Abstract
There is limited analysis of the role of tourism in rural revitalization (RR) from a high-quality development perspective. To address this gap, this study analyzes the spatiotemporal patterns and coupling coordination degree (CCD) of tourism high-quality development (THD) and RR in the Silk Road Economic Belt from 2011 to 2020 using coupling coordination and gravity models. A geographic detector is employed to quantitatively elucidate the factors influencing the CCD. The findings are as follows. (1) The comprehensive RR level increased 86% from 2011 to 2020, whereas the THD level first increased and then decreased. The southwest region outperformed the northwest in RR and THD levels. (2) The CCD between RR and THD displayed various degrees of increase, with a spatial pattern of higher levels in the southwest and lower levels in the northwest. The spatial linkage strength of the CCD first increased and then decreased, with tighter linkages among the southwestern provinces. (3) Public fiscal expenditure, per capita GDP, and science and education spending significantly affected the CCD. In conclusion, the effective coordination of THD and RR requires a focus on their spatiotemporal coupling characteristics and the joint regulation of multiple factors.
1. Introduction
As a critical initiative for the rejuvenation of the Chinese nation in the new era, a rural revitalization (RR) strategy is essential for achieving agricultural modernization and reshaping urban–rural relationships [1]. Tourism, recognized as a strategic pillar of the national economy and a new impetus for RR, plays a key role in optimizing rural industrial structures, reconstructing rural production spaces, and increasing farmers’ income [2,3]. In the new high-quality development phase, the primary tasks and development goals of RR and tourism are endowed with new connotations and requirements. The 14th Five-Year Plan for Tourism Development underscores the need to promote tourism high-quality development (THD) and positions it as a key driver of RR [4]. Therefore, achieving harmonious and mutually beneficial RR and THD development within the framework of high-quality development has become a focal point in tourism and geographical research.
Rural reconstruction and revitalization have consistently been critical priorities for countries around the world. Under the influence of industrialization and urbanization, rural areas globally face common issues, such as low living standards, outdated industrial structures, and ecological pollution [5]. Since the 1950s, many Western countries have implemented various policies, such as rural development policies, new rural movements, and rural development visions, to promote structural and functional changes in rural areas [6,7,8]. It is widely believed that regional policy, sustainable transition, digital technology, and renewable resources are key factors in promoting rural development and revitalization [9]. Furthermore, the development process has evolved from theoretical analysis of implementation strategies to emphasizing resident and community participation [10]. For China, the introduction of the RR strategy in 2017 marked a significant step towards addressing the underdevelopment of rural areas [11]. Scholars have explored various aspects of RR, including its conceptual framework, development trajectory, implementation pathways, evaluation indicator systems, alignment with high-quality development, and Chinese-style modernization [12,13,14]. Research indicates that RR must emphasize key elements such as talent, land, and capital, leveraging these factors to facilitate urban–rural integration and tourism development during the process of agricultural modernization [15]. In quantitative research, many scholars have evaluated RR development levels at national, provincial, and village scales by constructing indicator systems in line with the “Twenty-Character Policy” for RR [16,17,18]. Findings reveal that China’s overall level of RR is relatively low, with considerable room for improvement in terms of high-quality development [19]. Additionally, there were marked regional disparities, with the eastern regions demonstrating higher levels of RR than the central and western regions. However, variations in research perspectives and indicator systems have led to different assessments of RR, and the mechanisms driving these changes remain unclear.
The tourism industry is widely recognized as a pivotal instrument for augmenting income, generating employment opportunities, and ameliorating urban–rural disparities, owing to its strong interconnectivity and wide coverage [20]. Nevertheless, despite China entering the era of mass tourism, contradictions persist in terms of insufficient development, low quality, and imbalanced supply and demand for tourism [21]. The tourism industry must explore innovative models and initiatives to enhance quality and efficiency, thereby fostering high-quality development. Scholarly research on THD has evolved from initial single-perspective analyses focusing on tourism service quality, tourism product quality, tourism economic growth, and tourism industry efficiency to multifactor, multi-perspective, and multidimensional interpretations [21,22,23]. Scholars commonly employ a combination of objective and subjective methods, including the entropy method, analytic hierarchy process, health-distance model, and expert scoring methods [21,24]. To construct evaluation indicator systems, scholars primarily measure the level of national, provincial, or specific type of THD from the perspectives of tourism efficiency, sustainable development theory, and the five major development concepts [25,26,27]. The results indicate significant regional disparities at the THD level, with notable spatial spillover effects in high-level regions [28]. Although the existing research has laid the foundation for qualitative and quantitative studies on THD, they have predominantly focused on interpreting the economic efficiency of tourism. However, this focus is not aligned with the comprehensive and complex requirements for high-quality development. Furthermore, given substantial regional economic disparities, research on the heterogeneity and dynamic evolution of high-quality tourism development remains inadequate and requires further enhancement.
As an essential bridge between the East and West, the Silk Road Economic Belt plays a significant role in promoting regional social, economic, and cultural connectivity. This region boasts abundant tourism resources and historical cultural relics; however, significant regional disparities in tourism development levels exist because of differences in geographical location and resource endowments. Current research on Silk Road tourism has primarily focused on tourism economics, cultural tourism heritage, tourism transportation, and their relationships with the ecological environment. However, studies analyzing the developmental levels and interactive relationships between THD and RR from a high-quality perspective are scarce. Therefore, this study considers the Silk Road Economic Belt as the research object to analyze the interactive relationships and driving mechanisms between THD and RR. The main questions addressed in this study are as follows: (1) What are the RR and THD levels? (2) What are the spatiotemporal evolutionary patterns of the coupling coordination degree (CCD) between RR and THD? (3) What are the key factors driving the CCD? This study aims to provide a reference for effectively coordinating the development of tourism and RR in the Silk Road Economic Belt and for policy implementation in the context of high-quality development.
2. Literature Review
In the context of high-quality regional development, the interactive relationship and impact mechanism between RR and THD have become the focus of academic attention. Tourism drives changes in rural spatial functions through its radiating influence, thereby accelerating the development of RR. Conversely, RR provides the necessary development space for THD by improving living environments, restructuring industries, and enhancing governance capabilities. Specifically, tourism plays a significant role in driving various aspects of rural development, including industrial growth, the ecological environment, cultural heritage preservation, and grassroots governance [3]. First, THD promotes the return of economic, human, and technological resources to rural areas. This influx facilitates local economic restructuring and the aggregation of related industries, such as agricultural product sales, homestay catering, and logistics, thus laying the foundation for industrial revitalization [29]. Moreover, the integration of technologies, such as artificial intelligence and big data, with rural industries under high-quality development promotes industrial upgradation and transformation. Second, the development of the tourism industry improves local production and living space infrastructure by guiding residents to adopt low-carbon green lifestyles and fostering an awareness of ecological conservation [30]. Third, THD fosters the reconstruction and transmission of a multidimensional rural culture. On the one hand, driven by capital and policy, physical cultural landscapes, such as settlements and agricultural landscapes, are preserved and restored [31]. On the other hand, tourism stimulates the preservation and adaptation of spiritual culture, such as cultural heritage, festivities, and folk activities [29], thereby enhancing residents’ cultural confidence and local identity and contributing positively to rural cultural revitalization. Lastly, the cultural consciousness and return of talent driven by THD elevate the governance awareness of grassroots autonomous organizations and optimize the governance system [32].
