Digital Biometry as an Obesity Diagnosis Tool: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
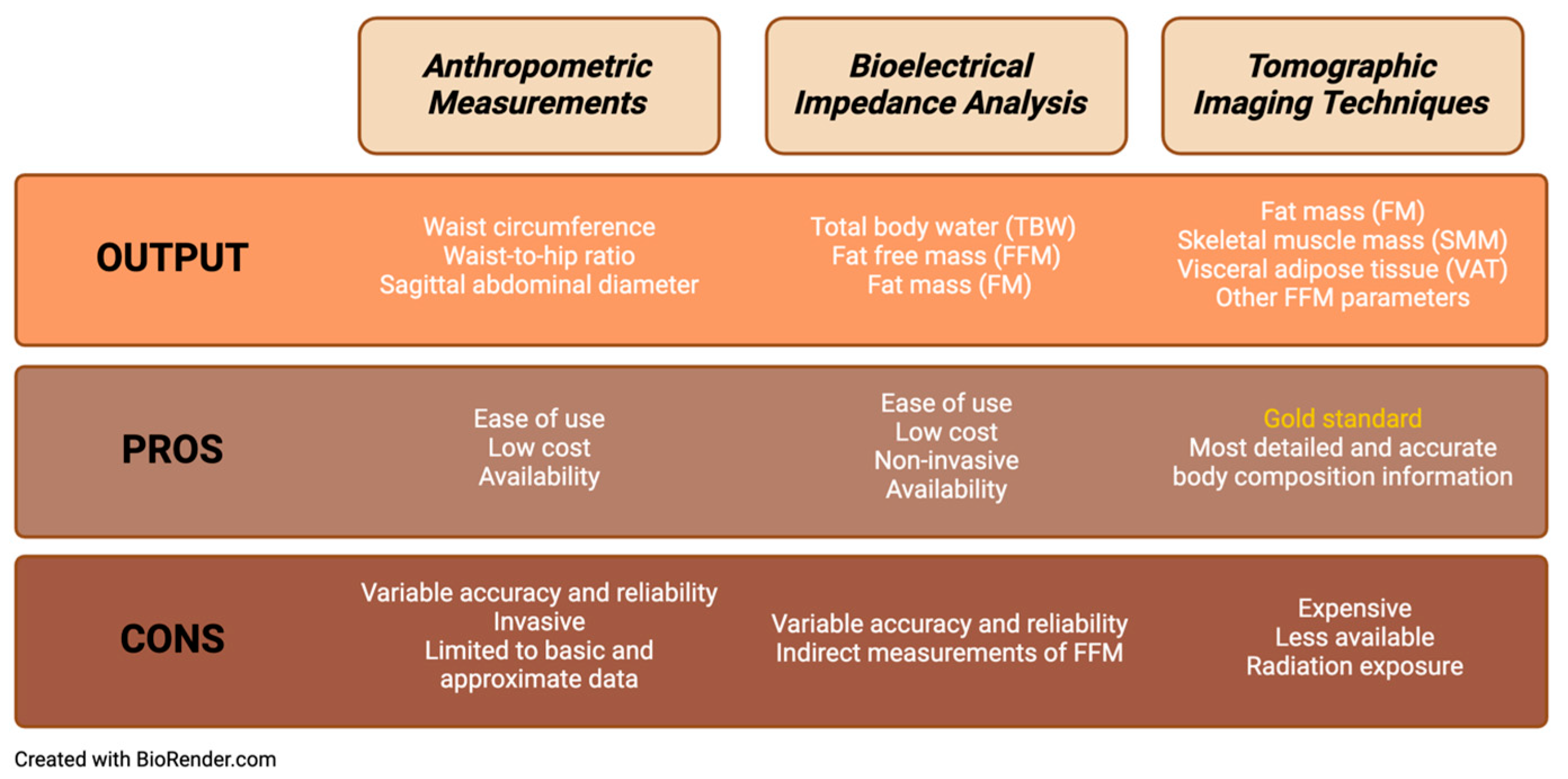
2. Indirect Estimation of Body Composition
2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
3. Gold-Standard Measurement of Body Composition
4. Objective
5. Methods
6. Results
6.1. 2D Body Scanners
6.2. 3D Body Scanners
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, G.A.; Kim, K.K.; Wilding, J.P.H.; World Obesity, F. Obesity: A chronic relapsing progressive disease process. A position statement of the World Obesity Federation. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas. 2024. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/WOF-Obesity-Atlas-v7.pdf (accessed on 28 March 2024).
