Abstract
The majority of myxosporean species (Cnidaria: Myxozoa) of the genera Myxobolus (35 species), Henneguya (8 species), and Myxidium (9 species) from freshwater or brackish fish in Japan were recorded more than 30 years ago (accumulatively 81.1% [43/53]). The re-discovery and molecular–genetic characterization of these species is a current research priority. During our myxosporean survey in Japanese freshwater fish, we detected three species that had never been recorded in Japan, but in the Russian Far East (Sakhalin Island, and Maritime Province): Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n., forming cysts in the gills of Tribolodon sachalinensis (syn. M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000; M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015, recorded from the gills of Pseudaspius (syn. Tribolodon) spp.); Henneguya pungitii Achmerov, 1953, forming cysts in the subcutis of external skin and buccal submucosa of Pungitius sinensis; and Myxidium salvelini Konovalov et Shulman, 1966, in the urinary bladder of Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae. These new isolates were characterized by integrated taxonomic approaches, i.e., myxospore morphology and molecular–genetic characterization of the small subunit ribosomal RNA gene (SSU rDNA). These new isolates were phylogenetically differentiated from any species whose SSU rDNA sequences were deposited in the DNA databases, and concurrently compared with recorded species based on classical morphological criteria. All three species were differentiated from myxosporeans previously recorded in Japan, indicating new distribution records out of the Russian Far East. For reliable species identification, accumulation of at least SSU rDNA sequences of known species worldwide is critically important.
1. Introduction
Endoparasitic cnidarians of the subclass Myxosporea Bütschli, 1881 (phylum Cnidaria Hatschek, 1888: class Myxozoa Grassé, 1970), take invertebrate (annelids) and vertebrate hosts (mainly fish) alternatively in their life cycles in aquatic environment [1]. They are often incriminated as causatives of a variety of symptomatic or moribund diseases of farmed fish, causing significant economic damage to the aquaculture and fishery industries [2,3,4]. Except for such symptomatic cases, myxosporean infection is generally latent, with patchy spatial distribution, and geographical knowledge of myxozoans can be biased, reflecting predilections of investigators. There are few incentives to investigations on parasites of fishes, as they have little commercial value [5]. Nevertheless, more than 2600 myxozoan species have been described, and extensive uncharted biodiversity of myxozoans remains to be investigated [5,6,7].
Two orders—Bivalvulida Shulman, 1959, and Multivalvulida Shulman, 1959—are divided in the subclass Myxosporea based on the numbers of shell valves (SVs) and polar capsules (PCs) in a myxospore [6,8]. Members of Bivalvulida are characterized by two SVs and two PCs in a myxospore (exceptionally, four PCs in a myxospores with two SVs in the genus Chloromyxum Mingazzini, 1890), and currently, 57 genera are classified in Bivalvulida [6,8]. The most speciose genus, Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882, contains more than 970 nominal species [8,9,10,11]. The genera Ceratomyxa Thélohan, 1892; Myxidium Bütschli, 1882; Henneguya Thélohan, 1892; Chloromyxym; and Thelohanellus Kudo, 1933 are also speciose, counting more than 270, 230, 210, 140, and 100 species, respectively [6,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Approximately sixty myxosporean species of the Bivalvulida have been recorded from freshwater and brackish fish in Japan, but most of them were recorded more than 30 years ago when specific descriptions were made solely based on myxospore morphology. For example, among nominal species of the genera Myxobolus (35 species), Henneguya (9 species), and Myxidium (9 species), 49.1% (26/53) were recorded more than 90 years ago and 81.1% (43/53) more than 30 years ago, as shown in Supplementary Table S1. Furthermore, the majority of these species have never been re-isolated or re-characterized with modern taxonomic viewpoints, i.e., specific characterization based on myxospore morphology and nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA), as has been recommended recently [21]. To date, only 37.7% (20/53) of species of the aforementioned three genera in Japan have been characterized using molecular–genetic techniques (Supplementary Table S1).
To address the taxonomic issues mentioned above, we are conducting a survey of myxosporean infection in freshwater fish in Japan. In the present study, we characterize three myxosporean species of the genera Myxobolus, Henneguya, and Myxidium and compare them with previously recorded species from Japan and other regions, particularly in the Russian Far East and China, where multiple myxosporean species recorded in freshwater and brackish fishes are shared with Japan [22,23,24].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Samples
The World Fresh Water Aquarium Gifu (Aquatotto Gifu) in Kakamigahara City, Gifu Prefecture, Japan, which exhibits approximately 28,500 freshwater fish of 260 species worldwide, regularly collects native Japanese fish species for exhibition. After careful acclimatization in aquarium water, these introduced fish are transferred to exhibition tanks. Surveillance checks for dead fish are carried out daily and the dead specimens are subsequently frozen and provided to us, as described previously [25]. For this study, the bodies of 92 dead fish of 34 species (13 families) were examined between 10 October 2017 and 22 September 2018 (Supplementary Table S2).
2.2. Parasitological Examination
The frozen fish bodies were thawed, and the body weights and total and standard body lengths were recorded. The external and internal organs were then individually examined with the naked eye and under a dissection microscope. To detect myxosporeans microscopically, the contents of the luminal organs, such as the gallbladder, urinary bladder, and gastrointestinal tract, were smeared on glass slides and treated with Diff-Quik™ stain (Sysmex Co., Kobe, Japan).
Myxosporean cysts found in the gills and subcutis/submucosa were opened using fine forceps in physiological saline. Similarly, the contents of the urinary bladder containing myxospores were diluted with physiological saline. These were then observed using a light microscope (OLYMPUS BX60; OLYMPUS Co., Hachioji, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with differential interference contrast optics, photographed at a magnification of ×800, then transformed into digital images using Adobe® Photoshop® ver. 11.0 (Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA, USA). The photographs were then printed at a high magnification. Measurements were conducted on multiple printed photographs following the guidelines of Lom and Arthur [26]. All measurements are expressed in micrometers (µm) unless otherwise stated. Ranges with the means in parentheses are presented. Following the removal of a portion of the myxospores for DNA extraction, the parasite was fixed in either 10% neutral-buffered formalin solution or 70% ethanol solution. The specimens collected in the present work were deposited in the Meguro Parasitological Museum, Tokyo, Japan, under collection nos. 21656–21658.
2.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and Sequencing
Parasite DNA was extracted from collected myxospores using an Illustra™ tissue and cells genomicPrep Mini Spin Kit (GE Healthcare UK, Buckinghamshire, UK) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. PCR amplification of the small subunit (SSU) rDNA was performed in a 20 µL volume containing a DNA polymerase, Blend Taq-Plus- (TOYOBO, Dojima Hama, Osaka, Japan), and a combination of universal eukaryotic primers, Eurib1 (5′-ACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAG-3′) and reverse Eurib2 (5′-CTTCCGCTGGTTCACCTACGG-3′), was used to amplify almost the complete length of the SSU rDNA at once [27,28]. The PCR products were purified using a FastGene Gel/PCR Extraction Kit (NIPPON Genetics Co., Tokyo, Japan), and the purified PCR products were cloned into the plasmid vector pTA2 (TArget Clone™; TOYOBO) and transformed into Escherichia coli JM109 cells (TOYOBO) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Following propagation, the plasmid DNA was extracted using a FastGene Plasmid Mini Kit (NIPPON Genetics Co., Tokyo, Japan), and inserts from multiple independent clones, at least three, were sequenced using universal M13 forward and reverse primers (5′-GTAAAACGACGGCCAGT-3′; and 5′-GGAAACAGCTATGACCATG-3′, respectively). For sequencing purposes, some additional primers were chosen from our stocks used in the previous works [25,28,29]; NSR581/18 (5′-TCTCAGGCTCCCTCTCCGG-3′), Myxo18S_794R (5′-CGCCTGCTTTGAGCACTCTGT-3′), Myxo18S_1009R (5′-CGCATCTGTTAGTCCTTGG C-3′), Myxo 18S_575F (5′-CGCGGTAATTCCAGCTCCAG-3′), Myxo18S_887F (5′-AATGG TCGAGGGCAACTTTG-3′), Myxo18S_1028F (5′-GCCAAGGACTAACAGATGCG-3′), or Myxo18S_1217F (5′-GGGAGAGTATGGTCGCAAGT-3′).
The nucleotide sequence obtained in the present study is available from the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under accession nos. LC544125–LC544127.
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
Fragments of the newly obtained rDNA sequences were analyzed to identify highly similar nucleotide sequences using the Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information website (NCBI; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 7 July 2020). For phylogenetic analysis, the newly obtained SSU rDNA nucleotide sequences in the present study and related myxosporean sequences retrieved from the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases were aligned using the MEGA7 software [30], with subsequent manual adjustments. The accession numbers of the sequences analyzed in the present study are provided in the figure showing a phylogenetic tree. Regions judged to be poorly aligned and characters with a gap in any sequence were excluded; 920 characters, of which 416 were variable, were retained for subsequent analysis. Maximum likelihood (ML) analysis was performed using the PhyML program ver. 3.0 [31,32] provided on the ‘phylogeny.fr’ website (http://www.phylogeny.fr/). The probability of inferred branch was assessed by the approximate likelihood-ratio test (aLRT), an alternative to the non-parametric bootstrap estimation of branch support [33].
3. Results
Three myxosporean species of the genera Myxobolus, Henneguya, and Myxidium were found separately in three fish species (Figure 1). Four Myxobolus plasmodia were found in the gills of a rosyface dace, Pseudaspius sachalinensis (Nikolskii, 1889) (syn. Tribolodon sachalinensis (Nikolskii, 1889)), measuring 11.0 cm in standard body length (BL) and 20.6 g body weight (BW), collected originally in May 2018 from a river running through Akkeshi-cho Town, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. Four cysts at the subcutis of the external surface in the anterior body and more than 20 cysts in the oral submucosa were found in an Amur stickleback, Pungitius sinensis (Guichenot, 1869), measuring 4.9 cm BL and 1.2 g BW, collected originally in May 2018 from the same river running through Akkeshi-cho Town. These cysts contained Henneguya plasmodia. Numerous Myxidium myxospores were found in the urinary bladder of a masu salmon, Oncorhynchus masou (Brevoort, 1856) (syn. Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae (Jordan et McGregor, 1925)), measuring 30.5 cm BL and 599 g BW, collected originally in May 2018 from the Nagaragawa River running through Gifu Prefecture, Japan. Since the myxospore morphology and SSU rDNA nucleotide sequences of the aforementioned species were differentiated from previously recorded species in Japan, we carefully conducted their specific identification with species recorded from other locations.
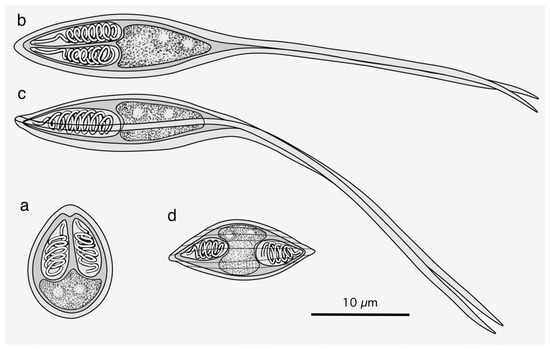
Figure 1.
Stylized illustrations of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. from Pseudaspius sachalinensis (a), Henneguya pungitii from Pungitius sinensis (b,c), and Myxidium salvelini from Oncorhynchus masou (d). Frontal view (a,b,d) and sutural view (c) at the same magnification.
Figure 1.
