Abstract
Lake sediment records are of great importance for understanding the evolution of watershed environments. Various studies have been carried out to determine the depositional ages of lake sediments and to examine their physical, chemical, and biological characteristics. The aim is to construct the historical vegetation, environment, and climate patterns in Chinese lake watersheds. In this review, we obtained relevant studies on lake sediment records by searching the key word ‘age-depth’ from the following databases: Web of Science and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI, the largest Chinese academic database). We analyzed the literature based on its type (published in a Chinese/English journal or as a Master’s/PhD thesis), period of publication, journal (if published in a journal), key authors, study area, dating scale, and main aims. The results suggest that the lakes in the plateau regions are the most popular research topic, typically covering 100–200 years (short-term) and 500–30,000 years (long-term). The literature focuses on a wide range of topics, from past environmental evolution in watersheds to lake ecology, and it provides a solid foundation for a better understanding of the regional climate change and the preservation of lake environments and ecosystems. In the future, the resulting data obtained from environmental reconstructions with lake sediments will need to be integrated with emerging information processing technologies (e.g., artificial intelligence and meta-analysis) to disentangle the complex interplay between the Earth’s surface processes and global climate change; furthermore, strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration will deepen our comprehension of the man-land relationship and promote the sustainable management of lake ecosystems in the context of global climate change.
1. Introduction
Lakes, within the terrestrial hydrosphere, crucially regulate regional hydrological climates and ecological environments, and they play a key role in linking Earth’s surface systems [1,2]. They can provide substantial natural resources and ecological services, and thus support the development of our economy and society. As such, the study of lakes is of great importance across various multidisciplinary fields. The excellent continuity and high resolution offered by lake sediments shape the unique depositional environments of lakes [3]; thus, the deposits in lakes are valuable records for unravelling past environmental change in watersheds, the evolution of lake ecosystems, and the human impacts on environments [4,5].
Research on lake sediments can be dated back to the late 19th century with the systematic investigations conducted by Russel and Gilbert on lakes in the western United States [1]. Subsequently, in the 1960s, the first batch of international initiatives for the collection and characterization of lake sediments were undertaken [4]. Concurrently, Chinese scientists began to embark on expeditions and hydrological measurements of lakes such as Lop Nor and Qinghai Lake [6,7]. The 1970s and 1980s witnessed a focus of study on the late Quaternary stratigraphy of lake sediments alongside investigations into the evolution of paleoclimates and the geological units of basins during the Meso–Cenozoic with stratigraphy [8]. The studies on lake sediments expanded further with a burgeoning importance on the implications of global climate and environmental change. Scientists reconstructed regional environmental successions with the physical, chemical, and biological information derived from lake sediments [9,10]; moreover, they established databases to facilitate comparative analyses [11] with records from ice cores and the ocean [12]. In addition, researchers began to elucidate the environmental disparities between regions. In recent years, people have gradually become aware of the impact of human activities on lake environments [13] based on the anthropogenic record in lake sediments. With the high-resolution data derived from lake sediments, researchers have reconstructed the evolutionary history of lake environments that is driven by human activities [14,15]. These efforts aim to unveil the extent of the impact of human activities and climate change on the evolution of lake ecology and environments [16,17].
Due to the complexity of the studies on lake sediments, they are usually related to knowledge and methods from different disciplines, including geology, geography, ecology, and environmental science. The indicators of environmental change for lake sediments include physical (e.g., grain size composition and magnetic susceptibility [18]), chemical (e.g., organic matter, isotopes, carbonates, and various geochemical elements [19]), and biological (e.g., pollen, alkanes, and diatoms [20,21,22]) proxies. By analyzing these proxies, we can obtain key information on the environmental evolution of lakes, including paleoclimate changes; the evolution of ecosystems, biodiversity variation, and the adaptation of lake ecosystems to environmental change [23]; and the impact of human activities on lake environments [24]. Furthermore, by analyzing environmental indicators (e.g., pollutants and nutrients from lake sediments), we can evaluate the health of lake ecosystems; this will place a solid basis for developing strategies to protect and manage lake resources.
In this review, with a retrospective literature evaluation on the lake sediments in China over the past thirty years, we aim to provide valuable information and a reference from different aspects for the purpose of further promoting the comprehensive development of research on lake sediments in the future. This will be achieved by quantitative analyses, summarizing research statuses (including methods), and examining deficiencies.
2. Data Collection and Methods
Bibliometrics serve as an objective, comprehensive, and systematic approach for examining the current status and trends in the field of lake sediment research from multiple perspectives [25,26]. A bibliometric analysis on the literature (categorized by type of literature, date of publication, journal published, key authors, and studied region) can uncover the development tendencies within this field, evaluate academic achievement and its influence, identify opportunities for collaboration, and aid in the optimization of academic resources [27,28]. By analyzing the dating scale and content of the related literature, this review seeks to attain a better understanding of the evolution patterns of the Earth’s environments, changes in lake environments, and the research topics and the cutting edge in the research field of lake sediments across different regions.