The development of RR also feeds back into the supply and demand of THD. RR promotes industrial development and increases residents’ income levels, which, in turn, stimulates the demand for cultural tourism [33]. Moreover, the reconstruction of rural living, ecology, and production spaces improves the image and attractiveness of tourist destinations, offering greater potential for tourism [34]. Additionally, RR employs rural civilization as a vehicle, fostering the integration of culture and tourism through the preservation and utilization of traditional rural culture. Despite the close relationship between RR and tourism development, existing research has primarily explored the interactive relationship between specific fields of tourism and rural areas. Empirical studies on the coupling coordination and driving mechanisms of THD and RR under high-quality conditions are limited.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area
The Silk Road Economic Belt encompasses five northwestern (Xinjiang, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Shaanxi) and four southwestern provinces (Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, and Yunnan) (Figure 1), covering approximately 44% of China’s land area. This region spans various climate types, including subtropical monsoon, temperate monsoon, temperate continental, and plateau continental. It is rich in natural, cultural, and tourism resources, positioning it as China’s new frontier for opening up to the world. The provinces and cities along the belt have interconnected yet diverse locational conditions, resource endowments, infrastructure, and economic development levels. The construction of the Silk Road Economic Belt offers a historical opportunity for these regions to enhance their regional connectivity and cooperation, aiming for coordinated economic and social development.
Figure 1.
Location of the study area. Note: This map is based on the standard map of GS (2020) 4619 downloaded from the standard map service website of the Ministry of Natural Resources.
3.2. Construction of the Indicator System and Data Sources
Adhering to the principles of scientific construction, comparability, and data availability of indicators and incorporating the content of the Rural Revitalization Strategic Plan (2018–2022) along with previous research findings, an RR evaluation index system was established. The RR subsystem mainly includes five primary indicators and 22 secondary indicators: industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, affluent living, and effective governance (Table 1) [3]. THD should adapt to the changes in the primary social contradictions and needs of the people in the new era, emphasizing technological innovation, the well-being of the people, and sustainable development. Therefore, this study combined the five new development concepts of innovation, coordination, greenness, openness, and sharing to construct a THD system. This system comprises 18 secondary indicators across five dimensions: tourism innovation-driven development, coordinated development, open vitality, green development, and shared development (Table 1) [25]. The entropy method was used to calculate the weight of each indicator.

Table 1.
RR and THD indicators system.
Given that China’s tourism industry entered a stage of mass consumption, quality demand, and holistic development during the 12th Five-Year Plan period, this study selected the period from 2011 to 2020 for analysis. The indicator data used in this study were sourced from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Tourism Statistical Yearbook, China Culture and Tourism Statistical Yearbook, China Civil Affairs Statistical Yearbook, and China Science and Technology Statistical Yearbook from 2012 to 2021. Tourism research and experimental development expenditure was calculated as the proportion of tourism revenue to the GDP. The tourism engine coefficient is derived from the proportion of spending on transportation, healthcare, education, culture, and entertainment to total consumption expenditure. The number of authorized tourism patents is obtained by searching for the keyword “tourism” in the Innojoy patent search engine (http://www.innojoy.com/, accessed on 6 December 2023). The data were then filtered and cleaned based on the authorization year and the applicant’s province or city, excluding irrelevant tourism data. Additionally, all data were mapped using Origin9.0 (Origin Lab, Northampton, MA, USA) and ArcGIS 10.2(ESRI, Redlands, CA, USA).
3.3. Research Methodology
3.3.1. Entropy Method
To avoid the drawbacks of subjective weighting methods, this study employed the entropy weighting method to determine the weights of each indicator. First, the raw data were standardized to eliminate the influence of different measurement units on the results. Subsequently, the entropy weight method was applied to the processed data to determine the weights of each indicator, following the specific calculation formulas referenced in the existing research [35]. Finally, a linear weighted function was used to calculate the comprehensive levels of the two subsystems: RR and THD. The calculation formula is as follows:
where U represents the comprehensive level of RR or THD, m is the number of indicators in the two subsystems, Wn is the standardized value of the n-th indicator, and Mn is the weight of the n-th indicator.
3.3.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
The degree of coupling refers to the extent of mutual influence and promotion between systems. The degree of coupling between RR and THD was calculated as follows [2]:
where C is the coupling degree between RR and THD, and U1 and U2 are the comprehensive levels of RR and THD, respectively.
To reflect the degree of coordinated development between RR and THD systems more objectively, this study introduced a CCD model. The calculations are as follows:
where D represents the CCD of RR and THD, ranging from 0 to 1. T is the comprehensive coordination index between the systems. α and β represent the contribution of RR and THD to the CCD, respectively. Considering their importance in social development and based on previous research, both α and β are set to 0.5. To describe the stages of RR and THD more accurately, the CCD was divided into 10 levels, as described in previous studies [36] (Table 2).

Table 2.
Ten levels of the CCD.
3.3.3. Gravity Model
This study employed the gravity model to analyze the spatial connection strength and network spatial structure characteristics of CCD in different provinces [37]. The calculation formula is as follows:
where Gij represents the spatial connection strength, Ei(j) is the CCD of city i(j), and is the distance between two cities.
3.3.4. Geographical Detector
Factor detection analysis in a geographic detector was used to examine the influence of independent variables on the CCD between THD and RR [38]. The calculation is as follows:
where q denotes the explanatory power of the independent variables on ecosystem services and their trade-off and synergistic relationships, with a value closer to 1.0000 indicating a higher explanatory power; m is the number of layers of the variable; N and n are the sample sizes of the study area and layer i, respectively; and δ2 and are the variances of the study area and layer i, respectively.
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of RR and THD
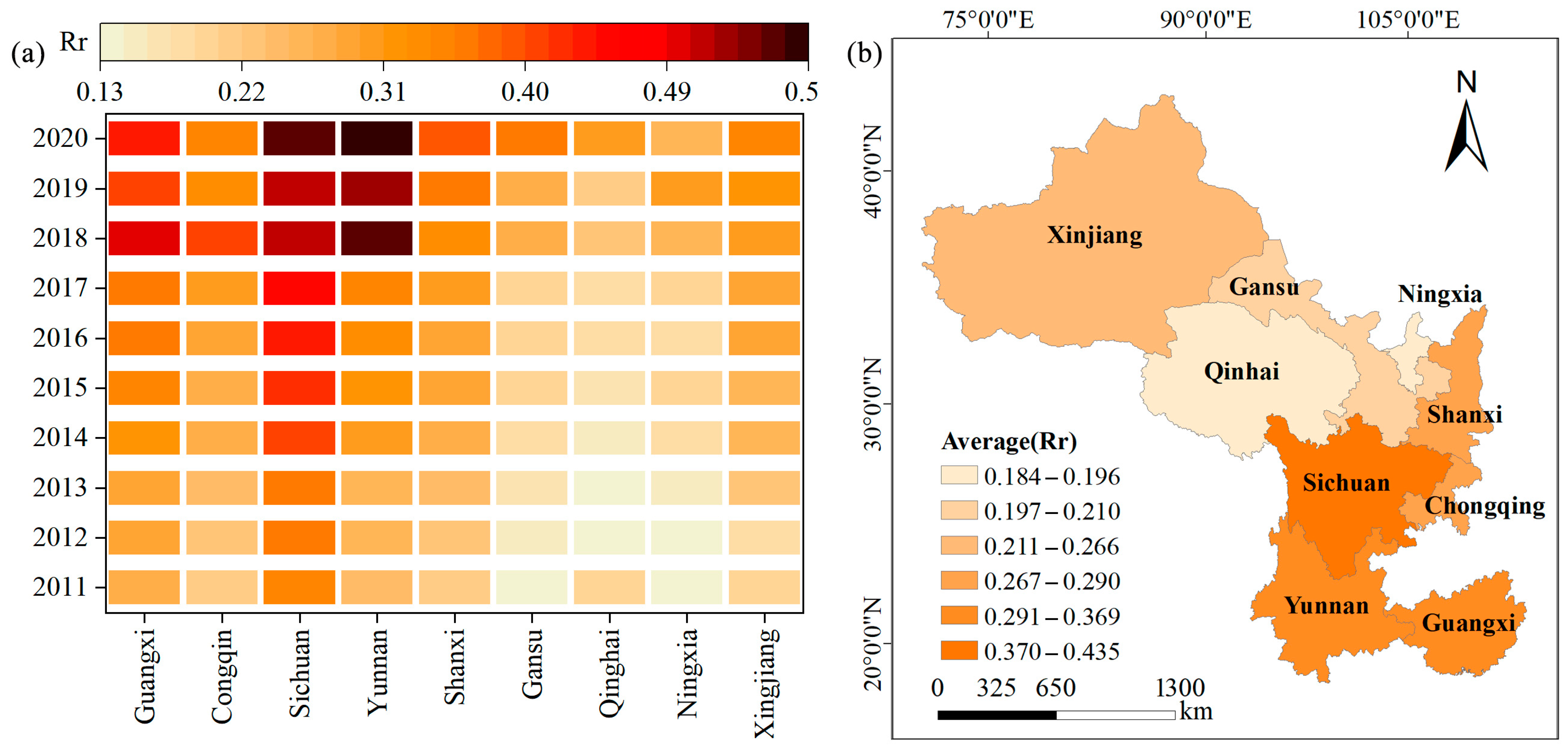
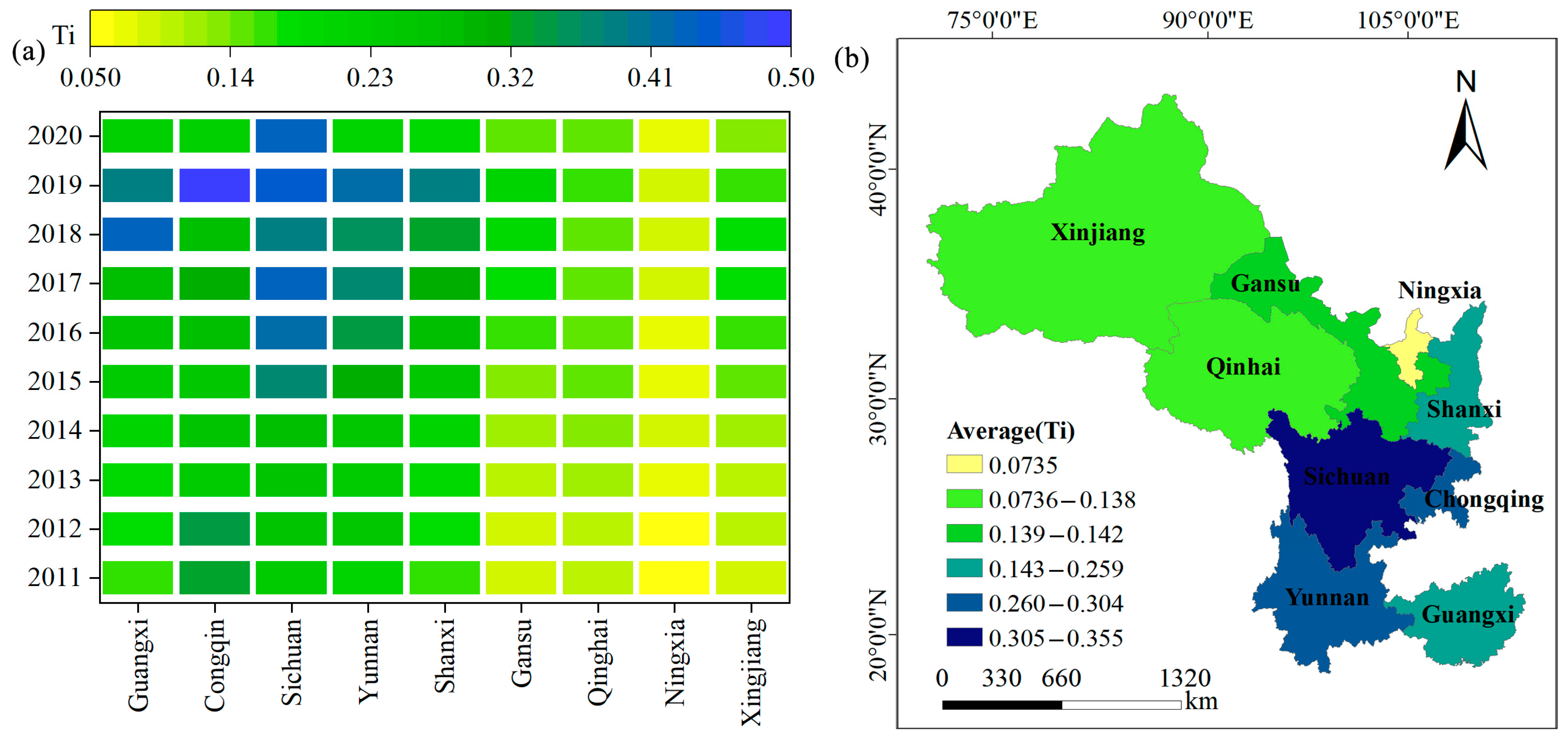
From 2011 to 2020, the comprehensive RR level in the Silk Road Economic Belt exhibited an upward trend (Figure 2a). The average RR increased from 0.212 in 2011 to 0.395 in 2020, with an average annual growth rate of approximately 86% (Figure 2a). The comprehensive THD level exhibited a trend of first increased and then decreased (Figure 3a). From 2011 to 2019, the comprehensive THD increased from 0.158 to 0.309, with an average annual growth rate of 94%. However, by 2020, the THD level reached 0.198, representing a 35% decline. Overall, RR in the Silk Road Economic Belt (average annual value of 0.288) was higher than the level of THD (0.217) (Figure 3a).
Figure 2.
Spatiotemporal characteristics of the comprehensive level of RR. Note: the southwest four provinces (Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Yunnan) and the northwest five provinces (Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang) (a) temporal changes in RR; (b) spatial variation changes in RR.
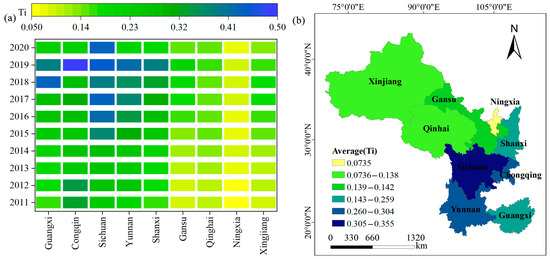
Figure 3.
Spatiotemporal characteristics of the comprehensive level of THD (a) temporal changes in THD; (b) spatial variation changes in THD.
Spatially, the RR and THD levels in the southwestern provinces were generally higher than those in the northwestern provinces (Figure 2b). The average annual values of RR levels, ranked from highest to lowest, were Sichuan (0.435), Yunnan (0.369), Guangxi (0.358), Shaanxi (0.290), Chongqing (0.287), Xinjiang (0.266), Gansu (0.210), Ningxia (0.196), and Qinghai (0.184). The spatial pattern of RR is closely related to the regional natural environment, agricultural development level, and socioeconomic conditions. Regarding the THD, Sichuan exhibited the highest comprehensive development level (0.355). By contrast, the THD level in Ningxia was lower than that in the other provinces, with an annual average of only 0.074 (Figure 3b). Sichuan boasts an advanced economy, a well-developed industrial structure, and rapidly advancing infrastructure, including transportation. These factors facilitate the efficient flow and allocation of urban and rural resources, providing strong support for tourism development. In contrast, Qinghai faces challenges such as a fragile natural environment, inadequate tourism service facilities, and a shortage of specialized talent, which hinder the development of THD.
4.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of the Coupling Coordination between RR and THD Levels
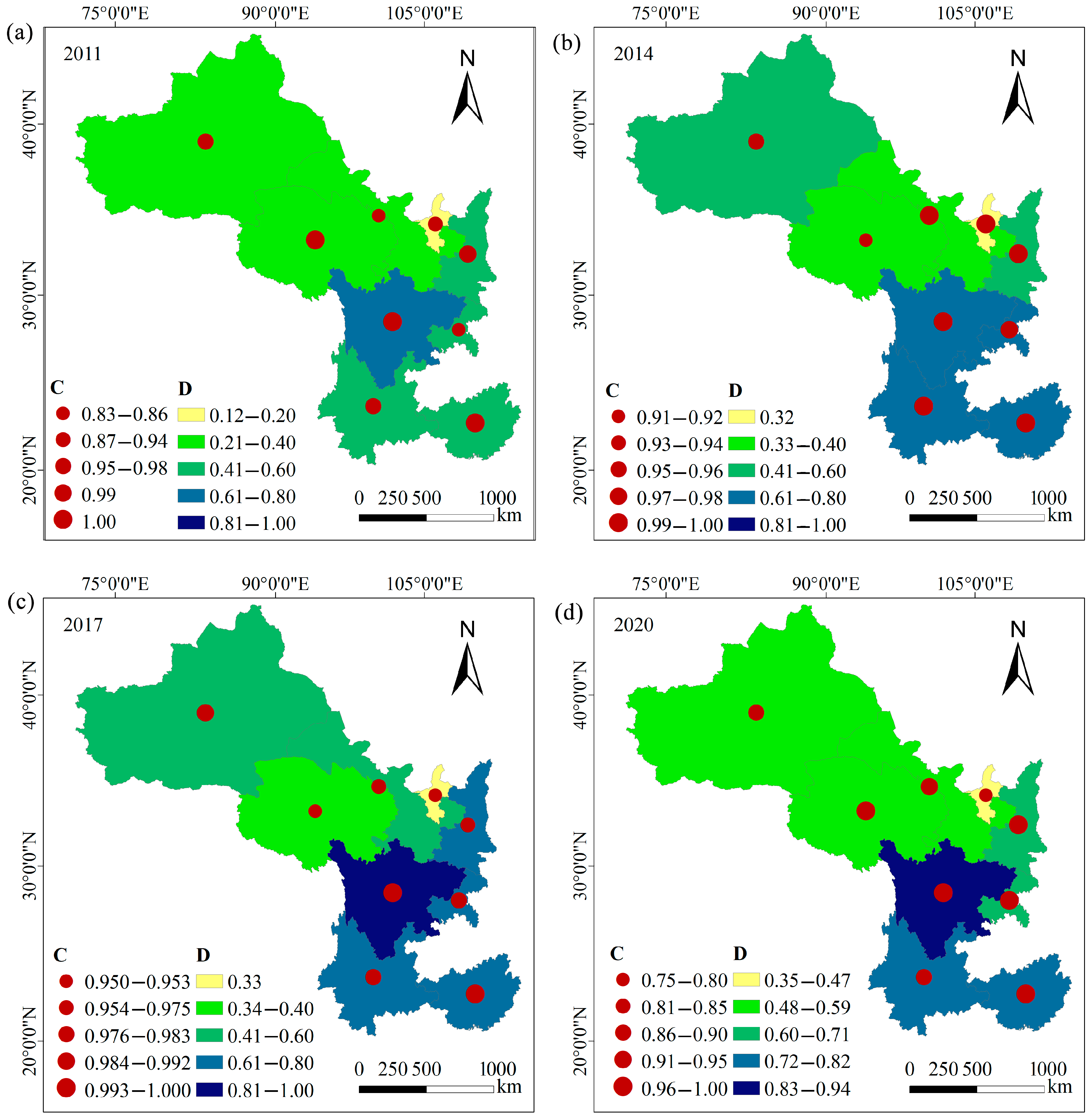
From 2011 to 2020, the overall degree of coupling between RR and THD along the Silk Road Economic Belt ranged from 0.75 to 1, indicating a stage of adaptation, high-level interaction, and beneficial resonance (Figure 4). Sichuan exhibited the highest degree of coupling, whereas Qinghai had the lowest. The analysis of the variation in CCD revealed an overall increasing trend from 2011 to 2019, followed by a slight decline in 2020 (Figure 4).
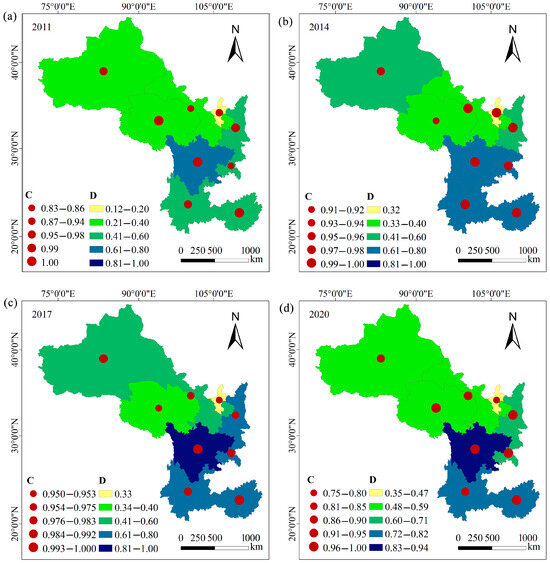
Figure 4.
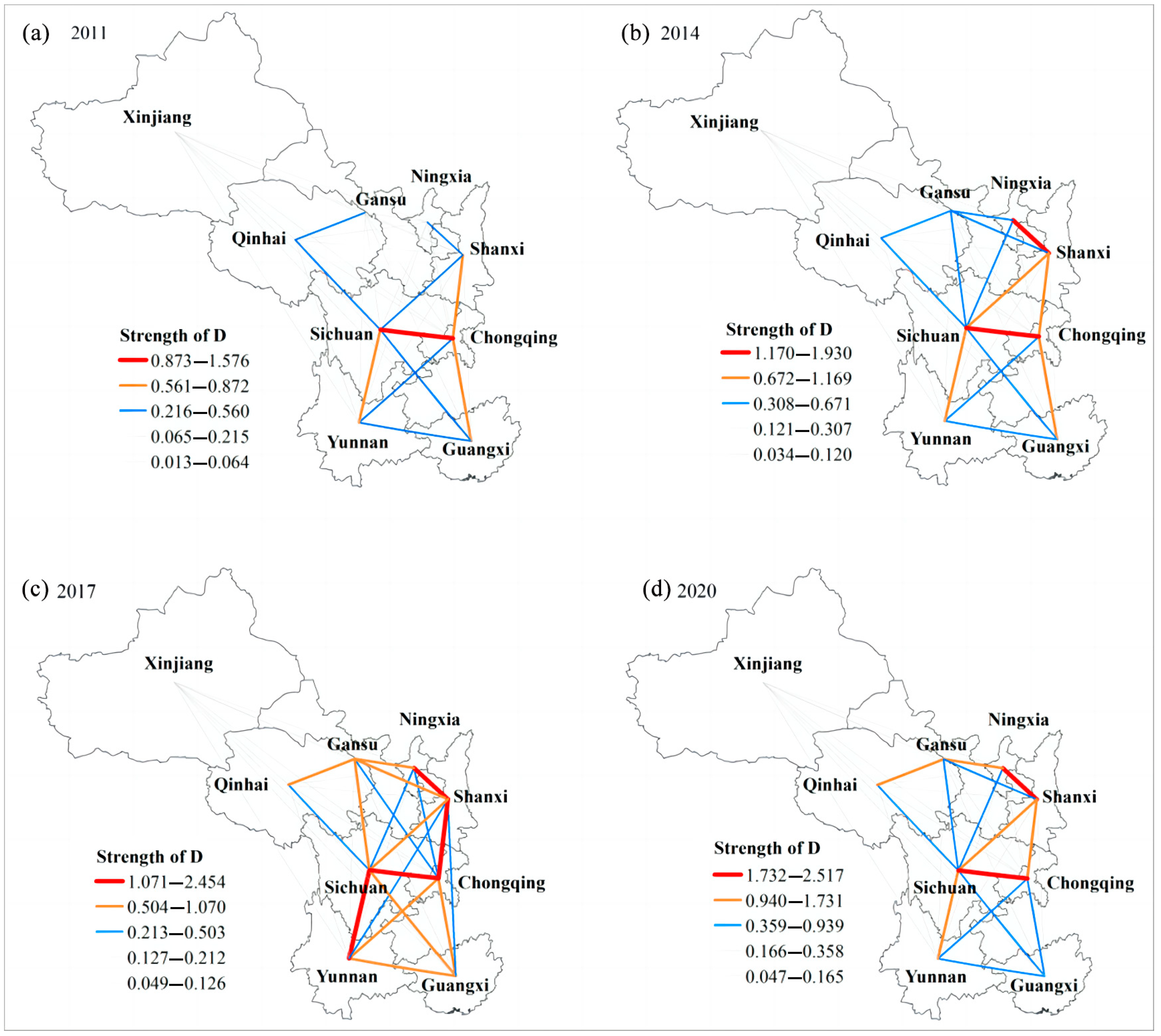
Characteristics of the coupling degree and CCD between RR and THD levels: (a) C and D in 2011; (b) C and D in 2014; (c) C and D in 2017; (d) C and D in 2020.
Spatially, the CCD varied significantly among the provinces, with the four southwestern provinces exhibiting higher values than the five northwestern provinces (Figure 4). Specifically, the coupling coordination types in the southwestern provinces evolved from primary and barely coordinated to primary, intermediate, and high-quality coordination (Figure 4, Table 2). By contrast, the northwestern provinces transitioned from various degrees of imbalance to primary and barely coordinated states. Furthermore, Sichuan demonstrated the highest CCD, progressing through the primary, intermediate, good, and high-quality coordination stages from 2011 to 2020 (Figure 4, Table 2). Conversely, Ningxia exhibited the lowest CCD among all the provinces, characterized by severe, moderate, and mild imbalances bordering on dysfunction (Figure 4, Table 2).
To further understand the spatial connection characteristics of RR and THD, a gravity model was employed to analyze the connection strength of the CCD between different provinces (Figure 5). As the figure shows, the spatial connection strength and network complexity of the CCD from 2011 to 2020 exhibited an initial increase, followed by a decrease. In 2011, the connection strength between Sichuan and Chongqing was higher than that between the other provinces (Figure 5a). By 2020, the spatial connection strengths between Sichuan and Chongqing and between Ningxia and Shaanxi were the highest (Figure 5d). In addition, the connection strength between Ningxia, Gansu, and Qinghai gradually increased (Figure 5d). Additionally, the degree of association between Xinjiang and the other provinces remained consistently weak across different periods, primarily due to its inland location, inconvenient transportation, and distance from major source markets.
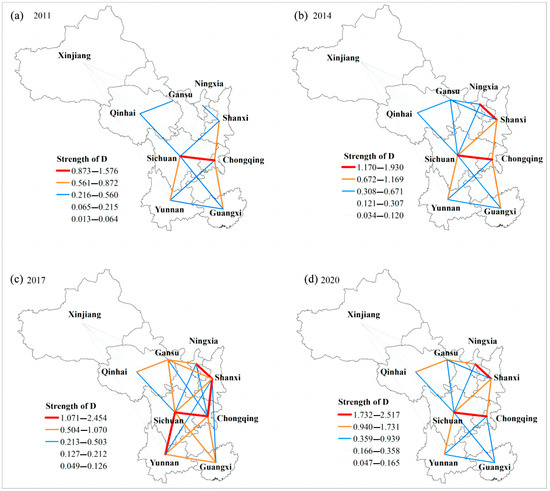
Figure 5.
Characteristics of CCD and connection strength between RR and THD: (a) strength of D in 2011; (b) strength of D in 2014; (c) strength of D in 2017; (d) strength of D in 2020.
4.3. Factors Influencing the CCD between RR and THD
4.3.1. Single-Factor Detection
The results of the single-factor driving force detection show that different indicators have varying degrees of impact on the CCD of RR and THD (Table 3). Specifically, public fiscal expenditure (p = 0.00), per capita GDP (p = 0.017), and scientific and educational spending (p = 0.00) reached significant or extremely significant levels of influence on the CCD of RR and THD. The magnitudes of the driving-force effects were ranked as follows: public fiscal expenditure (q = 0.693), scientific and educational spending (q = 0.662), and per capita GDP. In recent years, the government has provided guidance for rural revitalization and high-quality tourism development through the issuance of policy documents and increased financial investment. Public fiscal support has become the economic foundation for the coordinated development of both. During the phase of high-quality development, technological investment not only provides fundamental support for the innovation of tourism products and services but also promotes diversification in tourism consumption and enhances visitor engagement.

Table 3.
Results of single-factor driving force detection.
4.3.2. Interaction Detection
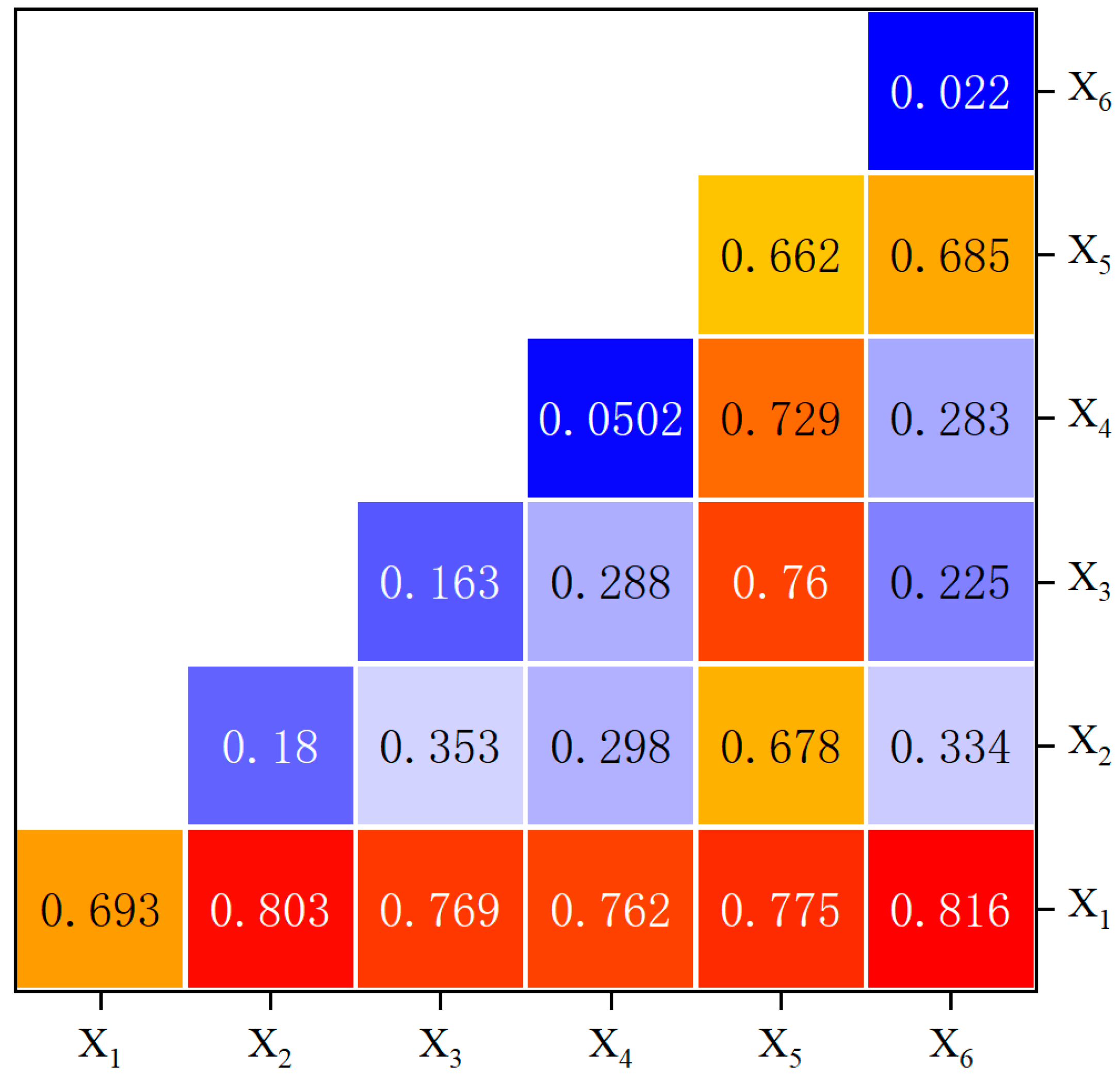
Because the evolution of the CCD between RR and THD is influenced by multiple factors, interaction detection was employed to discern the interaction effects among different factors. As shown in Figure 6, the interaction between X1 and each of the other factors was greater than the individual effects of each single factor (interaction values exceeded 0.75). This indicates that national macro policies promote the coordinated development of RR and THD by influencing resource allocation, industrial structure, and urban–rural income. Additionally, the interactions between X5 and X2, X3, and X4 also exhibited nonlinear enhancement. This suggests that the emergence of new technologies and knowledge will alter the development models and rates of rural industries and tourism. Thus, the CCD of RR and THD resulted from the interplay of multiple factors.
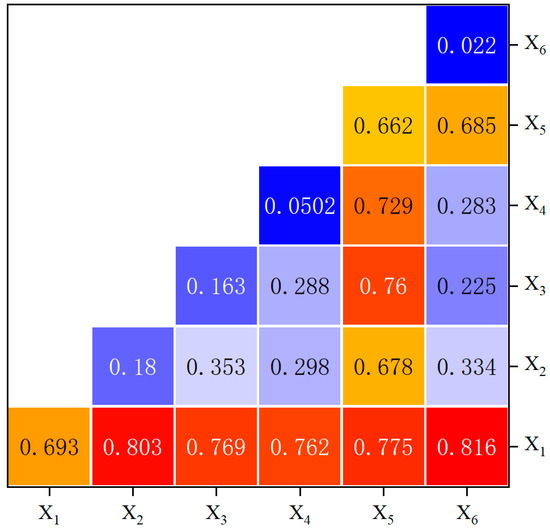
Figure 6.
Interaction detection of driving factors for CCD between RR and THD. Note: X1: Public fiscal expenditure, X2: The ratio of the value-added of the tertiary industry to the secondary industry, X3: Per capita GDP, X4: Per capita years of education, X5: Scientific and educational expenditure, X6: Urbanization rate. The driving force behind the coupling between RR and THD.
5. Discussion
5.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics Analysis of RR and THD
The comprehensive level of RR in the Silk Road Economic Belt showed an upward trend from 2011 to 2020 (Figure 2a), which aligns with the findings of Qiao et al. (2023), indicating an RR level of 0.38 in the Yellow River Basin [39]. This suggests that provinces and municipalities have increasingly prioritized issues related to agriculture, rural areas, and farmers in response to the “No. 1 Central Document” policies. Particularly after the introduction of the RR strategy, provinces and municipalities promoted the transformation of rural infrastructure, industrial integration, the ecological environment, and farmers’ living standards through increased investments in funds, technology, and human resources. These findings differ from those of Chao et al. (2023), who reported a slow growth rate in China’s RR from 2011 to 2020 [19]. This discrepancy may be attributed to differences in the evaluation indicator systems and the influence of the Road Initiative. The present study also indicated that the THD exhibited an initial increase, followed by a decline during 2011–2020 (Figure 3a). On one hand, following the issuance of documents such as the “Outline for Quality Tourism Development (2013–2020)” and “Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Tourism”, provinces and municipalities have promoted the transition of the tourism industry from factor-driven to innovation-driven growth by protecting tourism resources and the environment and optimizing industrial structures, thereby enhancing the quality of tourism development. On the other hand, influenced by the concept of “high-quality development”, regions have started to focus more on the intrinsic growth of the tourism industry, significantly enhancing the effects of cultural and tourism integration and technological empowerment [26]. However, the THD level declined from 2019 to 2020, owing to the impact of the pandemic.
Spatially, Sichuan exhibited the highest RR, while Qinghai had the lowest (Figure 2b). This discrepancy can be attributed to several factors. As a rapidly developing province in the western region, Sichuan benefits from favorable agricultural conditions and a supportive policy environment, which lay the foundation for comprehensive rural development. Sichuan has continuously improved its rural infrastructure and enhanced its residents’ education and living standards, leading to rapid progress in various dimensions of RR [40]. By contrast, Qinghai’s weaker natural conditions and resource endowments have resulted in lagging economic development and infrastructure [41]. The province’s limited public and cultural services and low living standards further hinder agricultural production and rural economic growth. Regarding THD, Sichuan ranked the highest, while Ningxia ranked the lowest (Figure 3b). Sichuan has rich tourism resources and a strong cultural heritage. Local governments have promoted quality and efficiency in the tourism industry by offering high-quality cultural and tourism products; enhancing the integration of tourism with other industries; developing a “fast-in, slow-travel” transportation network; and improving inbound tourism services [42]. Conversely, despite some developments in tourism driven by media exposure, Ningxia faces challenges, such as low ecological carrying capacity, poor transportation accessibility, and a lack of tourism professionals, which constrain its tourism innovation and openness. In summary, the overall development level and spatial distribution indicate that the levels of RR and THD across the provinces and cities of the Silk Road Economic Belt remain relatively low, highlighting significant potential for improvement.
5.2. Analysis of the Driving Factors of CCD between RR and THD
The CCD between RR and THD is influenced by multiple factors, including economic development, technological innovation, and institutional policies [25,43]. This study demonstrates that public fiscal expenditure has the greatest impact on the CCD between RR and THD, with a q-value of 0.693, indicating a significant policy orientation (Table 3). In the process of promoting RR and tourism development, the government facilitates the flow of factors and integration of resources between urban and rural areas through strategies, such as the Belt and Road Initiative and RR, thereby enhancing the strength of regional connections and resource sharing [39]. In addition, by investing substantial funds in transportation infrastructure, public service facilities, and industrial integration, the government enhanced the exogenous driving forces of RR and THD.
Our results indicate that technological innovation is also a crucial factor influencing the CCD between RR and THD (Table 3). This finding aligns with the conclusion of Shi et al. (2021), who identified technological innovation as an endogenous driving force for the coordinated development of these two sectors [26]. Technological innovation promotes the informatization of rural agricultural production, ecological protection, rural e-commerce, and the internet of things, thereby transforming production, living, and ecological spaces [44,45]. Simultaneously, the advancement of digital technology supports RR by diversifying cultural products, enhancing presentations, and revitalizing intangible cultural heritage. Technological innovation facilitates service convenience, product personalization, and industry diversification, thereby improving tourism economic efficiency and achieving THD [46]. Additionally, smart and virtual tourism based on advanced audiovisual technology and big data provides conditions for optimizing the structure of the tourism industry and upgrading tourism consumption demand [47]. Furthermore, the application of cloud computing and machine learning in tourism market forecasting can effectively mitigate issues related to unbalanced supply and demand, such as disorderly resource development and increased carbon emissions, ultimately providing an environmental foundation for THD.
Economic development is also a key factor driving the CCD of RR and THD (Table 3). On one hand, sound economic development increases residents’ demand for tourism consumption in terms of quantity, quality, and structure, thereby promoting the upgrading of tourism consumption patterns and laying a material foundation for THD [48]. On the other hand, favorable economic conditions provide financial support for tourism infrastructure, environmental protection, talent cultivation, and technological research and development in the process of THD. For RR, the government invests substantial funds in various aspects, such as agricultural production, infrastructure construction, and ecological environment governance in rural areas, thereby promoting industrial revitalization, improving the living environment, and enhancing living standards [49].
Furthermore, our results indicate that the interaction between institutional policies and technological innovation, along with other factors, enhances the driving force behind the coupling between RR and THD (Figure 6). Macroeconomic regulations and policy support from governments at different stages can guide the flow of funds, technology, and talent, thereby promoting RR and THD. Technological innovation is an intrinsic requirement of RR and THD. This has led to the emergence of new technologies, models, and concepts by overlaying elements such as education, talent, and industries, ultimately resulting in the digitization of rural and tourism industries, the integration of production factors, and the transformation of supply–demand relationships.
6. Conclusions
In this study, we constructed an evaluation index system for THD and RR based on the concept of high-quality development. The spatiotemporal patterns, coupling coordination, and influencing factors of THD and RR in the Silk Road Economic Belt from 2011 to 2020 were investigated using CCD models, gravity models, and geographical detectors. During the study period, the overall RR level showed an upward trend, whereas the THD level exhibited an initial increase, followed by a decrease. Additionally, RR was higher than THD. Spatially, RR and THD generally presented a pattern of higher in the southwest than in the northwest. The degree of coupling between RR and THD experienced three stages: adaptation, high-level, and benign resonance. Spatially, the CCD displayed higher levels in the southwest and lower levels in the northwest. The CCD types in the four southwestern provinces gradually evolved from primary and tentative coordination to primary, intermediate, and high-quality coordination. Transitions from various degrees of imbalance to coordination were observed in five northwestern provinces. The CCD of RR and THD is jointly regulated by various factors. Among these, public fiscal expenditure, per capita GDP, and expenditure on science and technology education have a significant impact on the CCD, with the interaction effects between public fiscal expenditure, science and technology education, and other factors enhanced.
Overall, there are significant disparities in the levels of RR and THD. For the more developed southwestern region, it is crucial to enhance technological innovation, cultural empowerment, and the strengthening of tourism brands. The region should leverage urban agglomerations to expand the impact of tourism on the rural economy on a larger scale, thereby promoting a positive feedback loop between tourism development and rural revitalization. In contrast, the northwestern region should capitalize on national policy support and resource advantages to develop border tourism and winter tourism. Meanwhile, the tourism development model in the northwest provinces should shift from resource dependency to technological innovation and improve the role of tourism in rural residents’ income and spatial reconstruction by expanding tourism formats and optimizing industries. Furthermore, provinces should overcome regional policy barriers and engage in deep exchanges and joint planning in areas such as funding, talent, and technology to achieve regional sharing and mutual benefits. The findings of this study provide a theoretical reference for promoting the coordinated development of RR and THD among different regions along the Silk Road Economic Belt.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.Z.; methodology, H.Z.; software, H.Z., J.T. and Z.D.; data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Z.; writing—review and editing, H.Z. and L.G.; visualization, J.T. and Z.D.; supervision, X.X. and L.G.; funding acquisition, H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 42261041), Tianchi Talent Project, and the Key Laboratory for Sustainable Development of Xinjiang’s Historical and Cultural Tourism, Xinjiang University, China (grant no. LY2022-06).