Stylized illustrations of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. from Pseudaspius sachalinensis (a), Henneguya pungitii from Pungitius sinensis (b,c), and Myxidium salvelini from Oncorhynchus masou (d). Frontal view (a,b,d) and sutural view (c) at the same magnification.
3.1. Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida: Myxobolidae)
(syn. Myxobolus marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000; M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015)
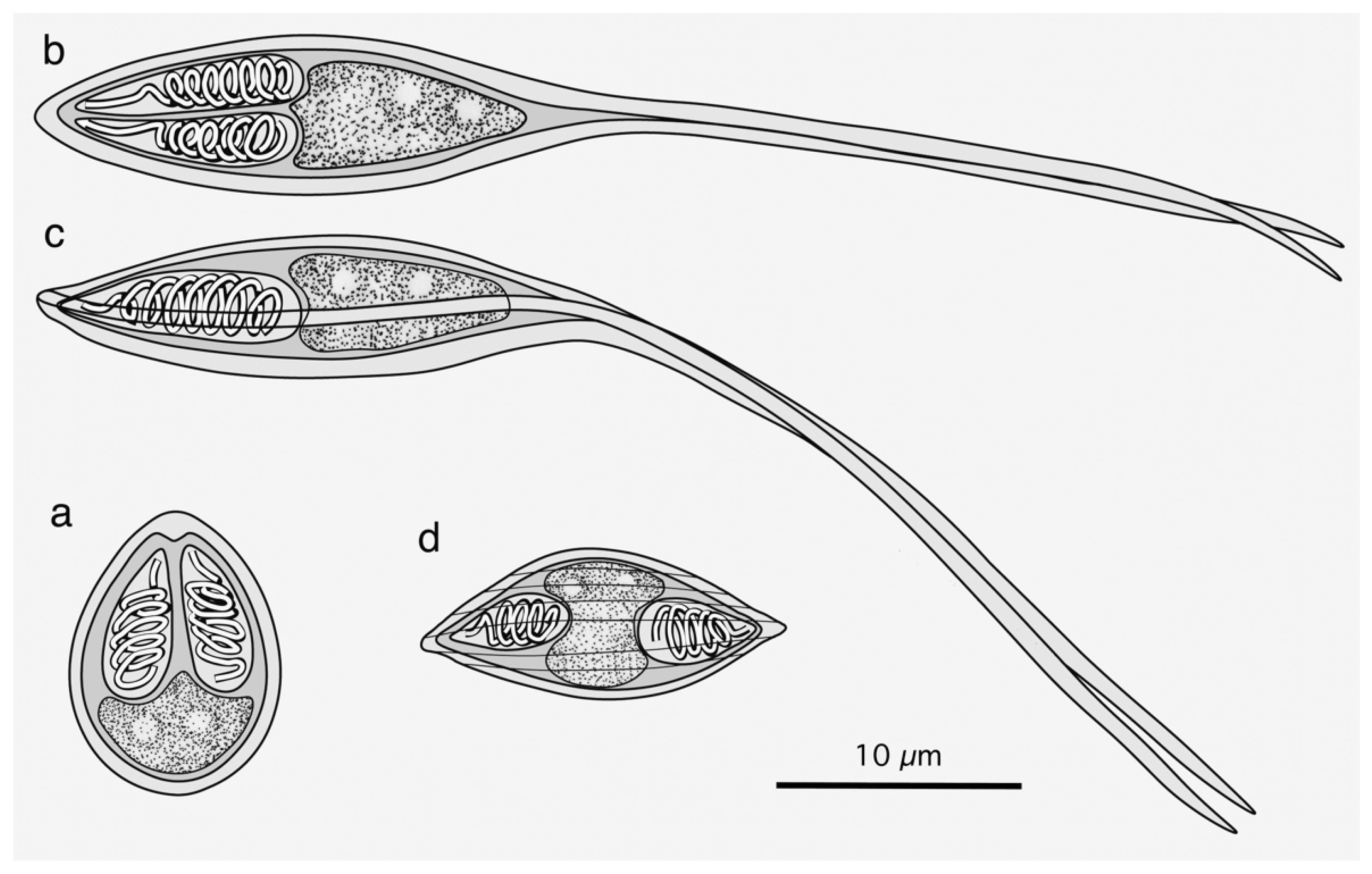
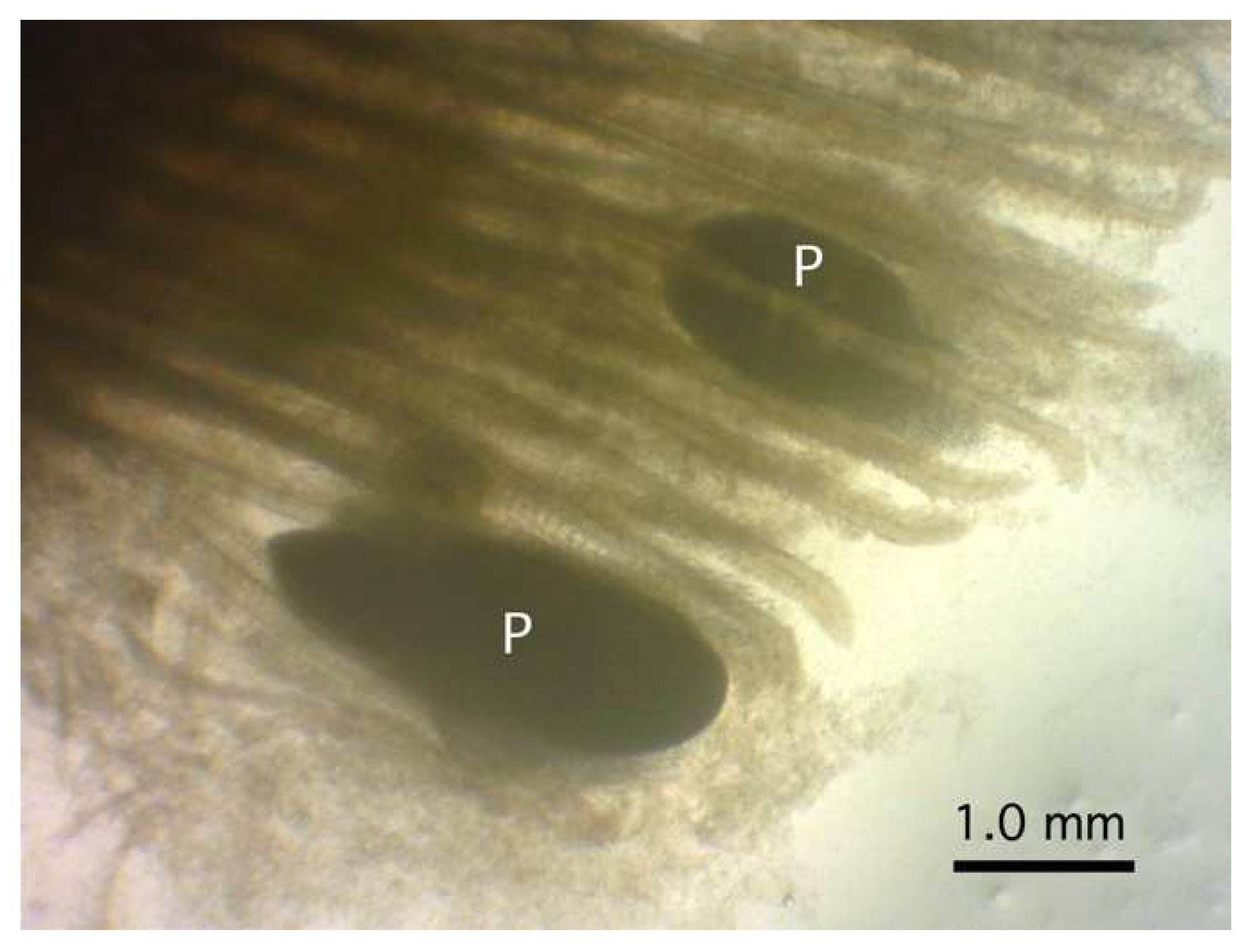
Four large-sized oval plasmodia were detected between the gill filaments at their upper half portion of a rosyface dace (Figure 2). The largest plasmodium measured 2.35 mm by 0.87 mm, and the other three were smaller, measuring 1.13–1.29 (1.24) mm by 0.44–0.77 (0.64) mm.
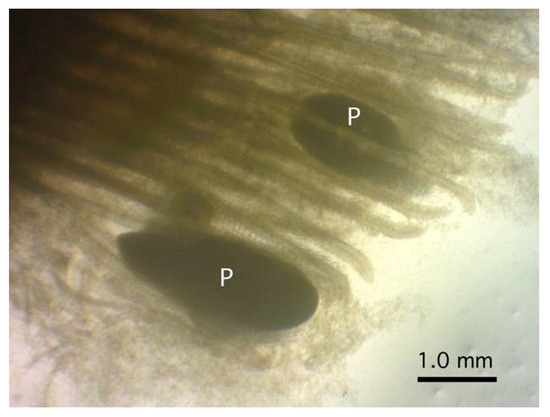
Figure 2.
Plasmodia (P) of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. attached to the gill filaments of Pseudaspius sachalinensis under a dissection microscope.
Figure 2.
Plasmodia (P) of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. attached to the gill filaments of Pseudaspius sachalinensis under a dissection microscope.
3.1.1. Description
Bivalvular myxospores pyriform from the frontal view, measuring 8.7–9.6 (9.2) in length, 6.5–7.5 (7.0) in width (n = 11). Valvular surface smooth. Two almost equal PCs, bullet-shaped, 4.6–6.0 (5.1) in length and 1.7–2.1 (1.9) in width, pointing towards the apical end, and the posterior end of PCs beyond the mid-line of myxospore length. Binucleated sporoplasm in the remaining space. A small-sized intercapsular appendix, and 4–5 turns of polar tubules.
3.1.2. Molecular–Genetic Characterization
A newly obtained, almost complete SSU rDNA nucleotide sequence was 2007 bp in length (DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. LC544125), and showed the highest identities (up to 95.11% [1538/1617]) with sequences from certain Myxobolus spp. such as M. alvarezae (accession no. FJ716097), M. intimus (accession no. FJ716098), M. sitjae (accession no. JF311898), M. obesus (accession no. AY325286), and M. szentendrensis (accession no. KP025684), which had 5–11 nucleotide insertion/deletion sites (indels) over an rDNA sequence comparable with that of the new species. The nucleotide identity of the SSU rDNA sequence of Myxobolus macrocapsularis Reuss, 1906, from Abramis brama (L., 1758) or Blicca bjoerkna (L., 1758) in Hungary (accession nos. AF507969 and FJ716095, respectively) with that of the present new species was 83.58% (1308/1565) with 33 indels, or 81.01% (1058/1306) with 27 indels. Shulman [22] considered M. macrocapsularis as a senior synonym of M. marinus Dogiel, 1948, from the gills of Alburnus alburnus (L., 1758) in the Russian Far East (Amur River basin and other rivers flowing to the Sea of Japan).
