Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Phytoplankton Analysis and Examining the Chemical Composition of Water
2.4. DNA Extraction, Cloning, Sequencing and Phylogenetic Agnalysis
3. Results
3.1. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of the Studied Lakes’ Water
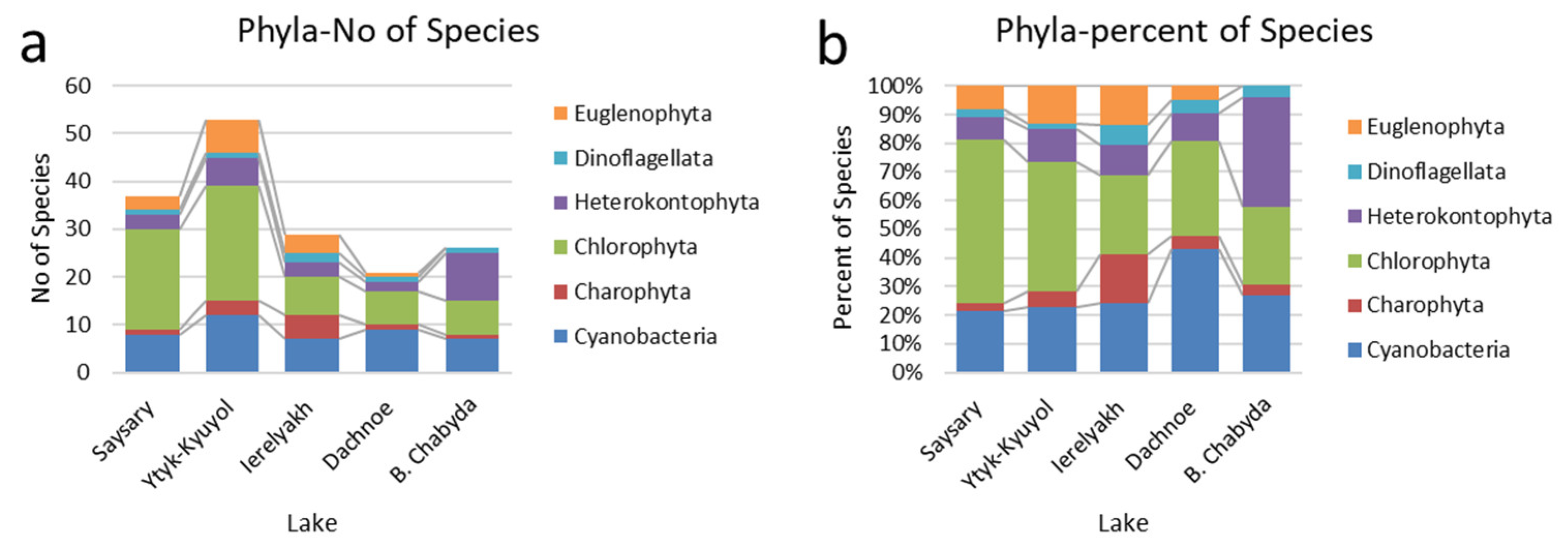
3.2. Composition of Phytoplankton Community and Dominant Species
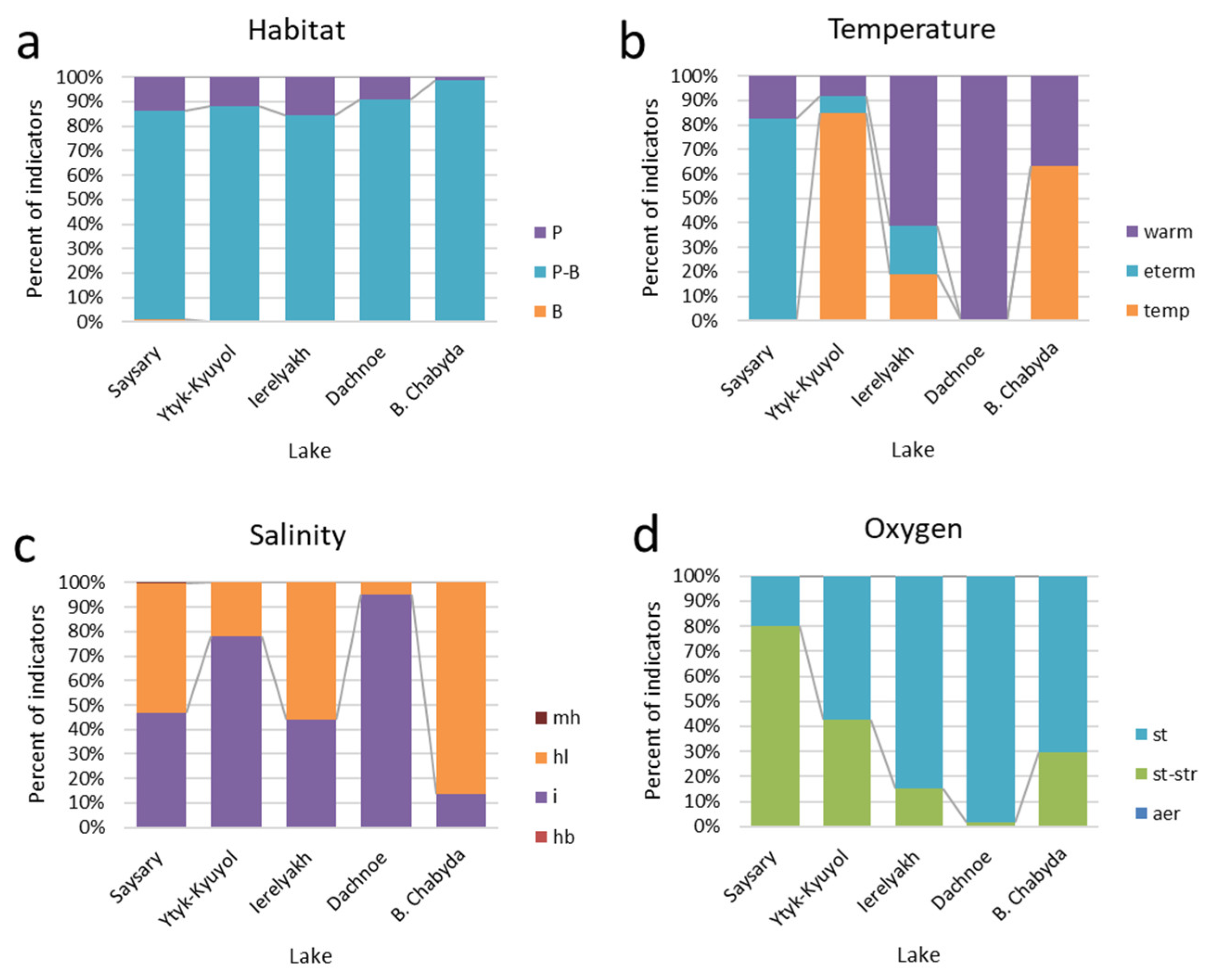
3.3. Bioindicators
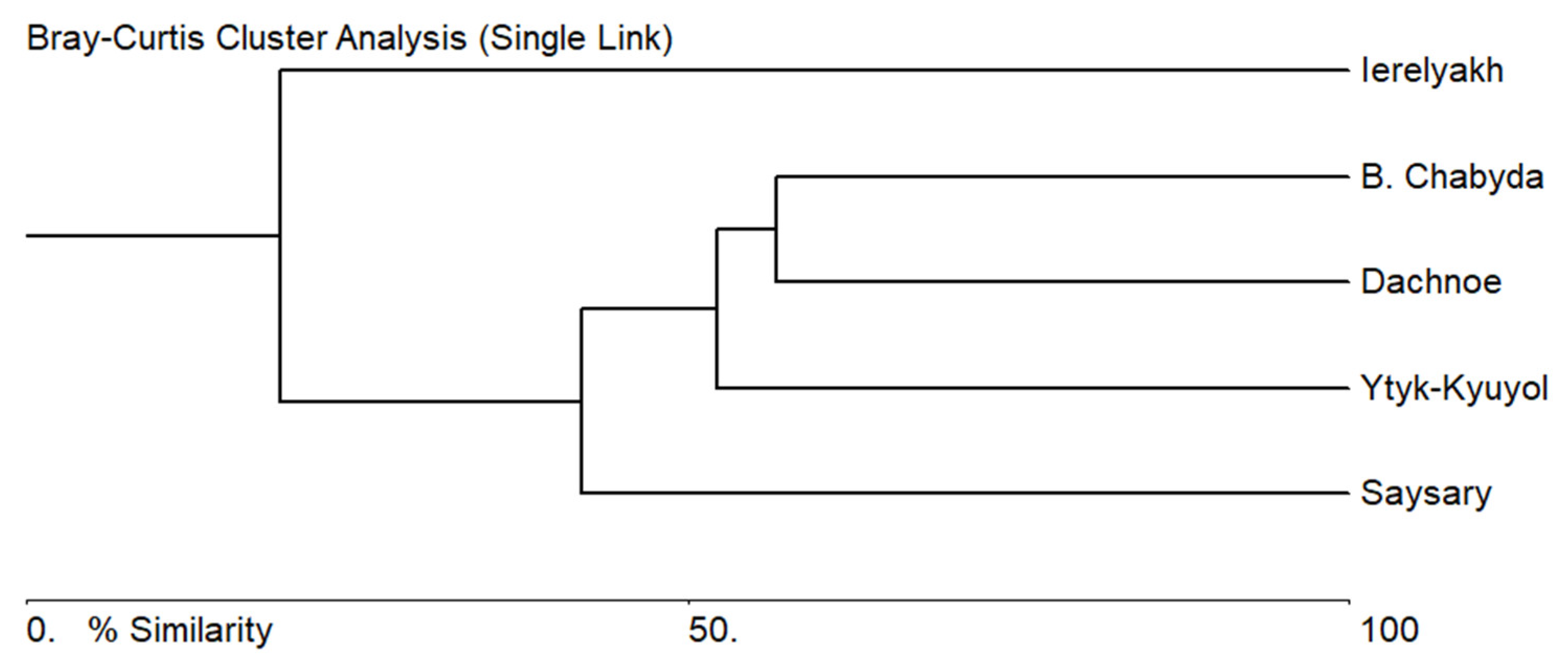
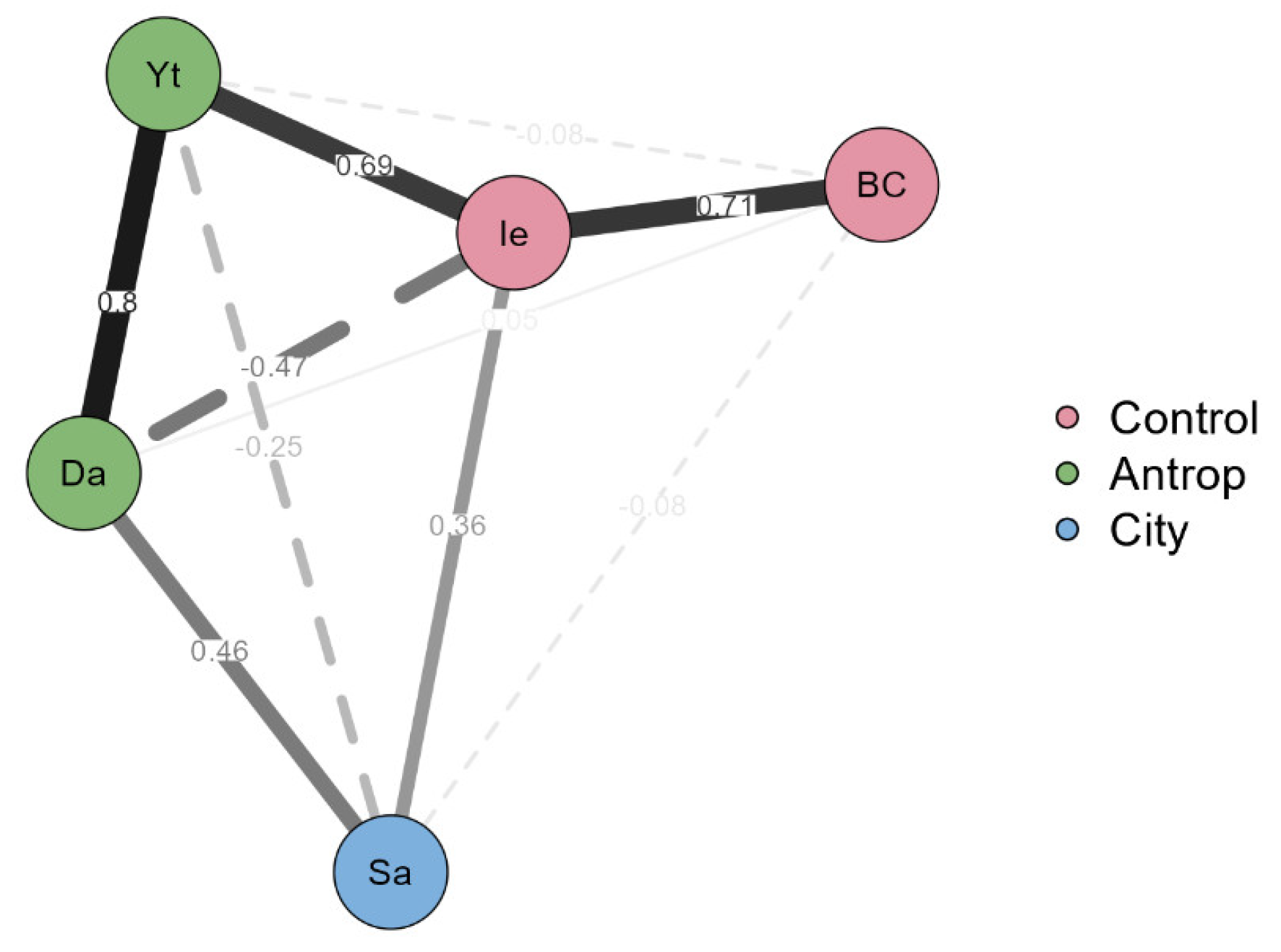
3.4. Comparative Analysis
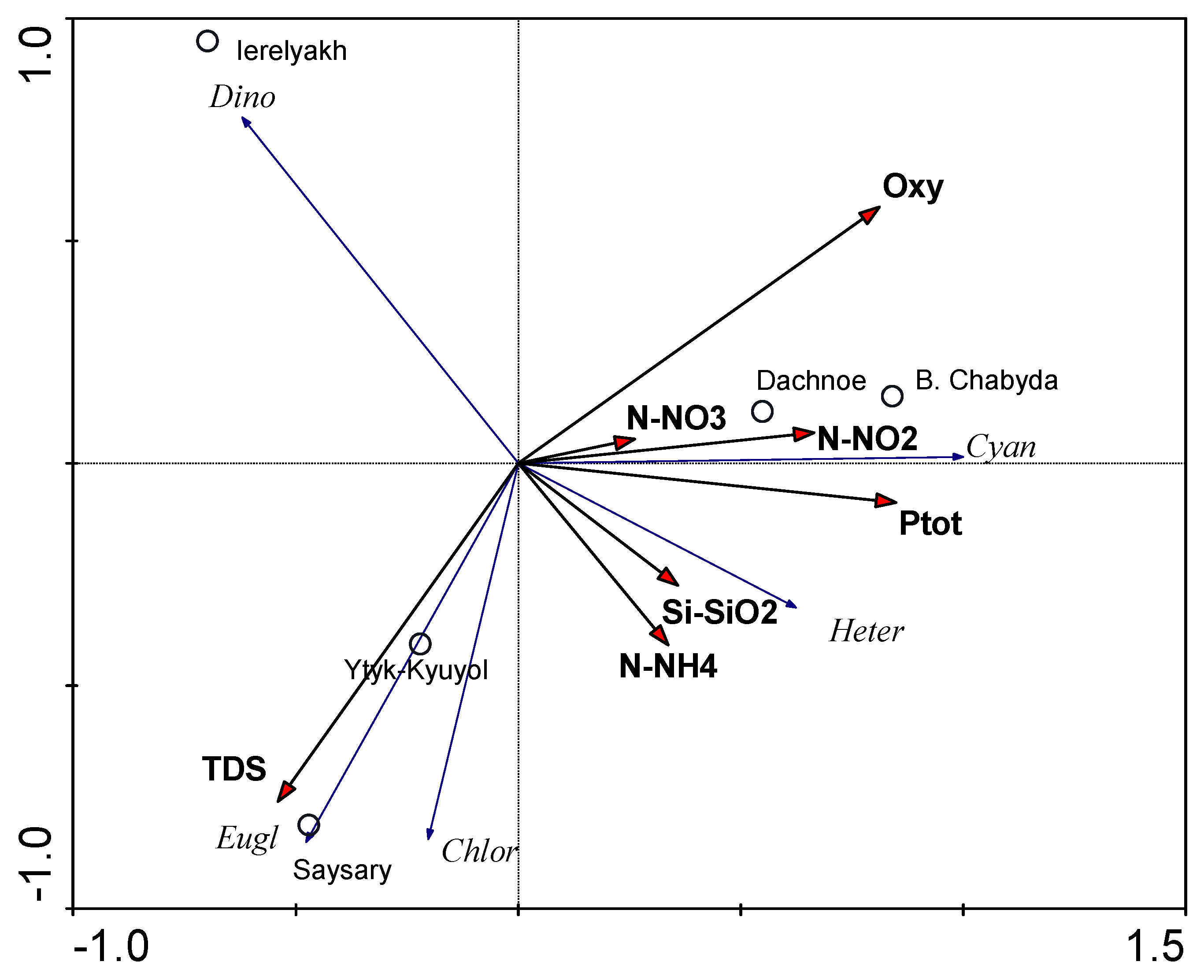
3.5. Species–Environmental Relationships
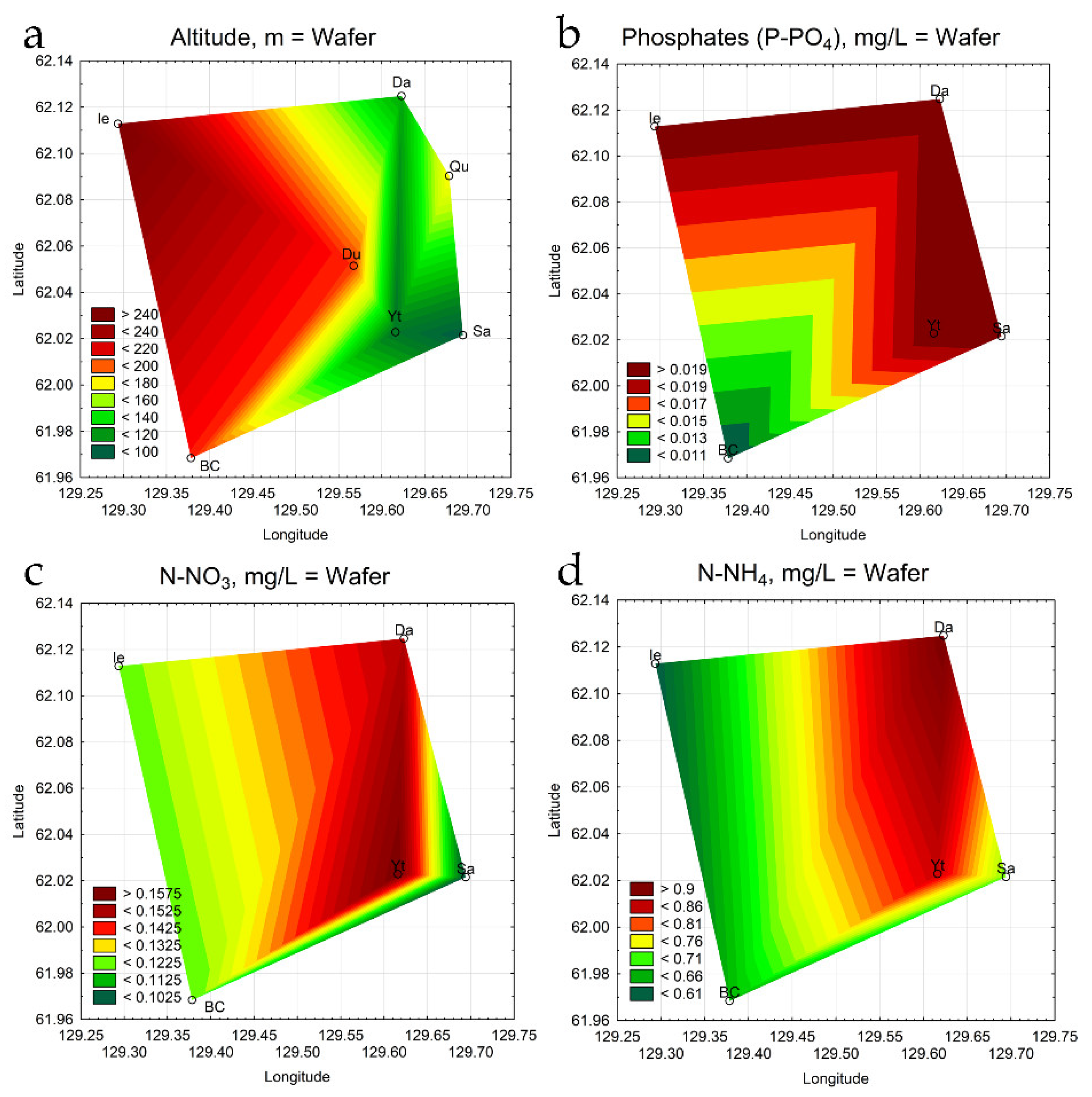
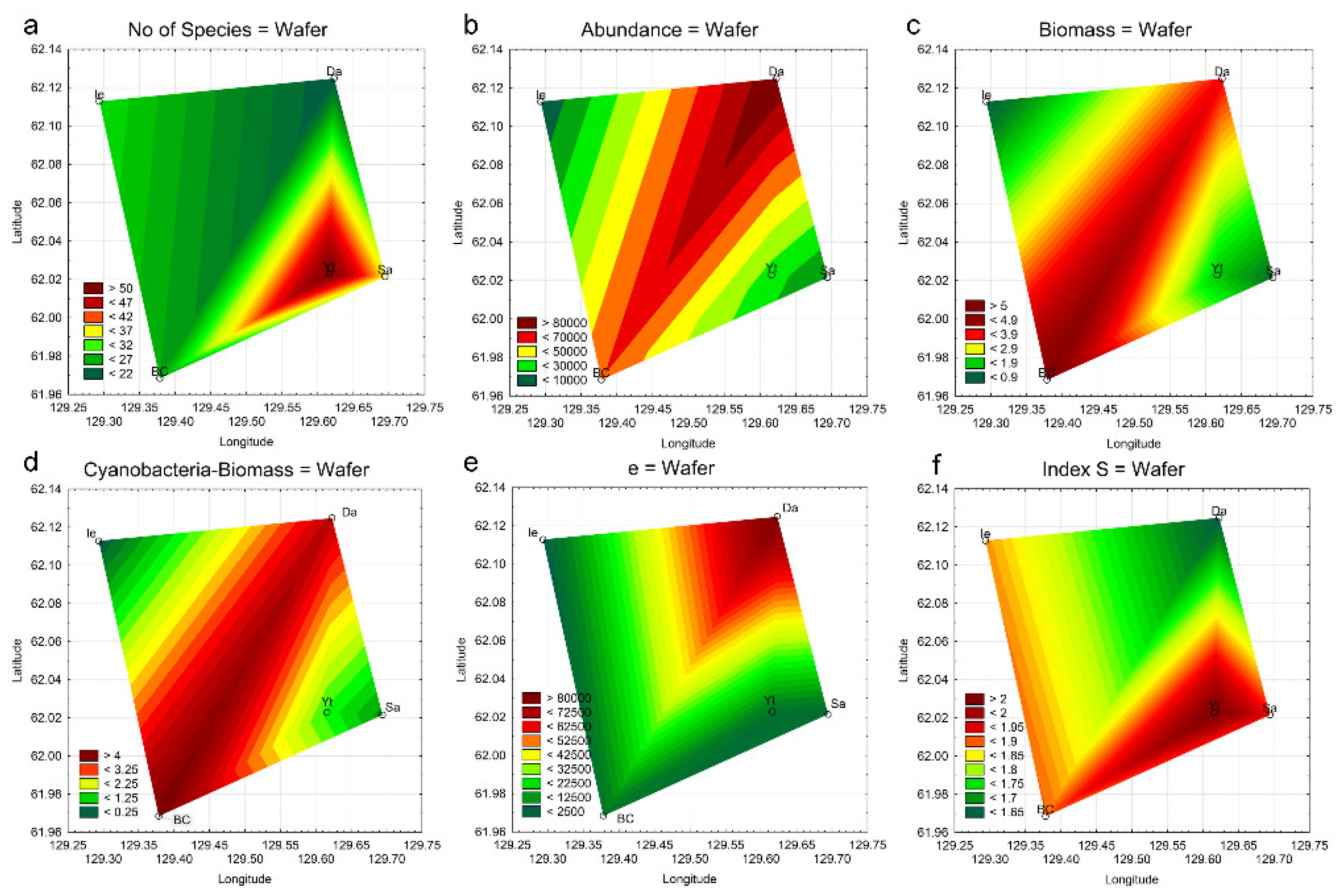
3.6. Statistical Mapping
3.7. Cyanotoxin Synthesis Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| JASP | Jeffreys’s Amazing Statistics Program |
| WESI | Water Ecosystem State Index |
| CCA | Canonical correspondence analysis |
| TDS | Total dissolved solids |
| TSS | Total suspended solids |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
Appendix A
| Variables | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water temperature, °C | 26.90 | 25.50 | 23.80 | 23.40 | 22.10 |
| pH | 8.44 | 8.28 | 8.47 | 7.98 | 8.41 |
| O2, mg L−1 | 7.31 | 11.37 | 14.63 | 20.15 | 20.96 |
| COD, mg L−1 | 104.90 | 118.30 | 118.00 | 104.70 | 142.90 |
| Pt-Co units | 44 | 75 | 47 | 85 | 36.00 |
| TDS, mg L−1 | 609.96 | 512.86 | 337.28 | 235.09 | 346.14 |
| Hardness, mmol. L−1 | 5.84 | 4.80 | 3.12 | 2.48 | 2.77 |
| Ca2+, mg L−1 | 49.70 | 49.70 | 19.24 | 30.46 | 42.00 |
| Mg2+, mg L−1 | 40.82 | 28.19 | 26.24 | 11.66 | 8.19 |
| Na+, mg L−1 | 60.00 | 50.60 | 30.40 | 14.30 | 38.00 |
| K+, mg L−1 | 8.24 | 7.72 | 12.10 | 4.97 | 8.04 |
| HCO3−, mg L−1 | 332.00 | 274.00 | 189.00 | 130.00 | 150.00 |
| Cl−, mg L−1 | 100.00 | 77.35 | 54.20 | 25.70 | 12.21 |
| SO42−, mg L−1 | 19.20 | 25.30 | <10.0 | 18.00 | 87.70 |
| N-NH4+, mg L−1 | 0.71 | 0.85 | 0.60 | 0.92 | 0.66 |
| N-NO2−, mg L−1 | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.021 | 0.010 |
| N-NO3−, mg L−1 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| P-PO43−, mg L−1 | 0.02 | <0.02 | <0.02 | 0.02 | <0.02 |
| Ptot, mg L−1 | 0.80 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 0.90 | 1.84 |
| Si, mg L−1 | 1.88 | 3.55 | 1.51 | 3.88 | 1.93 |
| Fetot, mg L−1 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.57 | 0.35 |
| Species | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charophyta | |||||
| Closterium acutum var. linea (Perty) West & G.S.West | 5.6 | ||||
| Closterium leibleinii Kützing ex Ralfs | 0.0002 | ||||
| Cosmarium formosulum Hoff | 0.1 | 0.0008 | 0.002 | ||
| Staurastrum boreale West & G.S.West | 1.5 | 0.6 | |||
| Staurastrum gracile Ralfs ex Ralfs | 0.004 | ||||
| Staurastrum manfeldtii Delponte | 0.0007 | ||||
| Staurastrum tetracerum Ralfs ex Ralfs | 1.6 | 0.02 | |||
| Chlorophyta | |||||
| Actinastrum hantzschii Lagerheim | 363.9 | 162.3 | |||
| Ankistrodesmus arcuatus Korshikov | 180.7 | ||||
| Ankistrodesmus fusiformis Corda | 158.4 | ||||
| Botryococcus braunii Kützing | 366.6 | 161.1 | 53.7 | 620.7 | 1521.9 |
| Coelastrum astroideum De Notaris | 60.2 | 22.4 | 0.3 | ||
| Desmodesmus armatus (Chodat) E.H.Hegewald | 599.6 | 59.6 | 0.3 | 3.1 | |
| Desmodesmus spinosus (Chodat) E.Hegewald | 522.2 | 2.2 | 154.6 | ||
| Dicellula geminata (Printz) Korshikov | 30 | ||||
| Kirchneriella lunaris (Kirchner) Möbius | 160.4 | ||||
| Lagerheimia genevensis (Chodat) Chodat | 200.4 | ||||
| Lagerheimia subsalsa Lemmermann | 211.5 | ||||
| Lemmermannia tetrapedia (Kirchner) Lemmermann | 306.7 | 94 | |||
| Micractinium pusillum Fresenius | 164 | 52.9 | |||
| Monoraphidium contortum (Thuret) Komárková-Legnerová | 283.5 | 92.1 | |||
| Monoraphidium griffithii (Berkeley) Komárková-Legnerová | 142.7 | 53.7 | |||
| Mucidosphaerium pulchellum (H.C.Wood) C.Bock, Proschold & Krienitz | 164 | 54 | 2.4 | 17.4 | |
| Oocystis borgei J.W.Snow | 90.1 | ||||
| Oocystis lacustris Chodat | 0.4 | ||||
| Pandorina morum (O.F.Müller) Bory | 135.2 | 22.5 | 133.2 | 14.6 | 38.3 |
| Parapediastrum biradiatum (Meyen) E.Hegewald | 7.9 | ||||
| Pediastrum duplex Meyen | 14.7 | 5.3 | 0.2 | ||
| Pseudopediastrum boryanum (Turpin) E.Hegewald | 23.8 | 42.4 | 0.9 | 4.1 | 15.9 |
| Scenedesmus obtusus f. disciformis (Chodat) Compère | 70.4 | 0.6 | |||
| Scenedesmus obtusus Meyen | 177.7 | 14.8 | |||
| Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turpin) Brébisson | 481 | ||||
| Schroederia setigera (Schröder) Lemmermann | 67.4 | 19.7 | |||
| Selenastrum bibraianum Reinsch | 25.6 | ||||
| Tetradesmus lagerheimii M.J.Wynne & Guiry | 497.3 | 282.8 | 376.5 | ||
| Tetradesmus obliquus (Turpin) M.J.Wynne | 52.2 | ||||
| Tetraëdron caudatum (Corda) Hansgirg | 13.2 | ||||