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this research are available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Yin, Q.Q.; Sui, X.Y.; Ye, B.; Zhou, Y.J.; Li, C.Q.; Zou, M.M.; Zhou, S.L. What role does land consolidation play in the multi-dimensional rural revitalization in China? A research synthesis. Land Use Policy 2022, 120, 106261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Su, M.M.; Gan, C.; Yu, Z. A coordination analysis on tourism development and resident well-being in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 421, 138361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tang, J.; Dombrosky, J.M. Coupling relationship of tourism urbanization and rural revitalization: A case study of Zhangjiajie, China. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, Z. Exploring the Rural Revitalization Effect under the Interaction of Agro-Tourism Integration and Tourism-Driven Poverty Reduction: Empirical Evidence for China. Land 2024, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, X.X.; Wang, Z.F.; Xu, L.Y. Where to Revitalize, and How? A Rural Typology Zoning for China. Land 2021, 10, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapping, M.B.; Scott, M. The evolution of rural planning in the Global North. In The Routledge Companion to Rural Planning; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; pp. 28–45. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, J.; McManus, P. Rural Revival? Place Marketing, Tree Change and Regional Migration in Australia; Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.: Farnham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- ESPON. Rural Areas: An Eye to the Future: TerritoriALL; The ESPON Magazine, ESPON, Eds.; ESPON: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahlmeyer, F.; Volgmann, K. What Can We Expect for the Development of Rural Areas in Europe?—Trends of the Last Decade and Their Opportunities for Rural Regeneration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazorla-Montero, A.; de los Ríos-Carmenado, I. From “Putting the Last First” to “Working with People” in Rural Development Planning: A Bibliometric Analysis of 50 Years of Research. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Ge, D.Z.; Sun, P.; Sun, D.Q. The Transition Mechanism and Revitalization Path of Rural Industrial Land from a Spatial Governance Perspective: The Case of Shunde District, China. Land 2021, 10, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J. Prioritizing agricultural, rural development and implementing the rural revitalization strategy. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 2020, 12, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.B.; Hu, X. Improving the framework for analyzing community resilience to understand rural revitalization pathways in China. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 94, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.K.; Li, D.C.; Wu, H.D.; Wang, Y.J.; Yu, H.; Zeng, Z. Extracting and evaluating typical characteristics of rural revitalization using web text mining. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 38, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.S.; Jiang, M.H.; Sun, D.Y.; Zhang, S.K. Does financial development matter the accomplishment of rural revitalization? Evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 88, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, Y.Y.; Jiang, N. County-rural revitalization spatial differences and model optimization in Miyun District of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 86, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.S.; Kong, C.L. The Impact of Digital Inclusive Finance on Rural Revitalization: Evidence from China. J. Organ. End User Comput. 2024, 36, 337970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.Q.; Liu, L.W.; Chen, L.Y. Rural revitalization of China: A new framework, measurement and forecast. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 89, 101696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Liu, J.; Wan, S.W.; Zheng, H.L.; Chen, S. Agricultural insurance and rural revitalization-an empirical analysis based on China’s provincial panel data. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1291476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irfan, M.; Ullah, S.; Razzaq, A.; Cai, J.Y.; Adebayo, T.S. Unleashing the dynamic impact of tourism industry on energy consumption, economic output, and environmental quality in China: A way forward towards environmental sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 387, 135778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tuo, S.H.; Lei, K.W.; Gao, A.X. Assessing quality tourism development in China: An analysis based on the degree of mismatch and its influencing factors. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 9525–9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.T.; Lee, T.J.; Kim, D.K. Relationships between motivation, service quality, tourist satisfaction, quality of life, and spa and wellness tourism. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2024, 26, e2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.B.; Dong, K.; Wang, F.F.; Ayamba, E.C. The spatial effect of tourism economic development on regional ecological efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38241–38258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, Z.; Wang, J. Spatiotemporal Changes in China’s Tourism Industry Development. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Guo, L.; Zhao, R.; Ji, R. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Driving Factors of the High-quality Development of Provincial Tourism in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Xu, D.H.; Xu, L.D. Spatiotemporal characteristics and impact mechanism of high-quality development of cultural tourism in the Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.N.; Mei, X.H.; Xiao, Z.Q. Impact of the Digital Economy in the High-Quality Development of Tourism-An Empirical Study of Xinjiang in China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. The Measurement of High-Quality Development Level of Tourism: Based on the Perspective of Industrial Integration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Fang, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, Y.; Zong, Z.H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.N.; Ou, Z.P.; Wang, M. How can tourism help to revitalize the countryside? Content analysis based on the case of tourism enabling rural revitalization. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Liu, J.M.; Deng, Y.; Du, A. Tourism sectorization opportunity spectrum model and space partition of tourism urbanization area: A case of the Mayangxi ecotourism area, Fujian province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2017, 14, 595–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhou, Y.M.; Zeng, L.; Tang, X.Q. Aesthetic heterogeneity on rural landscape: Pathway discrepancy between perception and cognition. J. Rural Stud. 2022, 92, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.C.; Zhu, Z.X. Exploring the Factors of Rural Tourism Recovery in the Post-COVID-19 Era Based on the Grounded Theory: A Case Study of Tianxi Village in Hunan Province, China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Zang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.Y. China’s rural revitalization and development: Theory, technology and management. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 1923–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, C.J.; Liu, Z.W.; Yang, L.S.; Wang, L. Evaluation of Spatial Reconstruction and Driving Factors of Tourism-Based Countryside. Land 2022, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.W.; Shao, Z.F.; Fang, S.H.; Huang, X.; Huq, M.E.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q.W. Finer-scale spatiotemporal coupling coordination model between socioeconomic activity and eco-environment: A case study of Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 131, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.Y.; Zhong, K.Y.; Liao, Y.J.; Xiong, R.L.; Wang, F.B.; Pang, M. Coupling coordination degree of environment, energy, and economic growth in resource-based provinces of China. Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Han, D.D.; Wang, T.T.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y.T. Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Tourism Industry and Urbanization in Marginal and Less Developed Regions-Taking the Mountainous Border Areas of Western Yunnan as a Case Study. Land 2023, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Wang, L.; Du, P. Contradiction or harmony? Spatial and temporal relationships between new urbanization and rural revitalization in the Yellow River Basin from a coupling perspective. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Yang, Y.R.; Ye, W.; Liu, L.; Gu, X.C.; Chen, H.P.; Zhang, Y.H. Study on the Efficiency, Evolutionary Trend, and Influencing Factors of Rural-Urban Integration Development in Sichuan and Chongqing Regions under the Background of Dual Carbon. Land 2024, 13, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Guo, X.R.; Liu, C.Y.; Ma, Q.Y.; Guo, S.D. Analysis on the Influencing Factors of Rural Infrastructure in China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, H.; Li, X.M. Risk assessment of mountain tourism on the Western Sichuan Plateau, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 3360–3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Li, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Chen, H.; Lai, M.; Zhao, S.D. The Dynamics and Driving Mechanisms of Rural Revitalization in Western China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, C.; Wang, J. How Can the Digital Economy Promote the Integration of Rural Industries-Taking China as an Example. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, Y. Endogenous inclusive development of e-commerce in rural China: A case study. Growth Chang. 2020, 51, 1611–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Shim, C. Social capital, knowledge sharing and innovation of small- and medium-sized enterprises in a tourism cluster. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2018, 30, 2417–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Um, T.; Chung, N. Does smart tourism technology matter? Lessons from three smart tourism cities in South Korea. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2021, 26, 396–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.P.; Thanh, S.D.; Nguyen, B. Economic uncertainty and tourism consumption. Tour. Econ. 2022, 28, 920–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.T.; Wang, N.; Xiao, H.L.; Zhou, Z.B. Efficiency of funding to rural revitalization and regional heterogeneity of technologies in China: Dynamic network nonconvex metafrontiers. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2024, 92, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).