We employed ‘lake sediment*’ and ‘China’ as keywords for a literature search in the Web of Science (https://www.webofscience.com/; accessed on 2 June 2023) and CNKI (China National Knowledge Infrastructure, the largest Chinese academic database, https://www.cnki.net/; accessed on 2 June 2023) databases. We initially identified 5181 articles with the criterion that the article must contain a detailed sedimentological description on the lake core profile. To ensure that the lake sediments were age-constrained, we then manually checked the literature, screened those with ‘age-depth’ models, and obtained 413 articles as datapoints for the statistical analysis of this review. We classified these lake sedimentary profiles based on the length of their dated age intervals to understand their temporal resolution and coverage.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Number of Studies in the Literature and Dates of Publication
A statistical analysis of the literature types from 1994 to 2023 indicated that Chinese articles (35), English articles (315), and Master’s/PhD dissertations (65) accounted for 8.5%, 76.2%, and 15.3%, respectively (Figure 1a). The articles on lake sediments published during 1994–2023 increased year by year based on the quantity and date of the publications, with a particularly marked surge having occurred from 2006 onwards; this suggests that studies on lake sediments have received more attention in the past two decades. Notably, the number of English articles also evidently increased from 2006, indicating the development and increasing influence of Chinese research on lake sediments in the international academic community (Figure 1b). It was found that 2016–2019 were the peak years for publications on lake sediment research; in particular, the number of publications reached a peak of 80 per year during 2018–2019. The results indicate that lake sediment research in China has received widespread attention, and related researchers have made significant progress both domestically and internationally.
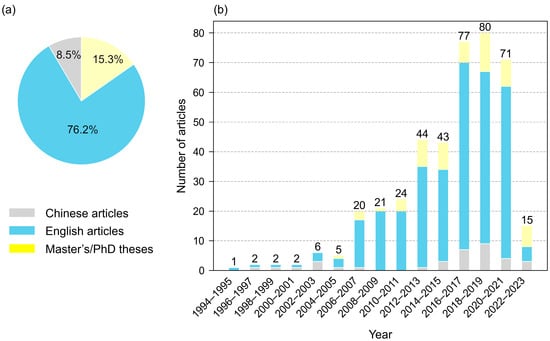
Figure 1.
Type of studies in the literature and their respective percentages. (a) Number of different publication types. (b) The lake sediment research in China during 1994–2023.
3.2. Journals Published
An analysis of the publication sources across Chinese and English journals, with a particular focus on the top 10 journals by frequency of publication, identified ‘Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology’, ‘Quaternary Science Reviews’, and ‘Quaternary International’ as leading journals in lake sediment research in China (Table 1). Among them, ‘Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology’ stands out with the highest number (41 articles) of publications. This highlights the journal’s substantial influence within the lake sediment research community, which has thus attracted a diverse range of researchers to publish their findings there. This is attributed to the journal’s broad interdisciplinary scope, which encompasses fields such as geology, climatology, and paleoecology; this makes it an important platform for the academic exchange of lake sediment research. Similarly, ‘Quaternary Science Reviews’ and ‘Quaternary International’ are comprehensive journals that cover a wide range of topics on Quaternary geology (including climate change and geomorphic and biological evolution); the number of their publications is second only to ‘Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology’, and it has also received widespread attention. From the above journal names, we can see that long-term scale lake sediment research in China has been primarily published in domestic and international journals that are focused on themes of paleoenvironments and the Quaternary. Among the most influential (highly cited) articles, most were published in prestigious journals (e.g., Earth and Planetary Science Letters), and their themes are related to the Earth’s climate systems and paleomonsoons (e.g., [29,30,31]).

Table 1.
The top 10 journals in terms of the number of published articles on lake sediment research in China from 1994 to 2023. NA = not applicable.
3.3. Key Authors
An analysis of authors (with >8 articles) and their affiliations during 1994–2023 indicates that Ji Shen, Enlou Zhang, and Liping Zhu have published the most articles (20, 17, and 17; Table 2). Researchers who publish a large number of articles in the field of lake sediment research typically possess excellent knowledge and experience, and their affiliated institutions often have strong research teams and resources. The result of the analysis on the affiliations of key authors shows that the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has published the most studies in the lake sediment literature, thus suggesting its strong research capabilities in the field of lake sediment research. Additionally, several researchers from the Tibetan Plateau Research Institute (CAS), Institute of Geographic Sciences and Resources (CAS), the School of Resources, Environment, and Tourism at Capital Normal University, and the School of Resources and Environment at Lanzhou University have also published a significant number of articles in the field of lake sediment research. The author list also includes some foreign researchers, such as Ulrike Herzschuh and Steffen Mischke, who are affiliated with the Helmholtz Center for Polar and Marine Research at the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany and the School of Geosciences at the University of Iceland, respectively, thus suggesting extensive international collaboration in this field. China, as a country rich in lake resources, possesses various types of lakes including freshwater, salt, and plateau lakes. These lakes have unique geographical locations, hydrological characteristics, and sedimentary processes, and they attract attention from researchers worldwide. Domestic and international collaboration has provided a broader perspective and resource support for lake sediment research.

Table 2.
Authors with more than 8 publications on the study of lake sediments in China from 1994 to 2023. CAS = Chinese Academy of Sciences.
