Abstract
The spatial organization within ancient settlements offers valuable insights into the evolution of social complexity. This paper examines spatially and chronologically contextualized architectural structures and artifacts uncovered at the Late Bronze Age Shirenzigou site to explore the relationship between the use of space and underlying social dynamics in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains of Xinjiang (China). Central to our findings is a distinctive centripetal compound structure, consisting of a larger non-domestic building surrounded by smaller dwellings. This arrangement, along with the variety and distribution of the artifacts, reveals a complex interplay between private and communal spaces at the site, reflecting a growing complexity within the social fabric of the community. The formation of conglomerates of houses around a central communal structure which occurs across the Tianshan Mountains appears to be a strategic adaptation in response to environmental challenges and socio-political transformations across this region at the end of the second millennium BCE.
1. Introduction
The study of space use and organization is crucial to our appreciation of the development of past societies [1,2,3]. The layout of the settlements and the location, form, and size of the buildings, sometimes (cautiously) comparable with ethnographic evidence, can provide critical understanding of the living strategies, economic activities, social interactions, and other facets of ancient communities [4,5,6,7]. Recent studies have underscored the significance of the materials and methods used in construction to gain insights into ancient lifestyles [8,9,10]. On an even smaller scale, examining the spatial arrangement of artifacts at archeological sites has proven crucial for pinpointing areas of specific activities, thereby aiding in the reconstruction of past behaviors and social interactions [11,12,13].
In the last century, Chang [14,15,16] introduced the concepts of ‘microstructure’ (i.e., the cultural and social system of a settlement) and ‘macrostructure’ (i.e., the broader culture and social organization) in settlement patterns in China and drew attention to the importance of anthropological approaches to address issues of social organization and complexity. His works were critical for the reevaluation of traditional theories and definitions related to social complexity in Chinese archeology, challenging established notions of states, cities, and their material implications [17,18]. Despite advancements, critiques highlight biased data from surveys favoring accessible, large, low-elevation sites, overlooking diverse environments, and a lack of control over the chronology of the findings [19,20,21]. While recent works in the Chifeng region, in present-day Inner Mongolia, and the high-altitude Ngawa area of Western China have broadened archeological methodologies and challenged traditional site selection and dating methodologies [22,23,24], research still largely relies on extensive surveys and analyses of published preliminary excavation reports, focusing on large-scale variations, with much less attention paid to small-scale studies.
The Eastern Tianshan region of Xinjiang, a crucial prehistoric cultural crossroad connecting the Hexi Corridor with the eastern Steppe and the Inner Asian Mountains [25,26,27,28], too has seen research emphasizing long-distance interactions and large-scale cultural variations. In-depth analysis of individual sites and localized social phenomena is scarce (but see [13]), which has significantly limited our understanding of the social contexts that underlay the development of these ancient societies.
The Late Bronze Age in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains (ca. 1300–800 BCE) witnessed an intensification of pastoralism [29], the expansion of crop exchange [30,31,32], the spread of new technologies [33,34], and the emergence of a greater social complexity, which was largely driven by the increasing diversity in pastoral mobility patterns [35,36]. Over 200 sites, dating between the second and first millennium BCE, were identified in the grasslands across both slopes of the Eastern Tianshan Range, allowing a preliminary understanding of human–environment relationships and settlement preferences [37,38]. These sites typically featured stone houses and graves, with many yielding an array of artifacts indicative of significant population growth and cultural flourishing [38,39]. The discovery of painted pottery [40,41,42,43], cast bronze items [44,45,46,47,48], and crops, such as wheat, barley, and millets [40,49,50], points to heightened interactions with neighboring regions to the east and west. Over 30 of these sites have been carefully surveyed revealing a unique structure, referred to as ‘centripetal compound buildings’ (向心式复合建筑) [51], distinctively shaped radially or as an isosceles triangle or a fan, with a central building encircled by smaller houses. Previous research has suggested that this architecture may signify a hierarchical society [52], sacred spaces [53,54], defensive strongholds [38], communication hubs [51,55] or labor division within the site [56]. However, insufficient evidence and the lack of detailed studies of the individual sites, including the architectural structures and artifacts found therein, continue to obscure the underlying function of these buildings and their potential socio-political implications on a local and regional scale.
In order to fill this gap, this article focuses on the late Bronze Age settlement of Shirenzigou, on the northern foothills of the Eastern Tianshan Mountains. Systematic excavations conducted by Northwest University and the Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, among others, in 2006 and 2007 uncovered a distinctive centripetal compound building at the site [57]. This study compiles and examines the data from the excavation of Shirenzigou, incorporating both previously published findings and fresh insights from the excavation records, within a precise chronological and spatial framework to explore the relationship between the material sphere and the multifaceted social dynamics at the site. In doing so, it offers important insights into the complexity of the pastoral societies in the Eastern Tianshan Range in the first millennium BCE.
The Site
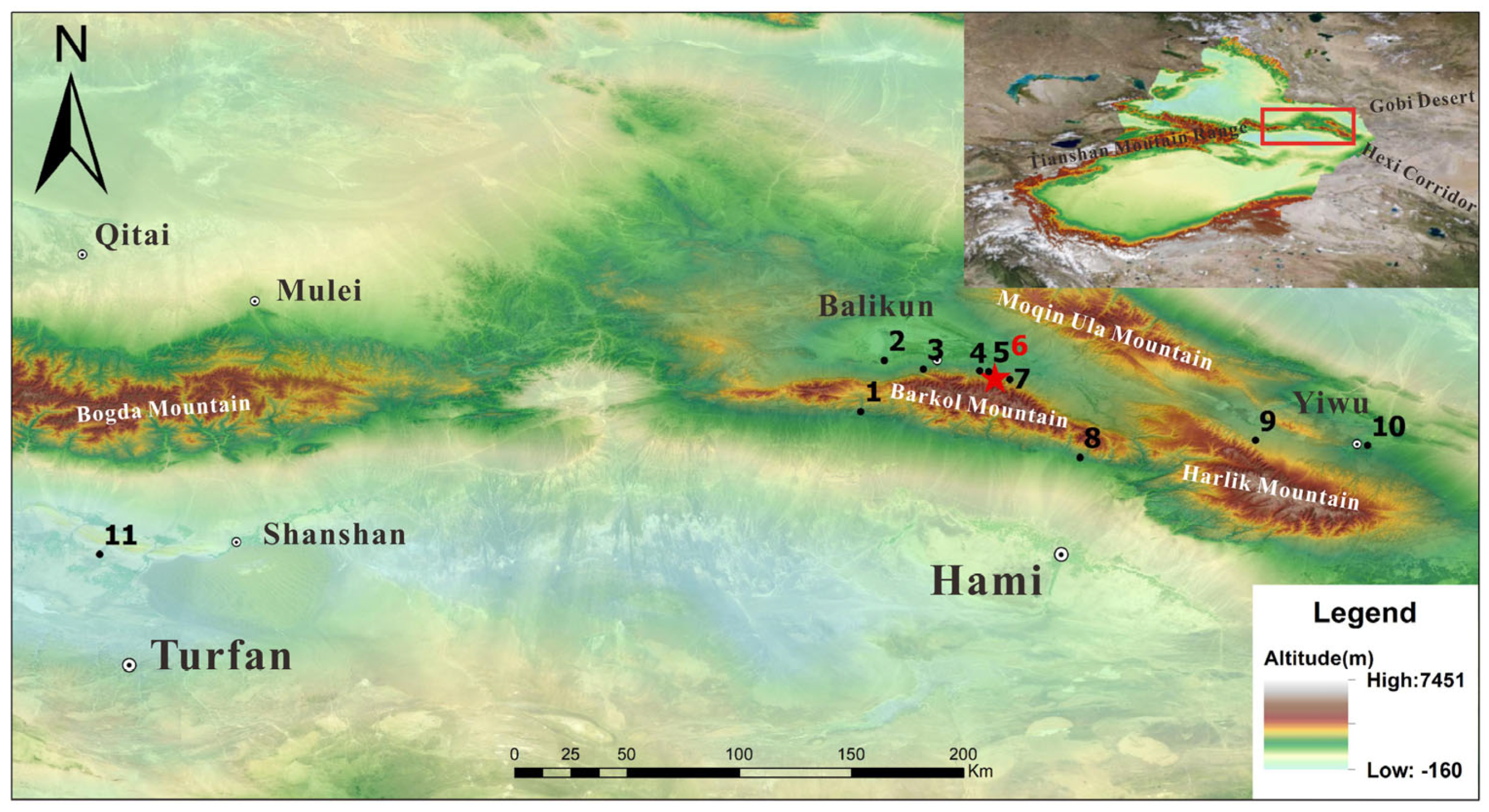
The site of Shirenzigou, also known as Dongheigou, lies on the northern side of the Tianshan Mountains, in present-day Balikun County (Figure 1). The landscape around the site includes meadows and areas covered in gravel from ancient glaciers. Towards the north, there is a large valley with wide areas of alluvial fans. The elevation of the lower river plain ranges between 1800 and 2000 m asl. While today it supports irrigated wheat farming, there is no evidence to suggest historical irrigation practices. The northern mountains, rising above 3600 m, are covered in forests and have peaks that are frozen year-round. The reliable water sources and efficient drainage system render this locale an optimal grazing area during summer. The inhabitants seem to have practiced transhumance [29], congregating in the lower lands during winter and migrating to the mountain foothills in summer, a lifestyle documented in various regions [7,58].
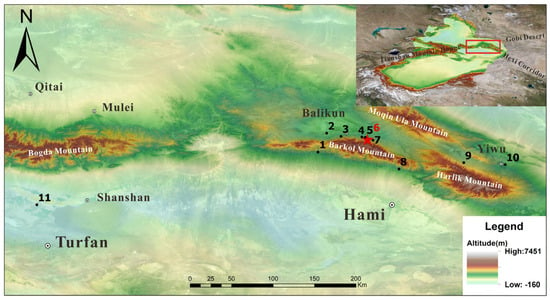
Figure 1.
Location of Shirenzigou and other sites associated with this study. 1. Liushugou; 2. Haiziyan; 3. Yuegongtai-Xiheigou site group; 4. Xiaoheigou; 5. Xigou; 6. Shirenzigou; 7. Hongshankou No. 1; 8. Wulanbuluke; 9. Kuola northern building complex; 10. Baiqier; 11. Yanghai. The image was made using QGIS 2024 (www.qgis.org) and CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2016 (www.corel.com).
First discovered in 1957, with initial examinations carried out in 1958 and 1981 [59], Shirenzigou underwent a thorough investigation and was mapped in the summer of 2005 by the Cultural Heritage and Archaeology Research Center of Northwest University, the Hami District Cultural Relics Bureau, and the Barkol County Cultural Management Office [60]. A large context covering roughly 8.75 km2 was revealed, including mound-platforms, architectural structures, burials, and sacrificial pits. The site is believed to have been used by pastoral communities on a seasonal basis. Scattered radiocarbon dates situate the habitation of the site between 1300 BCE and 300 CE, spanning the local Bronze to Iron Ages [32,36,61].
In 2006 and 2007, a team comprising Northwest University, the Xinjiang Institute of Archaeology, and other institutions embarked on meticulous excavations of a radially structured compound building in Shirenzigou. Located in isolation on the southern section of the site, this structure comprised diverse features such as wooden and stone walls, postholes, hearths, and multifunctional pits, along with a significant collection of artifacts and bioarcheological material. Preliminary findings have been reported [57], and various studies on selected archeological evidence from the site have shed light on local livelihoods and cultural exchanges [13,29,30,31,35,36]. Yet, a comprehensive and detailed analysis of this unique complex within a chronological and spatial context is still pending and is the focus of the discussion in this article.
2. Materials and Methods
Seven excavation seasons have yielded extensive archeological insights at the site, with thorough investigations into the living spaces of F7 and F2. In the case of units F1, F5, F8, and F10, only the rear sections were excavated to preserve the slope of F7 and its overall structure. Excavations of units F3, F4, F6, and F9 were only partially conducted, limited by the scope of the excavation permit. Early findings have been documented in a series of preliminary reports and scholarly articles by the Shirenzigou research team [51,53,54,57,59]. Integrating this previously published information with new insight from the excavation record, we have compiled a detailed architectural overview of the centripetal compound structure. Through spatial analysis and statistical tools, we investigated the layout and interrelationships of various structural elements [8,62].
