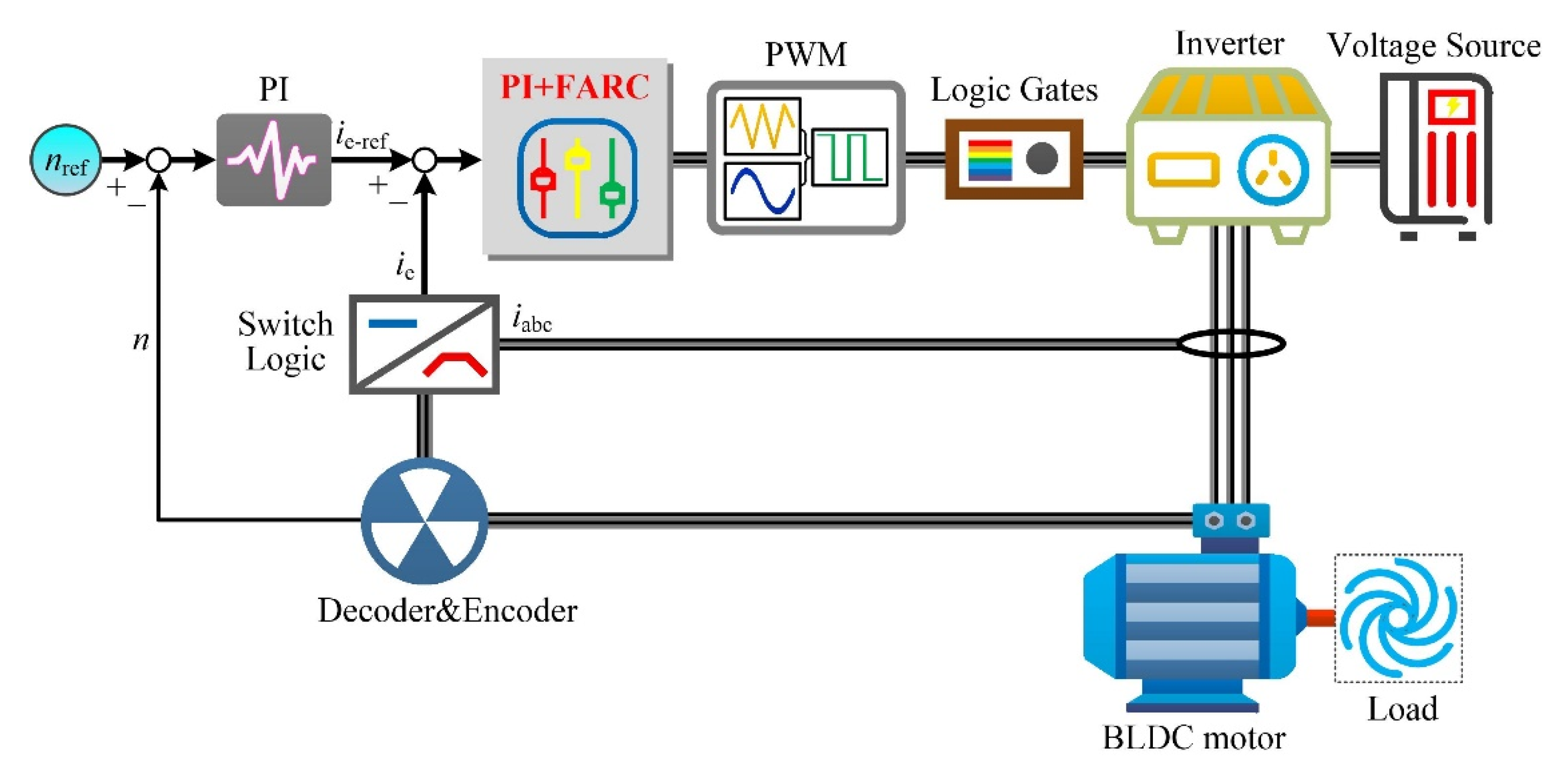
Current Harmonic Suppression of BLDC Motor Utilizing Frequency Adaptive Repetitive Controller
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Due to the real sampling number of the delay element in the BLDC, the motor control system is maybe not an integer, the parameters designing process of FARC are studied, and an adaptive internal model controller and a novel decomposition rule for FARC is designed based on Lagrange interpolation theory;
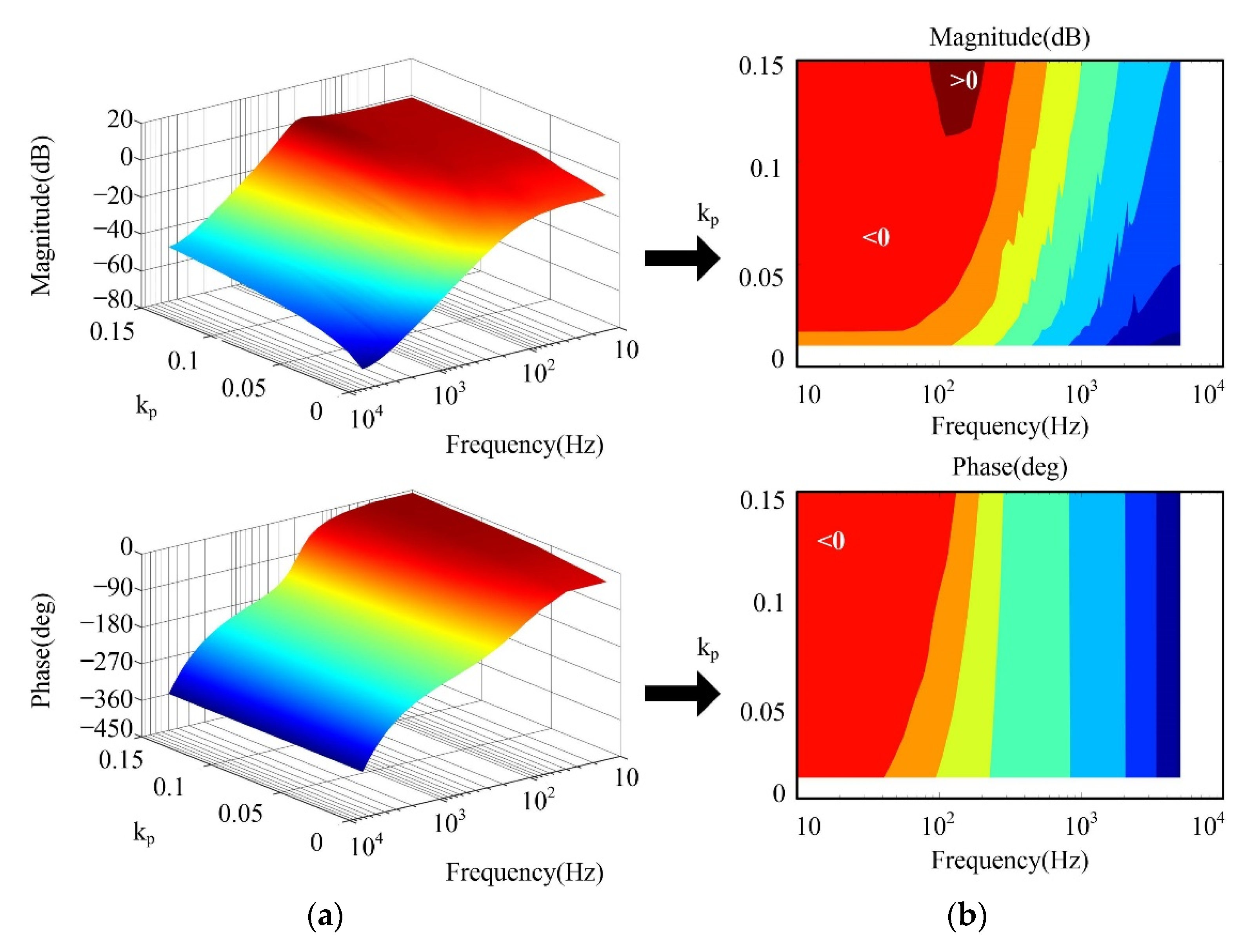
- In order to simplify the control system scheme and obtain the appropriate parameters for the current loop controllers, the Bode diagrams and the Nyquist diagrams of different systems and controllers were analyzed, which can provide the intuitive analysis for the parameter designing process of the current loop;
- To improve the dynamic performance of the control system, a composite controller was proposed through adding a froward channel in the novel current loop. Consequently, the stability and robustness of the composite controller were verified by Lyapunov theorem and minimum gain theory.
2. Analysis of Current Harmonics
2.1. Mathematical Model of BLDC Motor
2.2. Analysis of Harmonic Sources
- The air gap magnetic field harmonics caused by the motor structure.
- The control signal harmonics caused by the dead zone time.
