Abstract
For the main grain-producing areas worldwide that balance multi-tasks of grain production, ecological protection, and economic development, quantitatively revealing the correlation between human activity intensity (HAI) and ecosystem service value (ESV) is conducive to formulating adapted ecological protection policies and promoting the coordinated development of the regional economy, society, and ecosystem. In this paper, we took the Songnen Plain of China as an example, employed a modified Equivalent Factor Method (integrating socio-economic data, the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), and land use data), and the HAI Assessment Model (based on the data of land use, night-time light, and population spatial distribution) to measure the ESV and HAI in the Songnen Plain of China for the years 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020. We further applied the standard deviational ellipse method, the coupled coordination degree model, and the bivariate spatial autocorrelation models to reveal the spatiotemporal dynamics and correlation characteristics of ESV and HAI. The results showed the following: (1) Temporally, the ESV declined from 950.96 billion yuan in 1990 to 836.31 billion yuan in 2015, and then increased to 864.60 billion yuan in 2020, with the total loss attributed to the significant decline in the ESV of the natural ecosystem. Spatially, the ESV in the western and northeastern regions was relatively high, with a significant increase in the northeast. (2) HAI showed an upward trend from 1990 to 2020, while the high HAI levels gradually shrank after reaching the peak in 2000. Low HAI levels were mainly distributed in the northeast and southwest, aligning with the ecological space, while high HAI levels were distributed in the middle and southeast. (3) The interaction between ESV and HAI was marked by a negative correlation, transitioning from conflict to coordination. The spatial pattern of HAI and ESV showed H (HAI)-L (ESV) and L-H clustering, with H-H and L-L scattered distributions. This study contributes to providing a framework, methods, and suggestions for the sustainable planning and utilization of land and ecological protection in order to offer scientific references for the Songnen Plain, other major grain-producing areas, and related studies.
1. Introduction
Ecosystem services, including provision services, regulation services, support services, and cultural services, refer to the life-supporting goods and services that humans obtain from the properties, processes, and functions of natural ecosystems directly or indirectly [1,2,3,4]; meanwhile, they are also the natural environmental conditions and benefits that human beings depend on for survival and development [5,6]. However, with urbanization, industrialization, and agricultural modernization as well as the rapid development of economic and population aggregation, human activities have altered the direction, structure, and rate of land use, which has damaged the supply and health of natural ecosystem services, and in turn, greatly weakened the value of ecosystem services (ESV) [7,8,9,10]. The global assessment report from the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) noted that three-quarters of the terrestrial environment and about 66% of the marine environment have been affected by human activities, which has and will continue to pose a significant threat to ecosystem services [11,12,13]. Meanwhile, the deterioration of ecosystems could, in turn, restrict the sustainable development of human societies [13]. Therefore, the 15th goal of the United Nations 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development has been proposed to control the impact of human activities on terrestrial ecosystems and promote the harmonious coexistence between humanity and nature [14,15]. Accordingly, the study of the correlation between human activities and ecosystem services has become an important issue in the field of human–land interactions [16]. Based on the background of human–land conflict, quantitatively evaluating the changing trend of ESV and HAI, and portraying the correlation between human activity and ecosystem services are of great significance for revealing the degradation mechanisms and improvement methods of regional ecosystems and formulating policies that promote harmony between ecosystems and humans.
This study on the relationship between human activity intensity (HAI) and ESV depends on the accurate evaluation of ESV, the quantification of human activities, and the revelation of the relationship between them.
The calculation of ESV is to quantify the products and services provided by the ecosystem, which is crucial to improving the public awareness of ecosystem preservation and promoting regional sustainable development [17]. At present, many scholars have evaluated ESV by using the physical assessment method [18], energy assessment method [19], and monetary valuation method [1,17], and each method has its own advantages and disadvantages [6]. The monetary valuation method is widely used because its research results can be adopted by the socio-economic management system. Meanwhile, it can be used to conduct large-scale and long time series comparative studies, and is more friendly to regions that lack relevant basic data [17,20]. The monetary valuation method was first proposed by Costanza et al. [1], which is based on land use data and the classification of ecosystem service functions and evaluates the value of ecosystem services at the global scale by establishing the table of equivalence values per unit area of ecosystem services. Subsequently, in light of the findings of Costanza et al. [1], Chinese scholars Xie et al. [21] proposed the table of equivalent values per unit area of ecosystem services in China depending on the characteristics of China’s terrestrial ecosystems and the magnitude of biomass and is continuously improved to reflect the health status of Chinese ecosystems [17,20,22,23]. This kind of method uses land use data to calculate ESV, but the reality remains that the ESV per unit area varies even with the same land use types due to different ecosystem health and vegetation growth conditions. Therefore, the NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) and the NPP (net primary productivity) have been applied by scholars to further modify the monetary valuation method in line with the table of equivalence values per unit area of ecosystem services [14,24], aiming at reflecting the change in ESV caused by the ecosystem’s structure and function. In conclusion, the existing and improved ecosystem service value assessment methods can provide useful references for this study.
Human activity, which is commonly defined by human activity intensity, is a general term for a range of behaviors or activities that humans adopt to meet their needs for survival and development [25,26]. Among the existing measures of HAI, some studies have adopted a single indicator to analyze human activities, such as land use data [27], night-time lighting data [28], population density [29], agriculture [30], and urbanization level [31]. Since the methods relying on one indicator can only reflect HAI from a certain aspect, which is a simplification of human activities, it is difficult to present HAI in different regions and stages in the process of socio-economic development, and the accuracy of this assessment is still to be discussed [8,32]. Conversely, other scholars have developed an integrated indicator system to evaluate HAI, including a variety of indicators. For example, Correa Ayram et al. [33] assessed the intensity of human impact by selecting seven variables, such as land use type, rural population density, distance to roads, distance to settlements, the fragmentation index of natural vegetation, the biomass index relative to natural potential, and the time of intervention on ecosystems in years, and the results demonstrated that HAI increased during the study period. Zhang et al. [13] selected 27 indicators involving five aspects, such as agricultural activities, industrial activities, tertiary industry activities, social development, and ecological engineering, to construct human activity impact indicators in order to evaluate the interaction between human activities and the ecological environment. However, the method of constructing comprehensive indicators encounters several challenges: variations in indicator selection across different locations and individuals, difficulties in obtaining extensive and long-term data series, discrepancies in weighting methods, and obstacles to regional comparisons [25,32]. Recently, considering the limitations of the two methods as well as the complexity and diversity of human activities, some scholars have begun to calculate HAI from the perspective of the power sources and impact of human activities by using three types of data: population density, night-time light, and land use [34,35]. This method can provide reliable and comparable data support for analyzing ecological problems and formulating policies in different regions, owing to the availability of data (night-time light data and land use data are derived from remote sensing data, population density data as regional basic data have data accessibility), limited indicators, comparability, and revealing characteristics of HAI.
In the study of the interaction between human activities and ESV, previous studies have employed the spatial autocorrelation analysis [36], the grey correlation analysis [13], and the coupling coordination degree analysis [37] to reveal the spatial–temporal correlation and coupling coordination relationship of the two systems at different scales (including the global scale [38], national scale [10], and regional scale [39]) based on Geoda [40] and ArcGIS software [33]. The results suggest that the relationship between human activities and ecosystem services is diverse, non-linear, or complex in different regions and stages of development [16,41,42]. For example, Huang et al. [37] found that there was an inverted U-shaped curve between human footprint and ESV in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration (PRDUA) from 2000 to 2020, indicating a non-linear coupling relationship between the two indicators. Ai et al. [40] elucidated the relationship between human disturbance intensity (HDI) and ESV using the Bivariate Local Moran Index and spatial autocorrelation analysis, and the results showed that areas with high ecosystem service values were relevant to low levels of HDI, while regions with low ecosystem service values were impacted by high levels of HDI. Quintas-Soriano et al. [43] discussed the relationship between land use change and ecosystem services in Spain and pointed out that different human activities have diverse impacts on ecosystem services, such as the fact that greenhouse horticulture negatively affects all ecosystem services, while intensive agricultural services have a positive effect on it. The variations in results are associated with the scale of the study and the regional natural, social, and economic characteristics. For China, a country undergoing rapid socio-economic development and transformation, and at the same time affected by global climate change, scholars have been actively exploring the relationship between human activities and ecosystem services in ecologically fragile areas such as arid and semi-arid regions and the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau [16,24], and the economically developed regions such as the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration and the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration [37,40], and attempting to reveal the spatial and temporal correlation between them. However, there is a lack of theoretical and empirical studies on the major grain-producing areas, particularly in Northeast China, which plays an important role in guaranteeing food security and ecological security in the north. This study may provide a useful reference for other similar areas to promote socio-economic development, improve human well-being, and realize the virtuous cycle of ecosystems. In addition, the results of previous studies have focused more on the quantitative analysis of results [44], and the application of the results concentrated on the extraction of the main controlling factors [13] and the measures to promote the improvement of ESV [40]. Currently, there are few thorough studies on ecological policies that aim to promote socio-economic and ecological development in the region from the perspective of serving government management, especially in the context of climate change and the spatial variations of ecosystems.
The Songnen Plain, located in the world’s four major black soil belts, is also an important grain-producing area and commodity grain base in China [45], yet the ecological environment is relatively fragile [46]. With the rapid development of the economy and global warming in the past 30 years, the region is experiencing a series of problems such as the expansion of build-up land, the sharp decline of ecological land, serious soil erosion, the degradation of black soil, salinization, and the deterioration of the ecological environment [45,47]. Among them, the irrational land use (land use transformation) triggered by the high intensity of human disturbances has been proven to be the main reason for the decline in ecological service functions and quality in the study area [48]. As the cornerstone for ensuring national food security and an important ecological function area in northern China, it is necessary to balance the relationship between economic development and ecological protection and then promote the improvement of the ecological environment. However, existing studies on the ecosystem services of Songnen Plain have focused on wetland ecosystems [49,50], the impact of land use change on ESV [48], and the ecological environment of a certain part of the study area [36]. There are research gaps in this area. Firstly, a long time series study on the spatial and temporal patterns of ESV evolution for the whole region is insufficient. Secondly, there are few studies on the mechanisms of ESV change from the perspective of the interaction between human activities and ecosystems. Thirdly, there is a lack of policy recommendations to serve the high-quality development of the main grain-producing areas, considering grain production, ecological protection, and economic revitalization in the context of climate change. The objectives of this research are to (1) calculate the spatiotemporal changes of ESV and HAI in the Songnen Plain; (2) quantitatively reveal the spatial and temporal relationship between ESV and HAI over the past 30 years in the Songnen Plain; and (3) put forward the policy recommendations on ecological protection to realize the sustainable development of the region’s society, economy, and ecology. The research framework and methods employed in this study are suitable for other regions worldwide that are investigating ESV, HAI, and their interactive feedback relationships. The policy implications provided in this study for balancing food security, protecting the ecological environment, and promoting economic development, as well as addressing climate warming, are applicable to other major grain-producing areas facing similar challenges and threats.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
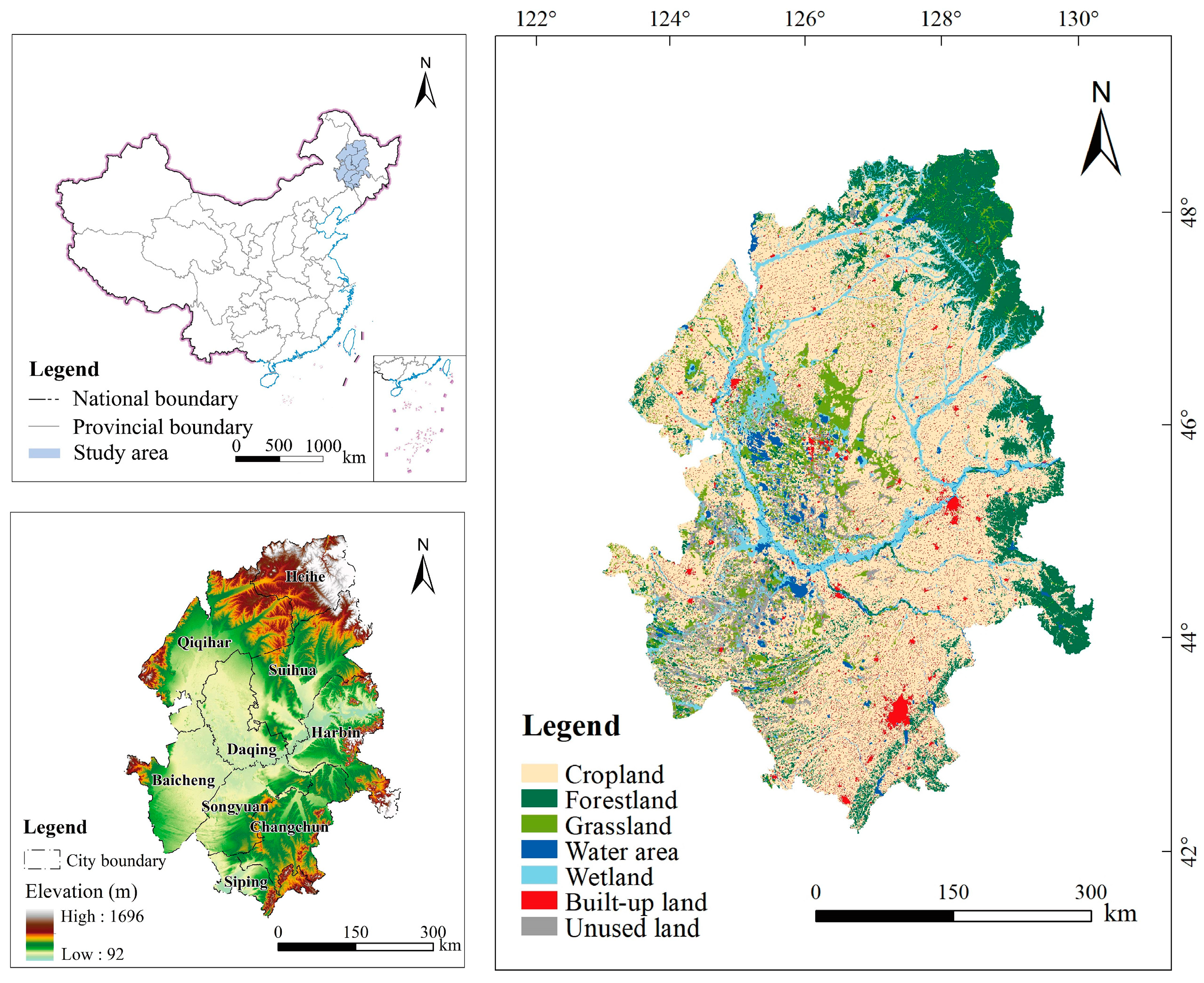
The Songnen Plain, one of the three major plains in Northeast China, located in the central part of Northeast China (42°30′–51°20′ N,121°40′–128°30′ E), has a total area of 230,300 km2. It includes the provinces of Heilongjiang and Jilin and looks like a rhombus shape formed by the Songhua and Nenjiang rivers’ alluvial deposits (Figure 1), with an elevation ranging from 92 m to 1696 m. The terrain is characterized by a high value in the surroundings and a low value in the middle. It has a temperate semi-humid and semi-arid continental monsoon climate with four distinct seasons, and rain and heat simultaneously. The mean annual temperature ranges from −2 °C to 7 °C, and the mean annual precipitation occurs from 350 mm to 600 mm [45]. The main soil types are black soil, black calcium soil, and meadow soil [45]. The land use types include cropland, forestland, wetland, grassland, water area, built-up land, and unused land, among which wetlands are widespread, and most wetlands are inland saline wetlands concentrated in ecologically fragile areas transitioning from semi-humid to semi-arid areas. This area, with adequate conditions of light, heat, and water resources, is one of China’s five major grain-producing areas and an important commercial grain production base, which plays an important role in guaranteeing national food security [46]. Moreover, it is also an important energy and heavy industry base in China. However, during the last 30 years, with the rapid development of the economy and global warming, the region has experienced deforestation, the return of farmland to forests, the conversion of dry land to paddy land, overgrazing, urbanization, and the outflow of population, etc. The ecological environment in this region is highly fragile due to the continuing disturbances from human activities [46].
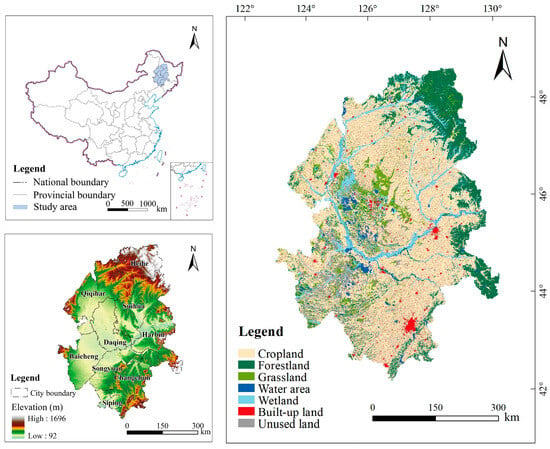
Figure 1.
Location of the Songnen Plain.
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
The data in this study mainly included land use data, socio-economic statistical yearbook data, night-time light data, and population spatial distribution data, etc.
2.2.1. Land Use Data
The land use remote sensing monitoring data for 1990, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, with a resolution of 30 m × 30 m, were obtained from the Data Center for Resources and Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (RESDC) [51], and projection transformation, mask extraction, and reclassification were performed in the ArcGIS platform. The land use types included cropland (dry land and paddy land), forestland (broad-leaved and shrub), grassland, water area, wetland, built-up land, and unused land, and the overall classification accuracy was above 90% [52].
2.2.2. Socio-Economic Data
The socio-economic data such as sown area and the production data of grain crops from 1990 to 2020 were acquired from the Statistical Yearbook of Heilongjiang Province and Statistical Yearbook of Jilin Province, the China Economic and Social Big Data Research Platform [53]. The data were used to calculate the value of ecosystem services per unit area of cropland.
2.2.3. The Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI)
The NDVI data from 1990 to 2020 (five-year interval) came from RESDC [51], which is a year-by-year maximum NDVI dataset calculated based on Landsat 5/8 remote sensing imagery from the United States of America, reflecting the distribution and change of vegetation cover. The data, at a 1 km spatial resolution, was used to adjust ESV in the study area.
2.2.4. Night-Time Light Data
The night-time light data for 1992, 1995, 2000, 2005, 2010, 2015, and 2020, reflecting the intensity of human social and economic activities on the land surface, were provided by the Harvard Dataset Platform [24,54,55]. Night-time light data in 1990 was replaced by 1992 data because of data unavailability. The spatial resolution of the night-time light data is 1 km.
2.2.5. Population Density Data
The population density data from 1990 to 2019 (five-year interval), revealing the spatial distribution pattern of population in a certain area, were derived from the China Population Spatial Distribution Kilometer Grid Dataset of RESDC [51]. The data have a spatial resolution of 1 km. Due to the lack of data in 2020, the data from 2019 were used as a substitute.
To ensure the accuracy of the data, we preprocessed the spatial data in ArcGIS. The spatial coordinate systems were uniformed to the Krasovsky_1940_Albers and the resolution of all data was unified to 30 m. The detailed information of the data is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Details about the data in this study.
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Evaluation of Ecosystem Service Value
This study evaluated ESV based on the table of equivalent values per unit area of ecosystem services proposed by Xie et al. [20] and coupled with the conditions of the Songnen Plain. We took the cell as the study unit to measure ESV and HAI. After many repeated experiments, the study area generated a total of 26,339 cells, and each cell had a size of 3 km × 3 km by using ArcGIS. In the calculation steps, the key of the method was to determine the value of a standard equivalent factor, the equivalent factor coefficient, and the correction coefficient of ESV, on the basis of which ESV was estimated.
(1) Value of the standard equivalent factor
The standard equivalent factor in the study area was determined by 1/7 of the economic value of the grain yield per unit area [21]; the expression is as follows:
where stands for the standard equivalent factor, P denotes the price per unit of grain yield (yuan/kg), and Q represents the grain yield per unit area (kg/hm2).
In this study, Q was the grain yield per unit area of the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020, which is 5479.02 kg/hm2. Meanwhile, to eliminate the influence of grain price changes on ESV each year and to reflect the real ecosystem service function and ecological environment quality in the study area, P was determined by the price per unit of grain yield of the region in 2020, which is 2.73 yuan/kg. Thus, the standard equivalent factor for the area was calculated to be CNY 2136.82/hm2.
(2) Equivalent factor coefficients and the correction coefficient of ESV
The equivalent factor coefficient of Xie et al. [20] was determined according to the vegetation biomass of China’s terrestrial ecosystem. For the Songnen Plain, the equivalent factor coefficient would be adjusted in accordance with the biomass of the region. The formula of the correction coefficient is as follows [16]:
where indicates the average value of vegetation cover in the study area, designates the average value of vegetation cover in China, and refers to the correction coefficient of ESV in the study area. The average correction coefficient of the plain was finally calculated to be 1.33.
In addition, since broad-leaved forests accounted for more than 85% of the arbor (coniferous, mixed coniferous, and broad-leaved) [56,57], the equivalent factor coefficient of forests other than shrubs adopted the value of broad-leaved forests. The grassland in the region is dominated by meadow [58], so the equivalent factor coefficient of grassland was equal to the meadow. Referencing the research by Chu et al. [59], we set the built-up land equivalent factor coefficient as the value of desert due to the lack of the equivalent factor coefficient for built-up land in the table of equivalent values per unit area of the ecosystem services of Xie et al. [20].
Finally, the ESV coefficients of different ecosystem service types in the study area were obtained by multiplying the standard equivalent factor of the region with the coefficients of the equivalent factor (Table 2).

Table 2.
The ESV coefficients of different ecosystem service types in the Songnen Plain (CNY/hm2).
(3) Calculation of ESV
ESV was measured using the following equation:
In the formula, indicates the estimated ecosystem service value; refers to the ESV coefficient of land use type (CNY/hm2); stands for the area of land use type (hm2); is the value of the ecosystem service function ; and denotes the value coefficient of ecosystem service function for the land use type .
2.3.2. Standard Deviational Ellipse Method
The standard deviation ellipse was used to analyze the spatial distribution trend of ESV in different periods, in which the mean center, long, and short axes of the ellipse can reveal the dynamics of its center of gravity, extension direction, and range [60]. The formula is expressed as follows:
where signifies the weighted mean center; ) represents the geometric center coordinates; represents the ESV of the i-th grid; denotes the azimuth angle of the standard deviation ellipse; and refer to the deviation of the coordinates from the center of the study area to the mean center, respectively; and and stand for the and axes of the standard deviation ellipse’s spatial distribution for ESV.
2.3.3. Assessment of Human Activity Intensity
Considering the power sources of human disturbance to the ecosystem and its consequences [34], the HAI comprehensive evaluation model was constructed using the night-time light index, population density, and conversion coefficients of different land use types for the built-up land equivalent (CI) proposed by Xu et al. [25] to depict the intensity of human activity in the study area. The model is more applicable for calculating the ESV of the Songnen Plain, which has undergone urbanization, industrialization, LUCC, and population loss.
The CI in the study area was determined according to the land use types of the Songnen Plain (shown in Table 3) [25]. The HAI could be calculated with Equation (8):
where NTL represents the normalized night-time lighting index; PD denotes population density; CI refers to the conversion coefficients of different land use types for built-up land equivalents; and , , and stand for the indicator weights of NTL, PD, and CI. Referring to the research results of Chen et al. [34], , , and are set as 0.3, 0.3, and 0.4, respectively, and the HAI is standardized to [0, 100].

Table 3.
Conversion coefficients of different land use types for the built-up land equivalent of the Songnen Plain [25].
2.3.4. Coupled Coordination Degree Model
The degree of coupled coordination is widely used to evaluate the degree of coordinated dependence between different systems in an interaction relationship [61]. In this paper, the coupled coordination degree model was applied to quantify the degree of interaction between ESV and HAI in the study area. The specific formula is as follows:
where C refers to the degree of coupling between ESV and HAI, 0 ≤ C ≤ 1; a higher value indicates a closer relationship between the two systems. ESV and HAI are standardized values, T signifies the integrated development coefficient, α and β stand for the degree of importance of ESV and HAI; both α and β are assigned a value of 0.5 due to their equal importance [62], D designates the degree of coordination between ESV and HAI, 0 ≤ D ≤ 1; a larger value indicates that the coordination of the two systems is higher, and vice versa.
2.3.5. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Models
Spatial autocorrelation is an important indicator reflecting the correlation between the attribute values or phenomena of adjacent spaces, and the characteristics of local spatial agglomeration, which is specifically divided into global spatial autocorrelation and local spatial autocorrelation (denoted by global Moran’s I and local Moran’s I, respectively) [62]. Given the great spatial correlation between HAI and ESV, this paper applied the bivariate spatial autocorrelation model to analyze the spatial correlation between the two indicators. The global Moran’s I index was calculated as follows:
where I refers to the bivariate global spatial autocorrelation index; n is the number of spatial units; and denote the attribute values of spatial units i and j; represents the average value of the observed values of all grids; and stands for the spatial weight matrix based on the proximity relationship of spatial units i and j.
The local Moran’s I index is expressed as follows:
where designates the observed value of the attribute of spatial unit i; denotes the observed value of the attribute of spatial unit ; and stand for the variances of the observed values of attributes and , respectively; represents the bivariate local spatial autocorrelation index; and and are the normalized values of the standard deviation of spatial cell and cell for attribute value and attribute value .
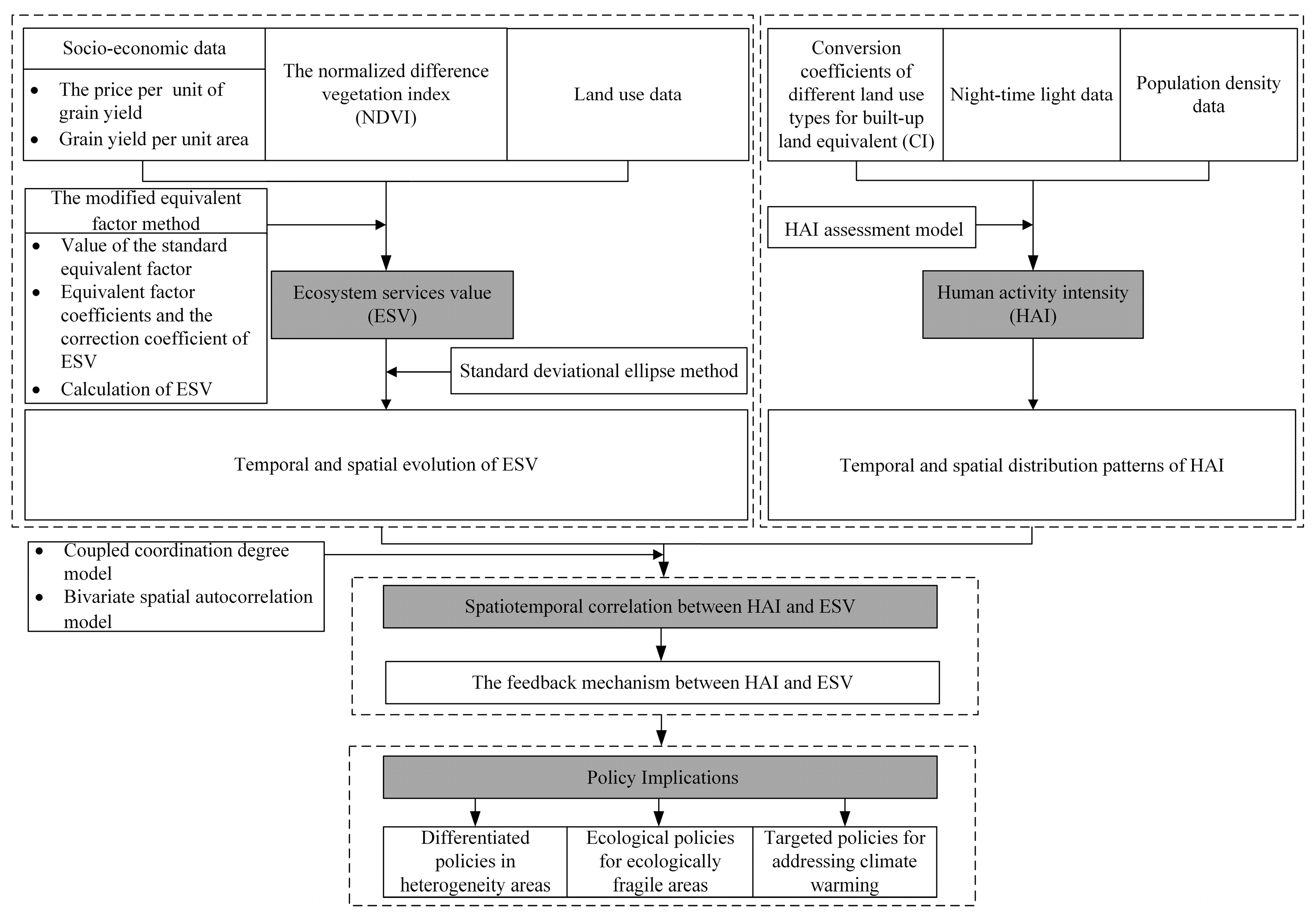
This study’s technical framework is depicted in Figure 2.
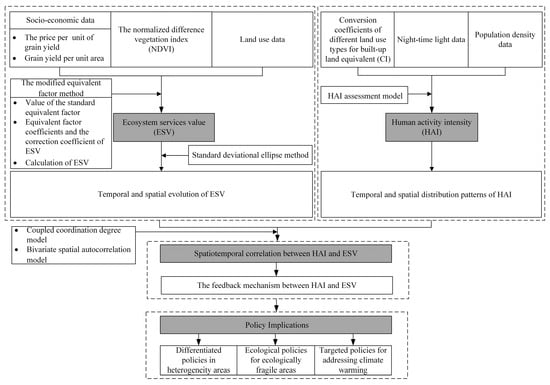
Figure 2.
The technical framework of this article.
3. Results
3.1. Land Use Changes in 1990–2020
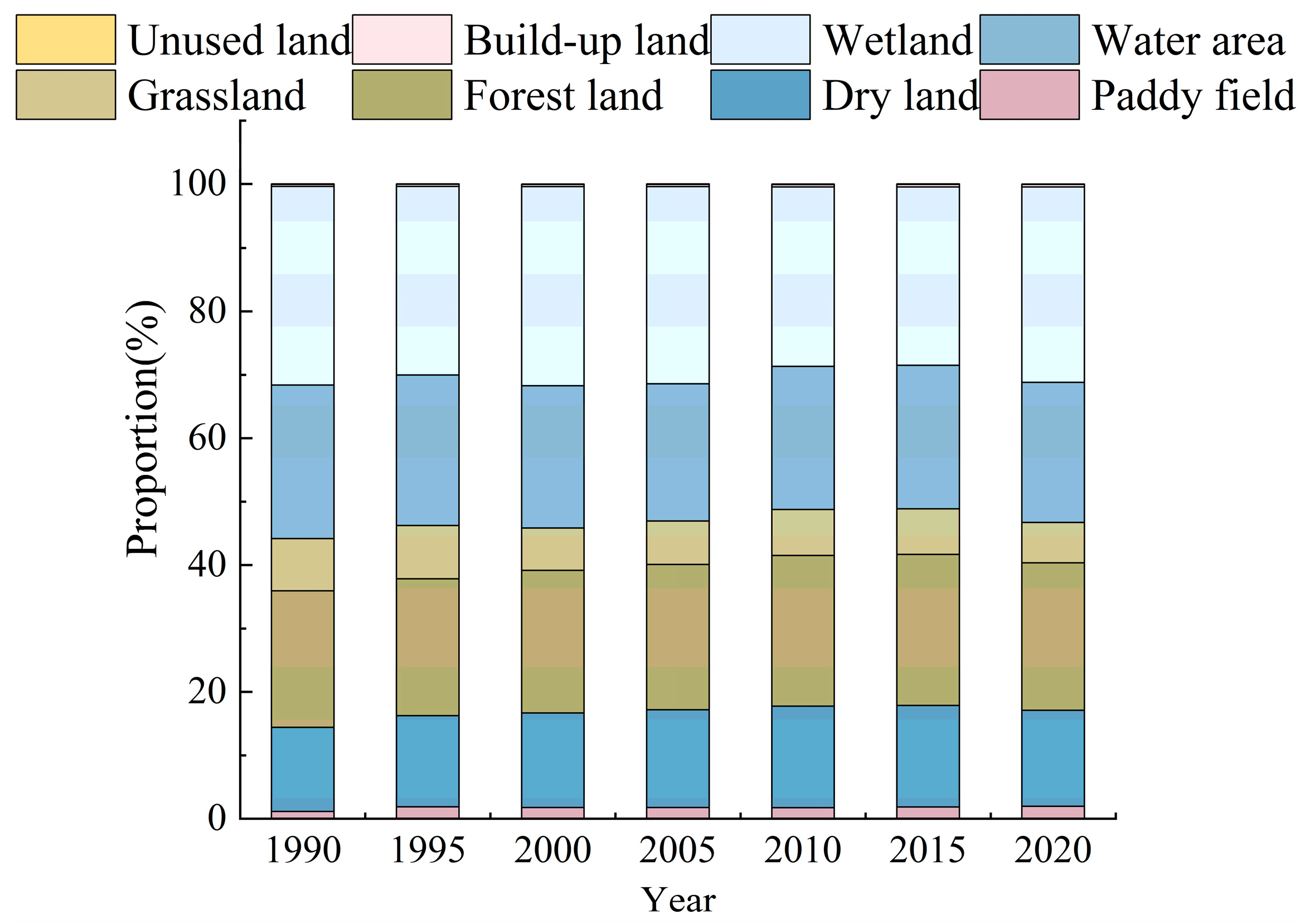
The dominant land types in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 were dry land (about 49.2–52.4% of the total area), forestland (about 14.0–14.6% of the total area), grassland (about 7.5–10.7% of the total area), and wetland (about 7.0–8.9% of the total area), among which dry land made up the largest proportion, accounting for approximately 50% of the total area (Table 4). Regarding to the degree of change, the paddy fields, dry land, and built-up land showed an overall upward trend during 1990–2020, with growth rates of 56.43%, 3.94%, and 15.53% respectively, while grassland area had the highest loss of 29.64% with a decrease in area of 7319.47 km2, followed by water area and wetland, which decreased by 17.10% and 10.54%, respectively.

Table 4.
Land use type changes in the Songnen Plain in 1990–2020.
In terms of the direction and intensity of land conversion during the period of 1990 to 2020 (Table 5), the conversion between paddy fields and dry land was one of the significant land use change characteristics. Specifically, the area of paddy fields that was converted into dry land is 1694.65 km2, while 4375.20 km2 of dry land was converted into paddy fields, meaning that the net inflow of paddy fields was massive. Moreover, most of the increased cropland (paddy field and dry land) was converted from ecological land (forestland, grassland, and wetland). For instance, 3140.08 km2 of forestland, 6415.21 km2 of grassland, and 1286.72 km2 of wetland were transferred into dry land; meanwhile, 1190.63 km2 of grassland and 1861.87 km2 of wetland were converted into paddy fields. Thirdly, the expansion of built-up land came primarily from the transfer of dry land, with an area of 2328.59 km2. Moreover, the conversion of dry land to forestland, water area, and wetland (Ecological De-farming) could not be ignored (Table 2). Overall, the region represented the characteristics of cropland converted into build-up land, ecological land converted into cropland, and dry land transformed into paddy fields.

Table 5.
Conversion matrix of land use change in the Songnen Plain during 1990–2020 (km2).
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of ESV
3.2.1. Temporal and Spatial Patterns of Change in ESV
The ESV of the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 was calculated (Table 6) using Formulas (3) and (4). The results indicated that ESV fell continuously and then rose in 1990–2020. The total value decreased from 950.96 billion yuan in 1990 to 836.31 billion yuan in 2015 and then increased to 864.60 billion yuan in 2020. In terms of the contribution of various land use types to ESV, taking 2020 as an example (Table 6, Figure 3), wetlands had the highest contribution of 30.74% (although only accounting for 7.99% of the total area), followed by forestland (23.23%) and water area (22.08%). It is noticeable that wetlands, forestland, and water areas were the primary contributors to ESV in the region. During the period of 1990–2020, the natural ecosystem of the study area (i.e., forestland, grassland, water area, and wetland) declined from 810.55 billion yuan to 712.73 billion yuan, which dropped by 12.07% (Table 6). Among them, the reduction in ESV for water area, wetland, and grassland made up 40.25%, 32.03%, and 23.76% of the total ESV loss, respectively. The artificial (semi-artificial, semi-ecological) ecosystem (i.e., paddy field, dry land, and built-up land) increased by 8.21%, from 139.74 billion yuan to 151.22 billion yuan, with paddy field and dry land contributing 52.78% and 43.28%, respectively.

Table 6.
Ecosystem service value and its change in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020.
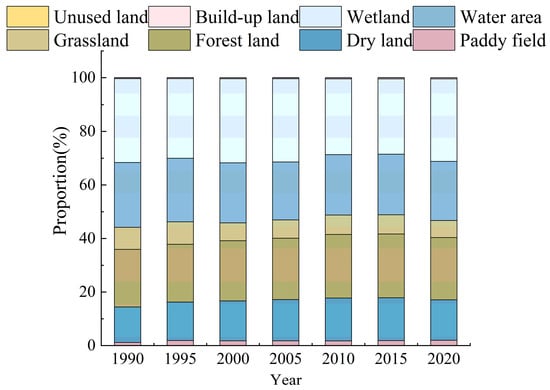
Figure 3.
The proportion of the Songnen Plain’s different ecosystem service values in 1990–2020.
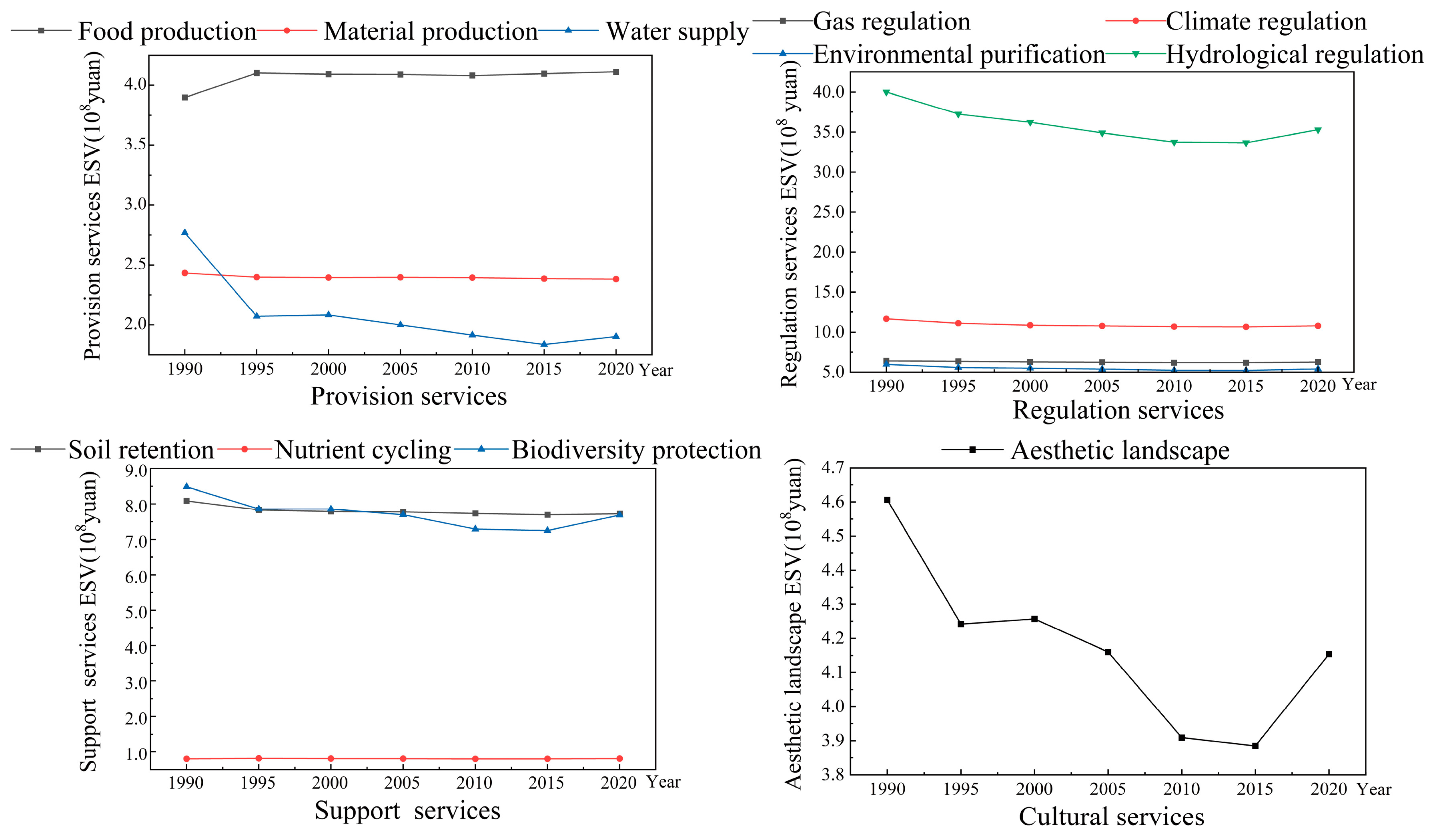
The values of ecosystem service functions in the Songnen Plain are displayed in Figure 4. Taking the value in 2020 as an example, among the value of primary services, regulation services contributed the highest (66.73%), followed by support services (18.76%), provision services (9.71%), and cultural services (4.80%). Of the secondary service values, hydrological regulation service had the highest value, with a proportion of 40.82%, making it the primary ecosystem service function in the region. Moreover, ecosystem service functions such as biodiversity, soil protection and retention, gas regulation, environmental purification, and food production also contributed markedly, accounting for 8.89%, 8.93%, 7.22%, 6.23%, and 4.75%, while the contribution of nutrient cycling service was lowest at only 0.93%. According to the rate of change from 1990 to 2020 (Figure 4), the overall ecosystem service function showed a downward trend except for food production (which increased by 5.44%). The ESV of water supply decreased significantly by 31.23%, followed by hydrological regulation (−11.81%), esthetics landscape (−9.82%), and biodiversity (−9.42%). The declining rate of material production was the lowest (−2.09%).
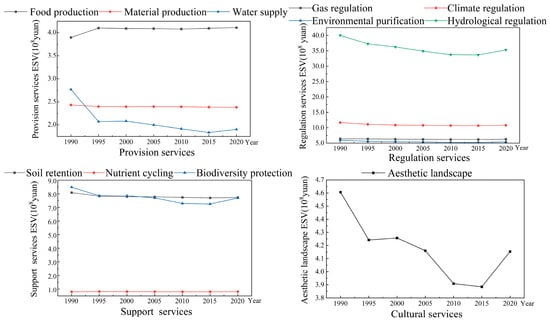
Figure 4.
Value changes of ecosystem service functions during 1990–2020.
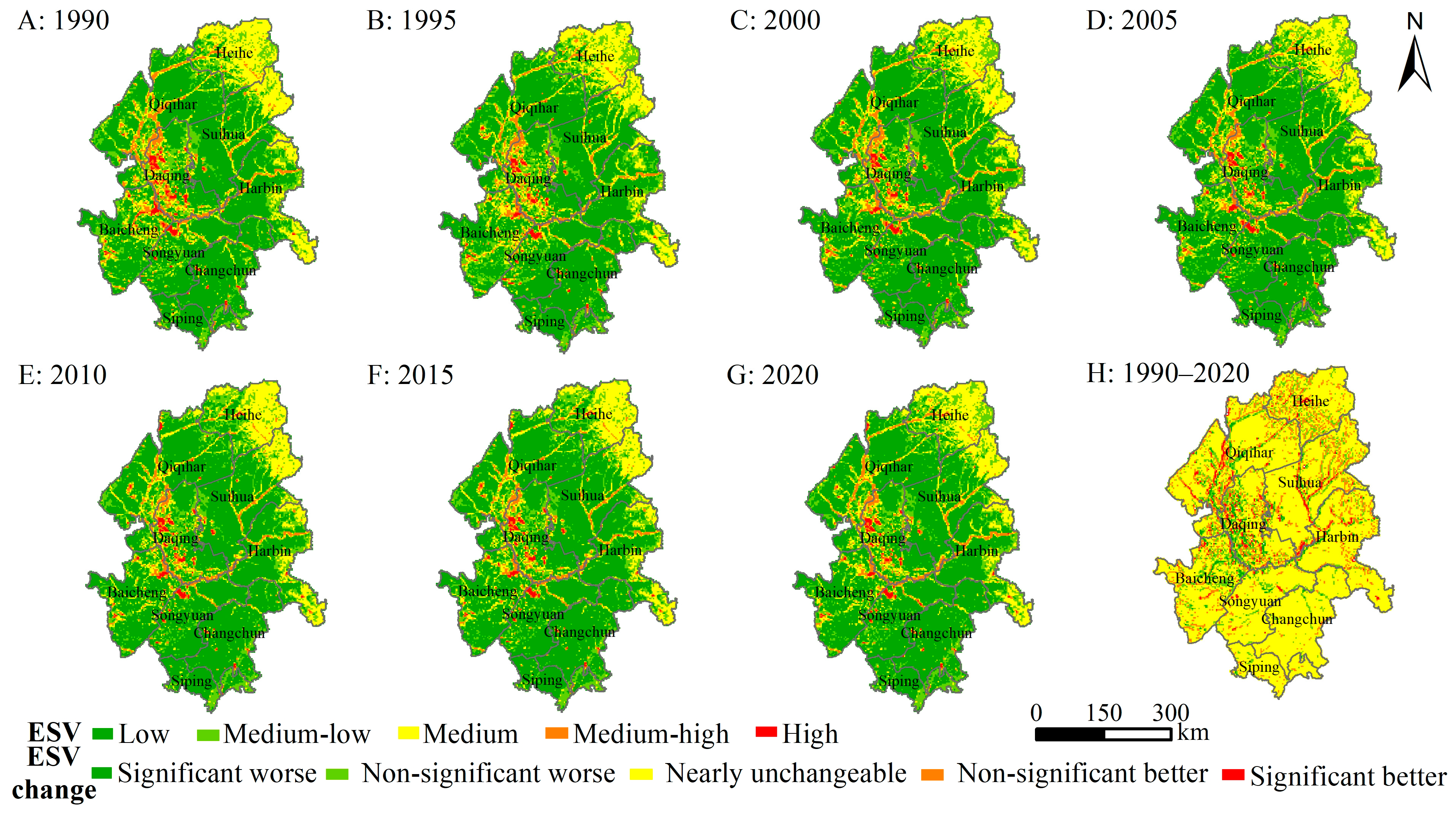
To exhibit the spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of ESV, we used the natural breaks method and classified ESV into five levels, namely low value (ESV ≤ 2373), medium-low value (2373 < ESV ≤ 5023), medium value (5023 < ESV ≤ 9708), medium-high value (9708 < ESV ≤ 19,078), and high value (ESV > 19,078) (Figure 5). Overall, the ESV in the western and northeastern regions was relatively high, and was the opposite in other regions. The high-value areas of ESV mainly occurred in the ecological areas, including water areas, wetlands, and forested areas, while the low value of ESV overlapped with areas of intensive human activity and ecological vulnerability, especially located in the dry land, built-up land, and unused land. Moreover, there were no significant changes in most areas during 1990–2020 (Figure 5), and the areas with a significant increment in ESV were mostly clustered in water areas and wetlands, while the areas with a significant decline in ESV were centered on the northeast of Baicheng, the west of Daqing, and certain areas in Qiqihar.
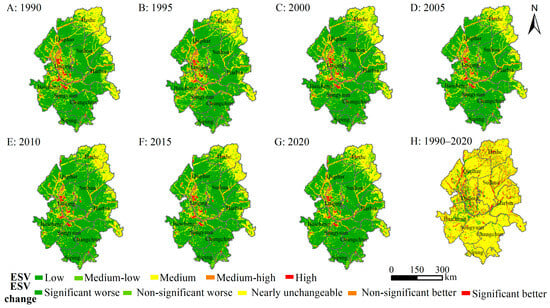
Figure 5.
The spatial distribution of ESV and its changes in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020. (Notes: A–G denotes the ESV of study area. H represents the changing trend of ESV).
3.2.2. The Spatial Pattern Evolution Characteristics of ESV
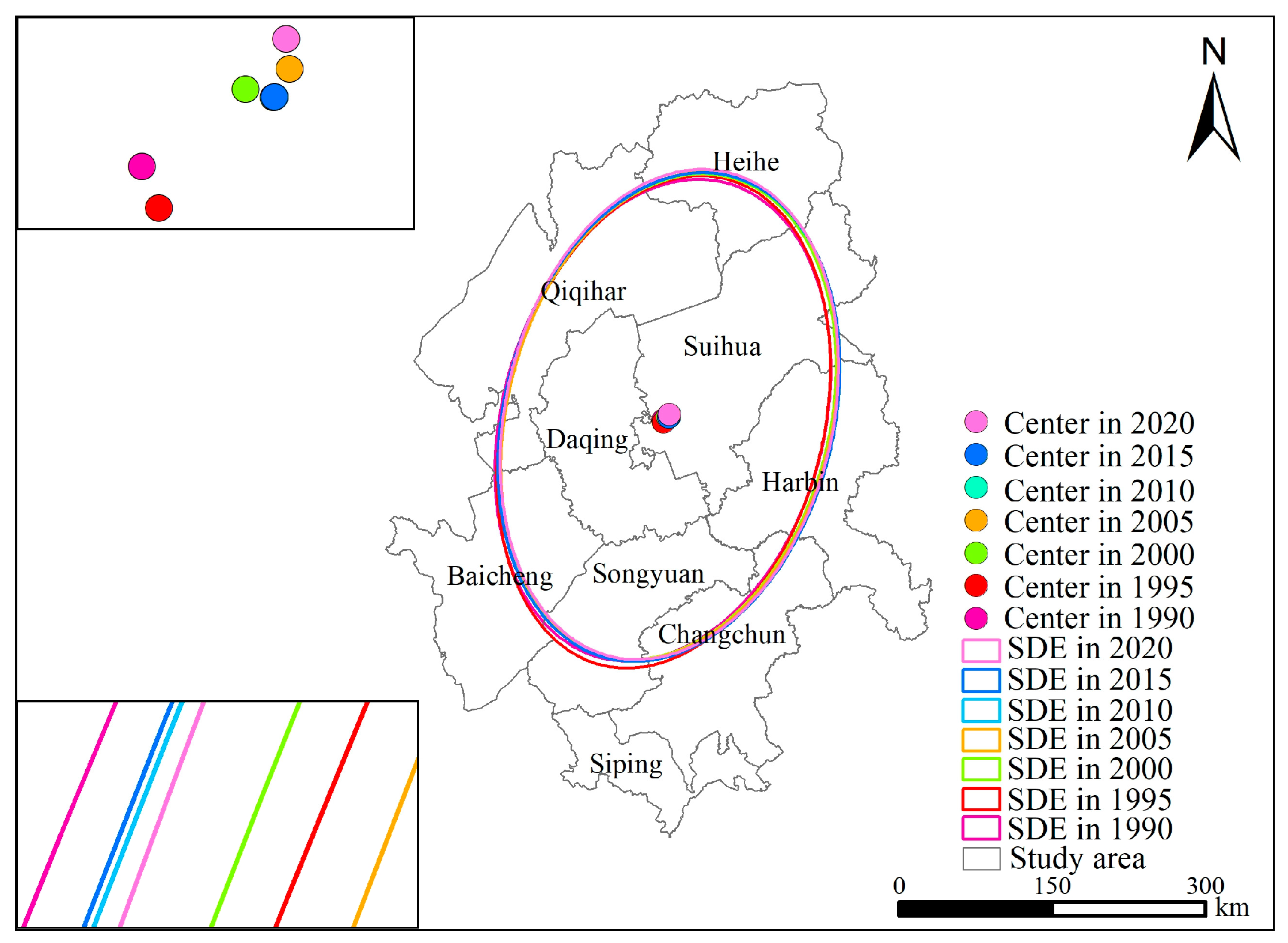
The spatial change characteristics of ESV in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 were analyzed based on Formulas (5)–(7), and the results are shown in Table 7, Figure 6. The area of the standard deviation ellipse showed an overall expanding trend, meaning that the difference in ESV between the inside and outside of the ellipse was reduced, and areas of poor ecological quality were improved.

Table 7.
Standard deviation ellipse parameters of ESV.
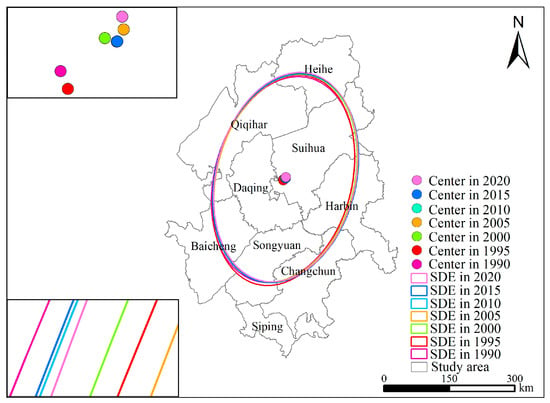
Figure 6.
Standard deviation ellipse of ESV and its center of gravity change in the Songnen plain (1990–2020).
The centroid of ESV was located in the central part of the study area, which is the southwest of Suihua City. Temporally, the centroid of ESV first migrated to the southeast by 1.98 km and then moved to the northeast by 12.56 km as a whole, which confirmed that the ESV in the northeast has increased significantly and the ecological structure and function have improved. Meanwhile, the rotation angle of the standard deviation ellipse fluctuated around 14°, indicating that the spatial distribution of ESV followed a northeast–southwest direction, which is basically consistent with the distribution pattern of the study area.
3.3. Temporal and Spatial Distribution Patterns of HAI
In this paper, we measured HAI in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 using Formula (8), and analyzed the spatiotemporal pattern characteristics at the grid scale (Figure 7 and Figure 8). According to the data distribution, HAI was classified into five levels: low impact (HAI ≤ 7), medium-low impact (7 < HAI ≤ 15), medium impact (15 < HAI ≤ 20), medium-high impact (20 < HAI ≤ 30), and high-impact (HAI > 30).
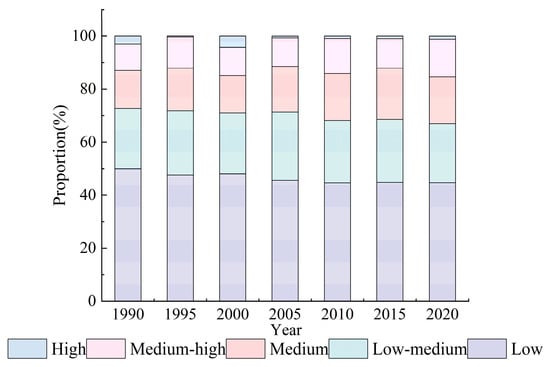
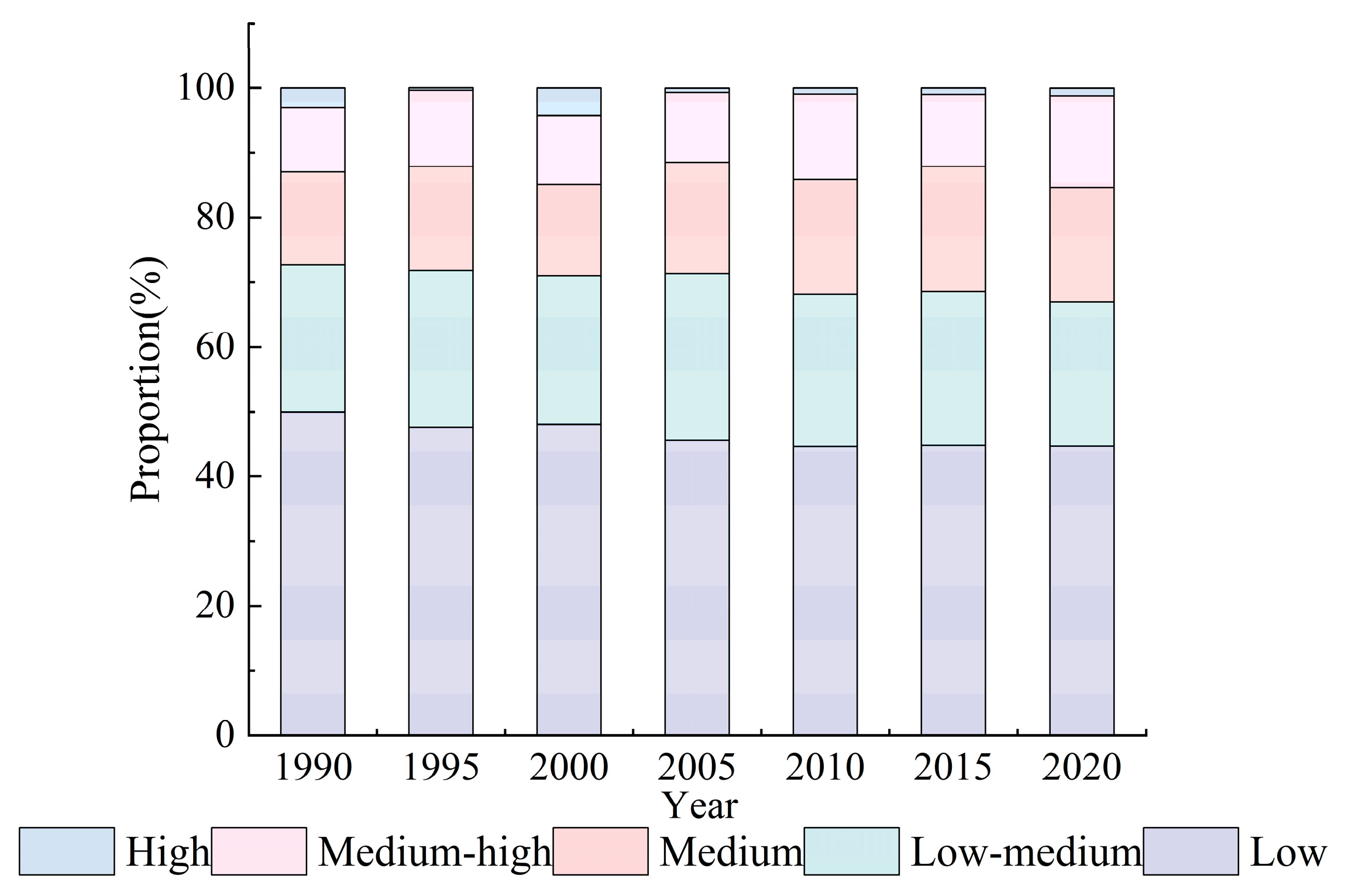
Figure 7.
The proportion of human activity intensity.
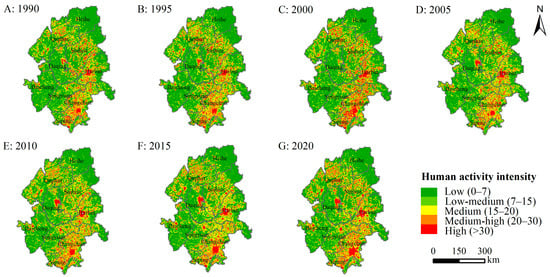
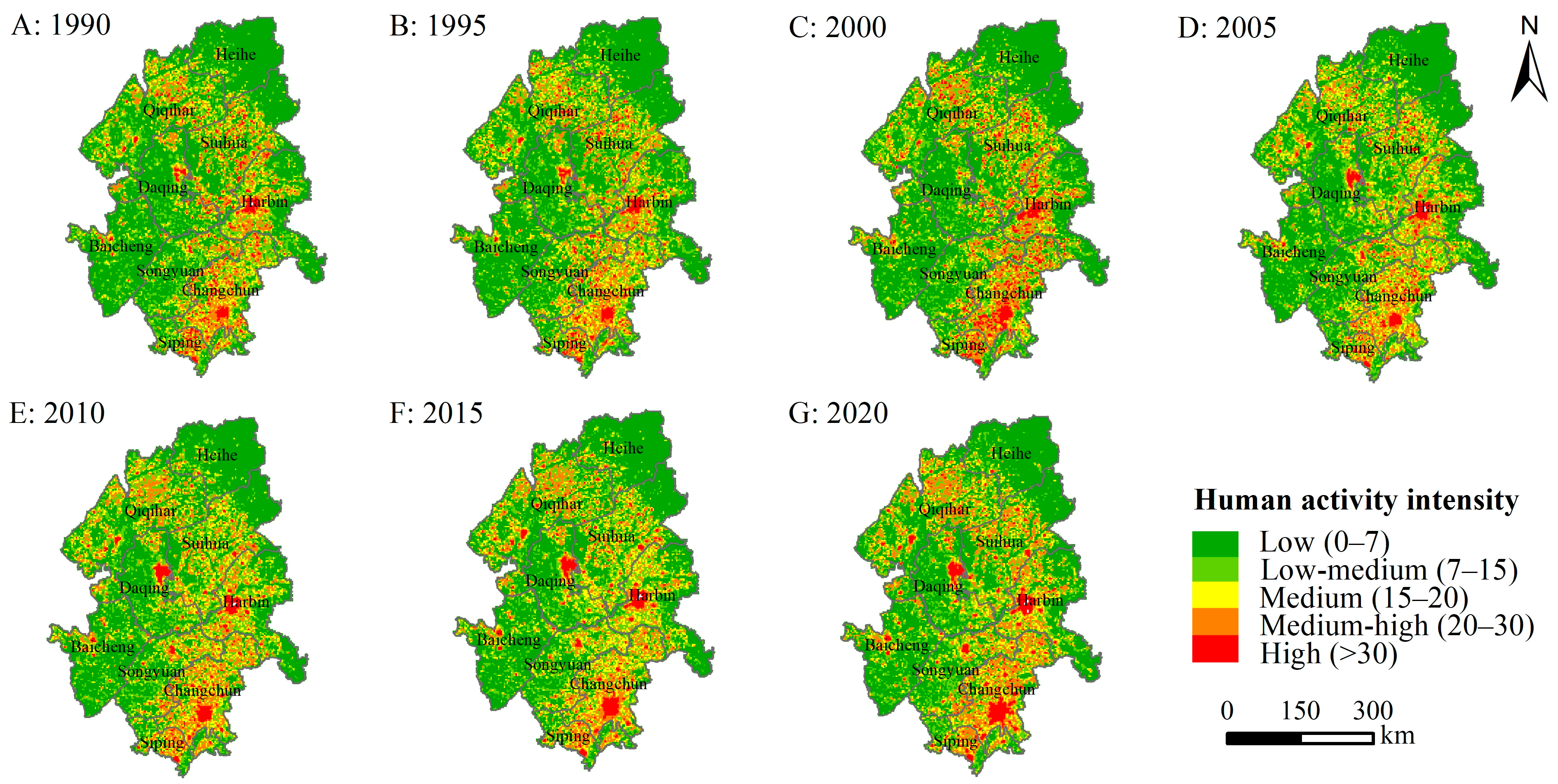
Figure 8.
Spatial distribution of human activity intensity in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020.
For the temporal dimension, the highest proportion of the low HAI level showed an overall slowly declining tendency (decreased by 10.14%), and the medium-low HAI level exhibited a slight decrease (reduced by 4.27%). However, the medium-high and medium HAI levels showed a fluctuating upward trend generally (increased by 25.78%), confirming that the study area’s HAI gradually increased. Moreover, the high HAI level gradually shrank after reaching the peak in 2000, occupying 4.16% (Figure 7).
For the spatial dimension, HAI was generally characterized by a low level in the northeast and southwest, and a high level in the middle and southeast during 1990–2020 (Figure 8). The high HAI level mostly occurred in Qiqihar, Suihua, Harbin, and Changchun and was dispersed as dots in the urban centers, including Harbin, Changchun, and Daqing, which are relatively economically developed regions. The medium-high HAI level overlapped with the medium HAI level in space and was distributed in the shape of a “7”. The areas with a low HAI level were mainly located in the ecological space, including forestland areas in the northeastern and eastern regions as well as wetland and water area in the western part of the region.
3.4. Analysis of Coupling Coordination Degree between HAI and ESV
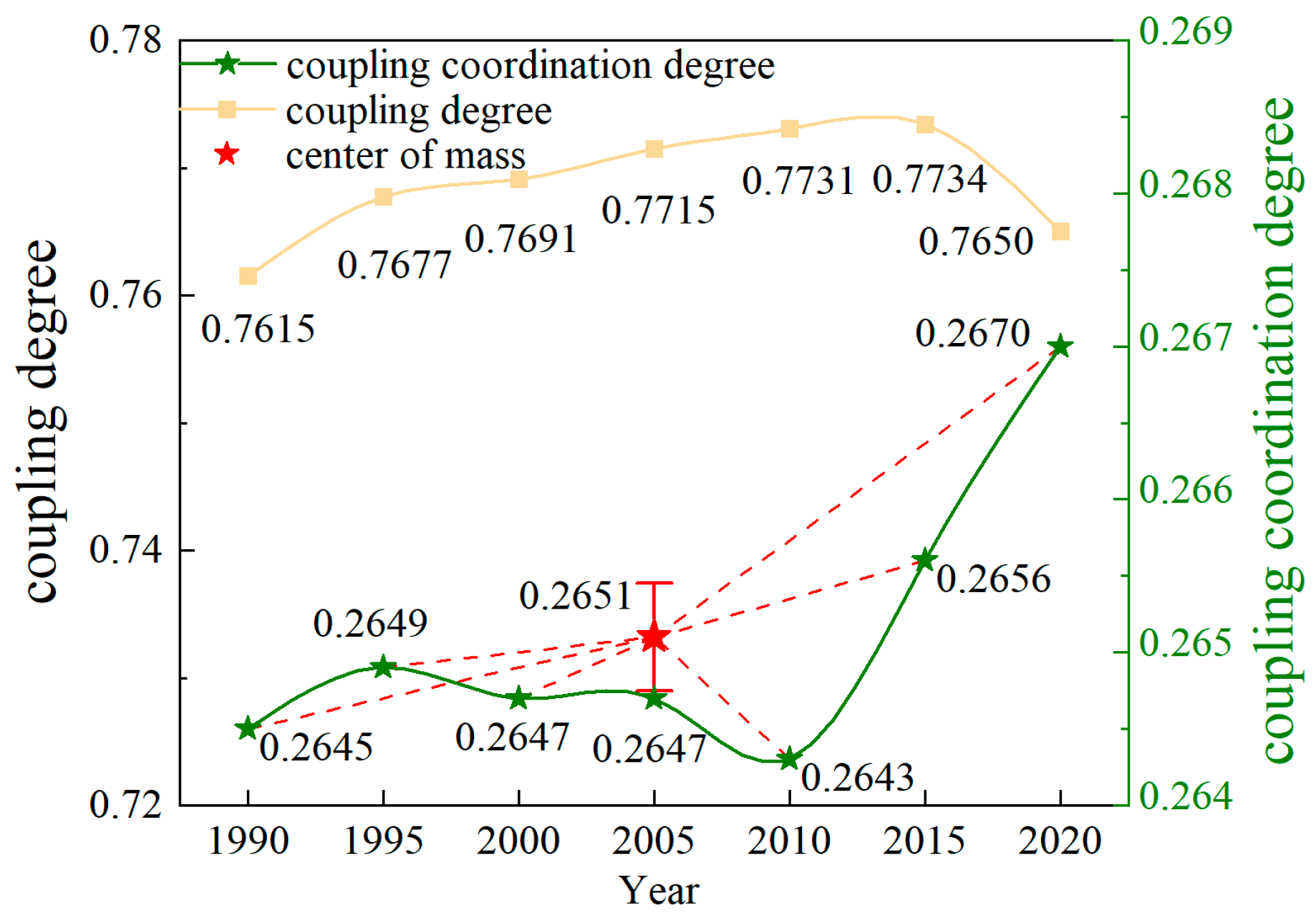
The coupling degree and coordination degree of HAI and ESV in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 were calculated based on Formulas (9)–(11) (Figure 9). The coupling degree was relatively stable and within the range of 0.7–0.8, which was in the running-in stage [13], indicating that HAI and ESV interacted with each other closely. Meanwhile, the coordination degree increased from 0.2645 in 1990 to 0.2670 in 2020, and the value of “center of mass” was 0.2651, revealing that the coordination level was in a moderate disorder stage [62], but it clearly showed an upward trend. This study indicates that, although the high HAI level had an adverse effect on the ecosystem service, the two systems are transitioning from conflict to coordination.
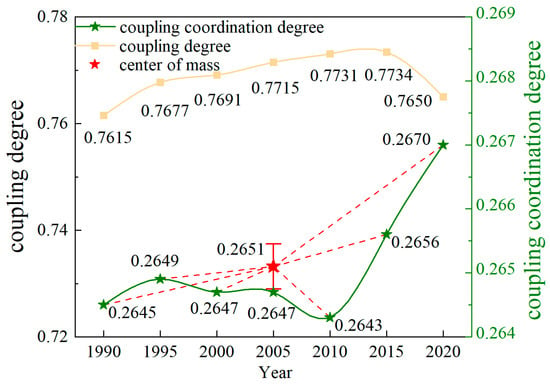
Figure 9.
The coupling degree and coupling coordination degree between ESV and HAI from 1990 to 2020 in the Songnen Plain.
3.5. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of HAI and ESV
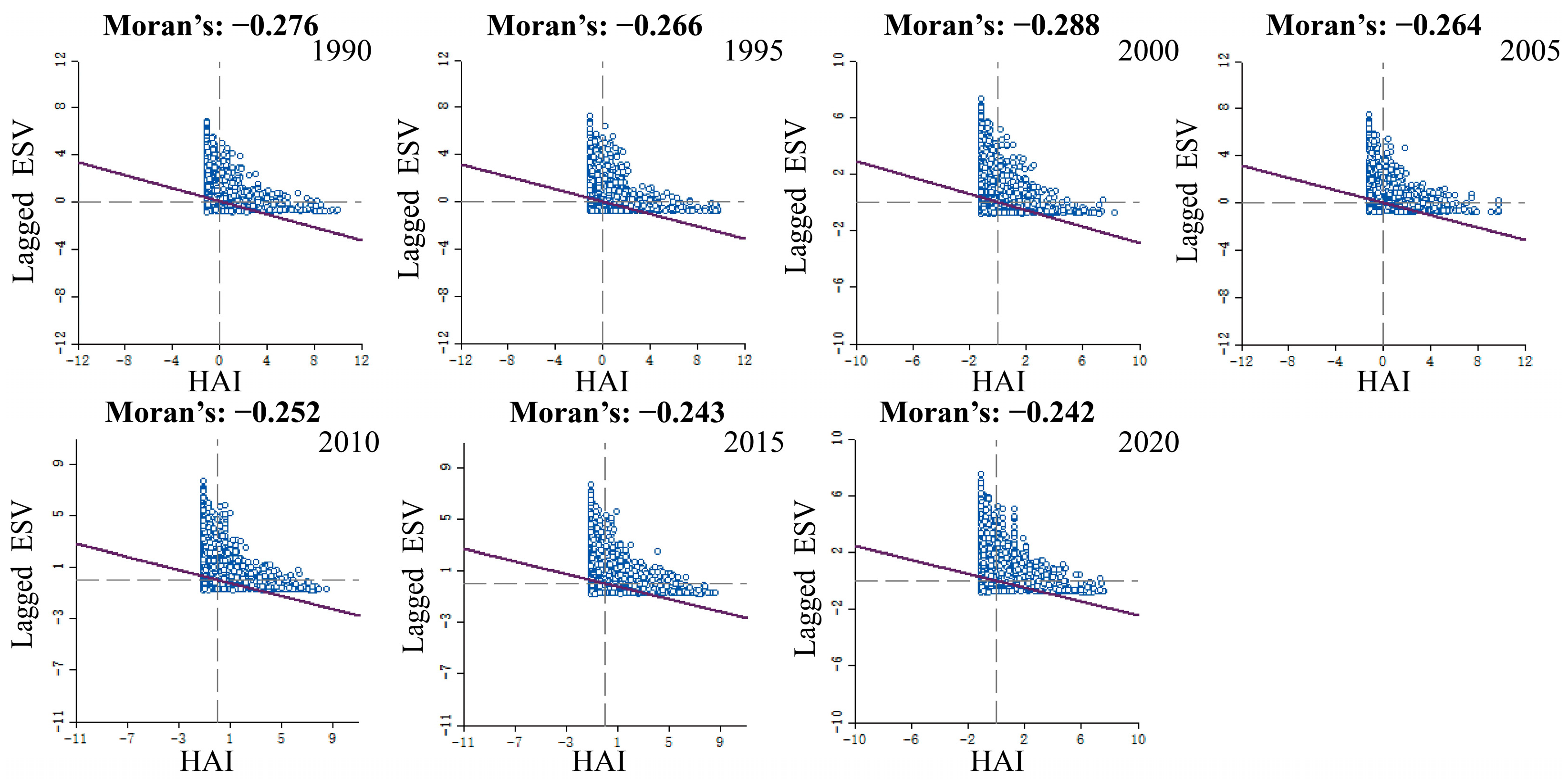
Based on the bivariate spatial autocorrelation model, we constructed the spatial weight matrix and plotted a Moran’s I scatterplot by using the GeoDa spatial analysis tool (Figure 10). The global Moran’s I values between HAI and ESV were significant with P = 0.001 at 99.9% confidence level and were −0.276, −0.266, −0.288, −0.264, −0.252, −0.243, and −0.242, respectively, for the seven years. The results indicate that there is a negative spatial correlation between the two in the study area. During 1990–2020, the Moran’s I values were all less than 0 and had the weakest correlation in 2020, indicating that human activity and ecosystems are shifting from conflict to coordination. The results can be corroborated by the study on the degree of coupling coordination.
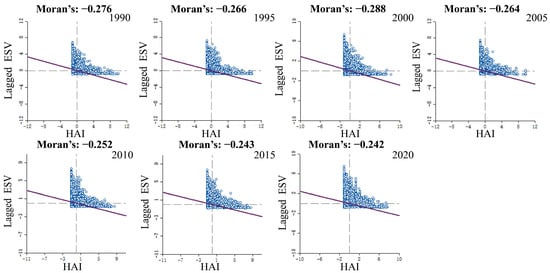
Figure 10.
Songnen plain ESV and HAI Moran’s I.
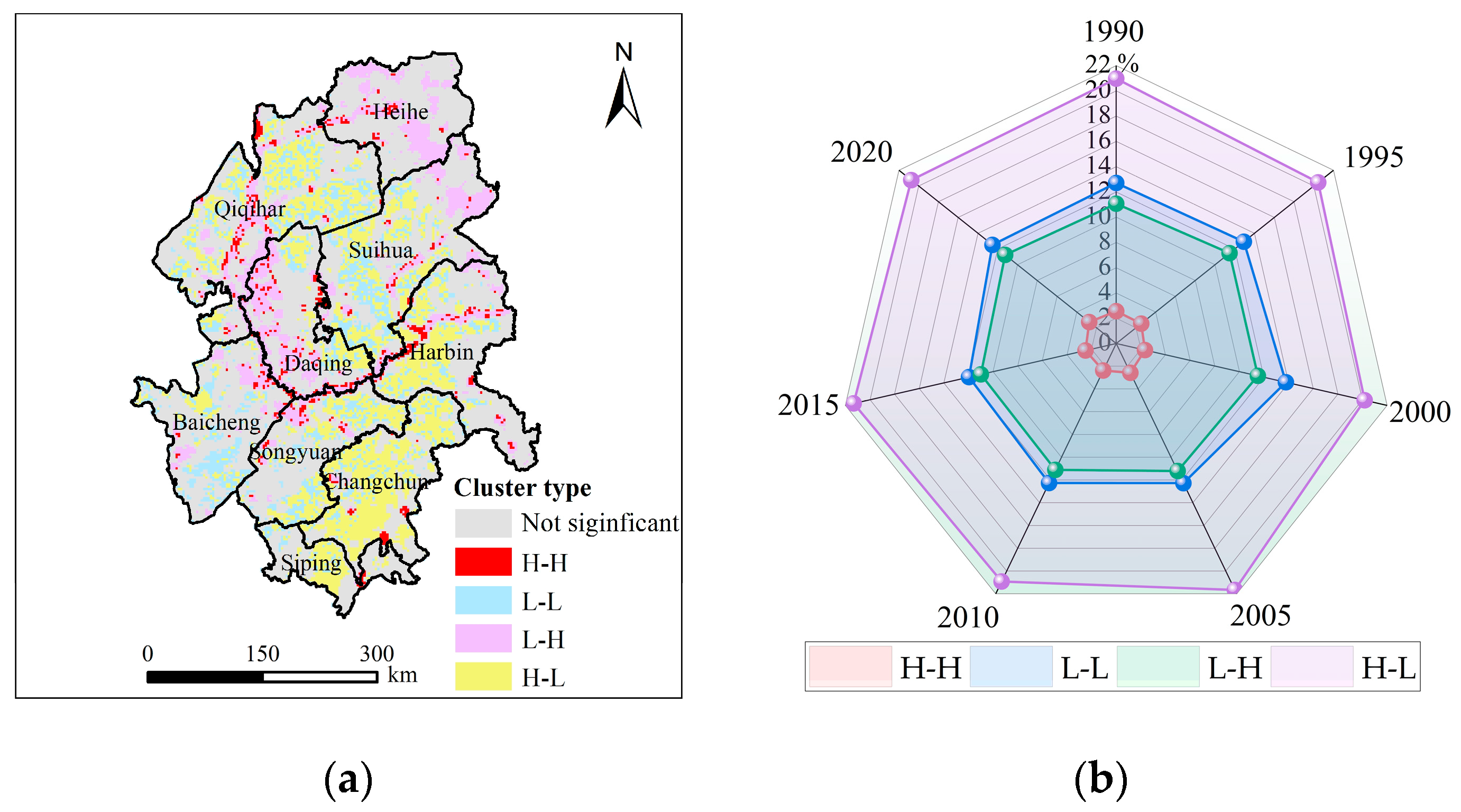
By using the local spatial autocorrelation analysis, the bivariate LISA clustering map of HAI and ESV in the study area was obtained (Figure 11a). In Figure 11a, H-H stands for high HAI and high ESV; L-L denotes low HAI and low ESV; L-H signifies low HAI and high ESV; and H-L represents high HAI and low ESV. Taking the 2020 LISA clustering map as an example, the region had significant spatial heterogeneity. The areas with the H-L cluster had the widest distribution (20.75% of the total area), concentrating in the majority of Changchun, the western part of Harbin, the eastern part of Qiqihar, and the northern and southern regions of Suihua. The L-H areas mainly occurred in the water area and the eastern forestland. The areas with H-H cluster were scattered in the study area, accounting for only 2.73% of the region (Figure 11b). The L-L areas were mainly located in the parts of Qiqihar, Suihua, Baicheng, and Songyuan. In general, the study area was characterized by the clustering of H-L and L-H, and the scattered distribution of H-H and L-L.
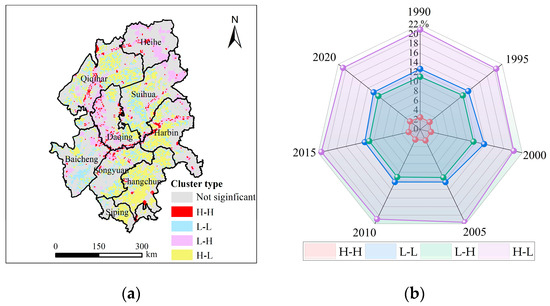
Figure 11.
LISA clustering map of HAI and ESV (a) and relative proportions of different clustering types to the grid (b).
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial–Temporal Change Characteristics of Land Use and ESV
This study identified the significant spatial and temporal heterogeneity of ESV in the study area. Temporally, ESV in the Songnen Plain exhibited a trend of initially declining and then increasing from 1990 to 2020. Moreover, the rate of decline slowed down distinctly after 2010 and reached the lowest value in 2015 (Table 6). This may be the result of the intensity and direction of human activities on the ecosystem, which changed the land use pattern and regional ESV. From 1990 to 2010, the Songnen Plain, serving as an important national commodity grain base and heavy industry base, faced the dual pressures of ensuring food security and promoting economic development [48]; therefore, the areas of wetland, forestland, grassland, and water area declined considerably, while paddy field, dry land, and built-up land significantly increased (Table 4). The decline in ESV during this period is largely attributed to the conversion of natural ecosystems into artificial (semi-artificial) ones. After 2010, the rate of ESV decline slowed, and ESV bottomed out after 2015, which is related to the downturn in the regional economy, population outflow, the construction of ecological civilization, and the implementation of the second round of policies on returning farmland to forestland and grassland, etc. In detail, the population of the region decreased by 13%, from 4.19 107 people in 2010 to 3.65 107 people in 2020 [63,64], which greatly lessened the pressure on the ecological environment. Meanwhile, China put forward the goal of “ecological civilization construction” in 2007 [65]; subsequently, in 2012, ecological protection and sustainable socio-economic development were placed in equally important positions, deepening the concept of ecological protection [66]. Moreover, in 2014, China launched a new round of returning farmland to forestland (grassland and wetland) [67]. In the year 2015, policy documents such as the Guidelines on Accelerating Ecological Civilization and the Integrated Reform Plan for Promoting Ecological Civilization were successively issued [66]; concurrently, relevant measures were implemented in order to improve the eco-environment, such as the drawing of the ecological protection red line and compensating for ecological protection activities [66]. These policies and measures had a positive impact on stabilizing and increasing the area of natural ecosystems and improving ecosystem service capabilities, which enabled ESV increases. In terms of the degree of change in various service functions, the ESV of water supply experienced the most significant decline, followed by hydrological regulation, esthetic landscape, and biodiversity (Figure 4). In the Songnen Plain, due to climate warming, the decline of precipitation [68], and the expanding of croplands (paddy fields and dry lands) (Table 4), the high water resource demand for agricultural irrigation [69,70] has led to a significant decline in the ESV of water supply. In addition, the long-term transformation of natural ecosystems to artificial (semi-artificial) ones in the study area (Table 5) diminished the functions of biodiversity and hydrological regulation, which in turn weakened the value of the corresponding ecosystem services. Spatially, regions with high ESV values were primarily concentrated in ecological areas such as water areas, wetlands, and forestland, while areas with low ESV values were mainly located in areas with intensive human activities and ecological fragility (dry land, built-up land, and unused land). Overall, this spatial pattern is related to the fact that natural ecosystems have higher ecosystem service value equivalents and provide more ESV than artificial (semi-artificial) ones.
4.2. The Feedback Mechanism between HAI and ESV
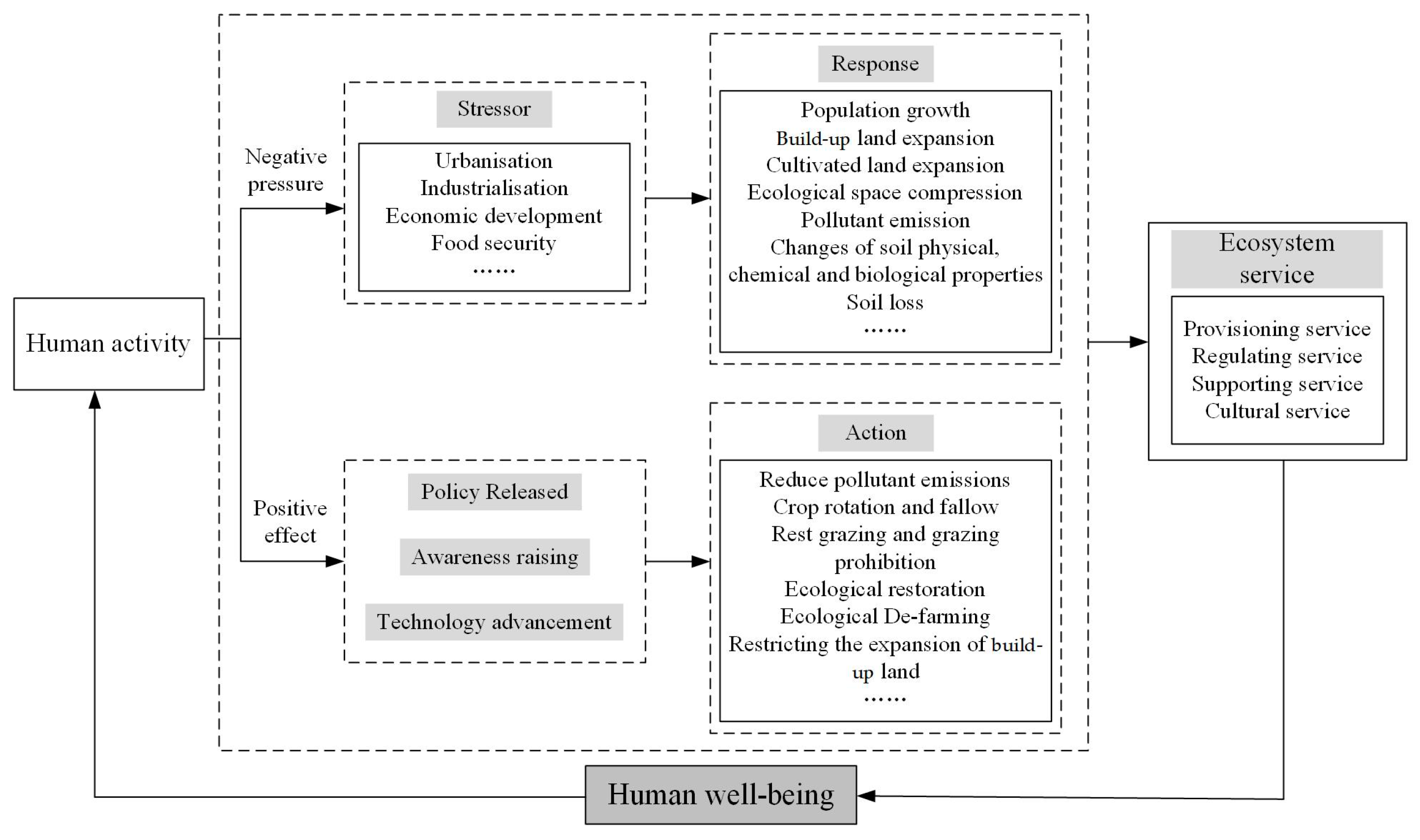
The results of the coupling coordination degree between HAI and ESV illustrated that human activities and ecosystem services were closely related and interactive (Figure 9). This is consistent with previous studies [13,16,37]. Zhang et al. [13] analyzed the coupling relationship between human activities and ESV in Xinjiang during 2000–2015 based on the coupling degree model, and the results demonstrated that the two were highly coupled (all higher than 0.797), indicating a strong interaction. Huang et al. [37] observed that there was a non-linear coupling relationship between human footprint and ESV in the Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration from 2000 to 2020, with mutual influences and constraints. Eigenbrod et al. [71] concluded that there would be an interaction between urbanization and ecosystem service provision in the UK, meaning that ecosystem services were affected by human activities. The main reason for the mutual feedback between human activities and ecosystem service is that human production and survival are inseparable from the support of ecological products and ecosystem service functions. For example, provision services provide raw materials such as food and wood for human survival, and cultural services fulfil spiritual pleasures [1,72]. Meanwhile, human activities also have an effect on the ecosystem by altering the structure and function of the ecosystem [73,74], which includes negative pressure [74,75,76] and positive effect [77] (Figure 12). It can be seen that human activities and ecosystem services are interrelated and mutually restrained.
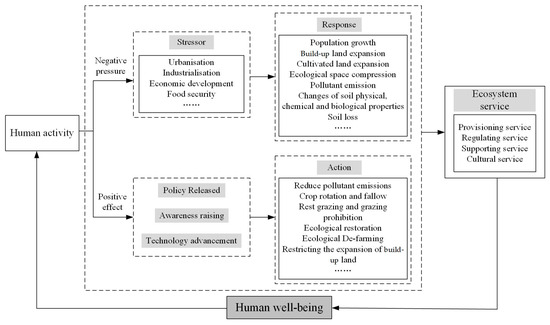
Figure 12.
Relationship between human activity and ecosystem service (modified and integrated through [13,75]).
Furthermore, the temporal pattern of the coordination degree and the bivariate spatial autocorrelation between ESV and HAI in the Songnen Plain showed that high HAI levels exerted a strong negative impact on ESV, but they are transitioning from conflict to coordination. The results demonstrated that the positive effects of human activities on ecosystems in the study area were gradually increasing, and the negative pressures were lowering steadily (Figure 9 and Figure 10). Relevant studies have shown that human activities had varied bearing on ecosystems in different regions and stages of socio-economic development [13,77,78]. Zhang et al. [13] pointed out that, since the agricultural expansion from 2000 to 2015, the ESV in Xinjiang declined with the exception of the value of food supply, indicating an overall negative influence of human activities on the ESV in the region. Sinchembe and Ellery et al. [78] noticed that the hydrological health of wetlands in South Africa has suffered from road construction and invasive alien plants, resulting in wetland degradation and a reduction in the supply capacity of wetland indirect ecosystem services, suggesting a negative implication of human activities on wetland ecosystems. Conversely, Mao et al. [77] found that ecological conservation policies and ecological projects can increase ecological land and improve regional ecosystem service capacity, which suggested that human activities can aid the betterment of ecosystem services as well. The possible mechanisms for the impact of human activities on ecosystems are as follows: In the stage of rapid urban development, along with the advancement of urbanization, industrialization, and agricultural modernization, human beings intend to achieve urban development and economic growth through the expansion of built-up land and cropland, as well as the compression of ecological space [79]. At the same time, high-intensity human activities also affect the physical, chemical, biological, and hydrological properties of the soil [8,80]. Such changes in the quantity and quality of ecosystems bring about the alterations in ecosystem structure and function and the decline of ecosystem service capacity [37,81]. When ecosystems reach a certain level of degradation and begin to constrain socio-economic development, the government is inclined to enact ecological conservation policies; simultaneously, with the deepening of the concept of ecological conservation and the promotion of ecological conservation technology, humans tend to balance economic development and ecological conservation [77]. For example, measures such as crop rotation and fallow, rest grazing, and grazing prohibition are adopted to improve the ecological service capacity of cropland and grassland [82]; the red line of the urban development boundary is delineated to restrict the expansion of built-up land; Ecological De-farming is promoted to increase the supply area of ecosystem service [46]; and the improvement of ecosystem service capacity is achieved by reducing pollutant emissions and through ecological restoration [77] (Figure 12).
4.3. Policy Implications
Benefiting from ecological conservation policies and its implementation, pressures on ecological systems induced by human activities have been alleviated to some extent (the proportion of the high HAI level in the study area decreased (Figure 7)). Nevertheless, most of these policies were promoted at the national level and fell short of considering the special ecosystem structure and function and the socio-economic development situation of the Songnen Plain. In addition, the research area also undertakes multiple tasks such as revitalizing Northeast China, ensuring national food and ecological security, protecting the black soil, and facing the challenges of climate change. Taking into account the regional characteristics, spatial differences, and climate challenges, the following recommendations can be given.
Firstly, differentiated policies should be formulated to achieve accurate management in heterogeneity areas. In the H-L areas with relatively well developed economic activity, such as Changchun City, Harbin City, and Qiqihar City (Figure 11a), the occupation of ecological land and cropland by build-up land should be strictly controlled, and the existing build-up land should be fully used. Additionally, green industries should be actively developed to reduce pollution emissions. Whereas, in the L-H zones, namely the areas of water area, wetland, and forestland (Figure 11a), it is urgent to identify ecological protection zones, strictly abide by ecological red lines, construct ecological corridors, and enhance the regional ecosystem service capacity. For cropland that needs to harmonize grain production and ecological services, the red line for 1.8 billion acres of cropland should be safeguarded to prevent the uncontrolled expansion of cropland; meanwhile, conservation tillage and other technologies should be promoted to increase soil organic matter, protect the biodiversity of cropland ecosystems, reduce the dosage of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and improve ecosystem service capacity and health [82].
Secondly, it is necessary to formulate targeted ecological policies for ecologically fragile areas to curb ecosystem deterioration. In the Songnen Plain, there are many rolling hilly regions (Keshan County, Baiquan County, and Kedong County in Qiqihar City) with severe soil and water erosion [36]. In these areas, service functions of cultivated ecosystems, such as soil conservation, water supply, and food production, have been declining under the dual influence of natural and human factors. Moreover, the region also includes ecologically fragile areas such as saline-alkali land [9] and agro-pastoral ecotone [83]. In light of this, the intensity of human disturbance in the fragile ecological environment should be weakened, and the ecological restoration should also be implemented. In addition, it is essential to monitor the carrying capacity and carrying threshold of the ecosystem dynamically, provide early warning of ecological disasters, and restore the degraded ecosystem.
Thirdly, the government should unveil ecological policies to actively respond to the challenges posed by climate warming on the regional ecosystems. Previous studies have shown that climate warming and economic interests have led to a gradual expansion of rice planting areas and a northward shift of the cultivation area [69,77]. This phenomenon, the significant expansion of the paddy field area at the end of the study period in the Songnen Plain, is also proved by this study (Table 4). The expansion of paddy fields, along with the existing dry land planting, will further aggravate the consumption of water resources, lower the capacity of water supply in ecosystem services, increase additional pressure on groundwater, river, and lake resources [13,84], and also bring about soil degradation and a series of related problems [85]. Consequently, policymakers ought to enact relevant policies in response to climate change, controlling the scale of dry land-to-paddy conversion and implementing water-saving irrigation technology and soil and water conservation measures so as to promote the coordinated development of humans and ecosystems.
Finally, it is worth mentioning that, apart from the Songnen Plain, such grain production areas worldwide as the Midwestern United States, Brazil’s Cerrado Region, and the Pampas Region of Argentina [86,87,88] may face multiple challenges in sustainable food production, ecosystem conservation, economic development, and adaptation to global climate change. These regions (and their countries), when formulating sustainable development policies, could conduct research based on the “assessment-correlation-policy” framework of this study to enhance the specificity and scientific rigor of their policies. They could also apply the “modified Equivalent Factor Method” and the “HAI Assessment Model” from this study, which adequately consider local social, economic, and natural conditions, to assess ESV and HAI, offering high applicability. Based on further understanding of the spatiotemporal correlation between regional ESV and HAI and using the research outcomes and policy measures from the Songnen Plain as a reference, targeted strategies could be developed for diverse regions and ecologically fragile areas. These strategies may include monitoring ecosystem dynamics, controlling land conversion, expanding ecological reserves, and implementing ecological technologies, aiming to achieve regional socio-economic synergy and sustainable development.
5. Conclusions
In this research, we analyzed the Songnen Plain land use changes using land use data every five years between 1990 and 2020 and measured ESV and HAI, employing the modified Equivalent Factor Method and HAI Assessment Model (based on land use, night-time light, and population spatial distribution data). Furthermore, we explored the spatiotemporal correlations between the two utilizing the coupled coordination degree and the bivariate spatial autocorrelation model. The conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The dominant land types in the Songnen Plain from 1990 to 2020 were dry land (about 49.2–52.4% of the total area), forestland (about 14.0–14.6% of the total area), grassland (about 7.5–10.7% of the total area), and wetland (about 7.0–8.9% of the total area); overall, the region represented the following characteristics: cropland converted into build-up land, ecological land converted into cropland, and dry land transformed into paddy fields.
- (2)
- From 1990 to 2020, ESV declined from 950.96 billion yuan in 1990 to 836.31 billion yuan in 2015, and increased to 864.60 billion yuan in 2020. The ESV of natural ecosystems showed a declining tendency, while artificial (semi-artificial) ones showed a rising trend. Except for the significant increase in ESV of food production (5.44%), the ESV of other ecosystem service functions showed a downward trend. Among them, the ESV of water supply decreased dramatically (31.23%). In terms of spatial distribution, the ESV in the western and northeastern regions was relatively high, and the ESV in other regions was the opposite. The high ESV areas were mainly distributed in the ecological areas such as water areas, wetlands, and forestland. The distribution of the low ESV areas coincided with the areas of intensive human activities and ecological fragility, such as dry land, build-up land, and unused land. Moreover, ESV increased significantly in the northeast during the study period.
- (3)
- During 1990–2020, HAI showed an upward trend, and the spatial distribution characteristic was generally low in the northeast and southwest, as well as high in the middle and southeast. The high HAI levels gradually shrank after reaching their peak in 2000 and were dispersed as dots in the urban centers, including Harbin, Changchun, and Daqing, which are relatively economically developed regions; the areas of medium-high HAI levels overlapped with the areas of medium HAI levels in a ‘7’ shape; the areas of low HAI levels were highly coincident with the ecological space.
- (4)
- HAI had a strong interaction with ESV (the coupling degree was between 0.7 and 0.8), and the degree of coordination was in a moderate disorder (from 0.2645 to 0.2670). Although human activities had a negative impact on ESV, they were transitioning from conflict to coordination. For the spatial dimension, the two systems were H-L and L-H clustering and H-H and L-L scattered distribution.