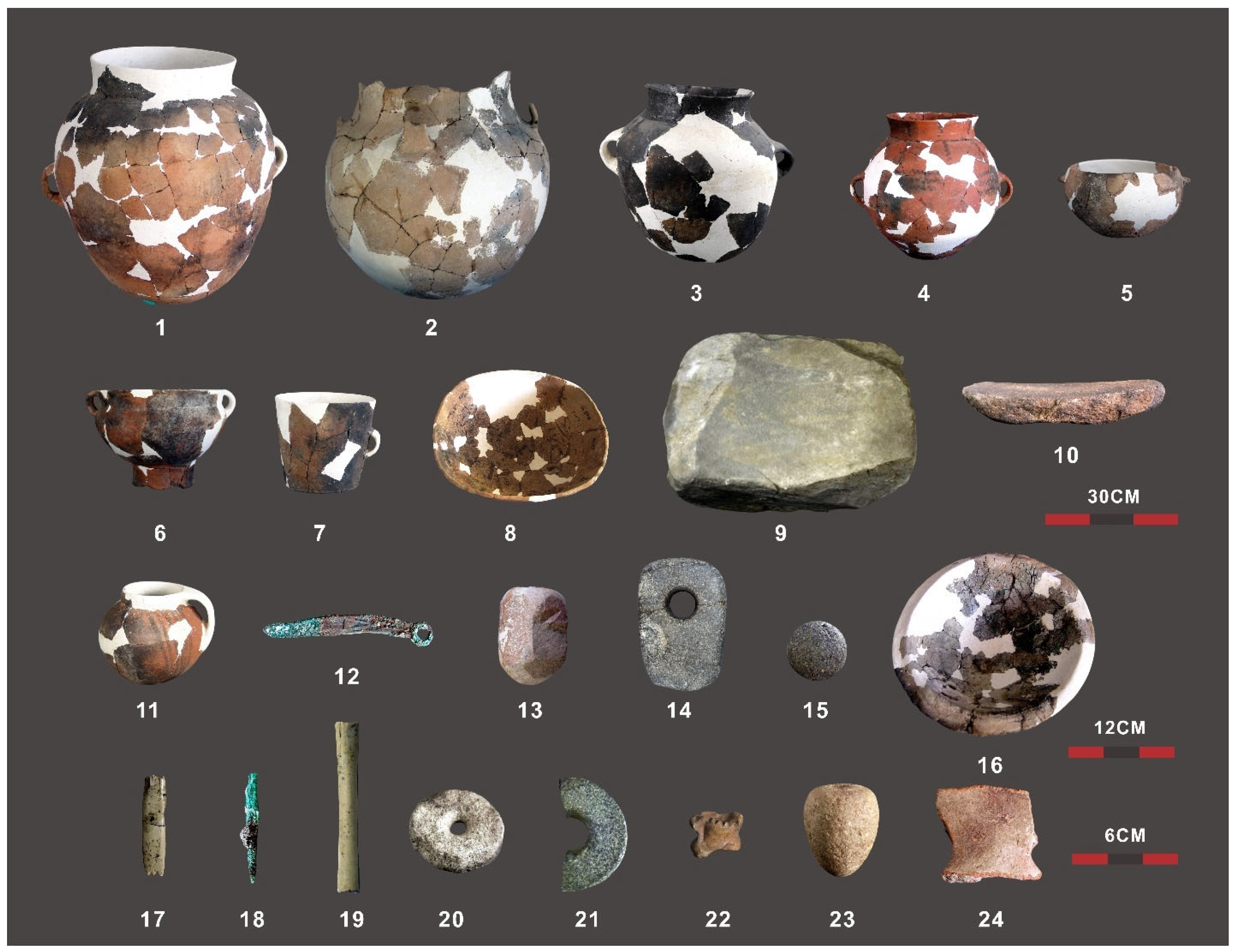
All artifacts and botanical and faunal remains recovered at the site were recorded (Figure 2). The artifacts were firstly divided into four large categories according to relevant activities (Food, Production, Leisure, and Others). These large divisions were further split into 16 smaller groups on the basis of the specific function of the recovered artifacts, according to published references on the topic (e.g., [63]) (Table 1). When appropriate, the evidence was further divided according to sub-type (e.g., grain processing tools were further classified into ‘grinding stone plate’, ‘grinding stone pestles’, and ‘smashers’) and size as follows: extra-large vessel: belly diameter ≥ 50 cm and height ≥ 50 cm; large vessel: belly diameter between 50 cm and 40 cm and height between 50 cm and 30 cm; medium vessel: belly diameter between 40 cm and 30 cm and height between 30 and 25 cm; small vessel: belly diameter ≤ 30 cm and height ≤ 25 cm. Bioarcheological material was divided in cereals grains and weed, all under the category of botanical findings and faunal remains (Table 1).

Figure 2.
Artifacts excavated from various structures of the centripetal compound building in Shirenzigou: 1. double-handle jar (F7); 2. four-handle pot (F7); 3. double-belly pot with two handles (F7); 4. painted double-belly pot with two handles (F7); 5. double-ring flat-bottomed cauldron (F2); 6. double-handle ring-footed pot (F7); 7. single-handle cup (F7); 8. basin (F3); 9. stone grinding plate (F7); 10. stone grinding rod (F7); 11. painted single-handle pot (F4); 12. bronze knife (F7); 13. stone pestle (F1); 14. stone hoe (F1); 15. stone ball (F2); 16. crucible (F7); 17. tooth harpoon (F7); 18. bronze awl (F7); 19. bone tube (F7); 20. stone spindle whorl (F7); 21. scepter head (F7); 22. toy made out of a sheep astragalus (F3); 23. stone spinning top (F3); 24. pottery shard (F4). The image was made using CoreDRAW Graphics Suite 2016 (www.corel.com).

Table 1.
Classification of the artifacts and bioarcheological material (botanical and faunal findings) from Shirenzigou used in this study.
During the excavation, the contexts of the artifacts and bioarcheological material were recorded to the nearest cm. The number and type of artifacts were recorded to the layer or feature in which they were recovered. These features were identified as ash pits, ash heaps, post holes, stoves, and kilns. These elements were mapped in-field and the plan digitized using CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2016 (www.corel.com). This plan was then annotated to show the arrangement of finds within the site. The analysis of artifacts and bioarcheological evidence, considering both quantity and the temporal and spatial distribution of the finds, was carried out to identify potential activity areas [11,12,13].
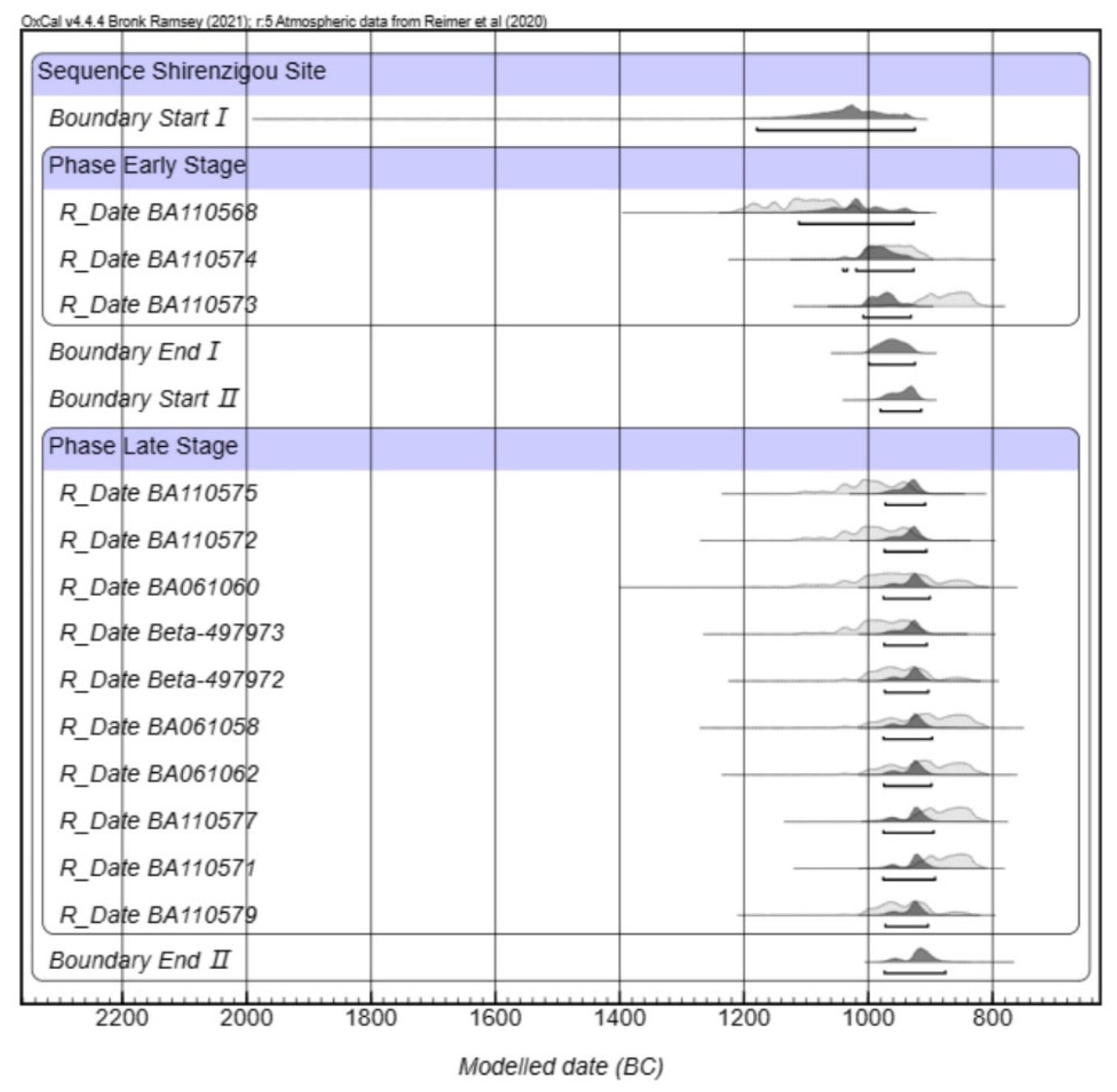
In order to chronologically contextualize the site and to better understand the patterns of occupation of the houses, we introduced 5 new radiocarbon dates, which were generated at the Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Dating Laboratory of Peking University. Our results were re-evaluated in light of previously published AMS C14 dating. All the dates were calibrated using the most recent calibration curves, OxCal and IntCal20 [64,65] (OxCal online version 4.4.4). Given the well-documented stratigraphic sequence of all the samples, the Bayesian modeling primarily adhered to the sequence model proposed by Ramsey [66], which enabled the integration of excavation stratigraphy to obtain the most precise dating resolution possible. Radiocarbon dates, organized according to their excavation layers, were grouped into a single phase when originating from the same stratigraphic layer.
