Abstract
Previous studies of the literature show that there are great uncertainties regarding costs and gains for peatland restoration strategies and that the monetary estimation of peatland restoration and possible alternatives can be complicated. The research aims to compare the economic costs and benefits of existing peatland restoration strategies and alternative use of peat and peatlands. A core method for the evaluation of the economic aspects of each strategy used is the composite index method. Information for constructing the composite index is based on data from the scientific literature, reports, and local project studies. In the study, peatland strategies, peat extraction, and alternative use in products were mutually compared with existing strategies. The highest composite index among strategies was for the production of insulation boards and cultivation of paludicultures using cattail or sphagnum farming. Cultivation of paludicultures can be an economically viable strategy if costs and gains are evaluated. Cultivation of cattail or sphagnum can make economic gains for landowners and farmers, and solutions for the reduction in necessary initial investments should be sought. Harvested biomass can be used for high-added-value products, in this case, insulation boards from cattail (Typha). Therefore, peat biomass can be used as an economically valuable resource, and raw material for insulation board production is obtained without the extraction of peat. Also, ecosystem services and potential income are not reduced.
1. Introduction
Organic soils include land with a peat layer at the surface [1]. Peatlands are crucial for carbon storage and the conservation of endangered species [2]. Peatlands are crucial carbon sources, accounting for 21% of global carbon stocks due to their high carbon density [3]. As a result of drainage, oxygen enters the soil, promoting peat microbial decomposition and leading to greenhouse gas emissions (GHG). Drained peatlands are sources of GHG emissions such as methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), as well as carbon dioxide (CO2) [3]. As the depth of peatland drainage increases, the amount of GHG emissions also increases. It is estimated that 1 hectare (ha) of drained soil emits approximately 30–40 tons of GHG emissions [1]. Degraded peatlands are known to account for ~5% of human-caused GHG emissions, releasing ~2 gigatonnes (Gt) of CO2 annually. Globally, agriculture, including the production of agricultural products and the extraction of peat for horticulture, is one of the largest anthropogenic producers of peat emissions [1].
It is estimated that approximately 50% of the area of peatlands in Eastern Europe and the Nordic countries (~350,000 km2) has been assessed as degraded, mentioning peat extraction, forestry, and the use of peat in agriculture and horticulture as the main causes of degradation [4]. In the context of GHG emissions from peatlands, the second highest emission rate is indicated in the European Union (EU) member states, accounting for around 15% of the total emissions emitted by peatlands. It is estimated that the volume of emissions in the EU is approximately 230 megatons (Mt) of CO2 equivalent (eq) [5,6]. In the EU, Germany, Finland, Poland, Ireland, Sweden, Romania, Latvia, Lithuania, and the Netherlands are the countries where the largest amount of GHG emissions from peatlands is estimated. In the Baltic States, it is estimated that the amount of annual emissions from peatlands is greater than 50 Mt CO2, ranking them as one of the largest emitters of GHG emissions from peatlands within the EU [7].
A total of 12% of Latvia’s territory consists of peatlands, of which approximately 39,500 ha have been identified as degraded peatlands [7]. In Latvia, from a total land area, there are ~40% wetlands, 5% grassland, more than 3% peat extraction sites, and below 1% rewetted peatlands [8]. In deteriorated peatlands in Latvia, one of the most used peatland strategies is afforestation, which can be realised in ~50% of drained peatlands [8].
To achieve the climate neutrality set by the Paris Agreement by 2050, it is necessary to stop the drainage of peatlands altogether, supporting environmental and climate policy measures that promote the reduction in emissions from degraded peatlands [9]. In order to move towards this goal, the developed Common Agricultural Policy Plan (CAP) is of great importance in relation to the further use and restoration of peatlands [10]. Within the framework of the CAP, policy strategies and measures aimed at reducing emissions from degraded peatlands are developed [9]. The common agricultural policy plan determines that large rewetting of organic soils needs to be carried out in order to achieve the reduction in GHG emissions in forestry and agriculture. Also, a reduction in peat extraction for agriculture or forestry is required [11,12]. From strategies for peatland restoration, one of the most used is peatland rewetting in peatland policy. Peatland rewetting’s aim is a deliberate rise of water level using filling ditches, dam constructions, drain blocking, or other rewetting methods [6,13]. Following Latvian guidelines for the sustainable use of peat for 2030 [7], Latvia’s Strategy of Drained and Degraded Peatland Restoration has a high potential for GHG emission reduction [4]. The Sustainable Use of Peat (2020–2030) sets out peat restoration strategies and aspects of peat extraction [14].
Some countries use peatlands as a source of income for national economies or local communities. Before restoring peatlands, a reliable analysis of costs and benefits should be carried out [1,2]. In peatland restoration, cost-effectiveness is crucial for decision-makers in implementing strategies [15]. Emissions from peatlands cause not only environmental and climate damage but also economic losses to the national economy. Germany, as one of the biggest emitters from degraded peatlands in the EU, suffers from losses estimated at 7.4 billion every year. In order to promote the reduction in emissions from peatlands, approximately EUR 410 million is allocated to it in the form of subsidies within the framework of the CAP. It is known that further use of degraded peatlands in agriculture is often low productivity, and agricultural production is only possible due to the financial support granted by the state [9].
The scientific literature and statistics are uncertain regarding precise peatland restoration costs [13]. Based on the literature, it can be complicated to estimate the monetary value of the results of peatland restoration projects [16]. Non-market evaluation methods should be used to evaluate the monetary value of ecosystem services [1,2]. To evaluate the results of restoration projects, ecosystem conditions before and after restoration are compared [2,10,16]. In the scientific literature and reports, there is a scarcity of information related to precise peatland restoration investments. The cost interval mentioned in the literature [17] is between 200 and 10,000 EUR/ha [17,18,19]. For peatland restoration strategies, initial implementation costs are in the range of 300 EUR/ha for heathland peats and 500 EUR/ha for previously drained peatlands [19].
In the recent literature, paludiculture and water management are considered effective strategies for GHG emission reduction while having a high initial cost [20]. Additional opportunity costs might be expected regarding the loss of production volumes. Some costs can arise related to the gaps in knowledge in the transition phase from agriculture to paludiculture practice [20]. According to the literature, financing mechanisms can be one of the solutions for farmers [21]. The research aims to evaluate peatland restoration strategies and alternative use economic aspects, defining costs, gains, and emissions from each of the strategies using the composite index (CI). Studies are based on the scientific literature and reports combined with average values from local existing project optimisation models and assumptions. Information for constructing the composite index is based on data from the scientific literature, reports, and local project studies. In the study, peatland strategies and alternative use in products were mutually compared with existing strategies, which are determined in the Guidelines for the Sustainable Use of Peat 2020–2030 of Latvia [14].
2. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Peatlands and Economic Aspects of Peat
2.1. Main Greenhouse Gas Emission and Economic Aspects of Peatland Strategies
GHG emissions from organic soils are classified as emissions from agricultural activities, as well as land use, and forestry activities [22]. In order to estimate the total contribution of GHG emissions, CO2, CH4, and N2O emissions must be transformed into the CO2 eq. [22]. The amount of released GHG emissions is affected by whether the bog is considered nutrient-poor or nutrient-rich, so it must first be defined [22,23,24].
Costs for restoring peatlands include initial investments, annual maintenance costs, monitoring costs, and costs for loss of production volumes and previous incomes [9]. Peatland restoration costs may also include establishment costs, which contain expenditure work costs, costs regarding land acquisition, and further permanent costs of maintenance and monitoring if necessary [15]. Cost and gain analysis should include potential gains from ecosystem services from restored peatlands [2].
Average peatland restoration costs in Scotland by the year 2020 were about 1227 EUR/ha, but in 2021 they were ~1878 EUR/ha. It is assumed that the average cost per ha for peatland restoration in 2022 is about EUR 1026 [25]. In other sources, costs for peatland restoration vary from 5000 EUR/ha to 150,000 EUR/ha [21]. In the Netherlands and Germany [14], the average restoration costs of peatland vary from~1500 EUR/h to ~3500 EUR/ha. For France, it is calculated that, on average, peatland restoration costs are in the range of 10,000 EUR/ha—40,000 EUR/ha [21]. On the other hand, from Peatland Code restoration projects, it is known that the cost necessary for restoration can be between 5000 EUR/ha and 15,000 EUR/ha on average [21].
