Exploring the Impact of Terminators on Transgene Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Synthetic Biology Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. reinhardtii Strain Information
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Plasmid Design and Assembly
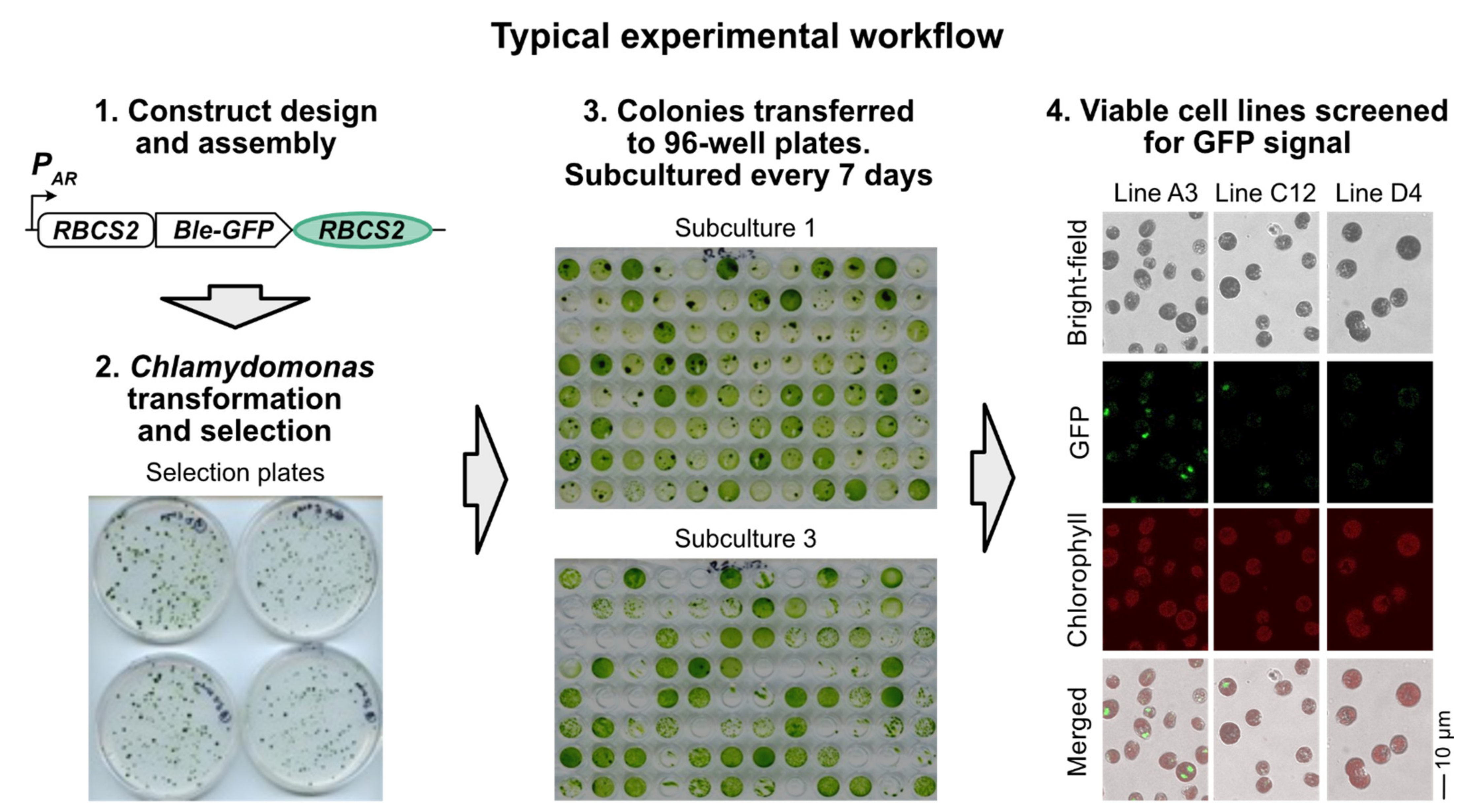
2.4. Chlamydomonas Transformation and Culturing
2.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.6. Statistical Tests
3. Results
3.1. Transgene Instability: A Recurrent Problem in C. reinhardtii
3.2. Influence of Terminators on Transgene Expression in C. reinhardtii
3.3. Activity of Terminators in Different C. reinhardtii Host Strains
3.4. Analysis of the Effect of Promoter Choice on Transgene Expression
3.5. Testing Promoter and Terminator Combinations to Drive Expression of a Selection Marker-Independent Transgene
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sproles, A.E.; Fields, F.J.; Smalley, T.N.; Le, C.H.; Badary, A.; Mayfield, S.P. Recent advancements in the genetic engineering of microalgae. Algal Res. 2021, 53, 102158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, S.; Finazzi, G.; Wollman, F.-A. The dynamics of photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 463–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wingfield, J.L.; Lechtreck, K.-F. Chlamydomonas basal bodies as flagella organizing centers. Cells 2018, 7, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scaife, M.A.; Nguyen, G.T.; Rico, J.; Lambert, D.; Helliwell, K.; Smith, A. Establishing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as an industrial biotechnology host. Plant J. 2015, 82, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinkerson, R.; Jonikas, M.C. Molecular techniques to interrogate and edit the Chlamydomonas nuclear genome. Plant J. 2015, 82, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomé, P.A.; Merchant, S.S. A series of fortunate events: Introducing Chlamydomonas as a reference organism. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1682–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harris, E.H.; Stern, D.B.; Witman, G.B. (Eds.) The Chlamydomonas Sourcebook, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-12-370873-1. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, S.S.; Prochnik, S.E.; Vallon, O.; Harris, E.H.; Karpowicz, S.J.; Witman, G.B.; Terry, A.; Salamov, A.; Fritz-Laylin, L.K.; Maréchal-Drouard, L.; et al. The Chlamydomonas genome reveals the evolution of key animal and plant functions. Science 2007, 318, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tran, N.T.; Kaldenhoff, R. Achievements and challenges of genetic engineering of the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Algal Res. 2020, 50, 101986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimogawara, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Grossman, A.; Usuda, H. High-efficiency transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by electroporation. Genetics 1998, 148, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindle, K.L. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1228–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrmann, M.; Oertel, W.; Hegemann, P. A synthetic gene coding for the green fluorescent protein (GFP) is a versatile reporter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 1999, 19, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sizova, I.; Fuhrmann, M.; Hegemann, P. A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 2001, 277, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasala, B.A.; Barrera, D.J.; Ng, J.; Plucinak, T.M.; Rosenberg, J.N.; Weeks, N.P.; Oyler, G.A.; Peterson, T.C.; Haerizadeh, F.; Mayfield, S.P. Expanding the spectral palette of fluorescent proteins for the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2013, 74, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, J.; Sarkar, N.; Balenger, S.; Jeong, B.-R.; Cerutti, H. Tandem inverted repeat system for selection of effective transgenic RNAi strains in Chlamydomonas. Plant J. 2004, 40, 611–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molnar, A.; Bassett, A.; Thuenemann, E.; Schwach, F.; Karkare, S.; Ossowski, S.; Weigel, D.; Baulcombe, D. Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2009, 58, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczi, A.; Pyott, D.E.; Xipnitou, A.; Molnar, A. Efficient targeted DNA editing and replacement in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using Cpf1 ribonucleoproteins and single-stranded DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13567–13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crozet, P.; Navarro, F.J.; Willmund, F.; Mehrshahi, P.; Bakowski, K.; Lauersen, K.; Pérez-Pérez, M.