3.4. The Five Lake Regions
According to the localities of the lakes in the literature [32], lake sediment records were divided into five lake regions (Figure 2): the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP), Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau (YGP), Mongolia-Xinjiang Plateau (MXP), East Plain (EP), and Northeast Region (NR). The results of the analysis on lake distribution data suggest that there are relatively more articles on the QTP (124), MXP (117), and YGP (108). In contrast, there are fewer articles on the EP (40) and NR (24). This may be related to the distribution of lakes in China: plateau regions typically possess more abundant lake resources and unique climatic conditions, and they attract a significant number of researchers, while the lake resources in plains are relatively limited.
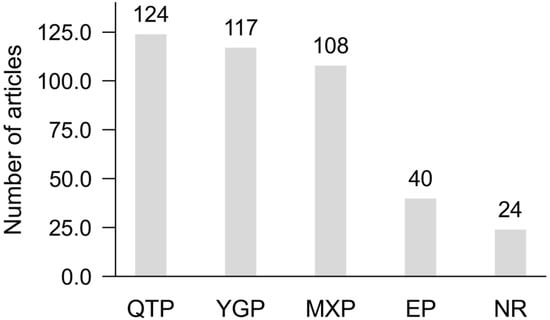
Figure 2.
The number of articles published on lake sediments from the five lake regions. Abbreviation: QTP = Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau; YGP = Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau; MXP = Mongolia-Xinjiang Plateau; EP = East Plain; and NR = Northeast Region.
The data on the lake elevation show that there are 135, 179, and 99 lakes with elevational ranges of >3000 m, between 1000 and 3000 m, and <1000 m, respectively; this is related to China’s specific location (at the junction of the Eurasian Plate) and the resulting hierarchical distribution of geological structures and geomorphologic formations (Figure 3a). The data on lake type suggest that there are 218 closed lakes, 172 open lakes, 18 dried-up lakes, and 5 seasonal lakes (Figure 3b). Due to the topographic features and land-sea distribution patterns, closed, open, and dried-up lakes are generally concentrated in the QTP and MXP; YGP and EP; and MXP, respectively, while seasonal lakes have a scattered distribution in the QTP, MXP, and EP. In the QTP, rivers and streams are formed by snowmelt and rainfall converge in high-altitude areas, and they go on to constitute closed lakes [33]. The MXP, located in Central Asia [34], is characterized by geographical barriers that prevent water flow directly into the ocean, thus leading to the formation of closed lakes in lower-lying areas. In contrast, although the YGP has a high elevation, its proximity to the ocean and large rivers facilitates the outflow of lake water and thus the formation of open lakes. The EP, with flat terrain and abundant river systems, allows water to easily flow into the ocean, thus forming open lakes. Additionally, the dry climate and unfavorable hydrological conditions in the MXP result in insufficient lake water maintenance; thus, dried-up lakes predominate [35,36].
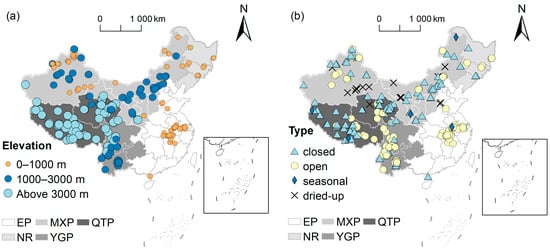
Figure 3.
The elevations (a) and types (b) of the studied lakes in China. Abbreviation: EP = East Plain; MXP = Mongolia-Xinjiang Plateau; QTP = Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau; NR = Northeast Region; and YGP = Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. The base map is from ‘Chinese Standard Map—Approval Number GS (2022) 1873’.
3.5. Dating Scales
The dating scale is primarily concentrated in two time intervals: 100–200 years and 500–30,500 years. This is because the studies in the literature focusing on the impact of human activities on lake environments and ecosystems tend to concentrate on short time scales, while the research studying climate and vegetation changes in lake basins emphasize long time scales (Figure 4). The traditional methods for dating sediment mainly involve paleomagnetism and radioisotope dating (including 14C, 210Pb, and 137Cs) [37]. Recently, methods such as uranium-thorium (U/Th) dating, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) dating, and volcanic ash dating have been increasingly employed for determining the age of lake sediments. Different dating methods are suitable for dating at different time scales. For example, 137Cs and 210Pb dating methods are mainly applicable to short-term scales (e.g., 50–60 and 100–200 years), while radiocarbon, U/Th, and OSL dating methods are typically used for longer time scale research. It is worth noting that the dating time scale of sediment profiles in 38.7% of the literature exceeds 10,000 years. This indicates that the study of long-term sedimentary processes of lakes is becoming increasingly important for understanding environmental change, and they can provide a broader perspective for exploring significant time intervals and processes in Earth’s history.
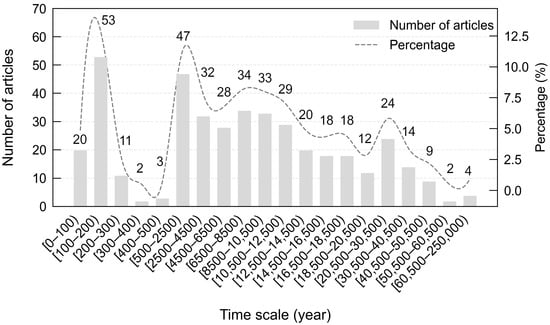
Figure 4.
