Scrutinizing Urbanization in Kathmandu Using Google Earth Engine Together with Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
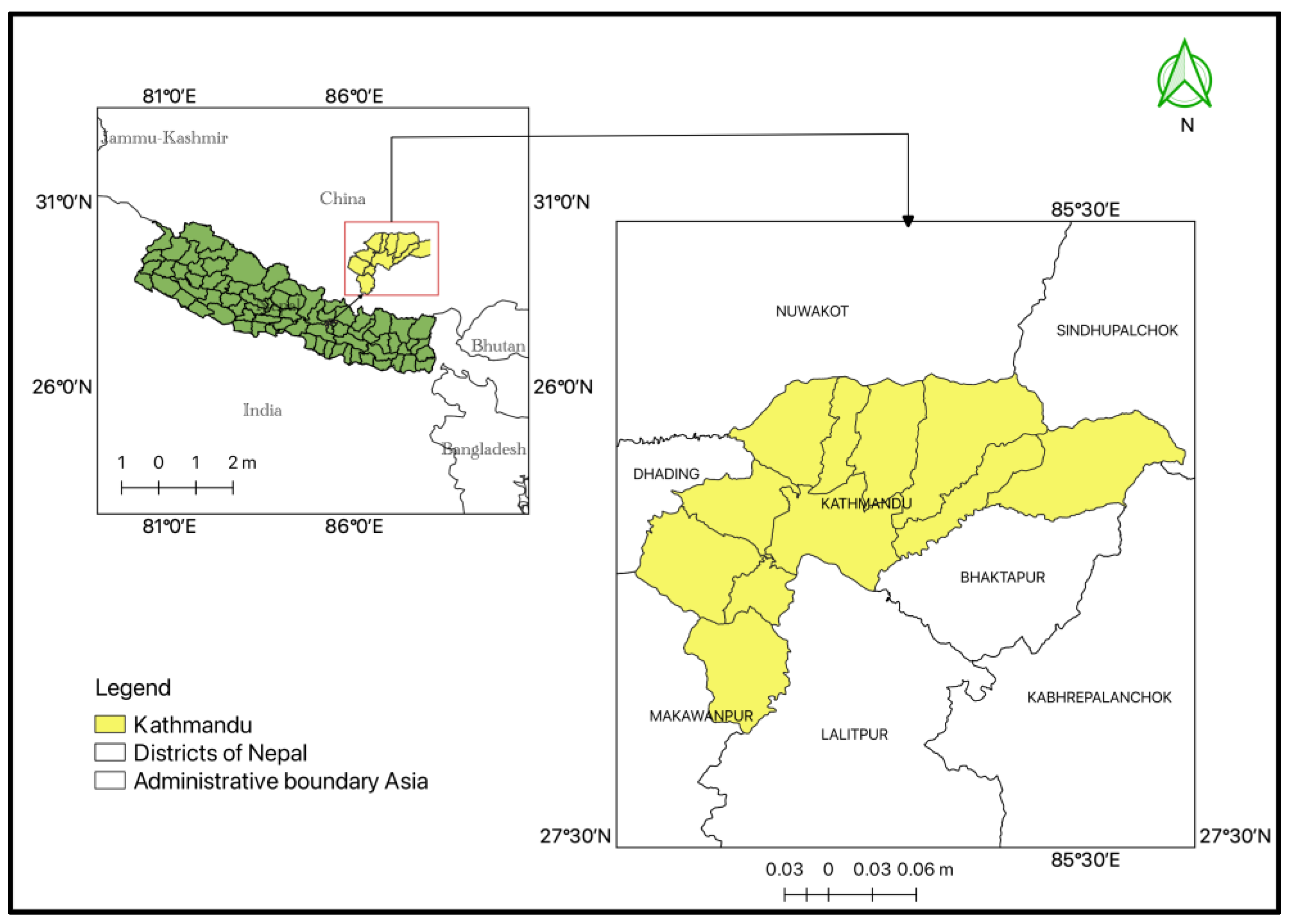
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Used
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Image Pre-Processing
2.3.2. Image Normalization
2.3.3. Land-Cover Classes and Sample Data Collection
2.3.4. Random Forest Classification
2.3.5. Accuracy Assessment
2.4. Scenario Modelling in InVEST
3. Results
3.1. Land-Cover Change over 20 Years
Accuracy Assessment of the Classification
3.2. Geographic Trend of Urbanization
3.3. Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGranahan, G. Urbanization. The International Encyclopedia of Social and Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Wright, J.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; Volume 24, pp. 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Beall, J.; Guha-Khasnobis, B.; Kanbur, R. Urbanization and Development: Multidisciplinary Perspectives; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinelli, L.; Black, D. Urbanization and growth. J. Urban. Eco. 2004, 56, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuddus, A.; Tynan, E.; McBryde, E. Urbanization: A problem for the rich and the poor? Public Health Rev. 2020, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Clemente, R.; Strano, E.; Batty, M. Urbanization and economic complexity. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, R.K. Urbanization and Related Environmental Issues of Metro Manila. J. Adv. Coll. Eng. Manag. 2018, 3, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Aziz, B.; Liu, X.-H. The relationship between urbanization, technology innovation, trade openness, and CO2 emissions: Evidence from a panel of Asian countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35349–35363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, V. Urbanization in Developing Countries. World Bank Res. Obs. 2002, 17, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basyal, G.K.; Khanal, N.R. Process and characteristics of urbanization in Nepal. Contrib. Nepal. Stud. 2001, 28, 187–225. Available online: http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/contributions/pdf/CNAS_28_02_03.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- UN. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development; UN General Assembly 21 October 2015, A/RES/70/1; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- UNFCCC. Adoption of the Paris Agreement, 21st Conference of the Parties; An official publication; United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change: Paris, France, 2015; Available online: https://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/l09r01.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- UN DESA. World Urbanization Prospects: 2018 Revision; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/publications/2018-revision-of-world-urbanization-prospects.html (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Thapa, R.B.; Murayama, Y. Examining Spatiotemporal Urbanization Patterns in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: Remote Sensing and Spatial Metrics Approaches. Remote. Sens. 2009, 1, 534–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoUD. National Urban Development Strategy 2017; Ministry of Urban Development, Government of Nepal: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2017. Available online: https://www.moud.gov.np/storage/listies/July2019/NUDS_PART_A.