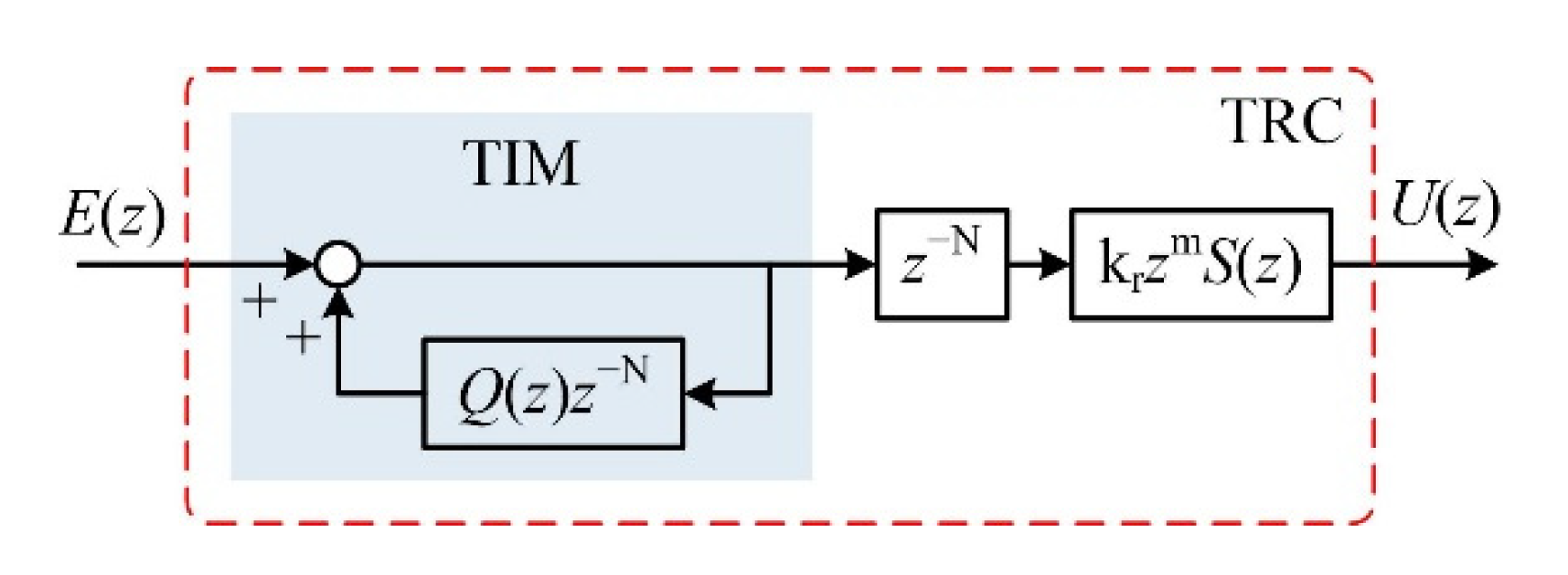
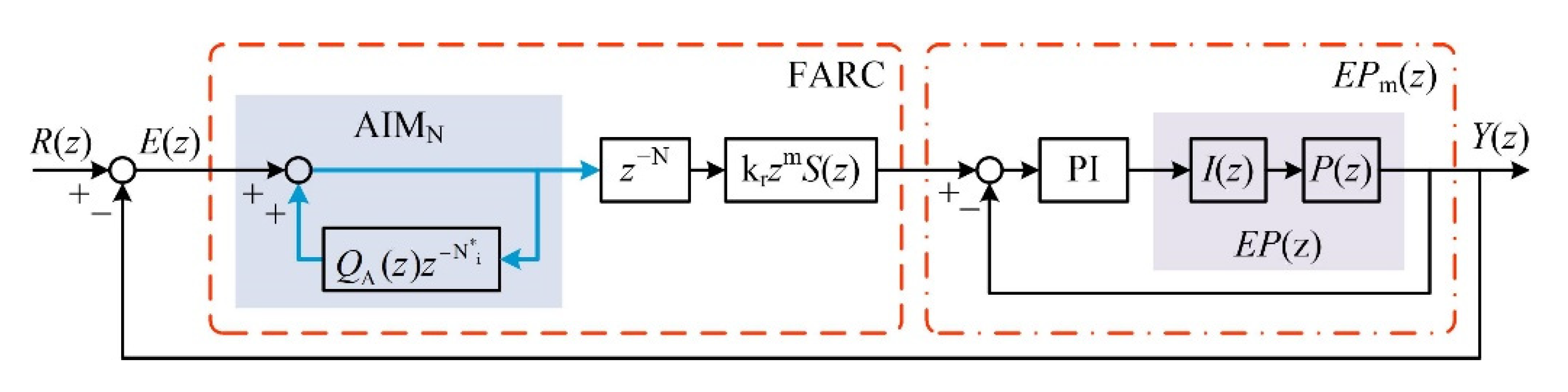
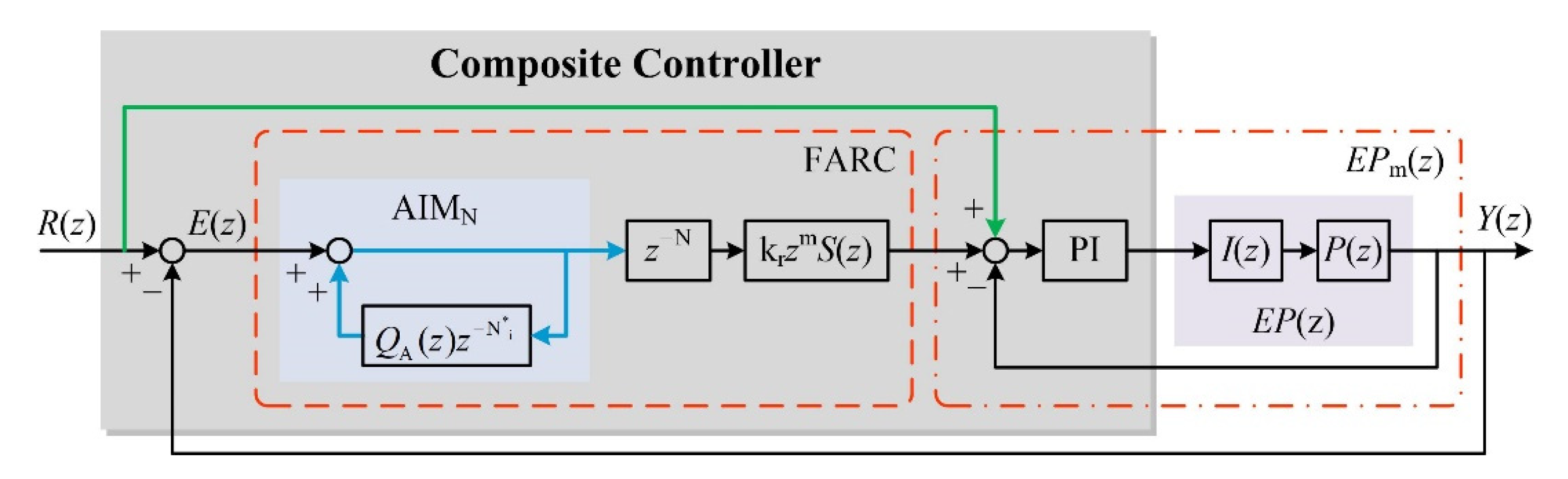
3. Design of FARC
3.1. Adaptive Internal Model Controller
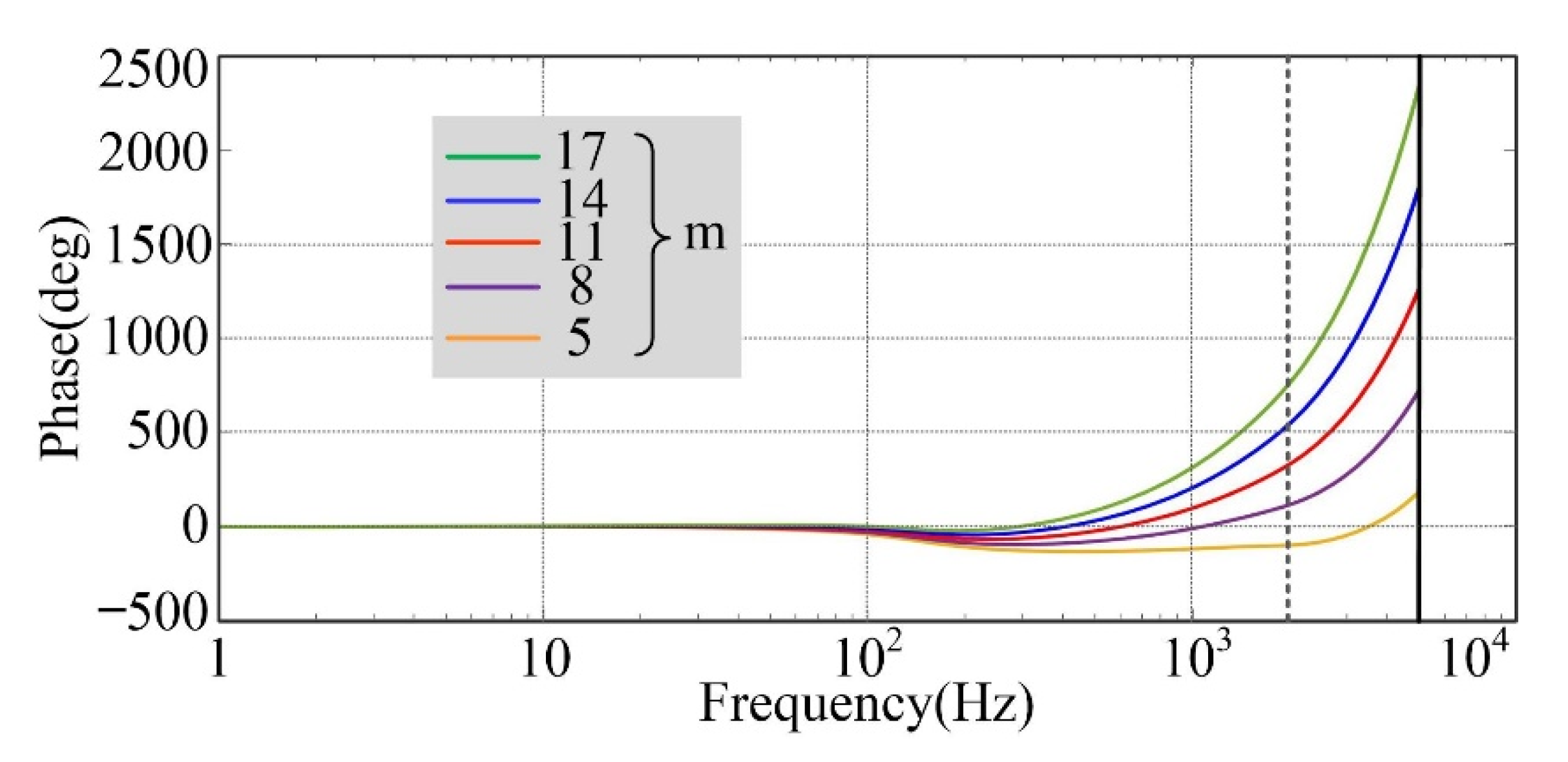
3.2. Novel Decomposition Rule
4. Analysis of the Novel Current Loop Controllers Parameters
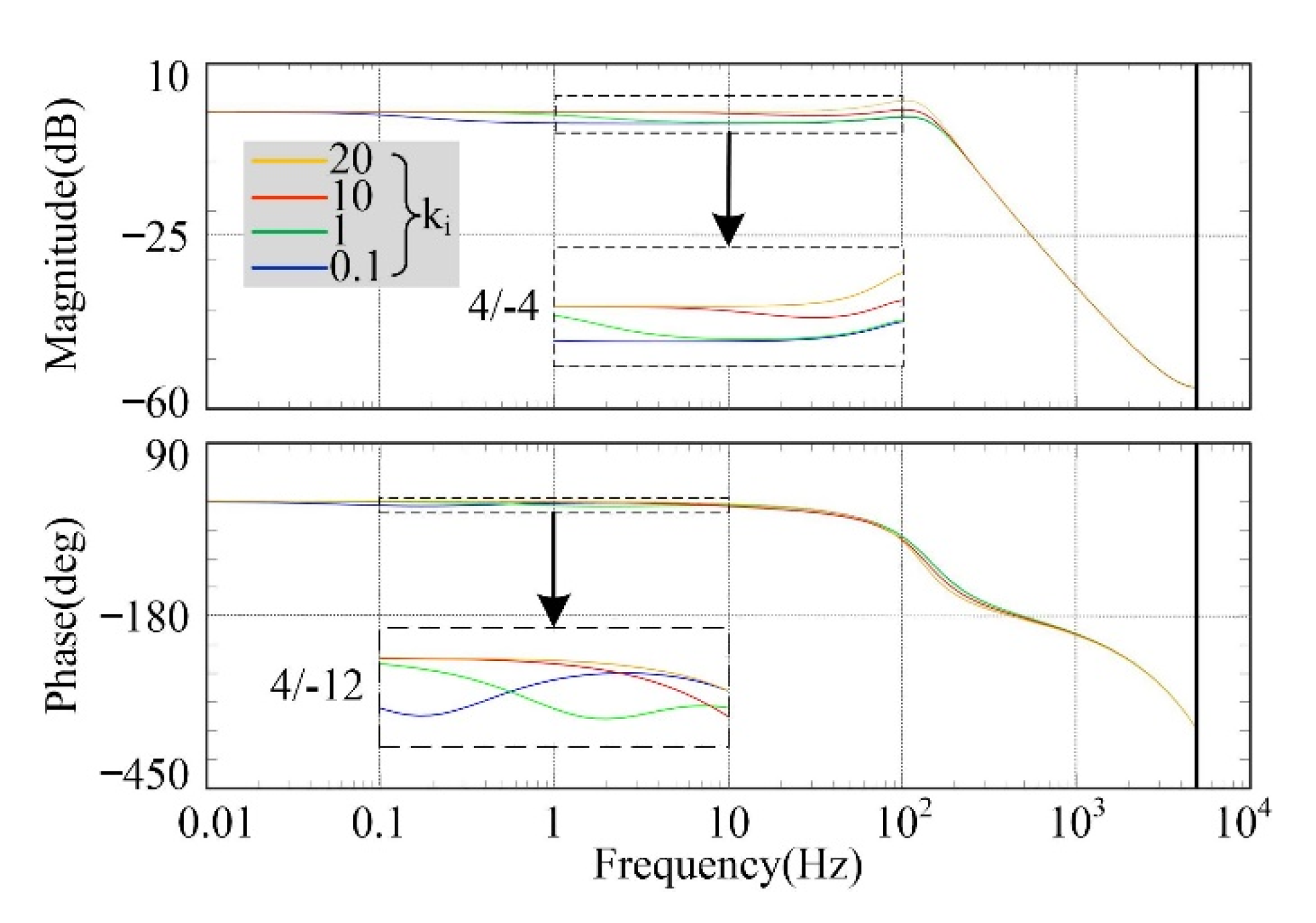
4.1. PIC
4.2. FARC
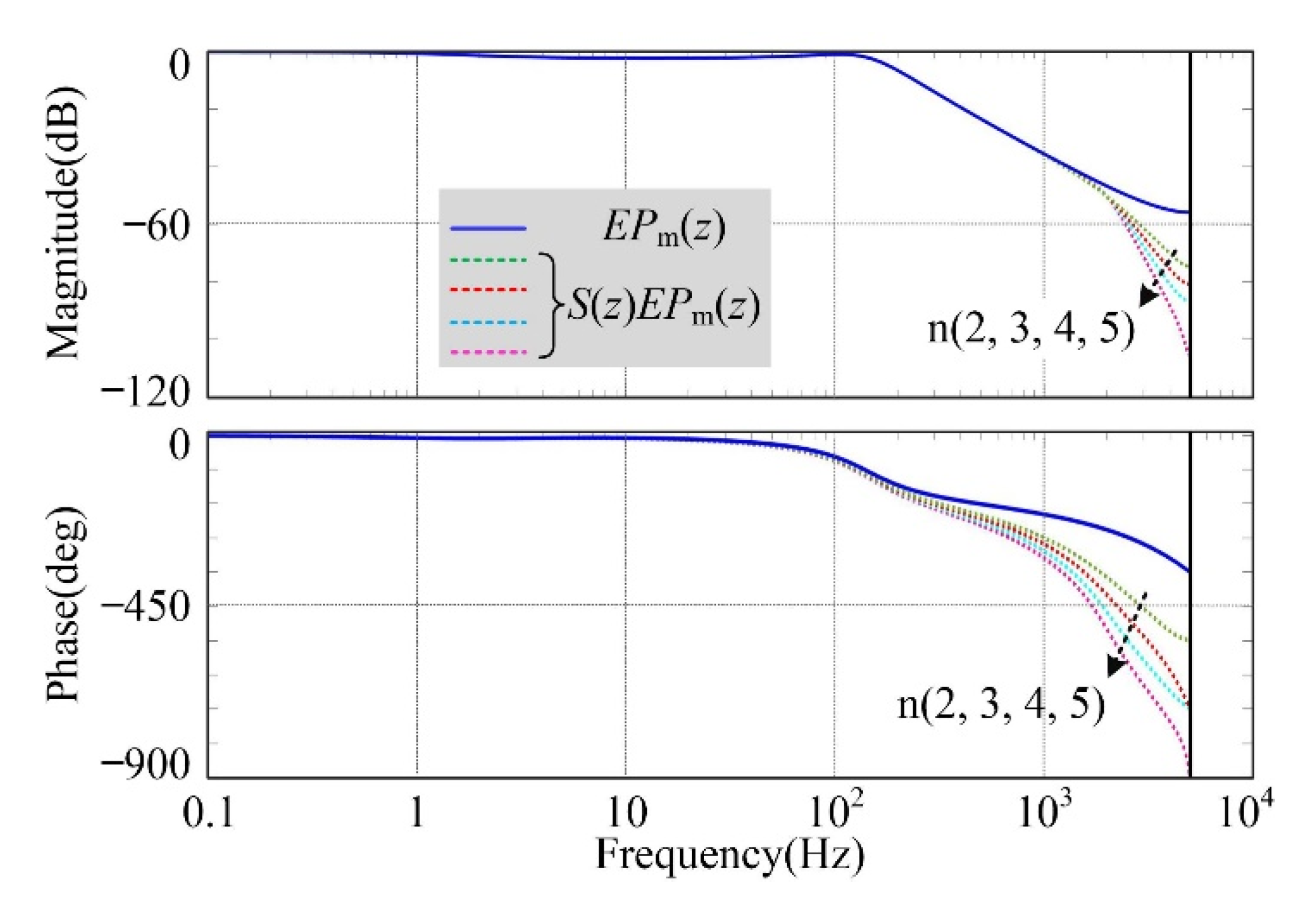
4.3. Composite Controller
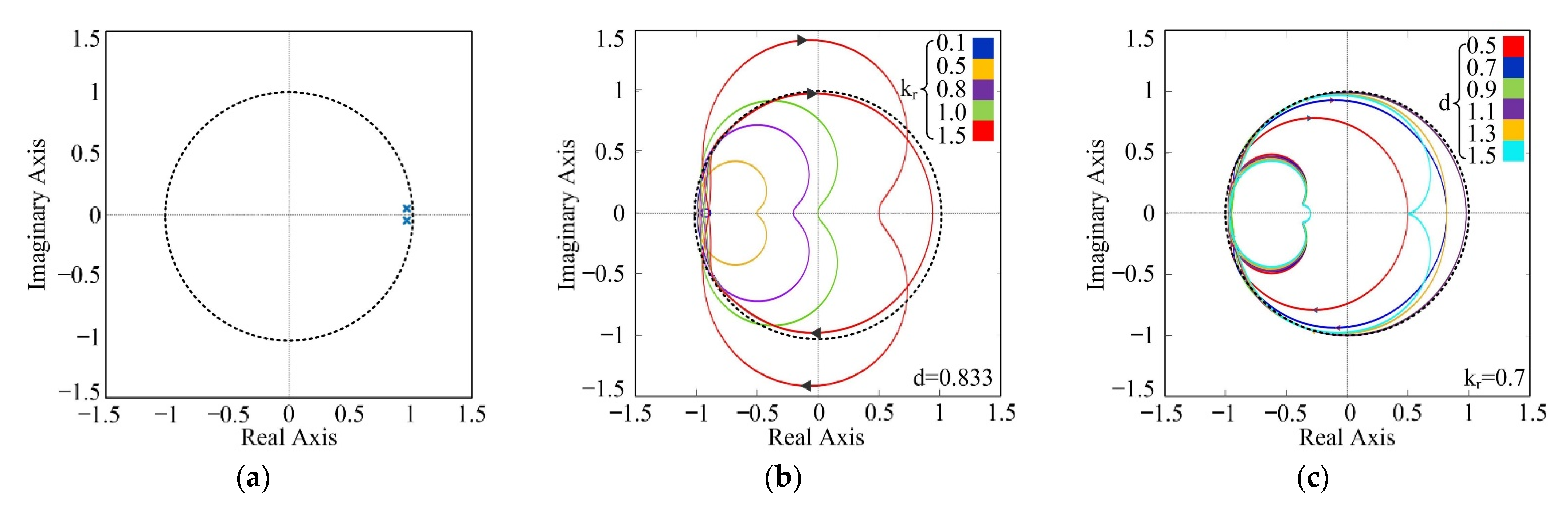
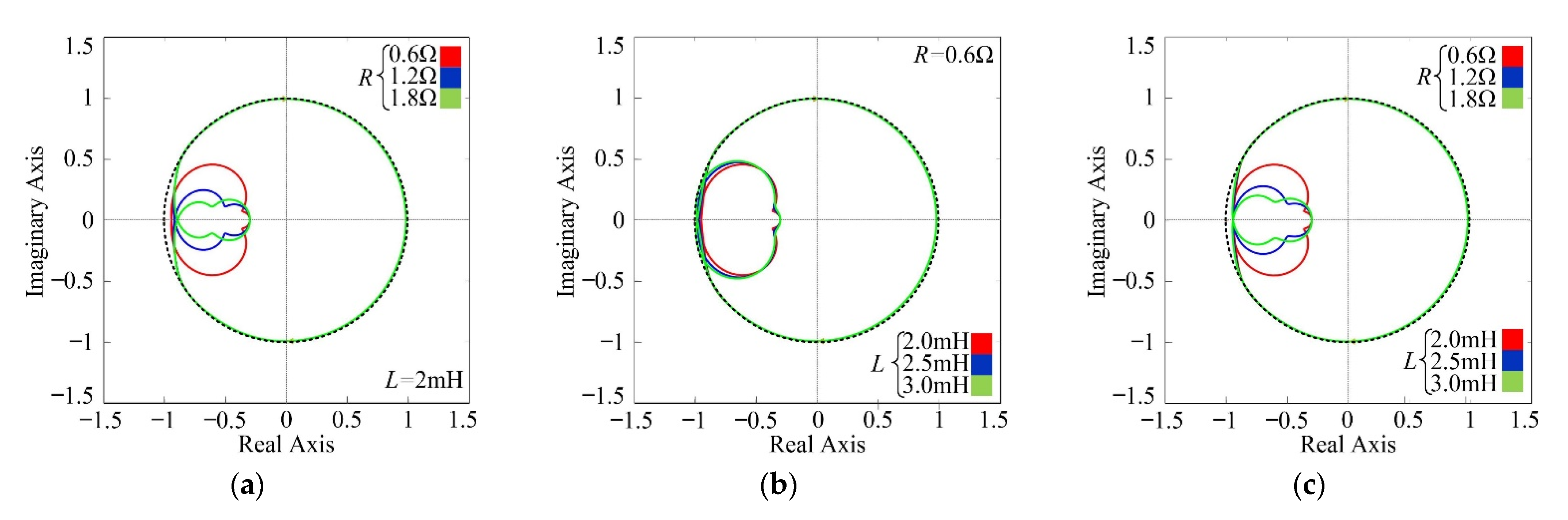
4.4. Analysis of the Control System Stability and Robustness
5. Simulation
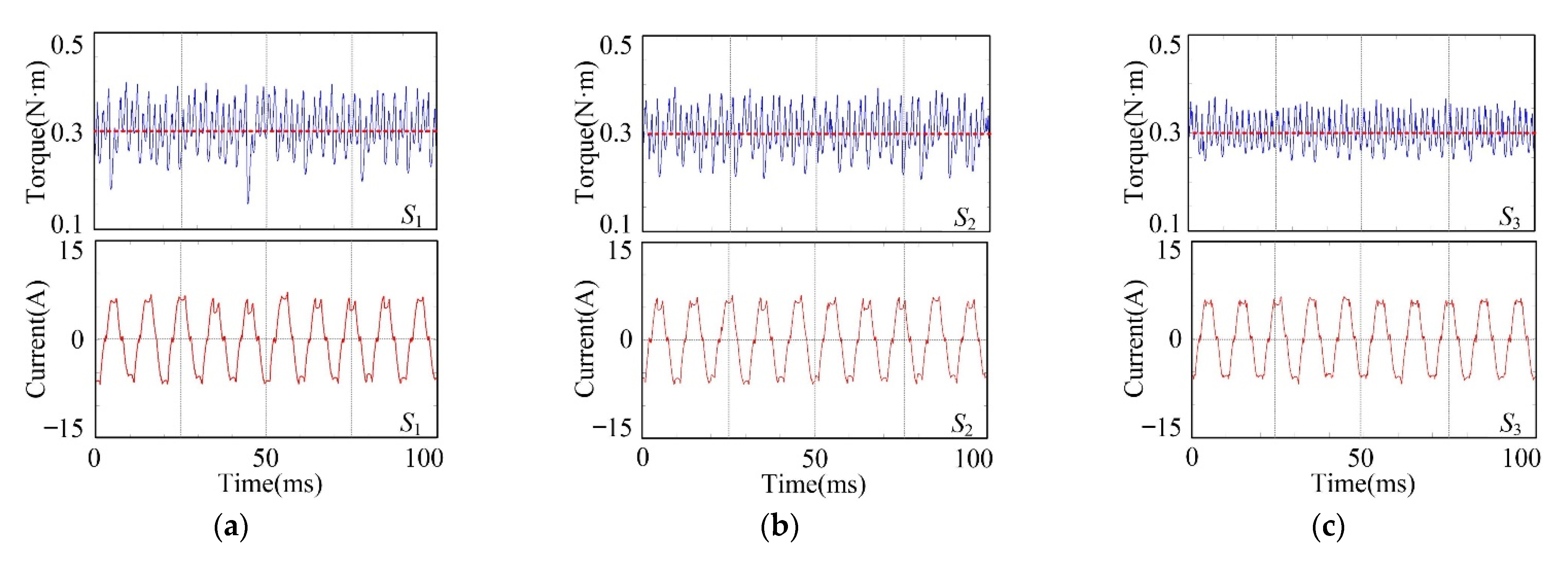
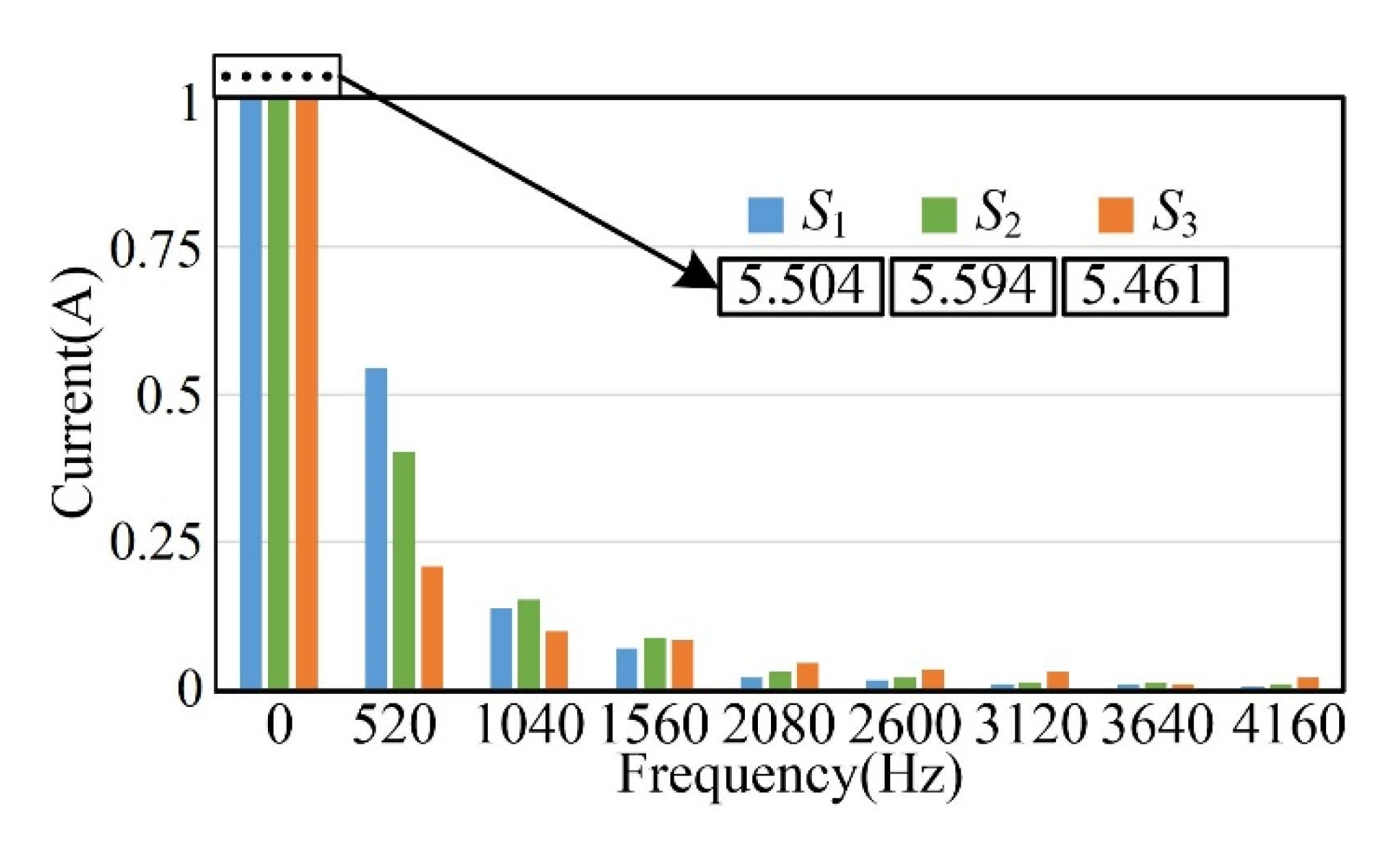
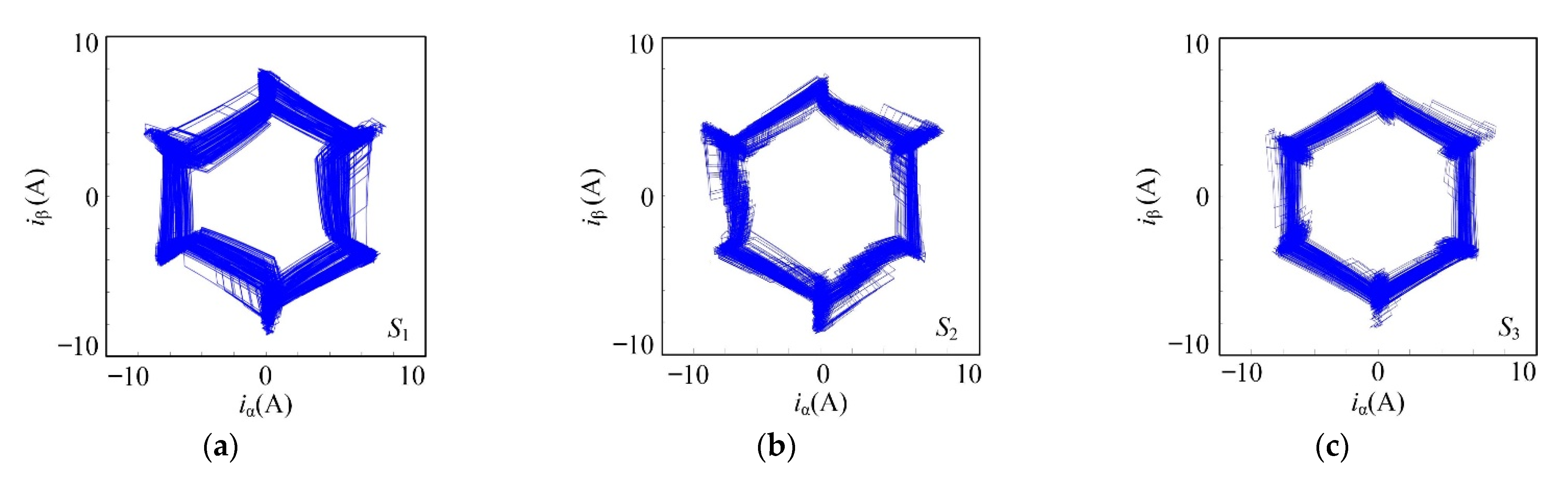
5.1. Steady-State Performance
5.2. Dynamic Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Bin, H.; Gong, L. Spectral Analysis and Sideband Harmonic Cancellation of Six-Step Operation with Low Carrier–Fundamental Frequency Ratio for High-Speed Brushless DC Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 7778–7792. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, D.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D. Eddy-current loss in the rotor magnets of permanent-magnet brushless machines having a fractional number of slots per pole. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 2462–2469. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Bin, H. PWM Switching Delay Correction Method for High-Speed Brushless DC Drives. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 81717–81727. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, S.J.; Jang, G.H.; Lee, H.J. Torque Ripple and Unbalanced Magnetic Force of a BLDC Motor due to the Connecting Wire Between Slot Windings. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3319–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Performance improvement for PMSM control system based on composite controller used adaptive internal model controller. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11078–11087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Jin, G. Resonance Mechanism Analysis of Grid-connected Inverter Based on System Admittance. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2022, 42, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhonghua, Z.; Jianbo, Z.; Jingchao, F. Colpitts chaotic circuits of linear feedback control and adaptive feedback control. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. A New Feedback Method for PR Current Control of LCL-Filter-Based Grid-Connected Inverter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 57, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiguo, L.; Hongwei, L.; Xinyu, L.; Liming, C.; Lijun, G. Voltage synchronization signal detection technology based on improved SOGI-PLL. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Son, I.; Lukman, G.F.; Shah, M.H.; Jeong, K.-I.; Ahn, J.-W. Design Considerations and Selection of Cost-Effective Switched Reluctance Drive for Radiator Cooling Fans. Electronics 2021, 10, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanyan, L.; Yijun, W.; Huafeng, J.; Jingnan, W. Harmonic detection method of power system based on improved hilbert huang transform. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 119–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, C.; Taylor, A.; Kotrba, A.; Yetkin, A.; Gundogan, A. Design of a High-Efficiency Minimum-Torque-Ripple 12-V/1-kW Three-Phase BLDC Motor Drive System for Diesel Engine Emission Reductions. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2014, 63, 3107–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutian, W.; Xiaofei, L.; Chao, S. Control strategy and modeling analysis of multi-resonant high-frequency link matrix rectifier based on double transformers. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Liu, K.; Wei, J.; Wang, H. Multirate model predictive current control of a permanent magnet synchronous machine for a flywheel energy storage system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 11579–11591. [Google Scholar]