The distribution of dating scales of the studied lake sediment profiles.
3.6. Key Themes
According to their key themes, the articles on lake sediment research were divided into two main categories: (1) reconstruction of the paleoenvironmental change in watersheds (301 articles, 72.9% of the total); and (2) the evolution of the lake ecosystems (91 articles, 22.0%) (Figure 5). Four subcategories were further classified and shown by representative proxies: (1) paleoclimate reconstruction (245 articles, 59.3%); (2) paleovegetation reconstruction (56 articles, 13.6%); (3) lake ecosystems (40 articles, 9.7%); and (4) the lake environment (51 articles, 12.3%) (Figure 5).
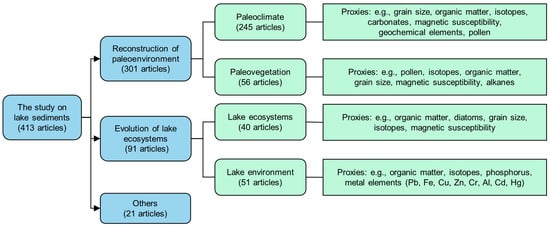
Figure 5.
The key themes and their proxies of lake sediment research.
In addition to the abovementioned key themes, lake sediment records are also applied to analyze the social-ecological systems and their changes for a better sustainable catchment management in the Anthropocene, which is an emerging topic [38]. Integrated with socio-economic data, environmental parameters such as water quality, soil stability, air quality, sediment quality, and sediment regulation can be better addressed for a comprehensive understanding of the interaction between human activities and the sustainable development of the catchment [39,40]. In China, the sustainable management of lakes and their catchments has become a critical issue, involving water quality monitoring and protection, soil stability, and air quality, etc. [38]. For example, the study of the catchment of the Erhai lake in Yunnan Province reveals the risks associated with water quality changes and related socio-economic factors [41]. The long-term dynamics of ecosystem services in the catchment of the Taihu lake provide a theoretical basis for developing adaptive management strategies [42].
3.6.1. Paleoclimate Reconstruction
Paleoclimate reconstruction mainly focuses on multiple proxies in lake sediments, including grain size composition, organic matter, isotopic and carbonate composition, magnetic susceptibility, geochemical elements, and pollen. Among these, grain size composition is an important indicator for analyzing the physical properties of lake sediment [43]. It can provide information about past precipitation and humidity change [44], and reveal the relationship between lake hydrodynamic changes, precipitation variability, and climate change [45]. Organic matter analysis evaluates the source and composition of organic matter in lake sediment [46]. By measuring the content of total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), and the carbon/nitrogen ratio (C/N) in sediment, the productivity and organic matter input of ancient lakes can be evaluated [47,48]. Stable isotopes (e.g., 13C, 15N, 18O, and 2H) can reveal the hydrological and climatic change in paleolakes [49,50], including the precipitation and compositional change in lake water in watersheds [51,52]. Isotopic and carbonate composition further aids in studying the chemical characteristics of lake water and carbon cycling processes, thereby reflecting the variations in water composition and temperature of the paleolake [47]. Magnetic susceptibility can be employed to infer precipitation change [53] and the surface soil erosion [54] in watersheds. The content and ratios of geochemical elements [55] can be used to study the impact of climate change on weathering processes in watersheds. For example, the Climate Change Index (CCI) is represented by the ratio of concentration of elements such as iron, manganese, chromium, and vanadium to the concentration of elements including sodium and potassium [56]. Higher CCI values typically indicate warm and humid climatic conditions, whereas lower values suggest arid or semi-arid climatic conditions [57]. Pollen assemblages primarily comprise tree and shrub, meso-herbs, xero-herbs, and wetland pollen types [58], corresponding to warm and moist climates and cold and arid climates, respectively [59,60]. Early human activities, particularly deforestation, resulted in a decline in the concentration of tree and shrub pollen and a concurrent increase in herbaceous pollen in the assemblages. Furthermore, human settlement and agricultural expansion prompted a rise in the content of cereal grain pollen in lake sediments, which is indicative of the proliferation of adjacent shoreline farming practices [54]. A comprehensive analysis of these proxies is helpful for understanding the trends and cycles of past climate change, thereby gaining insights into the global climate system, unveiling the driving mechanism of climate change, and predicting future climate change. Future study should be focused on integrating and analyzing climate data from various lakes on a broader spatial scale to further explore the spatial differences and driving factors of climate change.
