Regional Differences in Carbon Budgets and Inter-Regional Compensation Zoning: A Case Study of Chongqing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Accounting for Carbon Emissions
2.1.2. Accounting for Carbon Sequestration
2.1.3. Calculation of the Carbon Deficit
2.1.4. Estimation of the Regional Carbon Compensation Cost
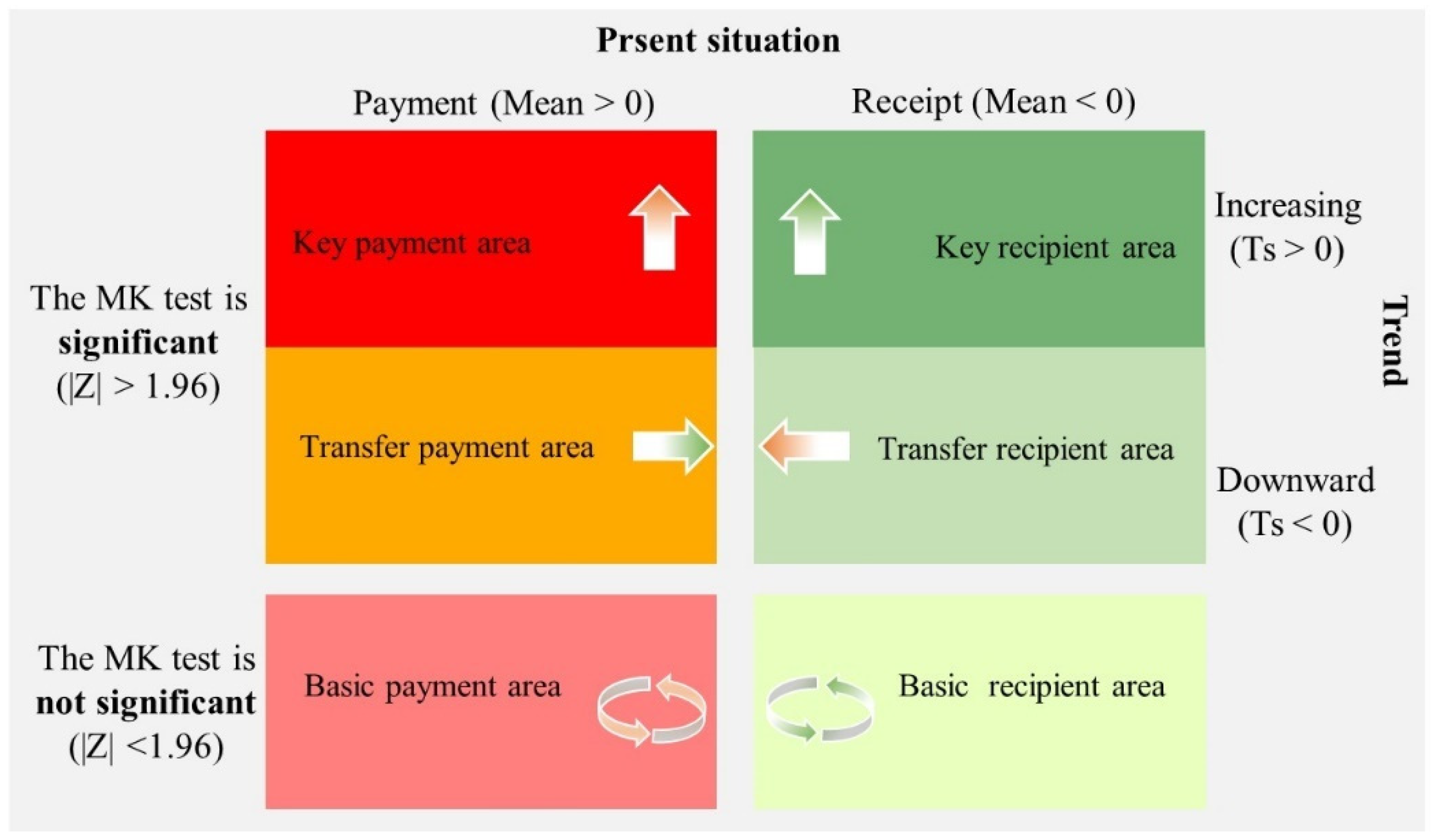
2.1.5. Identify the Type of Carbon Compensation Area
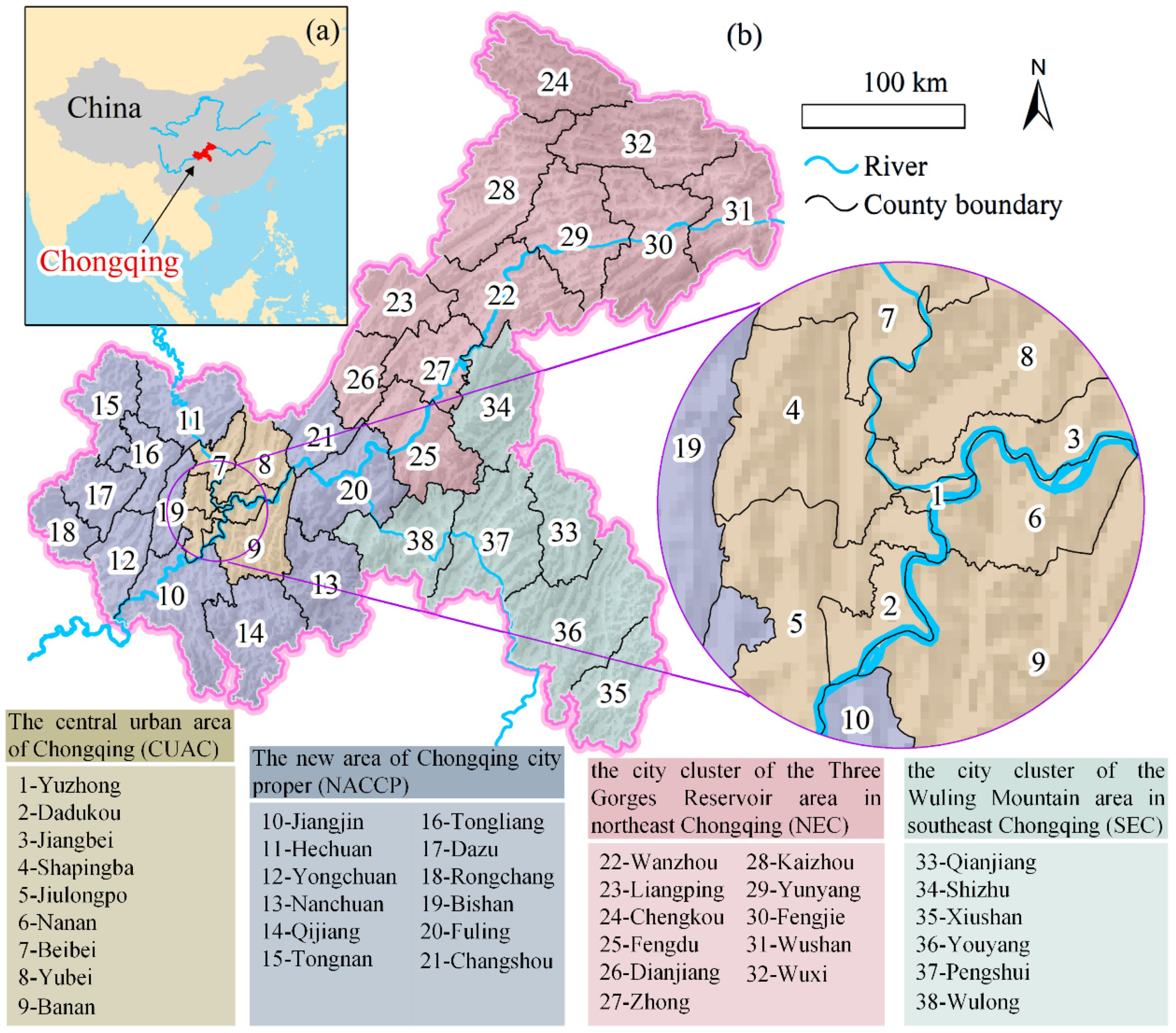
2.2. Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Carbon Emissions
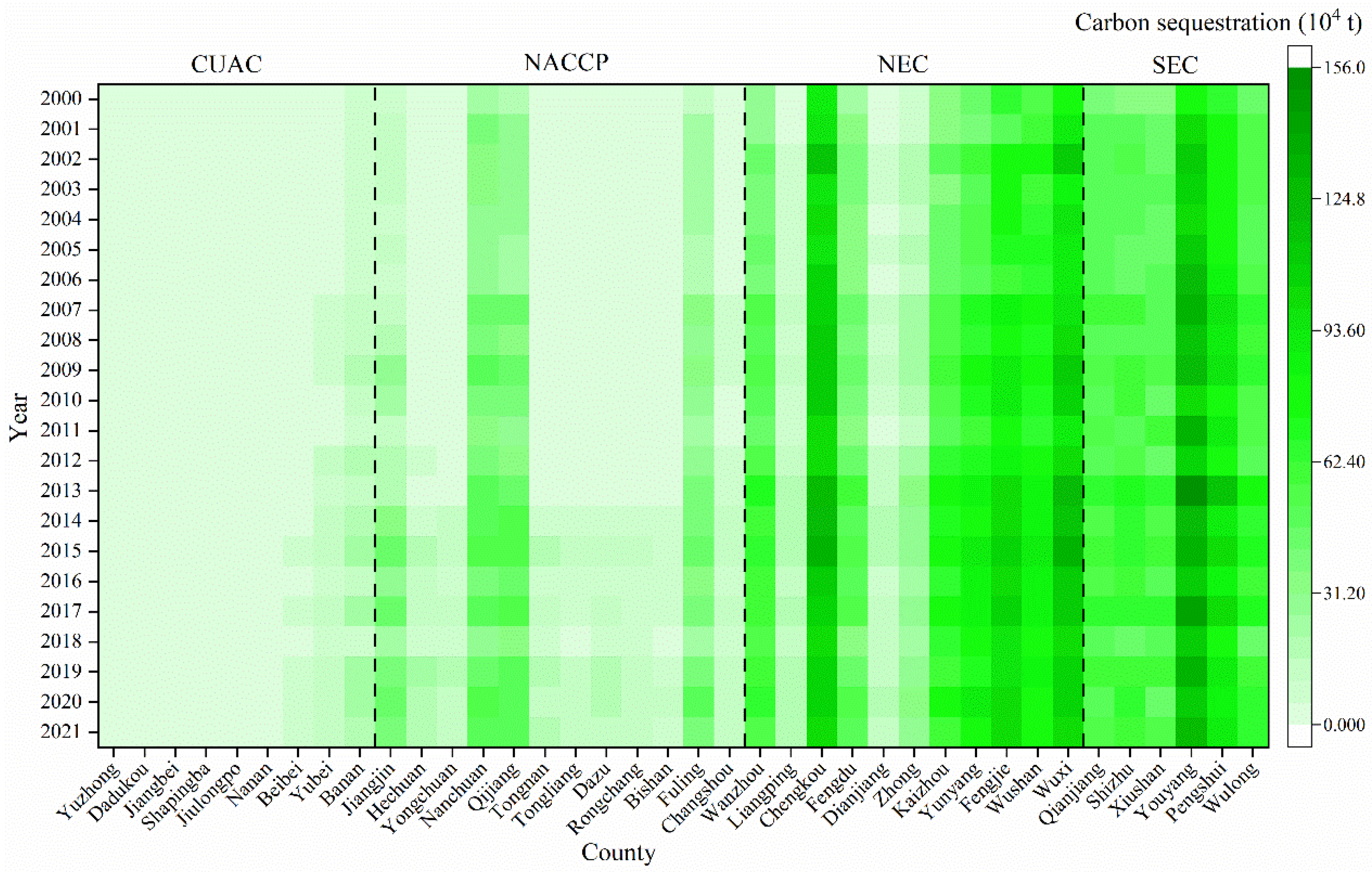
3.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Carbon Sequestration
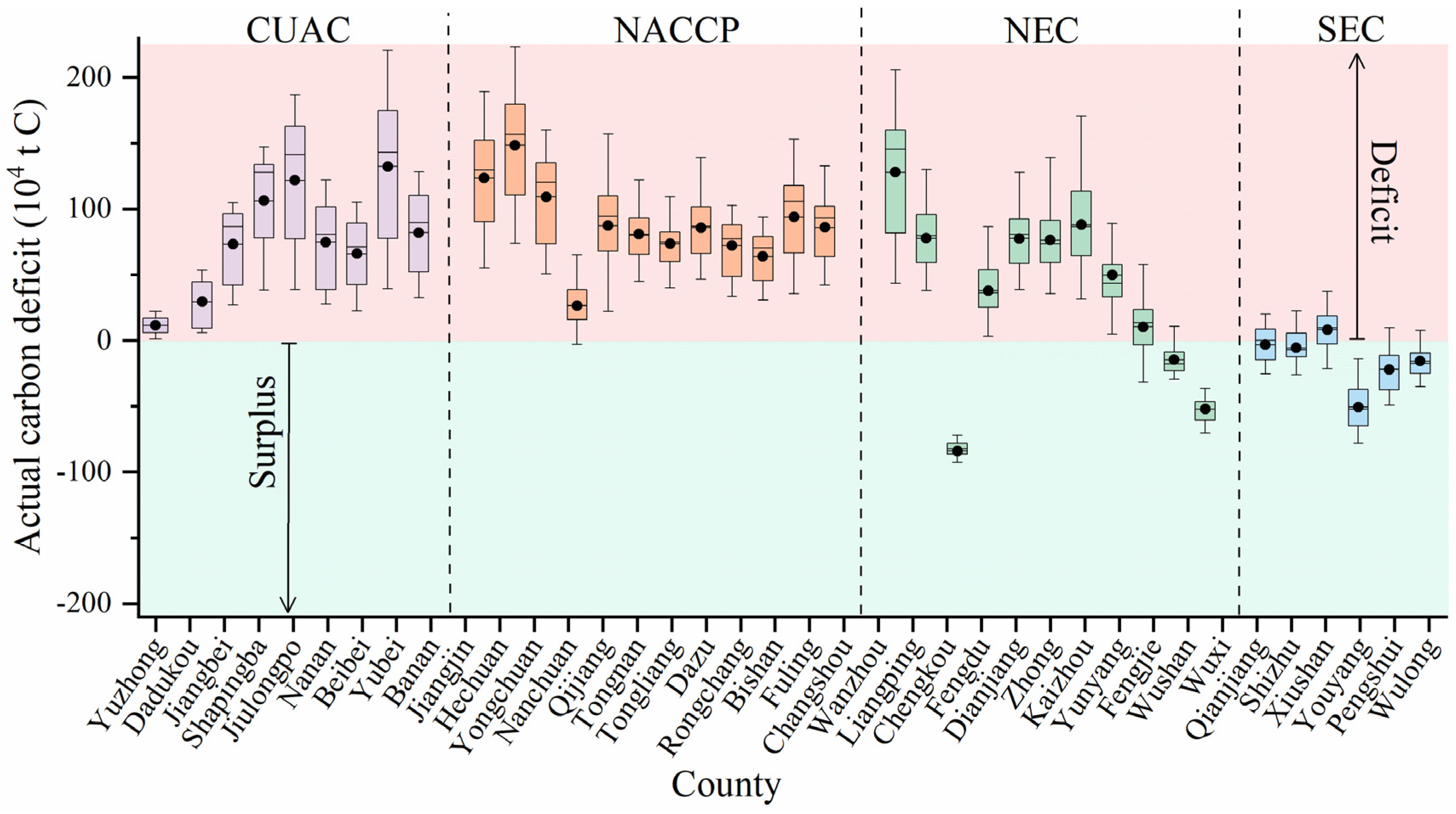
3.3. Carbon Deficits at the Municipality and County Levels
3.4. Lateral Carbon Compensation across Counties
3.5. Inter-Regional Carbon Compensation Zoning
4. Discussion
4.1. Reliability of Carbon Budget Capacity
4.2. The Coordination of Carbon Compensation with Regional Development
4.3. The Contributions of the Carbon Compensation Zoning Scheme
4.4. Problem Statement and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huo, J.; Meng, J.; Zheng, H.; Parikh, P.; Guan, D. Achieving decent living standards in emerging economies challenges national mitigation goals for CO2 emissions. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Page, J.; Shi, R.; Cong, C.; Cai, Z.; Barthel, S.; Thollander, P.; Colding, J.; Kalantari, Z. Contribution of prioritized urban nature-based solutions allocation to carbon neutrality. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2023, 13, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonter, L.J.; Simmonds, J.S.; Watson, J.E.M.; Jones, J.P.G.; Kiesecker, J.M.; Costa, H.M.; Bennun, L.; Edwards, S.; Grantham, H.S.; Griffiths, V.F.; et al. Local conditions and policy design determine whether ecological compensation can achieve No Net Loss goals. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Stewardson, M.J. Eco-compensation in China: Theory, practices and suggestions for the future. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Sun, X.; Guo, H.; Long, Q.; Li, S.; Mao, X.; Niu, T.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yue, D. The establishment of a cross-regional differentiated ecological compensation scheme based on the benefit areas and benefit levels of sand-stabilization ecosystem service. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Wu, C.; Zheng, X.; Xie, L. Carbon sinks and carbon emissions balance of land use transition in Xinjiang, China: Differences and compensation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Lu, B. Horizontal ecological compensation mechanism and green low-carbon development in river basins: Evidence from Xin’an River basin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 88463–88480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.; Chuai, X.; Xu, H.; Cai, H.H.; Xiang, A.; Lu, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, M. Carbon deficit checks in high resolution and compensation under regional inequity. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Study on the initial carbon quota allocation and spatial balance compensation strategy at the provincial level in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 67150–67173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, K.; Du, Z.; Chen, Y. Correlating CO2 emissions of cities with the inter-city carbon compensation mechanism: A regional perspective in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River (MRYR), China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 9185–9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Z.; Chuai, X.; Jiao, S. Overview of regional carbon compensation: Mechanism, pattern and policy suggestions. Areal Res. Dev. 2015, 34, 116–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Zhang, L. Spatiotemporal variation of per capita carbon emissions and carbon compensation zoning in Chinese counties. Land 2023, 12, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Shang, P.; He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y. Interregional carbon compensation cost forecast and priority index calculation based on the theoretical carbon deficit: China as a case. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 786–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Nazir, M.F.; Chang, M.; Ma, Y.; Cai, E.; Ding, G.; Zhao, C.; Li, L.; et al. Ecological compensation in the context of carbon neutrality: A case involving service production-transmission and distribution-service consumption. Land 2022, 11, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Fine allocation of sectoral carbon emissions at block scale and contribution of functional zones. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 78, 102293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Kong, C.; Wang, L.; Mu, J.; Lu, X.; Bao, J.; Li, H. A provincial lateral carbon emissions compensation plan in China based on carbon budget perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 692, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.; Chen, X.; Ding, B.; Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, T. Spatially explicit carbon emissions at the county scale. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Z. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics, influencing factors of land use carbon emissions, and low-carbon development in Hubei Province, China. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 81, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Quan, J.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Research on the fine-scale spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of carbon emissions based on nighttime light data: A case study of Xi’an city. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, M.; Liu, D.; Ma, Y.; Wang, T.; Han, X. Fine mapping and multidimensional analysis of carbon emission reduction in China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1163308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, A.E.; Oda, T.; Sorichetta, A.; Stevens, F.R.; Bondarenko, M.; Bun, R.; Krauser, L.; Yetman, G.; Nghiem, S.V. Evaluating nighttime lights and population distribution as proxies for mapping anthropogenic CO2 emission in Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos. Environ. Res. Commun. 2019, 1, 091006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Zhou, T.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Spatial patterns of China’s carbon sinks estimated from the fusion of remote sensing and field-observed net primary productivity and heterotrophic respiration. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 76, 102152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuai, X.; Qi, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, X.; Park, S.; Zhao, R.; Xie, X.; et al. Land degradation monitoring using terrestrial ecosystem carbon sinks/sources and their response to climate change in China. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3489–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J. Assessment of carbon balance attribution and carbon storage potential in China’s terrestrial ecosystem. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 189, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Xie, P.; Zhao, D. Spatial and temporal disparities of carbon emissions and interregional carbon compensation in major function-oriented zones: A case study of Guangdong province. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yang, Y. Examining spatio-temporal variations in carbon budget and carbon compensation zoning in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration based on major functional zones. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1911–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Zhou, X. Spatial-temporal evolution of agricultural carbon balance at township scale and carbon compensation zoning: A case study of Guangshui City, Hubei Province. Land 2024, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, D.; Marland, G. CDIAC-FF: Global and national CO2 emissions from fossil fuel combustion and cement manufacture: 1751–2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 1667–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangini, C.; Peregon, A.; Ciais, P.; Weddige, U.; Vogel, F.; Wang, J.; Bréon, F.