Spatial Distribution of the Cropping Pattern Exerts Greater Influence on the Water Footprint Compared to Diversification in Intensive Farmland Landscapes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Basic Data
2.3. Spatial Sampling
2.4. Calculation of Water Footprint
2.5. Calculation of Landscape Heterogeneity
2.6. Influences of Landscape Heterogeneity on Water Footprint
2.7. Statistics and Mapping
3. Results
3.1. Water Footprints of Crops and Cropping Patterns
3.2. Variations in Water Footprint and Landscape Heterogeneity
3.2.1. Variations in Water Footprint
3.2.2. Variations in Landscape Metrics at the Landscape Scale and in WM Patches
3.3. Influences of Landscape Heterogeneity on Water Footprint
3.3.1. Correlations between Water Footprint and Landscape Metrics at the Landscape Scale and in WM Patches
3.3.2. Time-Based Effects of Landscape Metrics on Water Footprint at the Landscape Scale and in WM Patches
3.3.3. Time-Disregarded Impacts of Landscape Metrics on Water Footprint at the Landscape Scale and in WM Patches
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversification and Water Footprint
4.2. Spatial Distribution and Water Footprint
4.3. Interactive Influences of Landscape Heterogeneity on Water Footprint
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Shah, F.; Wu, W. Environmental and socio-economic performance of intensive farming systems with varying agricultural resource for maize production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, M.C.; Smith, R.G.; Schipanski, M.E.; Atwood, L.W.; Mortensen, D.A. Agriculture in 2050: Recalibrating Targets for Sustainable Intensification. Bioscience 2017, 67, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food Security: The Challenge of Feeding 9 Billion People. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potts, S.G.; Imperatriz-Fonseca, V.; Ngo, H.T.; Aizen, M.A.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Breeze, T.D.; Dicks, L.V.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Hill, R.; Settele, J.; et al. Safeguarding pollinators and their values to human well-being. Nature 2016, 540, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Xing, G.X.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, L.J.; Liu, X.J.; Cui, Z.L.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.L.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbell, F.; Adler, P.R.; Eisenhauer, N.; Fornara, D.; Kimmel, K.; Kremen, C.; Letourneau, D.K.; Liebman, M.; Polley, H.W.; Quijas, S.; et al. Benefits of increasing plant diversity in sustainable agroecosystems. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainese, M.; Martin, E.A.; Aizen, M.A.; Albrecht, M.; Bartomeus, I.; Bommarco, R.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Gagic, V.; Garibaldi, L.A.; et al. A global synthesis reveals biodiversity-mediated benefits for crop production. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax0121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.A.; Dainese, M.; Clough, Y.; Báldi, A.; Bommarco, R.; Gagic, V.; Garratt, M.P.D.; Holzschuh, A.; Kleijn, D.; Kovács Hostyánszki, A.; et al. The interplay of landscape composition and configuration: New pathways to manage functional biodiversity and agroecosystem services across Europe. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, G.; Bommarco, R.; Wanger, T.C.; Kremen, C.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Liebman, M.; Hallin, S. Agricultural diversification promotes multiple ecosystem services without compromising yield. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xiao, H.; Luo, S.; Hodgson, J.A.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; He, H.; van der Werf, W.; Zou, Y. Can landscape level semi-natural habitat compensate for pollinator biodiversity loss due to farmland consolidation? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, Z. Responses of landscape structure to the ecological restoration programs in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Manevski, K.; Fu, M.; Yin, X.; Chen, F. A Framework for the Heterogeneity and Ecosystem Services of Farmland Landscapes: An Integrative Review. Sustainability 2021, 22, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L.; Baudry, J.; Brotons, L.; Burel, F.G.; Crist, T.O.; Fuller, R.J.; Sirami, C.; Siriwardena, G.M.; Martin, J.L. Functional landscape heterogeneity and animal biodiversity in agricultural landscapes. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, P. Influences of landscape pattern evolution on regional crop water requirements in regions of large-scale agricultural operations. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 327, 129499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, Z.; Zou, X.Q.; Zuo, P.; Song, Q.C.; Wang, C.L.; Wang, J.J. Impact of landscape patterns on ecological vulnerability and ecosystem service values: An empirical analysis of Yancheng Nature Reserve in China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.F.; Buyantuev, A.; Wu, J.G.; Niu, J.M.; Yu, D.Y.; Zhang, Q. Intensive land-use drives regional-scale homogenization of plant communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, M.; Gerstner, K.; Akin-Fajiye, M.; Ceausu, S.; Kambach, S.; Kinlock, N.L.; Phillips, H.R.P.; Verhagen, W.; Gurevitch, J.; Klotz, S.; et al. Conventional land-use intensification reduces species richness and increases production: A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1941–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annika, L.; Hass, U.G.K.T. Landscape configurational heterogeneity by small-scale agriculture, not crop diversity, maintains pollinators and plant reproduction in western Europe. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Polasky, S. Agricultural sustainability and intensive production practices. Nature 2002, 418, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Landscape sustainability science (II): Core questions and key approaches. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2453–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Corstanje, R.; Meersmans, J. Promoting sustainable landscape pattern for landscape sustainability. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuyah, S.; Sileshi, G.W.; Nkurunziza, L.; Chirinda, N.; Ndayisaba, P.C.; Dimobe, K.; Öborn, I. Innovative agronomic practices for sustainable intensification in sub-Saharan Africa. A Rev. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, S. Identifying agronomic practices with higher yield and lower global warming potential in rice paddies: A global meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Four billion people facing severe water scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1500323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1577–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y. Virtual water trade. In Proceedings of the International Expert Meeting on Virtual Water Trade, Delft, The Netherlands, 12–13 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Zeng, W.; Wu, M.; Guo, X.; Wang, W. Hybrid analytical framework for regional agricultural water resource utilization and efficiency evaluation. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 231, 106027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; Aldaya, M.M.; Mekonnen, M.M. Water Footprint Assessment Manual: Setting the Global Standard; Earthscan: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Novoa, V.; Ahumada-Rudolph, R.; Rojas, O.; Saez, K.; de la Barrera, F.; Luis Arumi, J. Understanding agricultural water footprint variability to improve water management in Chile. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Wu, S.R.; Gong, M.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Spatial-temporal assessment of water footprint, water scarcity and crop water productivity in a major crop production region. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ding, D.; Si, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, W.; Schoenau, J. Temporal variability of water footprint for cereal production and its controls in Saskatchewan, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jia, R.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Olesen, J.E. Quantifying water footprint of winter wheat–summer maize cropping system under manure application and limited irrigation: An integrated approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 183, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Li, B.; Dang, Y. Assessing the hotspots of crop water footprint in Jilin Province of China. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 50010–50024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, D.; Agarwal, T. Carbon footprint and water footprint of rice and wheat production in Punjab, India. Agric. Syst. 2021, 186, 102959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouchane, H.; Krol, M.S.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Changing global cropping patterns to minimize national blue water scarcity. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 3015–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, L.; He, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X. Effects of different slopes and fertilizer types on the grey water footprint of maize production in the black soil region of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Geng, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, C. New insights from grey water footprint assessment: An industrial park level. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Hou, S.; Xia, Q. Measurement and driving factors of grey water footprint efficiency in Yangtze River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, Y. Study on Quality Evaluation of County Cultivated Land Based on Information Technology. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 36, 8202–8204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, P.; Muhammad, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, Y. Subsystem-level groundwater footprint assessment in North China Plain–The world’s largest groundwater depression cone. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Yin, X.; Yang, Z. Contributions of climate change and human activities to changes in the virtual water content of major crops: An assessment for the Shijiazhuang Plain, northern China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Shum, C.; Zhong, M.; Pan, Y. Groundwater Storage Changes in China from Satellite Gravity: An Overview. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DWRHP (Department of Water Resources of Hebei Province). Heibei Water Resources Bulletin. 2020. Available online: http://slt.hebei.gov.cn/a/2021/08/04/F3A8F2A53BD44494B6F0A253372F4530.html (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- BSW (Bureau of Statistics in Wuqiao). Yearbook of Wuqiao; Bureau of Statistics in Wuqiao: Shijiazhuang, China, 2019.
- Wang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, M.; Yin, X.; Chen, F. Cropping patterns and farmland landscape at the county level using remote sensing in Haihe Lowland Plain. Trans. CSAE. 2022, 38, 297–304. Available online: http://www.tcsae.org/article/doi/10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2022.01.033 (accessed on 8 July 2024).
