of rapid urbanization. The middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin, China, are characterized by water shortage. In order to improve water use efficiency, taking the 43 prefecture-level units in this region as the study area, industrial and agricultural water use efficiency is calculated based on the undesired SBM-DEA model. Then, the Tobit model is used to explore their influencing factors. The results show that the regional average agricultural water use efficiency is greater than the industrial water use efficiency. The temporal trend indicates that the agricultural water use efficiency shows a fluctuating upward trend, while industrial water use efficiency has a fluctuating downward trend. The gravity center of industrial water use efficiency moves from northwest to southeast in a “Z” shape, while the gravity center of agricultural water use efficiency moves westward as a whole. From the perspective of spatial patterns, the standard deviation ellipse of industrial water use efficiency shows that the industrial water use efficiency is higher in the east–west direction, while the agricultural water use efficiency is higher in the northwest–southeast direction. The improvement of urbanization level is conducive to the improvement of industrial water use efficiency; however, the development of urbanization has a significant inhibitory effect on improving agricultural water use efficiency.
1. Introduction
Ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River basin have become national strategies in China; however, the total amount of water resources in the Yellow River Basin is insufficient and the per capita possession is low. With the rapid advancement of urbanization process, the economy of the Yellow River Basin has received a boost; meanwhile the contradiction between water resource shortages and water resource demand is becoming increasingly prominent [1,2], which has become one of the key problems restricting the high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. In terms of water use structure, the proportion of industrial and agricultural water use in the Yellow River Region in 2020 was 78.66%, of which 66.87% was used in agriculture, nearly 5 percentage points higher than that of the national agricultural water use [3]. Improving agricultural water use efficiency is an important focus point to alleviate the contradiction between the high volume of agricultural water use and the shortage of regional water resources [4,5]. Additionally, in the context of rapid urbanization and industrialization, the ratio of agricultural water use shows a downward trend, while the proportion of industrial water use rises with fluctuation. Especially, industrial wastewater pollution is a key factor influencing regional ecological protection and high-quality development [6]. Research on industrial water use efficiency considering undesired output could help to improve the industrial green level, further enhancing comprehensive strength and competitiveness. Given that agriculture and industry are both important for human survival and regional development, we intend to reveal the difference between industrial and agricultural water use efficiency in the context of urbanization in order to improve water use efficiency and reduce wastewater pollution. The middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River region are complex in terms of human activities, and the amount of water resources used for industrial and agricultural production is large, emitting lots of pollutants. Therefore, there are higher requirements for the degree of intensive utilization of water resources [7]. With the rapid progress of urbanization, the degree of intensive use of industrial and agricultural water resources is one of the key challenges to regional high-quality development. By comparing the characteristics and drivers of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, it will help the common development of industry and agriculture, and contribute to the alleviation of water conflicts [8].
Fruitful achievements have emerged in research on water use efficiency. Firstly, the main methods used to evaluate water use efficiency are stochastic frontier analysis [9,10,11], the water footprint method [12], the fuzzy elements method [13], the comprehensive indicator system [14], factor decomposition [15,16,17] and data envelopment analysis (EDA) [18,19]. Among them, EDA is a mainstream research method which examines the output of water resource input from both input and output dimensions, and is widely used in measuring efficiency [20,21,22]. Secondly, studies related to water use efficiency mainly focus on spatial and temporal variations [23,24,25], spatial autocorrelation [12,26], transfer path analysis [27], convergence effect [28] and influencing factors [29]. Thirdly, influencing factors are mainly selected from economic, social, resource endowment and ecological environment aspects, such as the level of economic development, industrial structure, technological progress, urbanization rate, population density, water resource possession, water use structure and environmental protection input [30]. In terms of the model for revealing the influencing factors of water use efficiency, Tobit regression is the most common method [31,32]. In addition, some studies have used systematic GMM [33], structural decomposition [34], geographically weighted regression [35] and spatial econometric models [36].
After the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin was elevated to a national strategy, important progress has also been made in the conservation and intensive use of water resources. For example, Gong et al. [37] used a super-efficient DEA model containing desired and non-desired outputs to measure the water use efficiency of cities along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, and employed GIS spatial analysis and systematic GMM to analyze the spatial and temporal patterns of water use efficiency and the influencing factors. Wu et al. [38] discussed the green efficiency of water resources from agricultural, industrial, domestic, and ecological aspects. Zuo et al. [39] constructed a multiple input–output index system of resource–environment–economy–society to measure and identify the level of water resource use in the Yellow River Basin at provincial, regional and city-level scales. Liu et al. [40] employed the SBM-DEA to calculate water use efficiency along the Yellow River at the city level, and then analyzed the drivers of water use efficiency. Lu et al. [41] evaluated the agricultural water efficiency based on the undesired DEA model, and assessed the coordination degree of the efficiency and resilience of the agricultural water resources system in the Yellow River Basin. Overall, literature related to water use efficiency in the Yellow River Basin has improved in four respects. (1) The research object has gradually shifted from a single type of efficiency evaluation to multi-category (agricultural, industrial, domestic and ecological) water use efficiency evaluation. (2) The evaluation analysis focuses more on a combination of dynamic and static assessments. (3) The research scale highlights multi-scale analysis. (4) Model frameworks pays equal attention to the role of desired and undesired outputs rather than only taking into account the desired outputs.
There has been a wealth of studies exploring water conservation and intensive utilization in the Yellow River Basin, providing the necessary support to protect the ecological resources and promote the high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin. However, there is still room for further improvement in the following three aspects. (1) Most studies focus on evaluations of comprehensive water use efficiency and single types of water use efficiency. In the evaluation of comprehensive water use efficiency, the indicators related to industry and agriculture are generally mixed and integrated into the input and output, while the undesired output is mostly adopted by the general indicator, such as sewage discharge, wastewater discharge, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide, etc. For the studies of single types of water use efficiency, such as industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, the evaluation results of different types of water use efficiency cannot be directly compared due to the differences in research perspectives, methods and indicators. (2) In the studies distinguishing the types of water resource utilization, comprehensive indicator systems are mainly used for evaluation, and parametric and non-parametric models are rarely used. (3) In the context of rapid urbanization, insufficient attention is paid to the impact of urbanization on water use efficiency in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, where production and living are more intensive. Therefore, this paper takes 43 prefecture-level units in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin, China, as the study area, evaluates industrial and agricultural water use efficiency based on the undesired SBM-DEA model, analyzes the spatial transfer path of water use efficiency using the center of gravity and the standard deviation ellipse, and then reveals the impact of urbanization on water use efficiency in the context of urbanization. Furthermore, three different indicators closely related to urbanization development are selected from three dimensions (population, land and space dimensions), namely, urbanization level, status of urban space development, and population density, and the Tobit model is used to reveal the drivers affecting water use efficiency and explore ways to improve water use efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China, were selected as the study area, covering five provinces (Inner Mongolia, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, Shandong) and 43 prefecture-level cities. The location was displayed in Figure 1. The average precipitation in this region ranges from 600 mm to 800 mm, and the average amount of total water resources is 1.2 billion cubic meters. The population size was about 160 million people in 2003, almost reaching at 180 million people in 2019. The gross regional product was CNY 1600 billion in 2003, increasing to CNY 7500 billion in 2019 (at 2003 constant prices). The urbanization rate has increased substantially, from 30% to 60%.
Figure 1.
Study area.