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Timsina, N.P.; Shrestha, A.; Poudel, D.P.; Upadhyaya, R. Trend of Urban Growth in Nepal with a Focus in Kathmandu Valley: A Review of Processes and Drivers of Change; The University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoLRM. Land Use Policy, Government of Nepal; Ministry of Land Reform and Management Singhadurbar: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2015. Available online: https://molcpa.gov.np/downloadfile/land%20use%20policy__2015_1505895657_1536124080.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Rimal, B. Application of remote sensing and GIS, land use/land cover change in Kathmandu Metropolitan city, Nepal. J. Theo. Appl. Infor. Tech. 2011, 23, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.W.; Gebru, B.M.; Lamchin, M.; Kayastha, R.B.; Lee, W.-K. Land Use and Land Cover Change Detection and Prediction in the Kathmandu District of Nepal Using Remote Sensing and GIS. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Shrestha, M.; Chhetri, N. Rapid Urban Growth in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal: Monitoring Land Use Land Cover Dynamics of a Himalayan City with Landsat Imageries. Environments 2017, 4, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Shakya, N.M. Integrated Assessment of Climate Change and Land Use Change Impacts on Hydrology in the Kathmandu Valley Watershed, Central Nepal. Water 2019, 11, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, B.K. Impact of Land Use Change on Flow and Sediment Yields in the Khokana Outlet of the Bagmati River, Kathmandu, Nepal. Hydrology 2018, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarif, O.; Rimal, B.; Stork, N.E. Assessment of Changes in Land Use/Land Cover and Land Surface Temperatures and Their Impact on Surface Urban Heat Island Phenomena in the Kathmandu Valley (1988–2018). ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyamba, A.; Kline, E.K.; Collins, E. Remote Sensing. In International Encyclopedia of the Social and Behavioral Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Acker, J.; Williams, L.; Ardanuy, C.P.; Miller, S.; Schueler, C.; Vachon, P.W.; Manore, M. Remote Sensing from Satellites. In Reference module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C.; San Lim, H.; MatJafri, M.Z.; Abdullah, K. A comparison of radiometric correction techniques in the evaluation of the relationship between LST and NDVI in Landsat imagery. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 184, 3813–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Sanga-Ngoie, K. The integrated radiometric correction of optical remote sensing imageries. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 5957–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Mutanga, O. Google Earth Engine Applications Since Inception: Usage, Trends, and Potential. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Tallis, H.T.; Ricketts, T.; Guerry, A.D.; Wood, S.A.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST +VERSION+ User’s Guide. The Natural Capital Project, Stanford University, University of Minnesota, The Nature Conservancy, and World Wildlife Fund. 2018. Available online: https://invest-userguide.readthedocs.io/_/downloads/en/3.5.0/pdf/ (accessed on 8 September 2022).