It is estimated that the drainage of peatland forests aims to increase the production of wood and generate losses that can be evaluated in the amount of EUR 309 million a year [26]. Regarding peatland rewetting, there are studies that have evaluated economic gains that yearly reach approximately EUR 170 million [26]. It is calculated that drainage has significantly lower maintenance costs than rewetting peatland forests using dams. Estimations have shown that maintenance costs for drainage annually reach EUR 1.7 million, but for rewetting, are approximately EUR 17 million a year [26].
One-off payment
Although peatland restoration strategies and methods remain more common and their importance in climate policy and society increases, agricultural drainage continues to be subsidised, hindering landowners’ desire to carry out peatland restoration measures [24]. As one of the encouraging instruments for the restoration of degraded peatlands, there are one-off payments for the performed restoration measures. One of the examples where one of the payments is implemented in peatland management is Scotland, where a one-time payment is received for restoring the hydrological regime of peatlands. A one-time payment is granted for peat rewetting, including using methods such as drain breaking or ditch blocking. Denmark can receive one-off payments for the feasibility study of peatlands and to reduce the costs of peatland project construction. Since peatland restoration is a long-term activity, it is recognised that support funding for the implementation of peatland restoration projects is possible for a period of approximately five years. In England, receiving support payments can take up to ten years in some cases [10].
One-time payments for peatland restoration projects can even be covered by 100% of the initial costs, including construction costs [10]. When rewetting degraded peatlands, farmers often suffer economic losses because, after the hydrological level has increased, rewetting makes it no longer possible to carry out the previous agricultural activity. To compensate for economic losses, landowners can receive one-time support payments. The amount of support varies considerably in the literature and can be, on average, from 40 EUR/ha to more than 467 EUR/ha over a 20-year period [10].
2.1.1. Peatland Rewetting
Previous studies of the literature show that in order to stop the release of GHG emissions from degraded peatlands, a partial increase in the water level is not enough, but extensive rewetting measures must be taken to maintain a high hydrological regime in peatlands [4]. As a result of rewetting, by taking measures to raise the water level, for example, by using drain blocking or ditching blocks, similar conditions and hydrological regimes are restored in the peatlands as before the peatlands were drained. Rewetting has been evaluated as one of the most promising methods for reducing CO2 emissions from degraded peatlands. However, increasing the hydrological regime increases the amount of CH4 emissions, which is one of the GHGs [27]. Despite the increase in CH4 emissions after rewetting, this GHG remains in the atmosphere for a shorter time (~12 years) before being converted to CO2 compared to CO2. After peat rewetting, under the influence of anaerobic conditions, a rapid increase in CH4 emissions is observed, which decreases over the years to the level found in wetlands. The type of bogs influences the amount of emitted emissions; it is estimated that in transition bogs, the amount of CH4 emissions is around 274 kg CH4-C ha−1 per year, while in high years, the amount of CH4 reaches ~133 kg CH4-C ha−1 [28].
At the EU level, it is calculated that rewetting 35% of degraded peatlands used in agriculture, including grasslands and croplands, could reduce GHG emissions by 45 Mt CO2 eq. [4]. The possible emission reduction after the type of land use influences the result of rewetting. It has been numerically proven that rewetting of former peat drainage sites can reduce GHG emissions, which can be measured by 6 Mt CO2 per ha, reaching 39 Mt CO2 eq. annually. On the other hand, by rewetting former peatlands that are used for croplands, it is possible to achieve a reduction in emissions that is ten tons CO2 eq. greater than the reduction in GHG emissions from rewetting grasslands [4].
It is estimated that by primarily performing cropland rewetting, it would be possible to annually achieve ~57 Mt CO2 eq. higher GHG emission reduction compared to grassland [4].
Hydrological-level restoration measures can be classified as one-off measures, such as filling ditches or dams, or a set of measures that aim to ensure active regulation of the groundwater level. It is calculated that restoring the hydrological regime and vegetation in previously drained and degraded peatlands can be expensive [21].
In previous studies, it was calculated that rewetting degraded peatland forests yearly could save EUR 170 million [26]. Gains from rewetting peatlands exceed conditions where the drained peatland forests are left without restoration [26]. The cost of 1 dam is in the range of EUR 196 to EUR 3153 [26]. Thereby, on average, the cost per dam reaches EUR 1487 [26]. For Lithuania, previous studies estimated, based on a 40-year period, that the lowest costs for rewetting previously drained forests of peatlands using wood constructions of dams are ~8 EUR/ha yearly; on the other hand, costlier rewetting methods—ditch dams of rock and wood—are 120.4 EUR/ha annually [26].
Restoration costs for rewetting peatlands are highly variable. As a result of peatland rewetting, new short-term and long-term costs arise for farmers and landowners related to the cessation or reduction in production volumes in the long term [21]. One mechanism for economically viable rewetting could be to implement long-term measures regarding carbon credits and ecosystem service payments [29,30]. It is possible to use carbon credits from rewetting to partly reduce rewetting costs. The carbon credit described avoided CO2 emissions from the atmosphere [29].
Carbon credits serve as a compensation mechanism for farmers and landowners after rewetting. Germany’s established MoorFutures provided the first carbon credits for the implementation of peatland rewetting [10] The price of carbon credits depends on the amount of reduction in CO2 emissions after rewetting [30]. The amount of carbon credits per ton of CO2 eq. for rewetting depends on the total costs of projects. Depending on the size of the projects, carbon credits vary from EUR 35 to more than EUR 670 per ton of mitigated CO2 eq. [10] Based on studies from the Netherlands, raising the water level from 60 cm to 40 below the level can have a minimum compensation of ~26 EUR/ ton CO2 for carbon emissions, but raising the level by 40 cm increases the compensation to 57 EUR/ton CO2 [31]. In the Netherlands, carbon credit sales reached 70 EUR/ha in 2020 [29].
2.1.2. Paludiculture
The concept of paludiculture has been known for many years, but it has become more common in recent years. It can be described as a world-recognized milkfish management practice, especially in areas where rewetting has already been carried out. Paludiculture gives landowners the opportunity to use the land specifically for the cultivation of plants and their further use [24]. Paludiculture as a peatland management strategy is included in the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, as well as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) GHG emission guidelines [24]. In order to restore peatlands using the practice of paludiculture, it is first necessary to perform rewetting. With paludiculture, it is possible to reduce GHG emissions from already rewetted peatlands. Paludiculture provides not only environmental benefits but also socio-economic ones. Financial benefits can be obtained both from the harvested biomass and also from using the harvested biomass for the production of high-added-value products [24,32]. Sometimes, there is a misconception that paludiculture is the same restoration strategy as rewetting peatlands. Paludiculture can be defined as agriculture or forestry on rewetted peatlands [12]. Opposite to conditions in rewetted peatlands, paludiculture uses water close to the groundwater level [12].
In sites where paludiculture practices are used, carbon sequestration and storage are promoted. Biotopes in which wetland plants are cultivated using the paludiculture approach contribute to the preservation of biological diversity [24].
As a prerequisite for the implementation of paludiculture practice and avoiding carbon losses, there is regulation of the water level that should be close to the surface throughout the seasons [24]. The essence of paludiculture includes cultivating wetland plants in sites where the water level is close to the surface. Cultivated wetland plants can capture CO2 emissions released from peatlands, reducing the total emissions from peatlands. Another solution for reducing GHG emissions is the use of harvested wetland plant biomass in high-value products, where the storage of CO2 emissions can be an option [24,33,34].
Depending on the species of cultivated wetland plants, the amount of possible biomass that can be harvested after growth also differs. Reed canary grass is one of the wetland plants suitable for paludiculture practice on drained former peatland soils. Compared to other wetland plants, it is rated with a high potential yield [23]. One factor hindering the wider development of paludiculture is the lack of appropriate policies and support mechanisms. It is estimated that the EU policy hinders the cultivation of wetland plants with high yields from harvested biomass, such as peat mosses, reeds, and cattails [10].
Regarding paludiculture practices, there are uncertainties and variabilities in the necessary initial costs for implementation and expected gains [35]. Based on studies of the literature [35], paludiculture practices can be evaluated as effective, economically justified solutions [35]. In Latvia, one of the sites where sphagnum farming in ~1 ha areal is Rāķa bog [12]. Previous studies calculated that capital costs for the implementation of sphagnum farming in Rāķa bog reach ~38,540 EUR/ha [12]. Another peatland where previous studies have been carried out is Ķemeru bog, where initial costs for sphagnum farming introduction reach 32,300 EUR/ha [12]. Previous studies show that for Rāķa bog, total water management costs were EUR 12,701, but in Ķemeru bog, they were EUR 1530 for overflow construction. Sphagnum farming provides economically viable land use and opportunity for long-term carbon storage [12]
The Paludiculture approach provides ecosystem services, including emissions reduction and biodiversity promotion; these services can be monetarily valued, but it is often not included in the financial benefits [1].
Peat Biomass Options for High-Added-Value Products
Wetland plant species for commercial use in raw materials and products in paludiculture exceed even 200 species. Wetland biomass products occupy an increasingly high place in the market and, in the construction sector, create competition for existing construction materials. According to their thermal conductivity, thermal insulation panels have been evaluated as a promising alternative. Wetland plant biomass can also be used as a growth substrate or in raw material packaging [9].
Previous studies evaluated the possibilities of using individual wetland plants as raw materials or for the production of value-added products. Reed, canary grass, or common reed can be used for biogas production, and the potential for use has also been evaluated in cattails. Cattails can also be used as raw materials in construction and as alternative solutions for wastewater treatment [1].
The possibilities of using peat-based thermal insulation boards grown from cattails are still being researched. However, it is estimated that cattail-based insulation panels can compete with similar insulation materials [34]. Peat-based panels are mould-resistant and provide suitable humidity and air quality conditions. These products can store biogenic carbon [34].
Previous studies using the life cycle approach show that cultivation of cattail produces ~2.6 CO2 eq. ha−1. To use the harvested cattail biomass to produce thermal insulation panels, it is first necessary to dry it so that the moisture content does not exceed 6%. It is estimated that the impact caused by drying cattail biomass is approximately ~2.6 tons of CO2 eq. [34]. The panel production process itself includes fibre shredding (0.6 tons CO2 eq. ha−1). Development of a single panel, including manufacturing, fibre processing, and packaging cutting, has a combined impact of ~4 tons of CO2 eq. ha−1 [34]. Total life cycle emissions in cattail cultivation and panel production are ~9.7 tons of CO2 eq. [34].
2.1.3. Afforestation of Peatlands
A study was conducted in Latvia, where afforestation with coniferous trees was carried out in a former peat extraction site. Emissions that would be formed if peat extraction continued at this site (~1.09 tons of CO2 eq. ha−1 per year) and the emissions after afforestation with coniferous trees (~0.96 tons of CO2-C ha−1 per year) were calculated. Emissions from afforestation are affected by previous land use. In the context of CH4 emissions, it is estimated that afforestation can achieve low emissions in afforested croplands (producing ~1 kg CH4 ha−1 per year) [28].
Initial investments are necessary for seedlings or seeds, shading trees, thinning, and maintenance of new tree growth for peatland afforestation. Previously drained peatland afforestation can reduce GHG emissions and, after the afforestation, mineralisation [33]. In peatland afforestation, the main costs are regarding plantation—preparation of soil and planting site and investments for planting [36]. Implementing restoration in a large area is necessary to carry out the afforestation of peatlands so that it is economically beneficial [25].
Restoration of peatlands where drainage has previously occurred using the afforestation strategy includes land opportunity costs, planting costs, and the costs of restoration [37].
The costs required for afforestation include the initial costs of tree planting, labour, and fertilizer, as well as logistics. The average total cost is estimated to be about 1100 EUR/ha−1yr−1 [34].
2.1.4. Perennial Cultivated Grasslands
One of the tasks defined within the CAP is to promote the preservation of perennial grasslands [1]. The study calculated that the transformation of former peat fields into grassland can have a negative impact on CO2 emissions, resulting in 3.2 tons CO2-C ha−1 [28].
Compared to other restoration methods, a smaller amount of funding is necessary for the introduction of grasslands. For the establishment of perennial grasslands, traditional agriculture techniques can be used [33]. The establishment of perennial cultivated grasses includes peat extraction site transformation into agricultural lands that are regularly mowed and grazed afterwards [33]. Fertilisation controls environmental conditions in cultivated grasslands. Perennial cultivated grass is used for energy production from biomass and fodder [33]. The most crucial aspect of successful recultivation using perennial cultivated grasses is evaluating the correct hydrology conditions [33].
In Estonia, one of the determined soil protection measures includes support for the cultivation of perennial grasses under the condition that 90% of the soil composition consists of peat [10].
2.1.5. Water Reservoir
Restoration foresees the establishment of artificial water reservoirs in former peat extraction sites. The peat extraction site is being flooded, and the water reservoir is used as a habitat for flora and fauna or for recreation. Artificial reservoirs have the potential to use the land for recreation or fisheries [33]. According to the guidelines for the sustainable use of peat in Latvia, as mentioned before, the establishment of water reservoirs is one of the methods of restoring peatlands suitable for Latvian conditions. It is estimated that the establishment of an artificial water reservoir is suitable for former peat extraction sites where a swamp has formed due to overgrowth of the water body [33].
2.1.6. Growing Cranberries and Blueberries
Previous studies have calculated that the average amount of CO2 emissions from cranberry fields per year is approximately ~2.6 tons of CO2–C ha−1 [28]. Therefore, it is assumed that the conversion of former peat fields into cranberry plantations can lead to a reduction in GHG emissions [28]. The milling peat extraction method can be used to get a level field. If no field alignment is required, then it is possible to reduce cranberry field establishment costs. Successful restoration using cranberry cultivation can have gains regarding the reduction in GHG emissions [33].
2.1.7. Peat Extraction
One of the sources of GHG emissions in the energy sector is peat extraction [33]. In the peat extraction process, peat is taken off together with carbon [33,38].
Peat extraction has socio-economic value; it promotes rural employment and develops the local economy [33]. After 2003, peat extraction used for energy has significantly decreased [33]. In Latvia, peat deposits form 1.5 billion tons of peat, which compose 0.4% of peat resources globally [33].
In Latvia, companies that can extract peat and that have received a license for peat extraction are also obliged to perform restoration after peat extraction [7]. According to the Latvia guidelines for the sustainable use of peat for 2030, it is significant to avoid further peat extraction in new peat deposits [33]. Also, it is important for the economy to restore former peat extraction sites using restoration strategies to renew degraded areas into economic activity [33]. Previous guidelines determined that more modernisation in technologies and processes should be carried out in the near future to reduce GHG emissions from peat extraction [33].
Tax revenues from peat extraction are estimated to be EUR 18.5 million annually [33,39]. There are no tax incentives in Latvia for peat extraction, and market principles are used [33].
2.1.8. Dairy Farming on Peat Soils
Previously conducted research is related to dairy farming on peat soils with grassland for grazing. The dairy farm of the study had 69 cows, and 35 ha were used as perennial grassland [34]. The average warming potential (GWP) of dairy production was 19.4 tons CO2-eq ha−1 year −1, with an average GWP of milk produced in the Netherlands (1.19 kg CO2·eq kg−1) [34,40,41]. The aforementioned research determined that the impact of dairy production was 20.9 tons CO2-eq ha−1 [34]. The research calculates that the net revenue is approximately 1350 EUr/ha−1 for 16,218 kg milk ha−1 on peatlands [34].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Framework of the Study
In this study, the first step is to select the peatland strategies based on the economic data available in the scientific literature, reports, and local peatland projects. The next steps until the development of scenarios are related to the construction of a composite index (CI). The CI is one of the methods, together with multicriteria decision analysis, that can be used in decision-making processes in cases where the best alternative needs to be sought.
The composite index is used to evaluate policy measures, to compare them before their implementation, or to assess progress in the implementation of defined objectives. Policymakers use the composite index in the decision-making process to make choices about the most effective solutions. The advantage of the composite index in this study is the ability to simultaneously assess several factors and their overall contribution. It is possible to include social indicators, but in this study, due to data availability, it was decided to use economic indicators and environmental indicators affecting GHG emissions.