2.2. Undesired SBM-DEA
DEA is a method of comprehensively evaluating the relative efficiency of the inputs and outputs of a decision-making unit (DMU). This method does not need to consider the functional relationship between input and output indicators, and also has no requirement of the dimensional differences of indicators. Consequently, DEA has been widely used to evaluate the input–output efficiency [42,43,44]. The SBM-DEA model is an improvement on traditional DEA, and avoids the problem of variable relaxation by adding slack variables to the objective function [45]. In addition, to capture the effect of undesired output on efficiency, Tone [46] constructed a new SBM-DEA model including undesired output to make the evaluation more realistic.
X is the input, assuming a total of m indicators; and are the desired and undesired outputs, assuming a total of s1 and s2 indicators, respectively. If both input and output indicators are greater than zero, the form of SBM-DEA including undesired outputs is as follows:
where is the efficiency value, and γ is the coefficient. , and represent the slack values in input, desired output and undesired output, respectively. When the efficiency of water use is high ( = 1), = = = 0, indicating that the DMUs have achieved DEA effectiveness; when the efficiency of water use is not high (), the input and output can be optimized to improve the efficiency value.
As the efficiency values range from 0 to 1, there may be multiple evaluation units with efficiency value equal to 1, thus giving rise to a problem of inefficient sorting among evaluation units. For that reason, the super-efficient SBM-DEA model is used in this paper with the following model form:
where the function value of is no longer restricted by the range [0, 1], enabling the effective ordering of water use efficiency of different units.
2.3. Malmquist–Luenberger Index
The super-efficient SBM-DEA measures the static efficiency for a certain year, and it does not fully reveal the temporal dynamic characteristics for time series. Therefore, the Malmquist–Luenberger (ML) index was employed to measure the temporal trend of water use efficiency. Based on the directional distance function, the distances between the efficiency of DMU and the production frontier in two adjacent years were calculated. The ML index is the ratio of the two distances and depicts the relative change in efficiency values. An ML index less than 1 indicates that the efficiency value has decreased, and an ML index greater than 1 means that the efficiency value has increased. The functional form of the ML index is detailed in [31,47].
2.4. Selection of the Evaluation Indicator System
There is not yet a unified standard building evaluation index system for water use efficiency. Most studies select input indicators from capital, labor force and production factors according to the Cobb–Douglas function. The most commonly used input indicators are fixed asset input, labor force and water consumption. Therefore, in this study, fixed asset investment, employment in the secondary industry and industrial water consumption were adopted as input indicators for industrial water use efficiency. In terms of agricultural water use efficiency, the employment in the primary industry and the agricultural water consumption were taken as input indicators. Additionally, as land is the natural capital of agricultural production, the area sown of grain was taken as the capital input element of agricultural production. As for output indicators, the GDP of secondary industry and grain yield, which were most directly related to industrial and agricultural production, were selected as the desired outputs for industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, respectively. From the perspective of pollution, industrial wastewater and agricultural fertilizer pollution were selected as the undesired outputs. The specific indicators are shown in Table 1. Data involved were obtained from the China Regional and Economic Statistical Yearbook, the China Urban Statistical Yearbook, the China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook, the corresponding provincial and prefecture-level municipal statistical yearbooks, and water resource bulletins.

Table 1.
Input and output indicators of the DEA model for water use efficiency.
2.5. Estimation for Center of Gravity and Standard Deviational Ellipse
The center of gravity was calculated according to the efficiency value of water resource use and spatial position. The form of the center of gravity was as follows:
where (X, Y) are the X- and Y-coordinate of the center of gravity; (xi, yi) is the coordinate of the space unit; wi is the weight, denoting the water use efficiency; and n is the number of space units.
The parameters of standard deviational ellipse include standard deviations along the X- and Y-axis and the azimuth angle in addition to the center of gravity:
where (, ) denotes the relative coordinates of the ith space unit to the center of gravity. (, ) represents standard deviations along the X- and Y-axis. θ is the azimuth angle, indicating the angle formed by clockwise rotation from true north to the X-axis of the ellipse.
2.6. Tobit Model and Selection of Variables
The efficiency values based on the super-efficient SBM-DEA model are all greater than 0, belonging to the left truncated data. The method of ordinary least squares cannot work effectively, and would lead to estimation bias [48]. The existing theories and literatures show that the Tobit model, proposed by Tobin [49], uses the maximum likelihood estimation, and can handle truncated and discontinuous data in parameter estimation [50,51]. Therefore, the Tobit model was used to reveal the drivers of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River.
In order to reflect the multidimensional development model of urbanization, three variables (including urbanization level, urban spatial development, and urban population density) were selected to reflect urbanization development. Among them, the urbanization level was represented by the urbanization rate, which showed the population dimension of urbanization development. The urban spatial development was represented by the area of urban construction land, which indicated the land dimension of urbanization development. The urban population density was represented by the amount of people per unit area in an urban area, which expressed the space dimension of urbanization development. Additionally, in reference to relevant literatures, this paper took population size, economic development level, the proportion of the primary industry, the proportion of the secondary industry, industrial and agricultural water consumption, the ratios of industrial and agricultural water consumption, resource natural endowment, and the index of water saving as variables in the Tobit model. Variables and their descriptions are displayed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Description of Tobit regression variables for water use efficiency.
3. Results
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Characteristics of Water Use Efficiency
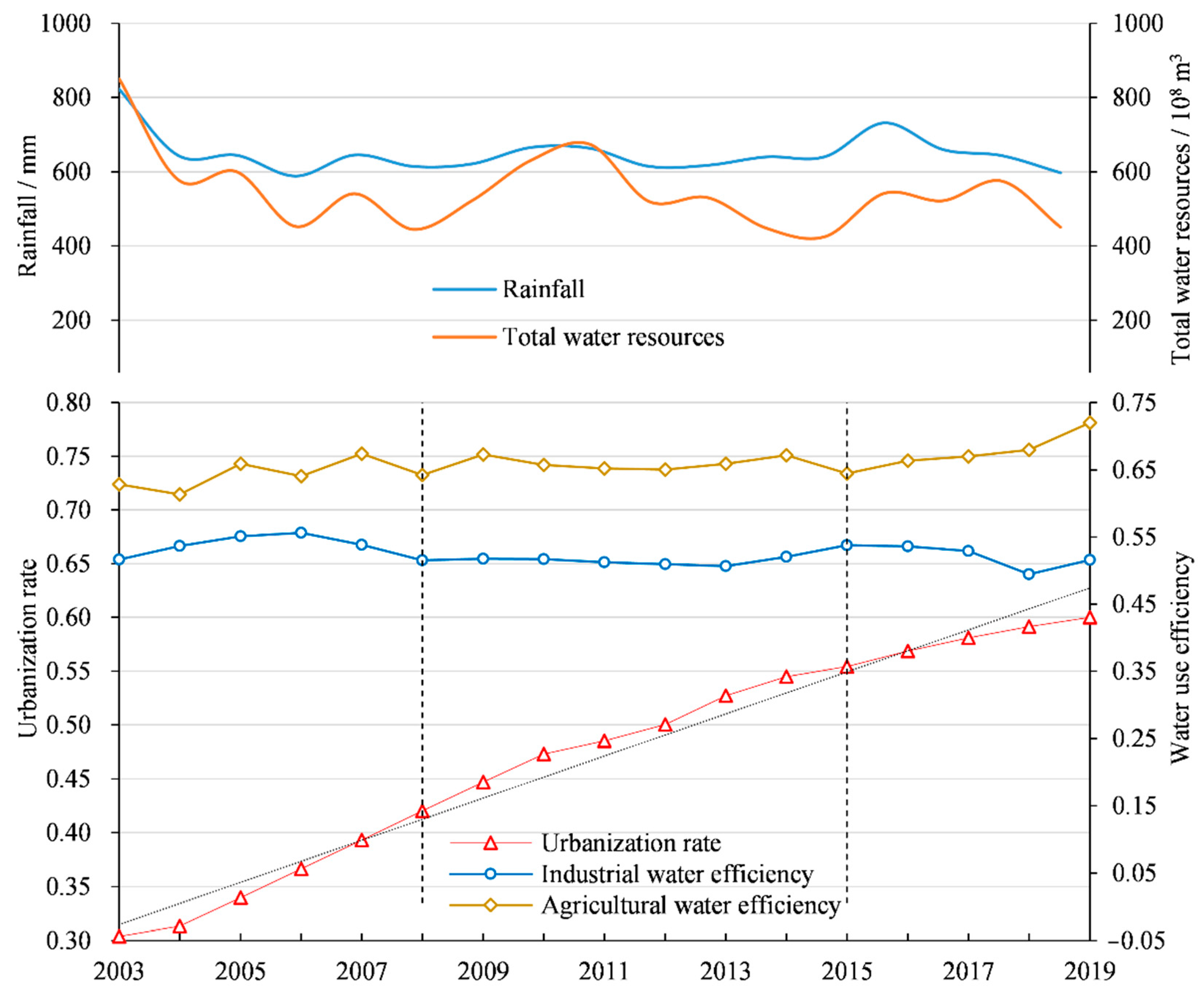
In terms of temporal trends (Figure 2), the mean values of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency showed a fluctuating trend over the study period, and the industrial water use efficiency was lower than the agricultural water use efficiency. Moreover, the agricultural water use efficiency showed an upward trend, negatively correlated with rainfall and total water resources, while the industrial water use efficiency had a downward trend, suggesting that water resources used for agricultural production had relatively better performance, with higher desired output and lower undesired output. Combining the linear trend in urbanization rates with the trends in industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, the study period was divided into three stages: 2003–2008, 2009–2015 and 2016–2019. In the first stage, the urbanization rate was low, but the growth rate was fast. At the same time, the agricultural water use efficiency showed a fluctuating upward trend, while the industrial water use efficiency showed an inverted U-shaped curve, rising first and then declining. In the second stage, the urbanization rate raised at a slightly slower rate, and the industrial and agricultural water use efficiency declined in a fluctuating manner. In the third stage, the process of urbanization slowed down; agricultural water use efficiency increased slowly, while industrial water use efficiency showed an obvious declining trend.
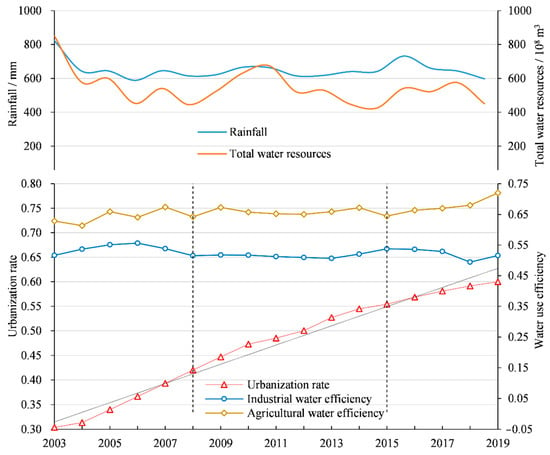
Figure 2.
Trends in rainfall, total water resources, urbanization rate and industrial and agricultural water use efficiency.
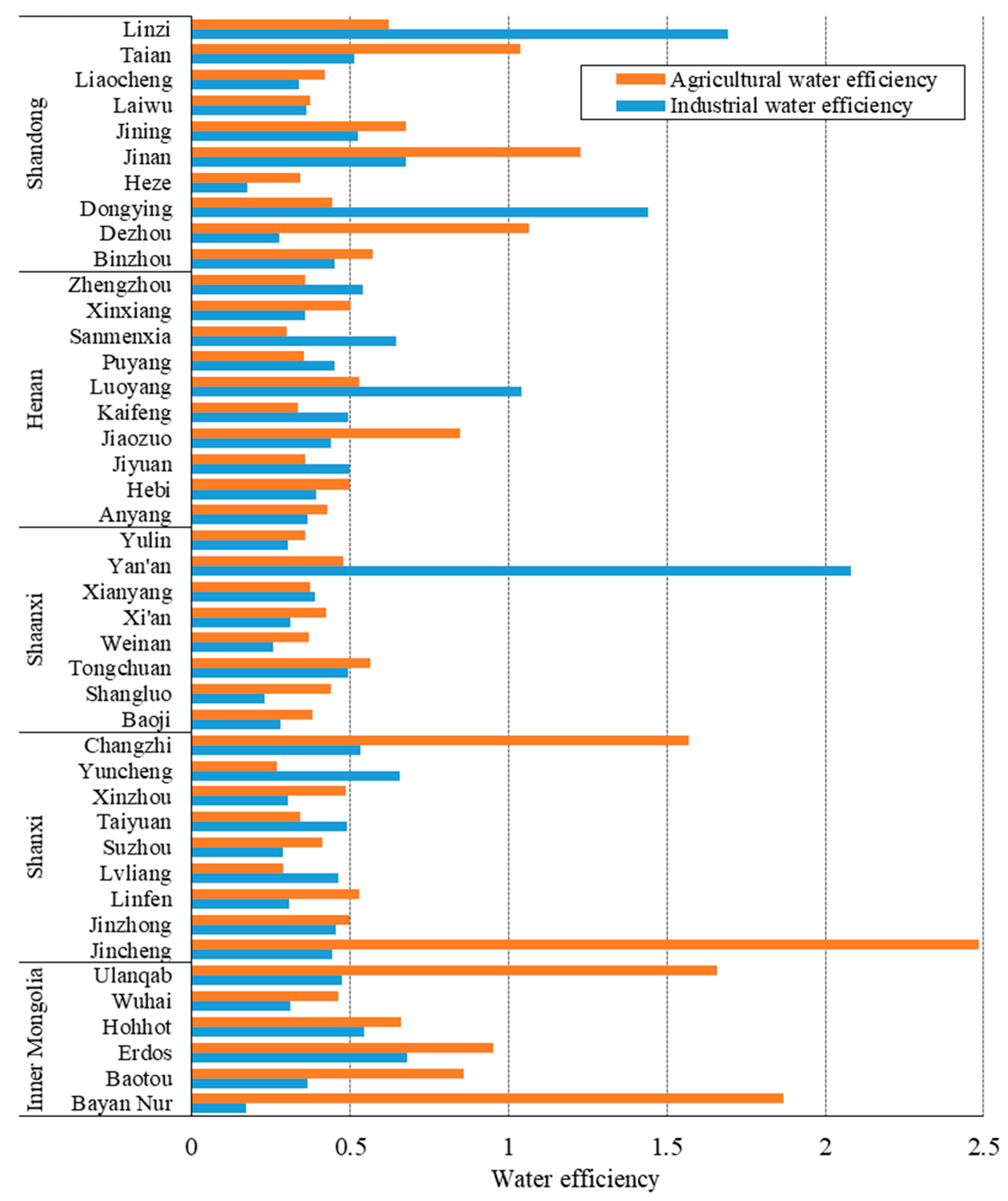
As for spatial characteristics (Figure 3), obvious regional heterogeneity existed in water use efficiency. In terms of industrial water use efficiency, cities with water use efficiency larger than one were Yan’ an, Zibo, Dongying and Luoyang. However, there was no city achieving DEA effectiveness in Inner Mongolia and Shanxi. The province of Shandong had the highest average industrial water use efficiency of 0.65, while efficiency values of Laiwu and Liaocheng were both less than 0.4. For agricultural water use efficiency, cities achieving DEA effectiveness were mainly Bayannur, Jincheng, Changzhi, Dezhou, Jinan and Tai’an. As a large agricultural province, Henan province had no cities with agricultural water use efficiency greater than one. Henan has a large area of arable land and high fertilizer and pesticide use, and the agricultural water use efficiency of Henan province reduced after adding the undesired output.