3.1.3. Remarks
Myxospores of this myxobolid species were pyriform, with a length of 8–10 µm, apparently classified in the genus Myxobolus according to Lom and Dyková [6]. More than 40% of ca. 970 nominal Myxobolus spp. showed an organ/tissue preference for the gills [9,10,11]. The morphologically identical myxospores were recorded from P. sachalinensis (type host of the present new species), Pseudaspius hakonensis (Günther, 1877) (syn. Tribolodon hakonensis (Günther, 1877)), and Pseudaspius brandtii (Dybowski, 1872) (syn. Tribolodon brandtii (Dybowski, 1872)) from the rivers on the Sakhalin Island or in the Maritime Province (Primorsky Kray) of the Russian Far East [34,35], as shown in Table 1. These isolates (M. tribolodonus sp. n., M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000, and M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015) had identical myxospore dimensions and proportions (myxospore length/width), with an index of approximately 1.2 (1.1–1.3). Myxobolus marinus Dogiel, 1948, was originally described from the gill lamellae of Alburnus alburnus (Cypriniformes: Leuciscidae: Leuciscinae) in the basin of the Amur River and the Sea of Japan [22,36,37], and is currently considered to be a junior synonym of Myxobolus macrocapsularis [22,37]. The dimensions of M. macrocapsularis myxospores, including the original description of M. marinus, are apparently larger than the myxospores found in Pseudaspius spp. in the Russian Far East region (Maritime Province (Primorsky Kray) and Sakhalin Island) and Hokkaido Island of Japan (Table 1). Although Shulman [22] characterized myxospores of the former species as pyriform with narrow and pointed anterior ends, none of the isolates from the gills of Pseudaspius spp. (M. tribolodonus sp. n., M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000, and M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015) showed such traits, but they showed comparatively bluntly pointed anterior ends of pyriform myxospores (Figure 1a and Figure 3 in the present study; also see [34,35]). Ellipsoidal plasmodia of M. macrocapsularis and M. tribolodonus sp. n. exhibited almost similar dimensions and localization near the tips of the gill filaments (Figures 3–5 in [37]; Figure 2 of the present study).
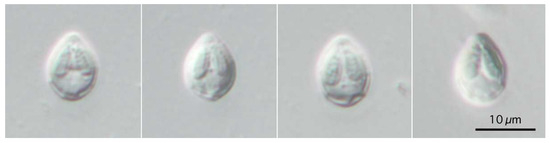
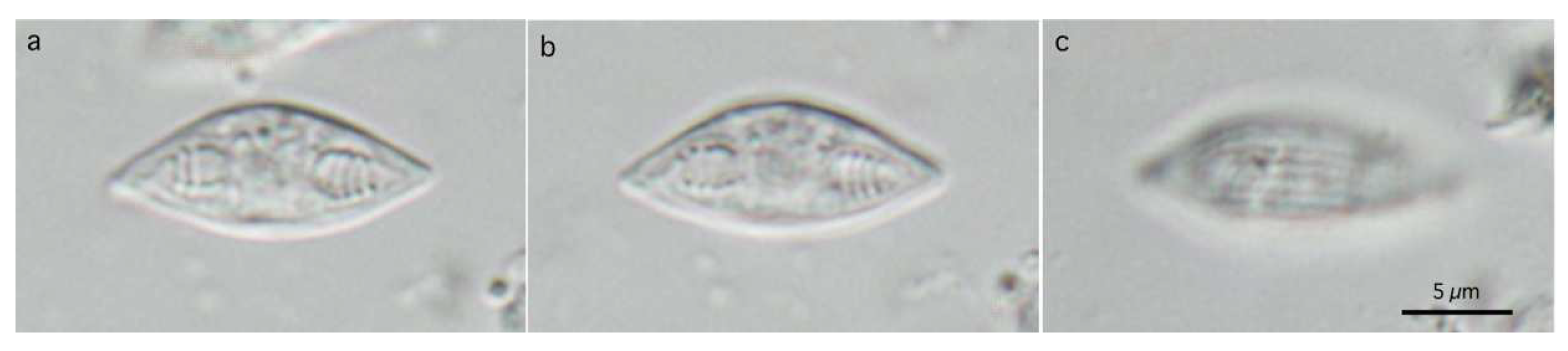
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. from Pseudaspius sachalinensis. Frontal view at the same magnification.
Figure 3.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Myxobolus tribolodonus n. sp. from Pseudaspius sachalinensis. Frontal view at the same magnification.
Further morphological comparisons with nominal Myxobolus spp. were conducted with 17 Myxobolus spp. (Supplementary Table S3), selected based on the myxospore shape (non-circular in the frontal view) and the myxospore length of between 8–10 µm using synoptic references [9,10,11]. Only four species (M. bengalensis, M. branchialis, M. flavus, and M. tambroides) have deposited SSU rDNA nucleotide sequences (DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession nos. KJ476883, MK412934, JQ388887, KF296346, KF296347, and JX028236), and these sequences show less than 90% identity with that of M. tribolodonus sp. n. (accesssion no. LC544125), in addition to a few to several indels within the 1520 bp to 1935 bp long sequences. Morphologically, the PCs of M. bengalensis, M. branchialis, M. flavus, and M. tambroides are wider than those of the present species (Supplementary Table S3) and situated closer to each other within a myxospore, in contrast to the distantly placed PCs in M. tribolodonus n. sp. For the remaining 13 species, no nucleotide sequences are available in the DNA databases. All of these species, except for M. funsienensis (Ma, 1998) Erias et al., 2005 (syn. Myxosoma fusienenesis Ma in Chen et Ma, 1998), differed apparently from M. tribolodonus sp. n. in their elliptical myxospore shape, wider PCs, smaller angle of two PCs, number of turns of polar tubules, and/or small dimensions of cysts (Supplementary Table S3). Although histological localization of cysts in the gills is known to have high importance in species identification [38], such data are not always available. The present new species shows similar myxospore morphology to that of M. fusienensis recorded in the gills of Spinibarbichthys yunnanensis (Tsü, 1977) (syn. Spinbarbus denticulatus yunnanensis (Tsü, 1977)) from the southernmost province in China (Yunnan), but these two species differ from each other in the shape of PCs (pyriform vs. bullet-shaped), the angular arrangement of PCs (wide vs. narrow), and the absence and presence of small intercapsular processes [9,23].

Table 1.
Comparison of Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n. with its related species a.
Table 1.
Comparison of Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n. with its related species a.
| Species | Host Fish | Location in Host | Locality | SL | SW | ST | PCL | PCW | SF | IP | NT | Cyst Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. tribolodonus sp. n. | Pseudaspius sachalinensis (syn. Tribolo-don sachalinensis) | Gills | Japan (Hokkaido) | 8.7–9.6 (9.2) | 6.5–7.5 (7.0) | — | 4.6–6.0 (5.1) | 1.7–2.1 (1.9) | Pyriform | Small | 4–5 | max. 2.35 by 0.87 mm | Present Study |
| M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000 | Pseudaspius brandtii (syn. Tribolodon brandtii); Pseudaspius hakonensis (syn. Tribolodon hakonensis) | Gills | Maritime Province (Primorsky Kray) of Russian Far East | 9.7–12.0 | 8.3–10.3 | — | 5.5–6.3 | — | pyriform | — | — | — | [34] |
| M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015 | Pseudaspius sachalinensis (syn. Tribolodon sachalinensis); Pseudaspius hakonensis (syn. Tribolodon hakonensis) | Gills | Sakhalin Island (Russian Far East) | 9.9–11.3 (10.7) | 8.1–9.2 (8.6) | — | 5.0–6.1 (5.7) | 2.5–3.4 (3.0) | pyriform | small | — | — | [35] |
| M. marinus Dogiel, 1948 | Alburnus alburnus | Gills | The basin of the Amur River and the Sea of Japan | 12.5–13.0 | 7.0–8.0 | — | 6.0–7.0 | 2.5–3.0 | pyriform | small | — | — | [22,36] |
| M. macrocapsularis (syn. Myxobolus physophilus Reuss, 1906; M. multiplex Achmerov, 1960; M. vescus Achmerov, 1960; M. oviformis Thélohan in Rostovschikov, 1952; M. marinus Dogiel, 1948) b | Rutilus rutilus (L., 1758) ; Leu-ciscus leuciscus (L., 1758); Leu-ciscus idus (L., 1758); Squalius cephalus (L., 1758) (syn. Leuci-scus cephalus (L., 1758); Scardi-nius erythrophthalmus (L., 1758); Leuciscus aspius (L., 1758) (syn. Aspius aspius (L., 1758); Barbus barbus (L., 1758); Gobio gobio (L., 1758) ; Abbottina rivularis (Basilewsky, 1855) (syn. Pseudo-gobio rivularis (Basilewsky, 1855)); Alburnus alburnus; Alburnoides bipunctatus (Bloch, 1782) (syn. Alburnus bipunctatus (Bloch, 1782)); Chondrostoma nasus (L., 1758); Pelecus cultratus (L., 1758): Opsariichthys uncirostris (Temminck et Schlegel, 1846); Carassius carassius (L., 1758); Cyprinus carpio L., 1758; Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes, 1844) ; Gasterosteus aculeatus L., 1758 | Gills, mesentery, intestinal wall, swimbladder | Basins of rivers in southern Karelia, Rivers flowing to the Baltic Sea, Rivers flowing to the Azov Sea, or Caspian Sea; and Amur River, | 9.0–14.5 | 6.0–9.5 | 4.5–6.0 | 5.0–8.6 | 2.4–3.6 | pyriform | small | — | Reaching 1.5 mm in diameter | [22] |
a Abbreviation: SL, myxospore length; SW, myxospore width; ST, myxospore thickness; PCL, polar capsule length; PCW, polar capsule width; SF, myxospore form; IP, intercapsular projection; NT, number of coil turns (polar tubles). All measurements are expressed in micrometers (µm) unless otherwise stated. Ranges are presented, with the means in parentheses. For M. flavus, means and standard variations are shown in parentheses. b All synonyms follow Shulman (1966).
3.1.4. Taxonomic Summary
- Host: Pseudaspius sachalinensis (syn. Tribolodon sachalinensis), rosyface dace (Actinopterygii: Cypriniformes: Leuciscidae: Pseudaspininae).
- Additional hosts: Pseudaspius hakonensis (syn. Tribolodon hakonensis) and Pseudaspius brandtii (syn. Tribolodon brandtii) [34,35].
- Type locality: Collected in Aquatotto Gifu, Gifu Prefecture, Japan, following its relocation from a river running through Akkeshi-cho Town, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. Circumstantially, the infection might originate from the water in the natural habitat and not in the aquarium.
- Additional locality: Rivers on the Sakhalin Island or in the Maritime Province (Primorsky Kray) of Siberia (Russia) [34,35].
- Site of infection: Gill filaments (histozoic).
- Materials deposited: Hapantotype no. 21656 (specimens in fixatives), Meguro Parasitological Museum, Tokyo, Japan.
- Deposited rDNA sequence: DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. LC544125.
- Etymology: The species name refers to the former genus name of the host fish.
3.2. Henneguya pungitii Achmerov, 1953 (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida: Myxobolidae)
Oval whitish cysts, measuring 1.1–1.5 mm in diameter, were found in the subcutis of the anterior body and oral submucosa of an Amur stickleback, Pungitius sinensis (Figure 4). From the subcutis of the ninespine stickleback, Pungitius pungitius (L., 1758), and Sakhalin stickleback, Pungitius tymensis (Nikolskii, 1889), in the Russian Far East (Rivers flowing to the Sea of Okhotsk on Kamchatka Peninsula and Sakhalin Island), similar cysts containing myxospores of Henneguya pungitii Achmerov, 1953, were recorded [22,35]. Recently, Dorovskikh [39] recorded myxospores of the same species from plasmodial cysts localized in the gills and liver of the ninespine sticklebacks from rivers on the Kolguyey Island, near the Kanin Peninsula, in northwestern Russia. Myxospores of H. pungitii recovered from the subcutis and submucosa, or from the gills and liver of Pungitius spp., distributed in northeastern and northwestern Russia, respectively, are relatively closer in morphology with each other, but apparently different in size (Table 2). For further research in the future, H. pungitii myxospores recovered from the cutaneous subcutis and oral submucosa of Amur Stickleback are described in detail here, along with its molecular–genetic characterization.

