Fluoroquinolones for the Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Are They Losing Ground?
Abstract
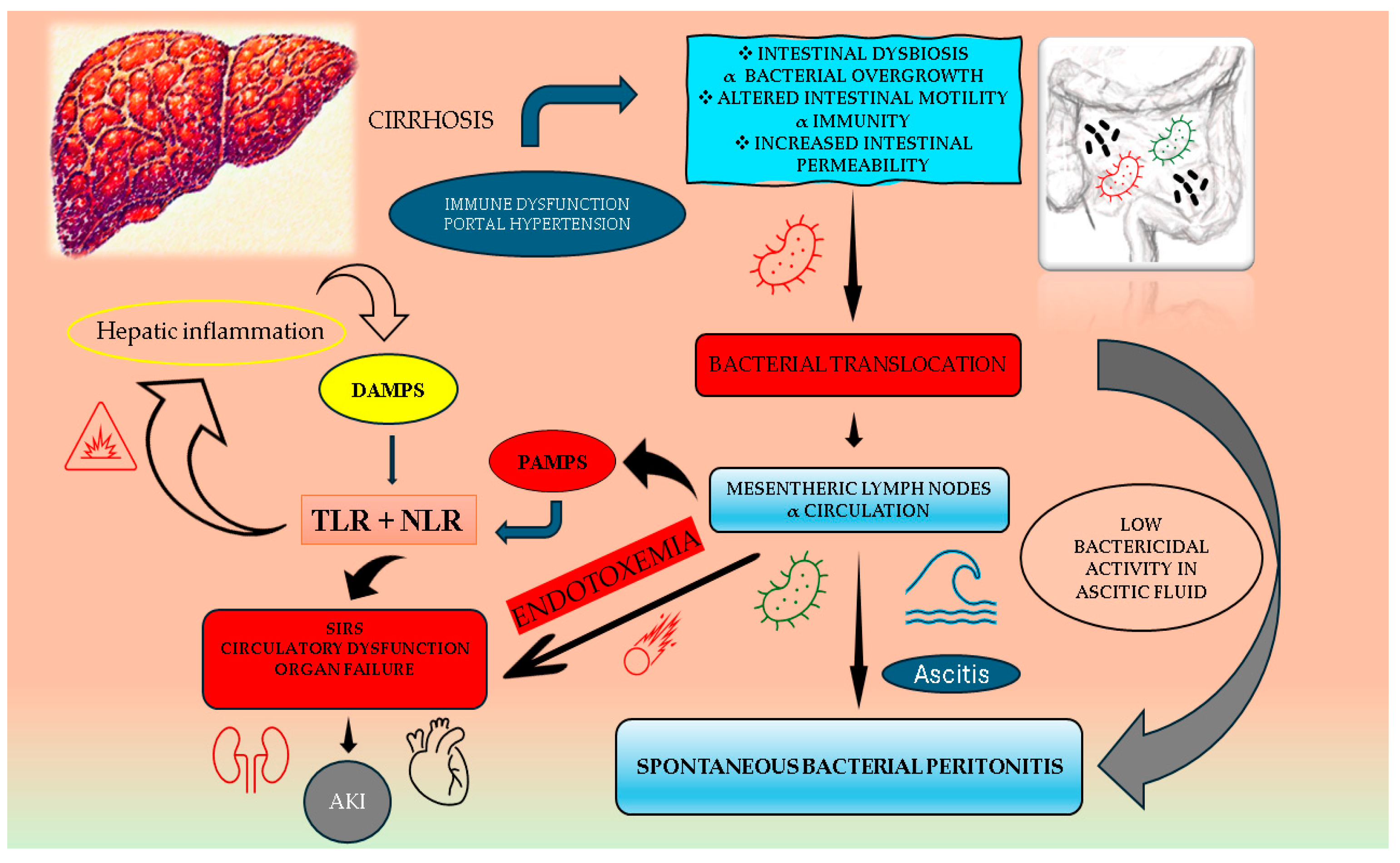
:1. Introduction
2. Multidrug-Resistant Organisms: A Rising Threat
3. The Etiological Spectrum of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: A Shift Toward Gram-Positive Organisms
4. Disease-Related Factors Impacting Standard SBP Prophylaxis
5. Adverse Events as Additional Limitations
6. Alternative Therapeutic Agents
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trebicka, J.; Fernandez, J.; Papp, M.; Caraceni, P.; Laleman, W.; Gambino, C.; Giovo, I.; Uschner, F.E.; Jansen, C.; Jimenez, C.; et al. PREDICT STUDY group of the EASL-CLIF CONSORTIUM. PREDICT identifies precipitating events associated with the clinical course of acutely decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpanyapong, S.; Reddy, K.R. Infections in Cirrhosis. Curr. Treat. Options Gastroenterol. 2019, 17, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tay, P.W.L.; Xiao, J.; Tan, D.J.H.; Ng, C.; Lye, Y.N.; Lim, W.H.; Teo, V.X.Y.; Heng, R.R.Y.; Yeow, M.W.X.; Lum, L.H.W.; et al. An Epidemiological Meta-Analysis on Worldwide Prevalence, Resistance, and Outcomes of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhosis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 693652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciano, S.; Diaz, J.M.; Dirchwolf, M.; Gadano, A. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis: Incidence, outcomes, and treatment strategies. Hepat. Med. 2019, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernández, J.; Piano, S.; Bartoletti, M.; Wey, E.Q. Management of bacterial and fungal infections in cirrhosis: The MDRO challenge. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S101–S117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimola, A.; García-Tsao, G.; Navasa, M.; Piddock, L.J.; Planas, R.; Bernard, B.; Inadomi, J.M. Diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A consensus document. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadi, M.H.; Khan, M.A.; Javeed, M.; Khan, A.; Nawaz, A. Frequency of Renal Impairment among Patients with Liver Cirrhosis with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. J. Pak. Soc. Intern. Med. 2024, 5, 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Devani, K.; Charilaou, P.; Jaiswal, P.; Patil, N.; Radadiya, D.; Patel, P.; Young, M.; Rockey, D.C.; Reddy, C.M. Trends in Hospitalization, Acute Kidney Injury, and Mortality in Patients with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2019, 53, e68–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, T.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Tseng, C.W.; Tsai, J.J. Effect of renal impairment on mortality of patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakani, A.J.; Awan, R.H.; Nayab, S.; Awan, K.H.; Awan, F.M. Renal impairment after Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis (SBP) in cirrhotic population. Prof. Med. J. 2019, 26, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, J.Y. Effect of acute kidney injury on long-term outcomes of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients using the International Club of Ascites-acute kidney injury criteria. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serper, M.; Tang, H.; Zhang, S.; McCullough, A.; Kaplan, D.E.; Taddei, T.H.; Mahmud, N. Clinical outcomes and care for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A national cohort study. Hepatology 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.; Kalman, R.; Mohan, N.; Hill, O.Y.; Moran, M.; Genkil, J.; Echikunwoke, B.B.; Balogun, O.; Bley, E.; Khan, A. S1341 Demographic Factors Associated With the Severity of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Retrospective Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, S1025–S1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sort, P.; Navasa, M.; Arroyo, V.; Aldeguer, X.; Planas, R.; Ruiz-del-Arbol, L.; Castells, L.; Vargas, V.; Soriano, G.; Guevara, M.; et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.; Kim, B.; Limketkai, B.N.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Woreta, T.; Chen, P.H. Mortality from Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Among Hospitalized Patients in the USA. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hassan, A.; Bhatti, R.; Hafeez, A.; Iqbal, J.; Jamali, L.; Sawai, S. Prediction of In-Hospital Mortality in Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Patients with Advanced Liver Disease. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2023, 17, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Kang, H.J.; Yu, S.Y.; Seo, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.O.; Lee, S.T.; Kim, I.H. Initial treatment response and short-term mortality of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hung, T.-H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C.; Lee, H.-F. Short and long-term mortality of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients. Medicine 2024, 103, pe40851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakareya, T.; El-Razek, A.; Mohamed, W.; Akl, R.M.; Abdallah, H.M.; El-Awady, A.A.; Abbasy, M.A. Clinical, biochemical and inflammatory predictors of mortality in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2022, 86, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, P.; Kumari, S.; Bai, R.; Nasir, A.; Ismail, H.; Majid, Z.; Tasneem, A.A.; Panezai, M.Q.; Ali, I.; Luck, N.H. Predictors of Mortality in Patients with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2024, 14, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mattos, A.; Wiltgen, D.; Jotz, R.; Dornelles, C.M.R.; Fernandes, M.V.; Mattos, Â.Z. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and extraperitoneal infections in patients with cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2020, 19, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaess, S.S.; Attridge, R.L.; Brady, R.L.; Attridge, R.T. Evaluation of prophylactic antibiotic regimens on recurrence and mortality in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, A.; Zuccaro, V.; Fagiuoli, S.; Bruno, R. Prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Is there still room for quinolones? J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1027–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; De, A.; Mehtani, R.; Angeli, P.; Maiwall, R.; Satapathy, S.; Singal, A.K.; Saraya, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Eapen, C.E.; et al. Asia–Pacific association for study of liver guidelines on management of ascites in liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 792–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggins, S.W.; Angeli, P.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Ginès, P.; Ling, S.C.; Nadim, M.K.; Wong, F.; Kim, W.R. Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of Ascites, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis and Hepatorenal Syndrome: 2021 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1014–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, P.; Bernardi, M.; Villanueva, C.; Francoz, C.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Trebicka, J.; Krag, A.; Laleman, W.; Gines, P. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 406–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, N.; Xie, N.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. Combination of PCT, sNFI and dCHC for the diagnosis of ascites infection in cirrhotic patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sandhu, S.; John, B.V. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: The Bug Matters. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 1667–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Amna, I.; Manesh, K.G.; Azizullah, B.; Dushyant, S.D.; Amir, H.S.; Wade, L.S.; Muhammad, A.; Mona, H. Nosocomial vs healthcare associated vs community acquired spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Network meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 366, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameer, M.A.; Foris, L.A.; Mandiga, P. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. [Updated 2023 Aug 8]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448208/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Millanao, A.R.; Mora, A.Y.; Villagra, N.A.; Bucarey, S.