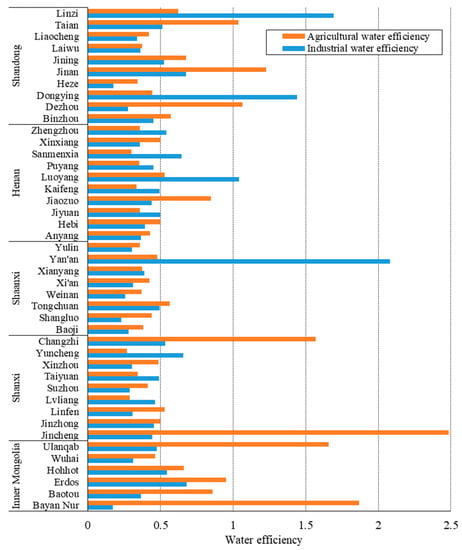
Figure 3.
Regional differences in water use efficiency.
3.2. Spatial Transfer Path of Water Use Efficiency
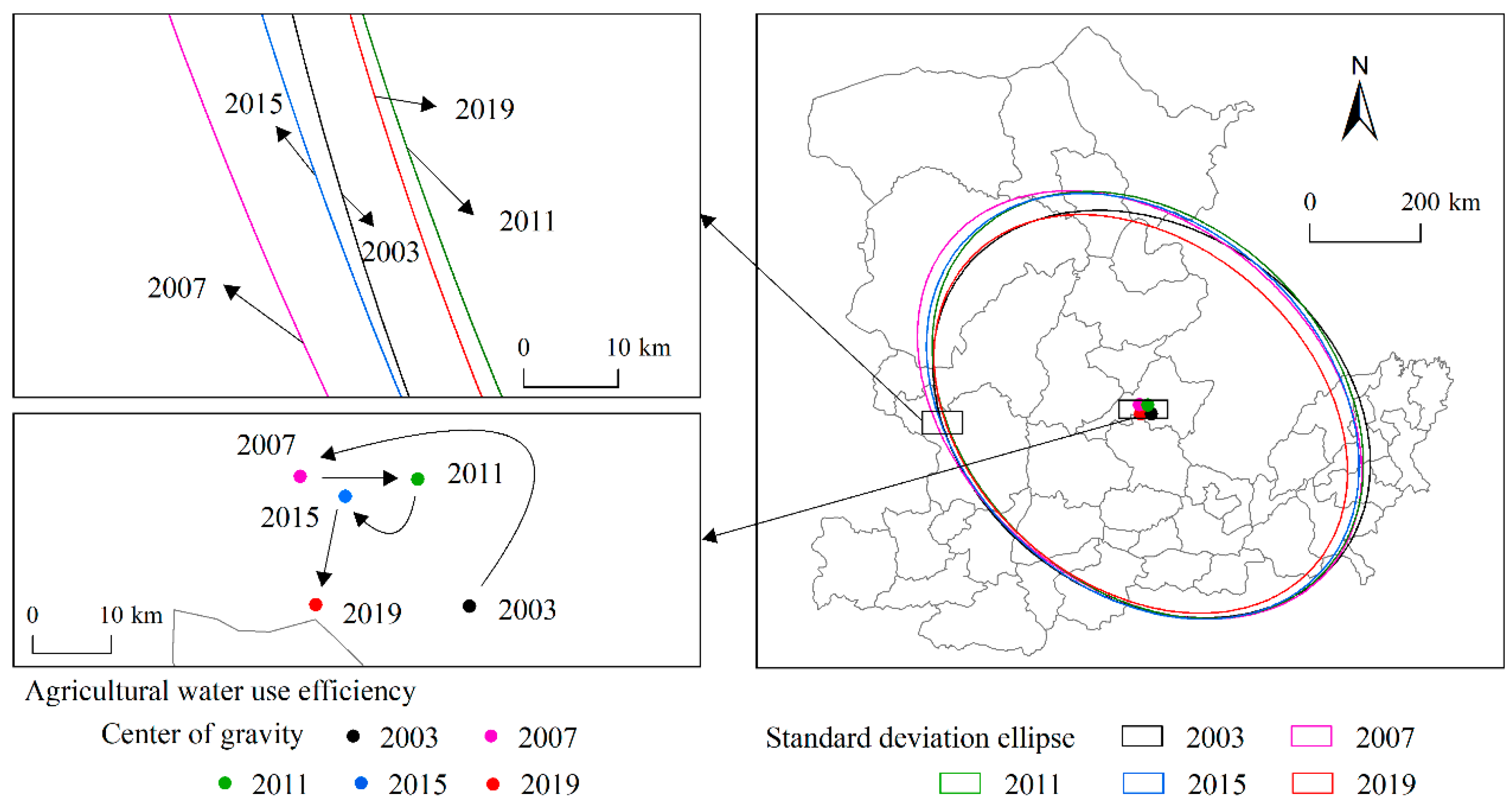
The center of gravity and standard deviation ellipse of water use efficiency could visually present the moving direction and spatial pattern in industrial and agricultural water use efficiency.