| Tetraëdron minimum (A.Braun) Hansgirg | 29 | 11.6 | |||
| Treubaria planctonica (G.M.Smith) Korshikov | 363.5 | ||||
| Cyanobacteria | |||||
| Anathece clathrata (West & G.S.West) Komárek, Kaštovský & Jezberová | 6250.4 | 35,419.2 | |||
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Bornet & Flahault | 3322.8 | 530.5 | 22,091.8 | ||
| Aphanocapsa conferta (West & G.S.West) Komárková-Legnerová & Cronberg | 8.7 | ||||
| Aphanocapsa delicatissima West & G.S.West | 980.8 | ||||
| Aphanocapsa incerta (Lemmermann) G.Cronberg & Komárek | 8575.2 | 255.7 | 5540.5 | ||
| Aphanocapsa planctonica (G.M.Smith) Komárek & Anagnostidis | 3434.5 | ||||
| Chroococcus turgidus (Kützing) Nägeli | 2 | ||||
| Dolichospermum sp. | 373.7 | ||||
| Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Richter) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | 158.1 | 8 | 10.3 | 2015.2 | |
| Dolichospermum perturbatum (H.Hill) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 173.6 | ||||
| Dolichospermum planctonicum (Brunnthaler) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 32.4 | 87.7 | |||
| Dolichospermum sigmoideum (Nygaard) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 382.4 | ||||
| Dolichospermum spiroides (Klebahn) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | 241.7 | ||||
| Lyngbya cincinnata (Itzigsohn) Compère | 0.6 | ||||
| Merismopedia tranquilla (Ehrenberg) Trevisan | 635.6 | ||||
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | 4847.8 | 1736.1 | 13,621.8 | ||
| Microcystis flos-aquae (Wittrock) Kirchner | 23,607.9 | 76,325.1 | 49,904.9 | ||
| Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek ex Komárek | 320.4 | 553.8 | 300 | 2353.8 | |
| Oscillatoria anguina Bory ex Gomont | 0.7 | ||||
| Oscillatoria limosa C.Agardh ex Gomont | 0.3 | ||||
| Oscillatoria princeps Vaucher ex Gomont | 17.4 | ||||
| Phormidium ambiguum Gomont | 76.7 | ||||
| Phormidium chalybeum (Mertens ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | 97 | ||||
| Snowella lacustris (Chodat) Komárek & Hindák | 954.9 | 9.5 | |||
| Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin | 1923.1 | 7777.8 | |||
| Dinoflagellata | |||||
| Ceratium hirundinella (O.F.Müller) Dujardin | 0.6 | 1.4 | 22.7 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| Peridinium cinctum (O.F.Müller) Ehrenberg | 0.0004 | ||||
| Euglenophyta | |||||
| Lepocinclis acus (O.F.Müller) B.Marin & Melkonian | 5.4 | 1.6 | 0.01 | ||
| Lepocinclis oxyuris (Schmarda) B.Marin & Melkonian | 0.2 | 0.003 | |||
| Monomorphina pyrum (Ehrenberg) Mereschkowsky | 4.2 | 2.3 | |||
| Phacus longicauda (Ehrenberg) Dujardin | 0.2 | ||||
| Phacus orbicularis Hübner | 0.8 | ||||
| Strombomonas acuminata (Schmarda) Deflandre | 0.4 | ||||
| Trachelomonas dybowskii Dreżepolski | 0.4 | ||||
| Trachelomonas granulosa Playfair | 0.01 | ||||
| Trachelomonas hispida (Perty) F.Stein | 0.005 | ||||
| Trachelomonas planctonica Svirenko | 2 | ||||
| Trachelomonas woycickii Koczwara | 3.6 | ||||
| Heterokontophyta | |||||
| Acanthoceras zachariasii (Brun) Simonsen | 4.5 | ||||
| Amphora ovalis (Kützing) Kützing | 0.1 | ||||
| Aulacoseira granulata (Ehrenberg) Simonsen | 19.1 | 26.6 | |||
| Craticula cuspidata (Kützing) D.G.Mann | 0.4 | ||||
| Dinobryon divergens O.E.Imhof | 10.6 | 0.3 | 4.4 | ||
| Dinobryon sociale (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg | 50.6 | ||||
| Frustulia saxonica Rabenhorst | 0.1 | ||||
| Navicula radiosa Kützing | 1.1 | ||||
| Nitzschia acicularis (Kützing) W.Smith | 57.2 | ||||
| Pseudostaurastrum limneticum (Borge) Guiry | 2.8 | ||||
| Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C.Agardh) Lange-Bertalot | 0.1 | ||||
| Stauroneis phoenicenteron (Nitzsch) Ehrenberg | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||
| Surirella librile (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg | 0.3 | ||||
| Tetraplektron laevis (Bourrelly) Ettl | 0.7 | ||||
| Ulnaria acus (Kützing) Aboal | 18.1 | 7 | 2.1 | 18.3 | 33.9 |
| Ulnaria ulna (Nitzsch) Compère | 28.1 |
| Taxa | Hab | T | OXY | HAL | pH | D | AUT-HET | TRO | Index S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charophyta | |||||||||
| Closterium acutum var. linea (Perty) West & G.S.West | P-B | - | - | - | ind | - | - | m | 2.2 |
| Closterium leibleinii Kützing ex Ralfs | P-B | - | st-str | - | ind | - | - | e | 2.6 |
| Cosmarium formosulum Hoff | P-B | - | - | - | ind | - | - | me | 1.8 |
| Staurastrum boreale West & G.S.West | B | - | - | - | ind | - | - | m | - |
| Staurastrum gracile Ralfs ex Ralfs | P-B | - | st | i | acf | - | - | m | - |
| Staurastrum manfeldtii Delponte | B | - | - | - | ind | - | - | e | - |
| Staurastrum tetracerum Ralfs ex Ralfs | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | om | 1.3 |
| Chlorophyta | |||||||||