-E.; Auroy, P.; Rovira, A.G.; Sauret-Gueto, S.; et al. Birth of a photosynthetic chassis: A MoClo toolkit enabling synthetic biology in the microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. ACS Synth. Biol. 2018, 7, 2074–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chlamydomonas Resource Center. Available online: https://www.chlamycollection.org (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Rasala, B.A.; Mayfield, S.P. Photosynthetic biomanufacturing in green algae; production of recombinant proteins for industrial, nutritional, and medical uses. Photosynth. Res. 2014, 123, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyo, Y.M.; Purton, S. The algal chloroplast as a synthetic biology platform for production of therapeutic proteins. Microbiology 2018, 164, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taunt, H.N.; Stoffels, L.; Purton, S. Green biologics: The algal chloroplast as a platform for making biopharmaceuticals. Bioengineered 2018, 9, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasala, B.A.; Chao, S.-S.; Pier, M.; Barrera, D.J.; Mayfield, S.P. Enhanced genetic tools for engineering multigene traits into green algae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chlamydomonas Spatial Interactome. Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/chlamyspatialinteractome (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Mackinder, L.C.; Chen, C.; Leib, R.D.; Patena, W.; Blum, S.R.; Rodman, M.; Ramundo, S.; Adams, C.M.; Jonikas, M.C. A spatial interactome reveals the protein organization of the algal CO2-concentrating mechanism. Cell 2017, 171, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Paz-Maldonado, L.M.T.; Soria-Guerra, R.E. Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as a viable platform for the production of recombinant proteins: Current status and perspectives. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 31, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauersen, K.J.; Wichmann, J.; Baier, T.; Kampranis, S.; Pateraki, I.; Møller, B.L.; Kruse, O. Phototrophic production of heterologous diterpenoids and a hydroxy-functionalized derivative from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab. Eng. 2018, 49, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Patena, W.; Armbruster, U.; Gang, S.; Blum, S.R.; Jonikas, M.C. High-throughput genotyping of green algal mutants reveals random distribution of mutagenic insertion sites and endonucleolytic cleavage of transforming DNA. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerutti, H.; Johnson, A.M.; Gillham, N.W.; Boynton, J.E. Epigenetic silencing of a foreign gene in nuclear transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroda, M. Good news for nuclear transgene expression in Chlamydomonas. Cells 2019, 8, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neupert, J.; Karcher, D.; Bock, R. Generation of Chlamydomonas strains that efficiently express nuclear transgenes. Plant J. 2009, 57, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupert, J.; Gallaher, S.D.; Lu, Y.; Strenkert, D.; Segal, N.; Barahimipour, R.; Fitz-Gibbon, S.T.; Schroda, M.; Merchant, S.S.; Bock, R. An epigenetic gene silencing pathway selectively acting on transgenic DNA in the green alga Chlamydomonas. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barahimipour, R.; Strenkert, D.; Neupert, J.; Schroda, M.; Merchant, S.S.; Bock, R. Dissecting the contributions of GC content and codon usage to gene expression in the model alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2015, 84, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eichler-Stahlberg, A.; Weisheit, W.; Ruecker, O.; Heitzer, M. Strategies to facilitate transgene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Planta 2009, 229, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baier, T.; Wichmann, J.; Kruse, O.; Lauersen, K. Intron-containing algal transgenes mediate efficient recombinant gene expression in the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 6909–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strenkert, D.; Schmollinger, S.; Gallaher, S.D.; Salomé, P.A.; Purvine, S.O.; Nicora, C.D.; Mettler-Altmann, T.; Soubeyrand, E.; Weber, A.; Lipton, M.S.; et al. Multiomics resolution of molecular events during a day in the