- Duflot, R.; Ernoult, A.; Aviron, S.; Fahrig, L.; Burel, F. Relative effects of landscape composition and configuration on multi-habitat gamma diversity in agricultural landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 241, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, E.S.; Luescher, G.; Knop, E. Disentangling direct and indirect drivers of farmland biodiversity a landscape scale. Ecol. Lett. 2022, 25, 2422–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirement; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, T.; Liu, H.; Fan, X.; Zou, G.; Liu, S. Handbook on Emission Factors of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in China; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Principles and Methods in Landscape Ecology: Towards a Science of the Landscape; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Syrbe, R.; Walz, U. Spatial indicators for the assessment of ecosystem services: Providing, benefiting and connecting areas and landscape metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 21, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sklenicka, P.; Janovska, V.; Salek, M.; Vlasak, J.; Molnarova, K. The Farmland Rental Paradox: Extreme land ownership fragmentation as a new form of land degradation. Land. Use Policy 2014, 38, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Luo, Y.; Wang, M.; Su, S.; Pi, J.; Li, G. Essential fragmentation metrics for agricultural policies: Linking landscape pattern, ecosystem service and land use management in urbanizing China. Agric. Syst. 2020, 182, 102833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šímová, P.; Gdulová, K. Landscape indices behavior: A review of scale effects. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yuan, Z. Water footprint of crop production for different crop structures in the Hebei southern plain, North China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 3061–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, S.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Cao, K. Crop pattern optimization for the coordination between economy and environment considering hydrological uncertainty. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltin, M.; Zasada, I.; Piorr, A.; Debolini, M.; Geniaux, G.; Perez, O.M.; Scherer, L.; Marco, L.T.; Schulp, C. Conceptualising fields of action for sustainable intensification-A systematic literature review and application to regional case studies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zeng, W.; Wu, M.; Li, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, W. Water resources efficiency