Figure 4.
Photomicrographs of plasmodia (arrowheads) of Henneguya pungitii at the subcutis of the external surface (a,b) and oral submucosa (c) of Pungitius sinensis under a dissection microscope. One grid = 5 mm.
Figure 4.
Photomicrographs of plasmodia (arrowheads) of Henneguya pungitii at the subcutis of the external surface (a,b) and oral submucosa (c) of Pungitius sinensis under a dissection microscope. One grid = 5 mm.
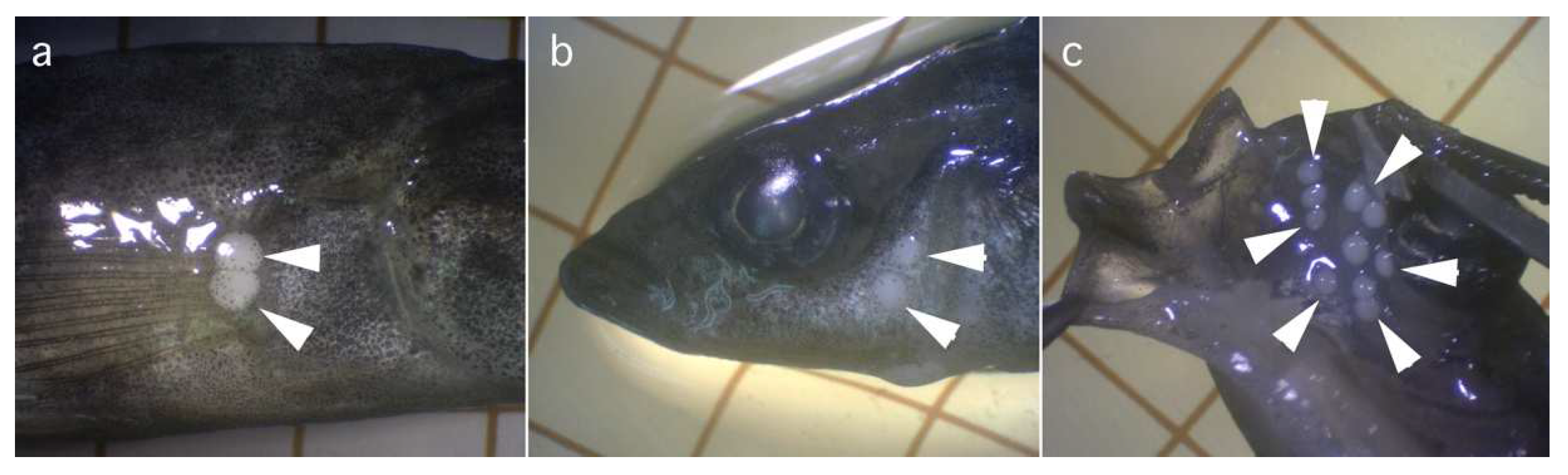


Table 2.
Henneguya spp. recorded from freshwater fish, resembling H. pungitii in spore shape and dimension a.
Table 2.
Henneguya spp. recorded from freshwater fish, resembling H. pungitii in spore shape and dimension a.
| Species | Host Fish | Location in Host | Locality | TSL | SBL | SBW | SBT | PCL | PCW | CP | NT | Cyst Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H. pungitii Achmerov, 1953 | Pungitius sinensis | Subcutis of External Surface and Oral Submucosa | Japan (Hokkaido) | 47.5–56.1 (49.6) | 19.3–22.9 (21.0) | 6.3–7.6 (6.8) | 4.8–6.0 (5.6) | 7.8–9.5 (8.4) | 1.8–2.5 (2.1) | 28.2–33.2 (28.6) | 7–8 | 1.1–1.5 mm in Diameter, Oval | Present Study |
| H. pungitii Achmerov, 1953 | Pungitius pungitius | Subcutis | Basins of Kamchatka and Paratunka Rivers (Russia) | — | 13.0–17.0 | 4.5–6.0 | — | 6.5–8.0 | 1.8–2.0 | 18.0–20.0 | — | 1–2 mm in diameter, round | [22] |
| H. pungitii Achmerov, 1953 | Pungitius tymensis (Nikolskii, 1889) | Subcutis | Sakhalin Island (Russia) | 52.9–62.2 (58.2) | 16.7–20.6 (18.4) | 4.7–5.7 (5.2) | — | 6.7–9.0 (8.2) | 2.1–2.6 (2.3) | 36.2–45.5 (39.8) | — | — | [35] |
| H. pungitii sensu Dorovskikh 2022 | Pungitius pungitius | Gills | Kolguyev Island, near Kanin Peninsula (Russia) | 35.5–40.2 (37.5) | 14.7–16.7 (16.1) | 5.4–6.0 (5.8) | 4.0 | 6.7–7.4 (7.1) | 1.3–2.0 (1.6) | 20.8–23.5 (21.4) | — | — | [39] |
| H. pungitii sensu Dorovskikh 2022 | Pungitius pungitius | Liver | Kolguyev Island, near Kanin Peninsula (Russia) | 27.5–32.8 (30.0) | 11.4–13.4 (12.7) | 6.1–7.7 (6.8) | 5.4–6.7 (5.7) | 5.4–7.4 (6.6) | 2.0–2.7 (2.5) | 14.7–19.4 (17.1) | — | — | [39] |
| H. alexeevi Shulman, 1962 | Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes, 1844); Perccottus glenii Dybowski, 1877 (syn. Percottus glehni Dybowski, 1877) | Gills, ovary | Amur basin | 40.8–52.8 (48.0) | 16.8–19.2 (18.2) | 5.0–7.2 (6.0) | 4.0–5.2 (4.8) | 7.8–10.8 (8.9) | 1.8–2.2 (1.9) | 24.0–33.6 (29.8) | 6–7 | Cyst: round to oval | [23] |
| H. sinensis Chen et Hsieh, 1960 | Channa argus (Cantor, 1842); Clarias batrachus (L., 1758); Misgurnus anguillicaudatus (Cantor, 1842) | Gills, external surface, fin, oral cavity, intestine, swimming bladder | China | 31.8–52.2 (42.7) | 13.8–16.2 (15.1) | 4.8–6.0 (5.4) | 3.6–4.2 (3.7) | 7.2–8.4 (7.9) | 1.4–2.4 (1.9) | 18.0–36.0 (27.6) | 7–8 | 0.04–0.28 mm in diameter, round | [23] |
| H. rhinogobii Li et Nie in Li et al., 1973 | Rhinogobius giurinus (Rutter, 1897); Rhodeus ocellatus (Kner, 1866) | Gills, intestine | China, Japan (Gifu) | 34.7–59.3 (47.2) | 15.4–19.3 (16.9) | 4.6–6.2 (5.5) | 4.2–5.4 (4.3) | 6.9–9.2 (7.9) | 1.5–2.0 (1.9) | 19.3–40.0 (30.3) | 9–10 | 0.42–1.20 mm by 0.29–0.52 mm, oval | [23] |
| H. pseudorhinogobii Kageyama et al., 2009 | Rhinogobius kurodai (Tanaka, 1908) (syn. Rhinogobius sp. OR) | Gills | Japan (Gifu) | 39.5–60.7 (50.7) | 14.2–17.8 (15.8) | 4.7–5.8 (3.5) | 4.5–5.4 (4.8) | 5.9–7.6 (6.5) | 1.1–1.7 (1.4) | 25.3–42.9 (34.9) | 8 | 0.05–0.25 mm in diameter | [40] |
| H. pilosa Azevedo et Matos, 2003 | Serrasalmus altuvei Ramírez, 1965 | Gills | Brazil | 52.3–56.0 (54.2) | 20.0–23.1 (21.1) | 5.5–6.3 (5.9) | 1.9–2.6 (2.2) | 7.1–7.6 (7.4) | 1.0–1.3 (1.2) | 30.5–34.9 (31.1) | 11–12 | max. 0.2 mm in diameter, round to ellipsoidal | [41] |
a Abbreviation: TSL, total spore length; SBL, spore body length; SBW, spore body width; SBT spore body thickness; PCL, polar capsule length; PCW, polar capsule width; CP, length of caudal processes; NT, number of coil turns (polar tubules). All measurements are expressed in micrometers (µm) unless otherwise stated. Ranges are presented, with the means in parentheses.
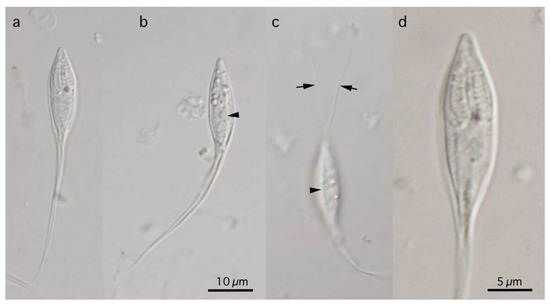
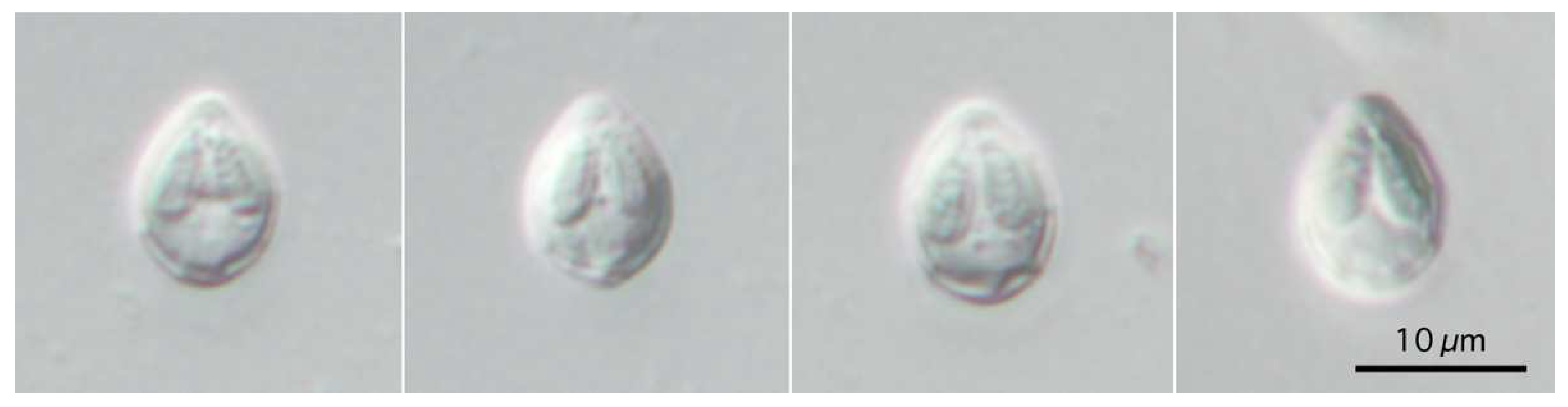
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Henneguya pungitii. Frontal view nearly at a sagittal plane (a,d), and sutural view nearly at surface (b,c). Photographs (a–c) at the same magnification with scale bar in (b). Photograph (d) is a twice-magnified view of the spore body shown in a photograph (a). Suture lines (arrowhead) and polar tubules (arrow) are shown.