3.6.2. Paleovegetation Reconstruction
Paleovegetation reconstruction primarily involves analyzing multiple proxies in lake sediments to reconstruct former plant composition, vegetation types and successions, and their relationship with climate change. Pollen and alkane analyses are the two principal methods for studying past vegetation composition and evolution; the former is achieved by analyzing the pollen types and their percentages in the pollen sum [57], while the latter studies the source of organic matter and vegetation history through the distribution of alkanes and isotopes in sediments. For example, by examining the carbon isotopes (13C) of individual alkanes, the change in the relative abundance of C3/C4 plants during geological history can be reconstructed [61]. By combining other proxies (e.g., isotopic composition, organic matter, grain size composition, and magnetic susceptibility) we can better understand vegetation dynamics and their response to environmental change. The paleovegetation reconstruction result is invaluable in understanding the response mechanisms of plants and vegetation to environmental change, which helps with predicting future ecosystem dynamics and developing effective strategies for ecological conservation and restoration. To further understand the drivers of past vegetation change, we will need to integrate the general information from watersheds to explore both natural and anthropogenic influences, as well as to analyze the impact of vegetation change on hydrological and geomorphological processes in watersheds.
3.6.3. The Evolution of Lake Ecosystems
Several proxies in sediments (e.g., organic matter, diatoms, grain size and isotopic composition, and magnetic susceptibility) have been used to investigate the evolution of lake ecosystems to understand the changes in the internal ecosystem and biological communities. Among these, diatoms are one of the primary methods for studying the evolution of lake ecosystems by analyzing the concentration and relative abundance of fossil diatoms in sediments, where the chemical environmental changes, as well as the biological responses of paleolakes, can be inferred [62]. In addition, diatoms are highly sensitive to environmental change; thus, they can be used as biological indicators to study the impacts of climate change and human activities on lake waters [63]. By combining fossil diatoms and other commonly used proxies, we can better obtain the information of the chemical environment and biological response of lake water bodies and thus understand the evolution of lake ecosystems. Study on the evolution of lake sediments is of great importance for protecting lake ecosystems, maintaining biodiversity, and sustainably utilizing lake resources. To better understand the dynamic changes in lake ecosystems, we will also need to consider the nutrient element input into lakes from watershed surface water and soil development, and we need to link the dynamic changes in lake ecosystems with the surface processes in watersheds.
3.6.4. Environmental Change in Lakes
The study of environmental change in lakes mainly focuses on issues such as heavy metal pollution, eutrophication, and anthropogenic-related pollution. By analyzing multiple proxies in lake sediments, including organic matter, isotopes, phosphorus, and metal elements, the quality and health status of lake environments can be assessed. Specifically, the total phosphorus content and metal element concentration are important indicators for assessing change in lake environments. Total phosphorus content is a key indicator used to assess the trophic status and degree of the eutrophication of lakes [64]. An analysis on metal elements can facilitate the evaluation of environmental change, particularly the degree of heavy metal pollution in lakes. Common metal elements include lead (Pb), iron (Fe), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), chromium (Cr), aluminum (Al), cadmium (Cd), and mercury (Hg). By calculating the enrichment factor [65], which involves comparing the concentration ratio of pollutant elements to reference elements, the extent to which elements such as heavy metals in sediments are influenced by human activities can be evaluated. Watershed-scale hydrological models will be needed to simulate the transport of nutrients and heavy metals across watersheds. Additionally, integrating different long-term scale lake sediment records can reveal the influence of socio-economic conditions on lake environments in watersheds. Study on lake environmental change contributes to the understanding of environmental issues such as heavy metal pollution and eutrophication. By assessing the quality and health status of lake environments, potential human health risks can be prevented.
4. Concluding Remarks
In recent years, lake sediment research that includes international collaboration in China has shown a rapid increase and attracted widespread attention both domestically and internationally; this is likely related to the growing prominence of global climate change and environmental issues. Lake sediment research provides an important scientific basis for understanding and addressing these problems. There are differences in the distribution of lake sediment research in different geographical regions. The studies in the QTP, MXP, and YGP are relatively numerous because these regions have rich lake resources, diverse landforms, and are significantly affected by climate change. The dating scale of lake sediment mainly focuses on two time intervals: 100–200 years and 500–30,000 years. Additionally, lake sediment dating is increasingly being integrated with various methods and techniques to investigate the influence of climate events on lake environments and regional climate evolution. The focus of lake sediment research not only includes hot topics such as paleoenvironmental change and lake ecosystem evolution, but also emerging issues such as lake environmental pollution. This indicates that lake sediment research is evolving in a more comprehensive and integrated direction.
In the past few decades, there have been extensive studies focusing on local paleoenvironmental reconstruction using lake sediment proxies, thus resulting in significant data on Holocene sediment, vegetation, and climate evolution. These data will help geoscientists further explore the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of lake sediment and its driving factors (e.g., climate and environmental change). Additionally, the development of information processing technologies (e.g., artificial intelligence and big data analysis) provides technical support for integrating lake sediment data in the Holocene, analyzing surface process, and coupling Earth’s climate. For example, Iwańska et al. [66] analyzed sedimentary DNA (sedDNA) from Lake Slone by utilizing next-generation sequencing (NGS). Their study explains the environmental changes and biodiversity in the Baltic Sea region, explores the factors influencing these changes and the evolutionary processes, and highlights the impact of human activities and Earth’s climate change on biodiversity. Szatten et al. [67] identified 103 watermill sites in the Chełmno Lake area and selected 65 mills for in-depth study. By employing a delimitation of the natural landscape and using the Maximum Entropy Method (MaxEnt), their study revealed how human activities have influenced the distribution and nature of lake sediments by altering the watershed network. Both studies showed that information processing technologies contribute to summarizing and forming data-driven methods and technical systems, thus promoting research on big data in Earth system science.