3. Results
3.1. Layout and Buildings
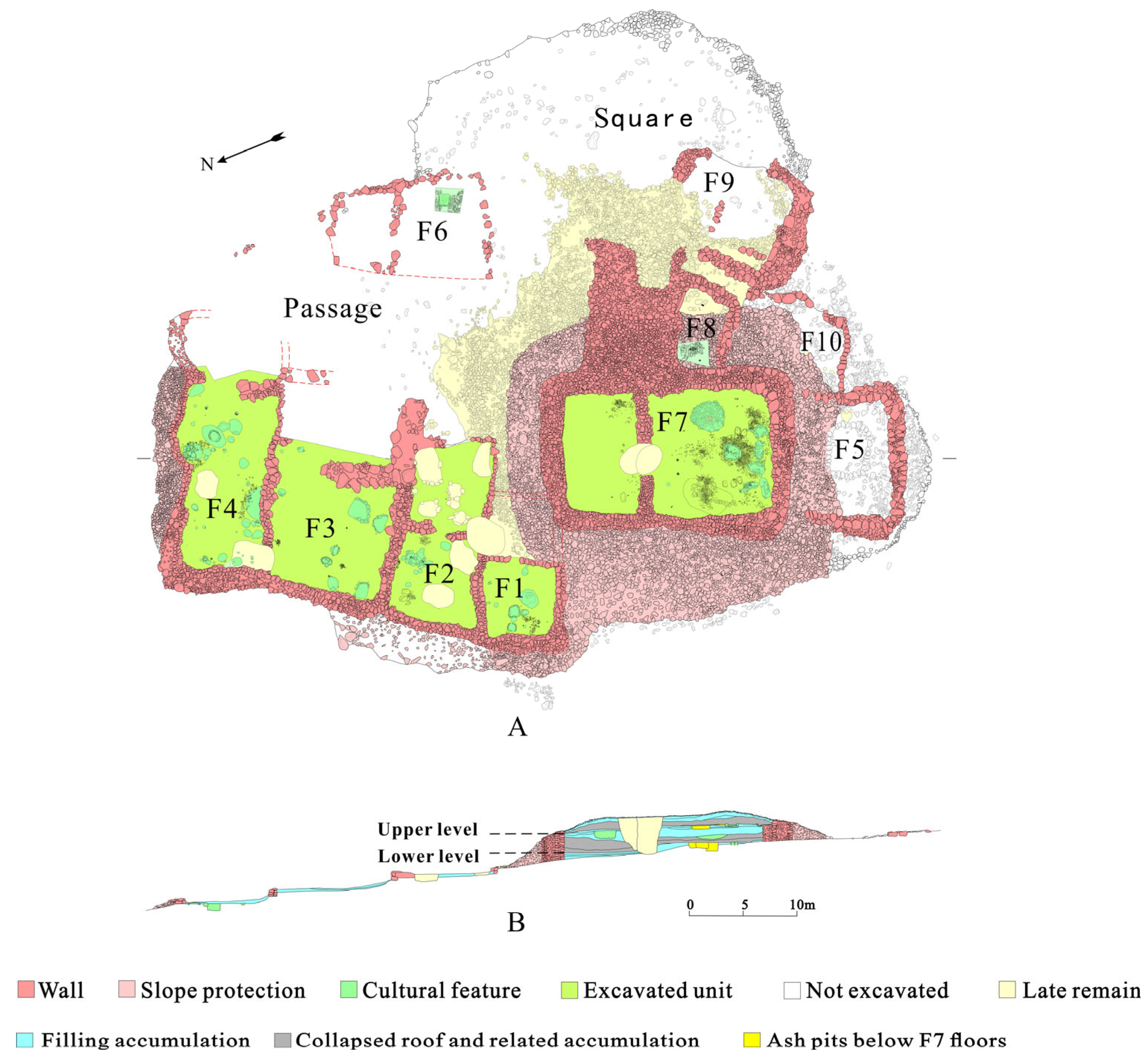
The multi-space structure spanned 73 m in length from north to south and 58 m at its widest from east to west. It was composed of 10 houses, an open space (possibly a square), and several pathways (Figure 3). The largest building was F7. It was located at the highest altitude in the south, with its entrance facing east and consisted of two rooms distributed on a north–south axis. Adjacent to F7 on the east, southeast, and south sides were four small, single-room annex structures (F5, F8–F10). Further east was an open space encircled by arranged stones. To the northwest of F7, a group of four smaller units (F1–F4) were distributed from north to south, also divided into two rooms with their doors opening on the eastern walls. These buildings were placed next to each other in a sequential order, with each subsequent structure positioned slightly higher or lower than the one before it. To their east and separated by a pathway, another small house, F6, was found. F6 was divided into two rooms and had a door to the north side.
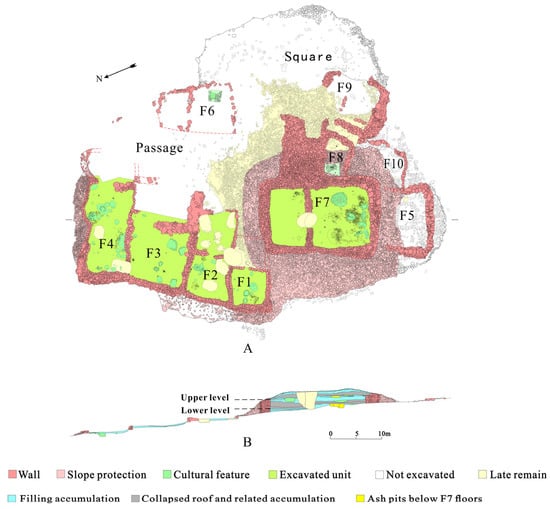
Figure 3.
Plan (A) and stratigraphy (B) of the buildings at the Shirenzigou site as per excavation records. The images were made using CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2016 (www.corel.com) on the basis of the data recorded in the field.
The archeological excavation revealed that this group of structures had undergone two main phases of use. Two layers of ground floors (lower and upper) were identified in F2, F3, and F7, while in F4 only one floor was found, with the late occupation occurring directly on the early ground. It is apparent that after the lower floor was abandoned, soil was added to form an upper layer of floor, while continuing to use the existing walls (Table 2). The standing walls of F7 are notably tall, exceeding 4 m in height and varying from 2.3 m to 3.6 m in thickness. In contrast, the wall heights of the smaller buildings range from 0.5 m to 0.7 m, with thicknesses between 0.7 m and 1 m [59].

Table 2.
Excavation details and relationship between floor levels from two identified phases at Shirenzigou.
In the first phase, the smaller structures F1–F4 and F6 were semi-subterranean, while F7 and its annex F8 were built at ground-level. The status of units F9 and F10, whether they were also ground-level constructions, remains unclear due to limited excavation data. In the later phase, the floor level of the smaller houses was raised slightly, approximately 0.45 m to 0.5 m, while the floor of F7 was elevated by 2 m, effectively turning it into a platform structure encircled by retaining walls. A sloping pathway leading to F7’s original entrance was built, linking this central structure with the rest of the settlement. In the late occupation phase, this path began 9 m below F7’s highest point, highlighting a significant elevation difference between the smaller structures and the central building. The walls of F7 pressed down F1 and the annexes F5, F8, and F10, which suggests that these structures had already been abandoned by the later period. The buildings retained abundant relics and artifacts in their original positions, supporting a rapid abandonment with minimal disturbance. Both layers of ground floor above F7 showed collapsed accumulations of burned wooden structure roofs, indicating that likely the abandonment was due to fire [51,53,54,57] (Figure 3).
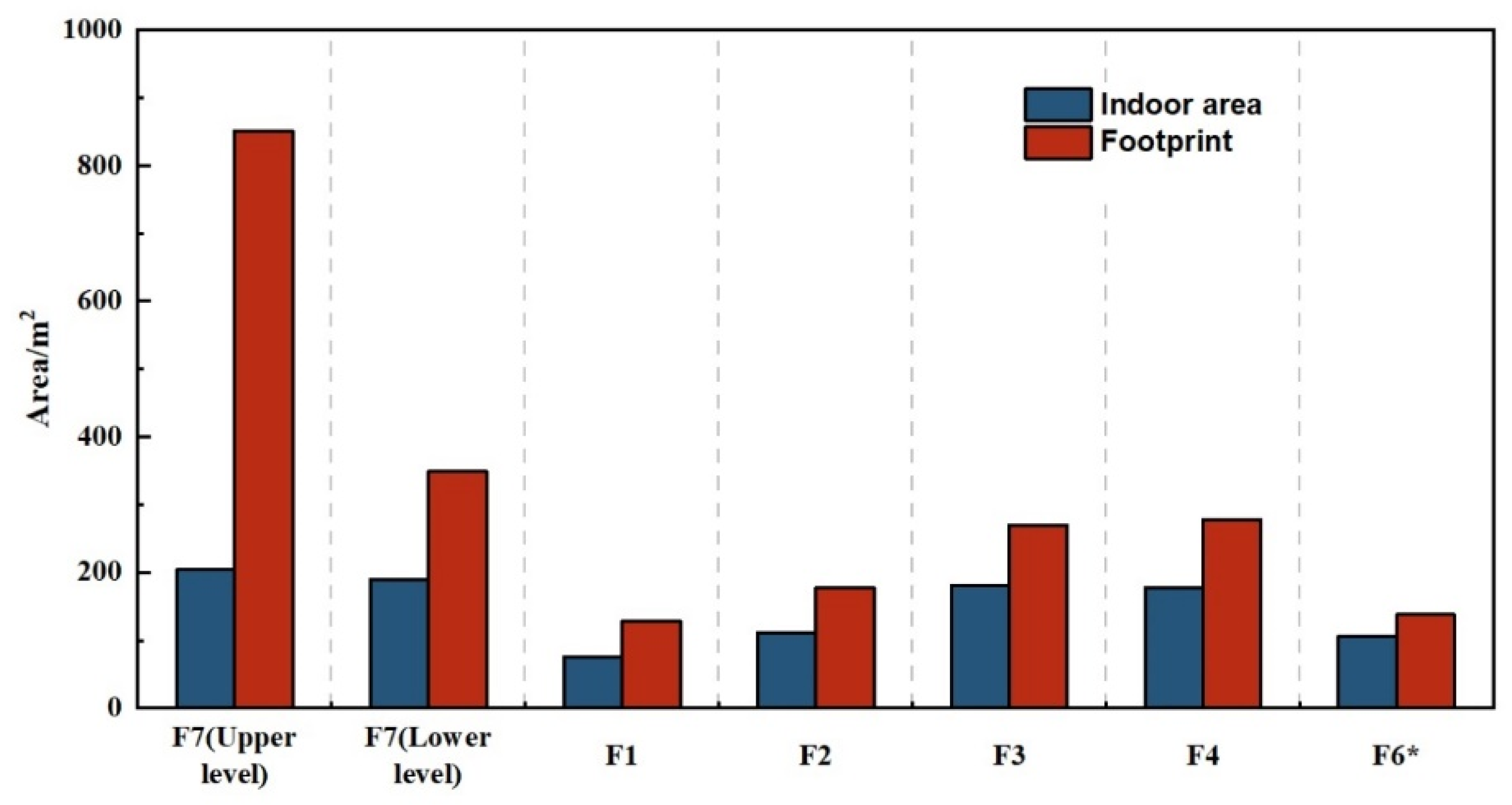
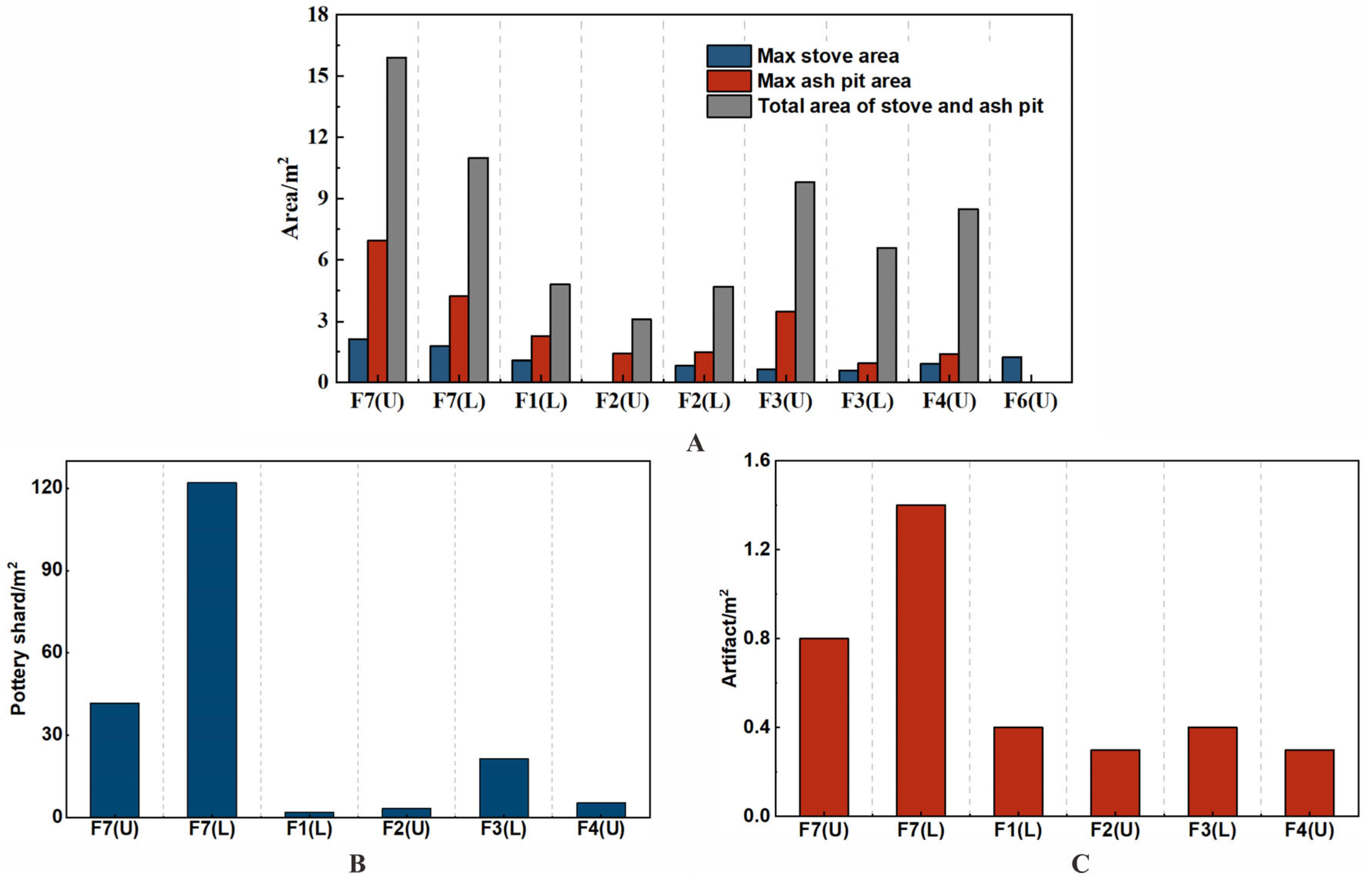
The indoor layout of all the structures is consistent across the lower and upper phases, with a division into two spaces, a spacious front room and a rear room, which contained most of the artifacts [57]. The smaller dwellings (F1–F4, F6) show little variation in size, maintaining a consistent ratio of indoor floor space to the overall footprint area at 1:2 (Figure 4). The interior space of F7 does not stand out when compared to the smaller units, being comparable to that of F3 and F4. Yet, considering the walls, surrounding slopes, and additional architectural elements, F7’s total area significantly exceeds that of the smaller structures in both periods (3 to 5 times larger in the early phase; 1.3 to 2 times larger in the later phase) (Figure 4; Table S1).
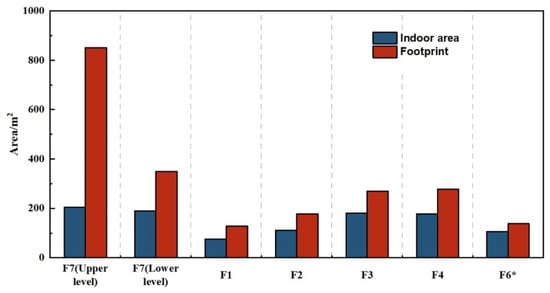
Figure 4.
Ratio of the interior floor space to the total footprint area for each building in Shirenzigou (* walls not fully exposed during excavations). The figure was made using Origin 2024 (www.originlab.com).
3.2. Features and Artifacts
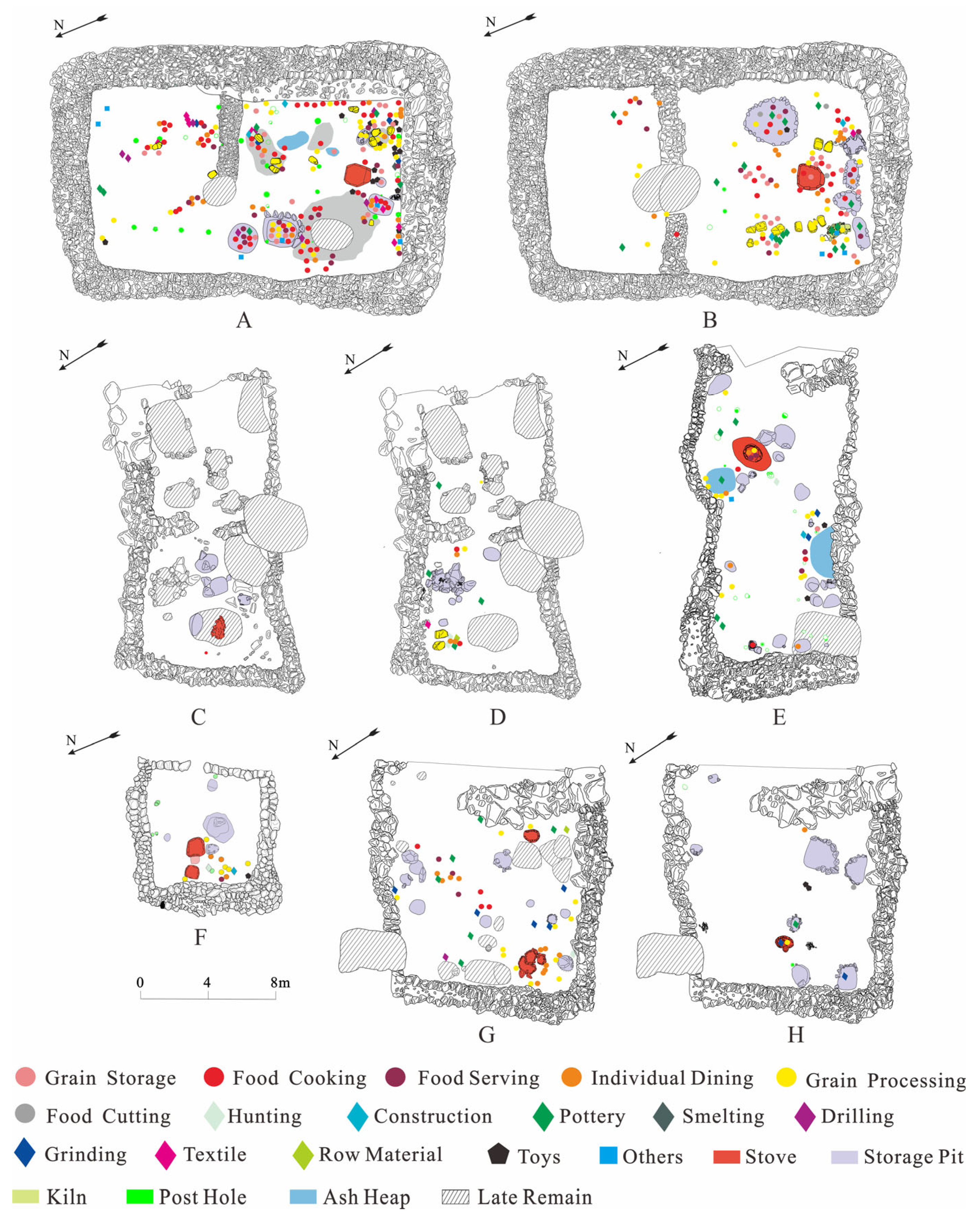
In all buildings, features were concentrated around the hearth, with grouped arrangements of large grinding stones, ash pits, and ash mounds distributed around it. Clustered collections of artifacts, including kitchenware and dining utensils, production and processing tools, and toys were found around the grinding stones, inside the ash pits, and under the foundations of the walls (Figure 5). Many of the features and artifacts showed signs of frequent use: for instance, the stones around the hearth were blackened and polished, some even cracked from the heat [57], and some pottery showed wear or repair marks. This suggests that these buildings were used for a relatively long period on a fairly regular basis.
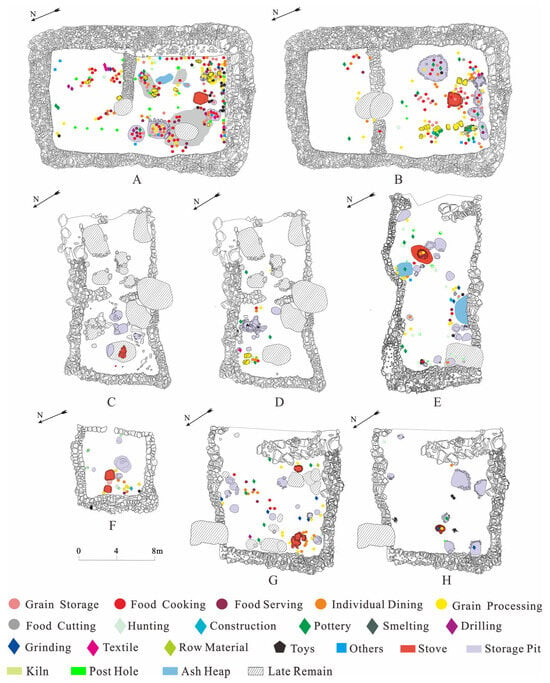
Figure 5.
Plan of the structures uncovered in Shirenzigou divided according to stratigraphy with features and artifacts marked on each layer: (A). lower floor level of F7; (B). upper floor level of F7; (C). lower floor level of F2; (D). upper floor level of F2; (E). upper floor level of F4 (only one floor was present in F4); (F). lower floor level of F1; (G). lower floor level of F3; (H). upper floor level of F3. The figure was made using CorelDRAW Graphics Suite 2016 (www.corel.com).
In structures F1–F4 and F6, the amount and volume of various types of features and artifacts were roughly proportional to the interior floor space (Table 3; Figure 5 and Figure 6A). The densities of pottery shards and other artifacts, including ceramic, stone, and metal items, as well as their distribution, type, size, ratio, and combination exhibited little variation across the smaller houses (Figure 5 and Figure 6B,C; Tables S2 and S3), indicating their similar nature. Yet, significant disparities were observed when compared to the larger structure, F7 (Figure 6; Tables S2 and S3). The stove and ash pit areas were considerably larger compared to those in the smaller dwellings (Figure 6A; Table S2). The artifact count in F7 was markedly higher, with cooking and dining utensils found in quantities ranging from 7 to 23 times those found in the other buildings. The dimensions of cooking implements, grain storage, and serving vessels in F7 were also substantially larger, with diameters and heights exceeding 0.5 m and some reaching up to 0.7 m in diameter and 0.6 m in height (Figure 2). Noteworthy were 11 and 9 large stone grinding plates found on the lower and upper floors of F7, respectively, along with 19 storage devices on each floor of the building. Unit F7 also contained unique relics and artifacts not found in other houses, including ceramic kilns, bronze ware, painted large pottery vessels, jars with double-looped ring feet, oversized single-handled goblets, crucibles, and stone scepter heads, among others (Figure 2; Table 3). These observations highlight the potential special function of F7 as a central architectural feature within the settlement.

Table 3.
Types and quantities of artifacts excavated from different structures and floor levels in Shirenzigou (* partially excavated).
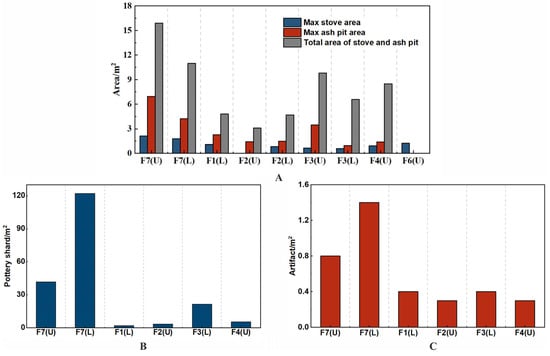
Figure 6.
Relationship between structures and artifacts excavated in Shirenzigou: (A). density of the features in each structure; (B). density of ceramics in the lower and upper floor of each structure; (C). density of artifacts (pottery, stone and metal items) in the lower and upper floor of each structure. Because it was only partially excavated, F6 was excluded from the counts. U = upper level; L = lower level. The figures were made using Origin 2024 (www.originlab.com).
During the first phase, botanical and faunal remains in F7 far surpassed those found in the other structures. Apart from a single cereal grain in F1, no plant remains were discovered in the smaller houses. In the subsequent phase, the quantity of plant and animal remains decreased in F7, with botanical findings being more prevalent in F3, hinting at a possible subtle shift in the dynamic between the two buildings (Table 4). Beneath both levels of F7, there was a notable concentration of large animal bone deposits, barley seeds, and pottery showing fire marks within ash pits. Directly under F7’s lower floor, pits H24 and H25 each contained seven relatively intact sheep skeletons bearing artificial marks [29]; pit H29 held a significant number of plant seeds, with around 4127 naked barley seeds extracted from about 40 L of soil [30]; pit H30 was rich in pottery fragments and animal bones [29]. Below the upper level, pit H19 was found to contain 681 animal bones and a large cache of barley seeds, estimated to total approximately 448,000 grains [30].

Table 4.
Types and quantities of bioarcheological findings (plants seeds and animal bones, teeth, and antlers) excavated from different structures and floor levels in Shirenzigou.
3.3. Chronology
Our radiocarbon dates were consistent with previous results, supporting a long-term occupation of the site between 1200 BCE and 900 BCE (Figure 7), with an early phase around 1200–1000 BCE and a later phase around 1000–900 BCE. More details on the radiocarbon dates can be found in Table S3.
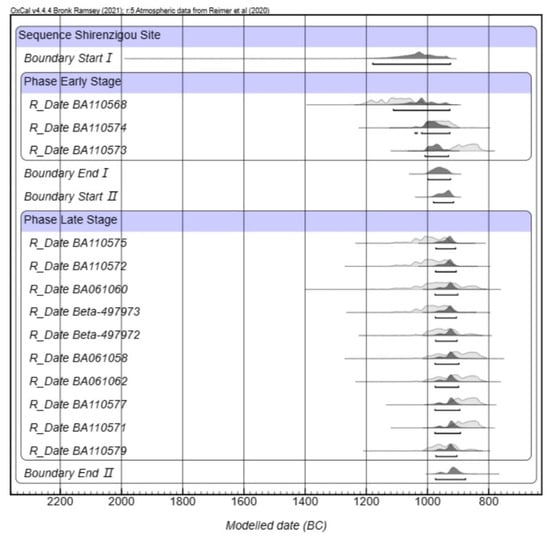
Figure 7.