Figure 5.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Henneguya pungitii. Frontal view nearly at a sagittal plane (a,d), and sutural view nearly at surface (b,c). Photographs (a–c) at the same magnification with scale bar in (b). Photograph (d) is a twice-magnified view of the spore body shown in a photograph (a). Suture lines (arrowhead) and polar tubules (arrow) are shown.
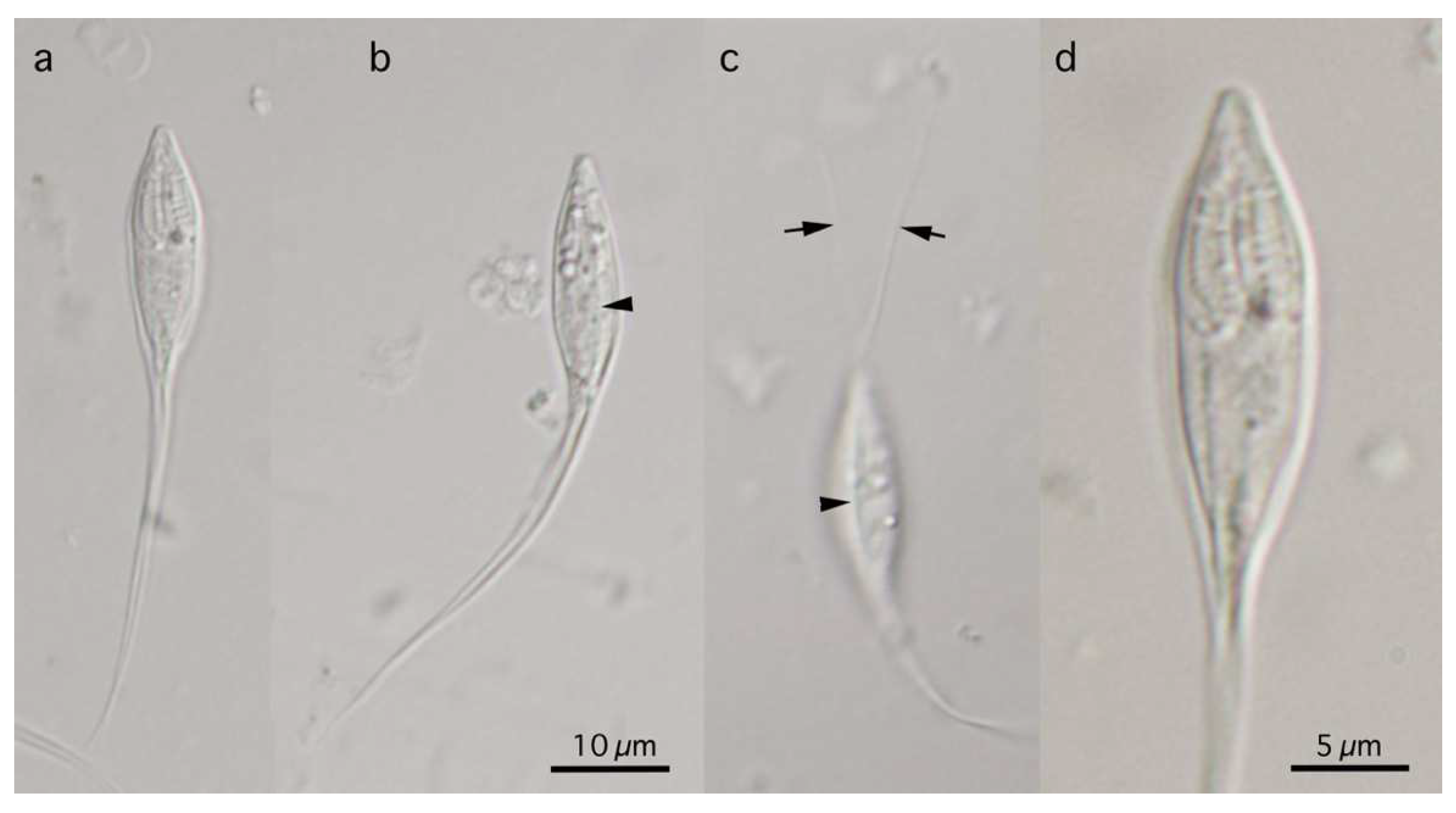
3.2.1. Description
Bivalvular myxospores with elongated spindle-shaped myxospore bodies and long caudal processes of individual valves. Myxospore bodies measuring 19.3–22.9 (21.0) in length, 6.3–7.6 (6.8) in width, and 4.8–6.0 (6.8) in thickness (n = 20). Two almost equal PCs, elongated pyriform, 7.8–9.5 (8.4) in length and 1.8–2.5 (2.1) in width. Binucleated sporoplasm in the remaining space. Turns of polar tubules 7–8. Caudal processes long and fine, measuring 28.2–33.2 (28.6) in length, and total myxospore length 47.5–56.1 (49.6). Valvular surface smooth.
3.2.2. Molecular-Genetic Characterization
A newly obtained, almost complete SSU rDNA nucleotide sequence was 2060 bp in length (accession no. LC544126) and showed the highest identities (91.7% [1741/1899] with 26 indels, or 91.6% [1878/2050] with 16 indels) with sequences from an unidentified Henneguya sp. and the aurantiactinomyxon KAB-2001 isolate (accession nos. U13826 and AF378356, respectively).
3.2.3. Remarks
Bivalvular myxospores of this species had two caudal processes which continued from each valve, and two elongated PCs were placed on the sutural plane, consistent with the definition of the genus Henneguya according to Lom and Dyková [6]. It is important to note that H. pungitii Achmerov, 1953, is characterized by fusiform myxospore bodies tapering to a point at both ends, although Henneguya spp. with myxospores having ellipsoid and rounded myxospore bodies in the frontal view are apparently predominant [12,18,20]. Henneguya spp. with myxospores exhibiting similar morphological characteristics to those of H. pungitii are selected in Table 2. Henneguya pungitii sensu Dorovskikh, 2022 [39], and the other five species have different organ preferences, e.g., the gills or visceral organs such as the liver, ovary, intestine, or swimming bladder and their myxospores are characterized by shorter (H. pungitii sensu Dorovskikh, 2022, H. sinensis, H. rhinogobii, and H. pseudorhinogobii) and/or thinner myxospore bodies (H. alexeevi, H. sinensis, H. rhinogobii, H. pseudorhinogobii, and H. pilosa), smaller PCs (H. pseudorhinogobii, and H. pilosa), and/or more turns of polar tubules (H. rhinogobii, and H. pilosa), as shown in Table 2.
Availability of the SSU rDNA nucleotide data of aforementioned Henneguya spp. with fusiform myxospore bodies (Table 2) is currently limited to three species (the current isolate of H. pungitii, H. rhinogobii, and H. pseudorhinogobii), and the latter two species show relatively high identity of the SSU rDNA (95.89% [1843/1922] with 10 indels over a 1930 bp length between accession nos. AB447993 and AB447994) with each other, whereas the SSU rDNA of the current H. pungitii isolate (accession no. LC544126) shows relatively low identities with those of H. rhinogobii and H. pseudorhinogobii (82.84% [1569/1894] with 61 indels over a 1958 bp length, and 87.58% [1664/1900] with 53 indels over a 1958 bp length, respectively). The phylogenetic relationships between H. pungitii from the subcutis of Pungitius spp., distributed in the Russian Far East, and H. pungitii sensu Dorovskikh 2022 from the gills and/or liver of Prungitiu pungitius, distributed in the northwestern Russia (Kolguyev Island, near Kanin Peninsula), should be elucidated in future research, since these two species show distinct tissue preferences and somewhat different myxospore morphology regardless of their identical host preference [22,35,39].
3.2.4. Taxonomic Summary of the Present Isolate
- Host: Pungitius sinensis, Amur stickleback (Actinopterygii: Gasterosteiformes: Gasterosteidae).
- Locality: Collected in Aqua Totto Gifu, Gifu Prefecture, Japan, following its relocation from a river running through Akkeshi-cho Town, Hokkaido Prefecture, Japan. Circumstantially, the infection might originate from the water in the natural habitat, and not in the aquarium.
- Site of infection: Subcutis of external surface and oral submucosa (histozoic).
- Materials deposited: Hapantotype no. 21657 (specimens in fixatives), Meguro Parasitological Museum, Tokyo, Japan.
- Deposited rDNA sequence: DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. LC544126.
3.3. Myxidium salvelini Konovalov et Shulman, 1966 (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida: Myxidiidae)
3.3.1. Morphological Characterization
Numerous free myxospores of M. salvelini Konovalov et Shulman, 1966, were found in the contents of the urinary bladder from the red spotted masu trout, Oncorhynchus masou, while coelozoic plasmodia were never found in the contents or wall of the organ. Bivalvular myxospores were fusiform (Figure 1d and Figure 6), or slightly more arcuate on one side, in the frontal view, measuring 13.6–16.7 (15.0) by 4.9–6.6 (5.7) (n = 20). Fusiform myxo-spores tapered to pointed ends at an angle 60°, and had fine striations (5–7 in number) on the surface of each valve. Two pyriform PCs, measuring 4.0–5.2 (4.4) in length and 2.1–2.8 (2.5) in width, were oriented towards the pointed ends of spores. Binucleated sporo-plasms were located in the middle parts of spores between PCs. Polar filaments formed 4–5 turns in PCs.
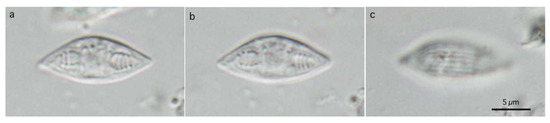
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Myxidium salvelini. Frontal view nearly at midline of sagittal plane (a,b), and spore surface (c) at the same magnification. Scale bar is shown in (c).
Figure 6.
Photomicrographs of myxospores of Myxidium salvelini. Frontal view nearly at midline of sagittal plane (a,b), and spore surface (c) at the same magnification. Scale bar is shown in (c).
3.3.2. Molecular-Genetic Characterization
A newly obtained, almost complete SSU rDNA nucleotide sequence was 2059 bp in length (accession no. LC544127), and showed the highest identity (95.02% [1812/1907] with 9 indels) with Sphaerospora onchorhynchus (accession no. AF201373).
3.3.3. Remarks
Myxospores of this myxosporean species were fusiform with pointed ends, and were classified in the genus Myxidium according to Lom and Dyková [6]. A synopsis of the Myxidium spp. by Eiras et al. [14] included 232 nominal species, of which a majority parasitize the gall bladder as coelozoic myxosporeans, whereas only a small proportion (12.5%) parasitize the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, and urinary bladder. Similarly, among 19 Myxidium spp. recorded in Japan (nine species from freshwater fish, and 12 species from marine fish; see Supplementary Table S1), only M. lentiforme (Fujita, 1927) Fujita, 1929 (syn. M. fusiforme Fujita, 1927), and M. uchiyamae Fujita, 1927, parasitize the urinary system, i.e., kidney, of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica Temminck et Schlegel, 1846) [42]. These species have morphologically distinct myxospores from those of the present new species (Table 3). Among Myxidium spp. recorded in the urinary bladder of freshwater fish worldwide, M. rimskykorsakowi Shulman, 1962, and M. salvelini have myxospores similar in morphology to those of the current isolate, but the myxospores of the former species are shorter and wider than those of the current isolate, with pointed ends at an angle of 70°–80° and rounded PCs [22]. In contrast, M. salvelini recorded from the urinary bladder and ureters of salmonids from the river basin of Kamchatka [22] and the current isolate from the masu salmon in the central Japan (Gifu, Honshu Island of Japan) are coincident in morphology with each other. In Hokkaido, Japan, M. oncorhynchi Fujita, 1923, was isolated from the gall bladder of the cherry salmon, Oncorhynchus masou masou (Brevoort, 1856) [43]. Mixidium oncorhynchi has myxospores with oval to globular PCs, differentiated from M. salvelini reported in the present study. No myxosporean species showed highly identical SSU rDNA sequences to that of the current M. salvelini isolate (accession no. LC544127). Exclusively, Sphaerospora onchorhynchus (accession no. AF201373) showed a high nucleotide identity with a limited number of indels (95.02% [1812/1907] with 9 indels).