- Davids, J.C.; Rutten, M.M.; Shah, R.D.T.; Shah, D.N.; Devkota, N.; Izeboud, P.; Pandey, A.; van de Giesen, N. Quantifying the connections—Linkages between land-use and water in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozovits, A.R.; Bustamante, M. Land use change, air pollution and climate change—Vegetation response in Latin America. Dev. Environ. Sci. 2013, 13, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, C.L.; Spracklen, D.V. Land Use Change Impacts on Air Quality and Climate. J. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4476–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taati, A.; Sarmadian, F.; Mousavi, A.; Pour, C.T.H.; Shahir, A.H.E. Land use classification using support vector machine and maximum likelihood algorithms by Landsat 5 TM images. Walailak J. Sci. Technol. (WJST) 2015, 12, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Shetty, A.; Singh, S.K.; Siddiqui, Z. Land use and land cover classification of LISS-III satellite image using KNN and decision tree. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, New Delhi, India, 16–18 March 2016; pp. 1277–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.A. (Ed.) Supervised Classification Techniques. In Remote Sensing Digital Image Analysis; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 263–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, K.; Bhaskaran, K. Supervised Classification Performance of Multispectral Images. J. Comput. 2010, 2, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, B.N.; Rafter, A. Urban growth analysis and modeling in the Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Habitat Int. 2006, 30, 1056–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN DESA. World Urbanization Prospects: 2014 Revision; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/publications/2014-revision-world-urbanization-prospects.html (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- DHM. Climate Normals, Department of Hydrology and Meteorology, Babarmahal, Kathmandu. 2022. Available online: https://dhm.gov.np/uploads/climatic/1805982474Climate%20Normal%201991-2020.pdf?fbclid=IwAR3dEwOkiY3e3z4Q6tGfBbmqy8aTkMZW46Z0hgGO8_XVPMTqBNhWnstXTTQ (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Bhuju, U.R.; Shakya, P.R.; Basnet, T.B.; Shrestha, S. Nepal Biodiversity Resource Book: Protected Areas, Ramsar Sites, and World Heritage Sites; International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD): Kathmandu, Nepal, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- CBS. Preliminary Report of Census 2021; Central Bureau of Statistics: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2021. Available online: https://censusnepal.cbs.gov.np/Home/Details?tpid=1 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- US Geological Survey. Landsat Collection 2 level- 3 science products. 2022. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-collection-2 (accessed on 22 August 2022).
- Government of Nepal. Kathmandu District Boundary. National Spatial Data Center: Geoportal. Ministry of Land Management, Cooperatives and Poverty Alleviation, Survey Department. 2022. Available online: https://nationalgeoportal.gov.np/#/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Google Earth. Kathmandu district, 277172° N, 853240° E, 1400 m. 2022. Available online: https://www.google.com/earth/index.html (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Clinton, N.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Z. Mapping major land cover dynamics in Beijing using all Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, M.; Herold, M. Mapping imperviousness using NDVI and linear spectral unmixing of ASTER data in the Cologne-Bonn region (Germany). In Remote Sensing for Environmental Monitoring, GIS Applications, and Geology, 3rd ed.; SPIE: St. Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; Volume 5239, pp. 274–284. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.V.; Setia, R.; Sahoo, S.; Prasad, A.; Pateriya, B. Evaluation of NDWI and MNDWI for assessment of waterlogging by integrating digital elevation model and groundwater level. Geocarto Int. 2015, 30, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, G.; Shi, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Hao, Y. Land use/cover classification in an arid desert-oasis mosaic landscape of China using remote sensed imagery: Performance assessment of four machine learning algorithms. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maingi, J.K.; Kepner, S.E.; Edmonds, W.G. Accuracy Assessment of 1992 Landsat-MSS Derived Land Cover for the Upper San Pedro Watershed (US/Mexico); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Manonmani, R.; Suganya, G.M.D. Remote sensing and GIS application in change detection study in urban zone using multi temporal satellite. Int. J. Geom. Geos. 2010, 1, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis Group, LLC: Abingdon, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- InVest. Integrated valuation of ecosystem services and tradeoffs. 2022. Available online: https://invest.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Anderson, J.R. A Land Use and Land Cover Classification System for Use with Remote Sensor Data; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1976; Volume 964. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0964/report.pdf (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Campbell, J.B. Introduction to Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, P.K. Population Growth, Migration and Urbanisation. Environmental Consequences in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. In Environmental Change and its Implications for Population Migration; Unruh, J.D., Krol, M.S., Kliot, N., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 2004; pp. 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, N.; Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Tenneson, K. Automatic Detection of Spatiotemporal Urban Expansion Patterns by Fusing OSM and Landsat Data in Kathmandu. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijal, S.; Rimal, B.; Acharya, R.P.; Stork, N.E. Land use/land cover change and ecosystem services in the Bagmati River Basin, Nepal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Li, S.-C.; Liu, L.-S.; Wu, X.; Khanal, N.R. Review of studies on land use and land cover change in Nepal. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Sloan, S.; Keshtkar, H.; Sharma, R.; Rijal, S.; Shrestha, U.B. Patterns of Historical and Future Urban Expansion in Nepal. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, D.O.; Schröder, D.; Forkuo, E.K.; Bugri, J.T. Application of Geo-Information Techniques in Land Use and Land Cover Change Analysis in a Peri-Urban District of Ghana. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1265–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaakob, U.; Masron, T.; Masami, F. Ninety years of urbanization in Malaysia: A geographical investigation of its trends and characteristics. J. Rits. Soc. Sci. Hum. 2010, 4, 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Halmy, M.W.A.; Gessler, P.E.; Hicke, J.A.; Salem, B.B. Land use/land cover change detection and prediction in the north-western coastal desert of Egypt using Markov-CA. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrop, M. Landscape change and the urbanization process in Europe. Landsc. Urban Plan 2004, 67, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.B. Spatial Process of Urbanization in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Ph. D. Dissertation, Graduate School of life and Environmental Sciences, The Univesrity of Tsukuba, Kathmandu Valley, Nepal, 2009. Available online: http://giswin.geo.tsukuba.ac.jp/sis/thesis/rbthapa.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Schiavina, M.; Melchiorri, M.; Corbane, C.; Freire, S.; Batista e Silva, F. Built-up areas are expanding faster than population growth: Regional patterns and trajectories in Europe. J. Land Use Sci. 2022, 17, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Dong, T.; Cobbinah, P.B.; Jiao, L.; Sumari, N.S.; Chai, B.; Liu, Y. Urban expansion and form changes across African cities with a global outlook: Spatiotemporal analysis of urban land densities. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.P.; Best, M.J.; Betts, R.A. Climate change in cities due to global warming and urban effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L09705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, S. Urbanisation and Food Insecurity Risks: Assessing the Role of Human Development. Oxf. Dev. Stud. 2016, 44, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayenhoff, E.S.; Moustaoui, M.; Broadbent, A.M.; Gupta, V.; Georgescu, M. Diurnal interaction between urban expansion, climate change and adaptation in US cities. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2018, 8, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokal, M.; Bai, Z.; Franssen, W.; Hofstra, N.; Koelmans, A.A.; Ludwig, F.; Ma, L.; van Puijenbroek, P.; Spanier, J.E.; Vermeulen, L.C.; et al. Urbanization: An increasing source of multiple pollutants to rivers in the 21st century. npj Urban Sustain. 2021, 1, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.K. Housing provision in the Kathmandu Valley: Public agency and private sector initiation. Urbani izziv 2010, 21, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Marwasta, D. Urbanisation trends in developing countries: Comparative study of Yogyakarta City and Kathmandu Valley. J. Nat. Resour. Dev. 2015, 5, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, K.B.; Thapa, B.R.; Aihara, Y.; Shrestha, S.; Bhattarai, A.P.; Bista, N.; Kazama, F.; Shindo, J. Hidden Cost of Drinking Water Treatment and Its Relation with Socioeconomic Status in Nepalese Urban Context. Water 2018, 10, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.; Prajapati, R.N. Drawdown and Dynamics of Groundwater Table in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Open Hydrol. J. 2014, 8, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.K.; Regmi, R.K.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K.; Kumar, P.; Saraswat, C. Assessment of Bagmati river pollution in Kathmandu Valley: Scenario-based modeling and analysis for sustainable urban development. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2017, 9, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.A.; Huang, X.; Sillanpää, M. Effects of urbanization on water quality of the Bagmati river in Kathmandu valley. Nepal. Stud. Ori. Elec. 2011, 109, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, K.B.; Pant, R.R.; Rimal, B.; Mishra, A.D. Comparative assessment of water quality in the Bagmati River basin, Nepal. ZOO-J. 2019, 5, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, K.; Shrestha, S.M.; Rawal, D.S.; Pant, B.R. Quality of drinking water in Kathmandu valley, Nepal. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2019, 5, 1995–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, B.R.; Breu, T.; Ghale, Y. New Challenges in Land Use in Nepal: Reflections on the Booming Real-estate Sector in Chitwan and Kathmandu Valley. Scott. Geogr. J. 2017, 133, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Shakya, N.M. Land Use Land Cover (LULC) Change Projection in Kathmandu Valley using the CLUE-S Model. J. Adv. Coll. Eng. Manag. 2021, 6, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Park, T.; Wang, X.; Piao, S.; Xu, B.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Fuchs, R.; Brovkin, V.; Ciais, P.; Fensholt, R.; et al. China and India lead in greening of the world through land-use management. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, C.; Li, R.; Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Du, G.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010–2015. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Data | Source | Spatial Resolution | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| LANDSAT 8 Surface Reflectance Collection 2 Tier 1 | US Geological Survey (USGS) [43] | 30 m | 2021 |
| LANDSAT 5 Surface Reflectance Collection 2 Tier 1 | USGS [43] | 30 m | 2011 2001 |
| Kathmandu district boundary (shape file) | Government of Nepal, Survey Department [44] | - | 2021 |
| Reference points | Google Earth Pro [45] | 15 cm–15 m | 2021 2011 2001 |
| Year | Number of Images |
|---|---|
| 2021 | 18 |
| 2011 | 15 |
| 2001 | 7 |
| Spectral Indices | Formula |
|---|---|
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | |
| Enhanced vegetation index (EVI) | |
| Normalized difference built-up index (NDBI) | |
| Built-up areas (BU) | |
| Modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI) |
| Accuracy | Formulae |
|---|---|
| Overall accuracy | |
| Producer accuracy | |
| Consumer accuracy | |
| Kappa coefficient [53] | |
|
where i = class number; n = total number of classified pixels; nii = number of correctly classified pixels in class i; Ci = total number of classified pixels belonging to class i; Gi = total number of actual data pixels of class i. |
| Land Use | Forest (km2) | Agriculture (km2) | Built-Up Area (km2) | Green Space (km2) | Surface Water Bodies (km2) | Bare Land (km2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | |||||||
| 2021 | 177.97 | 101.35 | 117.47 | 8.52 | 4.65 | 3.60 | |
| 2011 | 187.33 | 132.14 | 84.69 | 4.82 | 4.48 | 0.14 | |
| 2001 | 215.95 | 137.50 | 50.02 | 1.10 | 5.68 | 3.31 | |
| Difference in 20 years | −37.98 | −36.15 | 67.45 | 7.42 | −1.03 | 0.29 | |
| Overall Training Accuracy | Kappa Coefficient | |
|---|---|---|
| 2021 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| 2011 | 0.96 | 0.95 |
| 2001 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Year | Accuracy | Forest | Agriculture | Built-Up Area | Green Space | Surface Water | Bare Land |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | CA | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.98 | |
| 2011 | CA | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.94 | 0.91 |
| PA | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.99 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 2001 | CA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| PA | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Land Use | 2001–2011 | 2011–2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Forest | 1.20% | 1.86% |
| Agriculture | 19.71% | 25.80% |
| Green space | 10.27% | 7.77% |
| Surface water | 0.08% | 0.05% |
| Bare land | 0.35% | 1.32% |
| Land Use | Area Prone to Transition |
|---|---|
| Forest | 33.33 km2 |
| Agriculture | 66.67 km2 |
| Green space | 0.35 km2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aryal, A.; Bhatta, K.P.; Adhikari, S.; Baral, H. Scrutinizing Urbanization in Kathmandu Using Google Earth Engine Together with Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling. Land 2023, 12, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010025
Aryal A, Bhatta KP, Adhikari S, Baral H. Scrutinizing Urbanization in Kathmandu Using Google Earth Engine Together with Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling. Land. 2023; 12(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleAryal, Anisha, Kishor Prasad Bhatta, Sanot Adhikari, and Himlal Baral. 2023. "Scrutinizing Urbanization in Kathmandu Using Google Earth Engine Together with Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling" Land 12, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010025
APA StyleAryal, A., Bhatta, K. P., Adhikari, S., & Baral, H. (2023). Scrutinizing Urbanization in Kathmandu Using Google Earth Engine Together with Proximity-Based Scenario Modelling. Land, 12(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/land12010025