| Actinastrum hantzschii Lagerheim | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Ankistrodesmus arcuatus Korshikov | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | - | 2.1 |
| Ankistrodesmus fusiformis Corda | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | e | 2.0 |
| Botryococcus braunii Kützing | P-B | - | st | i | ind | - | - | - | 1.5 |
| Coelastrum astroideum De Notaris | P | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 2.2 |
| Desmodesmus armatus (Chodat) E.H.Hegewald | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 1.9 |
| Desmodesmus spinosus (Chodat) E.Hegewald | P-B | - | st-str | - | alf | - | - | - | 2.0 |
| Dicellula geminata (Printz) Korshikov | P-B | - | st | - | - | - | - | me | 2.2 |
| Kirchneriella lunaris (Kirchner) Möbius | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | e | - |
| Lagerheimia genevensis (Chodat) Chodat | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | - | 2.1 |
| Lagerheimia subsalsa Lemmermann | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | - | 1.2 |
| Lemmermannia tetrapedia (Kirchner) Lemmermann | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | 2.0 |
| Micractinium pusillum Fresenius | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | m | 0.3 |
| Monoraphidium contortum (Thuret) Komárková-Legnerová | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | - | - |
| Monoraphidium griffithii (Berkeley) Komárková-Legnerová | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | e | 2.5 |
| Mucidosphaerium pulchellum (H.C.Wood) C.Bock, Proschold & Krienitz | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | 1.8 |
| Oocystis borgei J.W.Snow | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | 1.7 |
| Oocystis lacustris Chodat | P-B | - | st-str | hl | - | - | - | - | - |
| Pandorina morum (O.F.Müller) Bory | P | - | st | i | - | - | - | m | - |
| Parapediastrum biradiatum (Meyen) E.Hegewald | P-B | - | - | i | alb | - | - | - | 2.9 |
| Pediastrum duplex Meyen | P | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | - |
| Pseudopediastrum boryanum (Turpin) E.Hegewald | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | 2.1 |
| Scenedesmus obtusus f. disciformis (Chodat) Compère | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | e | 1.9 |
| Scenedesmus obtusus Meyen | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 1.8 |
| Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turpin) Brébisson | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | - | 2.1 |
| Schroederia setigera (Schröder) Lemmermann | P | - | st-str | i | alf | - | - | e | 1.7 |
| Selenastrum bibraianum Reinsch | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 1.7 |
| Tetradesmus lagerheimii M.J.Wynne & Guiry | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | 2.15 |
| Tetradesmus obliquus (Turpin) M.J.Wynne | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | ot | 2.4 |
| Tetraëdron caudatum (Corda) Hansgirg | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | e | 2.0 |
| Tetraëdron minimum (A.Braun) Hansgirg | P-B | - | st-str | i | alf | - | - | e | 2.1 |
| Treubaria planctonica (G.M.Smith) Korshikov | P | - | st | - | - | - | - | - | 1.9 |
| Cyanobacteria | |||||||||
| Anathece clathrata (West & G.S.West) Komárek, Kaštovský & Jezberová | P-B | - | - | hl | - | - | - | me | 1.8 |
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Bornet & Flahault | P-B | - | - | hl | alb | - | - | m | 1.95 |
| Aphanocapsa conferta (West & G.S.West) Komárková-Legnerová & Cronberg | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | me | - |
| Aphanocapsa delicatissima West & G.S.West | P-B | - | - | i | - | - | - | m | - |
| Aphanocapsa incerta (Lemmermann) G.Cronberg & Komárek | P-B | - | - | i | - | - | - | me | 2.2 |
| Aphanocapsa planctonica (G.M.Smith) Komárek & Anagnostidis | P-B | - | - | i | - | - | - | o-e | - |
| Chroococcus turgidus (Kützing) Nägeli | P-B | - | aer | hl | alf | - | - | e | 0.8 |
| Dolichospermum sp. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Richter) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | e | - |
| Dolichospermum perturbatum (H.Hill) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | m | - |
| Dolichospermum planctonicum (Brunnthaler) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 2.0 |
| Dolichospermum sigmoideum (Nygaard) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | e | 1.7 |
| Dolichospermum spiroides (Klebahn) Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & Komárek | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | e | 1.3 |
| Lyngbya cincinnata (Itzigsohn) Compère | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Merismopedia tranquilla (Ehrenberg) Trevisan | P-B | - | - | i | ind | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | P-B | - | - | hl | acf | - | - | me | 2.2 |
| Microcystis flos-aquae (Wittrock) Kirchner | P-B | - | - | i | - | - | - | e | 1.6 |
| Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek ex Komárek | P-B | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Oscillatoria anguina Bory ex Gomont | B | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Oscillatoria limosa C.Agardh ex Gomont | P-B | - | st-str | hl | alf | - | - | - | - |
| Oscillatoria princeps Vaucher ex Gomont | P-B | - | st-str | - | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Phormidium ambiguum Gomont | B | eterm | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Phormidium chalybeum (Mertens ex Gomont) Anagnostidis & Komárek | P-B | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | 3.3 |
| Snowella lacustris (Chodat) Komárek & Hindák | P | - | - | i | alb | - | - | me | 1.6 |
| Woronichinia naegeliana (Unger) Elenkin | P | - | st | - | - | - | - | e | 1.8 |
| Dinoflagellata | |||||||||
| Ceratium hirundinella (O.F.Müller) Dujardin | P | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | e | 1.3 |
| Peridinium cinctum (O.F.Müller) Ehrenberg | P-B | - | st-str | i | - | - | - | - | 1.4 |
| Euglenophyta | |||||||||
| Lepocinclis acus (O.F.Müller) B.Marin & Melkonian | P | eterm | st | i | ind | - | - | - | 2.4 |
| Lepocinclis oxyuris (Schmarda) B.Marin & Melkonian | P-B | - | st-str | mh | ind | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Monomorphina pyrum (Ehrenberg) Mereschkowsky | P-B | eterm | st-str | mh | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Phacus longicauda (Ehrenberg) Dujardin | P-B | - | st | i | ind | - | - | - | 2.8 |
| Phacus orbicularis Hübner | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Strombomonas acuminata (Schmarda) Deflandre | P | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Trachelomonas dybowskii Dreżepolski | P | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Trachelomonas granulosa Playfair | P | eterm | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2.2 |
| Trachelomonas hispida (Perty) F.Stein | P-B | eterm | st-str | i | acf | - | - | - | 2.2 |
| Trachelomonas planctonica Svirenko | P | eterm | st-str | I | ind | - | - | - | 2.1 |
| Trachelomonas woycickii Koczwara | P | - | st | - | - | - | - | - | 2.3 |
| Heterokontophyta | |||||||||
| Acanthoceras zachariasii (Brun) Simonsen | P | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | 1.4 |
| Amphora ovalis (Kützing) Kützing | B | temp | st-str | i | alf | sx | ate | e | 1.5 |
| Aulacoseira granulata (Ehrenberg) Simonsen | P-B | temp | st-str | i | alf | es | ate | e | 2.0 |
| Craticula cuspidata (Kützing) D.G.Mann | B | temp | st-str | i | alf | es | - | me | 2.45 |
| Dinobryon divergens O.E.Imhof | P-B | - | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | 1.2 |
| Dinobryon sociale (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg | P | - | - | i | - | - | - | - | 1.3 |
| Frustulia saxonica Rabenhorst | B | temp | st-str | hb | acf | - | ate | - | - |
| Navicula radiosa Kützing | B | temp | st-str | i | ind | sx | - | - | - |
| Nitzschia acicularis (Kützing) W.Smith | P-B | temp | st | i | alf | es | ats | om | 1.4 |
| Pseudostaurastrum limneticum (Borge) Guiry | P | - | st-str | - | - | - | - | e | - |
| Rhoicosphenia abbreviata (C.Agardh) Lange-Bertalot | B | temp | st-str | i | alf | es | ate | me | 1.9 |
| Stauroneis phoenicenteron (Nitzsch) Ehrenberg | P-B | temp | st-str | i | ind | - | - | - | - |
| Surirella librile (Ehrenberg) Ehrenberg | P-B | temp | st-str | i | alf | - | hne | - | - |
| Tetraplektron laevis (Bourrelly) Ettl | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ulnaria acus (Kützing) Aboal | P-B | warm | st-str | i | alf | es | ate | me | 1.85 |
| Ulnaria ulna (Nitzsch) Compère | P-B | temp | st-str | i | alf | es | ate | e | 2.4 |
| Variable | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Habitat | |||||
| B | 76.676 | 1.502 | 0.780 | 0 | 2.318 |
| P-B | 7671.032 | 44,310.455 | 6568.461 | 106,745.137 | 104,459.438 |
| P | 1446.599 | 3034.493 | 175.086 | 7976.926 | 2534.584 |
| Temperature | |||||
| temp | 0 | 76.293 | 0.068 | 0.013 | 56.677 |
| eterm | 86.255 | 5.881 | 0.028 | 0 | 0 |
| warm | 18.145 | 7.031 | 2.109 | 18.281 | 33.867 |
| Oxygen | |||||
| aer | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.962 |
| st-str | 3885.325 | 1917.010 | 31.691 | 131.160 | 656.791 |
| st | 874.278 | 2195.718 | 186.919 | 8413.130 | 1560.230 |
| Salinity | |||||
| hb | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.065 |
| i | 3541.633 | 38,973.991 | 489.403 | 82,551.148 | 55,429.458 |
| hl | 3322.785 | 5378.215 | 6250.760 | 23,828.256 | 49,042.966 |
| mh | 4.188 | 2.496 | 0.003 | 0 | 0 |
| Water pH | |||||
| acf | 0 | 4847.756 | 0.009 | 1736.111 | 13,621.860 |
| ind | 1572.928 | 1365.943 | 57.407 | 642.309 | 1920.507 |
| alf | 636.709 | 114.592 | 4.671 | 18.281 | 245.941 |
| alb | 3322.785 | 1493.276 | 9.549 | 22,091.772 | 0 |
| Watanabe | |||||
| sx | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.235 |
| es | 18.145 | 83.324 | 2.177 | 18.281 | 88.937 |
| Autotrophy-Heterotrophy | |||||
| ats | 0 | 57.165 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ate | 18.145 | 26.159 | 2.177 | 18.281 | 88.769 |
| hne | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.291 |
| Trophic state | |||||
| ot | 0 | 0.052 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| om | 0.002 | 0.057 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| m | 3.622 | 0.136 | 0.134 | 2.480 | 0.138 |
| me | 0.018 | 14.389 | 0.902 | 2.309 | 49.075 |
| e | 2.401 | 5.252 | 0.025 | 84.201 | 5.674 |
| o-e | 0 | 3.434 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Class of Water Quality | |||||
| Class 1 | 164.49 | 52.932 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Class 2 | 378.917 | 674.433 | 77.0084 | 63.15 | 1528.872 |
| Class 3 | 6929.046 | 20,904.405 | 901.52 | 88,820.915 | 57,521.776 |
| Class 4 | 97.43 | 8.083 | 0.0002 | 0 | 0 |

References
- Carmichael, W.W.; Boyer, G.L. Health impacts from cyanobacteria harmful algae blooms: Implications for the North American Great Lakes. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 194–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, J.; Codd, G.A.; Paerl, H.W.; Ibelings, B.W.; Verspagen, J.M.H.; Visser, P.M. Cyanobacterial blooms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; p. 858. [Google Scholar]
- Gaevaya, I.K.; Batozhergalova, I.I.; Konstantinova, V.A. Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia): Statistical Abstract; Printing House Smik: Yakutsk, Russia, 2023; p. 544. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Vasilieva, I.I. Composition and Seasonal Dynamics of Phytoplankton in Lakes Around the City of Yakutsk. Ph.D. Thesis, Central Siberian Botanic Garden, Novosibirsk, Russia, 1968. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Vasilyeva, I.I.; Ivanova, A.P.; Pshennikova, E.V. Species composition and seasonal dynamics of algae of lakes of Yakutsk and it’s environs (middle flow of Lena River). Algologia 1997, 7, 30–34. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, A.P. Algae of Urban and Suburban Lakes of the Middle Lena Valley. Ph.D. Thesis, Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia, 2000. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Kopyrina, L.I. Phytoplankton of the lake Dienkyudya. Nauka I Obraz. [Sci. Educ.] 2007, 2, 13–18. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kopyrina, L.; Pshennikova, E.; Barinova, S. Diversity and ecological characteristic of algae and cyanobacteria of thermokarst lakes in Yakutia (northeastern Russia). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2020, 49, 99–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S.; Gabyshev, V.A.; Gabysheva, O.I. Response of the Cyanobacteria Plankton Community to Anthropogenic Impact in Small Lakes of Urbanized Territory in the Permafrost Zone of Northeast Asia (Eastern Siberia, Yakutia). Water 2024, 16, 2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Voronov, I.V.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A. Limnological Characterization and First Data on the Occurrence of Toxigenic Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins in the Plankton of Some Lakes in the Permafrost Zone (Yakutia, Russia). Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2023, 16, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Vilnet, A.A.; Davydov, D.A.; Barinova, S.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A.; Voronov, I.V. Year-Round Presence of Microcystins and Toxin-Producing Microcystis in the Water Column and Ice Cover of a Eutrophic Lake Located in the Continuous Permafrost Zone (Yakutia, Russia). Toxins 2023, 15, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elovskaya, L.G. Classification and Diagnostics of Frozen Soils in Yakutia; Publishing House of the Yakut Branch of the Siberian Division of the RUSSIA Academy of Sciences: Yakutsk, Russia, 1987; p. 172. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fouché, J.; Christiansen, C.T.; Lafrenière, M.J.; Grogan, P.; Lamoureux, S.F. Canadian permafrost stores large pools of ammonium and optically distinct dissolved organic matter. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izyumenko, S.A. (Ed.) Climate of the Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Atlas); Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1968; p. 33. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Arzhakova, S.K.; Zhirkov, I.I.; Kusatov, K.I.; Androsov, I.M. Rivers and Lakes of Yakutia: A Brief Guide; Bichik: Yakutsk, Russia, 2007; p. 176. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- WorldClim. Available online: https://www.worldclim.org/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Hillebrand, H.; Durselen, C.D.; Kirschtel, D.; Pollingher, U.; Zohary, T. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 403–424. [Google Scholar]