3.2.1. The Center of Gravity
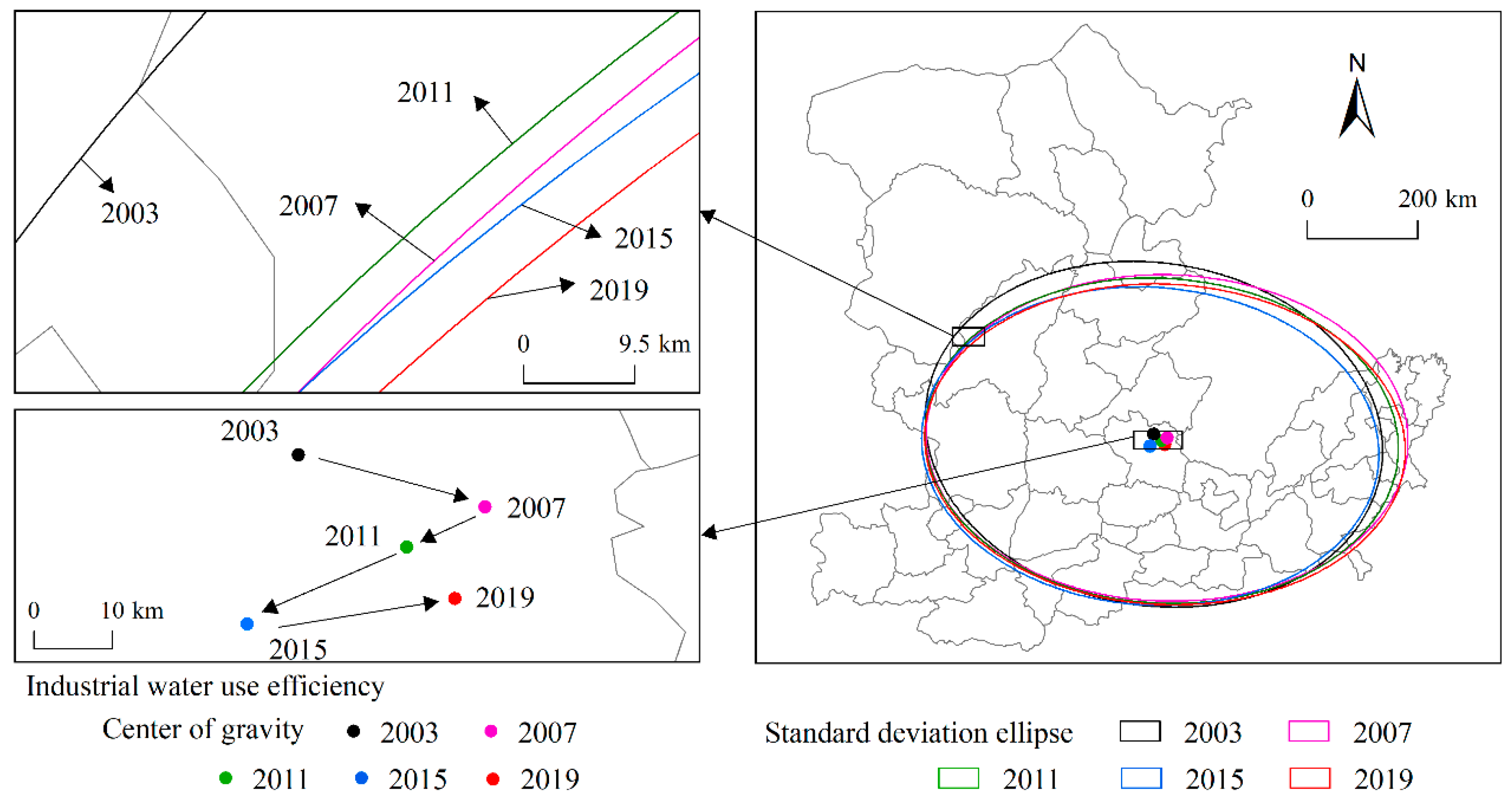
The centers of gravity of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency were slightly different. The center of gravity of industrial water use efficiency was distributed in the range of 112.90–113.26° E and 36.52–36.74° N, in the northeast of Changzhi. The center of gravity for agricultural water use efficiency was distributed in the range of 112.60–112.88° E and 37.12–37.32° N, in central Jinzhong. In terms of the moving amplitude, the centers of gravity of industrial water use efficiency had a large move range, with an average distance of 10.08 km, while the average distance of the centers of gravity of agricultural water use efficiency moved 8.71 km. Decomposing the trajectory of the center of gravity in the east–west and north–south directions, it could be found that the center of gravity moved more in the east–west direction than that of the north–south direction. Therefore, the temporal characteristics of the trajectory depended mainly on the changes in the east–west direction. Specifically, the moving amplitude of the center of gravity of industrial water use efficiency in the east–west direction first declined and then rose. The slowest change in the center of gravity of industrial water use efficiency appeared between 2010 and 2014, indicating that the spatial distribution pattern of industrial water use efficiency was relatively stable over the period. As for the agricultural water use efficiency, the moving of the center of gravity showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing in an east–west direction, with a large change between 2007 and 2010. The moving of the center of gravity has tended towards stability since 2011.
In terms of the direction of movement, the trajectory of the center of gravity of industrial water use efficiency moved from northwest to southeast in a “Z” shape (Figure 4). In the early stage and at the end of the study period, the center of gravity moved from west to east, while in the middle of the study period (2007–2015), the center of gravity moved from northeast to the southwest. As for the agricultural water use efficiency, the center of gravity moved first to the northwest, and then to the south counterclockwise. As a result, the center of gravity of agricultural water use efficiency moved from east to west as a whole during the study period (Figure 5). The centers of gravity of both industrial and agricultural water use efficiency moved from north to south, indicating that the water use efficiency increased gradually in the south of the study area, but slowly in the northern region.
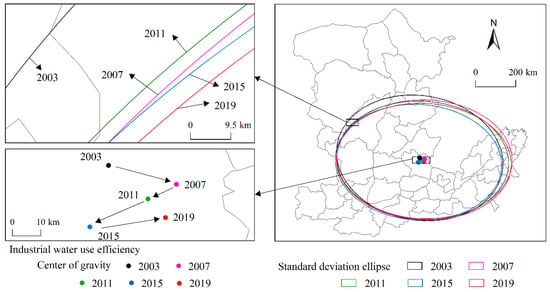
Figure 4.
Trajectory of the center of gravity and standard deviation ellipse of industrial water efficiency.
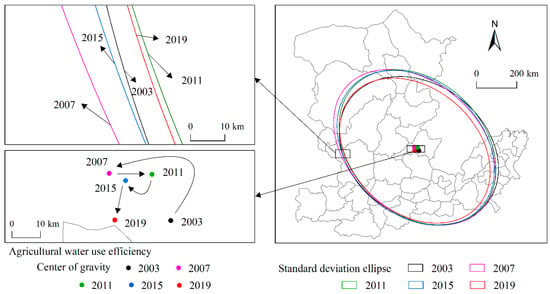
Figure 5.
Trajectory of the center of gravity and standard deviation ellipse of agricultural water use efficiency.
3.2.2. The Standard Deviation Ellipse
Table 3 lists the area, perimeter, and standard deviations along the X- and Y-axis, and the shape index of the standard deviation ellipse.

Table 3.
Changes in center of gravity and standard deviational ellipse of water use efficiency.
The standard deviation ellipses of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency mainly covered the central and southern parts of the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. The area of standard deviation ellipse of the industrial water use efficiency showed a fluctuating downward trend, decreasing from 0.4063 million km2 in 2003 to 0.3968 million km2 in 2019, indicating an overall clustering trend in areas with continuous improvement in industrial water efficiency. The area of the standard deviation ellipse of agricultural water use efficiency first increased from 0.4434 million km2 in 2003 to 0.4529 million km2 in 2015, and then decreased to 0.4044 million km2 in 2019. This result indicated that areas with increasing agricultural water efficiency first showed a trend of fragmentation, and then the degree of concentration increased in recent years. In terms of the direction of the standard deviation ellipse, the industrial water use efficiency showed an “east–west” trend, while the agricultural water use efficiency showed a “northwest–southeast” trend, indicating that the industrial water use efficiency was high in the east–west direction, while the agricultural water use efficiency was high in the northwest–southeast direction.
In terms of the standard deviation along the X- and Y-axis, the industrial water use efficiency showed a gradual decrease from 310.32 km to 290.40 km, indicating that industrial water use efficiency had a clustering trend in the Y-axis direction. Similarly, agricultural water use efficiency showed a fluctuating decrease in the Y-axis direction. Both the industrial and agricultural water use efficiency presented an obvious centripetal effect. In the direction of the X-axis, the standard deviation of industrial water use efficiency fluctuated, while the standard deviation of agricultural water use efficiency showed an increasing and then decreasing trend. During 2007–2019, the standard deviation of agricultural water use efficiency had an obvious decreasing trend along the X-axis, representing an agglomeration effect. Consequently, it could be concluded that the standard deviation ellipse of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency varied mainly in a flattened and elongated manner; that is to say, the X-axis became longer and the Y-axis became shorter over time. The fact that the shape index tended to increase further confirmed that the spatial directional distribution of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency was more prominent.
3.3. Influencing Factors of Water Use Efficiency
To further explore the influencing factors of industrial and agricultural water use efficiency in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, this paper used the Tobit model to reveal the main drivers and proposed corresponding suggestions and countermeasures to promote water use efficiency. The results of the Tobit regression are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Results of Tobit on water use efficiency.
Firstly, there was a clear difference in the impact of urbanization rate on industrial and agricultural water use efficiency. The increase in urbanization level was conducive to an increase in industrial water use efficiency. During the urbanization process, technology progress has been promoted rapidly, and industries with high water consumption and high pollution have been effectively reorganized and improved. In addition, water conservancy facilities have gradually improved. As a result, the input of water resources and the discharge of water pollution have reduced. However, the increase in urbanization rate had a significant role in reducing the agricultural water use efficiency. The differentiated effects of urbanization rate on industrial and agricultural water use efficiency echo the dual structure of urban and rural development in China. As the urbanization and industrialization process accelerates, there is a serious brain drain from rural areas, with high-end talents and advanced technology flowing to the cities. All these elements promote the rapid development of cities. However, agriculture develops slowly due to a lack of advanced production factors, and thus the replacement of irrigation and water conservancy facilities is delayed. Additionally, the outdated irrigation method and unscientific fertilizer application have become obstacles to the improvement of agricultural water use efficiency.
The area of urban construction land, indicating the expanding size of a city, had a negative effect on agricultural water use efficiency at the 1% level of significance, which was consistent with the effect of urbanization rate. For industrial water use efficiency, the area of urban construction land played a negligible role in promoting water use efficiency, suggesting that industrial water use efficiency was not sensitive to the spatial expansion of cities. This may be due to the fact that industry is predominantly located in suburban areas and the water saving benefits through urban expansion are low.
Urban population density represents the degree of population concentration; an increasing urban population density indicates compact and intensive development for a city. Urban population density had a negative effect on water use efficiency, and the effect on agricultural water use efficiency was slightly higher than that on industrial water use efficiency, with estimated coefficients of −0.00596 and −0.00402, respectively. The negative effect of urban population density on agricultural water use efficiency was significant at the 1% level, which was consistent with the effect of urbanization rate and urban construction land area. Urban population agglomeration promotes the one-way flow of capital, talents and technology to cities, while the backwardness of technology and equipment in rural areas limits agricultural development. As a result, agricultural water use efficiency was slow to increase. However, the effect of urban population density on industrial water use efficiency differed with expectation, showing an unstable negative effect. This result suggests that increased population increased water consumption and decreased water use efficiency, a hypothesis further confirmed by the significant negative effect of total population on water use efficiency in the regression results.
An increase in the economic development level was correlated significantly with the rise in water use efficiency, indicating that the rapid development of economy could pull and promote the increase in water use efficiency. Each unit increase in GDP was related to an increase of 0.00006 and 0.00005 for industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, respectively. Although the estimated coefficients were low, they were statistically significant at the levels of 5% and 10%, respectively, indicating that the impact of economic development level on water use efficiency was stable. Regions with a high level of economic development have the ability to attract capital and technology, introduce advanced water conservation facilities and improve water-saving capacity in industrial and agricultural production processes. As a consequence, this can reduce water losses and pollution emission, and thus improve water use efficiency.
The impact of industrial structure on water use efficiency was significant, with the increasing ratio of secondary industry conducive to an increase in industrial water use efficiency, which was in line with expectations. Areas with a large proportion of secondary industries have a high probability of a great degree of industrial agglomeration, promoting the development of advanced water saving technology and water conservation facilities. This has the potential to reduce the input of water resources and improve an increase in water use efficiency. The impact of the primary industry on agricultural water use efficiency was negative, indicating that an increase in the proportion of the primary industry did not contribute to an increase in agricultural water use efficiency. This may be due to the fact that there is no scale effect yet in agriculture water use. The increase in the proportion of primary industry leads to an increase in the amount of water use and water losses in agricultural production, which in turn lowers the agricultural water use efficiency.
Both absolute (industrial and agricultural water consumption) and relative (ratios of industrial and agricultural water consumption) indicators were adopted to characterize the impact of water use structure on water use efficiency. The industrial water consumption and the ratio of industrial water consumption had a positive effect on industrial water use efficiency. For each unit increase in industrial water use, industrial water use efficiency increased by 0.052, statistically significant at the 1% level. Contrastively, the ratio of industrial water consumption had a small and insignificant effect on industrial water use efficiency. This result indicated that the absolute water consumption played a more important role in promoting industrial water use efficiency compared with the relative water consumption indicator.
The effects of agricultural water consumption and the ratio of agricultural water consumption on agricultural water efficiency were significant at the 1% level. However, the directions of the effects were different. The agricultural water consumption positively contributed to the improvement of agricultural water use efficiency, while the ratio of agricultural water consumption was negatively correlated with agricultural water use efficiency. Obviously, the estimated coefficient of the absolute indicator of water consumption was significantly higher than that of the relative indicator of water consumption. Therefore, agricultural water consumption played a more important role than the relative indicator of water consumption in influencing agricultural water use efficiency. Due to the large water consumption of agricultural irrigation, a further increase in agricultural irrigation water is not conducive to the water demand of industry, residents and ecological conservation. Therefore, for agricultural production, it is necessary to improve irrigation technology, popularize drip pipe and sprinkler irrigation facilities, and save agricultural water consumption.
In terms of resource natural endowment, total water resources showed positive effects on water use efficiency. However, the effect failed to pass the significance test, indicating that the total water resources showed an unstable and positive influence on water use efficiency. By comparison, water resource endowment had little difference on industrial and agricultural water use efficiency, with the estimation coefficients of 0.00131 and 0.00172, respectively. It can be concluded that both industrial and agricultural water use efficiency had little dependence on water natural endowment, and the key to improving water use efficiency lies in technological improvements and management optimization.
The index of water saving, characterized by water consumption per unit of GDP, represents water-saving technology. The smaller the index is, the more advanced the water saving technology is. The regression results showed a weak negative correlation between the index of water saving and industrial water use efficiency, suggesting that the improvement of water-saving technology had a role in improving industrial water use efficiency. However, as water-saving technology changed by a small margin, the estimation coefficients were smaller. Therefore, it is important to invest in improving water saving technology to promote water use efficiency in the urbanization and industrialization process.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Related Studies
Urbanization played a different role in affecting water use efficiency, mainly promoting the increase in industrial water use efficiency, and correlating negatively with agricultural water use efficiency. Urbanization has presented different effects in relevant studies. Addae et al. [52] showed that urbanization had a vital impact on improving water use efficiency in West Africa. Bao and Chen [53] demonstrated that urbanization contributed to improving water use efficiency by industrial structure optimization. Furthermore, Mu et al. [54] and Wang et al. [55] indicated that urbanization correlated negatively with water consumption. However, Liu et al. [40] concluded that urbanization rate had a negative effect on water use efficiency due to the increasing undesired output. Different types of urbanization have various effects on water use efficiency. Ding et al. [56] showed that both population urbanization and land urbanization had a negative effect on industrial water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River economic belt, which is not consistent with our results. The probable reason is regional differences. Zhou and Tong [57] showed that population urbanization had no significance on green water use efficiency; industrial urbanization and land urbanization affected green water use efficiency positively, while social urbanization showed a significant negative effect. With a two-stage DEA, Liang et al. [58] showed that urbanization had a significant positive impact on the wastewater treatment efficiency of water resource systems, while having an insignificant negative effect on water use efficiency.
From the perspective of agricultural water utilization, Zhang X et al. [59] indicated that population urbanization, economic urbanization, and balanced urbanization correlated negatively with agricultural water utilization efficiency, which is consistent with our results. Ding et al. [60] showed that population urbanization had a significantly positive effect on agricultural green water utilization, and economic urbanization had a negative effect. For different stages of water utilization, Lu et al. [61] showed that urbanization had a significant positive short-term effect on agricultural water use efficiency, and a different long-term effect among different regions, with a mainly negative effect for China overall. In addition, urbanization influenced agricultural water use efficiency by affecting the irrigation area. Urbanization would skew water resources towards urban areas, and result in a decline in water consumption in agriculture and irrigated areas [62,63]. Moreover, Wang et al. [64] indicated that irrigation area showed a negative effect on agricultural water use efficiency.