- Jagiela, M.; Garbiec, T.; Gwozdz, J.; Kolodziej, J. Fast Steady-State Field-Circuit Model for SMPM-BLdc Motors Driven From 120° and 180° Quasi-Square Wave Inverters. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darba, A.; de Belie, F.; D’haese, P.; Melkebeek, J.A. Improved Dynamic Behavior in BLDC Drives Using Model Predictive Speed and Current Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 728–740. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Odhano, S.; Formentini, A.; Zanchetta, P. Reuse of a Damaged Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for Torque Ripple and Acoustic Noise Elimination Using a Novel Repetitive Observer. IEEE Trans Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 3790–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Chen, S.; Wen, S.; Qu, B.; Ye, Y. A Frequency Adaptive PIMR-Type Repetitive Control for a Grid-Tied Inverter. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 65418–65428. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Q.; Xu, X. Prediction of the remaining useful life of PEMFC based on particle filter and genetic algorithm. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, D.; Xiong, Y.; Liang, B.; Qi, Y. A modified Sage-Husa adaptive Kalman filter for state estimation of electric vehicle servo control system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Enshu, J.; Qiushi, T.; Siyu, L.; Jiangdong, Z. Coordinated control strategy of MMC circulating current and capacitor voltage under unbalanced grid conditions. J. Northeast Electr. Power Univ. 2021, 41, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Gu, C.; Sun, Q.; Peng, C.; Pang, G. Reduction of Rotor Harmonic Eddy-Current Loss of High-Speed PM BLDC Motors by Using a Split-Phase Winding Method. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1593–1602. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shi, L.; Man, Z.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Yu, M.; Jiang, C.; Kong, H.; Cao, Z. Continuous Fast Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Automotive Electronic Throttle Systems Using Finite-Time Exact Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7160–7172. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, K.; Ye, Y.; Ni, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P. Model Predictive Control Method of Torque Ripple Reduction for BLDC Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- An, Q.; Zhang, J.; An, Q.; Shamekov, A. Quasi-proportional-resonant controller based adaptive position observer for sensorless control of PMSM drives under low carrier ratio. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2564–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.; Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Torque ripple suppression of PMSM using fractional-order vector resonant and robust internal model control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 7, 1437–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Ye, Y. A PIMR-Type Repetitive Control for a Grid-Tied Inverter, Structure, Analysis, and Design. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2730–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiangsong, Z.; Shasha, C.; Xiaoyu, Z.; Xiaolei, W.; Shuanghong, W. Analysis and design of combination controller based on repetitive control and proportional control for harmonics suppression of grid-tied inverters. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2019, 34, 5189–5198. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Liu, L.; Xu, J.; Shen, A. Frequency adaptive proportional-repetitive control for grid-connected inverters. IEEE Trans Ind. Appl. 2021, 68, 7965–7974. [Google Scholar]
- Xuliang, Y.; Jicheng, Z.; Jingfang, W.; Shengqi, H.; Yishu, J. Research on Suppressing Commutation Torque Ripple of Brushless DC Motor Based on an Auxiliary Step-up Front End. Proc. CSEE 2020, 40, 3021–3031. [Google Scholar]





| M = 1 | M = 2 | M = 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| l(0) | 1−d | (d−1) (d−2)/2 | −(d−1) (d−2) (d−3)/6 |
| l(1) | d | −d(d−2) | d(d−2) (d−3)/2 |
| l(2) | 0 | d(d−1)/2 | −d(d−1) (d−3)/2 |
| l(3) | 0 | 0 | −d(d−1) (d−2)/6 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| DC voltage | 24 V |
| Resistance | 0.6 Ω |
| Inductance | 2 mH |
| Pole pairs | 4 |
| Sampling frequency | 10 kHz |
| Rated speed | 1500 rpm |
| Rated torque | 0.3 N·m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y. Current Harmonic Suppression of BLDC Motor Utilizing Frequency Adaptive Repetitive Controller. Machines 2022, 10, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111071
Yuan T, Zhang Y. Current Harmonic Suppression of BLDC Motor Utilizing Frequency Adaptive Repetitive Controller. Machines. 2022; 10(11):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111071
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Tianqing, and Yupeng Zhang. 2022. "Current Harmonic Suppression of BLDC Motor Utilizing Frequency Adaptive Repetitive Controller" Machines 10, no. 11: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111071
APA StyleYuan, T., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Current Harmonic Suppression of BLDC Motor Utilizing Frequency Adaptive Repetitive Controller. Machines, 10(11), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/machines10111071