Table 3.
Myxidium spp. resembling M. salvelini in spore shape and dimension a.
3.3.4. Taxonomic Summary of the Present Isolate
- Host: Oncorhynchus masou, masu salmon (syn. Oncorhynchus masou ishikawae, satsukimasu salmon, or red spotted masu trout) (Actinopterygii: Salmoniformes: Salmonidae).
- Locality: Collected in Aqua Totto Gifu, Gifu Prefecture, Japan, following its relocation from the Nagaragawa River running through Gifu Prefecture, Japan. Circumstantially, the infection might originate from the water in the natural habitat, and not in the aquarium.
- Site of infection: Urinary bladder (coelozoic).
- Materials deposited: Hapantotype no. 21658 (specimens in fixatives), Meguro Parasitological Museum, Tokyo, Japan.
- Deposited rDNA sequence: DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. LC544127.
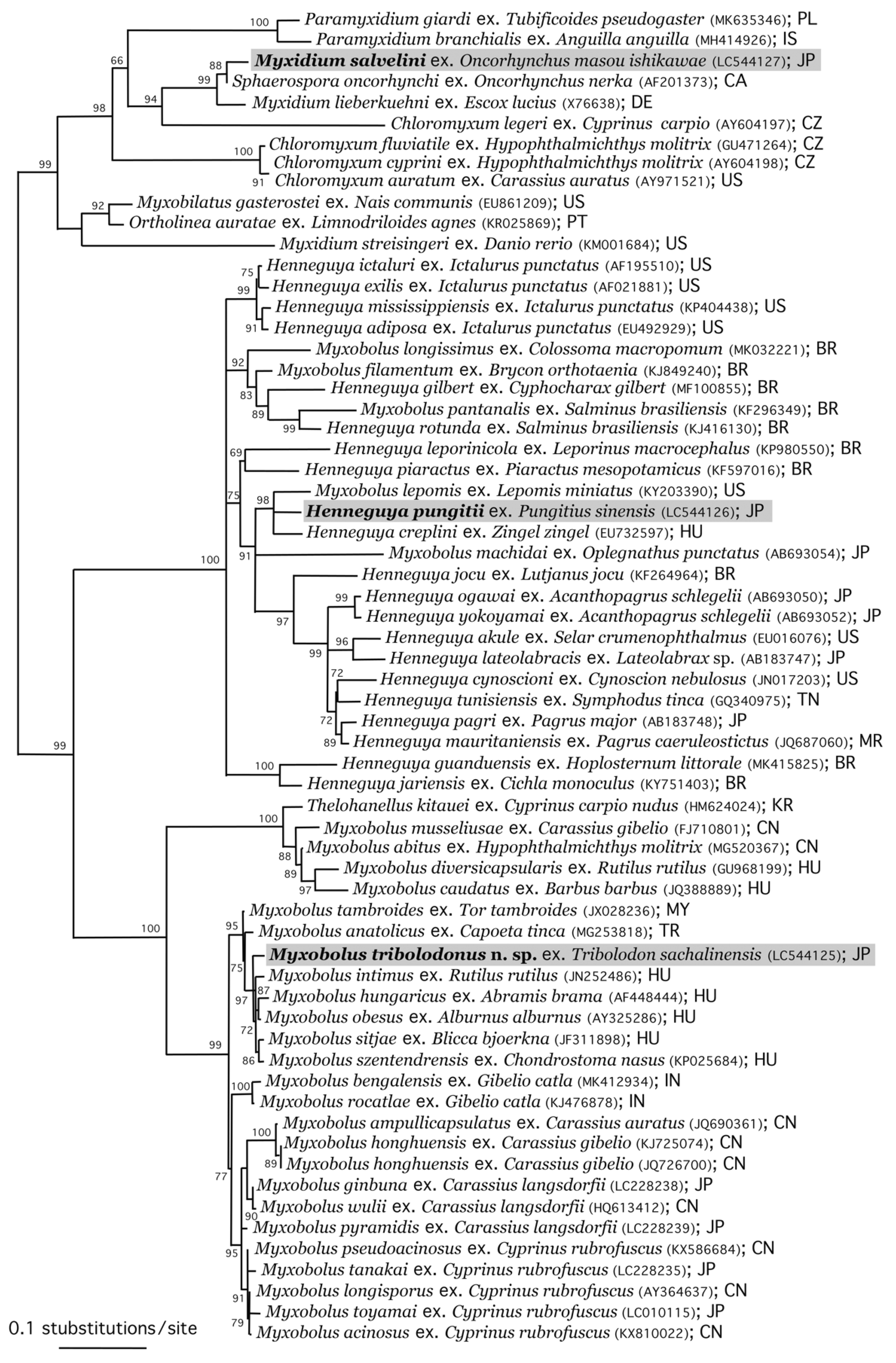
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
The phylogenetic relationships of the three new isolates described above with other myxospoean species are shown in Figure 7. Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n., parasitizing the gills of the rosyface dace, formed a highly supported clade with M. intimus Zaika, 1965, from the gill lamellae of the common roach Rutilus rutilus (L., 1758); M. hungaricus Jaczó, 1940, from the gill filaments of Abramis brama; M. obesus from the gills of Alburmus alburmus; M. sitjae Cech et al., 2012, from the gill filaments of Blicca bjoerkna; and M. szentendrensis from the gills of the common nase Chondrostoma nasus (L., 1758). All these myxobolid species with pyriform myxospores parasitize the gill filaments of cyprinid fishes of the subfamily Leuciscinae, distributed in the northern Far East (M. tribolodonus sp. n.) and Europe (the other five species). This clade is the sister group to the clades of myxobolid species parasitizing the gills of cyprinid fishes of the subfamilies Cyprininae (China and Japan) and Labeoninae (India).
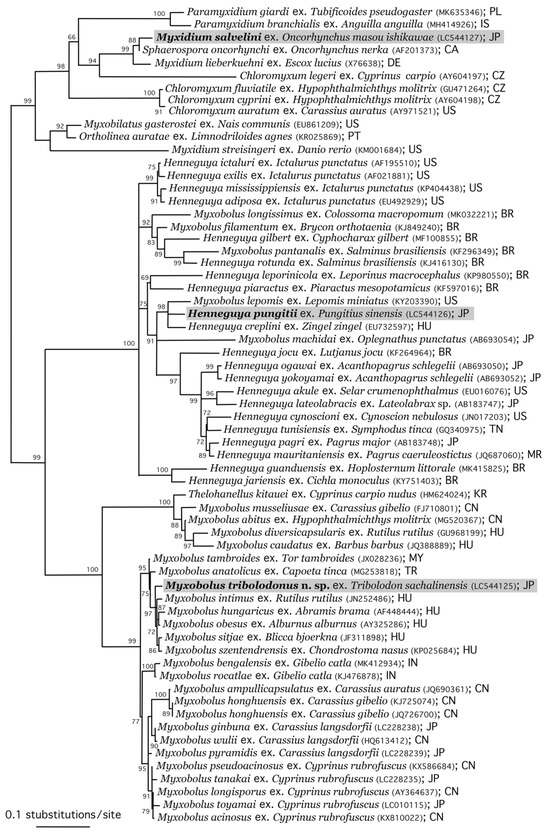
Figure 7.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on the SSU rDNA sequence of representative myxosporeans of the Bivalvulida. Species names are followed by host fish species, DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession numbers in parentheses, and country names as the collection localities. Abbreviations of country names: BR, Brazil; CA, Canada; CN, China; CZ, Czech Republic; DE, Germany; HU, Hungary; IN, India; IS, Iceland; JP, Japan; MR, Mauritania; KR, Korea; MY, Malaysia; PL, Poland; PT, Portugal; TN, Tunisia; and US, United States. Sequences newly obtained in this study are marked with gray background.
Henneguya pungitii, parasitizing the external subcutis and oral submucosa of the Amur stickleback, forms a clade with Henneguya creplini (Gurley, 1894) Labbé, 1899, from the gills of the zingel Zingel zingel (L., 1758) in Europe, and with Myxobolus lepomis Rosser et al., 2017, from the gills of the redspotted sunfish Lepomis miniatus (Jordan, 1877) and the dollar sunfish Lepomis marginatus (Holbrook, 1855) in Texas, USA. The SSU rDNA sequences of these three species showed 86.14% [1392/1616] to 90.30% [1461/1618] identities and 9–18 indels with each other. This clade is the sister group to the clade of Henneguya spp. from marine fish.
Myxidium salvelini, parasitizing the urinary bladder of the satsukimasu salmon, formed a highly supported clade with Sphaerospora onchorhynchus Kent et al., 1993, from the kidney of the sockeye salmon Oncorhynchus nerka (Walbaum, 1792) in the North Pacific Ocean, and Myxidium lieberkuehni Bütschli, 1882, from the kidney of the northern pike Esox lucius L., 1758, in the north parts of the Northern Hemisphere. This clade is rather isolated from other myxosporeans (Figure 7; see also Figure 4 of Sekiya et al. [25]).
4. Discussion
Classical taxonomy of Myxozoa based on morphological criteria uses phenotypical characteristics of myxospores such as the number of SVs and PCs, arrangement of the PCs, and SV ornamentation, together with host specificity, site preference of the plasmodium, and geographical distribution [6,8]. A high degree of phenotypical plasticity of myxospores and multiple examples of convergent evolution often render the specific identification difficult [37,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57]. Currently, phylogenetic analyses based on nucleotide sequences of SSU rDNA and/or other genes, e.g., the internal transcribed spacer region 1, the elongation factor 2 gene, mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase (cox-1), and mitochondrial small and large subunit ribosomal RNA genes, have become ineluctable techniques for reliable species differentiation [5,21,58,59]. An apparent obstruction for the current taxonomic approach is the unavailability of sufficient molecular–genetic data of myxosporeans, particularly those of the species recorded from wild fish.
In the present study, three new myxosporean isolates from Japan, i.e., Myxobolus tribolodonus sp. n. (syn. M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000; and M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015 from the gills of Pseudaspius spp. in the rivers on the Sakhalin Island and Maritime Province (Primorsky Kray) of Russian Far East), Henneguya pungitii, and Mixidium salvelini, could be differentiated based on the classical taxonomic criteria. All of these species from freshwater fishes in Japan are new distribution records, but their host species have been recorded for each species from the Russian Far East [24,35]. Concurrent molecular–genetic characterization of these new isolates of known species could make it possible to perform reliable identification of the species isolated from the field and clarify their phylogenetic relationships with closely-related species in morphology and/or other biological traits (host specificity, site preference, geographical distribution, etc.). As discussed above, Russian researchers [34,35] identified Myxobolus sp. from the gills of Pseudaspius spp. (Cyprinidae) in the Russian Far East as M. marinus Dogiel, 1948, which had been synonymized by Shulman [22] to Myxobolus macrocapsularis, parasitizing the gills and other visceral organs of a variety of cyprids. Morphologically, these two isolates, i.e., M. marinus sensu Aseeva, 2000 and M. marinus sensu Sokolov et Frolova, 2015, are identical to the new isolate from the gills of Pseudaspius sachalinensis in Hokkaido, Japan, although the myxospores of the former isolates are marginally larger than those of the Japanese isolate. It is interesting to explore phylogenetic relationships of species collected from geographically separated host populations (Russian Far East and Hokkaido Island of Japan).