Calibrated radiocarbon dates for Shirenzigou. Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Dating Laboratory of Peking University and Beta Lab, calibrated using OxCal and IntCal20 [64,65] (OxCal online version 4.4.4).
4. Discussion
4.1. The Shirenzigou Community
The findings at Shirenzigou, marked by an abundance of caprine skeletal elements and plant remains, indicate that the late Bronze Age inhabitants led a pastoral lifestyle complemented by farming and hunting [13,31,57,67], a practice still observable in the area today [29,67].
The arrangement of the settlement, including the positioning, forms, and dimensions of the buildings, along with the organization of their internal areas, suggests a certain degree of intentional spatial division. Although it is challenging to determine the degree of the potential site planning at Shirenzigou, the alignment of buildings along pathways and the establishment of an open space in front of the larger building lend further credence to the notion that there was a deliberate conceptual framework guiding the construction of the site [9,68,69]. The arrangement of the site with devoted activities’ areas, which is discussed below, provides additional support for this structured approach.
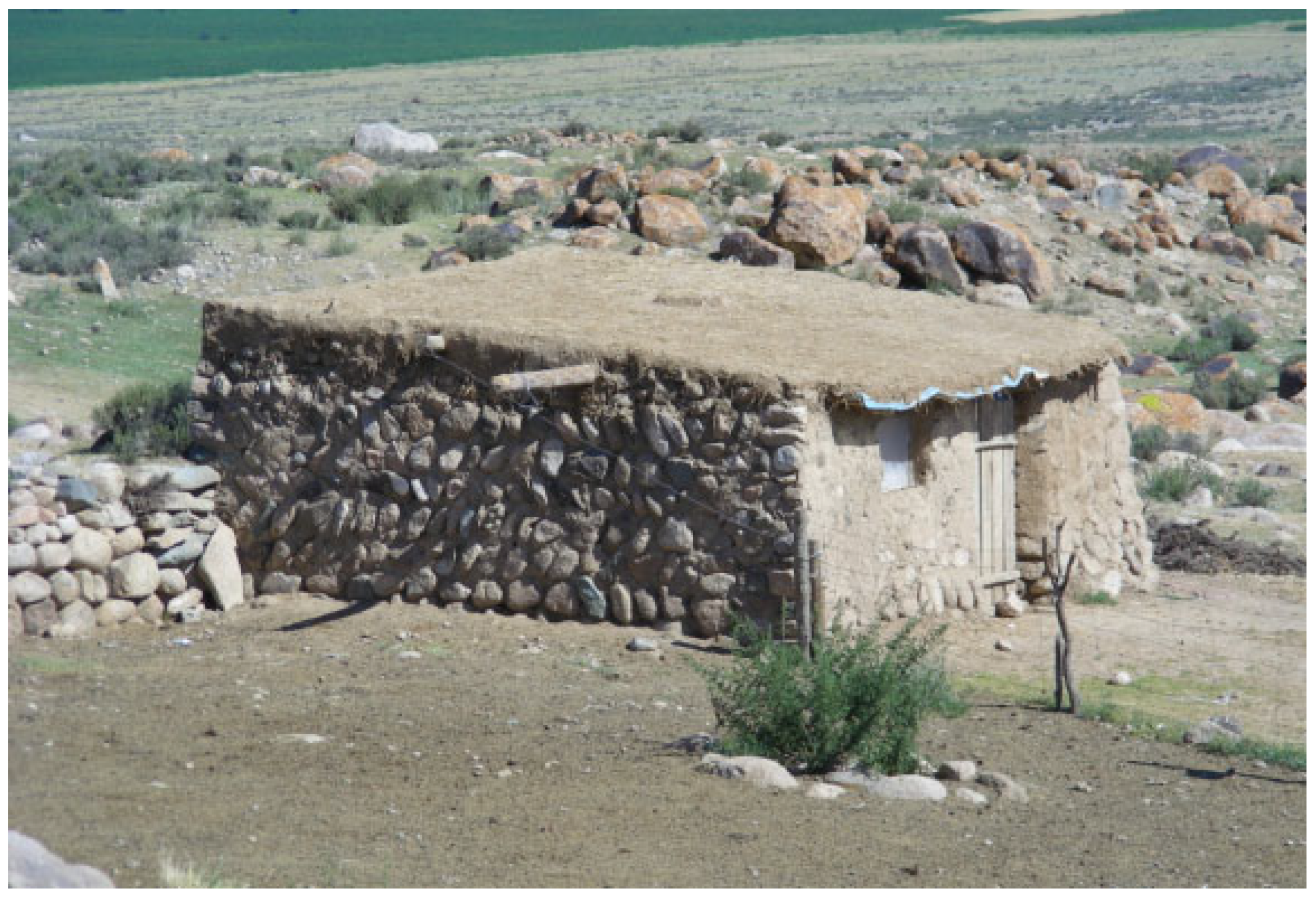
Units F1–F4 and F6 exhibited consistent architectural layout and spatial organization. Their parallel arrangement, lacking direct connection between them, suggests a deliberate effort to maintain a degree of autonomy [5,70]. Their dual-suite design further underscores this emphasis on privacy [8]. The larger front room likely fulfilled various roles, such as hosting guests, providing limited storage, and possibly serving as a temporary waste disposal area. The rear room, organized around the stove, was designated for cooking and probably sleeping. Near ash pits and walls, areas were seemingly assigned for food preparation, storage, and elementary crafts like weaving and pottery making. The significant number of basic cooking and dining utensils, greatly outnumbering other artifacts, along with animal bones bearing signs of processing, highlights the domestic nature of these spaces and their primary function as dwellings for small households. Comparable buildings have been found in nearby pastoralist Bronze Age settlements at Liushugou (F1 and F2; [71,72]) and Wulanbuluke (F5; [73]). Today similar structures are employed by small groups engaged in seasonal pastoralism for their routine living and dining needs across the Eastern Tianshan Mountains [7,29,67] (Figure 8). The archeological evidence and our observations of modern pastoralist households on-site suggest that these ancient spaces could potentially accommodate up to 4–6 people.

Figure 8.
Dwelling of pastoralists in Xigou, Shirenzi village, Barkol. The photo was taken by Ren Meng in August 2015.
The variety of cultural material excavated from units F1–F4 and F6, including artifacts for cooking, production, and leisure, suggests a diverse community engagement in domestic life, potentially involving men, women, children, the elderly, and other identities. The consistency in the distribution and types of remains in the smaller houses indicates minimal wealth differentiation among the occupants. The coeval funerary contexts of Liushugou [71] and Baiqier [74], located on the northern slopes of the Eastern Tianshan Mountains in Barkol and Yiwu, respectively, suggest a similar scenario: burials were grouped in clusters of similar scales and included comparable grave goods, providing no evidence for social stratification.
Building F7 stands out due to its larger size and strategic placement. It was not only the tallest structure in the settlement but was also raised to a higher elevation in the second construction phase. A pathway ascended from the ordinary dwellings to F7, climbing 9 m and winding through terraced houses to reach this central structure, thereby emphasizing its prominence within the settlement. F8, with its small, single-room layout, likely functioned as F7′s storage space for various cooking devices [57]. F5 and F10 were single-room spaces sharing their walls with F7. Their doors, when present, faced various directions. For this reason, it is suggested they were designed as annexes to support the main activities of the central building. The status of F9 is unclear, due to the lack of excavation data. The presence of these annexes indicates a complex centered around F7.
F7 stands also out for the greater scale and sophistication of its indoor facilities and artifacts. Notable is the inclusion of 19 unique grain storage devices, absent in standard residential units, which hints at a cohesive community structure in Shirenzigou, at least partially, reliant on shared food resources. Communal approaches to storage are usually more evident in strategic arrangements for ‘livestock storage’—utilizing fenced areas, repurposed structures, and pens—which are fairly well documented for both historical and contemporary pastoral communities throughout the Eastern and Western Tianshan Mountains [7,29,75]. The identification of grain storage containers in unit F7 not only corroborates previous arguments about small-scale agriculture practices at the site [31,61,75], but also further challenges the notion of this building serving merely as dwelling. Instead, it repositions F7 as a potential communal hub, central to the sustenance and social interaction of the Shirenzigou residents.
F7 exhibited a clear abundance of artifacts, outnumbering those in other houses and surpassing what would be expected for ordinary household needs. For example, the presence of large stone grinding plates—11 on the lower floor and 9 on the upper floor—far exceeds the 1–2 plates typically found in ordinary houses in Shirenzigou and elsewhere [57,76]. This lends further credence to the notion that this building was dedicated to collective activities, potentially including foundation-laying events, food-sharing ceremonies, and feasts. The accumulation of large quantities of animal bones, seeds, and pottery deposits beneath both floors of F7 [29,30] corroborates this argument. Similar prehistoric sites with ceremonial activities, characterized by oversized cooking facilities and numerous animal and plant remains, have been identified across the Tianshan Mountain [77,78,79]. Notably, the late Bronze Age centripetal compound structures at Lanzhouwanzi [80], and Haiziyan [81,82], in Barkol County, featured these elements prominently in their core houses, suggesting they served as community gathering points. Ethnographic research on current pastoralist groups in Shirenzigou by [29,67] documents seasonal collective ceremonies involving food distribution and sharing within the community. One of these studies estimates that the seven sheep found beneath F7 (in H24 or H25) could have been consumed by about 70 people in a single event [29]. The existence of a plaza to the east of F7 reinforces the interpretation of this space as being designed for communal gatherings. Distinctive artifacts such as large painted pottery vessels, bronze items, and scepter heads, predominantly discovered in F7, mirror the types of objects typically found in late prehistoric high-status burial sites across the Eastern Tianshan Mountains, like Yanghai M21 and Xigou M1 [83,84], further hinting at F7’s special role in the Shirenzigou settlement.
The architectural layout of the Shirenzigou centripetal compound building, characterized by strategic placement, varied forms and sizes of buildings around a central structure (F7), suggests a communal and possibly deliberate organization of space. Coupled with the extent, volume, and arrangement of relics and artifacts, this setup indicates different degrees of engagement in site activities, ranging from everyday tasks likely conducted at the household level in regular dwellings to broader participation in communal events associated with F7.
4.2. Centripetal Compound Buildings in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains: The Interplay between Environment and Social Change
The distinctive configuration of the centripetal compound building in Shirenzigou suggests an increasing complexity in the community’s social organization. Similar late Bronze Age structures identified across the Tianshan Mountains, such as in Hongshankou [85], Lanzhouwanzi [80], and Haiziyan [81,82] (Figure 9), indicate a broader adoption of this architectural style, reflecting substantial social ramifications at a regional scale.

Figure 9.
Centripetal compound structures identified in the Tianshan Mountains: (A). Shirenzigou [57]; (B). Xiaoheigou [86]; (C). Hongshankou [85,87]; (D). Kuola North Building Group [88]; (E). Yuegongtai-Xiheigou (Nijiaebo Group) [80,89]; (F). Yuegongtai-Xiheigou (Shuangzhe’ebo Group) [80,89].
[37] proposes that the selection of settlement locations and the site architectural arrangement during the late prehistory of Xinjiang were strategically based on climatic conditions, implying that these historical communities might have intentionally chosen their sites to mitigate the challenges of an increasingly hostile climate. The climate of Xinjiang during the late Holocene closely resembled its current state, being significantly more arid than in eastern China [90,91,92]. There is broad consensus that aridity in Northwest China has increased since 2000 BCE, leading to the expansion of deserts and the shrinkage of lake surface [93,94,95,96]. It has been argued that climatic deterioration in Xinjiang from the second millennium BCE was a crucial factor in settlement relocation, with a shift from lowland basins to the more sheltered mountain piedmonts and valleys [37]. This shift is evidenced by the decline and disappearance of the ‘Xiaohe civilization’ in the Lop Nur region around 1500 BCE [97]. Surveys across the Eastern Tianshan region have revealed various early burials, yet only one or two houses dating to 1500–1300 BCE have been identified in the Liushugou area [71]. While it is possible that the more obvious funerary contexts were documented, whereas less visible residential sites might have been overlooked [98], the current archeological evidence suggests sparse occupation during the Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with main human activities located in the lowlands of the Hami Basin [99,100]. The identification of numerous house conglomerates on the mountains’ piedmonts and valleys of the Eastern Tianshan Range, dating to the Late Bronze Age, indicates a significant increase in the inhabitation of this area in the late second millennium BCE. Archaeological evidence shows that during this period, the Tianshan Beilu cultural groups, who had settled in the Hami oasis since around 2000 BCE [99,100], expanded northwards to the grasslands in front of the mountains on both the southern and northern slopes, forming the Nanwan and Shirenzigou cultures [101].
Climate deterioration has often spurred people to congregate around available (albeit increasingly diminishing) resources [102,103]. A growing number of studies have shown historical examples of such phenomena in Northwest China [104,105]. The steady water supply and good drainage in the Shirenzigou area make it an optimal summer pasture, allowing large herds to be grazed there. Additionally, until the middle of the last century, the area around the site was extensively covered with green forests and grass, making it suitable for hunting wild fauna [29]. It is probable that, in response to increasing aridity, ancient communities would have clustered around these key resources. Most of the centripetal compound buildings in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains are located in similar settings, suggesting they could have been structural adaptations aimed at strengthening communal bonds among the increasing number of occupants of these new key locations.
Between the second and first millennium BCE, the mountainous regions of Central Asia and Xinjiang saw significant transformations, including a growing demography, the emergence of different pastoral models, an increased degree of mobility, a greater dependence on herding—primarily of caprines and, to a lesser extent, cattle—low-investment agricultural practices, and the development of new metallurgical technologies [31,33,36,106,107]. These new socio-economic patterns would have prompted changes in the use of the landscape, as well as a re-negotiation of relationships within and between communities [28,108]. The pasture at Shirenzigou is expansive and allows prolonged grazing, therefore it could have been used simultaneously by multiple people, as it happens today. Research conducted in Central Asia and Xinjiang documents that winter and summer camps were central gathering spots for herders to share pastures, while engaging in social and political interactions face-to-face [7,98,108]. In the Neolithic period in Western Asia, the emergence of clustered neighborhoods, special buildings, and feasting practices were linked to growing cooperation in crop production and shared beliefs and identities, in response to enhanced aridity, aiming to ensure social cohesion to allow survival of increasingly populated communities [8,69,109,110]. In China, the historical Yi Li (仪礼or Liji 礼记Book of Rites) describes a social structure extant in Northern China in the first millennium BCE, characterized by family-based clans where people ‘异居而同财, 有余则归之宗, 不足则资之宗’ (live separately but share wealth; the surplus goes to the clan, and in times of need, the clan supports) [111], emphasizing a blend of separate living with shared communal wealth and support to reinforce economic production and social cohesion. The development of centripetal compound buildings in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains could represent a regional adaptive strategy in response to emerging socio-political shifts. In Shirenzigou, this strategy would have particularly focused on reinforcing social cohesion among individuals and groups and securing resource availability by allocating individual tasks in ordinary houses and collective efforts in unit F7.
The Shirenzigou centripetal compound building, positioned in a valley surrounded by mountains and rivers with mountains at its back and facing steep slopes, is visible from a significant distance. During our surveys, we could see F7 from the highway in the lowlands north of the Tianshan Range, at a distance of at least 8 km. This strategic positioning likely added symbolic meaning to the structure, perhaps even serving as a social marker recognizable by nomadic pastoral groups from afar. This is in line with previous archeological and geomorphological research across Xinjiang, which has shown that during the Bronze and Iron Ages, special buildings devoted to collective ceremonies and rituals were strategically placed in locations like mountain peaks, open valleys, and occasionally alluvial fans, chosen for their ecological, climatic, environmental, and socio-political and symbolic significance [112,113,114]. Centripetal structures, which have been identified across the Eastern Tianshan region, were located in similar settings. For instance, the Yuegongtai-Xiheigou Group, in Barkol County, is sited on open slopes [52,80,89], while the Hongshankou Site No. 1, also in Barkol County, was atop a hill on an open slope [85]. The largest such structure identified to date—the Kuola Site North Building Group, in Yiwu County—lies on a piedmont slope with an extensive core house’s footprint of 70 m in diameter and a notable height of 6 m, emphasizing its prominence within the grasslands [88,115] (Figure 1 and Figure 9). The prominence of these structures could suggest they were a manifestation of the power of an emerging elite [116]. The relationship between the ordinary dwellings and the main unit F7 in Shirenzigou, however, seem to indicate that the centripetal compound building was part of a comprehensive strategy to create a stable social landscape. This meant that pastoralists in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains could have fostered greater social and political integration among people (and groups of people) based on cooperation and the regularity of face to face interaction during seasonal communal ceremonies.
In addition, the strategically positioned centripetal compound buildings could have served as measures to manage and control the movement of people, as well as regulating access to pastures and the settlement. However, this function may have been secondary. A Bronze Age structure, located less than two kilometers from the centripetal compound building, was identified in a higher position (approximately 20 m higher). This building would have had a broader view of the landscape [117]. Nevertheless, a more thorough analysis needs to be conducted on-site to better understand its nature and potential function.
In the Late Bronze Age, a significant number of non-ordinary dwellings and non-residential structures, alongside ordinary houses, appeared in the Tianshan Mountains, reflecting a growing regional socio-political complexity [10,13,98,118]. From this perspective, the emergence of the centripetal compound buildings across the Tianshan region may reflect a broader social strategy of integration of, but also divisions between, pastoralist groups in response to socio-political shifts between the second and first millennium BCE.
5. Conclusions
The late Bronze Age site of Shirenzigou was characterized by the emergence of a distinctive structure known as the centripetal compound building. This configuration, featuring smaller, independent dwellings encircling a larger, centrally located communal structure, illustrates a nuanced balance between private living spaces and public, communal areas. The arrangement points to an evolving social complexity within the pastoral communities of the Eastern Tianshan region. The proliferation of such communal-centric dwellings across the region may reflect a broader social strategy aimed at enhancing communal bonds among pastoral groups, possibly in reaction to environmental pressures and socio-political shifts in the late second millennium BCE.
Yet, several aspects remain unclear. Investigations at Shirenzigou have uncovered a systematic spatial division, with uniformly sized living quarters suggesting an organized setup potentially linked to household units. The question of whether these units were family-based remains open. While ethnographic studies suggest the predominance of nuclear families [29], genetic analyses from various prehistoric Eurasian sites reveal complex dynamics of household compositions, hinting at both genetic ties and social relationships as key in the structuring of ancient communities [119,120,121]. Moreover, while this study has demonstrated the unique role of unit F7, the specifics of its accessibility—whether it was exclusive to certain individuals or open to the wider community—still need to be clarified, raising further questions about the nature of social relationships within and across households. Despite significant research effort [29,31,36,75], further examination of production activities at the site are essential to uncover the complex processes and interactions that influenced daily life in Shirenzigou over time.
On a broader scale, the development and diffusion of centripetal compound buildings across the Eastern Tianshan Mountains likely had significant regional social implications. While our study provides important insights into the social landscape at the end of the second millennium BCE, a deeper understanding of these regional transformations—and their implications for the emergence of complex, potentially even proto-urban and urban societies in Xinjiang—requires more comprehensive excavations and analyses at both macro and micro levels
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/land13050576/s1, Table S1: Data relevant to the ratio of interior floor space to the total footprint area in the Shirenzigou structures; Table S2: Data relevant to the density of the features, ceramics, and other artifacts (pottery, stone and metal items) in the Shirenzigou structures; Table S3: Calibrated radiocarbon dates for Shirenzigou from the Accelerator Mass Spectrometry Dating Laboratory of Peking University and calibrated using OxCal and IntCal20 [64,65]. Reference [122] is cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.R.; methodology: M.R. and M.F.; validation: M.R. and L.C.; formal analysis: M.R. and L.C.; resources: J.W., M.R., J.M. and T.X.; data curation: L.C., Y.Y. and D.T.; original draft preparation: M.R. and L.C.; review and editing: M.F., J.M., M.R. and L.C.; visualization: M.R. and L.C.; supervision: J.M.; funding acquisition: J.W., J.M., M.F.; M.R. and L.C. equally contributed to this work and act as first authors; J.W., M.F. and J.M. act as corresponding authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the China National Social Science Foundation (No. 14ZDB052) and the China National Foreign Young Talents Program (No. QN203152300001).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
Ran Wanli, Zhang Feng, Mo Zhanxiong, Xi Lin, Huang Shan, Shinohara Norio, Miyawaki Shiro, and Kanasugi Taishiare are gratefully acknowledged for their support during the excavations. Thanks are due to Ma Zhikun for providing some of the novel information about the site. We are grateful to the three anonymous reviewers and the editors for their insightful comments and suggestions on this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kent, S. Domestic Architecture and the Use of Space: An Interdisciplinary Cross-Cultural Study; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA; Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kent, S. Partitioning Space: Cross-Cultural Factors Influencing Domestic Spatial Segmentation. Environ. Behav. 1991, 23, 438–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willey, G. The Virú Valley Settlement Pattern Study. In Archaeological Research in Retrospect; Willey, G., Ed.; Winthrop Publishers: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1974; pp. 149–178. [Google Scholar]
- Flannery, K.V. The Origins of the Village as a Settlement Type in Mesoamerica and the Near East. In Man, Settlement and Urbanism; Ucko, P.J., Tringham, R., Dimbleby, G.W., Eds.; Duckworth: London, UK, 1972; pp. 23–53. [Google Scholar]
- Flannery, K.V. The origin of the village revisited: From nuclear to extended households. Am. Antiq. 2002, 67, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, Y.; Miller, M. Sha‘ar Hagolan Vol. 1. Neolithic Art in Context. J. Am. Orient. Soc. 2003, 123, 872–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Caspari, G.; Betts, A.; Mohamadi, B.; Balz, T.; Cong, D.; Shen, H.; Meng, Q. Seasonal movements of Bronze Age transhumant pastoralists in western Xinjiang. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duru, G.; Ozbasaran, M.; Yelozer, S.; Uzdurum, M.; Kuijt, I. Space making and home making in the world’s first villages: Reconsidering the circular to rectangular architectural transition in the Central Anatolian Neolithic. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2021, 64, 101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banning, E.B.; Chazan, M. Domesticating Space: Construction, Community and Cosmology in the Late Prehistoric Near East; Ex Oriente: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Ge, L. Xinjiang Wenquan faxian yichu guimo pangda de Qingtong Shidai zaoqi yizhi 新疆温泉发现遗存规模庞大的青铜时代早期遗址 (Large-scale early bronze age sites found in Wenquan, Xinjiang). Zhongguo Wenwu Bao 2016, 8, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, C. The nature of organization of intra-site archaeological records and spatial analytic approaches to their investigation. Adv. Archeol. Method Theory 1984, 7, 103–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrer, F. Interpreting intra-site spatial patterns in seasonal contexts: An ethnoarchaeological case study from the Western Alps. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2017, 24, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Monteith, F.; Xi, T.; Ren, M.; Li, D.; Hu, S.; Wang, J.; Festa, M.; Ma, J. New evidence for regional pastoral practice and social complexity in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains in the first millennium BCE. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.C. Settlement Archaeology; National Press: Paolo Alto, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.C. Tan Juluo Xingtai Kaogu 谈聚落形态考古 (Discussion on Archaeology of Settlement Form). In Kaoguxue Zhuanti Liujiang; Chang, K.C., Ed.; Wenwu Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.C. Ancient China and Its Anthropological Significance. In Archaeological Thought in America; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA; Cambridge, UK, 1989; pp. 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Flad, R. Urbanism as Technology in Early China. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2018, 14, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X. State Formation in Early China; Duckworth: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe, Y.Y.; Castellano, L.; Shelach-Lavi, G.; Campbell, R.B. Mismatches of scale in the application of paleoclimatic research to Chinese archaeology. Quat. Res. 2021, 99, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X. Settlement Archaeology and the Study of Social Complexity in China. Rev. Archaeol. 2001, 22, 4–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hein, A. Theory and methods of settlement archaeology—The Chinese contribution. World Archaeol. 2023, 54, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelach, G. Leadership Strategies, Economic Activity, and Interregional Interaction: Social Complexity in Northeast China; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chifeng International Collaborative Archaeological Research Project. Regional Archaeology in Eastern Inner Mongolia: A Methodological Exploration; Kexue Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guedes, J.; Hein, A. Landscapes of Prehistoric Northwestern Sichuan: From Early Agriculture to Pastoralist Lifestyles. J. Field Archaeol. 2018, 43, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høisæter, T.L. Polities and nomads: The emergence of the Silk Road exchange in the Tarim Basin region during late prehistory (2000–400 BCE). Bull. Sch. Orient. Afr. Stud. 2017, 80, 339–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Ma, J.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Y.; Festa, M.; Xi, T.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, F. The Baigetuobie cemetery: New discovery and human genetic features of Andronovo community’s diffusion to the Eastern Tianshan Mountains (1800–1500 BC). Holocene 2021, 31, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Wang, C.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, F.; Nie, Z.; Tang, Y.; Robbeets, M.; et al. Ancient genomes reveal Yamnaya-related ancestry and a potential source of Indo-European speakers in Iron Age Tianshan. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 2526–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frachetti, M. Pastoralist Landscapes and Social Interaction in Bronze Age Eurasia; University of California Press: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y. Xinjiang Dongheigouyizhi Chutu Dongwuguge Yanjiu 新疆东黑沟遗址出土动物骨骼研究 (Study on Animal Bones Unearthed from Dongheigou Site in Xinjiang); Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS): Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D. Gongyuanqian Yiqianji Dongtianshandiqu de Zhiwukaoguxueyanjiu—Yi Shirenzigouyizhiqun Weizhongxin 公元前一千纪东天山地区的植物考古学研究——以石人子沟遗址群为中心 (Study on Plant Archaeology in the East Tianshan Mountains in the Millennium BC—Focusing on Shirengzigou Site Group); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Sun, M.; Ritchey, M.M.; Xi, T.; Ren, M.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Ling, X.; Liu, X. Varying cultivation strategies in eastern Tianshan corresponded to growing pastoral lifeways between 1300 BCE and 300 CE. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 966366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Ren, M.; Xun, X.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Ma, J. Xinjiang dongtianshandiqu balikun shirenzigouyizhi chuliangkeng fenxi 新疆东天山地区巴里坤石人子沟遗址储粮坑分析 (Analysis of Grain Storage Pit at Shirengzigou Site in Balikun, East Tianshan, Xinjiang). Disiji Yanjiu 2021, 41, 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J. Copper and Bronze Metallurgy in Late Prehistoric Xinjiang: Its Cultural Context and Relationship with Neighbouring Regions; BAR international Series; Archaeopress: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanks, B.; Linduff, K. Social Complexity in Prehistoric Eurasia: Monuments, Metals and Mobility; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA; Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J. The rise of nomads on the Barkol Steppe and their cultural interflow with the Altai Region during the 1st millennium BCE. In Eurasian Studies II; Yu, T., Li, J., Eds.; Asia Publishing Nexus: Sydney, Australia, 2014; pp. 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Taylor, W.; Chen, L.; Flad, R.; Boivin, N.; Liu, H.; You, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, M.; et al. Early evidence for mounted horseback riding in northwest China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29569–29576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yi, S.; Zhou, J.; Ma, C.; Dai, X. The study of early human settlement preference and settlement prediction in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, T. Qingtong Shidai Zhi Zaoqi Tieqi Shidai Dongtianshan Diqu Juluo Yizhi Yanjiu 青铜时代至早期铁器时代东天山地区聚落遗址研究 (Study on Settlement Sites in East Tianshan Mountains from Bronze Age to Early Iron Age); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W. Xinjiang Shiqian Wanqi Shehui Kaoguxue Yanjiu. 新疆史前晚期社会的考古学研究 (Archaeological Research on the Late Prehistoric Society in Xinjiang); Shanghai Guji Chubanshe: Shanghai, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Cong kaogufaxian kan gongyuanqian erqiannian dongxiwenhua pengzhuang he jiaoliu 从考古发现看公元前二千年东西文化的碰撞和交流 (The collision and communication between eastern and western cultures in 2000 BC from archaeological discoveries). Xinjiang Wenwu 1999, 1, 60–62. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. “The Painted Pottery Road” and Early Sino-Western Cultural Exchanges. Anabasis Stud. Class. Orient. 2012, 3, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Shiqian caitaozhilu: Zhongguo wenhua xilaishuo zhi zhongjie 史前彩陶之路: “中国文化西来说”之终结 (Prehistoric painted pottery road: The end of “China culture coming from the west”). Zhongguo Shehui Kexuebao 2012, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. Zailun Sichouzhiluqian de Caitaozhilu 再论丝绸之路前的彩陶之路 (Re-discussion on the road of painted pottery before the Silk Road). Wenbo Xuekan 2018, 1, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.; Liu, G.; Chang, X. Xinjiang Dongbudiqu chutu Zaoqi Tongqi de chubu fenxi he yanjiu 新疆东部地区出土早期铜器的初步分析和研究 (Preliminary analysis and research on early bronzes unearthed in eastern Xinjiang). Xiyu Yanjiu 2002, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.; Gao, B. Saiyimabinuo xianxiang he Zhongguo xibeidiqude zaoqi qingtongwenhua 塞伊玛图比诺现象和中国西北地区的早期青铜文化 (Saima Tubino Phenomenon and Early Bronze Culture in Northwest China). Xinjiang Wenwu 2003, 1, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W. Xinjiang Hamidiqu Shiqianshiqi Tongqi Jiqiyu Linjindiqude Guanxi 新疆哈密地区史前时期铜器及其与邻近地区文化的关系 (Prehistoric Bronzes in Hami, Xinjiang and Their Relationship with Neighboring Cultures); Zhishichanquan Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H. Dongfengxijian: Xibei Shiqianwenhua Zhi Jincheng 东风西渐: 西北史前文化之进程 (East Wind Spreading to the West: The Process of Prehistoric Culture in Northwest China); Wenwu Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 276–293. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Mei, J.; Qian, W. Sichouzhilu yu zaoqi tongtiejishu de jiaoliu 丝绸之路与早期铜铁技术的交流 (The Silk Road and the Exchange of Early Copper and Iron Technology). Xiyu Yanjiu 2018, 2, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Yang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, F. Nongzuowu chuanbo shijiaoxia de ouyadalu shiqian dongxifang wenhua jiaoliu农作物传播视角下的欧亚大陆史前东西方文化交流 (Cultural exchanges between East and West in Eurasia from the perspective of crop communication). Zhongguokexue Diqiukexue 2017, 47, 535–536. [Google Scholar]
- An, C.; Wang, W.; Duan, F.; Huang, W.; Chen, F. Yazhou zhongbu ganhanqu sichouzhilu yanxian huanjing yanbian yu dongxifang wenhua jiaoliu亚洲中部干旱区丝绸之路沿线环境演化与东西方文化交流 (Environmental Evolution along the Silk Road in Arid Area of Central Asia and cultural exchanges with the East and the West). Dili Xuebao 2017, 72, 880–886. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M. Gongyuanqian Yiqianji Dongtianshan Diqu Kaoguxue Wenhuayicun Yanjiu 公元前一千纪东天山地区考古学文化遗存研究 (Study on Archaeological Cultural Remains in the East Tianshan Mountains in the Millennium BC); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R. Xinjiang Balikun Yuegongtai-xiheigou yizhiqun chubu renshi 新疆巴里坤岳公台—西黑沟遗址群初步认识 (A preliminary understanding of Yuegongtai-Xihegou site group in Balikun, Xinjiang). Xibeidaxue Xuebao 2009, 39, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F. Xinjiang Dongheigouyizhi Shizhugaotai, Juzhi Yanjiu 新疆东黑沟遗址石筑高台, 居址研究 (Study on the Stone Platform and Residence of Dongheigou Site in Xinjiang); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M. Cong Heigouliangmudi, Dongheigouyizhi Kan Xihanqianqi Dongtianshandiqu Xiongnu Wenhua 从黑沟梁墓地, 东黑沟遗址看西汉前期东天山地区匈奴文化 (The Xiongnu Culture in the Eastern Tianshan Mountains in the Early Western Han Dynasty as Seen from Heigouliang Cemetery and Donghegou Site); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B. Dilixinxixitong Zai Gudai Daxing Youmuwenhua de Yingyong Yu Yanjiu—Yi hongshankou-Shirenzigouyizhiqun Weili 地理信息系统在古代大型游牧文化遗址的应用与研—以红山口-石人子沟遗址群为例 (Application and Research of Geographic Information System in Ancient Large-Scale Nomadic Cultural Sites—Taking Hongshankou-Shirengzigou Site Group as an Example); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.; Jiang, Y. Gongyuanqian yiqianji dongtianshandiqu youmurenqun de tuzaixingwei 公元前一千纪东天山地区游牧人群的屠宰行为 (Slaughtering behavior of nomadic people in the eastern Tianshan mountains in the first Millennium BC). Nongye Kaogu 2021, 6, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Ren, M.; Yahefu, J.; Yu, J. Xinjiang balikun dongheigouyizhi 2006–2007 nian fajuejianbao 新疆巴里坤县东黑沟遗址2006~2007年发掘简报 (Brief report on excavation of Dongheigou site in Barkun County, Xinjiang in 2006~200). Kaogu 2009, 1, 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Milne, S. Landscape learning and lithic technology: Seasonal Mobility, enculturation and tool apprenticeship among the Early Palaeo-Eskimos. In Structured Worlds: The Archaeology of Hunter-Gather Thought and Action; Cannon, A., Ed.; Equinox: Sheffield, UK, 2011; pp. 95–115. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, F.; Ren, M.; Yahefu, J.; Yu, J. Shirenzigouyizhi 2006–2007 Niandu Fajuebaogao石人子沟遗址2006~2007年度发掘报告 (Excavation Report of Shirenzigou Site in 2006~2007); Kexue Chubanshe: Beijing, China, in press.
- Chen, X.; Ren, M.; Wang, J.; Yahefu, J. Xinjiang balikun dongheigouyizhi diaocha 新疆巴里坤东黑沟遗址调查 (Investigation on Dongheigou Site in Barkol, Xinjiang). Kaogu Yu Wenwu 2006, 5, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, D.; Ma, J.; Ren, M.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z. Xinjiang Diqu De Zaoqi Damai Shengchan: Laizi Tianshan Beilu Shirenzigou Yizhi De Zhiwu Yicun Zhengju 新疆地区的早期大麦生产: 来自天山北麓石人子沟遗址的植物遗存证据 (Early Barley Production in Xinjiang: Evidence from Plant Remains of Shirengzigou Site at the Northern Foot of Tianshan Mountain). Zhongguo Nongshi 2021, 40, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Paliou, E.; Lieberwirth, U.; Polla, S. Spatial Analysis and Social Spaces: Interdisciplinary Approaches to the Interpretation of Prehistoric and Historic Built Environments; Topoi, 18; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S. Zhongguo Gudai Taoci Cidian 中国古代陶瓷辞典 (The Dictionary of Ancient Ceramics in China); Zhongguo Wenshi Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bronk, R.C. Bayesian analysis of radiocarbon dates. Radiocarbon 2009, 51, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, P.J.; Austin, W.; Bard, E.; Bayliss, A.; Blackwell, P.G.; Ramsey, C.B.; Butzin, M.; Cheng, H.; Edwards, R.L.; Friedrich, M.; et al. The IntCal20 Northern Hemisphere radiocarbon age calibration curve (0–55 cal kBP). Radiocarbon 2020, 62, 725–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, C.B. Radiocarbon calibration and analysis of stratigraphy: The OxCal program. Radiocarbon 1995, 37, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Zhong, H.; Yu, Y. Xinjiang Barkol Shirenzigou yizhi shengye kaogu de minzuxue diaocha yu yanjiu 新疆巴里坤县石人子沟遗址生业考古的民族学调查与研究 (Ethnology Investigation and Research on the Archaeology of Shirengzigou Site in Balikun County, Xinjiang). Nanfang Wenwu 2016, 2, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel, Y. The Social Organization at Neolithic Sha’ar Hagolan: The Nuclear Family, the Extended Family and the Community. In Domesticating Space. Construction, Community, and Cosmology in the Late Prehistoric Near East; Benning, T., Chazan, M., Eds.; Studies in Early Near Eastern Production, Subsistence and Environment 3; Ex Oriente: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Bogaard, A.M. Neolithic “Cooperatives”: Assessing Supra-Household Cooperation in Crop Production at Çatalhoyük and Beyond. In Neolithic Corporate Identities; Benz, M., Gebel, H.G.K., Watkins, T., Eds.; Studies in Early Near Eastern Production, Subsistence, and Environment 20; Ex Oriente: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Byrd, B.F. Public and Private, Domestic and Corporate: The Emergence of the Southwest Asian Village. Am. Antiq. 1994, 59, 639–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Xinjiang Hamishi liushugouyizhi he mudi de kaogufajue 新疆哈密市柳树沟遗址和墓地的考古发掘 (Archaeological Excavation of Liushugou Site and Cemetery in Hami City, Xinjiang). Xiyu Yanjiu 2015, 2, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Liushugouyizhi Yanjiu 柳树沟遗址研究 (Study on Liushugou Site); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Aihemaiti, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y. Xinjiang Hamishi wulanbulukeyizhi kaogu fajuejianbao 新疆哈密市乌兰布鲁克遗址考古发掘简报 (Brief report on archaeological excavation of Wulanbuluke site in Hami, Xinjiang). Tulufanxue Yanjiu 2022, 2, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinjiang Institute of Cultural Relics, Archaeology School of Cultural Heritage of Northwest University, Hami Municipal Cultural Heritage Administration and Yiwu County Cultural Heritage Administration Xinjiang. Xinjiang Baiqier Mudi—2004~2005 Niandu Fajue Baogao 新疆拜其尔墓地—2004~2005年度发掘报告 (Bechir Cemetery: Excavation Report 2004–2005); Wenwu Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Ren, M.; Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Wan, Z.; Tian, D.; Ren, W. Xinjiang Dongtian Diqu Shirenzigouyizhi nongmu huodong qingkuang: Tanhua zhongzi、zhiguiti he baofen zhengju 新疆东天山地区石人子沟遗址农牧活动情况: 炭化种子, 植硅体和孢粉证据 (Agricultural and pastoral activities of Shirenzigou site in eastern Tianshan area of Xinjiang: Evidence from carbonized seeds, phytoliths and sporopollen). Wenti Gushengwu Xuebao 2023, 40, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, X. Haiziyanyizhi 2017 nian fajue jianbao 新疆巴里坤海子沿遗址2017年发掘简报 (Brief Report on Excavation of Haiziyan Site in Balikun, Xinjiang in 2017). Wenwu 2020, 12, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. Xinjiang Yutianxian liushui qingtongshidaimudi kaogufajue yu wenhua qingkuang jianshu新疆于田县流水青铜时代墓地考古发掘与文化情况简述 (Brief introduction of archaeological excavation and cultural situation of bronze age cemetery in Yutian County, Xinjiang). Xinjiang Yishu 2020, 2, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Xinjiang Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology. Nilekexian wutulanmudi kaogufajue baogao 尼勒克县乌吐兰墓地考古发掘报告 (Archaeological Excavation Report of Wutulan Cemetery in Nileke County). Xinjiang Wenwu 2014, 1, 36–56. [Google Scholar]
- Xinjiang Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology. 2014 nian Nilekexian Wutulanmudi kaogufajue baogao 2014 年尼勒克县乌吐兰墓地考古发掘报告 (Archaeological Excavation Report of Wutulan Cemetery in Nileke County in 2014). Xinjiang Wenwu 2015, 2, 4–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Ding, Y.; Ya, H.; Yu, J. Xinjiang Balikun Yuegongtai-xiheigou yizhiqun diaocha 新疆巴里坤岳公台—西黑沟遗址群调查 (Investigation on Yuegongtai-Xihegou site group in Balikun, Xinjiang). Kaogu Yu Wenwu 2005, 2, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.; Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Tian, Y.; Ai, H.; Jiang, X. Xinjiang Balikun Haiziyanyizhi kaogufajue shouhuo yu sikao 新疆巴里坤海子沿遗址考古发掘收获与思考 (Harvest and Thinking of Archaeological Excavation of Haiziyan Site in Balikun, Xinjiang). Xiyu Yanjiu 2021, 4, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Tian, Y.; Ai, H.; Jiang, X. 2017、2018 niandu Xinjiang Balikun Haiziyanyizhi kaogu fajue 二〇一七, 二〇一九年度新疆巴里坤海子沿遗址考古发掘 (Archaeological Excavation of Haiziyan Site in Balikun, Xinjiang in 2017 and 2019). Wenwu Tiandi 2021, 7, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Lv, E.; Zhang, Y. Xinjiang Shanshan Yanghaimudi fajuejianbao 新疆鄯善洋海墓地发掘简报 (Excavation on the Yanghai Cemetery in Shangshan (Piqan) County, Xinjiang). Acta Archaeol. Sin. 2011, 1, 99–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Cheng, X.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, X. Xinjiang Hami Balikun Xigouyizhi 1haomu fajue jianbao 新疆哈密巴里坤西沟遗址1 号墓发掘简报 (Brief Report on Excavation of No.1 Tomb in Xigou Site of Balikun, Hami, Xinjiang). Wenwu 2016, 5, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Y. 2012~2013 Niandu Xinjiang Balikun Hongshankouyizhi Fajuejianbao 2012~2013年度新疆巴里坤红山口遗址发掘简报 (Brief report on excavation of Hongshankou site in Barkun, Xinjiang in 2012–2013). Wenwu in press.
- Ma, J.; Mou, J.; Xi, T.; Ren, M.; Tian, Y.; Aihemaiti, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fu, Y. 2018 nian Xinjiang Balikun Xiaoheigouyizhi diaocha jianbao 2018 年新疆巴里坤小黑沟遗址调查简报 (Brief Report on the Investigation of Xiaoheigou Site in Balikun, Xinjiang in 2018). Xibu Kaogu 2022, 1, 99–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Ren, M.; Wang, J. Xinjiang Balikun Hongshankouyizhi 2008 nian diaocha jianbao 新疆巴里坤红山口遗址2008年调查简报 (A Brief Report on the Investigation of Hongshankou Site in Balikun, Xinjiang in 2008). Wenwu 2014, 7, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xi, T.; Rou, Z.; Ma, J.; Ren, M. Xinjiang Yiwu Kuolayizhi 2017~2018 年 diaocha jianbao 新疆伊吾阔腊遗址2017~2018年调查简报 (A Brief Report on the Investigation of Yiwu Kuola Site in Xinjiang from 2017 to 2018). Wenwu 2020, 8, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y. Yuegongtai-Xiheigou Yizhiqun ji Xiangguanwenti Yanjiu 岳公台—西黑沟遗址群及相关问题研究 (Research on Yuegongtai-Xihegou Site Group and Related Issues); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Yu, Z.; Yang, M.; Ito, E.; Wang, S.; Madsen, D.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Sat, T.; Birks, H.; et al. Holocene moisture evolution in arid central Asia and its out-of-phase relationship with Asian monsoon history. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2008, 27, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünnemann, B.; Chen, F.; Riedel, F.; Zhang, C.; Mischke, S.; Chen, G.; Demske, D.; Ming, J. Holocene lake deposits of Bosten Lake, southern Xinjiang, China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 1429–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünnemann, B.; Mischke, S.; Chen, F. A Holocene sedimentary record from Bosten Lake, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology. Palaeoecology 2006, 234, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Shu, Q. Palaeoclimatic and Palaeohydrologic Oscillations Since about 12.0 ka B.P. at Bosien Lake, Southern Xinjiang. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2001, 32, 213–220. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Chen, C.; Jia, W.; An, C.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, J.; Jin, M.; Xia, D.; Chen, F.; Grimm, E. Vegetation and climate history reconstructed from an alpine lake in central Tienshan Mountains since 8.5 ka BP. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2015, 432, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Xiang, L.; Lei, G.; Sun, M.; Qiu, M.; Storozum, M.; Huang, C.; Munkhbayar, C.; Demberel, O.; Zhang, J.; et al. Sedimentary Pediastrum record of middle–late Holocene temperature change and its impacts on early human culture in the desert-oasis area of northwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2021, 265, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Liang, J.; Vachula, R.; Russell, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, M.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Chen, F. Changes in the hydrodynamic intensity of Bosten Lake and its impact on early human settlement in the northeastern Tarim Basin, Arid Central Asia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 576, 110499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mo, D.; Hu, K.; Bao, W.; Li, W.; Abuduresule, I.; Storzum, M.; Kidder, T. Holocene environmental changes around Xiaohe Cemetery and its effects on human occupation, Xinjiang, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 752–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Betts, A.; Dupuy, P.; Cong, D.; Jia, X. Bronze Age hill forts: New evidence for defensive sites in the western Tian Shan, China. Archaeol. Res. Asia 2018, 15, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, E.; Chang, X.; Wang, B. Xinjiang Qingtongshidai Kaogu Wenhua Qianlun 新疆青铜时代考古文化浅论 (Brief Discussion on Archaeological Culture of Bronze Age in Xinjiang). In Subingqi yu dangdai Zhongguo kaoguxue; Su, B., Ed.; Kexue Chubanshe, 2001; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J. Xinjiang de Qingtongshidai he Zaoqitieqishidai Wenhua 新疆的青铜时代和早期铁器时代文化 (Bronze Age and Early Iron Age Culture in Xinjiang); Wenwu Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H. Xinjiang Shiqianshiqi Wenhua Geju de Yanbian Jiqi yu Zhoulin Diqu Wenhua de Guanxi 新疆史前时期文化格局的演进及其与周邻地区文化的关系 (The Evolution of Prehistoric Cultural Pattern in Xinjiang and Its Relationship with the Cultures in Neighboring Areas); Jilin University: Jilin, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Liu, G. Relationship between climatic change and the nomadic southward migrations in eastern Asia during historical times. Clim. Change 1992, 22, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, N. Cultural responses to aridity in the Middle Holocene and increased social complexity. Quat. Int. 2006, 151, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, H.; Gui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lee, H.; Ding, D.; Hou, Y.; Dong, G. Chronology and Plant Utilization from the Earliest Walled Settlement in the Hexi Corridor, Northwestern China. Radiocarbon 2019, 61, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Francesca, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Ma, J.; Festa, M. Chronology of the Early Iron Age settlement of Koyuk Shahri in Xinjiang, China. Radiocarbon 2024, in press.
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Spate, M.; Reheman, K.; Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; et al. Inner Asian agro-pastoralism as optimal adaptation strategy of Wupu inhabitants (3000–2400 cal BP) in Xinjiang, China. Holocene 2021, 31, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachetti, M.; Benecke, N. From sheep to (some) horses: 4500 years of herd structure at the pastoralist settlement of Begash (south-eastern Kazakhstan). Antiquity 2009, 83, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frachetti, M.D. Multiregional emergence of mobile pastoralism and nonuniform institutional complexity across Eurasia. Curr. Anthropol. 2012, 53, 2–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K. Domestication and inequality? Households, corporate groups and food processing tools at Neolithic Çatalhöyük. J. Anthropol. Archaeol. 2014, 33, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogaard, A.; Charles, M.; Twiss, K.C.; Fairbairn, A.; Yalman, N.; Filipovic, D.; Demirergi, G.A.; Ertuğ, F.; Russell, N.; Henecke, J. Private pantries and celebrated surplus: Storing and sharing food at Neolithic Çatalhöyük. Antiquity 2009, 83, 649–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D. “Yi Li·Sangfu” Kao Lun 《仪礼·丧服》考论 (Textual Research on “The Yi-Li: Mourning”); Shehui Kexue Wenxian Chubanshe: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X. Mountain valleys, alluvial fans and oases: Geomorphologic perspectives of the mixed agropastoral economy in Xinjiang (3000–200 BC). Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.; Cong, D. Results of Field Research on Ancient Stonework in the River Valleys of Bortala and Ili in Western Tian Shan (Xinjiang, China). Asian Perspect. 2020, 59, 385–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspari, G. Quantifying Ritual Funerary Activity of the Late Prehistoric Southern Kanas Region (Xinjiang, China). Asian Perspect. 2020, 59, 421–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y. Kuolayizhi Diaocha Yanjiu 阔腊遗址调查研究 (Investigation and Study on Kuola Site); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houle, J.L. Socially integrative facilities and the emergence of social complexity on the Mongolian Steppe. In Social Complexity in Prehistoric Eurasia, Monuments, Metals and Mobility; Hanks, B.K., Linduff, K.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 358–377. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y. Xinjiang Balikun Shirenzigou Yizhi Juluo Xingtai Yanjiu 新疆巴里坤石人子沟遗址聚落形态研究 (The Study on the Settlement Patterns of the Shirenzigou Site in Barlow, Xinjiang); Northwest University: Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Xi, T.; Zhao, H.; Han, B.; Ye, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, A.; Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; et al. 2009 nian Xinjiang Balikun Shirenzigouyizhi F2 fajue baogao 2009年新疆巴里坤石人子沟遗址F2发掘报告 (Excavation report on F2 of Shirenzigou Site, Barkol, Xinjiang in 2009). Archaeol. Cult. Relics 2014, 5, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yaka, R.; Mapelli, I.; Kaptan, D.; Dogu, A.; Chyleński, M.; Erdal, Ö.D.; Koptekin, D.; Vural, K.B.; Bayliss, A.; Mazzucato, C.; et al. Variable kinship patterns in Neolithic Anatolia revealed by ancient genomes. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 2455–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, C.; Zhang, F.; Cao, Y.; Qin, L.; Hudson, M.; Gao, S.; Ma, P.; Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, C.; et al. Ancient genome analyses shed light on kinship organization and mating practice of Late Neolithic society in China. iScience 2021, 24, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Ning, C.; Zhang, J.; Ma, P.; Zhang, R.; Yun, Z.; Duan, C.; Cai, D. Haibing Yuan Ancient genomes reveal the origin and kinship burial patterns of human remains during the 11th to 13th centuries in northern China. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2023, 34, e3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mei, J.; Wang, J. Xinjiang Balikun Dongheigou yizhi chutu Tieqi Yanjiu 新疆巴里坤东黑沟遗址出土铁器研究 (Study on the Iron Objects unearthed from Dongheigou Site in Balikun, Xinjiang). Wenwu 2013, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).