- Starmach, K. Chrysophyceae und Haptophyceae; VEB Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1985; p. 515. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilyeva, I.I. Freshwater Euglenids and Yellow-Green Algae of Water Bodies of Yakutia; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1987; p. 265. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Palamar-Mordvintseva, G.M. Green Algae. Class Conjugates. Key to Freshwater Algae of the RUSSIA; Nauka: Leningrad, Russia, 1982; p. 483. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Popovský, J.; Pfiester, L.A. Dinophyceae (Dinoflagellida); Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena/Stuttgart, Germany, 1990; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Tsarenko, P.M. Brief Guide to Chlorococcal Algae of the Ukrainian SSR; Naukova Dumka: Kyiv, Russia, 1990; p. 208. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 1. Chroococcales; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Jena, Germany, 1998; p. 548. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 2. Oscillatoriales; Elsevier: München, Germany, 2005; p. 759. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J. Heterocytous Genera. Cyanoprokaryota. T. 3, P. 3; Springer Spektrum: Berlin, Germany, 2013; p. 1130. [Google Scholar]
- Kulikovskiy, M.S.; Glushchenko, A.M.; Genkal, S.I.; Kuznetsova, I.V. Identification Book of Diatoms from Russia; Filigran: Yaroslavl, Russia, 2016; p. 804. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase; World-Wide Electronic Publication, University of Galway: Galway, Ireland, 2024; Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Semenov, A.D. Guidance on the Chemical Analysis of Surface Waters of the Land; Gidrometeoizdat: Leningrad, Russia, 1977; p. 541. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fresenius, W.; Quentin, K.E.; Schneider, W. (Eds.) Water Analysis: A Practical Guide to Physico-Chemical, Chemical, and Microbiological Water Examination and Quality Assurance; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988; p. 830. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; The University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1949; p. 117. [Google Scholar]
- McAleece, N.; Gage, J.D.G.; Lambshead, P.J.D.; Paterson, G.L.J. BioDiversity Professional Statistics Analysis Software; Jointly developed by the Scottish Association for Marine Science and the Natural History Museum London: London, UK, 1997; Available online: https://www.sams.ac.uk/science/outputs/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.A.; Ly, A.; Gronau, F.Q.; Smira, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical statistical software for common statistical designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessa, P. Person Correlation (v1.0.13) in Free Statistics Software (v1.2.1); Office for Research Development and Education: 2025. Available online: https://www.wessa.net/rwasp_correlation.wasp/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Barinova, S.S.; Medvedeva, L.A.; Anissimova, O.V. Diversity of Algal Indicators in Environmental Assessment; Pilies Studio Publisher: Tel Aviv, Israel, 2006; p. 498. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Barinova, S.S.; Bilous, O.P.; Tsarenko, P.M. Algal Indication of Water Bodies in Ukraine: Methods and Prospects; Publishing House of Haifa University: Haifa, Israel; Kyiv, Ukraine, 2019; p. 367. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Barinova, S. Essential and practical bioindication methods and systems for the water quality assessment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2017, 2, 555588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Neilan, B.A. Molecular identification and evolution of the cyclic peptide hepatotoxins, microcystin and nodularin, synthetase genes in three orders of cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 185, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballot, A.; Fastner, J.; Wiedner, C. Paralytic shellfish poisoning toxin-producing cyanobacterium Aphanizomenon gracile in northeast Germany. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustedt, F. Systematische und Ökologische Untersuchungen über die Diatomeenflora von Java, Bali und Sumatra. Arch. Für. Hydrobiol. 1937, 15, 187–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hustedt, F. Die Diatomeen flora des Flußsystems der Weser im Gebiet der Hansestadt Bremen. Abh. Des. Naturwiss. Ver. Zu. Brem. 1957, 34, 181–440. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dam, H.; Mertens, A.; Sinkeldam, J. A coded checklist and ecological indicator values of freshwater diatoms from the Netherlands. Neth. J. Aquat. Ecol. 1994, 28, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sládeček, V. Diatoms as indicators of organic pollution. Acta Hydrochim. Et. Hydrobiol. 1986, 14, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Nürnberg, G.K.; Peters, R.H. Biological availability of soluble reactive phosphorus in anoxic and oxic freshwaters. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 757–765. [Google Scholar]