Henneguya pungitii isolates from the subcutis of Prungitius spp., distributed in the Russian Far East and Hokkaido Island of Japan, show highly identical morphology of myxospores (Table 3). On the other hand, H. pungitii from Pungitius pungitius in the rivers on Kolguyev Island, near Kanin Peninsula (Russia), which was reported recently by Dorovskikh [39], showed site preferences to the gills and liver, and its myxospores were apparently smaller than the isolates from the subcutis of the same host distributed in the Russian Far East and Hokkaido. Prungitius spp. are known to have multiple evolutionarily, geographically, and ecologically separated populations [60]. It is interesting to reveal coevolutional relationships of myxosporeans with their hosts using phenotypically and geographically separated populations of H. pungitii. In addition to the possible coevolutionary speciation, sympatric speciation of myxosporeans through occupation of distinct microhabitats within a single host species has also been suggested [53,61].
Currently, it is generally recognized that there is no phylogenetically consistent pattern congruent with host family, tissue tropism, or myxospore morphology [53,61]. At individual clade levels, however, apparent clustering of myxosporeans originating from the same order/family of the host fish has been demonstrated by many studies [3,62,63,64]. Moreover, polyphyly or paraphyly of multiple myxosporean genera such as Myxobolus, Henneguya, Sphaerospora, Myxidium, Zschokkella, and Chloromyxum have been demonstrated [8,25,58,59,61,65,66]. These phylogenetic relationships of taxa classified in different genera are reflected in Figure 7 in the present study.
5. Conclusions
The majority of myxosporean species of the genera Myxobolus, Henneguya, and Myxidium from natural freshwater fish in Japan (Supplementary Table S1) remain to be molecular-genetically characterized. Synchronized efforts to accumulate at least SSU rDNA sequences of known or unknown species worldwide will be invaluable, not only for reliable species identification, but also for further understanding of evolutional history and global dispersion of different myxosporean species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/life14080974/s1, Supplementary Table S1: Myxosporean species of the genera Myxobolus, Henneguya, and Myxidium, recorded in Japan; Supplementary Table S2: Fish specimens examined in our survey of myxosporeans in freshwater fish provided by Aquatotto Gifu, Japan; and Supplementary Table S3: Myxobolus spp. parasitizing the gills of freshwater fish, with myxospore length (SL) ranging between 7 µm and 10 µm and almost equal-sized polar capsules, like M. tribolodonus sp. n. All references cited in the supplementary materials [9,22,23,28,29,40,42,43,44,47,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118] are included in the reference list below.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S., H.S. (Haruya Sakai), and H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); methodology, M.S., H.S. (Haruya Sakai), Y.-C.L., and I.R.; software, I.R. and M.Y.; validation, I.R., M.Y., and H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); data curation, M.S., H.S. (Haruya Sakai), and Y.-C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S., H.S. (Haruya Sakai), and I.R.; writing—review and editing, Y.-C.L., M.Y., and H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); visualization, H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); supervision, H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); project administration, H.S. (Hiroshi Sato); funding acquisition, H.S. (Hiroshi Sato). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Food Science and Research 2019 from The Toyo Suisan Foundation (HS), JSPS Kakenhi (grant number 18K05995; HS), The Yanmar Environmental Sustainability Support Association (grant number KI0222007; HS), and a Grant-in-Aid for International Collaboration Research in Asia 2023 from the Heiwa Nakajima Foundation (M.Y., Y.C.L., and H.S.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Myxosporean specimens collected in this study are deposited in the Meguro Parasitological Museum, Tokyo, Japan, under collection nos. 21656–21658. The nucleotide sequence obtained in this study is available from the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under accession no. LC544125–LC544127. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to the staff of Gifu World Fresh Water Aquarium (Aqua Totto Gifu) for kindly providing the preserved fish materials for this study. Their daily health checks and dedicated care of the fish under their supervision enabled freshly dead samples to be promptly available for parasitological examination. We thank the anonymous reviewers for their careful reading of our manuscript and their many insightful comments and suggestions, which have helped improve the quality of our manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Okamura, B.; Gruhl, A.; Bartholomew, J.L. Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; p. 441. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, J.D.W.; Whitaker, D.J.; Kent, M.L. A review of the myxosporean genus Kudoa Meglitsch, 1947, and its impact on the international aquaculture industry and commercial fisheries. Aquaculture 1999, 172, 163–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.L.; Andree, K.B.; Bartholomew, J.L.; El-Matbouli, M.; Desser, S.S.; Devlin, R.H.; Feist, S.W.; Hedrick, R.P.; Hoffmann, R.W.; Khattra, J.; et al. Recent advances in our knowledge of the Myxozoa. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2001, 48, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Grabner, D.; Shirakashi, S. Transmission biology of the Myxozoa. In Health and environment in Aquaculure; Carvalho, E.D., David, G.S., Silva, R.J., Eds.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, B.; Hartigan, A.; Naldoni, J. Extensive uncharted biodiversity: The parasite dimension. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2018, 58, 1132–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lom, J.; Dyková, I. Myxozoan genera: Definition and notes on taxonomy, life-cycle terminology and pathogenic species. Folia Parasitol. 2006, 53, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q. Animal biodiversity: An introduction to higher-level classification and taxonomic richness. Zootaxa 2011, 3148, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, I.; Bartošová-Sojková, P.; Whipps, C.M. Classification and phylogenetics of Myxozoa. In Myxozoan Evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 85–110. [Google Scholar]
- Eiras, J.C.; Molnár, K.; Lu, Y.S. Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2005, 61, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C.; Zhang, J.; Molnár, K. Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) described between 2005 and 2013. Syst. Parasitol. 2014, 88, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C.; Cruz, C.C.; Saraiva, A.; Adriano, E.A. Synopsis of the species of Myxobolus (Cnidaria: Myxozoa: Myxosporea) described between 2014 and 2020. Folia Parasitol. 2021, 68, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C. Synopsis of the species of the genus Henneguya Thélohan, 1892 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2002, 52, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C. Synopsis of the species of Ceratomyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2006, 65, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, J.C.; Saraiva, A.; Cruz, C.F.; Santos, M.J.; Fiala, I. Synopsis of the species of Myxidium Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Bivalvulida). Syst. Parasitol. 2011, 80, 81–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C.; Lu, Y.S.; Gibson, D.I.; Fiala, I.; Saraiva, A.; Cruz, C.; Santos, M.J. Synopsis of the species of Chloromyxum Mingazinni, 1890 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Chloromyxidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2012, 83, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C.; Cruz, C.; Saraiva, A. Synopsis of the species of Ceratomyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Cnidaria, Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae) described between 2007 and 2017. Syst. Parasitol. 2018, 95, 427–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunter, N.; Adlard, R. The demise of Leptotheca Thélohan, 1895 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae) and assignment of its species to Ceratomyxa Thélohan, 1892 (Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae), Ellipsomyxa Køie, 2003 (Myxosporea: Ceratomyxidae), Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 and Sphaerospora Thélohan, 1892 (Myxosporea: Sphaerosporidae). Syst. Parasitol. 2010, 75, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiras, J.C.; Adriano, E.A. A checklist of new species of Henneguya Thélohan, 1892 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) described between 2002 and 2012. Syst. Parasitol. 2012, 83, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Gu, Z.M.; Kalavati, C.; Eiras, J.C.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.Y.; Molnár, K. Synopsis of the species of Thelohanellus Kudo, 1933 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Bivalvulida). Syst. Parasitol. 2013, 86, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, E.J. A Guide to the Identification of Tailed Myxobolidae of the World: Dicauda, Hennegoides, Henneguya, Laterocaudata, Neohenneguya, Phlogospora, Tetrauromena, Trigonosporus and Unicauda; Fish Creek Records: Logan, UT, USA, 2016; pp. 1–166, Textbooks. 1; Utah State University; Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/oer_textbooks/ (accessed on 23 August 2019).
- Atkinson, S.D.; Bartošová-Sojková, P.; Whipps, C.M.; Bartholomew, J.L. Approaches for characterising myxozoan species. In Myxozoan evolution, Ecology and Development; Okamura, B., Gruhl, A., Bartholomew, J.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, S.S. Myxosporidia of the USSR, Izdatel’stvo Nauka AN SSSR, Moscow-Leningrad, USSR.; English version in 1988; Kothekar, V.S., Ed.; Amerind Publishing Co.: New Delhi, India, 1966; pp. 1–631. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Ma, C. Fauna Sinica: Myxozoa, Myxosporea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998; pp. 1–806. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Aseeva, N.L.; Ermolenko, A.V.; Shedko, M.B. Myxosporidia (Myxozoa, Myxosporea) of the Marine and Anadromous Fish in Japan Sea Basin; FSCEATB FEB RAS: Vladivostok, Russia, 2022; pp. 1–229. ISBN 978-5-6048441-0-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya, M.; Rosyadi, I.; Zhang, J.; Sato, H. Morphological and molecular-genetic characterization of Chloromyxum trilineatum n. sp. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) in the gall bladder of pale chub (Zacco platypus) in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 3349–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lom, J.; Arthur, J.R. A guideline for the preparation of species descriptions in Myxosporea. J. Fish Dis. 1989, 12, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopečná, J.; Jirku, M.; Oborník, M.; Tokarev, Y.S.; Lukes, J.; Modrý, D. Phylogenetic analysis of coccidian parasites from invertebrates: Search for missing links. Protist 2006, 157, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-C.; Sato, H.; Kamata, Y.; Ohnishi, T.; Sugita-Konishi, Y. Three novel myxobolid species of genera Henneguya and Myxobolus (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) from marine fish in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, E.; Kasai, A.; Tomochi, H.; Li, Y.-C.; Sato, H. Four Myxobolus spp. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) from the gill lamellae of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Japanese silver crucian carp (Carassius langsdorfii) in the western part of Japan, with the description of three new species (M. tanakai n. sp.; M. paratoyamai n. sp.; and M. ginbuna n. sp.). Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereeper, A.; Guignon, V.; Blanc, G.; Audic, S.; Buffet, S.; Chevenet, F.; Dufayard, J.F.; Guindon, S.; Lefort, V.; Lescot, M.; et al. Phylogeny.fr: Robust phylogenetic analysis for the non-specialist. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aseeva, N.L. Myxosporidia of anadromous and marine coastal fishes of the northwestern part of the Sea of Japan. Izv. TINRO 2000, 127, 593–606. Available online: https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/miksosporidii-anadromnyh-i-morskih-pribrezhnyh-ryb-severo-zapadnoy-chasti-yaponskogo-morya/viewer (accessed on 6 July 2024). (In Russian).
- Sokolov, S.G.; Frolova, S.E. Data of the Parasite Fauna of the Sakhalin Fishes. VESTNIK SVNTS DVO RAN 2015, 2015, 90–97. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Sergey-Sokolov-5/publication/340435929_DATA_OF_THE_PARASITE_FAUNA_OF_THE_SAKHALIN_FISHES/links/5e889c13a6fdcca789f46961/DATA-OF-THE-PARASITE-FAUNA-OF-THE-SAKHALIN-FISHES.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2024). (In Russian with English summary).
