Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals New Ruminal Microbial Features Associated with Peanut Vine Efficiency in Dairy Cattle
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Situ Rumen Incubation and Forage Sample Collection
2.2. Biomass Degradation Analysis
2.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4. Analysis of Bacteria Attached to Peanut Vine by Illumina MiSeq Sequencing of 16S rRNA Genes
2.5. Bacterial Community and CAZyme Analysis of Bacteria Attached to Peanut Vine by Metagenome Shotgun Sequencing
2.5.1. DNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Metagenomic Sequencing
2.5.2. Sequence Quality Control and Genome Assembly
2.5.3. Gene Prediction, Taxonomy, and Functional Annotation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Degradation of Peanut Vine
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.3. Temporal Changes in Bacterial Communities Attached to Peanut Vine Determined by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
3.4. Temporal Changes in Bacterial Communities Attached to Peanut Vine and CAZymes Determined by Metagenomics
3.4.1. Profiling of the Rumen Metagenome
3.4.2. Functional Analysis of Bacteria Attached to Peanut Vine Predicted from Metagenome Shotgun Sequencing Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, H.Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.W.; Yang, Q.Y.; Dai, C.C. Application of Serratia marcescens RZ-21 Significantly Enhances Peanut Yield and Remediates Continuously Cropped Peanut Soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Du, F. Potential Use of Peanut By-Products in Food Processing: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Mapping Supply and Demand for Animal-Source Foods to 2030; Animal Production and Health Working Paper No. 2; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.R.; Yu, B.; Chiou, P.W.S. Roughage Energy and Degradability Estimation with Aspergillus oryzae Inclusion using Daisy (R) in vitro Fermentation. Asian Austral. J. Anim. 2004, 17, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Zhu, C.H.; Guo, J.; Tang, Q.P.; Li, H.F.; Zou, J.M. Metabolizable Energy and Fiber Digestibility of Uncommon Feedstuffs for Geese. Poultry Sci. 2013, 92, 1812–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Gao, T.; Phillips, C. Effect of Feeding a Diet Comprised of Various Corn Silages Inclusion with Peanut Vine or Wheat Straw on Performance, Digestion, Serum Parameters and Meat Nutrients in Finishing Beef Cattle. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.; Lu, J.; Cao, S.; Li, S.; Ma, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; et al. Effects of Diets Combining Peanut Vine and Whole-Plant Corn Silage on Growth Performance, Meat Quality and Rumen Microbiota of Simmental Crossbred Cattle. Foods 2023, 12, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, S.; Mizrahi, I. The Road Not Taken: The Rumen Microbiome, Functional Groups, and Community States. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, T.A.; Bae, H.D.; Jones, G.A.; Cheng, K.J. Microbial Attachment and Feed Digestion in the Rumen. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 3004–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharechahi, J.; Vahidi, M.F.; Ding, X.Z.; Han, J.L.; Salekdeh, G.H. Temporal Changes in Microbial Communities Attached to Forages with Different Lignocellulosic Compositions in Cattle Rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.E.; Huws, S.A.; Kim, E.J.; Kingston-Smith, A.H. Characterization of the Dynamics of Initial Bacterial Colonization of Nonconserved Forage in the Bovine Rumen. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 62, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Xue, C.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. Characterization and Comparison of the Temporal Dynamics of Ruminal Bacterial Microbiota Colonizing Rice Straw and Alfalfa Hay within Ruminants. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9668–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Sharpton, T.J.; Zhu, W. Progressive Colonization of Bacteria and Degradation of Rice Straw in the Rumen by Illumina Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handelsman, J.; Rondon, M.R.; Brady, S.F.; Clardy, J.; Goodman, R.M. Molecular Biological Access to the Chemistry of Unknown Soil Microbes: A New Frontier for Natural Products. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R245–R249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Jones, R.B.; Fodor, A.A. Inference-based Accuracy of Metagenome Prediction Tools Varies Across Sample Types and Functional Categories. Microbiome 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larue, R.; Yu, Z.T.; Parisi, V.A.; Egan, A.R.; Morrison, M. Novel Microbial Diversity Adherent to Plant Biomass in the Herbivore Gastrointestinal Tract, as Revealed by Ribosomal Intergenic Spacer Analysis and rrs Gene Sequencing. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, W.; Latimer, G.W. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 17th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orskov, E.R.; Mcdonald, I. The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 92, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W. Temporal Changes of the Bacterial Community Colonizing Wheat Straw in the Cow Rumen. Anaerobe 2018, 50, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.M.; Jisha, T.K.; Reddy, B.; Parmar, N.; Patel, A.; Patel, A.K.; Joshi, C.G. Microbial Profiles of Liquid and Solid Fraction Associated Biomaterial in Buffalo Rumen Fed Green and Dry Roughage Diets by Tagged 16S rRNA Gene Pyrosequencing. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, C.M.; Luo, R.; Sadakane, K.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT: An Ultra-Fast Single-Node Solution for Large and Complex Metagenomics Assembly via Succinct de Bruijn Graph. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1674–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, H.; Park, J.; Takagi, T. MetaGene: Prokaryotic Gene Finding from Environmental Genome Shotgun Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5623–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for Clustering the Next-Generation Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, Y.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP: Short Oligonucleotide Alignment Program. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schaffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-Source, Platform-Independent, Community-Supported Software for Describing and Comparing Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzant, E.S.; Cochran, R.C.; Titgemeyer, E.C. Standardization of In Situ Techniques for Ruminant Feedstuff Evaluation. J. Anim. Sci. 1998, 76, 2717–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancik, F.; Koukolova, V.; Homolka, P. Ruminal Degradability of Dry Matter and Neutral Detergent Fibre of Grasses. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 55, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, G.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. Steam Explosion Enhances Digestibility and Fermentation of Corn Stover by Facilitating Ruminal Microbial Colonization. Bioresource Technol. 2018, 253, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Chang, J.; Yin, Q.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Dang, X.; Gao, T.; Lu, F. Effect of Physicochemical Pretreatments Plus Enzymatic Hydrolysis on the Composition and Morphologic Structure of Corn Straw. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, H.; Lachman, M.; Malfatti, S.; Sczyrba, A.; Knierim, B.; Auer, M.; Tringe, S.G.; Mackie, R.I.; Yeoman, C.J.; Hess, M. Temporal Dynamics of Fibrolytic and Methanogenic Rumen Microorganisms During in situ Incubation of Switchgrass Determined by 16S rRNA Gene Profiling. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Kosaka, T.; Hotta, Y.; Watanabe, K. Simulating the Contribution of Coaggregation to Interspecies Hydrogen Fluxes in Syntrophic Methanogenic Consortia. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5093–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.S.; Eng, E.R.; Eik, L.O. Studies on Untreated and Urea-Treated Rice Straw from Three Cultivation Seasons. 3. Histological Investigations by Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 1999, 80, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Piccolo, G.; Bovera, F.; Zicarelli, F.; Gazaneo, M.P.; Infascelli, F. In vitro fermentation kinetics of fresh and dried silage. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2005, 123–124, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, F.L.; Colombatto, D.; Owen, E. The impact of particle size on the rate and extent of in vitro fermentation investigated using the reading pressure technique. In Annual Meeting of the British Society of Animal Science; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; p. 61. [Google Scholar]
- Bickhart, D.M.; Weimer, P.J. Symposium Review: Host-Rumen Microbe Interactions may be Leveraged to Improve the Productivity of Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7680–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.Y.; Sun, H.Z.; Wu, X.H.; Liu, J.X.; Guan, L.L. Multi-omics Reveals that the Rumen Microbiome and its Metabolome Together with the Host Metabolome Contribute to Individualized Dairy Cow Performance. Microbiome 2020, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zened, A.; Combes, S.; Cauquil, L.; Mariette, J.; Klopp, C.; Bouchez, O.; Troegeler-Meynadier, A.; Enjalbert, F. Microbial Ecology of the Rumen Evaluated by 454 GS FLX Pyrosequencing is Affected by Starch and Oil Supplementation of Diets. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2013, 83, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, M.; Ohkuma, M. Reclassification of Xylanibacter oryzae Ueki et al. 2006 as Prevotella oryzae comb. nov., with an amended description of the genus Prevotella. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 2637–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinberg, I.; Yin, G.; Borovok, I.; Berg Miller, M.E.; Yeoman, C.J.; Dassa, B.; Yu, Z.T.; Mizrahi, I.; Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; et al. Functional Phylotyping Approach for Assessing Intraspecific Diversity of Ruminococcus albus within the Rumen Microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huws, S.A.; Mayorga, O.L.; Theodorou, M.K.; Onime, L.A.; Kim, E.J.; Cookson, A.H.; Newbold, C.J.; Kingston-Smith, A.H. Successional Colonization of Perennial Ryegrass by Rumen Bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huws, S.A.; Edwards, J.E.; Creevey, C.J.; Rees Stevens, P.; Lin, W.; Girdwood, S.E.; Pachebat, J.A.; Kingston-Smith, A.H. Temporal Dynamics of the Metabolically Active Rumen Bacteria Colonizing Fresh Perennial Ryegrass. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiv137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.D.; Auffret, M.D.; Warr, A.; Wiser, A.H.; Press, M.O.; Langford, K.W.; Liachko, I.; Snelling, T.J.; Dewhurst, R.J.; Walker, A.W.; et al. Assembly of 913 Microbial Genomes from Metagenomic Sequencing of the Cow Rumen. Nat. Comm. 2018, 9, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chung, J.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Ren, N. Characteristics of Rumen Microorganisms Involved in Anaerobic Degradation of Cellulose at Various pH Values. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40303–40310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kaoutari, A.; Armougom, F.; Gordon, J.I.; Raoult, D.; Henrissat, B. The Abundance and Variety of Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in the Human Gut Microbiota. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, D.M.; Weimer, P.J. Dominance of Prevotella and Low Abundance of Classical Ruminal Bacterial Species in the Bovine Rumen Revealed by Relative Quantification Real-Time PCR. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynd, L.R.; Weimer, P.J.; van Zyl, W.H.; Pretorius, I.S. Microbial Cellulose Utilization: Fundamentals and Biotechnology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 506–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, E.A.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A.; Flint, H.J. From Cellulosomes to Cellulosomics. Chem. Rec. 2008, 8, 364–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Xin, H.; Zhang, Y. Metagenomic Analyses of Microbial and Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in the Rumen of Holstein Cows Fed Different Forage-to-Concentrate Ratios. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galand, P.E.; Pereira, O.; Hochart, C.; Auguet, J.C.; Debroas, D. A Strong Link Between Marine Microbial Community Composition and Function Challenges the Idea of Functional Redundancy. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2470–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

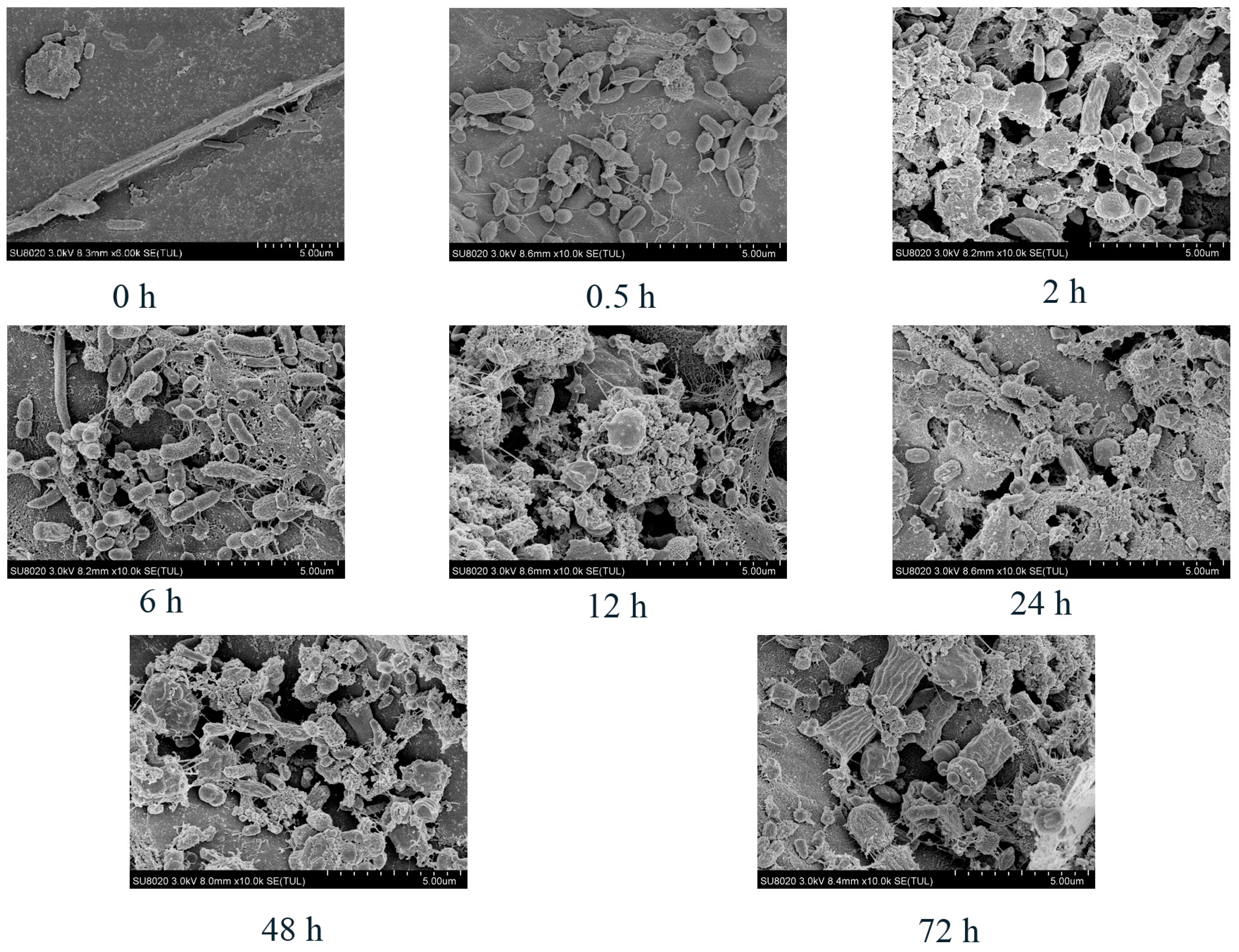

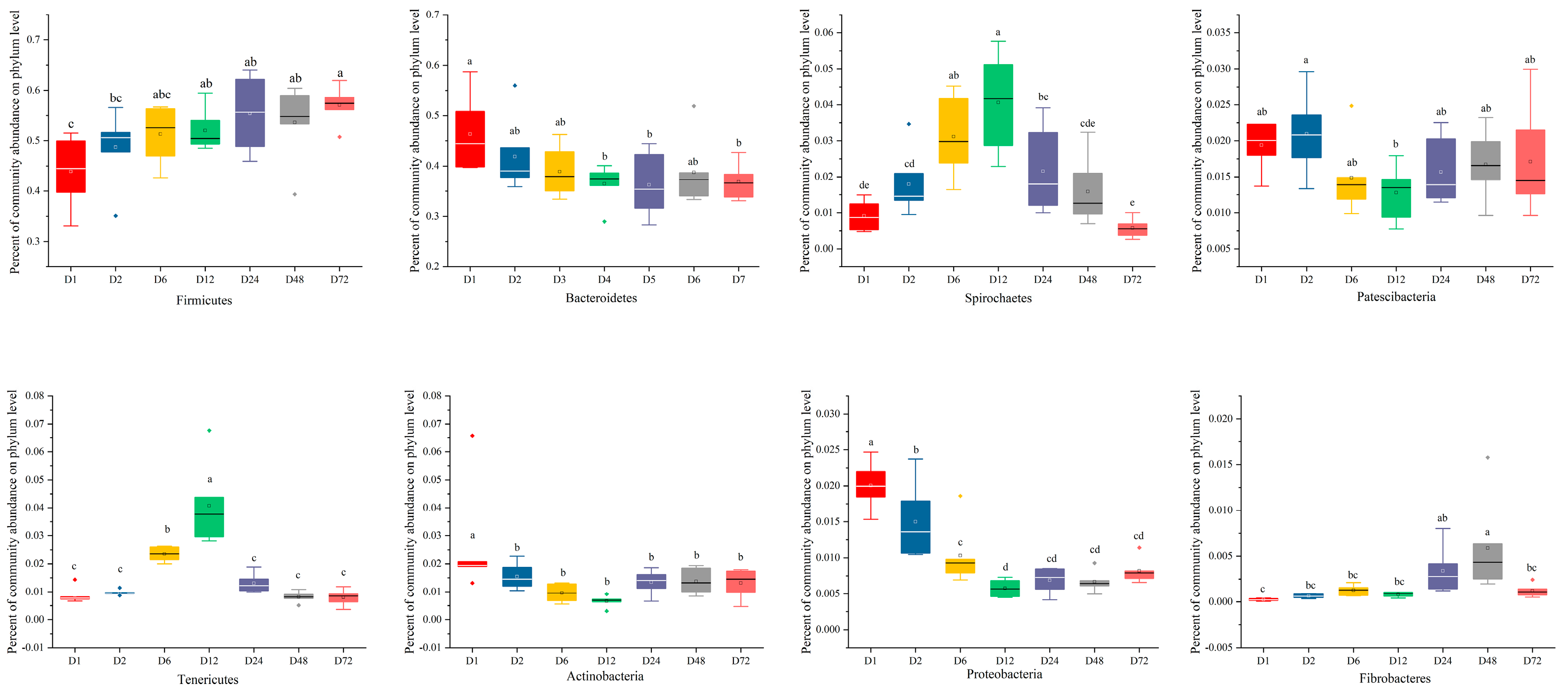


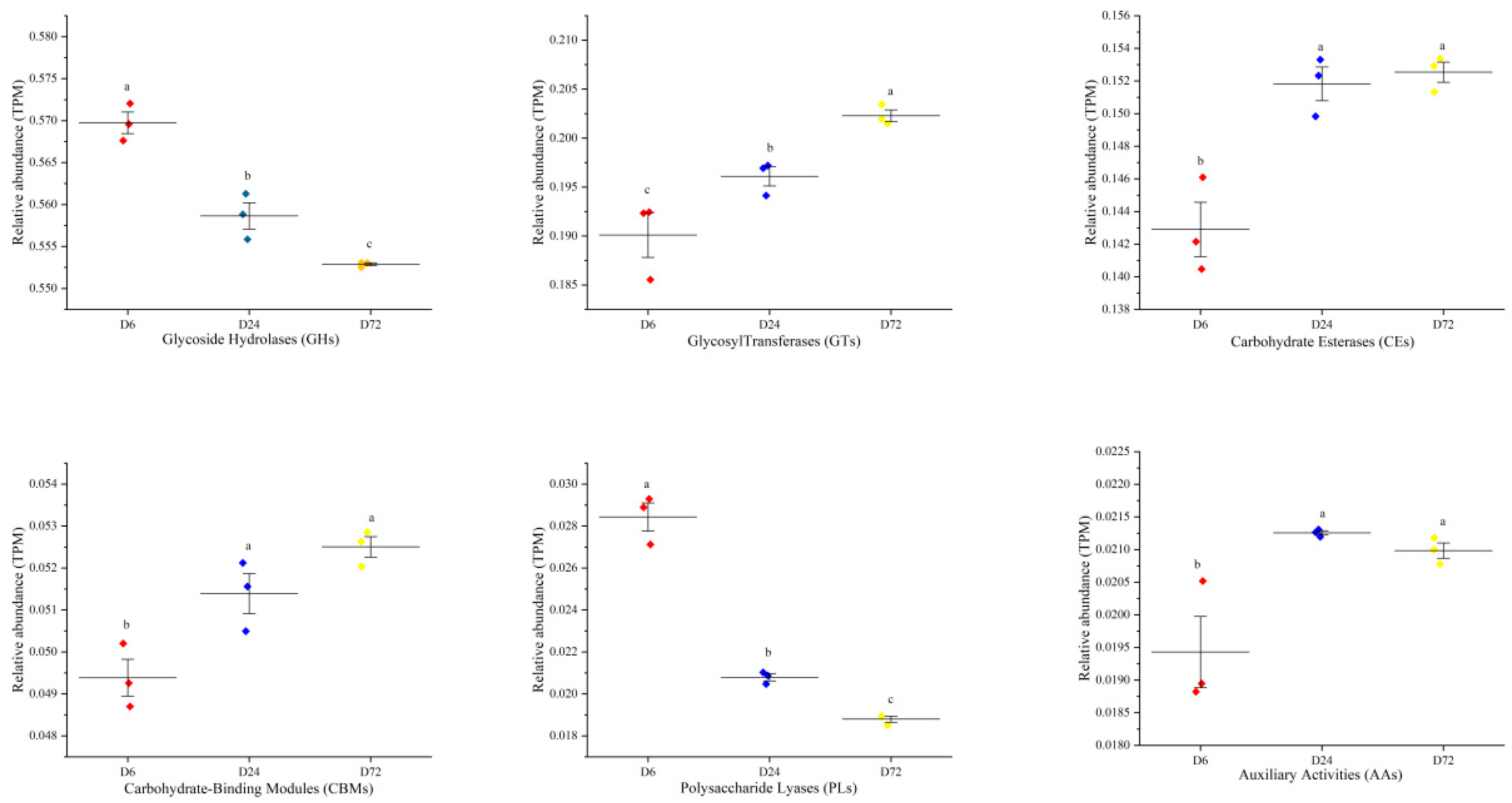
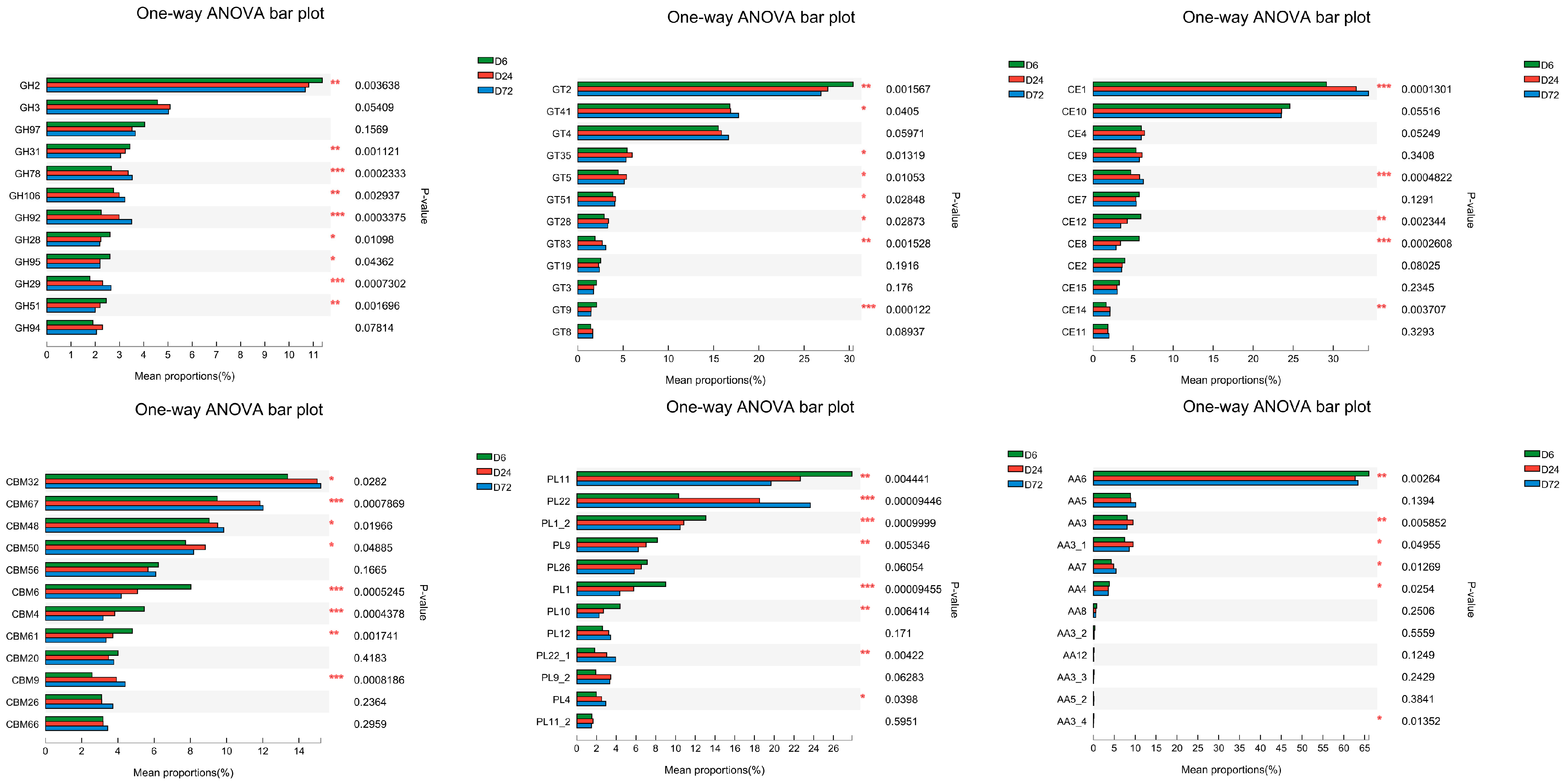

| Index | DM | NDF | ADF |
|---|---|---|---|
| rapid degradation fraction a (%) | 18.26 ± 0.96 | 2.33 ± 0.36 | 1.18 ± 0.15 |
| slow degradation fraction b (%) | 36.27 ± 1.81 | 32.51 ± 2.27 | 34.32 ± 2.07 |
| degradation rate constant of slow degradation fraction c (%/h) | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 |
| effective degradation rate ED (%) | 43.51 ± 1.16 | 22.90 ± 0.90 | 22.89 ± 0.79 |
| Alpha Diversity | 0.5 h | 2 h | 6 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h | SEM | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sobs | 1687 ab | 1713 a | 1658 bc | 1621 c | 1635 c | 1544 d | 1516 d | 23.27 | <0.001 |
| Shannon | 6.04 ab | 6.12 a | 6.04 ab | 5.91 c | 6.01 b | 5.76 d | 5.76 d | 0.047 | <0.001 |
| Simpson | 0.008 b | 0.008 b | 0.009 b | 0.012 a | 0.009 b | 0.013 a | 0.013 a | 0.001 | <0.001 |
| Ace | 2153 a | 2173 a | 2093 ab | 2042 bc | 2019 bcd | 1991 cd | 1935 d | 40.81 | <0.001 |
| Chao1 | 2170 ab | 2198 a | 2138 abc | 2087 bcd | 2059 cd | 1994 d | 1988 d | 48.80 | <0.001 |
| Coverage | 0.975 | 0.975 | 0.976 | 0.976 | 0.977 | 0.977 | 0.977 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teng, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Fu, T.; Wang, Q.; Gao, T. Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals New Ruminal Microbial Features Associated with Peanut Vine Efficiency in Dairy Cattle. Life 2024, 14, 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070802
Teng Z, Zhang N, Zhang L, Zhang L, Liu S, Fu T, Wang Q, Gao T. Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals New Ruminal Microbial Features Associated with Peanut Vine Efficiency in Dairy Cattle. Life. 2024; 14(7):802. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070802
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeng, Zhanwei, Ningning Zhang, Lijie Zhang, Liyang Zhang, Shenhe Liu, Tong Fu, Qinghua Wang, and Tengyun Gao. 2024. "Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals New Ruminal Microbial Features Associated with Peanut Vine Efficiency in Dairy Cattle" Life 14, no. 7: 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070802
APA StyleTeng, Z., Zhang, N., Zhang, L., Zhang, L., Liu, S., Fu, T., Wang, Q., & Gao, T. (2024). Integrated Multi-Omics Reveals New Ruminal Microbial Features Associated with Peanut Vine Efficiency in Dairy Cattle. Life, 14(7), 802. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14070802