-M.; Bachra, S.; Wang, Y.; Gurney, K.; et al. A global dataset of CO2 emissions and ancillary data related to emissions for 343 cities. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 180280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Chuai, X. Carbon sinks/sources’ spatiotemporal evolution in China and its response to built-up land expansion. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, D.; Sarkar, A.; Cui, Y.; Qian, L.; Minjuan, Z.; Das, J.C. Ecological compensation of grain trade within urban, rural areas and provinces in China: A prospect of a carbon transfer mechanism. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 16688–16712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, W.; Yang, X. Coupling coordination evaluation and sustainable development pattern of geo-ecological environment and urbanization in Chongqing municipality, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 61, 102271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Ren, Y.; Shen, L.; Xiao, J.; Lai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L. A guiding methodology for “urban physical examination”: Indicator checklist, benchmark setting and empirical study. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, P.; Sha, D. A spatial projection pursuit model for identifying comprehensive urban vitality on blocks using multisource geospatial data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 104998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Ge, R.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Ye, H.; Liao, J.; Yin, K. Dynamic changes of a city’s carbon balance and its influencing factors: A case study in Xiamen, China. Carbon Manag. 2016, 7, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Yuan, X. Region-county characteristic of spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factor on land use-related CO2 emissions in Chongqing of China, 1997–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 231, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ke, X. The study on spatial correlation of recessive land use transformation and land use carbon emission. China Land Sci. 2022, 36, 100–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal pattern of soil respiration of terrestrial ecosystems in China: The development of a geostatistical model and its simulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6074–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiken, M.; Li, S.; Abulaiti, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Prediction of extreme climate on the Tibetan Plateau based on NEX-GDDP-CMIP6. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2023, 29, 2260493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Console, R.; Greco, M.; Iacovino, C.; Trivigno, M.L.; Falciano, A. Assessing vegetation declinedue to pollution from solid waste management by a multitemporal remote sensing approach. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Anees, S.A.; Rehman, A.; Pan, S.a.; Tariq, A.; Zubair, M.; Liu, Q.; Rabbi, F.; Khan, K.A.; Luo, M. Exploring spatiotemporal dynamics of NDVI and climate-driven responses in ecosystems: Insights for sustainable management and climate resilience. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, R.; Almazah, M.M.A.; Hussain, I.; Al-Ansari, N.; Al-Rezami, A.Y.; Sammen, S.S. Modified standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index: Spatiotemporal analysis of drought. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 2195532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Shahid, S.; Ismail, T.; Chung, E.-S.; Al-Abadi, A.M. Long-term trends in daily temperature extremes in Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2017, 198, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Shi, W.; Zeng, W.; He, Y. Spatiotemporal spillover effect and efficiency of carbon emissions from land use in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 8915–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Guan, D.; Zheng, H.; Ou, J.; Li, Y.; Meng, J.; Mi, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. China CO2 emission accounts 1997–2015. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 170201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Liu, L. Upscaling Tower-Based Net Ecosystem Productivity to global 250m using the Data Augmentation Method by Considering their Spatial Distribution. Zenodo 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal pattern of carbon compensation potential and network association in urban agglomerations in the Yellow River Basin. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; Jones, M.W.; O’Sullivan, M.; Andrew, R.M.; Bakker, D.C.E.; Hauck, J.; Le Quéré, C.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; et al. Global carbon budget 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 1917–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Gregor, L.; Hauck, J.; Le Quéré, C.; Luijkx, I.T.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; et al. Global carbon budget 2022. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 4811–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlingstein, P.; O’Sullivan, M.; Jones, M.W.; Andrew, R.M.; Hauck, J.; Olsen, A.; Peters, G.P.; Peters, W.; Pongratz, J.; Sitch, S.; et al. Global carbon budget 2020. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 3269–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Hao, R.; Ma, L.; Xie, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, J. Characteristics of carbon budget based on energy carbon emissions and vegetation carbon absorption. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liu, L.; Gu, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Q. Examining the relationships between carbon emissions and land supply in China. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, H.; Yao, L. A study case of China on inter-regional carbon compensation from the perspective of carbon neutrality. World Dev. Sustain. 2023, 2, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, E.; Song, T.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Z. Four-quadrant modelling of carbon inequality in international trade and accounting for carbon compensation. Carbon Manag. 2024, 15, 2311655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lu, R.; Zhang, P.; Dai, E. Multilevel ecological compensation policy design based on ecosystem service flow: A case study of carbon sequestration services in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, F.S.; Seidl, R.; Le, Q.B.; Brändle, J.M.; Scholz, R.W. Constructing consistent multiscale scenarios by transdisciplinary processes: The case of mountain regions facing global change. Ecol. Soc. 2013, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.; Stotten, R.; Steinbacher, M.; Leitinger, G.; Tasser, E.; Schirpke, U.; Tappeiner, U.; Schermer, M. Participative spatial scenario analysis for alpine ecosystems. Environ. Manag. 2017, 60, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, W.; Walz, A. Generic regional development strategies from local stakeholders’ scenarios—The Montafon experience. Ecol. Soc. 2010, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auty, R.M. Natural resources, capital accumulation and the resource curse. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 61, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.A.; Tilton, J.E. The resource curse. Nat. Resour. Forum 2005, 29, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, W.; He, L.; Ma, M.; Peng, H.; Li, L.; Ke, Q.; Hang, P.; Wang, X. Assessment on China’s urbanization after the implementation of main functional areas planning. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chongqing Planning and Natural Resources Bureau (CPNRB). Announcement on Public Solicitation of Opinions and Suggestions on the Master Plan of Chongqing Territorial Space (2021–2035). Available online: https://www.cq.gov.cn/zwgk/zfxxgkml/zdjcygk/zdjcyjzj/202105/t20210527_11479457.html (accessed on 29 November 2023).