- Dogiel, V.A. Parasitic protozans of the Gulf of Peter the Great. Izv. Vsesoyuzn Nauchno-Issled. Inst. Ozern. I Rechn. Rybn. Khoz. 1948, 27, 17–66. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, K.; Cech, G.; Székely, C. Histological and molecular studies of species of Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in the gills of Abramis, Blicca and Vimba spp. (Cyprinidae), with the redescription of M. macrocapsularis Reuss, 1906 and M. bliccae Donec & Tozyyakova, 1984. Syst. Parasitol. 2011, 79, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, K. Site preference of fish myxosporeans in the gill. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 48, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorovskikh, G.N. Findings of myxosporidium Henneguya pungitii Achmerov, 1953 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in nine-spined stickleback Pungitius pungitius (Linnaeus, 1758) from reservoirs of Kolguev Island. Vestn. Syktyvkarskogo Universiteta. Seriya 2. Biol. Geol. Him. Ekol. (= Syktyvkar Univ. Bulletin. Ser. 2. Biol. Geol. Chem. Ecol.) 2022, 4, 39–52. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Kageyama, T.; Yanagida, T.; Ohara, K.; Yokoyama, H. Henneguya pseudorhinogobii n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) parasitizing the gills of the freshwater goby Rhinogobius sp. OR from the Nagara River and redescription of Henneguya rhinogobii. Fish. Sci. 2009, 75, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, C.; Matos, E. Fine structure of Henneguya pilosa sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea), parasite of Serrasalmus altuvei (Characidae), in Brazil. Folia Parasitol. 2003, 50, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, T. Studies on Myxosporidia of Japan. 5. On Myxosporidia in fishes of Lake Biwa. J. Coll. Agric. Hokkaido Imp. Univ. 1927, 16, 229–247. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, T. Studies on Myxosporidia of Japan. J. Coll. Agric. Hokkaido Imp. Univ. 1923, 10, 191–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, R.R. Studies on the Myxosporidia: A synopsis of genera and species of Myxosporidia. Ill. Biol. Monogr. 1920, 5, 1–265. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Pellitero, M.P.; Pereira-Bueno, J.M.; González-Lanza, C. Celozoic myxosporidians (Myxidium spp. and Chloromyxum spp.) of cyprinids from the river Esla (León, NW Spain). I. Description of the species. Angew. Parasitol. 1983, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg, J.H. Myxosporean parasites of the catfish Clarias lazera (Valenciennes). Syst. Parasitol. 1987, 9, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. The skin-disease of the eel. Annot. Zool. Jpn. 1929, 12, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Kalavati, C.; Nandi, N.C. Handbook on Myxosporean Parasites of Indian Fishes; Zoological Survey of India: Kolkata, India, 2007; pp. 1–294. [Google Scholar]
- Molnár, K.; Eszterbauer, E.; Marton, S.; Székely, C.; Eiras, J.C. Comparison of the Myxobolus fauna of common barbel from Hungary and Iberian barbel from Portugal. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2012, 100, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, K.Y.; Desser, S.S. Descriptions and phylogenetic systematics of Myxobolus spp. from cyprinids in Algonquin Park, Ontario. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2000, 47, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eszterbauer, E. Molecular biology can differentiate morphologically indistinguishable myxosporean species: Myxobolus elegans and M. hungaricus. Acta Vet. Hung. 2002, 50, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnár, K.; Eszterbauer, E.; Székely, C.; Dán, Á.; Harrach, B. Morphological and molecular biological studies on intramuscular Myxobolus spp. of cyprinid fish. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, J.A.; Atkinson, S.D.; Whipps, C.M.; Kent, M.L. Molecular and morphological analysis of Myxobolus spp. of salmonid fishes with the description of a new Myxobolus species. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 1322–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cech, G.; Molnár, K.; Székely, C. Molecular genetic studies on morphologically indistinguishable Myxobolus spp. infecting cyprinid fishes, with the description of three new species, M. alvarezae sp. nov.; M. sitjae sp. nov. and M. eirasianus sp. nov. Acta Parasitol. 2012, 57, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Yuan, S.; Zhao, Y.L.; Fang, P.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.Y. Morphological and molecular characterization of Myxobolus sheyangensis n. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) with intralamellar sporulation in allogynogenetic gibel carp, Carassius auratus gibelio (Bloch) in China. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 3567–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Kent, M.L.; Deng, J.; Whipps, C.M. Description of a new species of Myxobolus (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) based on morphological and molecular data. J. Parasitol. 2008, 94, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Li, N.N.; Tang, F.H.; Dong, J.L. Remarks on the validity of Myxobolus ampullicapsulatus and Myxobolus honghuensis (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) based on SSU rDNA sequences. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3817–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, I. The phylogeny of Myxosporea (Myxozoa) based on small subunit ribosomal RNA gene analysis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2006, 36, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, I.; Bartošová-Sojková, P. History of myxozoan character evolution on the basis of rDNA and EF-2 data. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, K.; Goto, A.; Yamazaki, F. Biochemical identification of a brackish water type of Pungitius pungitius, and its morphological and ecological features in Hokkaido, Japan. Jpn. J. Ichthyol. 1987, 34, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easy, R.H.; Johnson, S.C.; Cone, D.K. Morphological and molecular comparison of Myxobolus procerus (Kudo, 1934) and M. intramusculi n. sp. (Myxozoa) parasitising muscles of the trout-perch Percopsis omiscomaycus. Syst. Parasitol. 2005, 61, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriano, E.A.; Carriero, M.M.; Maia, A.A.; Silva, M.R.; Naldoni, J.; Ceccarelli, P.S.; Arana, S. Phylogenetic and host-parasite relationship analysis of Henneguya multiplasmodialis n. sp. infecting Pseudoplatystoma spp. in Brazilian Pantanal wetland. Vet Parasitol. 2012, 185, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriero, M.M.; Adriano, E.A.; Silva, M.R.; Ceccarelli, P.S.; Maia, A.A. Molecular phylogeny of the Myxobolus and Henneguya genera with several new South American species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capodifoglio, K.R.; Adriano, E.A.; Milanin, T.; Silva, M.R.; Maia, A.A. Morphological, ultrastructural and phylogenetic analyses of Myxobolus hilarii n. sp. (Myxozoa, Myxosporea), a renal parasite of farmed Brycon hilarii in Brazil. Parasitol. Int. 2016, 65, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, R.J.; Adlard, R.D. Phylogenetic relationships amongst Chloromyxum Mingazzini, 1890 (Myxozoa: Myxosporea), and the description of six novel species from Australian elasmobranchs. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Voronin, V.N.; Dudin, A.S.; Morozova, D.A.; Zhang, J.Y. Morphological and molecular characterization of a new cyprinid gall bladder-infecting Chloromyxum species, Chloromyxum peleci sp. n. (Myxozoa: Chloromyxidae), from Pelecus cultratus (L.) in Russia. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, R.R. A taxonomic consideration of the Myxosporidia. Trans. Am. Micros. Soc. 1933, 52, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsberg, J.H.; Lom, J. Taxonomy of the genera of the Myxobolus/Myxosoma group (Myxobolidae: Myxosporea), current listing of species and revision of synonyms. Syst. Parasitol. 1991, 18, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Notes on new sporozoan parasites of fishes. Zool. Anz. 1912, 39, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Awakura, T.; Kojima, H.; Sugiwaka, K.; Ogawa, T. Studies of parasites of masu salmon Oncorhynchus masou–III.; Myxobolus (Protozoa: Myxosporea) found in spinal cord. Sci. Rep. Hokkaido Fish. Hatch. 1982, 37, 37–47. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Awakura, T.; Nagasawa, K.; Urawa, S. Occurrence of Myxobolus arcticus and M. neurobius (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in masu salmon Oncorhynchus masou from northern Japan. Sci. Rep. Hokkaido Salmon Hatch. 1995, 49, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Urawa, S.; Nagasawa, K. Prevalence of Myxobolus arcticus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in five species of Pacific salmon in the North Pacific Ocean and Bering Sea. Sci. Rep. Hokkaido Salmon Hatch. 1995, 49, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Urawa, S.; Freeman, M.A.; Johnson, S.C.; Jones, S.R.M.; Yokoyama, H. Geographical variation in spore morphology, gene sequences, and host specificity of Myxobolus arcticus (Myxozoa) infecting salmonid nerve tissues. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 96, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Delgahapitiya, K.P.; Furuta, T.; Wakabayashi, H. Histological studies on the host response to Myxobolus artus Akhmerov, 1960 (Myxozoa: Myxobolidae) infection in the skeletal muscle of carp, Cyprinus carpio L. J. Fish Biol. 1992, 41, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Danjo, T.; Ogawa, K.; Arima, T.; Wakabayashi, H. Hemorrhagic anemia of carp associated with spore discharge of Myxobolus artus (Myxozoa: Myxosporea). Fish Pathol. 1996, 31, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Ishizaki, H. Myxosporidian parasites of Tridentiger obscurus (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Sci. Hiroshima Univ. Ser. B Div. 1 (Zool.) 1941, 9, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, H.; Ogawa, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Myxobolus cultus n. sp. (Myxosporea: Myxobolidae) in the goldfish Carassius auratus tranformed from the actinosporean stage in the oligochaete Branchiura sowerbyi. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S. Lentospora parasitic in the skin of the Japanese eel. Zool. Mag. 1915, 27, 471–474. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina, T. On a new myxosporidian parasite Myxobolus dermatobius n. sp. parasitic in the integument of Cyprinus carpio L. J. Tokyo Univ. Fish. 1953, 39, 209–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, R.R. Contributions to the study of parasitic protozoa. III. Notes on some Myxosporidia found in some fresh-water fishes of Japan, with the description of three new species. J. Parasitol. 1916, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Studies on myxosporidian infection of the crucian carp. Jpn. J. Zool. 1924, 1, 45–57. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, K.; Awakura, T.; Urakawa, S. A checklist and bibliography of parasites of freshwater fishes of Hokkaido. Sci. Rep. Hokkaido Fish Hatch. 1989, 44, 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.; Hoshina, T. Myxosoma gnathopogonae sp. nov. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) found in the cutis of the roach Gnathopogon elongatus caerulescens. Jpn. J. Parasitol. 1983, 32, 377–378. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, N. On a new myxosporidian Myxobolus koi nov. sp. parasitic in gills of the carp. J. Imp. Fish. Inst. Tokyo 1926, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshina, T. Notes on some myxosporidian parasites on fish of Japan. J. Tokyo Univ. Fish. 1952, 39, 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Yokoyama, H.; Inoue, D.; Kumamaru, A.; Wakabayashi, H. Myxobolus koi (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) forms large-and small-type ‘cysts’ in the gills of common carp. Fish Pathol. 1997, 32, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaki, H. Notes on two myxosporidian parasites of fish. Bull. Fukuoka Gakugei Univ. 1957, 7, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.-C.; Sato, H. Two novel myxosporean species (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida), Myxobolus marumotoi n. sp. and Cardimyxobolus japonensis n. sp.; from the dark sleeper, Odontobutis obscura, in Japan. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urawa, S.; Iida, Y.; Freeman, M.A.; Yanagida, T.; Karlsbakk, E.; Yokoyama, H. Morphological and molecular comparisons of Myxobolus spp. in the nerve tissues of salmonid fishes with the description of Myxobolus murakamii n. sp.; the causative agent of myxosporean sleeping disease. Fish Pathol. 2009, 44, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yokoyama, H.; Kageyama, T.; Ohara, K.; