Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
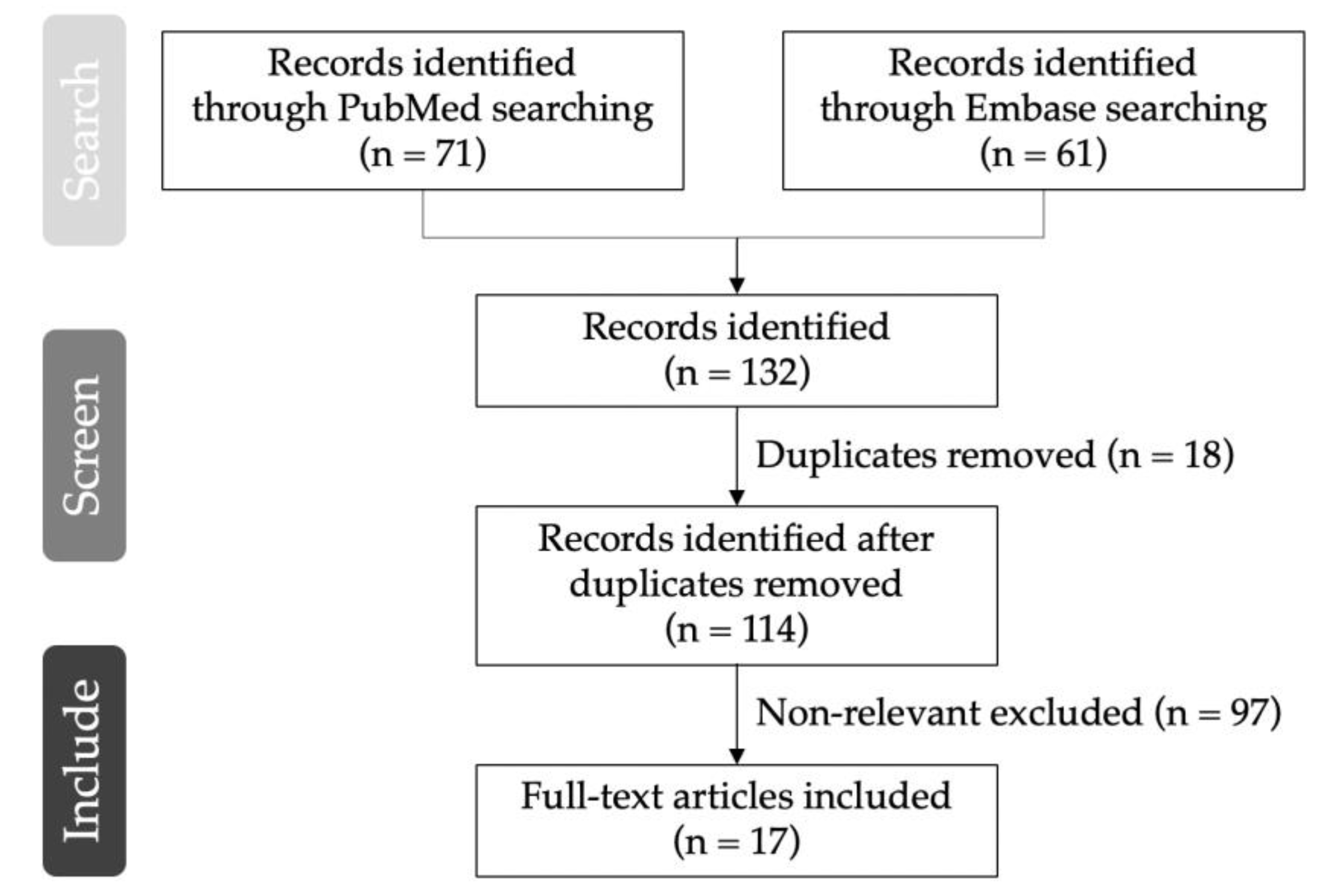
2. Literature Search
3. Therapeutic Application of rTMS in Neuropathic Pain
3.1. Central Post-Stroke Pain
3.2. Patients with SCI
3.3. Phantom Limb Pain
3.4. Radiculopathy
3.5. Diabetic Neuropathy
3.6. Post-Herpetic Neuralgia
3.7. Neuropathic Orofacial Pain
3.8. Brachial Plexus Injury
4. Parameters/Settings
5. Contraindications to rTMS Application
6. Adverse Effects of rTMS
7. Mechanism Underlying rTMS in Neuropathic Pain
7.1. HF-rTMS
7.2. LF-rTMS
8. rTMS for Comorbidities of Neuropathic Pain
9. Discussion/Future Perspective
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colloca, L.; Ludman, T.; Bouhassira, D.; Baron, R.; Dickenson, A.H.; Yarnitsky, D.; Freeman, R.; Truini, A.; Attal, N.; Finnerup, N.B.; et al. Neuropathic pain. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Hecke, O.; Austin, S.K.; Khan, R.A.; Smith, B.H.; Torrance, N. Neuropathic pain in the general population: A systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 2014, 155, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liampas, A.; Velidakis, N.; Georgiou, T.; Vadalouca, A.; Varrassi, G.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Tsivgoulis, G.; Zis, P. Prevalence and Management Challenges in Central Post-Stroke Neuropathic Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 3278–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, D.; Fullen, B.M.; Stokes, D.; Lennon, O. Neuropathic pain prevalence following spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Pain 2017, 21, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chang, K.V.; Wu, W.T.; Wang, J.C.; Özçakar, L. Effects of Ultrasound-Guided Peritendinous and Intrabursal Corticosteroid Injections on Shoulder Tendon Elasticity: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 102, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.P.; Chang, K.V.; Huang, Y.K.; Wu, W.T.; Özçakar, L. Regenerative Injections Including 5% Dextrose and Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helm, S.; Shirsat, N.; Calodney, A.; Abd-Elsayed, A.; Kloth, D.; Soin, A.; Shah, S.; Trescot, A. Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Chronic Pain: A Systematic Review of Effectiveness and Safety. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 985–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, T.R.; Hunter, C.W.; Mehta, P.; Sayed, D.; Grider, J.S.; Lamer, T.J.; Pope, J.E.; Falowski, S.; Provenzano, D.A.; Esposito, M.F.; et al. A Systematic Literature Review of Dorsal Root Ganglion Neurostimulation for the Treatment of Pain. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.-J.; Hu, W.-H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, B.-T.; Zhou, J.-J.; Zhang, K. Motor cortex stimulation: A systematic literature-based analysis of effectiveness and case series experience. BMC Neurol. 2019, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zortea, M.; Ramalho, L.; Alves, R.L.; Alves, C.F.d.S.; Braulio, G.; Torres, I.L.d.S.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation to Improve the Dysfunction of Descending Pain Modulatory System Related to Opioids in Chronic Non-cancer Pain: An Integrative Review of Neurobiology and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Chang, M.C. Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Pain Management: A Systematic Narrative Review. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klomjai, W.; Katz, R.; Lackmy-Vallée, A. Basic principles of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and repetitive TMS (rTMS). Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 58, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Classen, J.; Gerloff, C.; Celnik, P.; Wassermann, E.M.; Hallett, M.; Cohen, L.G. Depression of motor cortex excitability by low-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 1997, 48, 1398–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Leone, A.; Valls-Solé, J.; Wassermann, E.M.; Hallett, M. Responses to rapid-rate transcranial magnetic stimulation of the human motor cortex. Brain 1994, 117 Pt 4, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomeh, A.; Yusof Khan, A.H.K.; Inche Mat, L.N.; Basri, H.; Wan Sulaiman, W.A. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation of the Primary Motor Cortex beyond Motor Rehabilitation: A Review of the Current Evidence. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, A.; Donohue, M.; Xu, R.; Lee, R.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Khedr, E.M.; Saitoh, Y.; André-Obadia, N.; Rollnik, J.; Wallace, M.; et al. rTMS for suppressing neuropathic pain: A meta-analysis. J. Pain 2009, 10, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Drouot, X.; Menard-Lefaucheur, I.; Zerah, F.; Bendib, B.; Cesaro, P.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.P. Neurogenic pain relief by repetitive transcranial magnetic cortical stimulation depends on the origin and the site of pain. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, R.A.; de Andrade, D.C.; Mendonça, M.; Barros, R.; Luvisoto, T.; Myczkowski, M.L.; Marcolin, M.A.; Teixeira, M.J. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the left premotor/dorsolateral prefrontal cortex does not have analgesic effect on central poststroke pain. J. Pain 2014, 15, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, B.; Kesikburun, S.; Yaşar, E.; Tan, A.K. The effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on refractory neuropathic pain in spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2014, 37, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, B.S.; Shin, H.I.; Bang, M.S. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation over the hand motor cortical area on central pain after spinal cord injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 90, 1766–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Long, H.; Zhao, C.; Duan, Q.; Zhu, H.; Chen, C.; Sun, W.; Ju, F.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Analgesia-enhancing effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury:An fNIRS study. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2019, 37, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Sayed, D. Long-term antalgic effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of motor cortex and serum beta-endorphin in patients with phantom pain. Neurol. Res. 2011, 33, 953–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavera, A.; Silva, F.A.; Fregni, F.; Carrillo, S.; Garcia, R.G. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Phantom Limb Pain in Land Mine Victims: A Double-Blinded, Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial. J. Pain 2016, 17, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seifert, F.; Maihöfner, C. Functional and structural imaging of pain-induced neuroplasticity. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 24, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attal, N.; Ayache, S.S.; Ciampi De Andrade, D.; Mhalla, A.; Baudic, S.; Jazat, F.; Ahdab, R.; Neves, D.O.; Sorel, M.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; et al. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct-current stimulation in neuropathic pain due to radiculopathy: A randomized sham-controlled comparative study. Pain 2016, 157, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, L.; Feffer, K.; Lozano, C.; Giacobbe, P.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Blumberger, D.M.; Downar, J. Number of pulses or number of sessions? An open-label study of trajectories of improvement for once-vs. twice-daily dorsomedial prefrontal rTMS in major depression. Brain Stimul. 2018, 11, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Kwak, S.G.; Choi, G.S.; Chang, M.C. Short-term Effect of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation on Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain. Pain Physician 2022, 25, E203–E209. [Google Scholar]
- Onesti, E.; Gabriele, M.; Cambieri, C.; Ceccanti, M.; Raccah, R.; Di Stefano, G.; Biasiotta, A.; Truini, A.; Zangen, A.; Inghilleri, M. H-coil repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for pain relief in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.M.; Ni, J.X.; Li, X.Y.; Yang, L.Q.; Guo, Y.N.; Tang, Y.Z. High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Reduces Pain in Postherpetic Neuralgia. Pain Med. 2015, 16, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, Q.; Wu, B.; Tang, Y.; Yang, X.; Song, L.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Sun, C.; Ma, S.; Ni, J. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation at Different Frequencies for Postherpetic Neuralgia: A Double-Blind, Sham-Controlled, Randomized Trial. Pain Physician 2019, 22, E303–E313. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, P.; Lamusuo, S.; Taiminen, T.; Pesonen, U.; Lahti, A.; Virtanen, A.; Forssell, H.; Hietala, J.; Hagelberg, N.; Pertovaara, A.; et al. Right secondary somatosensory cortex-a promising novel target for the treatment of drug-resistant neuropathic orofacial pain with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Pain 2015, 156, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifácio de Assis, E.D.; Martins, W.K.N.; de Carvalho, C.D.; Ferreira, C.M.; Gomes, R.; de Almeida Rodrigues, E.T.; Meira, U.M.; de Holanda, L.J.; Lindquist, A.R.; Morya, E.; et al. Effects of rTMS and tDCS on neuropathic pain after brachial plexus injury: A randomized placebo-controlled pilot study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, J.; Vanhanen, J.; Harno, H.; Lioumis, P.; Vaalto, S.; Kaunisto, M.A.; Putaala, J.; Kangasniemi, M.; Kirveskari, E.; Mäkelä, J.P.; et al. A Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Targeting M1 and S2 in Central Poststroke Pain: A Pilot Trial. Neuromodulation 2022, 25, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetté, F.; Côté, I.; Meziane, H.B.; Mercier, C. Effect of single-session repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation applied over the hand versus leg motor area on pain after spinal cord injury. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2013, 27, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, R.; Höller, Y.; Langthaler, P.B.; Lochner, P.; Golaszewski, S.; Schwenker, K.; Brigo, F.; Trinka, E. rTMS of the prefrontal cortex has analgesic effects on neuropathic pain in subjects with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.G.; Sun, W.; Ju, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.L.; Mou, X.; Yuan, H. Analgesic Effects of Directed Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Acute Neuropathic Pain After Spinal Cord Injury. Pain Med. 2020, 21, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.D.; Lisanby, S.H.; Peterchev, A.V. Transcranial magnetic stimulation in the presence of deep brain stimulation implants: Induced electrode currents. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2010, 2010, 6821–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, T.H.; Dhamne, S.C.; Chen, J.J.; Carpenter, L.L.; Anastasio, E.M.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Rotenberg, A. Minimal heating of aneurysm clips during repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 1471–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lefranc, M.; Ko, J.Y.; Peltier, J.; Fichten, A.; Desenclos, C.; Macron, J.M.; Toussaint, P.; Le Gars, D.; Petitjean, M. Effect of transcranial magnetic stimulation on four types of pressure-programmable valves. Acta Neurochir. 2010, 152, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveles Jensen, K.H.; Navntoft, C.A.; Sindahl, C.H.; Cayé-Thomasen, P.; Jørgensen, M.B. Cochlear implant should not be absolute contraindication for electroconvulsive therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 1464–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pridmore, S.; Turnier-Shea, Y.; Rybak, M.; Pridmore, W. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) during pregnancy: A fetal risk factor. Australas. Psychiatry 2021, 29, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, N.S.; Carpenter, S.L.; Carpenter, L.L. Safe use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with implanted vagus nerve stimulators. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 608–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stultz, D.J.; Osburn, S.; Burns, T.; Pawlowska-Wajswol, S.; Walton, R. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Safety with Respect to Seizures: A Literature Review. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat 2020, 16, 2989–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Hallett, M.; Rossini, P.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 2008–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lerner, A.J.; Wassermann, E.M.; Tamir, D.I. Seizures from transcranial magnetic stimulation 2012–2016: Results of a survey of active laboratories and clinics. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2019, 130, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tringali, S.; Perrot, X.; Collet, L.; Moulin, A. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: Hearing safety considerations. Brain Stimul. 2012, 5, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overvliet, G.M.; Jansen, R.A.C.; van Balkom, A.; van Campen, D.C.; Oudega, M.L.; van der Werf, Y.D.; van Exel, E.; van den Heuvel, O.A.; Dols, A. Adverse events of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in older adults with depression, a systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, L.M.; Goetz, S.M.; Tucci, D.L.; Peterchev, A.V. Sound comparison of seven TMS coils at matched stimulation strength. Brain Stimul. 2020, 13, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishima, H.; Saitoh, Y.; Osaki, Y.; Nishimura, H.; Kato, A.; Hatazawa, J.; Yoshimine, T. Motor cortex stimulation in patients with deafferentation pain: Activation of the posterior insula and thalamus. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Larrea, L.; Peyron, R.; Mertens, P.; Gregoire, M.C.; Lavenne, F.; Le Bars, D.; Convers, P.; Mauguière, F.; Sindou, M.; Laurent, B. Electrical stimulation of motor cortex for pain control: A combined PET-scan and electrophysiological study. Pain 1999, 83, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanakawa, T. Neural mechanisms underlying deafferentation pain: A hypothesis from a neuroimaging perspective. J. Orthop. Sci. 2012, 17, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, M.; Ciurea, A.V. Neuronavigation. Principles. Surgical technique. J. Med. Life 2009, 2, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ayache, S.S.; Ahdab, R.; Chalah, M.A.; Farhat, W.H.; Mylius, V.; Goujon, C.; Sorel, M.; Lefaucheur, J.P. Analgesic effects of navigated motor cortex rTMS in patients with chronic neuropathic pain. Eur. J. Pain 2016, 20, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Ji, Y.; Voulalas, P.J.; Keaser, M.; Xu, S.; Gullapalli, R.P.; Greenspan, J.; Masri, R. Motor cortex stimulation suppresses cortical responses to noxious hindpaw stimulation after spinal cord lesion in rats. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Andrade, D.C.; Mhalla, A.; Adam, F.; Texeira, M.J.; Bouhassira, D. Neuropharmacological basis of rTMS-induced analgesia: The role of endogenous opioids. Pain 2011, 152, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleigh, J.; Harvey, M.; Voss, L.; Denny, B. Ketamine–More mechanisms of action than just NMDA blockade. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 2014, 4, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciampi de Andrade, D.; Mhalla, A.; Adam, F.; Texeira, M.J.; Bouhassira, D. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation induced analgesia depends onN-methyl-d-aspartate glutamate receptors. PAIN 2014, 155, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambriz-Tututi, M.; Sánchez-González, V.; Drucker-Colín, R. Transcranial magnetic stimulation reduces nociceptive threshold in rats. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, R.S.; Stein, D.J.; Sanches, P.R.S.; da Silva, L.S.; Medeiros, H.R.; Fregni, F.; Caumo, W.; Torres, I.L.S. rTMS induces analgesia and modulates neuroinflammation and neuroplasticity in neuropathic pain model rats. Brain Res. 2021, 1762, 147427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsch, B.; Reis, J.; Martinowich, K.; Schambra, H.M.; Ji, Y.; Cohen, L.G.; Lu, B. Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: Potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 2010, 66, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duric, V.; McCarson, K.E. Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene expression is differentially modulated in the rat spinal dorsal horn and hippocampus during inflammatory pain. Mol. Pain 2007, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, M.; Wille, G.; Klien, S.; Shanib, H.; Holle, D.; Gaul, C.; Broessner, G. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in primary headaches. J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radat, F.; Margot-Duclot, A.; Attal, N. Psychiatric co-morbidities in patients with chronic peripheral neuropathic pain: A multicentre cohort study. Eur. J. Pain 2013, 17, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherif, F.; Zouari, H.G.; Cherif, W.; Hadded, M.; Cheour, M.; Damak, R. Depression Prevalence in Neuropathic Pain and Its Impact on the Quality of Life. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 7408508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, R.H.; Andrews-Hanna, J.R.; Wager, T.D.; Pizzagalli, D.A. Large-Scale Network Dysfunction in Major Depressive Disorder: A Meta-analysis of Resting-State Functional Connectivity. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutter, D.J. Antidepressant efficacy of high-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation over the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in double-blind sham-controlled designs: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2009, 39, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seminowicz, D.A.; Moayedi, M. The Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Acute and Chronic Pain. J. Pain 2017, 18, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, J.; Minoshima, S.; Casey, K.L. Keeping pain out of mind: The role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in pain modulation. Brain 2003, 126, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Civardi, C.; Cantello, R.; Asselman, P.; Rothwell, J.C. Transcranial magnetic stimulation can be used to test connections to primary motor areas from frontal and medial cortex in humans. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.; Cash, R.F.H.; Luo, X.; Luo, H.; Lu, X.; Xu, F.; Zang, Y.F.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Fitzgibbon, B.M. High-frequency rTMS over the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on chronic and provoked pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain Stimul. 2021, 14, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Yan, W.; Wan, R.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, X.; Song, G.; Zheng, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on neuropathic pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 132, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, P.; Lamusuo, S.; Taiminen, T.; Virtanen, A.; Pertovaara, A.; Forssell, H.; Hagelberg, N.; Jääskeläinen, S. The analgesic effect of therapeutic rTMS is not mediated or predicted by comorbid psychiatric or sleep disorders. Medicine 2016, 95, e5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Nguyen, J.P. A practical algorithm for using rTMS to treat patients with chronic pain. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2019, 49, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre-Obadia, N.; Magnin, M.; Simon, E.; Garcia-Larrea, L. Somatotopic effects of rTMS in neuropathic pain? A comparison between stimulation over hand and face motor areas. Eur. J. Pain 2018, 22, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Hatem, S.; Nineb, A.; Ménard-Lefaucheur, I.; Wendling, S.; Keravel, Y.; Nguyen, J.P. Somatotopic organization of the analgesic effects of motor cortex rTMS in neuropathic pain. Neurology 2006, 67, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beam, W.; Borckardt, J.J.; Reeves, S.T.; George, M.S. An efficient and accurate new method for locating the F3 position for prefrontal TMS applications. Brain Stimul. 2009, 2, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peltz, E.; Seifert, F.; DeCol, R.; Dörfler, A.; Schwab, S.; Maihöfner, C. Functional connectivity of the human insular cortex during noxious and innocuous thermal stimulation. Neuroimage 2011, 54, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Drouot, X.; Ménard-Lefaucheur, I.; Nguyen, J.P. Neuropathic pain controlled for more than a year by monthly sessions of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2004, 34, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

|
| Author (Year) | Disease | Baseline Characteristics: Mean Age/Number (Male/Female) | rTMS (n = xx), Control or Sham (n = xx) | rTMS Site | rTMS Frequency | rTMS Intensity | rTMS Pulses | rTMS Session | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| de Oliveira et al. (2014) [18] | Post-stroke | 56.3 (l1/10) | 11, 10 | Left PMC/DLPFC | 10 Hz | 120% RMT | 1250 | Daily with 2-day weekend interval for a total of 10 consecutive sessions | No differences in pain reduction over 1 month compared to the hand motor cortex group and sham group |
| Ojala rt al (2022) [33] | Post-stroke | 55.8 (8/9) | 17, 17 | S2 contralateral to painful site | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 5050 (train duration, 10 s; intertrain pause, 50 s) | 10 sessions | Significant reduction of weekly pain intensity in S3 group compared with the sham group |
| Kang et al. (2009) [20] | SCI | 54.8 (6/5) | 11, 11 | FDI motor cortex | 10 Hz | 80% RMT | 1000 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 55 s) | Daily, 5 consecutive sessions | No differences in average NRS reduction compared to the sham group |
| Jetté et al. (2013) [34] | SCI | 50 (11/5) | 16, 16 | Hand: FDI motor cortex Leg: vertex motor cortex | 10 Hz | Hand: 90%RMT Leg: 110%RMT | 2000 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 25 s) | One session | About 10% NRS reduction over the first 49 h compared with the sham group |
| Yılmaz et al. (2014) [19] | SCI | 38.6 (16/0) | 9, 7 | Vertex motor cortex | 5 Hz | 110% RMT | 1500 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 25 s) | Daily for a total of 10 consecutive sessions | Not superior to the sham group |
| Nardone et al. (2017) [35] | SCI | 43.1 (9/3) | 6, 6 | PFC/DLPFC: 6 cm anterior to the FDI motor cortex | 10 Hz | 120% RMT | 1250 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 25 s) | 5 times per week for 2 weeks for a total of 10 consecutive sessions | Significant VAS reduction over 1 month compared with the sham group |
| Sun et al. (2019) [21] | SCI | 37 (15/2) | 11, 6 | Hand motor cortex | 10 Hz | 80% RMT | 1200 (train duration, 1.2 s; intertrain pause, 3 s) | Daily with 1-day interval per week for a total of 6 weeks | Greater NRS reduction after 2 weeks of rTMS sessions than the sham group |
| Zhao et al. (2020) [36] | SCI | 41.6 (NA) | 24, 24 | Hand motor cortex | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 1500 (intertrain pause, 3 s) | Daily with 1-day interval per week for a total of 3 weeks | Significant NRS reduction on the 3rd day and 1st week post-rTMS compared with the sham group |
| Ahmed et al. (2011) [22] | Phantom limb pain | 52.0 (13/140 | 27 | Motor cortex corresponding to the stump of painful site | 20 Hz | 80% RMT | NA (train duration, 10 s) | Daily, 5 consecutive sessions | Significant VAS reduction over 2 months compared with the sham group; 55%, 52% and 39% VAS reduction on the day, 1st month and 2nd month post-rTMS, respectively |
| Malavera et al. (2016) [23] | Phantom limb pain | 33.9 (50/4) | 27, 27 | Contralateral leg motor cortex | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 1200 (train duration, 6 s; intertrain pause, 54 s) | Daily, 10 consecutive sessions | 30.44% greater mean VAS reduction on the 15th day post-rTMS, and no differences on the 30th day post-rTMS, than the sham group |
| Attal et al. (2016) [25] | Lumbosacral radiculopathy | 52.7 (17/18) | 21, 11 | Thenar motor cortex | 10 Hz | 80% RMT | 3000 (train duration, 10 s; intertrain pause, 20 s) | Daily, 3 consecutive sessions | 30.4% mean pain reduction |
| Onesti et al. (2013) [28] | Diabetic neuropathy | 70.6 (14/9) | 23, 23 | Leg motor cortex | 20 Hz | 100% RMT | 1500 (intertrain pause, 30 s) | Daily, 5 sessions | Significant VAS reduction over 3 weeks compared with the sham group |
| Yang et al. (2022) [27] | Diabetic peripheral neuropathy | 60.4 (11/9) | 10, 10 | Left APB motor cortex | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 1000 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 55 s) | Daily, 5 sessions | Significant NRS reduction from 6.5 ± 0.9 to 3.6 ± 0.7 1 day post-rTMS; non-significant NRS reduction 1 week post-rTMS compared to the sham group |
| Ma et al. (2015) [29] | PHN | 66.4 (20/20) | 20, 20 | Motor cortex corresponding to a painful site | 10 Hz | 80% RMT | 1500 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 3 s) | 5 times per week for 2 weeks for a total of 10 consecutive sessions | 16.9% mean VAS reduction over 6 months |
| Pei et al. (2019) [30] | PHN | 66.2 (30/30) | 20, 20, 20 | Motor cortex corresponding to a painful site | 10 Hz | 80% RMT | 10 Hz group: 1500 (train duration, 0.5 s; intertrain pause, 3 s) | Daily, 10 sessions | Superior VAS reduction in 10 Hz group over 3 months compared with 5 Hz and sham groups |
| Lindholm et al. (2015) [31] | Drug-resistant neuropathic orofacial pain | 57.7 (7/13) | 10, 6 | Right S2 | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 2500 (train duration, 5 s; intertrain pause, 15 s; 15 min break in the middle of session) | One session | Lower NRS of pain over 1 month than S1/M1 or sham groups |
| Bonifácio de Assis et al. (2022) [32] | Traumatic BPI | 32.8 (20/0) | 12, 8 | Contralateral hand motor cortex | 10 Hz | 90% RMT | 2500 (train duration, 10 s; intertrain pause, 17 s) | Daily, 5 consecutive days | Superior continuous pain, paroxysmal pain and anxiety reduction over 1 month compared with the sham group |
| Contraindications to rTMS | Adverse Effects of rTMS |
|---|---|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, Y.-Y.; Wu, W.-T.; Han, D.-S.; Mezian, K.; Ricci, V.; Özçakar, L.; Hsu, P.-C.; Chang, K.-V. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life 2023, 13, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020258
Tsai Y-Y, Wu W-T, Han D-S, Mezian K, Ricci V, Özçakar L, Hsu P-C, Chang K-V. Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life. 2023; 13(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Yuan-Yuan, Wei-Ting Wu, Der-Sheng Han, Kamal Mezian, Vincenzo Ricci, Levent Özçakar, Po-Cheng Hsu, and Ke-Vin Chang. 2023. "Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review" Life 13, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020258
APA StyleTsai, Y.-Y., Wu, W.-T., Han, D.-S., Mezian, K., Ricci, V., Özçakar, L., Hsu, P.-C., & Chang, K.-V. (2023). Application of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in Neuropathic Pain: A Narrative Review. Life, 13(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13020258








