PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Myocardial Infarction (MI)
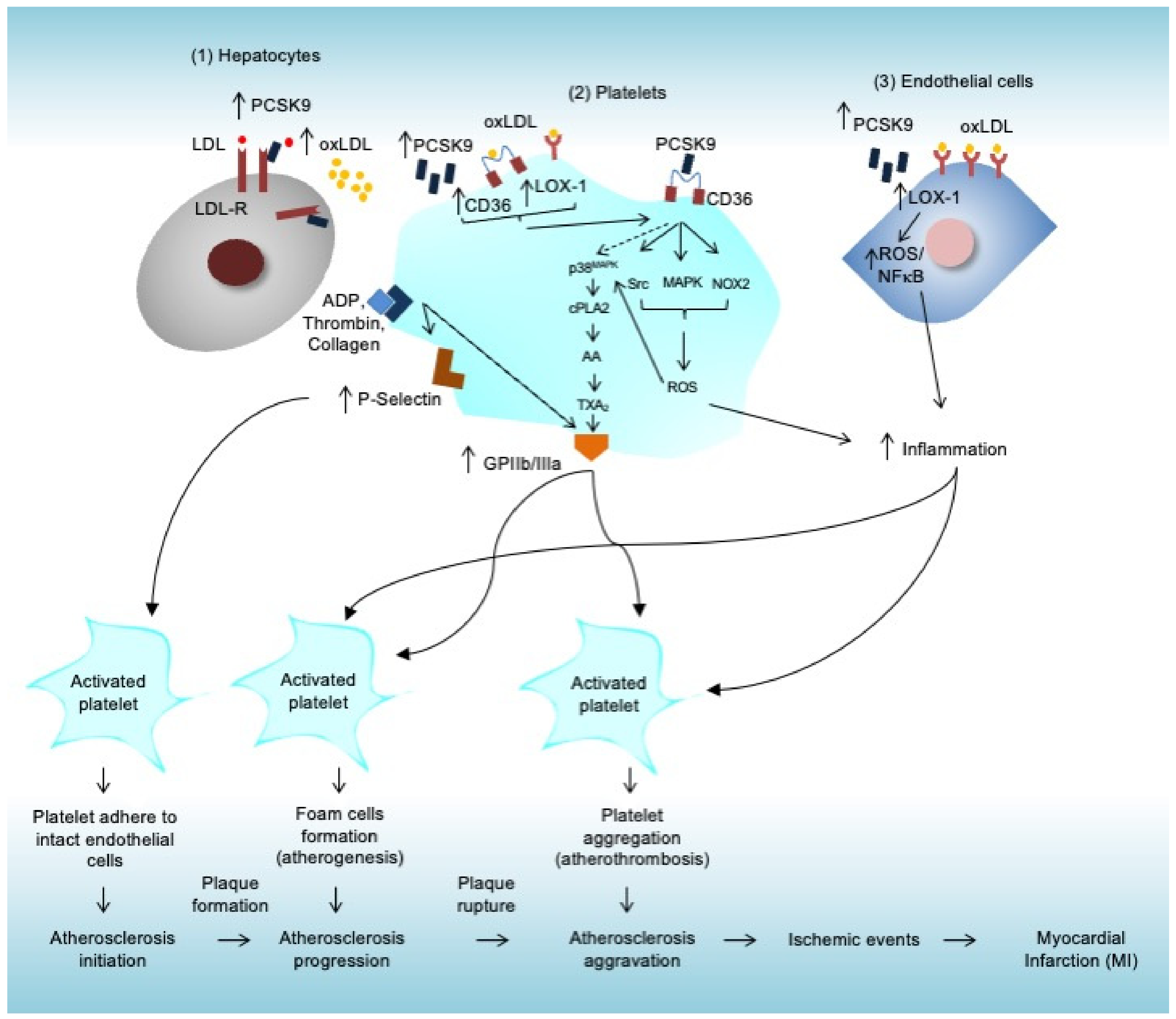
3. Roles of Platelets during Atherosclerosis-Induced MI
3.1. Atherosclerosis
3.2. Roles of Platelets during Atherosclerosis Initiation
3.3. Roles of Platelets during Atherosclerosis Progression (Atherogenesis)
3.4. Roles of Platelets during Atherosclerosis Aggravation (Atherothrombosis)
4. PCSK9 Contribution in Cardiovascular Events
4.1. The Discoveries of PCSK9
4.2. PCSK9 and LDL Cholesterol Metabolism
4.3. PCSK9 and MI
5. PCSK9 Promotes Platelet Activation
6. Discussion and Future Perspective
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators GDaI. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, S.B.; Khavjou, O.A.; Bakas, T.; Hunt, G.; Kirch, R.A.; Leib, A.R.; Morrison, R.S.; Poehler, D.C.; Roger, V.L.; Whitsel, L.P. Projected Costs of Informal Caregiving for Cardiovascular Disease: 2015 to 2035: A Policy Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e558–e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Stewart, J.; Manmathan, G.; Wilkinson, P. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A review of contemporary guidance and literature. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 6, 8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez, E.O.; Ballard, B.D.; Jan, A. Cardiovascular Disease [Updated 2021 Aug 11]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535419/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e563–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Jasmin, S.B.; Stifani, S.; Basak, A.; Prat, A.; Chrétien, M. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seidah, N.G. PCSK9 as a therapeutic target of dyslipidemia. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2008, 13, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Awan, Z.; Chrétien, M.; Mbikay, M. PCSK9: A key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabès, J.-P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; Cruaud, C.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Erlich, D.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melendez, Q.M.; Krishnaji, S.T.; Wooten, C.J.; Lopez, D. Hypercholesterolemia: The role of PCSK9. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2017, 625, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.S.; Fong, L.G.; Young, S.G. PCSK9 function and physiology. J. Lipid. Res. 2008, 49, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camera, M.; Rossetti, L.; Barbieri, S.S.; Zanotti, I.; Canciani, B.; Trabattoni, D.; Ruscica, M.; Tremoli, E.; Ferri, N. PCSK9 as a Positive Modulator of Platelet Activation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachem, A.; Hariri, E.; Saoud, P.; Lteif, C.; Lteif, L.; Welty, F. The Role of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Cardiovascular Homeostasis: A Non-Systematic Literature Review. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 13, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtazi, A.A.; Sabouri-Rad, S.; Gotto, A.M.; Pirro, M.; Banach, M.; Awan, Z.; E Barreto, G.; Sahebkar, A. PCSK9 and inflammation: A review of experimental and clinical evidence. Eur. Hear. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2019, 5, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, B.; Tai, S.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, X.L. PCSK9: Associated with cardiac diseases and their risk factors? Arch Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 704, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2231–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechanic, O.J.; Gavin, M.; Grossman, S.A. Acute Myocardial Infarction; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, P. Myocardial Infarction: Symptoms and Treatments. Cell Biophys. 2015, 72, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, J.P.; Thiele, H.; Barbato, E.; Barthélémy, O.; Bauersachs, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Dendale, P.; Dorobantu, M.; Edvardsen, T.; Folliguet, T.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 1289–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibanez, B.; James, S.; Agewall, S.; Antunes, M.J.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Bueno, H.; Caforio, A.L.P.; Crea, F.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Halvorsen, S. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: The Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 119–177. [Google Scholar]