Based on the literature, the first step in the construction of the CI is the development of the following:
- Suitable economic indicators, divided into two groups—(1) necessary costs, (2) incomes and possible gains from grants and subsidies, etc.
- GHG emissions of each strategy.
The next step is to calculate data for each strategy based on the literature, reports, and local projects. Where the literature does not provide precise or specific information, assumptions related to calculated data must also be developed.
To construct data normalisation for CI development, the Min–Max method was used. Equal weight indicator weighting was applied to each indicator, which was determined based on the number of indicators used. The final step is indicator aggregation into the CI Development of Scenarios (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
The framework of the study.
3.2. Selection of Strategies
Peatland strategies can be categorised into groups—(1) restoration strategies; peat biomass use in high-added-value products; (2) other land use replacing peatland—dairy farming; and (3) peat extraction. Restoration strategies—peatland rewetting; peatland rewetting; establishment of perennial cultivated grasses, paludiculture; establishment of water reservoir; cultivation of cranberries; and cultivation of blueberries, based on the Guidelines for the Sustainable Use of Peat 2020–2030 of Latvia [33].
Peat biomass is used in high-added-value products based on the available scientific literature and reports. Dairy farming is based on the scientific literature and reports, and peat extraction is based on reports (Table 1).

Table 1.
Selected peatland strategies.
3.3. Development of Indicators
Meaningful indicators should be introduced to evaluate the strategies, evaluating both the economic and environmental dimensions.
3.4. Economic and Environmental Data for Each Strategy
Table 2 shows calculated data based on the scientific literature, reports, and assumptions for each peatland strategy for the construction of the composite index. It is possible to compare the economic indicators of the strategies, but due to limited information, there are no specific values for CO2 and CH4 emissions for each of the strategies. Therefore, strategies such as dairy farming, production of panels using cattail, and paludiculture using cattails and sphagnum are evaluated in CO2 eq. ha−1. For restoration strategies, CH4 and CO2 emissions are also compared.

Table 2.
Economic indicators selected for peatland strategy evaluation.
The composite index cannot contain negative values or 0. If data could be used to construct the CSI, values equal to 0 are marked with 0.001 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Calculated economic data for each peatland strategy.
Calculations and assumptions of strategies
I1 Total investments, EUR/ha
Peat extraction:
It is estimated in [31] that prices defined in the 2016 methodology [21] are correct to use if the inflation rate is taken into account. In [31], it is defined that until objective information is available and a new methodology is developed regarding initial costs for peat extraction, it is correct to use costs from the 2016 methodology considering the inflation rate [31].
Total expenses with inflation compared to 2016 2801 EUR/ha + investments in peat extraction preparation with inflation compared to 2016 (9066.7 EUR/ha). The calculation is made based on the calculation of costs from the 2016 methodology, taking into account the 2016 inflation rate for goods and services (average costs EUR/ha *1.42) [43].
Production on insulation boards:
Costs for blow-in insulation.
EUR 1550 + costs for construction EUR 1850.
- Establishment of paludicultures—the cultivation of cattail: 7300/ha EUR [44].
- Establishment of paludicultures—the cultivation of sphagnum: capital investments 23,300/ha EUR [44]
I2 Income from ecosystem services, EUR/ha/yr.
The indicator describes the alternative monetary value (2020) for goods and services in Latvia (average investments EUR/ha * 1.309).
Production on insulation boards: it is assumed that using paludiculture for product production will not reduce the value of ecosystem services.
Peat extraction.
This calculation is based on income from peat extraction from the 2016 methodology, taking into account the 2016 inflation rate for goods and services (average costs, 1.42 EUR/ha *) [7]. Calculations of benefits from material (gross revenue from mineral extraction income from peat extraction), 665 EUR/ha.
Production of insulation boards from cattail: assuming that these are potential income from paludiculture cultivation, EUR 43,825.3.
Paludiculture for cattail and sphagnum cultivation:
Assuming that potential income from ecosystem services is equal to sphagnum farming and cattail cultivation.
Dairy farming:
It is assumed that when starting dairy farming, ecosystem services are 0, and there is no ecosystem, only land use.
I3 Maintenance costs, EUR/ha
For restoration strategies, restoration strategies–average based on the existing optimisation model from local project studies considering the inflation rate year 2018–2020 for goods and services in Latvia (average investments, 1.309 EUR/ha *).
Rewetting:
Maintenance costs 338 EUR + EUR 10,000 monitoring costs.
Peat extraction:
Repair and maintenance of peatland sites 266 EUR/ha + depreciation investments 159.3 EUR/ha.
It is assumed that the costs of peat development and management are about 60% of the income from the sale of the peat. The average maintenance cost for peat extraction is assumed to be 3.5% of the initial capital investments [47].
Production of insulation boards from cattail [44]:
A total of 700 EUR/ha + 700 EUR/ha.
Dairy farming:
A total of 1710 EUR + 2325 EUR/ha.
Paludiculture using cattail cultivation:
A total of 2640 EUR + 530 EUR/ha.
Paludiculture using sphagnum cultivation:
A total of 4000 EUR + 1175 EUR/ha.
I4 Income, EUR/ha
For restoration strategies, restoration strategies–average based on the existing optimisation model from local project studies considering the inflation rate from 2018 to 2020 for goods and services in Latvia (average investments, 1.309 EUR/ha *). Subsidies, one-time payments, and carbon credit are based on the literature and added together with net income to get total income.
Rewetting:
The average one-time income from case studies is 442 EUR/ha (based on + the amount of carbon credit for farmers and landowners, 1000 EUR/ha (one-time payment) [44].
Production of insulation boards: total exploitation costs EUR 7500 + annual CO2 credit 467 EUR/ha (CO2 credits based on 14,000 EUR/ha/30 years)
Perennial cultivated grasses 65.5 EUR + one-off payment 432 EUR/ha
Dairy farming:A total of 4600 EUR + 965 EUR + 400 EUR/ha
Paludiculture using cattail cultivation:
Annual potential profits 4800 EUR/ha+ annual net income 1630 EUR/ha + annual CO2 credit 466.7 EUR/ha (CO2 credits based on 14,000 EUR/ha/30 years)
Paludiculture using sphagnum cultivation [44]:
A total of 8800 EUR/ha + 2625 EUR/ha+ annual CO2 credit 466.7 EUR/ha (CO2 credits based on 14,000 EUR/ha/30 years)
Afforestation: minimum amount of support from funds 2400 EUR/ha [45]
3.5. Normalization of Data
To use the calculated data or data found in the literature, the data must first be normalised. The CI Min–Max method is used as a normalization method for data construction. This method is widely used in decision-making analysis; results are made on a scale of 0–1.
where
- —normalised indicator;
- —actual value of the indicator;
- —indicator minimum value;
- —indicator maximum value;
- i—specific indicator.
- [48,49,50]
3.6. Indicator Weighting
Each of the indicators got equal weight assuming that all selected economic indicators are equally important. For each scenario, the indicator weight is different based on the count of the indicator in each scenario.
- A total of 5 indicators were used with a weight 0.20 for each indicator.
- A total of 7 indicators were used with a weight 0.14 for each indicator.
3.7. Indicators Aggregation into CI
The final step is the aggregation in the CI results multiplied with the normalized indicator value.
where
- —composite index;
- —equal importance indicator weight [50,51];
- —normalized indicator value.
- [50,51]
4. Results
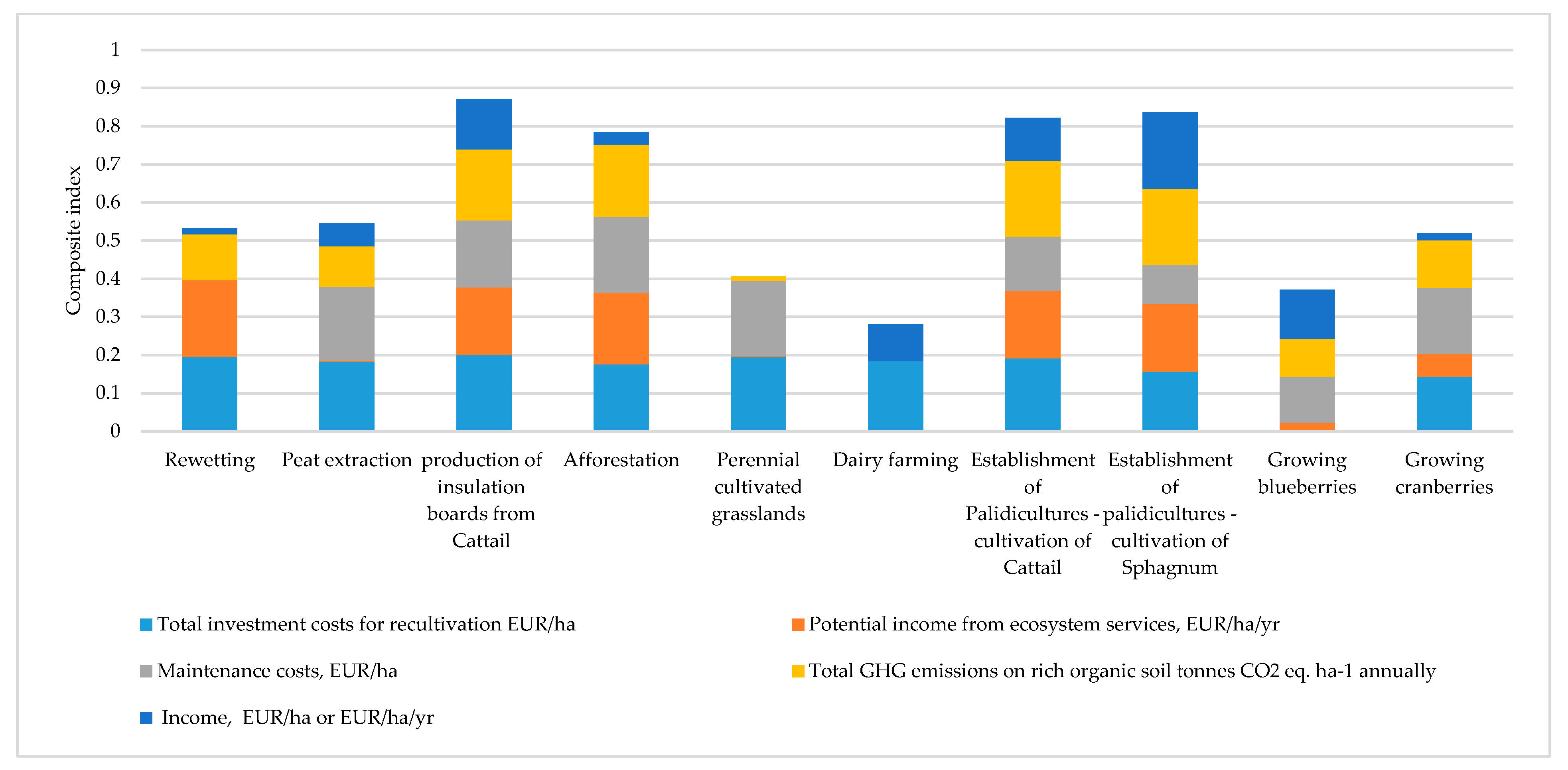
The highest score on the composite index for the production of insulation panels using cattail (typha) is (0.87). The indicators that most determine the advantages of thermal insulation panels are the required amount of investment and the relatively low emissions of CO2 eq. Also, paludicultures using sphagnum farming (0.84) and cattail (0.82) received the second and third highest results in the CI, respectively.
Peat rewetting received (0.53) due to the higher maintenance costs, including monitoring costs. Among the alternatives mentioned before, peatland rewetting has the highest potential income from potential ecosystem services (see Figure 2).
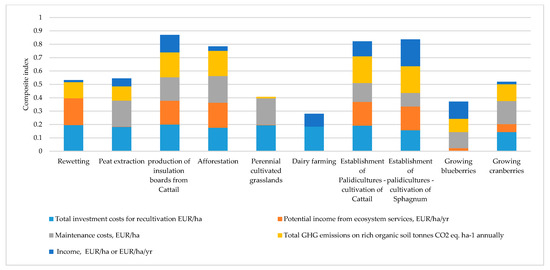
Figure 2.
Restoration strategies and alternative use of peat.
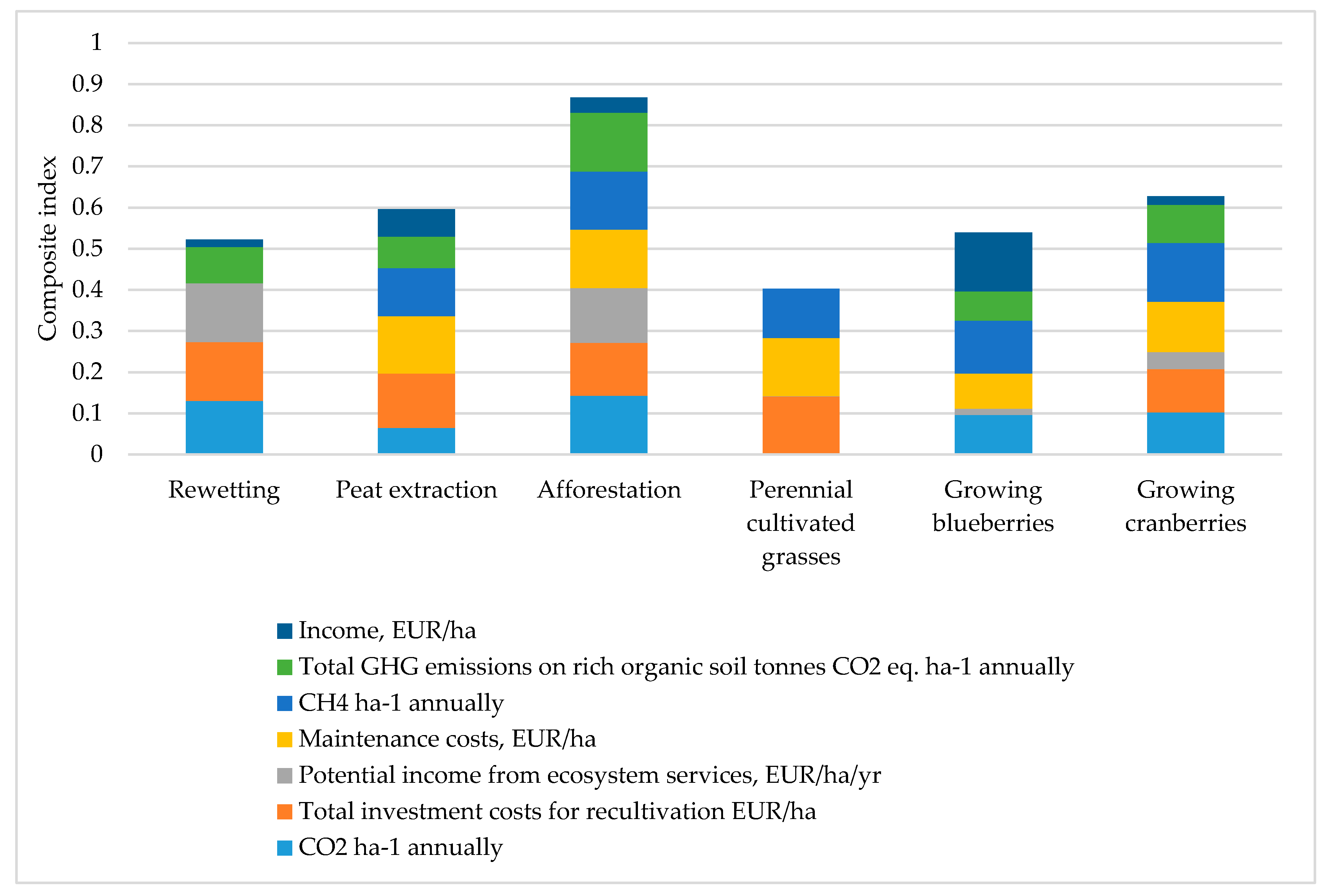
By directly comparing the costs, benefits, and GHG emissions of peatland restoration strategies, it is possible to assess which strategies are considered important in Latvian conditions. Among the restoration strategies, afforestation on drained organic soils (0.87) received the highest rating. The lowest rating was perennial cultivated grasslands, which have higher emissions compared to other strategies (0.40) (see Figure 3).