life of Chlamydomonas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroda, M.; Blocker, D.; Beck, C.F. The HSP70A promoter as a tool for the improved expression of transgenes in Chlamydomonas. Plant J. 2000, 21, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scranton, M.A.; Ostrand, J.T.; Georgianna, D.R.; Lofgren, S.M.; Li, D.; Ellis, R.C.; Carruthers, D.N.; Dräger, A.; Masica, D.L.; Mayfield, S.P. Synthetic promoters capable of driving robust nuclear gene expression in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Algal Res. 2016, 15, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Falcao, V.R.; Sayre, R.T. Evaluating nuclear transgene expression systems in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Algal Res. 2013, 2, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Paz, C.; Liu, D.; Geng, S.; Umen, J.G. Identification of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii endogenous genic flanking sequences for improved transgene expression. Plant J. 2017, 92, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Felippes, F.F.; McHale, M.; Doran, R.L.; Roden, S.; Eamens, A.L.; Finnegan, E.J.; Waterhouse, P.M. The key role of terminators on the expression and post-transcriptional gene silencing of transgenes. Plant J. 2020, 104, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehner, J.; Pearson, E.L.; Moore, C. Unravelling the means to an end: RNA polymerase II transcription termination. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapendano, C.K.; Lykke-Andersen, S.; Kjems, J.; Bertrand, E.; Jensen, T.H. Crosstalk between mRNA 3′ end processing and transcription initiation. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, P.K.; Jensen, T.H.; Lykke-Andersen, S. Making ends meet: Coordination between RNA 3′-end processing and transcription initiation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2013, 4, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.-H.; Kumar, S.; Zeng, J.; McEwan, R.; Wright, T.R.; Gupta, M. Transcription terminator-mediated enhancement in transgene expression in maize: Preponderance of the AUGAAU motif overlapping with poly (A) signals. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 570778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.A.; Shen, C.; Brown, A.; Hunt, A.G. Experimental genome-wide determination of RNA polyadenylation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davey, M.P.; Horst, I.; Duong, G.-H.; Tomsett, E.V.; Litvinenko, A.C.P.; Howe, C.J.; Smith, A. Triacylglyceride production and autophagous responses in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii depend on resource allocation and carbon source. Eukaryot. Cell 2014, 13, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kropat, J.; Hong-Hermesdorf, A.; Casero, D.; Ent, P.; Castruita, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Merchant, S.S.; Malasarn, D. A revised mineral nutrient supplement increases biomass and growth rate in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J. 2011, 66, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibson, D.G.; Young, L.; Chuang, R.Y.; Venter, J.C.; Hutchison, C.A.; Smith, H.O. Enzymatic assembly of DNA molecules up to several hundred kilobases. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.; Engler, C.; Gruetzner, R.; Werner, S.; Marillonnet, S. A modular cloning system for standardized assembly of multigene constructs. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, C.; Youles, M.; Gruetzner, R.; Ehnert, T.-M.; Werner, S.; Jones, J.; Patron, N.J.; Marillonnet, S. A golden gate modular cloning toolbox for plants. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrshahi, P.; Nguyen, G.T.D.T.; Rovira, A.G.; Sayer, A.; Llavero-Pasquina, M.; Sin, M.L.H.; Medcalf, E.J.; Mendoza-Ochoa, G.I.; Scaife, M.A.; Smith, A.G. Development of novel Riboswitches for synthetic biology in the green alga Chlamydomonas. ACS Synth. Biol. 2020, 9, 1406–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbreras, V.; Stevens, D.R.; Purton, S. Efficient foreign gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii mediated by an endogenous intron. Plant J. 1998, 14, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichmann, J.; Baier, T.; Wentnagel, E.; Lauersen, K.; Kruse, O. Tailored carbon partitioning for phototrophic production of (E)-α-bisabolene from the green microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab. Eng. 2018, 45, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liang, C.; Li, Q.Q. Unique features of nuclear mRNA poly (A) signals and alternative polyadenylation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Genetics 2008, 179, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helliwell, K.E.; Scaife, M.A.; Sasso, S.; Araujo, A.P.U.; Purton, S.; Smith, A. Unraveling vitamin B12-responsive gene regulation in algae. Plant Physiol. 2014, 165, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Wang, H.; Gargouri, M.; Deshpande, R.R.; Skepper, J.N.; Holguin, F.O.; Juergens, M.T.; Shachar-Hill, Y.; Hicks, L.M.; Gang, D.R. The response of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to nitrogen deprivation: A systems biology analysis. Plant J. 2015, 81, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purton, S.; Szaub, J.B.; Wannathong, T.; Young, R.; Economou, C.K. Genetic engineering of algal chloroplasts: Progress and prospects. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 60, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, C.; Wannathong, T.; Szaub, J.; Purton, S. A simple, low-cost method for chloroplast transformation of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 1132, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramundo, S.; Rahire, M.; Schaad, O.; Rochaix, J.-D. Repression of essential chloroplast genes reveals new signaling pathways and regulatory feedback loops in Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 167–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lauersen, K.J.; Berger, H.; Mussgnug, J.H.; Kruse, O. Efficient recombinant protein production and secretion from nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 167, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauersen, K.J.; Baier, T.; Wichmann, J.; Wördenweber, R.; Mussgnug, J.H.; Hübner, W.; Huser, T.; Kruse, O. Efficient phototrophic production of a high-value sesquiterpenoid from the eukaryotic microalga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Metab. Eng. 2016, 38, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zones, J.M.; Blaby, I.K.; Merchant, S.S.; Umen, J.G. High-resolution profiling of a synchronized diurnal transcriptome from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii reveals continuous cell and metabolic differentiation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 2743–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Gene ID | Name | Annotation | Length (bp) Gene Model | Length (bp) Used | Expression Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cre12.g489153 | RPL31 | Ribosomal protein L31 | 34 | 34 | 42 |
| Cre08.g358556 | RPS29 | Ribosomal protein S29 | 59 | 58 | 79 |
| Cre01.g027000 | RPL11 | Ribosomal protein L11 | 60 | 60 | 63 |
| Cre02.g120150 | RBCS2 | Rubisco small subunit 2 | 179 | 221 1 | 12 |
| Cre05.g238332 | PSAD | Photosystem I subunit D | 357 | 336 2 | 80 |
| Cre04.g214150 | THI4 | Thiamine thiazole synthase | 481 | 481 | 194 |
| Cre03.g180750 | METE | Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase | 733 | 733 | 345 |
| Cre04.g223100 | CA1 | Carbonic anhydrase 1 | 786 | 786 | 300 |
| Cre09.g410950 | NIT1 | Nitrate reductase 1 | 888 | 888 | 15537 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geisler, K.; Scaife, M.A.; Mordaka, P.M.; Holzer, A.; Tomsett, E.V.; Mehrshahi, P.; Mendoza Ochoa, G.I.; Smith, A.G. Exploring the Impact of Terminators on Transgene Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Synthetic Biology Approach. Life 2021, 11, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090964
Geisler K, Scaife MA, Mordaka PM, Holzer A, Tomsett EV, Mehrshahi P, Mendoza Ochoa GI, Smith AG. Exploring the Impact of Terminators on Transgene Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Synthetic Biology Approach. Life. 2021; 11(9):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090964
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeisler, Katrin, Mark A. Scaife, Paweł M. Mordaka, Andre Holzer, Eleanor V. Tomsett, Payam Mehrshahi, Gonzalo I. Mendoza Ochoa, and Alison G. Smith. 2021. "Exploring the Impact of Terminators on Transgene Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Synthetic Biology Approach" Life 11, no. 9: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090964
APA StyleGeisler, K., Scaife, M. A., Mordaka, P. M., Holzer, A., Tomsett, E. V., Mehrshahi, P., Mendoza Ochoa, G. I., & Smith, A. G. (2021). Exploring the Impact of Terminators on Transgene Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a Synthetic Biology Approach. Life, 11(9), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/life11090964