- Chen, B.; Chen, F.; Ciais, P.; Zhang, H.; Lü, H.; Wang, T.; Chevallier, F.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, W.; Peters, W. Challenges to achieve carbon neutrality of China by 2060: Status and perspectives. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 2030–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Zhang, Y.; Ch, P.; Aqdas, R.; Chupradit, S.; Nawaz, A. A step towards sustainable environment in China: The role of eco-innovation renewable energy and environmental taxes. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.D.; Friedlingstein, P. Quantifying process-level uncertainty contributions to TCRE and carbon budgets for meeting Paris Agreement climate targets. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 074019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengis, N.; Partanen, A.-I.; Jalbert, J.; Matthews, H.D. 1.5 °C carbon budget dependent on carbon cycle uncertainty and future non-CO2 forcing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.C.; Melnikov, N.B. Learning about parameter and structural uncertainty in carbon cycle models. Clim. Chang. 2008, 89, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, B.P.; Styc, Q.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B. Digital soil mapping of soil carbon at the farm scale: A spatial downscaling approach in consideration of measured and uncertain data. Geoderma 2017, 290, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Qin, W.M.; Wang, L.C.; Yang, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.J.; Qi, Q.H. Projection of future carbon benefits by photovoltaic power potential in China using CMIP6 statistical downscaling data. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Du, X.; Liu, W.; Pan, K. High-resolution temporal and spatial evolution of carbon emissions from building operations in Beijing. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








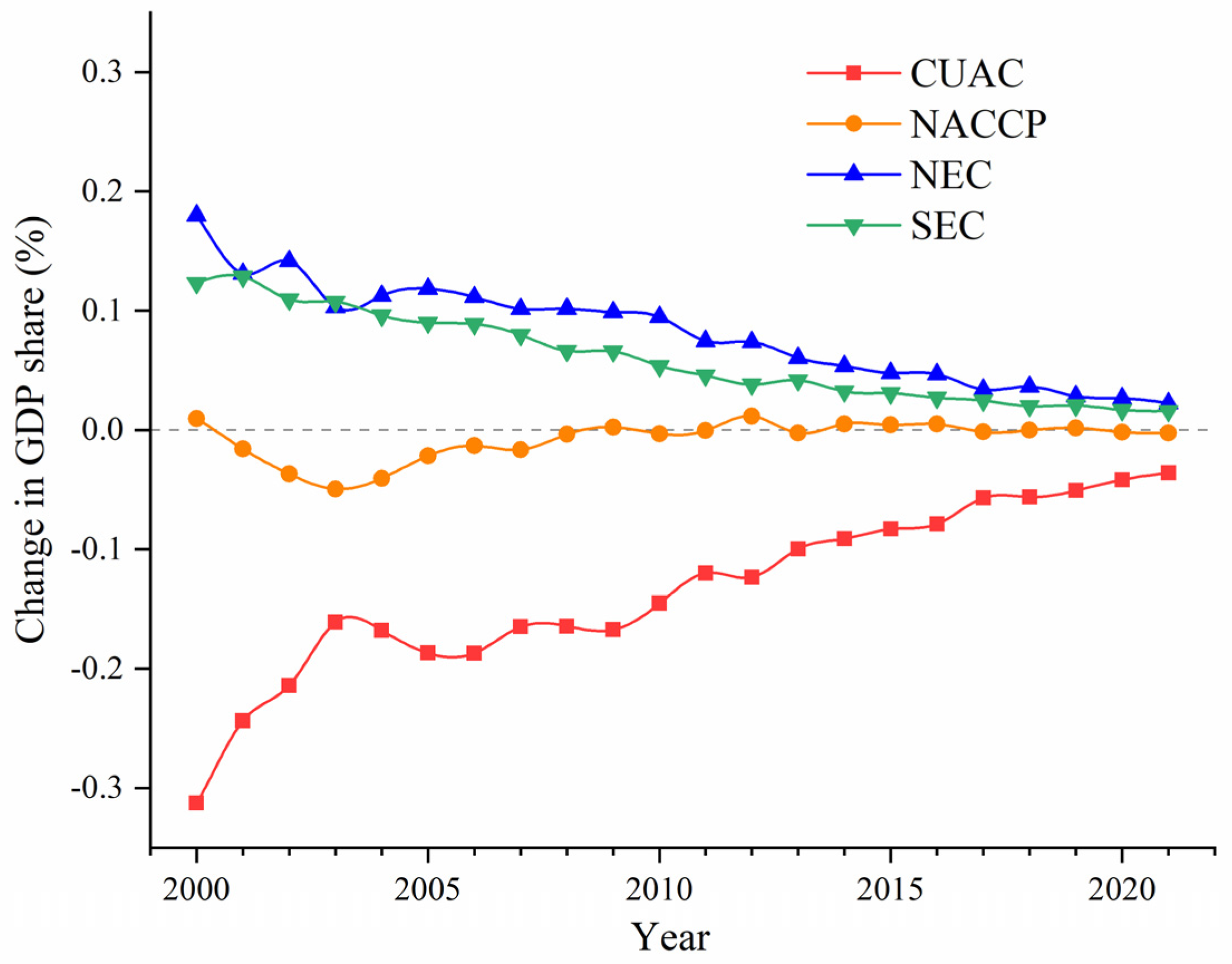
| Energy Types | Raw Coal | Coke | Crude Oil | Gasoline | Kerosene | Diesel Oil | Fuel Oil | Liquefied Petroleum Gas | Natural Gas | Electric Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard coal coefficient | 0.7143 | 0.9714 | 1.4286 | 1.4714 | 1.4714 | 1.4571 | 1.4286 | 1.7143 | 1.2143 | 0.1229 |
| Carbon-emission coefficient | 0.7559 | 0.8550 | 0.5857 | 0.5538 | 0.5714 | 0.5921 | 0.6815 | 0.5042 | 0.4483 | 0.7330 |
| Data | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption | Calculated the carbon emissions based on the consumption of 10 major energy sources | National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://www.stats.gov.cn) |
| Population | Supports demographic statistics, carbon emission calculation, and spatial distribution simulation | Oak Ridge National Laboratory (https://landscan.ornl.gov) |
| Net primary production (NPP) | Carbon sequestration calculation | NASA Earth Observation Data (https://www.earthdata.nasa.gov) |
| Temperature | Soil respiration calculation | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://auth.geodata.cn) |
| Precipitation | Soil respiration calculation | National Earth System Science Data Center (http://auth.geodata.cn) |
| SOC | Soil respiration calculation | A dataset of carbon density in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems (2010s) (http://www.csdata.org) |
| Land cover | SOC spatialization | The 30 m annual land cover datasets and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2021 (https://zenodo.org) |
| GDP and Engel coefficient | Calculation of the carbon compensation cost | Chongqing Bureau of Statistics (https://tjj.cq.gov.cn) |
| Carbon prices | Extract the highest and lowest trading prices | Carbon Trading Website (http://www.tanjiaoyi.com) |
| Type | Characteristics | Distribution | Counties |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key payment area | Mean > 0, Ts > 0 and |Z| > 1.96 |  | Banan, Beibei, Bishan, Changshou, Dazu, Dianjiang, Jiangbei, Liangping, Nanan, Rongchang, Tongliang, Tongnan, Yongchuan, Yubei, Yuzhong |
| Transfer payment area | Mean > 0, Ts < 0 and |Z| > 1.96 | None | None |
| Basic payment area | Mean > 0, |Z| < 1.96 |  | Dadukou, Hechuan, Jiulongpo, Shapingba, Zhong |
| Key recipient area | Mean < 0, Ts < 0 and |Z| > 1.96 |  | Fengdu, Fengjie, Fuling, Jiangjin, Kaizhou, Nanchuan, Pengshui, Qianjiang, Qijiang, Shizhu, Wanzhou, Wulong, Wushan, Wuxi, Xiushan, Youyang, Yunyang |
| Transfer recipient area | Mean < 0, Ts > 0 and |Z| > 1.96 | None | None |
| Basic recipient area | Mean > 0, |Z| < 1.96 |  | Chengkou |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, R.; Jin, X.; Zhou, H.; Ren, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; Yao, L.; Zhang, H. Regional Differences in Carbon Budgets and Inter-Regional Compensation Zoning: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Land 2024, 13, 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091495
Yang R, Jin X, Zhou H, Ren F, Zhang X, Ma Z, Yao L, Zhang H. Regional Differences in Carbon Budgets and Inter-Regional Compensation Zoning: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Land. 2024; 13(9):1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091495
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Renfei, Xianfeng Jin, Hongwen Zhou, Fu Ren, Xiaocheng Zhang, Zezhong Ma, Liwei Yao, and Hongwei Zhang. 2024. "Regional Differences in Carbon Budgets and Inter-Regional Compensation Zoning: A Case Study of Chongqing, China" Land 13, no. 9: 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091495
APA StyleYang, R., Jin, X., Zhou, H., Ren, F., Zhang, X., Ma, Z., Yao, L., & Zhang, H. (2024). Regional Differences in Carbon Budgets and Inter-Regional Compensation Zoning: A Case Study of Chongqing, China. Land, 13(9), 1495. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13091495