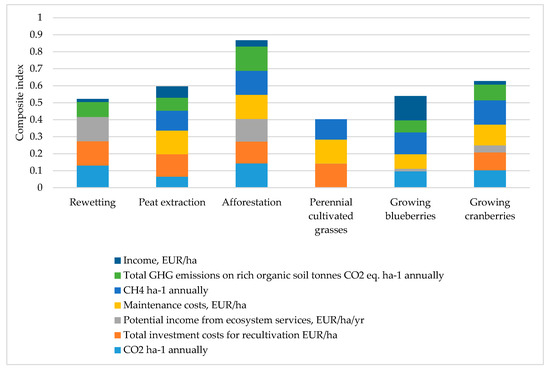
Figure 3.
Peatland restoration strategies.
5. Discussion
The distance impacts restoration costs; scale of restoration and terrain can play a role [52]. Whether restoration will be profitable depends on the areas of restored peatlands [15].
Regarding economic viability, some of the latest studies confirm that net present worth after peatland restoration is higher than restoration costs [15]. It should be taken into account that, besides capital costs for restoration, annual maintenance costs for restoration sites make up one part of the costs [29]. It is predicted that the monetary value of ecosystem services for non-timber products will rise in the coming years [26]. Paludiculture is considered a viable strategy for reducing GHGs while providing opportunities for landowners and the development of new services and products. Although paludiculture has several benefits, only a small area of peatlands is used in paludiculture [34]. Bog cultivation is not widely implemented due to socio-economic challenges and historical support for peatland drainage. Implementing paludiculture requires a joint decision of the landowners, which makes it difficult to expand the practice [1].
Transforming drained and pristine peatlands in paludiculture can promote several ecosystem services and, therefore, incomes from ecosystem services [35]. By switching to paludiculture, it is possible to reduce GHG emissions and land subsidence while providing productive use of land [40,41,45,47]. In paludiculture cultures, great results have been shown with cattail (Typha), peat moss, and black alder [53,54].
Cultivation of cattail (Typha) can promote suitable conditions for the development of ecosystem services. Cattail growth conditions are better in nutrient-rich biotopes, including freshwater wetlands and brackish bogs [53]. It is calculated that one ton of harvested dry cattail can make a return of about EUR 100–200 [44].
Previous studies show that after processing peat by separating fibres, incomes can reach 300 EUR/ton to 500 EUR/ton [44]. Cattail as a raw material can make a turnover of ~2000 EUR/year on average and ~4800 EUR/year in processed material [44]. Net incomes from paludiculture can also make carbon credits for landowners [44]. The literature confirms that better initiatives and monetary motivation for farmers should be introduced in order to facilitate more extensive paludiculture implementation [35]. It is crucial to promote innovative peat product export and production with high added value in the building sector, including peat-based thermal insulation panels and materials [33]. Harvested cattails have the potential to be used in different kinds of goods, including mats, baskets, and toys, and valuable products such as building materials and insulation boards where peat can be used as a raw material or additive [53]. Cattail characteristics make it appropriate and competitive as a use of insulation material. In cattail-based insulation material, it is feasible to store biogenic carbon for a long period of time [34].
In paludiculture using sphagnum farming, it should be taken into account that part of the white peat layer cannot be used to make a profit, and it should be conserved [12,55]. Regarding the implementation of sphagnum farming, several barriers can delay the broader use of paludicultures using sphagnum. One of the drawbacks is related to the high initial costs for land transformation into paludiculture. Also, revenues and incomes from sphagnum farming can greatly vary, and incomes can be expected after several years [55,56].
In the case of afforestation of peatlands, the necessary total capital investments highly depend on the tree species to be planted in previously drained peatlands. From the trees to be planted, one of the highest investments is necessary for the plantation of willow (~1549 EU/ha−1). The high costs of seed materials could explain that. It has been estimated that lower initial costs are for the planting of pine (1042 EUR/ha−1) and spruce—1090 EUR/ha−1 [36,57]. It is calculated that high market revenues in drained peatlands are from plantations of poplar (7557 EUR/ha)—in 20 years, and in 40 years—hybrid aspen. One of the lower incomes is from grey alder—in 20 years (3306 EUR/ha), and from pine—in 40 years [36,57].
Previous studies show that the average costs are 382.8 EUR/ha for preparing a site, 633.2 EUR/ha for labour and seedling costs, 374.8 EUR/ha for maintaining stands, 429.6 ha for thinning before commercialization, and 391.9 EUR/ha for fertilization [44,45]. Afforested peatlands might negatively impact the competition for land and result in increased food prices [37].
Previous studies in the literature confirm that capital costs for the implementation of rewetting as a restoration strategy are lower than for other GHG emission mitigation strategies [31]. In accordance with the previous literature, gains from rewetting raise the water table level and are mostly greater than the initial costs necessary for rewetting [58]. Peatland rewetting can be evaluated as an attractive solution regarding financial compensation (EUR/ha) after rewetting, although in the case of land rewetting, landowners can have serious negative effects on their further agricultural activities [31]. The negative effects of rewetting are related to the loss of income due to land use change [31]. Landowners, after rewetting, can experience a loss of income regarding farming, including limited availability of land and changes in pastures linked to unsuitable conditions for cows in wet periods [31]. One of the changes in income is related to the fact that cows should be brought in earlier in the spring or during the wet periods, as the grass reaches the ground later [31]. Land area after rewetting is not economically viable for landowners and nearby farmers for agricultural activities [34]. After rewetting, the soil is not suitable for further cultivation of crops or dairy farming, including rewetted soil limited by the capacity to carry agricultural equipment [8,34]. A previous study from the Netherlands shows that increasing the water level due to rewetting from 80 centimetres under the surface to 10 centimetres above the surface can cause a market income loss of up to 1358 EUR/ha [29]. Studies in the Netherlands estimated that by raising the water level by 20 cm in peat-based soil farmlands, economic income loss reached 846 EUR/ha [31].
According to the literature, one solution to reduce the loss of income after rewetting if it is planned to continue farming could be to reduce milk production and the number of cows [46]. Pressure drainage can be implemented after rewetting farmlands to stabilize the water level and reduce costs for fodder and manure [31].
The previous literature shows that compared to dairy farming on sandy soil, dairy farming on peat soils results in lower income and also higher global warming potential [59]. Incomes from dairy farming come from the production of milk and subsidies for dairy farming [29]. Conversion from peatland to dairy farming will make net income dairy production [34] and, at the same, reduce potential income from ecosystem services [34]. Although dairy farming makes income from the production of products, the negative aspect is related to the degradation of ecosystem services, transforming peatlands into grasslands for dairy farming [40]. Subsidies for dairy farming can be larger than incomes from milk production itself. In Germany, it was calculated that EUR ~35,000 can be made from subsidies but only EUR 10,000 from milk production [29]. In contrast, the average income in the Netherlands is from milk production, at EUR 90,000, and only EUR 20,000 is from subsidies for dairy farming [29].
It is possible to transform land use from dairy production into paludiculture. It is calculated that the capital costs for land transformation are approximately 7300 EUR/ha on average based on the North Netherlands study [44]. Previous studies confirm that the implementation of paludiculture cultivating cattail and sphagnum and harvesting might compete economically with dairy farming and income from milk production [44].
Restoration by introducing perennial cultivated grasses can have various establishment costs that depend on the methods used, ecology, and the specific restoration site [60]. Previous studies show (2019) that total incomes per ha can reach EUR 769, including direct incomes and incomes from subsidies (~356 EUR/ha) [29]. Cultivation of cranberries and blueberries ranks lower based on low income and high capital costs for blueberry cultivation. Latvia’s climate is appropriate for the cultivation of cranberries in previously drained peatlands. Income is not instant for cranberry cultivation; three years after planting cranberries, the first harvest might be expected [33]. For effective peatland management, cooperation between landowners, farmers, government, companies, scientists, and other related stakeholders should be promoted [19,61].
A united approach should be implemented for the better evaluation of the changes in ecosystem services and more precise cost-effectiveness of restoration by implementing unified protocols [16]. The experience of restoration workers and the availability of equipment might have a beneficial effect on the reduction in capital costs for restoration [16]. More attention should be focused on the techniques and necessary investment reduction for the cultivation of paludicultures as an alternative for the rewetting of peatlands. The connection between global indicators and national or local policy and reporting needs strengthening [62]. Indicators should be scalable where there are local or national data—which are typically more relevant to local policy and more accurate through the inclusion of local knowledge and data [62].