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenchaiah, S.; Pocock, S.J.; Wang, D.; Finn, P.V.; Zornoff, L.A.; Skali, H.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Yusuf, S.; Swedberg, K.; Michelson, E.L.; et al. Body mass index and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure: Insights from the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of Reduction in Mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation 2007, 116, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oreopoulos, A.; Padwal, R.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Fonarow, G.C.; Norris, C.M.; McAlister, F.A. Body mass index and mortality in heart failure: A meta-analysis. Am. Heart J. 2008, 156, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.H.; Eagle, K.A.; Montgomery, D.G.; Kline-Rogers, E.; Hu, Y.C.; Aaronson, K.D. Relation of body mass index to mortality after development of heart failure due to acute coronary syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2009, 103, 1736–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, S.; Canada, J.M.; Billingsley, H.E.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Elagizi, A.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity paradox in cardiovascular disease: Where do we stand? Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Rhee, C.M.; Chou, J.; Ahmadi, S.F.; Park, J.; Chen, J.L.; Amin, A.N. The Obesity Paradox in Kidney Disease: How to Reconcile it with Obesity Management. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chittal, P.; Babu, A.S.; Lavie, C.J. Obesity paradox: Does fat alter outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease? COPD 2015, 12, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouda, H.; Ruiz-Castell, M.; Karimi, M.; Bocquet, V.; Kuemmerle, A.; Chioti, A.; Dadoun, F.; Stranges, S. Metabolically healthy and unhealthy weight statuses, health issues and related costs: Findings from the 2013–2015 European Health Examination Survey in Luxembourg. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardesch, F.H.; Ruiter, R.; Mulder, M.; Lahousse, L.; Stricker, B.H.C.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C. The Obesity Paradox in Lung Cancer: Associations With Body Size Versus Body Shape. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 591110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Busetto, L.; Bischoff, S.C.; Cederholm, T.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Batsis, J.A.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Dicker, D.; et al. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Sarcopenic Obesity: ESPEN and EASO Consensus Statement. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, C.M.M.; Wells, J.C.K.; Smith, S.R.; Stephan, B.C.M.; Siervo, M. Sarcopenic obesity: A Critical appraisal of the current evidence. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 583–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, C.S.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Pou, K.M.; Maurovich-Horvat, P.; Liu, C.Y.; Vasan, R.S.; Murabito, J.M.; Meigs, J.B.; Cupples, L.A.; et al. Abdominal visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments: Association with metabolic risk factors in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2007, 116, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Haring, H.U.; Hu, F.B.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolically healthy obesity: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2013, 1, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N. Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Normal Weight and Obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Q.; Ahsan, M. Measurement of Visceral Fat, Abdominal Circumference and Waist-hip Ratio to Predict Health Risk in Males and Females. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 22, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, M.; Turcato, E.; Armellini, F.; Kahn, H.S.; Zivelonghi, A.; Santana, H.; Bergamo-Andreis, I.A.; Bosello, O. Sagittal abdominal diameter as a practical predictor of visceral fat. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1998, 22, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouda, H.; Dutour, A.; Chaumoitre, K.; Panuel, M.; Dutour, O.; Dadoun, F. VAT=TAAT-SAAT: Innovative anthropometric model to predict visceral adipose tissue without resort to CT-Scan or DXA. Obesity 2013, 21, E41–E50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Wang, M.; Jiang, C.M.; Zhang, Y.M. Anthropometric equation for estimation of appendicular skeletal muscle mass in Chinese adults. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Sergi, G.; De Rui, M.; Stubbs, B.; Veronese, N.; Manzato, E. Measurement of lean body mass using bioelectrical impedance analysis: A consideration of the pros and cons. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Sammarco, R.; De Lorenzo, A.; Iellamo, F.; Siervo, M.; Pietrobelli, A.; Donini, L.M.; Santarpia, L.; Cataldi, M.; Pasanisi, F.; et al. Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Using Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) and Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA): A Critical Overview. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, E.L.; Fitzpatrick, J.A.; Malik, S.J.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Bell, J.D. Whole body fat: Content and distribution. Prog. Nucl. Magn. Reson. Spectrosc. 2013, 73, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, H.; Chowdhury, B.; Grangard, U.; Tylen, U.; Sjostrom, L. Total and visceral adipose-tissue volumes derived from measurements with computed tomography in adult men and women: Predictive equations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 48, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klopfenstein, B.J.; Kim, M.S.; Krisky, C.M.; Szumowski, J.; Rooney, W.D.; Purnell, J.Q. Comparison of 3 T MRI and CT for the measurement of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue in humans. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, e826–e830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouda, H. Commentary: Anthropometric Indicators as a Tool for Diagnosis of Obesity and Other Health Risk Factors: A Literature Review. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 750613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyan, R. Body composition techniques. Indian. J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Williams, H.C.; Dean, R.S. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisuzzaman, D.; Al Walid, M.H.; Saif, A.S. Online trial room based on human body shape detection. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2019, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foysal, K.H.; Chang, H.-J.; Bruess, F.; Chong, J.-W. Body size measurement using a smartphone. Electronics 2021, 10, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.W.; Holanda, G.B.; Ivo, R.F.; Alves, S.S.; da Silva, S.P.; Nunes, V.X.; Loureiro, L.L.; Dias-Silva, C.; Rebouças Filho, P.P. Predicting body measures from 2D images using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W.; Kwon, H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, W.S.; Lee, J.C.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, S.U.; Kwak, Y.H. “Weighing Cam”: A new mobile application for weight estimation in pediatric resuscitation. Prehospital Emerg. Care 2020, 24, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widyanti, A.; Ardiansyah, A.; Yassierli, I.H. Development of anthropometric measurement method for body circumferences using digital image. In Proceedings of the PPCOE, The Eighth Pan-Pacific Conference on Occupational Ergonomics, Bangkok, Thailand, 17–19 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Majmudar, M.D.; Chandra, S.; Yakkala, K.; Kennedy, S.; Agrawal, A.; Sippel, M.; Ramu, P.; Chaudhri, A.; Smith, B.; Criminisi, A.; et al. Smartphone camera based assessment of adiposity: A validation study. npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepper, M.R.; Freeland-Graves, J.H.; Yu, W.; Stanforth, P.R.; Cahill, J.M.; Mahometa, M.; Xu, B. Validation of a 3-Dimensional Laser Body Scanner for Assessment of Waist and Hip Circumference. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2010, 29, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, L.; Steinbrecher, A.; Pischon, T. Measurement of Waist and Hip Circumference with a Body Surface Scanner: Feasibility, Validity, Reliability, and Correlations with Markers of the Metabolic Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Inojosa, J.; Somers, V.K.; Ngwa, T.; Hinshaw, L.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Reliability of a 3D Body Scanner for Anthropometric Measurements of Central Obesity. Obes. Open Access 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, G.M.; Harty, P.S.; Siedler, M.R.; Stratton, M.T.; Rodriguez, C. Improved precision of 3-dimensional optical imaging for anthropometric measurement using non-rigid avatar reconstruction and parameterized body model fitting. Clin. Nutr. Open Sci. 2023, 50, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, B.K.; Hinton, B.J.; Fan, B.; Kanaya, A.M.; Shepherd, J.A. Clinical anthropometrics and body composition from 3D whole-body surface scans. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, B.; Ng, B.K.; Latimer, D.; Stannard, C.R.; Romeo, L.; Li, X.; Shepherd, J.A.