- Wiese, M.; D’Agostino, P.M.; Mihali, T.K.; Moffitt, M.C.; Neilan, B.A. Neurotoxic alkaloids: Saxitoxin and its analogs. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2185–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barinova, S. Environmental Preferences of Cyanobacteria in the Gradient of Macroclimatic Factors and Pollution. Theor. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 1, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, L.A.; Nikulina, T.V. Catalogue of Freshwater Algae of the Southern Part of the Russian Far East; Dalnauka: Vladivostok, Russia, 2014; p. 271. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Galanin, A.A. The aeolian-cryogenic origin of the inter-permafrost taliks and underground water sources in Central Yakutia. In Proceedings of the 21st Northern Research Basins Symposium and Workshop Cold-Region Hydrology in a Non-Stationary World, Yakutsk, Russia, 5 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, T.; Stewart, W.D.P.; Reynolds, C.S. Bloom-forming cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa overwinters on sediment surface. Nature 1980, 288, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Jaworski, G.H.M.; Cmiech, H.A.; Leedale, G.F. On the annual cycle of the blue-green-alga Microcystis aeruginosa Kütz. emend Elenkin. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B-Biol. Sci. 1981, 293, 419–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspagen, J.M.H.; Snelder, E.O.F.M.; Visser, P.M.; Johnk, K.D.; Ibelings, B.W.; Mur, L.R.; Huisman, J. Benthic-pelagic coupling in the population dynamics of the harmful cyanobacterium Microcystis. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babanazarova, O.; Sidelev, S.; Schischeleva, S. The structure of winter phytoplankton in Lake Nero, Russia, a hypertrophic lake dominated by Planktothrix-like cyanobacteria. Aquat. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Korneva, E.S.; Sakirko, M.V.; Sherbakova, T.A. Presence and genetic diversity of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria (Anabaena and Microcystis) in Lake Kotokel (Russia, Lake Baikal Region). Hydrobiologia 2011, 671, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Naidanova, Y.A.; Belykh, O.I. Identification of microcystin producing cyanobacteria in the plankton of Lake Baikal and Irkutsk Reservoir. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 4, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.B.; Meyer, K.A.; Šulčius, S.; Brown, N.M.; Dick, G.J.; Cao, H.; Gasiūnas, G.; Timinskas, A.; Yin, Y.; Landry, Z.C.; et al. A closely-related clade of globally distributed bloom-forming cyanobacteria within the Nostocales. Harmful Algae 2018, 77, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, H.; Henriksen, P. Saxitoxins (PSP toxins) in Danish lakes. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapala, J.; Robertson, A.; Negri, A.P.; Berg, K.A.; Tuomi, P.; Lyra, C.; Erkomaa, K.; Lahti, K.; Hoppu, K.; Lepistö, L. First report of saxitoxin in Finnish lakes and possible associated effects on human health. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Tomberg, I.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Netsvetaeva, O.G.; Eletskaya, E.V.; Timoshkin, O.A. Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Nostocales) bloom in world’s deepest Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Abundance, toxicity and factors influencing growth. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 1, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karosienė, J.; Savadova-Ratkus, K.; Toruńska-Sitarz, A.; Koreivienė, J.; Kasperovičienė, J.; Vitonytė, I.; Błaszczyk, A.; Mazur-Marzec, H. First report of saxitoxins and anatoxin-a production by cyanobacteria from Lithuanian lakes. Eur. J. Phycol. 2020, 55, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Science 2008, 320, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinl, K.L.; Harris, T.D.; North, R.L.; Almela, P.; Berger, S.A.; Bizic, M.; Burnet, S.H.; Grossart, H.-P.; Ibelings, B.W.; Jakobsson, E.; et al. Blooms also like it cold. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2023, 8, 546–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurmans, J.M.; Brinkmann, B.W.; Makower, A.K.; Dittmann, E.; Huisman, J.; Matthijs, H.C.P. Microcystin interferes with defense against high oxidative stress in harmful cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 2018, 78, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilliges, Y.; Kehr, J.C.; Meissner, S.; Ishida, K.; Mikkat, S.; Hagemann, M.; Kaplan, A.; Börner, T.; Dittmann, E. The Cyanobacterial Hepatotoxin Microcystin Binds to Proteins and Increases the Fitness of Microcystis under Oxidative Stress Conditions. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Hu, L.; Song, L.; Gan, N. Microcystin-Bound Protein Patterns in Different Cultures of Microcystis aeruginosa and Field Samples. Toxins 2016, 8, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.F.; Martin, R.M.; Smith, L.E.; Wei, B.; Hellweger, F.L.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Microcystin aids in cold temperature acclimation: Differences between a toxic Microcystis wildtype and non-toxic mutant. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Asai, K.; Houki, A. Numerical estimation of organic pollution of flowing water by using the epilithic diatom assemblage—Diatom Assemblage Index (DAIpo). Sci. Total Environ. 1986, 55, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
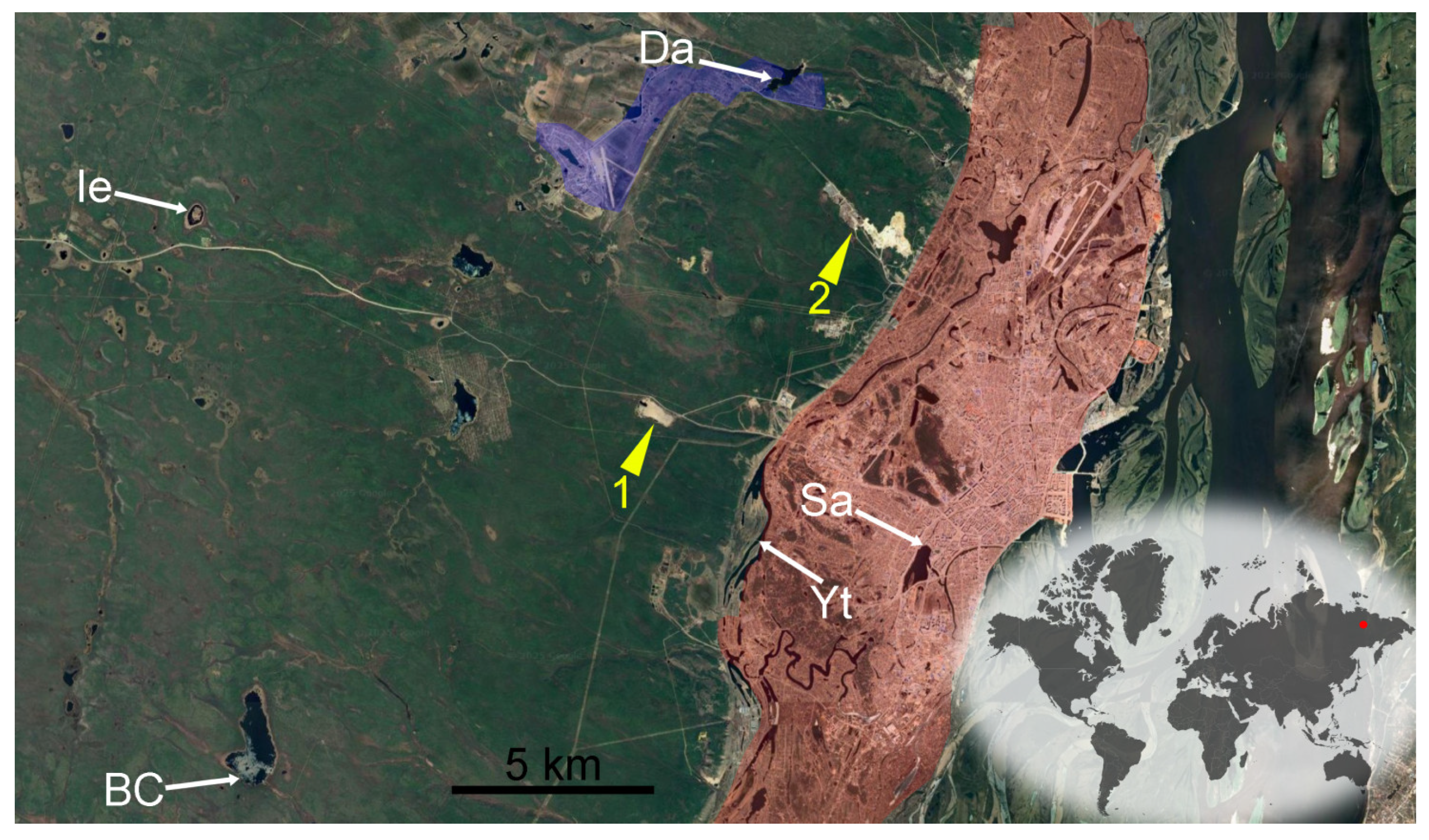




| Code | Lake Name | Area of Lake, km2 | Depth, m | Latitude, N | Longitude, E | Altitude, m a.s.l. | Type of Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sa | Saysary | 0.40 | 6.5 | 62°01′17.3″ | 129°41′39.6″ | 96 | R |
| Yt | Ytyk-Kyuyol | 0.79 | 3.0 | 62°01′22.02″ | 129°36′59.0″ | 108 | R |
| Ie | Ierelyakh | 0.10 | 1.2 | 62°06′46.20″ | 129°17′37.0″ | 258 | K |
| Da | Dachnoe | 0.23 | 3.5 | 62°07′29.30″ | 129°37′22.9″ | 122 | A |
| BC | Bolshaya Chabyda | 1.68 | 1.6 | 61°58′06.20″ | 129°22′42.5″ | 207 | D |
| Variable | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance, thou. cells L−1 | |||||
| Charophyta | 1.599 | 7.245 | 0.027 | 0.002 | 0.640 |
| Chlorophyta | 4730.839 | 1888.172 | 193.682 | 660.458 | 2603.003 |
| Cyanobacteria | 4748.504 | 45,345.389 | 6525.961 | 114,042.861 | 104,297.677 |
| Dinoflagellata | 0.585 | 1.410 | 22.708 | 0.041 | 0.041 |
| Euglenophyta | 13.143 | 7.500 | 0.030 | 0.407 | 0 |
| Heterokontophyta | 73.304 | 97.391 | 2.490 | 18.294 | 94.980 |
| Biomass, mg L−1 | |||||
| Charophyta | 0.0136 | 0.0179 | 0.0004 | 0.0001 | 0.0026 |
| Chlorophyta | 0.4276 | 0.1981 | 0.0396 | 0.0417 | 0.1953 |
| Cyanobacteria | 0.6309 | 1.4183 | 0.0020 | 3.8314 | 4.7496 |
| Dinoflagellata | 0.0220 | 0.0531 | 0.8550 | 0.0016 | 0.0015 |
| Euglenophyta | 0.0457 | 0.0423 | 0.0002 | 0.0012 | |
| Heterokontophyta | 0.0601 | 0.0703 | 0.0029 | 0.0242 | 0.1510 |
| Species | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aphanizomenon flos-aquae Ralfs ex Bornet & Flahault | 14 | 2 | - | 29 | - |
| Ceratium hirundinella (O.F.Müller) Dujardin | 2 | 3 | 95 | 0.04 | - |
| Dolichospermum sp. | 20 | - | - | - | - |
| Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Richter) P.Wacklin, L.Hoffmann & J.Komárek | 10 | 0.3 | - | 0.2 | 30 |
| Microcystis aeruginosa (Kützing) Kützing | - | 30 | - | 5 | 30 |
| Microcystis flos-aquae (Wittrock) Kirchner | - | 40 | - | 60 | 30 |
| Variable | Sa | Yt | Ie | Da | BC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abundance, thou. cells L−1 | 9568 | 47,347 | 6745 | 114,722 | 106,996 |
| Biomass, mg L−1 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 3.9 | 5.1 |
| No of Species | 37 | 54 | 29 | 21 | 26 |
| Shannon H’ | 1.072 | 0.91 | 0.565 | 0.251 | 0.528 |
| Index S | 1.93 | 2.04 | 1.88 | 1.64 | 1.89 |
| Index WESI | 2.00 | 2.50 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barinova, S.; Gabyshev, V.A.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Naidanova, Y.A.; Sorokovikova, E.G. Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions. Land 2025, 14, 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040721
Barinova S, Gabyshev VA, Gabysheva OI, Naidanova YA, Sorokovikova EG. Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions. Land. 2025; 14(4):721. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040721
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarinova, Sophia, Viktor A. Gabyshev, Olga I. Gabysheva, Yanzhima A. Naidanova, and Ekaterina G. Sorokovikova. 2025. "Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions" Land 14, no. 4: 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040721
APA StyleBarinova, S., Gabyshev, V. A., Gabysheva, O. I., Naidanova, Y. A., & Sorokovikova, E. G. (2025). Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions. Land, 14(4), 721. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14040721