Limitations of the Study
There is a lack of a specific cost-effectiveness assessment of the impact of peatland restoration strategies [6]. According to the literature, global funding for peatland restoration is assessed as insufficient [1]. It is estimated that both public and private financing is less than required for peatland restoration [2].
Defining peatland strategies and specific measures in peatland restoration requires initially providing and foreseeing adequate financing for their implementation [51].
One limitation of the study is the scarcity of specific data regarding costs and gains on thermal insulation panels. Revenues and incomes from sphagnum farming can greatly vary, but incomes can be expected after several years. Other environmental factors that could be included in future studies are the Ecosystem Health Index [62] and indicators that rely on land-use change and biodiversity such as the Species Habitat Index and Biodiversity Intactness Index [62].
6. Conclusions
In this study, peatland strategies and alternative uses in products were mutually compared with existing strategies, which are determined in Latvia’s Guidelines for the Sustainable Use of Peat 2020–2030.
The highest score in both scenarios is for the production of insulation boards by cultivating cattail. The second highest score in the composite index is for the cultivation of paludicultures—cattail and sphagnum—in the first scenario. The lowest score is for the cultivation of cranberries and blueberries based on lower incomes and high initial costs for blueberry cultivation.
Indicators such as net income, income from ecosystem services, and market revenue influence the low rating of these alternatives. It can be concluded that the significant impact on the sustainability rating in the CI comes from total investments EUR/ha and the net income realising strategy. If the strategy is not economically feasible to implement and the invested investments do not pay off, this determines that the peatland strategy will have a lower rating in the long-term evaluation. The analysis and creation of a CI based on real data and assumptions based on the scientific literature serve as an effective method that can be used in the decision-making process to simultaneously evaluate different factors related to economic feasibility.
After rewetting, the soil is not suitable for further cultivation of crops. It should be taken into account that incomes from rewetting like carbon credits or other subsidies of EUR/ha are one-time payments, in comparison to other strategies [31]. The practice of paludiculture can make gains for net income for landowners and farmers and make high income for potential ecosystem services. Production of thermal insulation boards based on paludicultures is a possible alternative, as it is possible to use peat in an economically justified way. In this case, peat is not used as an energy resource: biomass grown by palidiculture as a raw material for added value product production is possible without peat extraction. The cultivation of paludicultures and the production of high-added-value goods are closely linked. The biomass grown in paludicultures can be harvested and used for the production of products. One of the recommendations is to use peatland biomass based on cultivated cattail or sphagnum farming instead of the extraction of peat.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.B; methodology, L.B.; validation, D.B.; formal analysis, L.B.; investigation, L.B.; data curation, L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B.; writing—review and editing, L.B.; visualization, D.B.; supervision, D.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by the Latvian Council of Science, project “Climate Neutrality Decision Models in Action”, project No. VPP-KEM-Klimatneitralitāte-2023/1-0002.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Nomenclature
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| EU | European Union |
| Ha | Hectare |
| EUR/ha | EUR per hectare |
References
- Greifswald Mire Centre. Exchange of Views on Post 2020 CAP and Its Effect on Farming on Organic (Peat) Soils Report. 2020. Available online: www.repeat-project.com (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- Evans, B. Economics of Peatlands Conservation, Restoration and Sustainable Management Economics of Peatlands Conservation, Restoration and Sustainable Management Policy Report; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Roulet, N.T. Improved estimates of carbon dioxide emissions from drained peatlands support a reduction in emission factor. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifswald Mire Centre and Wetlands International Europe. Higher Ambition for Peatlands in the EU Nature Restoration Law Proposal. Policy Briefing. 2022. Available online: https://europe.wetlands.org/publications/higher-ambition-for-peatlands-in-the-eu-nature-restoration-law-proposal/ (accessed on 7 April 2024).
- Gren, I.-M. A trading market for uncertain carbon removal by land use in the EU. For. Policy Econ. 2024, 159, 103127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasny, B.; Adetsu, D.V.; Aitkenhead, M.; Artz, R.R.E.; Baggaley, N.; Barthelmes, A.; Beucher, A.; Caron, J.; Conchedda, G.; Connolly, J.; et al. Mapping and monitoring peatland conditions from global to field scale. Biogeochemistry 2023, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivrins, N.; Bikše, J.; Jeskins, J.; Ozola, I. Hands-On Approach to Foster Paludiculture Implementation and Carbon Certification on Extracted Peatland in Latvia. Land 2024, 13, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleja, S.; Bardule, A. Review of climate change mitigation measures applicable in degraded peatlands in Latvia. In Research for Rural Development 2022, Proceedings of the Annual 28th International Scientific Conference Proceedings, Jelgava, Latvia, 18–20 May 2022; Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies: Jelgava, Latvia, 2022; Volume 37, pp. 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifswald Mire Centre. Briefing Paper on the Role of Peatlands in the New European Union’s Common Agriculture Policy (CAP). 2019. Available online: https://greifswaldmoor.de/files/dokumente/Infopapiere_Briefings/GMC-briefing%20paper_CAP_final.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Wichmann, S. Economic incentives for climate smart agriculture on peatlands in the EU. In Proceedings of the Greifswald Mire Centre; Greifswald Mire Centre: Greifswald, Germany, 2018; Volume 1, Available online: www.greifswaldmoor.de (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- European Court of Auditors. Common Agricultural Policy and Climate—Half of EU Climate Spending but Farm Emissions Are Not Decreasing; Curia Rationum: Luxembourg, 2021; pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ozola, I.; Dauskane, I.; Aunina, I.; Stivrins, N. Paludiculture in Latvia—Existing Knowledge and Challenges. Land 2023, 12, 2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strategy for Responsible Peatland Management. 2019. Available online: www.peatlands.org (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- VARAM Develop ‘Guidelines for the Sustainable Use of Peat 2020-2030′|Vides Aizsardzības un Reģionālās Attīstības Ministrija. Available online: https://www.varam.gov.lv/en/article/varam-develop-guidelines-sustainable-use-peat-2020-2030 (accessed on 4 December 2023).
- Horsburgh, N.; Tyler, A.; Mathieson, S.; Wackernagel, M.; Lin, D. Biocapacity and cost-effectiveness benefits of increased peatland restoration in Scotland. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 306, 114486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artz, R.R.E.; Faccioli, M.; Roberts, M.; Anderson, R. Peatland Restoration—A Comparative Analysis of the Costs and Merits of Different Restoration Methods. 2018. Available online: www.climatexchange.org.uk (accessed on 31 August 2023).
- Moxey, A.; Moran, D. UK peatland restoration: Some economic arithmetic. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxey, A. Assessing the Opportunity Costs Associated with Peatland Restoration; National Committee United Kingdom: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glenk, K.; Martin-Ortega, J. The economics of peatland restoration. J. Environ. Econ. Policy 2018, 7, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhymes, J.M.; Arnott, D.; Chadwick, D.R.; Evans, C.D.; Jones, D.L. Assessing the effectiveness, practicality and cost effectiveness of mitigation measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from intensively cultivated peatlands. Land Use Policy 2023, 134, 106886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathias, Y. Financing Mechanisms in Europe for Restoring Peatlands; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N.; Couwenberg, J. Organic Soils in National Inventory Submissions of EU Countries. 2021. Available online: www.greifswaldmoor.de (accessed on 25 March 2024).
- Thers, H.; Knudsen, M.T.; Lærke, P.E. Comparison of GHG emissions from annual crops in rotation on drained temperate agricultural peatland with production of reed canary grass in paludiculture using an LCA approach. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootjans, A.P. Paludiculture—Productive Use of Wet Peatlands. Restor. Ecol. 2017, 25, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cost of Peatland Restoration in Scotland|SEFARI. Available online: https://sefari.scot/research/the-cost-of-peatland-restoration-in-scotland (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Makrickas, E.; Manton, M.; Angelstam, P.; Grygoruk, M. Trading wood for water and carbon in peatland forests? Rewetting is worth more than wood production. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 117952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Par Kūdras Ilgtspējīgas Izmantošanas Pamatnostādnēm 2020–2030. Gadam. Available online: https://likumi.lv/ta/id/319013-par-kudras-ilgtspejigas-izmantosanas-pamatnostadnem-20202030-gadam (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Greifswald Mire Centre. Peatland methane emissions and climate protection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priede, A.; Authors, A.G.; Aleksāns, O. Sustainable and Responsible after-Use of Peat Extraction Areas Editors. 2019. Available online: www.silava.lv (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Sechi, V.; van Bell, J.; Fritz, C.; Tilak, A.; Geurts, J.; Roehrig, N.; Nailon, P.; Cartmell-Done, K.; Liu, W.; Smits, T.; et al. Towards a Carbon Credit & Blue Credit Scheme for Peatlands; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Günther, A.; Böther, S.; Couwenberg, J.; Hüttel, S.; Jurasinski, G. Profitability of Direct Greenhouse Gas Measurements in Carbon Credit Schemes of Peatland Rewetting. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 146, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, K.; van Duinen, L.; de Koeijer, T. Reduction of Greenhouse Gases from Peat Soils in Dutch Agriculture. EuroChoices 2021, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brolchain, N.; Peters, J.; Tanneberger, F. CAP Policy Brief Peatlands in the New European Union Version 4.8; Greifswald Mire Centre: Greifswald, Germany, 2020; pp. 5–8. Available online: https://www.nhbs.com/paludiculture-productive-use-of-wet-peatlands-book (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- De Jong, M.; van Hal, O.; Pijlman, J.; van Eekeren, N.; Junginger, M. Paludiculture as paludifuture on Dutch peatlands: An environmental and economic analysis of Typha cultivation and insulation production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanneberger, F.; Birr, F.; Couwenberg, J.; Kaiser, M.; Luthardt, V.; Nerger, M.; Pfister, S.; Oppermann, R.; Zeitz, J.; Beyer, C.; et al. Saving soil carbon, greenhouse gas emissions, biodiversity and the economy: Paludiculture as sustainable land use option in German fen peatlands. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2022, 22, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doelman, J.C.; Stehfest, E.; van Vuuren, D.P.; Tabeau, A.; Hof, A.F.; Braakhekke, M.C.; Gernaat, D.E.H.J.; Berg, M.v.D.; van Zeist, W.; Daioglou, V.; et al. Afforestation for climate change mitigation: Potentials, risks and trade-offs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 1576–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrastiņa, E.; Straupe, I.; Lazdiņš, A. Afforestation of Abandoned Peat Extraction Sites with Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) as a Solution of Climate Change Mitigation. In Research for Rural Development 2021, Proceedings of the Annual 27th International Scientific Conference Proceedings, Jelgava, Latvia, 12–14 May 2021; Latvia University of Life Sciences and Technologies: Jelgava, Latvia, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUCN National Committee United Kingdom. IUCN UK Committee Peatland Programme Briefing Note No 6 Commercial Peat Extraction; IUCN National Committee United Kingdom: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vanags-Duka, M.; Bārdule, A.; Butlers, A.; Upenieks, E.M.; Lazdiņš, A.; Purviņa, D.; Līcīte, I. GHG Emissions from Drainage Ditches in Peat Extraction Sites and Peatland Forests in Hemiboreal Latvia. Land 2022, 11, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Fritz, C.; van Belle, J.; Nonhebel, S. Production in peatlands: Comparing ecosystem services of different land use options following conventional farming. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUCN UK Peatland Programme. Principles for Sustainable Peatland Paludiculture; IUCN UK Peatland Programme: Edinburgh, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- LIFE REstore—OPTIMIZĀCIJAS MODELIS. Available online: https://restore.daba.gov.lv/public/lat/optimizacijas_modelis1/ (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Normatīvie Akti—LĪVA. Available online: https://www.vertetaji.lv/normativie-akti (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Colbers, B.; Cornelis, S.; Geraets, E.; Gutiérrez-Valdés, N.; Tran, L.M.; Moreno-Giménez, E.; Ramírez-Gaona, M. A Feasibility Study on the Usage of Cattail (Typha spp.) for the Production of Insulation Materials and Bio-Adhesives; Wageningen University and Research Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Afforestation and Reforestation as Adaptation Opportunity. Available online: https://climate-adapt.eea.europa.eu/en/metadata/adaptation-options/afforestation-and-reforestation-as-adaptation-opportunity (accessed on 16 January 2024).
- Lazdiņš, A.; Lupiķis, A. 2019. LIFE REStore projekta pienesums Latvijas siltumnīcefekta gāzu emisiju uzskaitē. Grām.: Priede A., Gancone A. (red.) 2019. Kūdras ieguves ietekmētu teritoriju atbildīga apsaimniekošana un ilgtspējīga izmantošana. Baltijas krasti, Rīga. Available online: https://www.latvijaskudra.lv/upload/life_restore_gramata_1.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- KPMG Baltics SIA. Publiskas Personas Zemes Nomas Maksas Noteikšanas Metodika Derīgo Izrakteņu Ieguves Teritorijām; KPMG Baltics SIA: Rīga, Latvia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Balode, L.; Dolge, K.; Blumberga, D. The Contradictions between District and Individual Heating towards Green Deal Targets. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, C.; Bastini, K. Embracing multiple perspectives of sustainable development in a composite measure: The Multilevel Sustainable Development Index. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 118884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjoo, A.A.; Sumper, A.; Davarpanah, A. Development of sustainable energy indexes by the utilisation of new indicators: A comparative study. Energy Rep. 2019, 5, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarhus University. Emission Factors per GJ Fuel Input. Available online: https://envs.au.dk/fileadmin/envs/Emission_inventories/Emission_factors/Emf_internet_energy_GHG.htm (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Chapman, S.; Thomson, K.; Matthews, R. AFOLU Accounting: Implication for Implementing Peatland Restoration—Costs and Benefits. 2012. Available online: www.climatexchange.org.uk (accessed on 11 January 2024).
- Bansal, S.; Lishawa, S.C.; Newman, S.; Tangen, B.A.; Wilcox, D.; Albert, D.; Anteau, M.J.; Chimney, M.J.; Cressey, R.L.; DeKeyser, E.; et al. Typha (Cattail) Invasion in North American Wetlands: Biology, Regional Problems, Impacts, Ecosystem Services, and Management. Wetlands 2019, 39, 645–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Hallweit, T. Potential Paludiculture Plants of the Holarctic. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365853219_Potential_Paludiculture_Plants_of_the_Holarctic (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Wichmann, S.; Prager, A.; Gaudig, G. Establishing Sphagnum cultures on bog grassland, cut-over bogs, and floating mats: Procedures, costs and area potential in Germany. Mires Peat 2017, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makovskis, K.; Lazdina, D.; Popluga, D. Cut-Away Peatland Re-Cultivation with Fast Growing Woody Plantations: Cost-Benefit Analysis. Rural Dev. 2019, 2019, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachowicz, M.; Manton, M.; Abramchuk, M.; Banaszuk, P.; Jarašius, L.; Kamocki, A.; Povilaitis, A.; Samerkhanova, A.; Schäfer, A.; Sendžikaitė, J.; et al. To store or to drain—To lose or to gain? Rewetting drained peatlands as a measure for increasing water storage in the transboundary Neman River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boxmeer, E.; Modernel, P.; Viets, T. NC-ND license Environmental and economic performance of Dutch dairy farms on peat soil. Agric. Syst. 2021, 193, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.G.; Török, P.; Hermann, J.-M.; Kiehl, K.; Kirmer, A.; Kollmann, J.; Overbeck, G.E.; Tischew, S.; Allen, E.B.; Bakker, J.D.; et al. Challenges and opportunities for grassland restoration: A global perspective of best practices in the era of climate change. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 46, e02612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Written Evidence Submitted by the IUCN UK Peatland Programme. Available online: http://www.iucn-uk-peatlandprogramme.org/ (accessed on 22 September 2023).
- Nicholson, E.; Watermeyer, K.E.; Rowland, J.A.; Sato, C.F.; Stevenson, S.L.; Andrade, A.; Brooks, T.M.; Burgess, N.D.; Cheng, S.-T.; Grantham, H.S.; et al. Scientific foundations for an ecosystem goal, milestones and indicators for the post-2020 global biodiversity framework. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordbeck, R.; Hogl, K. National peatland strategies in Europe: Current status, key themes, and challenges. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2024, 24, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).