- Badimon, L.; Padró, T.; Vilahur, G. Atherosclerosis, platelets and thrombosis in acute ischaemic heart disease. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2012, 1, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajar, R. Risk factors for coronary artery disease: Historical perspectives. Hear. Views 2017, 18, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Davies, S.S.; Jerome, W.G.; Linton, E.F.; Song, W.L.; Doran, A.C.; Vickers, K.C. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kanuri, S.H.; Mehta, J.L. Role of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in Atherogenesis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Collot-Teixeira, S.; Martin, J.; McDermott-Roe, C.; Poston, R.; McGregor, J.L. CD36 and macrophages in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 75, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marwali, M.R.; Hu, C.-P.; Mohandas, B.; Dandapat, A.; Deonikar, P.; Chen, J.; Cawich, I.; Sawamura, T.; Kavdia, M.; Mehta, J.L. Modulation of ADP-Induced Platelet Activation by Aspirin and Pravastatin: Role of Lectin-Like Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-1, Nitric Oxide, Oxidative Stress, and Inside-Out Integrin Signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Massberg, S.; Brand, K.; Gruner, S.; Page, S.; Muller, E.; Muller, I.; Bergmeier, W.; Richter, T.; Lorenz, M.; Konrad, I.; et al. A Critical Role of Platelet Adhesion in the Initiation of Atherosclerotic Lesion Formation. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, S.; Krämer, B.; Seizer, P.; Gawaz, M. Platelets, inflammation and atherosclerosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamukcu, B.; Lip, G.Y.; Shantsila, E. The nuclear factor—Kappa B pathway in atherosclerosis: A potential therapeutic target for atherothrombotic vascular disease. Thromb. Res. 2011, 128, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Cooley, B.C.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Vasquez-Vivar, J.; Scoggins, N.O.; Cameron, S.J.; Morrell, C.N.; Silverstein, R.L. Platelet CD36 promotes thrombosis by activating redox sensor ERK5 in hyperlipidemic conditions. Blood 2017, 129, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lahav, J.; Jurk, K.; Hess, O.; Barnes, M.J.; Farndale, R.W.; Luboshitz, J.; Kehrel, B.E. Sustained integrin ligation involves extracellular free sulfhydryls and enzymatically catalyzed disulfide exchange. Blood 2002, 100, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barale, C.; Melchionda, E.; Morotti, A.; Russo, I. PCSK9 Biology and Its Role in Atherothrombosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Jia, D.; Yao, Z.; Chang, L.; Pan, G.; Zhong, H.; et al. PCSK9 (Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin 9) Enhances Platelet Activation, Thrombosis, and Myocardial Infarct Expansion by Binding to Platelet CD36. Circulation 2021, 143, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palasubramaniam, J.; Wang, X.; Peter, K. Myocardial Infarction-From Atherosclerosis to Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, e176–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrétien, M. My road to Damascus: How I converted to the prohormone theory and the proprotein convertases. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.F. On the Discovery of Precursor Processing. Program. Necrosis 2011, 768, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Seidah, N.G. The PCSK9 revolution and the potential of PCSK9-based therapies to reduce LDL-cholesterol. Glob. Cardiol. Sci. Pract. 2017, 2017, e201702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxwell, K.N.; Soccio, R.E.; Duncan, E.M.; Sehayek, E.; Breslow, J.L. Novel putative SREBP and LXR target genes identified by microarray analysis in liver of cholesterol-fed mice. J. Lipid Res. 2003, 44, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubuc, G.; Chamberland, A.; Wassef, H.; Davignon, J.; Seidah, N.G.; Bernier, L.; Prat, A. Statins Upregulate PCSK9, the Gene Encoding the Proprotein Convertase Neural Apoptosis-Regulated Convertase-1 Implicated in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1454–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abifadel, M.; Rabès, J.-P.; Devillers, M.; Munnich, A.; Erlich, D.; Junien, C.; Varret, M.; Boileau, C. Mutations and polymorphisms in the proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) gene in cholesterol metabolism and disease. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Molecular biology of PCSK9: Its role in LDL metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benjannet, S.; Rhainds, D.; Essalmani, R.; Mayne, J.; Wickham, L.; Jin, W.; Assenlin, M.-C.; Hamelin, J.; Varret, M.; Allard, D.; et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: Zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48865–48875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Lagace, T.A.; Garuti, R.; Zhao, Z.; McDonald, M.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Binding of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 to Epidermal Growth Factor-like Repeat A of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Decreases Receptor Recycling and Increases Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18602–18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denis, M.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Zaid, A.; Gauthier, D.; Poirier, S.; Lazure, C.; Seidah, N.G.; Prat, A. Gene Inactivation of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Reduces Atherosclerosis in Mice. Circulation 2012, 125, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rashid, S.; Curtis, D.E.; Garuti, R.; Anderson, N.N.; Bashmakov, Y.; Ho, Y.K.; Hammer, R.E.; Moon, Y.-A.; Horton, J.D. Decreased plasma cholesterol and hypersensitivity to statins in mice lacking Pcsk9. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5374–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paton, D. PCSK9 inhibitors: Monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Drugs Today 2016, 52, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, B. The Modification of Serum Lipids after Acute Coronary Syndrome and Importance in Clinical Practice. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2012, 7, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almontashiri, N.A.M.; Vilmundarson, R.O.; Ghasemzadeh, N.; Dandona, S.; Roberts, R.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Chen, H.-H.; Stewart, A.F.R. Plasma PCSK9 Levels Are Elevated with Acute Myocardial Infarction in Two Independent Retrospective Angiographic Studies. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laugsand, L.E.; Åsvold, B.O.; Vatten, L.J.; Janszky, I.; Platou, C.G.; Michelsen, A.E.; Damås, J.K.; Aukrust, P.; Ueland, T. Circulating PCSK9 and Risk of Myocardial Infarction. The HUNT Study in Norway. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2016, 1, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Xu, R.-X.; Sun, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.-J. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 expression is transiently up-regulated in the acute period of myocardial infarction in rat. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2014, 14, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benn, M.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Grande, P.; Schnohr, P.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A. PCSK9R46L, Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease: 3 Independent Studies and Meta-Analyses. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kathiresan, S. A PCSK9 missense variant associated with a reduced risk of early-onset myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2299–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J.C.; Boerwinkle, E.; Mosley, T.H., Jr.; Hobbs, H.H. Sequence Variations inPCSK9,Low LDL, and Protection against Coronary Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1264–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnier, M. PCSK9: From discovery to therapeutic applications. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 107, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.M.; Oemrawsingh, R.M.; Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Boersma, E.; van Geuns, R.-J.; Serruys, P.W.; Kardys, I.; Akkerhuis, K.M. PCSK9 in relation to coronary plaque inflammation: Results of the ATHEROREMO-IVUS study. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunzioni, I.; Tavori, H.; Covarrubias, R.; Major, A.S.; Ding, L.; Zhang, Y.; DeVay, R.M.; Hong, L.; Fan, D.; Predazzi, I.M.; et al. Local effects of human PCSK9 on the atherosclerotic lesion. J. Pathol. 2016, 238, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapiro, M.D.; Fazio, S. PCSK9 and Atherosclerosis—Lipids and Beyond. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gurbel, P.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Tantry, U.S. Exploration of PCSK9 as a Cardiovascular Risk Factor: Is There a Link to the Platelet? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1463–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciullo, F.; Momi, S.; Gresele, P. PCSK9 in Haemostasis and Thrombosis: Possible Pleiotropic Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Prevention. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petersen-Uribe, Á; Kremser, M.; Rohlfing, A.-K.; Castor, T.; Kolb, K.; Dicenta, V.; Emschermann, F.; Li, B.; Borst, O.; Rath, D.; et al. Platelet-Derived PCSK9 Is Associated with LDL Metabolism and Modulates Atherothrombotic Mechanisms in Coronary Artery Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pęczek, P.; Leśniewski, M.; Mazurek, T.; Szarpak, L.; Filipiak, K.; Gąsecka, A. Antiplatelet Effects of PCSK9 Inhibitors in Primary Hypercholesterolemia. Life 2021, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Hegele, R.A.; Fazio, S.; Cannon, C.P. The Evolving Future of PCSK9 Inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, C.-G.; Guo, Y.-L.; Xu, R.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, J.-J. The Relationship between the Plasma PCSK9 Levels and Platelet Indices in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pastori, D.; Nocella, C.; Farcomeni, A.; Bartimoccia, S.; Santulli, M.; Vasaturo, F.; Carnevale, R.; Menichelli, D.; Violi, F.; Pignatelli, P.; et al. Relationship of PCSK9 and Urinary Thromboxane Excretion to Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Hankey, G.J.; Thom, J.; Bhatt, D.L.; Steg, P.G.; Montalescot, G.; Johnston, S.C.; Steinhubl, S.R.; Mak, K.-H.; Easton, J.D.; et al. Incomplete Inhibition of Thromboxane Biosynthesis by Acetylsalicylic Acid: Determinants and Effect on Cardiovascular Risk. Circulation 2009, 119, e595–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarese, E.P.; Kołodziejczak, M.; Winter, M.-P.; Alimohammadi, A.; Lang, I.M.; Buffon, A.; Lip, G.Y.; Siller-Matula, J.M. Association of PCSK9 with platelet reactivity in patients with acute coronary syndrome treated with prasugrel or ticagrelor: The PCSK9-REACT study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, C.; Kleiman, K.; Meng, H.; Knight, J.S.; Eitzman, D.T. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) Deficiency is Protective Against Venous Thrombosis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cammisotto, V.; Pastori, D.; Nocella, C.; Bartimoccia, S.; Castellani, V.; Marchese, C.; Scavalli, A.S.; Ettorre, E.; Viceconte, N.; Violi, F.; et al. PCSK9 Regulates Nox2-Mediated Platelet Activation via CD36 Receptor in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Shahanawaz, J.; Reis, R.J.S.; Varughese, K.I.; Sawamura, T.; Mehta, J.L. Cross-talk between LOX-1 and PCSK9 in vascular tissues. Cardiovasc. Res. 2015, 107, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Theus, S.; Deng, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Mehta, J.L. PCSK9 regulates expression of scavenger receptors and ox-LDL uptake in macrophages. Cardiovasc. Res. 2018, 114, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barale, C.; Bonomo, K.; Frascaroli, C.; Morotti, A.; Guerrasio, A.; Cavalot, F.; Russo, I. Platelet function and activation markers in primary hypercholesterolemia treated with anti-PCSK9 monoclonal antibody: A 12-month follow-up. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puteri, M.U.; Azmi, N.U.; Kato, M.; Saputri, F.C. PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction. Life 2022, 12, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020190
Puteri MU, Azmi NU, Kato M, Saputri FC. PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction. Life. 2022; 12(2):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020190
Chicago/Turabian StylePuteri, Meidi Utami, Nuriza Ulul Azmi, Mitsuyasu Kato, and Fadlina Chany Saputri. 2022. "PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction" Life 12, no. 2: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020190
APA StylePuteri, M. U., Azmi, N. U., Kato, M., & Saputri, F. C. (2022). PCSK9 Promotes Cardiovascular Diseases: Recent Evidence about Its Association with Platelet Activation-Induced Myocardial Infarction. Life, 12(2), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020190