- (5)
- In the future, the decision makers should formulate differentiated policies. In economically developed areas (H-L areas) like Changchun, Harbin, and Qiqihar, strict control over land occupation and the promotion of green industries are crucial. For ecological zones (L-H areas), it is urgent to strictly abide by ecological red lines and construct ecological corridors. For fragile regions, it is essential to weaken the intensity of human disturbance and implement targeted restoration efforts. Additionally, they should control the scale of dry land-to-paddy conversion, promote water-saving irrigation technologies, and implement soil and water conservation measures to address climate warming.
- (6)
- The “assessment-correlation-policy” research framework proposed in this study is suitable for characterizing and understanding the mechanisms of ecosystem services and human activities. The approaches employed in this study, which fully consider regional uniqueness, data availability, and inter-regional comparability, can be applied to quantitatively studying the feedback relationship between ecosystem services and human activities in other similar regions. Additionally, the policies proposed in this study could be extended to other major grain-producing areas globally, offering Chinese theoretical insights and practical references for these regions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.G. and G.D.; methodology, X.G. and M.K.; software, Y.Y. and W.S.; validation, Y.Y., Y.Z. and W.S.; formal analysis, Y.Y.; investigation, Y.Y. and G.G.; resources, J.S. and G.G.; data curation, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.G., Y.Y. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, M.K. and G.D.; visualization, J.S.; supervision, X.G. and G.D.; funding acquisition, X.G. and G.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Northeast Agricultural University Academic Backbone Project, grant number 20XG22, the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2021YFD1500101, and the Program of China Scholarship Council, grant number 202306610035.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset is available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; de Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daily, G.C. Nature’s Services: Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 34, p. 534. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, B.; Turner, R.K.; Morling, P. Defining and classifying ecosystem services for decision making. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Mooney, H.; Agard, J.; Capistrano, D.; Defries, R.; Diaz, S.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.; Oteng-Yeboah, A.; Pereira, H.; et al. Science for managing ecosystem services: Beyond the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, T.; Fu, B. The value of ecosystem services in China: A systematic review for twenty years. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 52, 101365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; DeFries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global Consequences of Land Use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Fu, B.; He, C.; Lü, Y. Variation of ecosystem services and human activities: A case study in the Yanhe Watershed of China. Acta Oecol. 2012, 44, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Yang, H.; Bu, K. Effects of land use change on ecosystem services value in West Jilin since the reform and opening of China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, K.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Temporal and spatial heterogeneity of land use, urbanization, and ecosystem service value in China: A national-scale analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 137911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Lubchenco, J.; Melillo, J.M. Human Domination of Earth’s Ecosystems. Science 1997, 277, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Bruno, J.F.; Casey, K.S.; Ebert, C.; Fox, H.E.; et al. A Global Map of Human Impact on Marine Ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xia, F.; Yang, D.; Huo, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, H. Spatiotemporal characteristics in ecosystem service value and its interaction with human activities in Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Feng, C.; Xu, N.; Guo, L. Spatial heterogeneous relationship between ecosystem services and human disturbances: A case study in Chuandong, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.; Jiang, W.; Ling, Z.; Hou, P.; Deng, Y. Evaluating the potential impacts of land use changes on ecosystem service value under multiple scenarios in support of SDG reporting: A case study of the Wuhan Urban Agglomeration. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, F.; An, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal variations and coupling of human activity intensity and ecosystem services based on the four-quadrant model on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140721. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic changes in the value of China’s ecosystem services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnveden, G.; Moberg, Å. Environmental systems analysis tools—An overview. J. Clean. Prod. 2005, 13, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscieme, L.; Pulselli, F.M.; Marchettini, N.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S.; Sweeney, S. Emergy and ecosystem services: A national biogeographical assessment. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 7, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Leng, Y.; Zheng, D.; Li, S. Ecological assets valuation of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Nat. Resour. 2003, 18, 189–196. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, C. Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2008, 23, 9. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, C. The Value of ecosystem services in China. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Yu, H.; Tiando, D.S.; Rong, Y.; Luo, W.; Eme, C.; Ou, S.; Li, J.; Liang, Z. Impacts of human activities on ecosystem service value in Arid and Semi-Arid Ecological Regions of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Tang, Q. Human activity intensity of land surface: Concept, methods and application in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1349–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Zhou, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Guo, R.; Chen, S. Assessing the dynamics of human activity intensity and its natural and socioeconomic determinants in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Geogr. Sustain. 2023, 4, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, D.; Moreno-Sanchez, R.; Torres-Rojo, J.M.; Moreno-Sanchez, F. Estimation of human induced disturbance of the environment associated with 2002, 2008 and 2013 land use/cover patterns in Mexico. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 66, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ao, Y.; Han, L.; Kang, S.; Sun, Y. Effects of human activity intensity on habitat quality based on nighttime light remote sensing: A case study of Northern Shaanxi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.; Beazley, K.F. Changes in Human Population Density and Protected Areas in Terrestrial Global Biodiversity Hotspots, 1995–2015. Land 2018, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhatip, H.; Afşin, M.; Kuşçu, L.; Dirik, K.; Kurmaç, Y.; Kavurmacı, M. Influences of human activities and agriculture on groundwater quality of Kayseri-Incesu-Dokuzpınar springs, central Anatolian part of Turkey. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 490–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhou, D.; Jiang, G. Conflict or Coordination? Multiscale assessment of the spatio-temporal coupling relationship between urbanization and ecosystem services: The case of the Jingjinji Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Luo, L. Summary and prospect of spatialization method of human activity intensity: Taking the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as an example. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2021, 43, 1582–1593. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Correa Ayram, C.A.; Etter, A.; Díaz-Timoté, J.; Rodríguez Buriticá, S.; Ramírez, W.; Corzo, G. Spatiotemporal evaluation of the human footprint in Colombia: Four decades of anthropic impact in highly biodiverse ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, H.; Kang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal correlation between human activity intensity and surface temperature on the north slope of Tianshan Mountains. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 1244–1259. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Fang, B.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, C. Scale response and spatiotemporal correlations between landscape ecological risk and human activitiy intensity in the Yangtze River Delta region. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 210–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Song, G. Human disturbance changes based on spatiotemporal heterogeneity of regional ecological vulnerability: A case study of Qiqihaer city, northwestern Songnen Plain, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z. Spatiotemporal coupling analysis between human footprint and ecosystem service value in the highly urbanized Pearl River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudsepp-Hearne, C.; Peterson, G.D.; Tengö, M.; Bennett, E.M.; Holland, T.; Benessaiah, K.; MacDonald, G.K.; Pfeifer, L. Untangling the Environmentalist’s Paradox: Why Is Human Well-being Increasing as Ecosystem Services Degrade? Bioscience 2010, 60, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunyawat, S.; Shrestha, R.P. Assessing Land Use Change and Its Impact on Ecosystem Services in Northern Thailand. Sustainability 2016, 8, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q. Spatial correlation analysis between human disturbance intensity (HDI) and ecosystem services value (ESV) in the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochtcheeva, L.; Singh, A. An Assessment of Risks and Threats to Human Health Associated with the Degradation of Ecosystems; UNEP: Nairobi, Kenney, 2000; pp. 2–27. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Ren, J.; Lu, N.; Gao, Z.; Dong, X.; Kong, W. Relationships between ecosystem services and human well-being changes based on carbon flow—A case study of the Manas River Basin, Xinjiang, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019, 37, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintas-Soriano, C.; Castro, A.J.; Castro, H.; García-Llorente, M. Impacts of land use change on ecosystem services and implications for human well-being in Spanish drylands. Land Use Policy 2016, 54, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Pan, J.; Bi, F. Can human activities enhance the trade-off intensity of ecosystem services in arid inland river basins? Taking the Taolai River asin as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Yao, X.; Yun, W.; Ma, J.; Gao, L.; Li, P. Scenario simulation of the tradeoff between ecological land and farmland in black soil region of Northeast China. Land Use Policy 2022, 114, 105991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D. Relationships between Supply and Demand of Ecosystem Services in the Songnen Plain. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 1769–1776. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, C.; Xiang, H.; Chen, M.; Du, H. Spatiotemporal Variability in Ecological Vulnerability of Songnen Plain from 1980 to 2020. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 43, 366–374. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.; Song, K.; Liu, D.; Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Guo, Z. Research on Effects of Land Use Change on Regional Ecosystem Service Values of Songnen Plain, China. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2008, 18, 149–154. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Ren, C.; Jia, M. Monitoring the Evolution of Wetland Ecosystem pattern in Northeast China from 1990 to 2013 Based on Remote Sensing. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 31, 1253–1263. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.; Na, X.; Zang, S. Research on the evaluation of wetland ecosystem services of the Songnen Plain during 1980—2010. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2017, 29, 193–200. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- RESDC. Available online: http://www.resdc.cn/ (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Li, L.; Tang, H.; Lei, J.; Song, X. Spatial autocorrelation in land use type and ecosystem service value in Hainan Tropical Rain Forest National Park. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNKI. Available online: http://data.cnki.net/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Harvard Dataverse. Available online: https://dataverse.harvard.edu/ (accessed on 20 September 2023).
- Wu, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Chang, Z. Developing Improved Time-Series DMSP-OLS-Like Data (1992–2019) in China by Integrating DMSP-OLS and SNPP-VIIRS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, X. Regionalization and distribution pattern of vegetation Northeast China. J. Plant. Ecol. 2010, 34, 1359–1368. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Yu, C. Effects of climate change on the distribution of the main vegetation types in Northeast China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6511–6522. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Song, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, D.; Ren, C.; Luo, L.; Yang, T.; Huang, N.; Hu, L.; Yang, H.; et al. Shrinkage and fragmentation of grasslands in the West Songnen Plain, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Lu, Z.; Wei, D.; Lei, G. Effects of land use/cover change (LUCC) on the spatiotemporal variability of precipitation and temperature in the Songnen Plain, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Analysis of the evolution of ecosystem service value and its driving factors in the Yellow River Source Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; An, Y.; Shi, F.; Dong, S.; Liu, G. Spatio-temporal evolution scenarios and the coupling analysis of ecosystem services with land use change in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Fan, Z.; Feng, W.; Yuxin, C.; Keyu, Q. Coupling coordination degree spatial analysis and driving factor between socio-economic and eco-environment in Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 135, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilongjiang Statistical Yearbook. 2021. Available online: http://tjj.hlj.gov.cn/tjj/c106782/common_zfxxgk.shtml (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Jilin Statistical Yearbook. 2021. Available online: http://tjj.jl.gov.cn/tjsj/tjnj/ (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Wang, N.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Y. Comparing eco-civilization theory and practice: Big-data evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 380, 134754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.G.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, W.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, J. Development process and characteristics of China’s ecological protection policy. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1656–1667. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Liu, M. The Development Process, Current Situation and Prospects of the Conversion of Farmland to Forests and Grasses Project in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2022, 13, 120–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Jiang, M. Combined effects of multi-land use decisions and climate change on water-related ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of climate change on paddy expansion and potential adaption strategies for sustainable agriculture development across Northeast China. Appl. Geogr. 2022, 141, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, K.; Li, M. Assessing the impact of meteorological and agricultural drought on maize yields to optimize irrigation in Heilongjiang Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrod, F.; Bell, V.A.; Davies, H.N.; Heinemeyer, A.; Armsworth, P.R.; Gaston, K.J. The impact of projected increases in urbanization on ecosystem services. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNEP. Ecosystem and Human Well-Being-Synthesis; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Metzger, M.J.; Rounsevell, M.D.A.; Acosta-Michlik, L.; Leemans, R.; Schröter, D. The vulnerability of ecosystem services to land use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, A.; Marando, F.; Manes, F. Mismatch of regulating ecosystem services for sustainable urban planning: PM10 removal and urban heat island effect mitigation in the municipality of Rome (Italy). Urban For. Urban Green 2021, 57, 126938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, R.J. A revised framework for coupled human and natural systems, propagating thresholds, and managing environmental problems. Phys. Chem. Earth 2011, 36, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhan, J.; Zhao, F.; Yan, H.; Zhang, F.; Wei, X. Impacts of urbanization-induced land-use changes on ecosystem services: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Metropolitan Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; He, X.; Wang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Man, W.; Jia, M.; Ren, C.; Zheng, H. Diverse policies leading to contrasting impacts on land cover and ecosystem services in Northeast China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinchembe, M.; Ellery, W. Human impacts on hydrological health and the provision of ecosystem services: A case study of the eMthonjeni-Fairview Spring Wetland, Grahamstown, South Africa. Afr. J. Aquat. Sci 2010, 35, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, P.; Vera, A.; Tulla, A.F.; Salvati, L. Beyond urban–rural dichotomy: Exploring socioeconomic and land-use processes of change in Spain (1991–2011). Appl. Geogr. 2014, 55, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Ren, Z.; Stringer, L.C. Effects of grazing and enclosure management on soil physical and chemical properties vary with aridity in China’s drylands. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzolari, C.; Tarocco, P.; Lombardo, N.; Marchi, N.; Ungaro, F. Assessing soil ecosystem services in urban and peri-urban areas: From urban soils survey to providing support tool for urban planning. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.; Lee, Y. Effects of land use change and crop rotation practices on farmland ecosystem service valuation. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, S.; Wen, Y.; He, C.; Wang, X.; Sheng, L.; Guo, Y.; Cao, Y. Projecting the response of ecological risk to land use/land cover change in ecologically fragile regions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Disse, M. Sustainable land and water management of River Oases along the Tarim River. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2016, 373, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Han, X.; Li, N. Research Progress of Black Soil in Northeast China. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2018, 38, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Burras, C.; Kravchenko, Y.; Duran, A.; Huffman, T.; Morras, H.; Studdert, G.; Zhang, X.; Cruse, R.; Yuan, X. Overview of Mollisols in the world: Distribution, land use and management. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 383–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basche, A.; Archontoulis, S.; Kaspar, T.; Jaynes, D.; Parkin, T.; Miguez, F. Simulating long-term impacts of cover crops and climate change on crop production and environmental outcomes in the Midwestern United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 218, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, E.; Rodrigues, A.; Martins, E.; Bettiol, G.; Bustamante, M.; Bezerra, A.; Couto, A.; Vasconcelos, V.; Schüler, J.; Bolfe, E. Cerrado ecoregions: A spatial framework to assess and prioritize Brazilian savanna environmental diversity for conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 232, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).