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Bourgeois, B.; Ng, B.K.; et al. Clinically applicable optical imaging technology for body size and shape analysis: Comparison of systems differing in design. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouchey, J.D.; Tomkinson, G.R.; Rhoades, J.L.; Fitzgerald, J.S. Reliability of the Styku 3D whole-body scanner for the assessment of body size in athletes. Meas. Phys. Educ. Exerc. Sci. 2020, 24, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymsfield, S.B.; Bourgeois, B.; Ng, B.K.; Sommer, M.J.; Li, X.; Shepherd, J.A. Digital anthropometry: A critical review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.P.; Liu, Y.E.; Quon, B.K.; Kelly, N.N.; Wong, M.C.; Kennedy, S.F.; Chow, D.C.; Garber, A.K.; Weiss, E.J.; Heymsfield, S.B.; et al. Assessment of clinical measures of total and regional body composition from a commercial 3-dimensional optical body scanner. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harty, P.S.; Sieglinger, B.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Shepherd, J.A.; Bruner, D.; Stratton, M.T.; Tinsley, G.M. Novel body fat estimation using machine learning and 3-dimensional optical imaging. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, B.K.; Sommer, M.J.; Wong, M.C.; Pagano, I.; Nie, Y.; Fan, B.; Kennedy, S.; Bourgeois, B.; Kelly, N.; Liu, Y.E. Detailed 3-dimensional body shape features predict body composition, blood metabolites, and functional strength: The Shape Up! studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroh, A.; Peters, F.; Alizai, P.H.; Schmitz, S.; Hölzle, F.; Neumann, U.P.; Ulmer, F.T.; Modabber, A. 3D optical imaging as a new tool for the objective evaluation of body shape changes after bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2020, 30, 1866–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daanen, H.A.M.; Ter Haar, F.B. 3D whole body scanners revisited. Displays 2013, 34, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhofer, K.; Knopfli, C.; Achermann, B.; Lorenzetti, S.R. Feasibility of Using Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging Technology for Contactless 3D Body Scanning and Anthropometric Assessment of Athletes. Sports 2024, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmar, I.; Rizo, M.; Cortés-Castell, E. Adherence to an overweight and obesity treatment: How to motivate a patient? PeerJ 2014, 2, e495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbin, M.M.; Kasak, A.; Ostrem, J.D.; Dengel, D.R. Validation of a three-dimensional body scanner for body composition measures. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Sample No. (n) | Characteristics | Objective | Results | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anisuzzaman et al., 2019 [31] | 20 | Web-based application, called Online Trial Room, that measures body dimensions from 2D images for clothing size. | Compare automatic measurements generated by image processing techniques to anthropometry. | Root mean square error (RMSE): neck 0.808, shoulder 1.478, upper waist 4.454, lower waist 3.83, length 0.907 | Accurate predictions in 12 of 20 volunteers, but unable to accurately assess upper waist and lower waist measurements. |
| Foysal et al., 2021 [32] | 12 | Android-based application, entitled SmartFit Measurement, that measures waist, low hip and thigh circumferences from 2D images for accurate pant sizes. | Validate the application’s capability to correctly measure waist, low hip, and thigh circumferences compared to gold standard anthropometry. | Error range a with 95% CI: −0.72−0.34 inches, margin of error of 0.5346 in. 95.59% accuracy in measurements | No significant difference between application and manual measurements. |
| Souza et al, 2020 [33] | 38 | Computer-based program that uses digital image processing, CNNs and machine learning for body measurements. | Compare 2D image measurements obtained using CNNs and machine learning to skinfold measurements performed by a specialist. | Mean squared error (MSE) always below 4.606 ± 3.412 cm when using the Dense Human Pose Estimation and Expectation-Maximization (EM) approach | Overall accurate measurements that were similar to those obtained by specialists. |
| Park et al, 2020 [34] | 480 | Mobile app, The Weighing Cam, that estimates pediatric weight from 2D images. | Validate the accuracy of the application’s pediatric weight estimates compared to that of the Broselow tape. | Mean percent error (MPE) 0.99%, mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) 5.06%, and root mean square percentage error (RMSE) 11.32%. Compared to Broselow tape, the Weighing Cam had higher proportion of estimated weights within 10% of actual weights compared to Broselow tape (69.2% vs. 58.9%). | Estimates from imaging program were more accurate and precise than the Broselow tape. |
| Widyanti et al, 2007 [35] | 41 | Computer-based software generates body circumference measurements from digital images. | Compare digital measurements to manual measurement of 13 body parts. | Minimal differences between digital measurements and manual measurements with comparable TEM and reliability co-efficient. | Digital measurements of body circumferences are a valid and reliable alternative to manual measurements. |
| Majmudar, et al, 2022 [36] | 134 | Computer-based program, called Visual Body Composition (VBC), that uses 2D photos to estimate percentage total body fat (%BF) using a novel algorithm and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). | Evaluate the accuracy of VBC’s %BF estimates against BIA devices and ADP, with DXA as reference. | Mean absolute error (MAE) 2.16% ± 1.54%, MAPE 6.4%. Lowest MAE compared to all other devices (p < 0.05). Good concordance with DXA (CCC 0.96). | Most accurate and least biased method for estimating %BF compared to other devices. |
| Reference | Sample No. (n) | Characteristics | Objective | Results | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pepper et al., 2010 [37] | 70 | Portable 3-dimensional laser imaging device, called the Xu scanner, that measures body circumferences. | Compare the reliability and validity of a 3-dimensional laser body scanner to traditional anthropometry measurements with a tape measure. |
| The 3D laser yielded similar results to gold standard anthropometry and showed consistent measurements with minimal variations. |
| Jaeschke et al., 2015 [38] | 60 | Laser-based 3D body scanner device, VitussmartXXL, that creates a 3D image and calculates body measurements. | Evaluate the accuracy and reliability of waist and hip circumferences generated by the 3D body scanner compared to manual anthropometry. |
| WC and HC generated by the 3D body scanner were higher than manual anthropometry, but strongly correlated with anthropometry and were highly reliable. |
| Medina-Inojosa et al, 2016 [39] | 83 | Automated non-invasive 3D optical scanner entitled 3D Body Volume Index (BVI) scanning system, that produces body images and generates a maximum of 400 body measurements. | Assess reproducibility and reliability of anthropometric measures generated by 3D body scanner compared to anthropometry. |
| 3D body scanner showed lower variability in circumference measurements compared to manual measurements and were highly reliable. |
| Tinsley et al, 2023 [40] | 69 | Second-generation at-home 3D body scanner by Prism Labs, Inc. (Los Angeles, CA, USA) | Evaluate the precision of a 3D body scanner. |
| 3D body scanner showed precise and consistent measurements of WC and HC. |
| Ng et al, 2016 [41] | 39 | Commercially available 3D body scanner device, called Fit3D Proscanner (Fit3D, Redwood City, CA, USA), that generates a 360-degree body image and reports body circumferences. | Compare the accuracy of body circumference measurements generated by 3D scanner to manual anthropometry. |
| WC and HC generated by 3D scanner were strongly associated with those obtained using tape measurements, but there were significant mean differences between measurements. |
| Derouchey et al, 2020 [43] | 49 | Portable single stationary camera on a rotating platform, called the Styku S100, that generates 3D images and determines body circumference and composition measurements. | Assess the accuracy and test–retest reliability of the 3D scanner in determining body circumferences, surface areas, and volumes of athletes. |
| Styku S100 is a reliable tool to measure body circumference, surface areas, and volumes of athletes. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porterfield, F.; Shapoval, V.; Langlet, J.; Samouda, H.; Stanford, F.C. Digital Biometry as an Obesity Diagnosis Tool: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions. Life 2024, 14, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14080947
Porterfield F, Shapoval V, Langlet J, Samouda H, Stanford FC. Digital Biometry as an Obesity Diagnosis Tool: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions. Life. 2024; 14(8):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14080947
Chicago/Turabian StylePorterfield, Florence, Vladyslav Shapoval, Jérémie Langlet, Hanen Samouda, and Fatima Cody Stanford. 2024. "Digital Biometry as an Obesity Diagnosis Tool: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions" Life 14, no. 8: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14080947
APA StylePorterfield, F., Shapoval, V., Langlet, J., Samouda, H., & Stanford, F. C. (2024). Digital Biometry as an Obesity Diagnosis Tool: A Review of Current Applications and Future Directions. Life, 14(8), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14080947