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Biological Effects of Quinolones: A Family of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, M.; Oliphan, D.; Gary, M.; Green, M.D. Quinolones: A comprehensive review. Am. Fam. Physician 2002, 65, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Onorato, L.; Monari, C.; Capuano, S.; Grimaldi, P.; Coppola, N. Prevalence and Therapeutic Management of Infections by Multi-Drug-Resistant Organisms (MDROs) in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücke, M.; Mayer, A.; Kessel, J.; Mücke, V.; Bon, D.; Schwarzkopf, K.; Rüschenbaum, S.; Queck, A.; Göttig, S.; Vermehren, A.; et al. Quinolone and Multidrug Resistance Predicts Failure of Antibiotic Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baggio, D.; Ananda-Rajah, M.R. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics and adverse events. Aust. Prescr. 2021, 44, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang, C.H.; Lee, C.H.; Chang, C. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis—A Literature Review. Livers 2022, 2, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badal, B.; Bryan, D.; Silvey, S.; Dragilev, L.; O’Leary, J.G.; Morgan, T.; Cheung, R.; Patel, A.; Rogal, S.; Patton, H.; et al. Primary prophylaxis for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is linked to antibiotic resistance in the Veterans Health Administration. Hepatology 2023, 77, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Branco, J.C.; Barosa, R.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Ramos, L.; Martins, A.; Karvellas, C.J.; Cardoso, F.S. Clinical and microbiological characteristics associated with mortality in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A multicenter cohort study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, J.C.; Carrera, E.; Petry, R.C.; Deutschendorf, C.; Mantovani, A.; Barcelos, S.T.A.; Cassales, S.; Schacher, F.C.; Lopes, A.B.; Alvares-da-Silva, M.R. High Prevalence of Multidrug Resistant Bacteria in Cirrhotic Patients with Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: Is It Time to Change the Standard Antimicrobial Approach? Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 6963910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheong, H.S.; Kang, C.I.; Lee, J.A.; Moon, S.Y.; Joung, M.K.; Chung, D.R.; Koh, K.C.; Lee, N.Y.; Song, J.H.; Peck, K.R. Clinical significance and outcome of nosocomial acquisition of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, M.; Maraolo, A.E.; Gentile, I.; Borgia, G.; Leone, S.; Sansone, P.; Passavanti, M.B.; Aurilio, C.; Pace, M.C. Current concepts and future strategies in the antimicrobial therapy of emerging Gram-positive spontaneous bacterial perconcepts. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernández, J.; Prado, V.; Trebicka, J.; Amoros, A.; Gustot, T.; Wiest, R. Multidrug-resistant bacterial infections in patients with decompensated cirrhosis and with acute-on-chronic liver failure in Europe. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferstl, P.G.; Müller, M.; Filmann, N.; Hogardt, M.; Kempf, V.A.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Lange, C.M.; Vermehren, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Reinheimer, C.; et al. Noninvasive screening identifies patients at risk for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis caused by multidrug-resistant organisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 2, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohammed, A.M.K.; Osman, K.T.; Cappuccio, J.M.; Spencer, C.; Satapathy, S.K. Nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis is associated with high mortality—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 17, 1333–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piano, S.; Singh, V.P.; Caraceni, R.; Maiwall, C.; Alessandria, J.; Fernandez, E. Epidemiology and effects of bacterial infections in patients with cirrhosis worldwide. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, A.; Vasilieva, L.; Agiasotelli, D.; Siranidi, K.; Pouriki, S.; Tsiriga, A.; Toutouza, M.; Dourakis, S.P. Extensively drug-resistant bacteria are an independent predictive factor of mortality in 130 patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis or spontaneous bacteremia. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bruno, C.; Eliabe, S.; Guilherme, G.L.; De Oliveira, G.; Rocha, J.P.; Cunha, J.; Normando, L.; Melo, L.; Menezes, L.C.; Costa, L.; et al. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients: Prevalence and antibiotic resistance patterns. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.V.; Lahanas, A.; Xanthaki, A.; Kontou-Kastellanou, C.; Archimandritis, A.J. Increasing frequency of Gram-positive bacteria in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Liver Int. 2005, 25, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, A.; Papadopoulos, N.; Eliopoulos, D.G.; Alexaki, A.; Tsiriga, A.; Toutouza, M.; Pectasides, D. Increasing frequency of gram-positive cocci and gram-negative multidrug-resistant bacteria in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Emerging Gram-positive bacteria and drug resistance in cirrhosis patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A retrospective study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 4568–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gou, M.; Yanzi, A. Pathogens change in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis patients with cirrhosis. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Reuken, P.A.; Pletz, M.W.; Baier, M.; Pfister, W.; Stallmach, A.; Bruns, T. Emergence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis due to enterococci—Risk factors and outcome in a 12-year retrospective study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campillo, B.; Richardet, J.P.; Kheo, T.; Dupeyron, C. Nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and bacteremia in cirrhotic patients: Impact of isolate type on prognosis and characteristics of infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piroth, L.; Pechinot, A.; Di Martino, V.; Hansmann, Y.; Putot, A.; Patry, I.; Hadou, T.; Jaulhac, B.; Chirouze, C.; Rabaud, C. Evolving epidemiology, and antimicrobial resistance in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A two-year observational study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, Y.; Hassan, N.A.; Khalaf, S.A.; Esmat, M.A.; Askar, A.A.; Mahmoud, E.A. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Management and identification of commonest bacterial species. Microbes Infect. Dis. 2024, 5, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, P.; Delisle, A.; Topal, J.E.; Garcia-Tsao, G. High prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections among patients with cirrhosis at a US liver center. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Reginato, T.J.; Oliveira, M.J.; Moreira, L.C.; Lamanna, A.; Acencio, M.M.; Antonangelo, L. Characteristics of ascitic fluid from patients with suspected spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in emergency units at a tertiary hospital. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2011, 129, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elshamy, R.M.; Oda, M.S.; Saeed, M.A.; Ramadan, R.A. A comparative study on nosocomial and community-acquired spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis at a university hospital. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, R.; Leitão, J.; Santos, J.; Carvalho, A.; Fernando, P. Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhotic Patients: A Shift in the Microbial Pattern? A Retrospective Analysis. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 29, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ratnasekera, I.U.; Johnson, A.; Powell, E.E.; Henderson, A.; Irvine, K.M.; Valery, P.C. Epidemiology of ascites fluid infections in patients with cirrhosis in Queensland, Australia from 2008 to 2017: A population-based study. Medicine 2022, 101, e29217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Novovic, S.; Semb, S.; Olsen, H.; Moser, C.; Knudsen, J.D.; Homann, C. First-line treatment with cephalosporins in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis provides poor antibiotic coverage. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umgelter, A.; Reindl, W.; Miedaner, M.; Schmid, R.M.; Huber, W. Failure of current antibiotic first-line regimens and mortality in hospitalized patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Infection 2009, 37, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, J.; Navasa, M.; Gómez, J.; Colmenero, J.; Vila, J.; Arroyo, V.; Rodés, J. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: Epidemiological changes with invasive procedures and norfloxacin prophylaxis. Hepatology 2002, 35, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghamdi, H.; Al-Harbi, N.; Mokhtar, H.; Daffallah, M.; Memon, Y.; Aljumah, A.A.; Sanai, F.M. Changes in the patterns and microbiology of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Analysis of 200 cirrhotic patients. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2019, 82, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lutz, P.; Nischalke, H.D.; Krämer, B.; Goeser, F.; Kaczmarek, D.J.; Schlabe, S.; Parcina, M.; Nattermann, J.; Hoerauf, A.; Strassburg, C.P.; et al. Antibiotic resistance in healthcare-related and nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 47, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrich, K.; Nüssle, S.; Rehlen, T.; Stremmel, W.; Mischnik, A.; Eisenbach, C. Microbiology and resistance in first episodes of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: Implications for management and prognosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, P.R.L.; Leão, G.S.; Gonçalves, C.D.G.; Picon, R.V.; Tovo, C.V. Impact of microbiological changes on spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in three different periods over 17 years. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2018, 55, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, M.; Hazırolan, G. Rapid Bacterial Identification from Positive Blood Cultures by MALDI-TOF MS Following Short-Term Incubation on Solid Media. Infect. Dis. Clin. Microbiol. 2024, 6, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Kjellerup, B.V.; Xu, Z. Viable but nonculturable (VBNC) state, an underestimated and controversial microbial survival strategy. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.T.; Sun, L.C.; Jia, H.B.; Gao, W.; Yang, J.P.; Zhang, G.Q. Procalcitonin levels in bloodstream infections caused by different sources and species of bacteria. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 35, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepard, B.D.; Gilmore, M.S. Antibiotic-resistant enterococci: The mechanisms and dynamics of drug introduction and resistance. Microbes Infect. 2002, 4, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shizuma, T. Spontaneous bacterial and fungal peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis: A literature review. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bucsics, T.; Schwabl, P.; Mandorfer, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Prognosis of cirrhotic patients with fungi ascites and spontaneous fungal peritonitis (SFP). J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravito-Soares, M.; Gravito-Soares, E.; Lopes, S.; Ribeiro, G.; Figueiredo, P. Spontaneous fungal peritonitis: A rare but severe complication of liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, E.A.; Abd El-Rehim, A.S.; Hassany, S.M.; Ahmed, A.O.; Elsherbiny, N.M.; Mohammed, M.H. Fungal infection in patients with end-stage liver disease: Low frequency or low index of suspicion. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 23, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, R.; Elkrief, L.; Bureau, C.; Perarnau, J.M.; Thévenot, T.; Saliba, F.; Louvet, A.; Nahon, P.; Lannes, A.; Anty, R.; et al. Effects of Long-term Norfloxacin Therapy in Patients with Advanced Cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1816–1827.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mücke, M.M.; Mücke, V.T.; Graf, C.; Schwarzkopf, K.M.; Ferstl, P.G.; Fernandez, J.; Zeuzem, S.; Trebicka, J.; Lange, C.M.; Herrmann, E. Efficacy of Norfloxacin Prophylaxis to Prevent Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Fernández, J.; Tandon, P.; Mensa, J.; Garcia-Tsao, G. Antibiotic prophylaxis in cirrhosis: Good and bad. Hepatology 2016, 63, 2019–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komolafe, O.; Roberts, D.; Freeman, S.C.; Wilson, P.; Sutton, A.J.; Cooper, N.J.; Pavlov, C.S.; Milne, E.J.; Hawkins, N.; Cowlin, M.; et al. Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in people with liver cirrhosis: A network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 1, CD013125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Titó, L.; Rimola, A.; Ginès, P. Recurrence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis: Frequency and predictive factors. Hepatology 1988, 8, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, S.; Ahmed, S.; Memon, A. Factors predicting the recurrence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2011, 21, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Sheen, I.S. Recurrence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients non-prophylactically treated with norfloxacin: Serum albumin as an easy but reliable predictive factor. Liver Int. 2011, 31, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, K.; Kaur, J.; Mazal, H.L. To Study the Incidence, Predictive Factors and Clinical Outcome of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients of Cirrhosis with Ascites. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, OC09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bender, M.H.; Hartmann, L.; Nemüller, J.R.; Schepp, W.; Gundling, F. Calprotectin as Diagnostic Marker for Hepatic Encephalopathy and Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Cirrhosis. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josifovikj, F.L.; Stardelova, K.G.; Todorovska, B.; Dimitrova, M.G.; Joksimovikj, N.; Andreevski, V.; Trajkovska, M.; Serafimovski, V. Diagnostic potential of calprotectin for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites. Pril. 2021, 42, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbeit, W.; Maamoun, B.; Azzam, S.; Shahin, A.; Carmiel-Haggai, M.; Khoury, T. Ascites fluid calprotectin level is highly accurate in diagnosing spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A preliminary proof of concept prospective study. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mohamed, A.S.; Yousef, L.M.; Khodeary, A.; Salem, A.N. Ascitic Fluid Calprotectin as an Accurate Diagnostic Marker for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Sohag Med. J. 2024, 28, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- DTB select. MHRA issues further update on fluoroquinolone safety. Drug Ther. Bull. 2024, 62, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuula, L.S.M.; Viljema, K.M.; Backman, J.T.; Bolm, M. Fluoroquinolone-related adverse events resulting in health service use and costs: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Munteanu, A.-C.; Arbănași, E.-M.; Uivarosi, V. Overview of Side-Effects of Antibacterial Fluoroquinolones: New Drugs versus Old Drugs, a Step Forward in the Safety Profile? Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, J.M.; Mamdani, M.M.; Manno, M.; Juurlink, D.N. Fluoroquinolone Therapy and Idiosyncratic Acute Liver Injury: A Population-Based Study. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Taher, M.K.; Alami, A.; Gravel, C.A.; Tsui, D.; Bjerre, L.M.; Momoli, F.; Mattison, D.R.; Krewski, D. Systemic Quinolones and Risk of Acute Liver Failure I: Analysis of Data from the US FDA Adverse Event Reporting System. JGH Open 2021, 5, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Freeman, M.Z.; Cannizzaro, D.N.; Naughton, L.F.; Bove, C. Fluoroquinolones-Associated Disability: It Is Not All in Your Head. NeuroSci 2021, 2, 235–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althaqafi, A.; Ali, M.; Alzahrani, Y.; Ming, L.C.; Hussain, Z. How Safe are Fluoroquinolones for Diabetic Patients? A Systematic Review of Dysglycemic and Neuropathic Effects of Fluoroquinolones. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2021, 17, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, C.; Peng, S.; Lin, A.; Jiang, A.; Peng, Y.; Gu, T.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, P. Psychiatric disorders associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. EClinicalMedicine 2023, 59, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, B.; Thalody, A.A.; Miraj, S.S.; Kunhikatta, V.; Rao, M.; Saravu, K. Adverse Effects of Fluoroquinolones: A Retrospective Cohort Study in a South Indian Tertiary Healthcare Facility. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.M.; Li, L.; Monk, I.R.; Lee, J.Y.H.; Ingle, D.J.; Portelli, S.; Sherry, N.L.; Isles, N.; Seemann, T.; Sharkey, L.K.; et al. Rifaximin prophylaxis causes resistance to the last-resort antibiotic daptomycin. Nature 2024, 635, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Minato, Y.; Dawadi, S.; Kordus, S.L.; Sivanandam, A.; Aldrich, C.C.; Baughn, A.D. Mutual potentiation drives synergy between trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lontos, S.; Shelton, E.; Angus, P.W.; Vaughan, R.; Roberts, S.K.; Gordon, A.; Gow, P.J. A randomized controlled study of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole versus norfloxacin for the prevention of infection in cirrhotic patients. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lontos, S.; Gow, P.J.; Vaughan, R.B.; Angus, P.W. Norfloxacin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole therapy have similar efficacy in prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, N.; Yamada, A.; Haider, H.; Komaki, Y.; Komaki, F.; Micic, D.; Sakuraba, A. Systemic review and network meta-analysis: Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alhilly, A.; Hussain Gburi, A.A.; Alyouzbaki, A.Z. Microorganisms and antibiotic sensitivity/resistance patterns in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Rawal Med. J. 2023, 48, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaylyn, C.; Audis, B.; Schadler, A.; Kelley, J.L. Outcomes in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis utilizing first-line or alternative agents for secondary prophylaxis. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2023, 80, S123–S129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Solà, E.; Alessandria, C.; de Wit, K.; Trebicka, J.; Angeli, P.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Durand, F.; Pose, E.; et al. The Use of Rifaximin in Patients With Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, S. Efficacy and safety of rifaximin in the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Hepatol. 2021, 37, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, Y.; Geng, C.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, X. Norfloxacin versus alternative antibiotics for prophylaxis of spontaneous bacteria peritonitis in cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Elfert, A.; Abo, A.L.; Soliman, S.; Ibrahim, S.; Abd-Elsalam, S. Randomized-controlled trial of rifaximin versus norfloxacin for secondary prophylaxis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 1450–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.; Shamseya, M.A. Rifaximin: A reasonable alternative for norfloxacin in the prevention of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with HCV-related liver cirrhosis. Alex. J. Med. 2015, 52, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, D.L.; Premkumar, M.; Roy, A.; Verma, N.; Taneja, S.; Duseja, A.; Dhiman, R.K. Rifaximin Vs. Norfloxacin for Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Prophylaxis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Menshawy, A.; Mattar, O.; Barssoum, K.; AboEl-Naga, M.A.; Mohamed, H.; Mesbah, A.; Elegbaly, A.; Elsalam, S.A. Safety and Efficacy of Rifaximin in Prophylaxis of Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: A systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, S.; Ranah, T.H.; Lim, S.; Heaton, N.; Heneghan, M.; Aluvihare, V.; Patel, V.C.; Shawcross, D.L. Rifaximin reduces the incidence of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, variceal bleeding, and all-cause admissions in patients on the liver transplant waiting list. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Francés, R.; Zapater, P.; González-Navajas, J.M.; Muñoz, C.; Caño, R.; Moreu, R.; Pascual, S.; Bellot, P.; Pérez-Mateo, M.; Such, J. Bacterial DNA in patients with cirrhosis and noninfected ascites mimics the soluble immune response established in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology 2008, 47, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study, Year | Number of Patients with SBP | Incidence of AKI |
|---|---|---|
| Hadi et al. [7], 2024 | 212 | 45.7% |
| Devani et al. [8], 2019 | 115 | 46.7% |
| Hung et al. [9], 2012 | 2592 | 5.6% |
| Wakani et al. [10], 2019 | 147 | 27.2% |
| Sohn et al. [11], 2020 | 157 | 42% |
| Devani et al. [8], 2019 | 115,359 | 46.7% |
| Serper et al. [12], 2025 | 4330 | 65.1% |
| Shah et al. [13], 2023 | 168 | 50% |
| Study, Year | Number of Patients with SBP (n) | Mortality Rate %, Timeframe |
|---|---|---|
| Sort et al. [14], 1999 | 126 | 43%, in-hospital |
| Niu et al. [15], 2018 | 88,167 | 17.6%, in-hospital |
| Devani et al. [8], 2019 | 115,359 | 16.1%, in-hospital |