Overall, the effect of urbanization on water use efficiency varied. In order to improve water use efficiency, the general opinion is to strengthen the construction of agricultural water conservancy facilities, popularize the use of modern irrigation systems, and accelerate industrial transformation [40,63].
In terms of population density, Liu et al. [65] showed that population density correlated positively with industrial water use efficiency, which is consistent with our findings. The proportion of built-up areas affected industrial water use efficiency in different ways, with a negative effect in regions dominated by industrial economic development and a positive effect in regions dominated by industrial wastewater treatment. The proportions of the primary and the secondary industries were negatively correlated with the utilization efficiency of water resources [33]. Our results showed a negative relationship between industrial structure and agricultural water use efficiency. Due to the low utilization rate of agricultural irrigation water, the traditional agricultural irrigation mode caused a lot of water waste, leading a low utilization efficiency. Deng et al. [42] also indicated that the proportion of agricultural added value had a negative effect on water use efficiency.
From the view of resource endowment conditions, total water resources contributed to improving water use efficiency, a result that differs from the traditional view that water endowment is negatively related to water use efficiency [66]. However, the positive effects of total water resources and per capita water resources have been revealed in related studies [67]. Due to regional differences, different results are also presented in relevant studies for regional sample estimation and global estimation [68].
4.2. The Effect of Urbanization on Water Use Efficiency
Under the background of urban–rural dual structure in China, urbanization and industrialization are advancing rapidly, promoting the rapid concentration of production factors such as capital, labor and knowledge in urban areas. However, rural areas develop slowly, with outdated infrastructure, untimely updates, and backward technology. Large amounts of water resources are used for agricultural irrigation and cultivation with a lot of water loss. In addition, problems of outdated farming techniques and concepts, as well as the unscientific application of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, result in serious soil pollution on farmland and low water use efficiency. Guided by the policy of rural revitalization and common prosperity, the issue of the efficient use of water resources in the agricultural production cannot be ignored. Therefore, in the process of rapid urbanization and industrialization, emphasis should be paid to the tilt of technology towards rural areas, and drip facilities should be widely promoted to reduce water consumption in agricultural irrigation. Moreover, scientific fertilization and pesticide application should be emphasized to reduce pollution of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to improve agricultural water use efficiency.
For the industrial sector, urbanization rate and urban construction land area influenced industrial water use efficiency positively, which shows that, with the development of urbanization, industrial water technology improved, and the reorganization and regulation of industries with high pollution and water consumption resulted in a better performance. As a result, industrial water consumption and water pollution discharge declined, and thus industrial water use efficiency improved. However, the regression results showed that the effect was unstable, particularly for the indicator of urban construction land expansion, which had a small influence on industrial water use efficiency. Industrial production relies heavily on water resources, and the accelerated urbanization and industrialization lead to an increase in industrial scale and water inputs. However, technology is slow to improve, resulting in smaller increases in water use efficiency. Nevertheless, the coefficient of the index of water saving was significantly negative, suggesting that technological progress has led to a decline in water consumption, which is an effective means of improving water use efficiency. In the context of high-quality development aimed at water resource protection and efficient utilization, attention should be given to investments to improve water-saving technology, and then to improving water use efficiency.
5. Conclusions
Based on the undesired SBM-DEA model, this paper calculated the industrial and agricultural water use efficiency of 43 prefecture-level units in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. The spatial pattern of water use efficiency was revealed with the aid of a gravity center and standard deviation ellipse. The Tobit model was used to reveal the impacts of different urbanization indicators on industrial and agricultural water use efficiency. The results showed that, from the perspective of temporal trends, agricultural water use efficiency was greater than industrial water use efficiency. The agricultural water use efficiency showed a fluctuating upward trend, while industrial water use efficiency showed a fluctuating downward trend. In terms of regional heterogeneity, areas with an industrial water use efficiency higher than one were mainly located in Yan’an, Zibo, Dongying and Luoyang. Areas with agricultural water use efficiency higher than one mainly appeared in Bayannaoer, Jincheng, Changzhi, Dezhou, Jinan and Tai’an. Both the changes in centers of gravity and movement trajectory were different between the industrial and agricultural water use efficiency. The gravity center of industrial water use efficiency moved from northwest to southeast in a “Z” shape, while the gravity center of agricultural water use efficiency moved westward as a whole during the study period. Analysis of the influencing factors showed that the improvement of urbanization level was conducive to the improvement of industrial water use efficiency. However, the increase in urbanization rate had a significant negative effect on agricultural water use efficiency. The area of urban construction land had a negative effect on agricultural water use efficiency, while the effect on industrial water use efficiency was negligible. Urban population density had a negative effect on water use efficiency, while the effect on agricultural water use efficiency was slightly higher than that on industrial water use efficiency.
However, some limitations exist. First, the spatial autocorrelation was not taken into consideration in the regression model. Second, other types of water resources utilization, such as water use in households, were not included in this study. Future research will be more in depth.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.L.; methodology, J.Z. and X.Z.; software, Y.W.; formal analysis, Q.L.; resources, J.Z.; data curation, Y.W.; writing—original draft preparation, J.Z.; writing—review and editing, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 42001220 and 42171182, Soft Science Research Project of Henan Province (222400410427), and Innovation Team of Philosophy and Social Science of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province [No. 2021-CXTD-04].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, C.; Yang, T. Variability of water resource in the Yellow River Basin of past 50 years, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2009, 23, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Chen, S.; Dong, P.; Peng, J. Spatial and temporal variability of water discharge in the Yellow River Basin over the past 60 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 1013–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Water Resources Bulletin. 2020. Available online: http://www.mwr.gov.cn/sj/tjgb/szygb/202107/t20210709_1528208.html (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Wei, J.; Lei, Y.; Yao, H.; Ge, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, L. Estimation and influencing factors of agricultural water efficiency in the Yellow River basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ren, J.; Wu, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, W. Effective use rate of generalized water resources assessment and to improve agricultural water use efficiency evaluation index system. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 86, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, D. Water use characteristics and impact factors in the Yellow River basin, China. Water Int. 2020, 45, 148–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; He, F. Impacts of climate changes on water resources in Yellow River Basin, China. Procedia Eng. 2016, 154, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, M.M.; Ma, J. Sustainable development in the Yellow River Basin: Issues and strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, C.; Xiong, L.; Chang, Y. How can agricultural water use efficiency be promoted in China? A spatial-temporal analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, I.; Branca, G.; Zucaro, R. Evaluating input use efficiency in agriculture through a stochastic frontier production: An application on a case study in Apulia (Italy). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureti, T.; Benedetti, I.; Branca, G. Water use efficiency and public goods conservation: A spatial stochastic frontier model applied to irrigation in Southern Italy. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2021, 73, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhao, L.; Zou, W.; Zheng, D. Water resource utilization efficiency and spatial spillover effects in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Qin, H.; Meng, Y.; Wu, Z. Comprehensive evaluation of water-use efficiency in China’s Huai river basin using a cloud-compound fuzzy matter element-entropy combined model. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, X.; She, D.; Wang, J. The spatial and temporal variation of water use efficiency in the Huai River Basin using a comprehensive indicator. Water Supply 2017, 17, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hewings, J.D.; Chen, X.; Wang, S. A factor decomposing model of water use efficiency at sector level and its application in Beijing. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2016, 29, 405–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Lu, S.; Shang, L.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Lei, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H. Decomposition methods for analyzing changes of industrial water use. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 808–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Lu, S.; Shang, L.; Li, X.; Shi, H.; Li, W. Decomposition of industrial water use from 2003 to 2012 in Tianjin, China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2017, 116, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Storto, C. Benchmarking operational efficiency in the integrated water service provision. Benchmarking 2014, 21, 917–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Zhang, X.; Du, H.; Shi, H. Urban water resource utilization efficiency in China. Chinese Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, A.V.; Speelman, S.; Chandrakanth, M.G.; Van Huylenbroeck, G. Impact of groundwater markets in India on water use efficiency: A data envelopment analysis approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 2924–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Q.; Ren, Q.; Nolan, R.H.; Wu, P.; Yu, Q. Assessing China’s agricultural water use efficiency in a green-blue water perspective: A study based on data envelopment analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 96, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, T.K.; Paudel, K.P.; Guidry, K.M. An Evaluation of Irrigation Water Use Efficiency in Crop Production Using a Data Envelopment Analysis Approach: A Case of Louisiana, USA. Water 2020, 12, 3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurer, M.; Spahni, R.; Frank, D.; Joos, F.; Leuenberger, M.; Loader, N.; McCarroll, D.; Gagen, M.; Poulter, B.; Siegwolf, R.; et al. Spatial variability and temporal trends in water-use efficiency of European forests. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3700–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Peng, J.; Liang, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatial–temporal patterns of water use efficiency and climate controls in China’s Loess Plateau during 2000–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dekker, S.; Groenendijk, M.; Booth, B.; Huntingford, C.; Cox, P. Spatial and temporal variations in plant water-use efficiency inferred from tree-ring, eddy covariance and atmospheric observations. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2016, 7, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Pijanowski, B.C. Is there a relationship between water scarcity and water use efficiency in China? A national decadal assessment across spatial scales. Land Use Policy 2017, 69, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, P.; Wu, S.; Sun, B.; Feng, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, B.; Chen, G.; Duan, C.; Lei, L.; et al. Spatial-temporal distribution of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) roots and water use efficiency under ridge–furrow dual mulching. Agr. Water Manag. 2020, 240, 106301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xu, C. The difference and convergence of total factor productivity of inter-provincial water resources in China based on three- stage DEA-Malmquist index model. Sustain. Comput.-Infor. 2019, 22, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, W.; Hou, M.; Deng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, K. Spatial–temporal evolution characteristics and influencing factors of agricultural water use efficiency in Northwest China—Based on a Super-DEA model and a spatial panel econometric model. Water 2021, 13, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Ma, Q.F.; Zhao, L.S. Analysis of driving mechanism based on a GWR model of green efficiency of water resources in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Wang, R.; Zeng, X. Water resources utilization efficiency and influence factors under environmental restrictions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 184, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, L.; Ma, D.; Su, R.; Yang, Q. How agricultural water use efficiency varies in China—A spatial-temporal analysis considering unexpected outputs. Agr. Water Manag. 2022, 260, 107297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Wang, Z.L. Research on the impact of environmental regulation on water resources utilization efficiency in China based on the SYS-GMM model. Water Supply 2021, 21, 3643–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, G. Assessing China’s “developing a water-saving society” policy at a river basin level: A structural decomposition analysis approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wu, W. Determination of the effective utilization coefficient of irrigation water based on geographically weighted regression. Front. Earth Sci.-PRC 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Chen, X. Spatial econometric analysis on influencing factors of water consumption efficiency in urbanizing China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.J.; Xu, C.L.; Zhang, X.Q. Spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of water resources utilization efficiency of cities along the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 1930–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, M.; Yang, D.; Chen, W. Green efficiency of water resources in Northwest China: Spatial-temporal heterogeneity and convergence trends. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.T.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Ma, J.X. Relationship between water resource utilization level and socio⁃economic development in the Yellow River Basin. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Najmuddin, O.; Zhang, F. Evolution and the drivers of water use efficiency in the water-deficient regions: A case study on Ω-shaped region along the Yellow River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19324–19336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Ji, W.; Hou, M.; Ma, T.; Mao, J. Evaluation of efficiency and resilience of agricultural water resources system in the Yellow River Basin, China. Agr. Water Manag. 2022, 266, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Li, L.; Song, Y. Provincial water use efficiency measurement and factor analysis in China: Based on SBM-DEA model. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, A.; Qing, P.; Naseer, M.; Abid, M.; Anwar, M.; Javed, I. Can the informal groundwater markets improve water use efficiency and equity? Evidence from a semi-arid region of Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Yang, G.; Yang, D. Investigating industrial water-use efficiency in mainland China: An improved SBM-DEA model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with undesirable outputs in DEA: A Slacks-based measure (SBM) approach. Oper. Res. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Pasurka, C., Jr. Accounting for Air Pollution Emissions in Measures of State Manufacturing Productivity Growth. J. Reg. Sci. 2001, 41, 381–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, L.; Geng, X. Ecological efficiency of hog scale production under environmental regulation in China: Based on an optimal super efficiency SBM-Malmquist–Tobit model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53088–53106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J. Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 1958, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, S.; Fan, Z. Modeling the role of environmental regulations in regional green economy efficiency of China: Empirical evidence from super efficiency DEA-Tobit model. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalei, N.N.; Joshi, J.M. Estimating technical efficiency of petroleum refineries using DEA and tobit model: An India perspective. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 142, 107047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addae, E.A.; Sun, D.; Abban, O.J. Evaluating the effect of urbanization and foreign direct investment on water use efficiency in West Africa: Application of the dynamic slacks-based model and the common correlated effects mean group estimator. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Chen, X. The driving effects of urbanization on economic growth and water use change in China: A provincial-level analysis in 1997–2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Fang, L.; Dou, W.; Wang, C.; Qu, Y. Urbanization-induced spatio-temporal variation of water resources utilization in northwestern China: A spatial panel model based approach. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, R. Urbanization and water consumption at national- and subnational-scale: The roles of structural changes in economy, population, and resources. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Fu, Z.; Jia, H. Study on urbanization level, urban primacy and industrial water utilization efficiency in the Yangtze River economic belt. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Tong, C. Does rapid urbanization improve green water-use efficiency? Based on the investigation of Guangdong province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Li, J.; Guo, G.; Li, S.; Gong, Q. Evaluation for water resource system efficiency and influencing factors in western China: A two-stage network DEA-Tobit model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, Y.; Ding, X. How high-quality urbanization affects utilization efficiency of agricultural water resources in the Yellow River basin under double control action? Sustainability 2020, 12, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Cai, Z.; Fu, Z. Does the new-type urbanization construction improve the efficiency of agricultural green water utilization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64103–64112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Sarkar, A.; Hou, M.; Liu, W.; Guo, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, M. The impacts of urbanization to improve agriculture water use efficiency—an empirical analysis based on spatial perspective of panel data of 30 provinces of China. Land 2022, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Urbanization, agricultural water use, and regional and national crop production in China. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avazdahandeh, S.; Khalilian, S. The effect of urbanization on agricultural water consumption and production: The extended positive mathematical programming approach. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Wu, F.; Li, Z. An integrated analysis of agricultural water-use efficiency: A case study in the Heihe River Basin in Northwest China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 89–90, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Y.; Hou, R.; Wang, H. Does urbanization improve industrial water consumption efficiency? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. Evaluation of China’s water-resource utilization efficiency based on a DEA-Tobit two-stage model. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1764–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Xue, H.F. China’s industrial green total factor water efficiency under the constraints of environment and resource. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 5079–5091. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.L.; Huang, D.C.; Ma, J.G. Water resource utility efficiency and its influencing factors considering undesirable goods. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).