Currently, we are in a context where global climate change and environmental pollution impact sustainable human development. Therefore, factors such as policy support, research projects, and international collaboration in China will play an important role in promoting research on lake sediments. Lake sediment research, as an important interdisciplinary field, often requires collaboration across disciplines such as geography, geology, environmental science, and ecology to drive innovation and development. The Chinese lake sediment database presented in this review will place an excellent basis for further study on the relationship between natural conditions (e.g., climate) and human activities (e.g., land use) with geological elements (e.g., sedimentation rate). The impact of human activities on the Earth’s environment is becoming increasingly obvious. By studying the influence of ancient human activities on paleoenvironments with this database, we can provide an important theoretical framework for better protecting the environment and building human and natural life communities. Particularly in today’s era of artificial intelligence, combining deep learning and models can provide an important theoretical basis for the understanding of the evolution of the Earth’s systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.L., G.T. and H.H.; methodology, M.L.; validation, M.L. and H.H.; formal analysis, M.L.; data curation, M.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.L.; writing—review and editing, G.T. and H.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the starting grant for introduced talents from Sun Yat-sen University (to H.H.) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (no. 42171025 to G.T.).
Acknowledgments
We thank Robert J. Morley (Palynova Limited, UK) for improving an early version of this manuscript, particularly with respect to linguistic help.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shen, J. Progress and prospect of palaeolimnology research in China. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumin, W.; Hongshen, D. Compendium of Chinese Lakes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Pleskot, K.; Apolinarska, K.; Kołaczek, P.; Suchora, M.; Fojutowski, M.; Joniak, T.; Kotrys, B.; Kramkowski, M.; Słowiński, M.; Woźniak, M.; et al. Searching for the 4.2 ka climate event at Lake Spore, Poland. CATENA 2020, 191, 104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Bin, X.; Jinglu, W.; Yanhong, W.; Xingqi, L.; Xiangdong, Y.; Jian, L.; Sumin, W. Lake Sedimentation and Environmental Evolution; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, N.L.; Morley, D.; Appleby, P.G.; Battarbee, R.W.; Alliksaar, T.; Guilizzoni, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Korhola, A.; Punning, J.M. Sediment accumulation rates in European lakes since AD 1850: Trends, reference conditions and exceedence. J. Paleolimnol. 2011, 45, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changfu, L. An expedition to Lop Nur. NewAsia 1935, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fanli, T. Exploration in Qinghai. J. Geosci. 1910, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pinxian, W.; Chuanlian, L.; Jiashu, C.; Dongjing, C. Anthology of Paleolimnology; Maritime Press: Beijing, China, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Jenny, J.-P.; Koirala, S.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Francus, P.; Niemann, C.; Ahrens, B.; Brovkin, V.; Baud, A.; Ojala, A.E.K.; Normandeau, A.; et al. Human and climate global-scale imprint on sediment transfer during the Holocene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22972–22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mu, G.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, D. Abrupt climatic shift at ~4000 cal. yr B.P. and late Holocene climatic instability in arid Central Asia: Evidence from Lop Nur saline lake in Xinjiang, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Fan, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Sheng, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, T.; Zhan, P.; Luo, S.; Yuan, C.; et al. A comprehensive geospatial database of nearly 100 000 reservoirs in China. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4017–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, A.P.; Hobbs, W.O.; Birks, H.H.; Briner, J.P.; Holmgren, S.U.; Ingólfsson, Ó.; Kaushal, S.S.; Miller, G.H.; Pagani, M.; Saros, J.E.; et al. Stratigraphic expressions of the Holocene–Anthropocene transition revealed in sediments from remote lakes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 116, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-y.; Chen, G.; Meyer-Jacob, C.; Huang, L.; Liu, X.; Huang, G.; Klamt, A.M.; Smol, J.P. Land-use and climate controls on aquatic carbon cycling and phototrophs in karst lakes of southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 751, 141–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, F.; Poulenard, J.; Giguet-Covex, C.; Wilhelm, B.; Revillon, S.; Jean-Philippe, J.; Revel, M.; Enters, D.; Bajard, M.; Fouinat, L.; et al. Erosion under climate and human pressures: An alpine lake sediment perspective. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 152, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canziani, G.; Ferrati, R.; Rossi, C.; Ruiz-Moreno, D. The influence of climate and dam construction on the Ibera wetlands, Argentina. Reg. Environ. Change 2006, 6, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S. Assessment of nutrient sources and paleoproductivity during the past century in Longgan Lake, middle reaches of Yangtze River, China. Chin. J. Geochem. 2006, 25, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wu, D.; Niu, L.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Hillman, A.L.; Abbott, M.B.; Zhou, A. Contrasting ecosystem responses to climatic events and human activity revealed by a sedimentary record from Lake Yilong, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.-F.; Jiao, P.; Mischke, S. The Holocene history of Lop Nur and its palaeoclimate implications. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2016, 148, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Zong, Y.; Jia, G.; Zheng, Z.; Man, M. Synchronous change of temperature and moisture over the past 50 ka in subtropical southwest China as indicated by biomarker records in a crater lake. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 212, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichner, B.; Herzschuh, U.; Wilkes, H.; Schulz, H.-M.; Wang, Y.; Plessen, B.; Mischke, S.; Diekmann, B.; Zhang, C. Ecological development of Lake Donggi Cona, north-eastern Tibetan Plateau, since the late glacial on basis of organic geochemical proxies and non-pollen palynomorphs. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2012, 313–314, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, S.; Xue, B.; Tong, X. Vegetation history and dynamics in the middle reach of the Yangtze River during the last 1500 years revealed by sedimentary records from Taibai Lake, China. Holocene 2013, 23, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.F.; Song, X.Y.; Wortley, A.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Blackmore, S.; Li, C.S. Pollen-based reconstruction of vegetational and climatic change over the past ~30 ka at Shudu Lake in the Hengduan Mountains of Yunnan, southwestern China. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, A.L.; Abbott, M.B.; Yu, J.; Bain, D.J.; Chiou-Peng, T. Environmental legacy of copper metallurgy and Mongol silver smelting recorded in Yunnan Lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Shen, J.; Birch, G.F.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Xue, B. Human-induced change in sedimentary trace metals and phosphorus in Chaohu Lake, China, over the past half-millennium. J. Paleolimnol. 2012, 47, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, H.-C.; Ho, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-Z. Scientometric analysis of geostatistics using multivariate methods. Scientometrics 2007, 73, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Hong, S.; Yuan, J.; Peng, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Global trends in sediment-related research in earth science during 1992–2011: A bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 2014, 98, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peibo, C.; Xilin, L. Bibliometric Analysis of the Progress in Benggang Research in China. Trop. Geogr. 2015, 35, 895–900, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijie, W.; Gang, L.; Yaoyang, X. Network analysis of Literature in Formation of Lake Sediment: Research Status and Hotspot. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 192–201. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, B.W.; Polisar, P.J.; Lei, Y.B.; Thompson, L.G.; Yao, T.D.; Finney, B.P.; Bain, D.J.; Pompeani, D.P.; Steinman, B.A. A Tibetan lake sediment record of Holocene Indian summer monsoon variability. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 399, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, H.; Yang, X.; Herzschuh, U.; Zhang, E.; Stuut, J.-B.W.; Wang, Y. Late Holocene forcing of the Asian winter and summer monsoon as evidenced by proxy records from the northern Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009, 280, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; Zhen, X.L.; Wang, J.B.; Lü, H.Y.; Xie, M.P.; Kitagawa, H.; Possnert, G. A∼30,000-year record of environmental changes inferred from Lake Chen Co, Southern Tibet. J. Paleolimnol. 2009, 42, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Fang, Y. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of surface soil’s polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Yangtze River Delta. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 46, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liping, Z.; Guoqing, Z.; Ruimin, Y.; Chong, L.; Kun, Y.; Baojin, Q.; Boping, H. Lake variations on Tibetan Plateau of recent 40 years and future changing tendency. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2019, 34, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Running, S.W.; Nemani, R.R. Sensitivity of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) terrestrial primary production to the accuracy of meteorological reanalyses. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxian, S.; Chunlei, X.; Dan, Z.; Zhenzhou, Z.; Gaoqiang, Z. Distribution characteristics of lakes in China and suggestions for ecological protection and restoration of typical river basins. Geol. Surv. China 2021, 8, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenhui, J.; Ce, Z.; Bing, W.; En, Z.; Haiwei, N.; Jingyue, L.; Shuangfa, D. Remote sensing dynamic monitoring and ecological environmental changes of Bashang Plateau wetland from 2000 to 2018. Miner. Explor. 2020, 11, 2720–2728. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Lu, H.; Jin, C.; Gu, Z.; Zuo, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Application of multiple dating techniques to the Holocene sediments of Angrenjin Co in the southern Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Geochronol. 2021, 62, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearing, J.A.; Acma, B.; Bub, S.; Chambers, F.M.; Chen, X.; Cooper, J.; Crook, D.; Dong, X.H.; Dotterweich, M.; Edwards, M.E.; et al. Social-ecological systems in the Anthropocene: The need for integrating social and biophysical records at regional scales. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Crutzen, P.; McNeill, J. The Anthropocene: Are Humans Now Overwhelming the Great Forces of Nature. Ambio 2008, 36, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W.; Sanderson, A.; Tyson, P.D.; Jager, J.; Matson, P.A.; Moore, B.; Oldfield, F.; Richardson, K.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; Turner, B.L.; et al. Global Change and the Earth System: A Planet Under Pressure. In Global Change and the Earth System: A Planet under Pressure; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Dearing, J.A.; Langdon, P.G.; Zhang, E.; Yang, X.; Dakos, V.; Scheffer, M. Flickering gives early warning signals of a critical transition to a eutrophic lake state. Nature 2012, 492, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Zhang, K.; Shen, J.; Liu, E. Integrating long-term dynamics of ecosystem services into restoration and management of large shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y. A 40,000-year record of aridity and dust activity at Lop Nur, Tarim Basin, northwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2019, 211, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Hongwei, M.; Yuzhen, M.; Dandan, L.; Caili, H.; Jierui, L.; Congwen, L.; Kai, W. Environmental variations recorded by chemical element in the sediments of Lake Yamzhog Yumco on the southern Tibetan Plateau over the past 2000 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.G.; Jones, R.T.; Turney, C.S.M. Catchment instability and Asian summer monsoon variability during the early Holocene in southwestern China. Boreas 2013, 42, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.A.; Lan, H.