| Serper et al. [12], 2025 | 4330 | 15.5%, in-hospital |
| Hassan et al. [16], 2023 | 223 | 27.4%, in-hospital |
| Lee et al. [17], 2023 | 245 | 17.1%, in-hospital 36.3%, 30 days |
| Hung et al. [18], 2024 | 925 | 10.8%, 30 days |
| Zakareya et al. [19], 2022 | 200 | 20%, 30 days |
| Ramesh et al. [20], 2024 | 142 | 67%, 30 days |
| Clinical Setting | Antibiotic | Dosage | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cirrhosis and acute gastrointestinal bleeding | Ceftriaxone | 1 g intravenous daily | 5–7 days |
| Norfloxacin | 400 mg per os twice daily | ||
| Primary prophylaxis: cirrhosis, low (<1.5 g/dL) total protein in ascitic fluid, advanced liver disease or renal dysfunction | Norfloxacin | 400 mg per os daily | Indefinite if ascites is present |
| Ciprofloxacin | 500 mg per os daily | ||
| Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim | One double strength tablet per os daily | ||
| Secondary prophylaxis: previous history of SBP | Norfloxacin | 400 mg per os daily | Indefinite if ascites is present |
| Ciprofloxacin | 500 mg per os daily | ||
| Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim | One double strength tablet per os daily |
| High-Risk Patient Categories | Clinical Context and Additional Risk Factors | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with cirrhosis and acute gastrointestinal bleeding | Acute setting requiring hospitalization Increased risk of bacteremia and other infections beyond SBP | Ceftriaxone (1 g/24 h) for up to 7 days if decompensated cirrhosis, already on FQ, or if high local prevalence of FQ-resistance Oral norfloxacin (400 mg b.i.d.) for the rest |
| Patients with cirrhosis and low (<1.5 g/dL) total protein in ascitic fluid (primary prophylaxis) | Additional risk factors: renal dysfunction, advanced liver failure (Child–Pugh class C) Risk factors for MDR organisms: prior hospitalization, recent invasive procedures, previous antibiotic exposure, local high prevalence of MDR organisms | Standard oral norfloxacin (400 mg daily) Consider TMP–SMX or rotating antibiotic strategies if additional risk factors Perform rectal swab screening: if MDR colonization, individualized prophylaxis based on susceptibility patterns |
| Patients with previous history of SBP (secondary prophylaxis) | Additional risk factors for recurrence: bilirubin levels > 1 mg/dL, age > 55 years, history of urinary tract infection, serum albumin levels < 28.5 g/dL Risk factors for MDR organisms: prior hospitalization, recent invasive procedures, previous antibiotic exposure, local high prevalence of MDR organisms | Prior SBP caused by non-MDR organisms: standard oral norfloxacin (400 mg daily) Prior SBP caused by MDR organisms: guided prophylaxis based on isolates’ susceptibility Consider rifaximin (550 mg twice daily) as an alternative, particularly if concurrent hepatic encephalopathy Assessment for liver transplantation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juncu, S.; Minea, H.; Lungu, A.; Jucan, A.; Avram, R.; Buzuleac, A.-M.; Cojocariu, C.; Diaconu, L.S.; Stanciu, C.; Trifan, A.; et al. Fluoroquinolones for the Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Are They Losing Ground? Life 2025, 15, 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040586
Juncu S, Minea H, Lungu A, Jucan A, Avram R, Buzuleac A-M, Cojocariu C, Diaconu LS, Stanciu C, Trifan A, et al. Fluoroquinolones for the Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Are They Losing Ground? Life. 2025; 15(4):586. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040586
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuncu, Simona, Horia Minea, Andreea Lungu, Alina Jucan, Raluca Avram, Ana-Maria Buzuleac, Camelia Cojocariu, Laura Sorina Diaconu, Carol Stanciu, Anca Trifan, and et al. 2025. "Fluoroquinolones for the Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Are They Losing Ground?" Life 15, no. 4: 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040586
APA StyleJuncu, S., Minea, H., Lungu, A., Jucan, A., Avram, R., Buzuleac, A.-M., Cojocariu, C., Diaconu, L. S., Stanciu, C., Trifan, A., & Sîngeap, A.-M. (2025). Fluoroquinolones for the Prophylaxis of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis: Are They Losing Ground? Life, 15(4), 586. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040586