assessment in crop production from the perspective of water footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 309, 127371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrach, A.; Giménez García, A.; Allen Perkins, A.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Bartomeus, I. Increasing crop richness and reducing field sizes provide higher yields to pollinator-dependent crops. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, I.; Branca, G.; Zucaro, R. Evaluating input use efficiency in agriculture through a stochastic frontier production: An application on a case study in Apulia (Italy). J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrano, H.; Tomas, M.; Martorell, S.; Escalona, J.; Pou, A.; Fuentes, S.; Flexas, J.; Bota, J. Improving water use efficiency of vineyards in semi-arid regions. A Rev. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, V.; Mehrabi, Z.; Wittman, H.; James, D.; Ramankutty, N. Higher yields and more biodiversity on smaller farms. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebert, J.; Benner, R.; Kerr, R.B.; Bjorkman, T.; De Master, K.T.; Gennet, S.; Gomez, M.I.; Hart, A.K.; Kremen, C.; Power, A.G.; et al. Farm size affects the use of agroecological practices on organic farms in the United States. Nat. Plants. 2022, 8, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Duan, J.; Ren, C.; Liu, H.; Reis, S.; Xu, J.; Gu, B. Ammonia Emissions from Croplands Decrease with Farm Size in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 9915–9923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalos, J.; Molnarova, K.; Kottova, P. Land reforms reflected in the farming landscape in East Bohemia and in Southern Sweden-Two faces of modernisation. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Jin, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Kanter, D.; Wu, B.; Xi, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; et al. Fertilizer overuse in Chinese smallholders due to lack of fixed inputs. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrig, L.; Girard, J.; Duro, D.; Pasher, J.; Smith, A.; Javorek, S.; King, D.; Lindsay, K.F.; Mitchell, S.; Tischendorf, L. Farmlands with smaller crop fields have higher within-field biodiversity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 200, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.A.; Seo, B.; Park, C.R.; Reineking, B.; Steffan-Dewenter, I. Scale-dependent effects of landscape composition and configuration on natural enemy diversity, crop herbivory, and yields. Ecol. Appl. 2016, 26, 448–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Haan, N.L.; Landis, D.A. Landscape composition and configuration have scale-dependent effects on agricultural pest suppression. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomine, E.; Rusch, A.; Desneux, N. Predators do not benefit from crop diversity but respond to configurational heterogeneity in wheat and cotton fields. Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
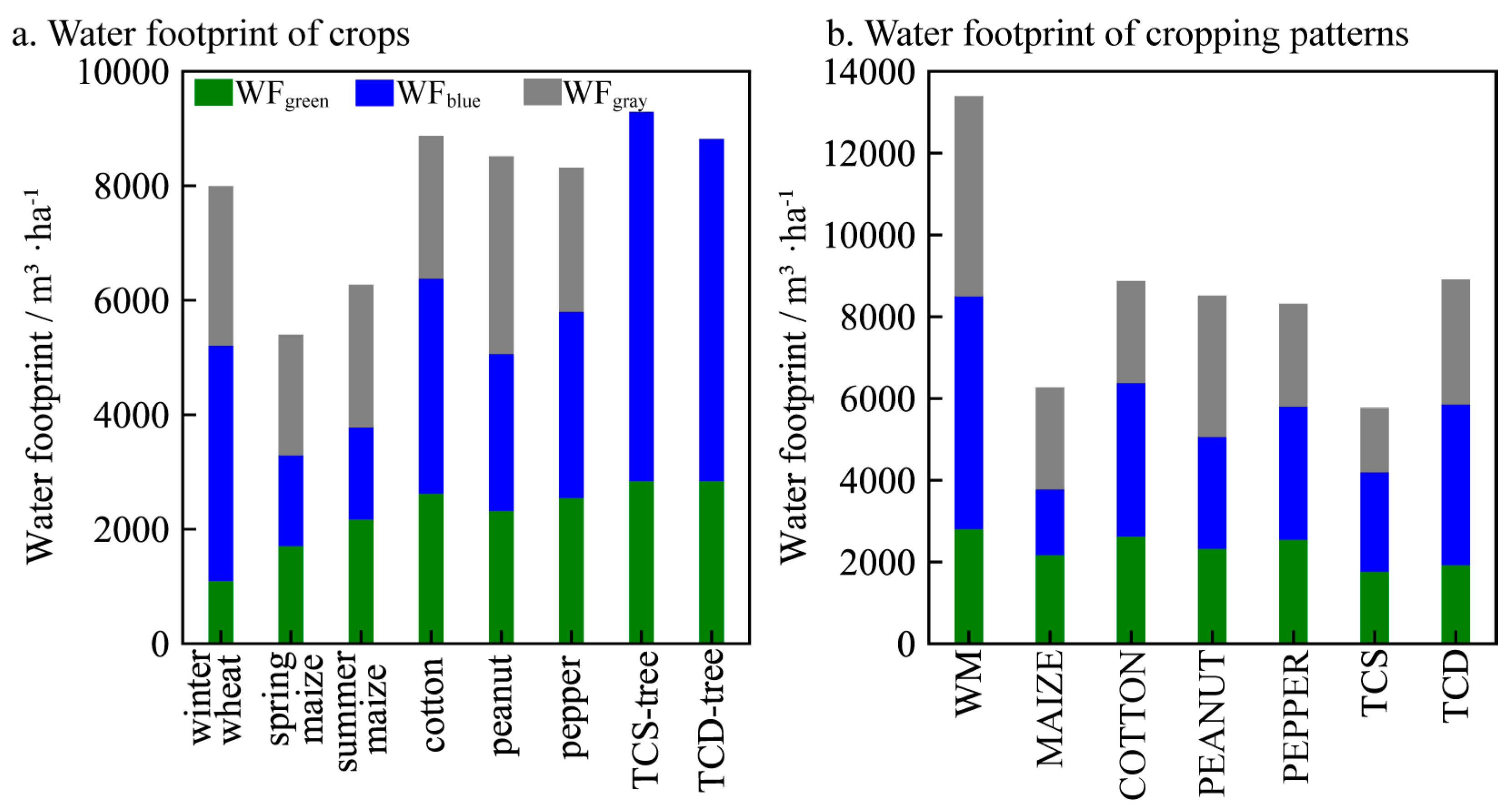
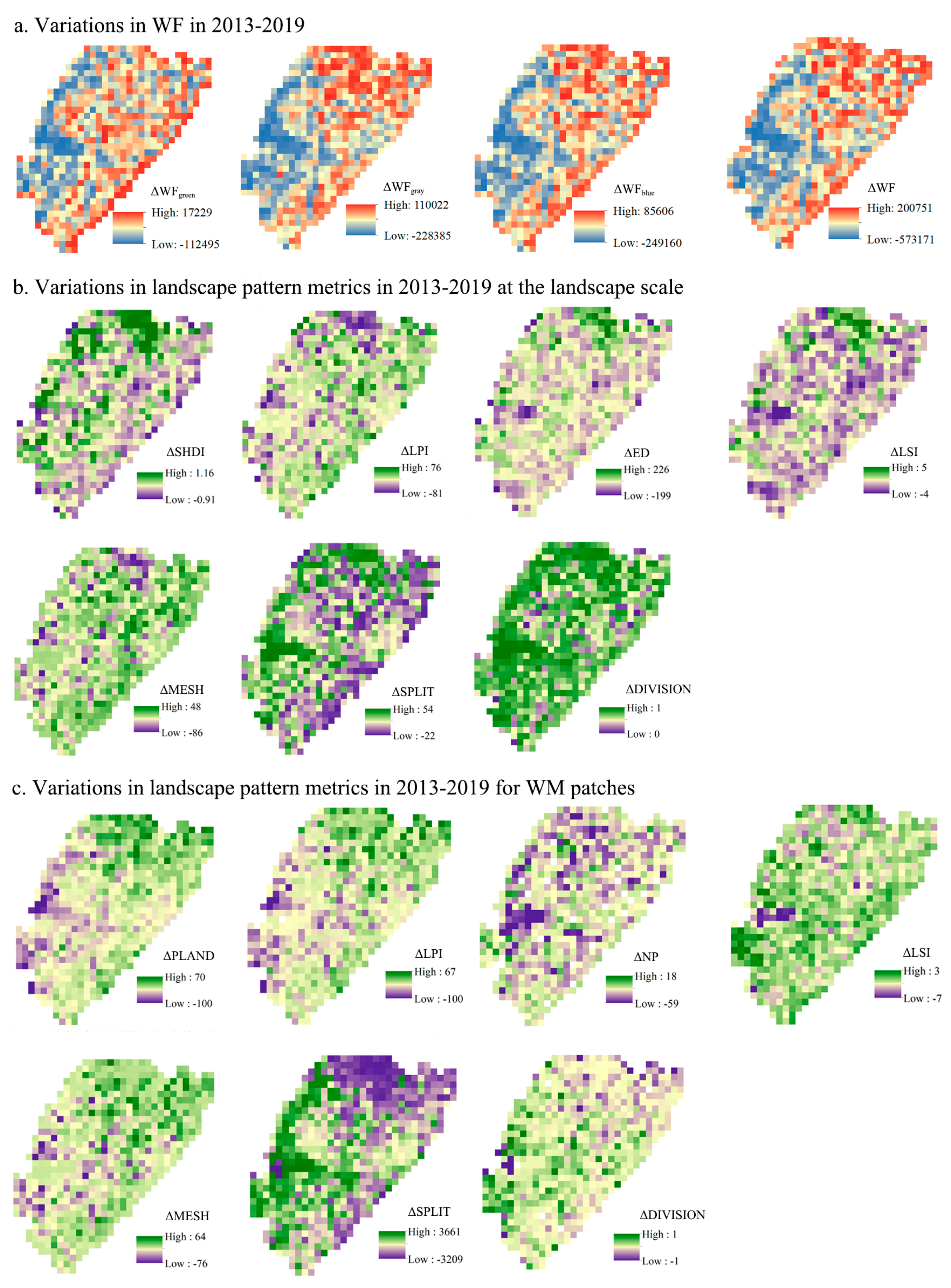
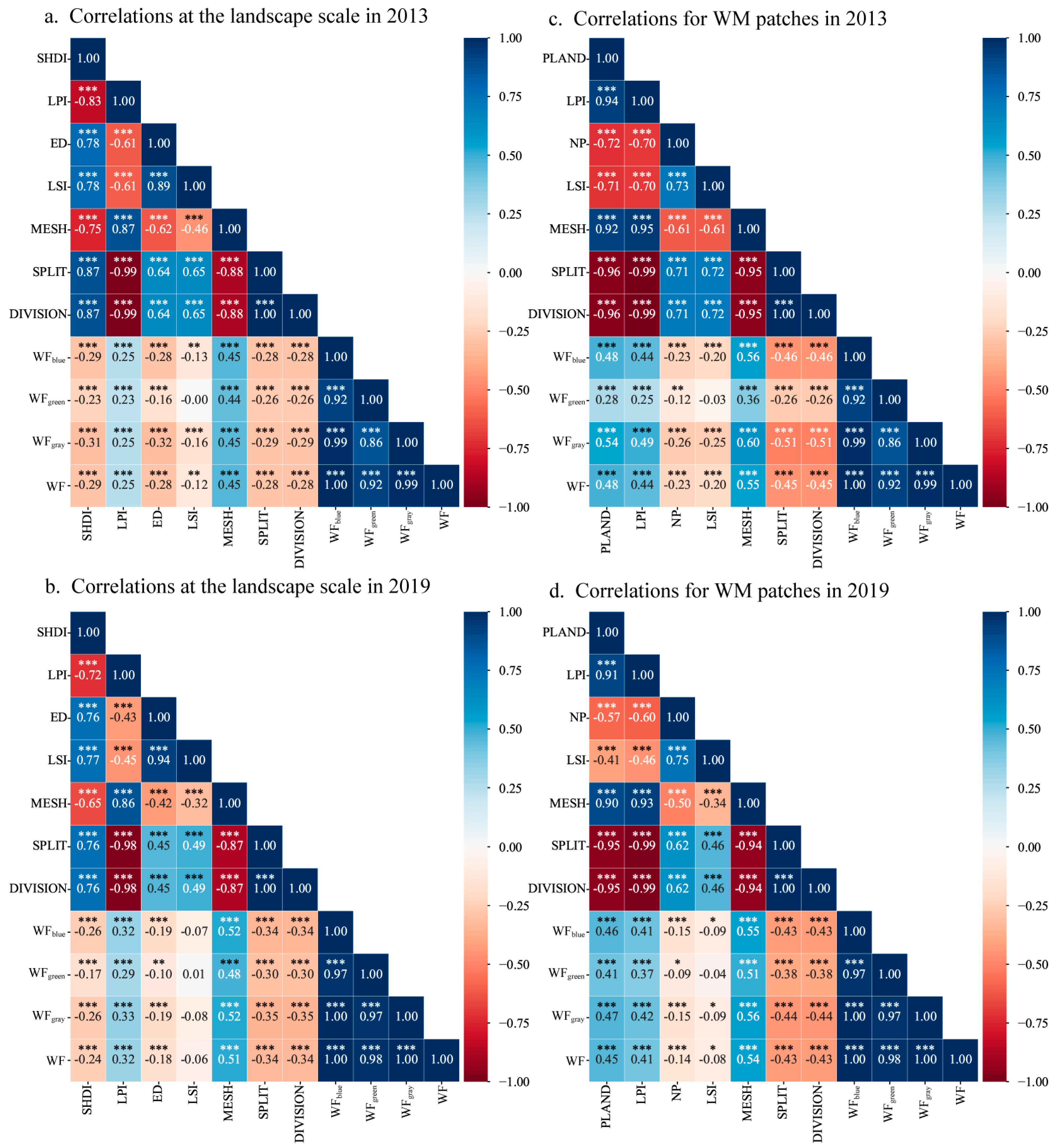

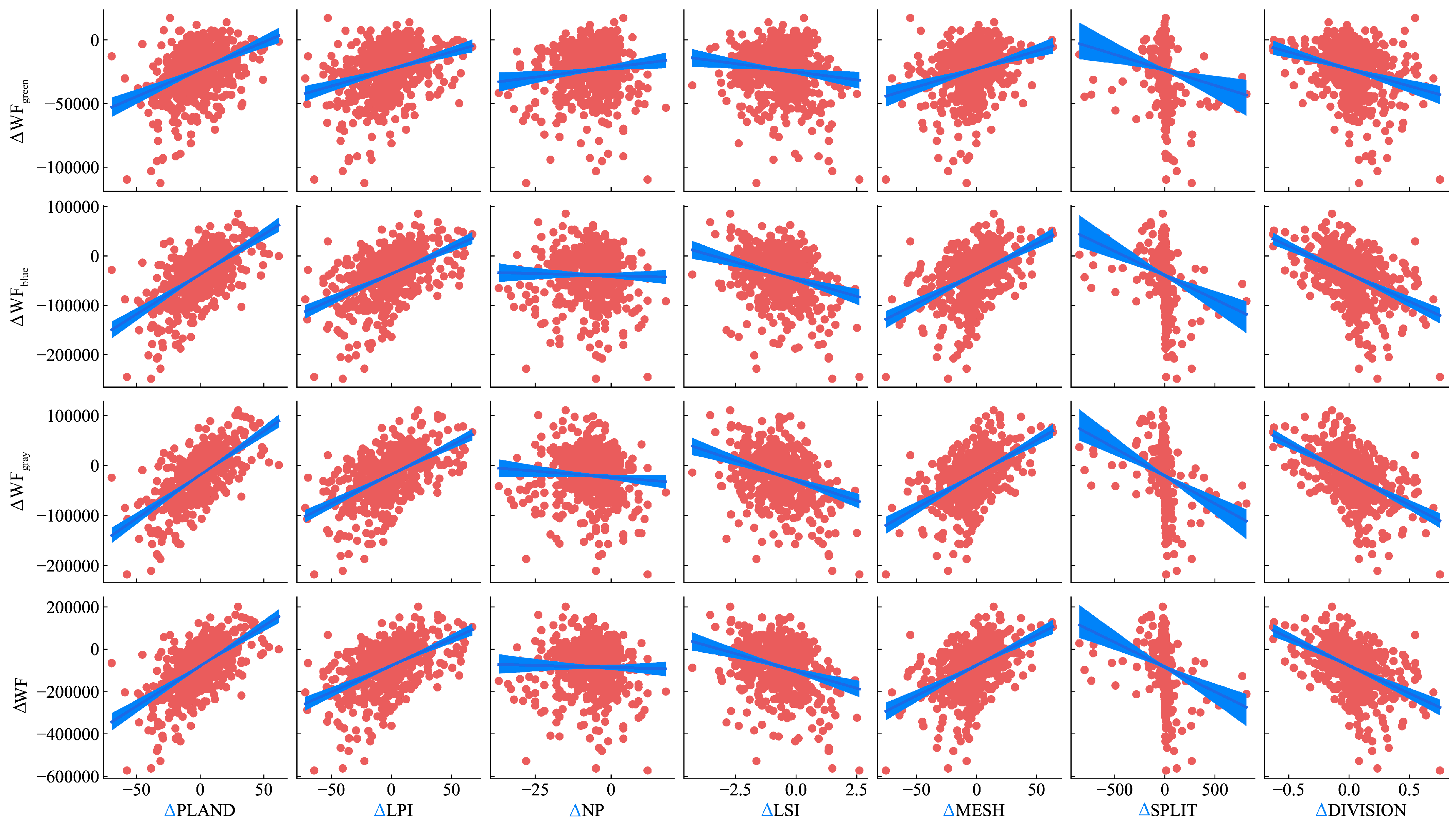
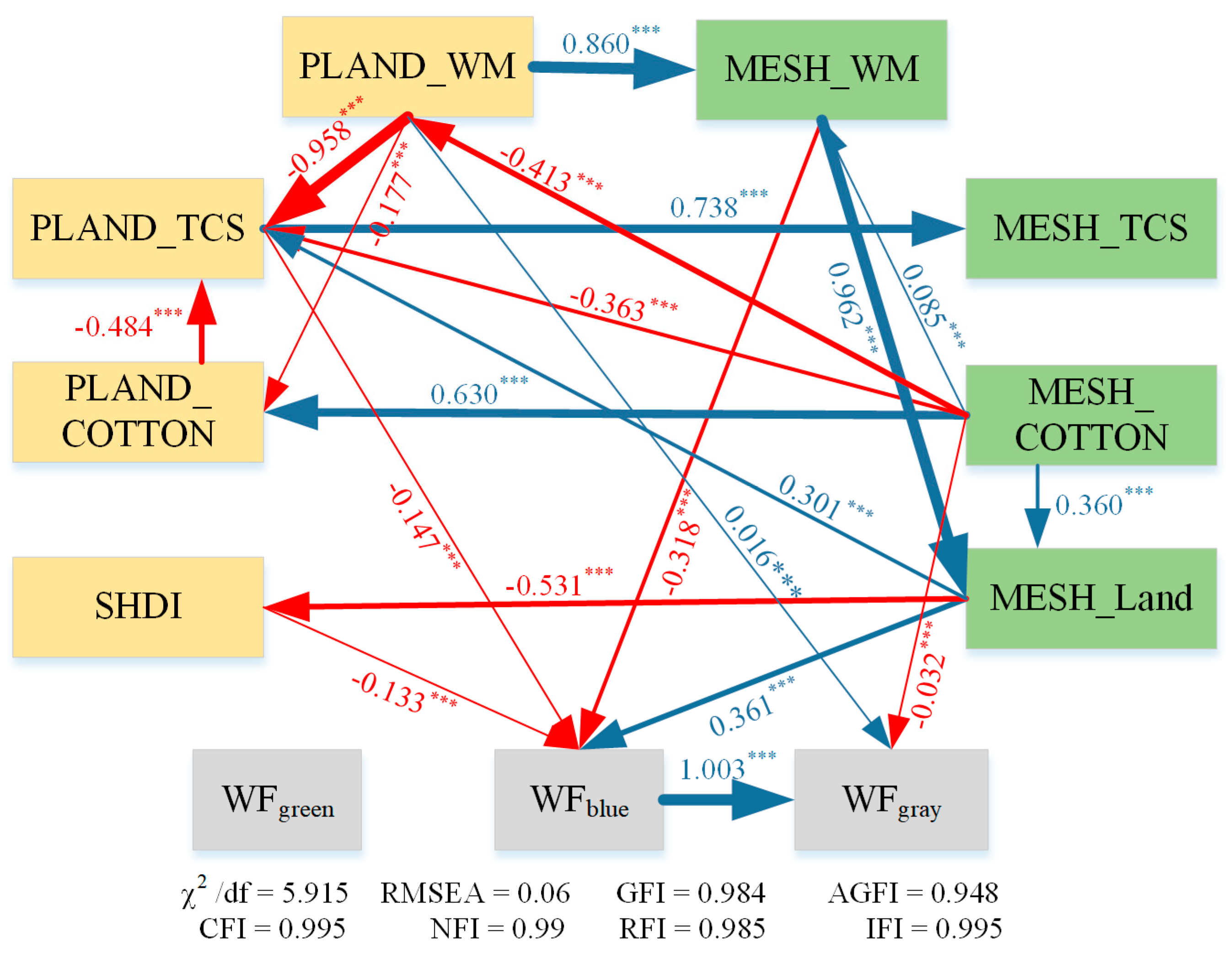
| Metrics | Value | Regression Slope/(m3 ha−1 per Unit) | Influence on WF/(m3 ha−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔWFgreen | ΔWFblue | ΔWFgray | ΔWF | ΔWFgreen | ΔWFblue | ΔWFgray | ΔWF | ||
| At the landscape scale | |||||||||
| ΔSHDI | 0.07 | −172.60 *** | −437.39 *** | −299.87 *** | −909.87 *** | −12.08 | −100.62 | −90.99 | −203.69 |
| ΔED | −3.16 | −0.42 *** | −1.18 *** | −0.62 *** | −2.22 *** | 1.33 | 3.73 | 1.96 | 7.02 |
| ΔMESH | −5.86 | 3.10 *** | 8.36 *** | 7.07 *** | 18.54 *** | −18.17 | −107.59 | −100.03 | −225.79 |
| In WM patches | |||||||||
| ΔPLAND | −1.14 | 4.27 *** | 16.16 *** | 17.40 *** | 37.84 *** | −4.87 | −18.42 | −19.84 | −43.13 |
| ΔMESH | −2.32 | 2.82 *** | 12.19 *** | 13.51 *** | 28.52 *** | −6.54 | −28.28 | −31.34 | −66.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Jia, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F. Spatial Distribution of the Cropping Pattern Exerts Greater Influence on the Water Footprint Compared to Diversification in Intensive Farmland Landscapes. Land 2024, 13, 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071042
Wang X, Jia H, Wang X, Zhang J, Chen F. Spatial Distribution of the Cropping Pattern Exerts Greater Influence on the Water Footprint Compared to Diversification in Intensive Farmland Landscapes. Land. 2024; 13(7):1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071042
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaohui, Hao Jia, Xiaolong Wang, Jiaen Zhang, and Fu Chen. 2024. "Spatial Distribution of the Cropping Pattern Exerts Greater Influence on the Water Footprint Compared to Diversification in Intensive Farmland Landscapes" Land 13, no. 7: 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071042
APA StyleWang, X., Jia, H., Wang, X., Zhang, J., & Chen, F. (2024). Spatial Distribution of the Cropping Pattern Exerts Greater Influence on the Water Footprint Compared to Diversification in Intensive Farmland Landscapes. Land, 13(7), 1042. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13071042