-C.; Lou, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C. The Dry Holocene Megathermal in Inner Mongolia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 193, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Ma, Q.; Xu, T. Paleoclimate changes over the past 13,000 years recorded by Chibuzhang Co sediments in the source region of the Yangtze River, China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2021, 573, 110433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Niu, J.; Ming, Q.; Shi, Z.; Lei, G.; Huang, L.; Long, X.E.; Chang, F. Holocene climatic fluctuations and periodic changes in the Asian southwest monsoon region. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 156, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hou, J.; Brown, E.T.; Xie, S.; Bao, Z. Timing of the Indian Summer Monsoon onset during the early Holocene: Evidence from a sediment core at Linggo Co, central Tibetan Plateau. Holocene 2017, 28, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xie, M.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Shang, W.; Wang, K.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Chu, G. Alkanes, compound-specific carbon isotope measures and climate variation during the last millennium from varved sediments of Lake Xiaolongwan, northeast China. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wu, J.; Abuduwaili, J. Climate and environmental changes over the past 150 years inferred from the sediments of Chaiwopu Lake, central Tianshan Mountains, northwest China. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2013, 102, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Ju, J.; Peng, P.; Lin, X.; Hu, J.; Nishimura, M. Paleohydrological processes revealed by n-alkane δD in lacustrine sediments of Lake Pumoyum Co, southern Tibetan Plateau, and their response to climate changes during the past 18.5 cal ka. J. Paleolimnol. 2016, 56, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, A.L.; O’Quinn, R.F.; Abbott, M.B.; Bain, D.J. A Holocene history of the Indian monsoon from Qilu Lake, southwestern China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2020, 227, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, X.; Matsumoto, R.; Tong, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Lake sediment records on climate change and human activities since the Holocene in Erhai catchment, Yunnan Province, China. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2005, 48, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-D.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. Role of late glacial to mid-Holocene climate in catchment weathering in the central Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Res. 2005, 63, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Ding, G. Variation of summer monsoon intensity in the North China Plain and its response to abrupt climatic events during the early-middle Holocene. Quat. Int. 2020, 550, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Herzschuh, U.; Ni, J.; Liao, M.; Xiao, X. Late Holocene vegetation and climate change on the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for the Indian Summer Monsoon and links to the Indian Ocean Dipole. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 177, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, Z.; Ran, M.; Zhang, C. Holocene climate and vegetation changes inferred from pollen records of Lake Aibi, northern Xinjiang, China: A potential contribution to understanding of Holocene climate pattern in East-central Asia. Quat. Int. 2013, 311, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzschuh, U.; Winter, K.; Wünnemann, B.; Li, S. A general cooling trend on the central Tibetan Plateau throughout the Holocene recorded by the Lake Zigetang pollen spectra. Quat. Int. 2006, 154–155, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, X.; Dodson, J.; Xinying, Z.; Atahan, P. Climate instability during the last deglaciation in central Asia, reconstructed by pollen data from Yili Valley, NW China. Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 2013, 189, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Yongli, W.; Zixiang, W.; Gen, W.; Youxiao, W. Compound-specific Carbon Isotopic Characteristics of n-alkanes in Xianghai Lake Sediments of Northeast China and Their Paleoenvironmental Implications. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 2014, 36, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, B.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y. Evolution of Lake Ailike (northern Xinjiang of China) during past 130 years inferred from diatom data. Quat. Int. 2018, 475, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.; Wang, J.; Jiang, J.; Yang, S. Response of diatom community in Lugu Lake (Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau, China) to climate change over the past century. J. Paleolimnol. 2014, 51, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xu, H.; Yang, M.; Lan, J.; Hou, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, K.; An, Z.; Goldsmith, Y. Responses of cyanobacteria to climate and human activities at Lake Chenghai over the past 100 years. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, L.; Yu, H.; Zeng, H.; Liu, W.; Abuduwaili, J. Sediment geochemical records of environmental change in Lake Wuliangsu, Yellow River Basin, north China. J. Paleolimnol. 2013, 50, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwańska, O.; Latoch, P.; Suchora, M.; Pidek, I.A.; Huber, M.; Bubak, I.; Kopik, N.; Kovalenko, M.; Gąsiorowski, M.; Armache, J.-P.; et al. Lake microbiome and trophy fluctuations of the ancient hemp rettery. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatten, D.; Brzezińska, M.; Maerker, M.; Podgórski, Z.; Brykała, D. Natural landscapes preferred for the location of past watermills and their predisposition to preserve cultural landscape enclaves. Anthropocene 2023, 42, 100376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).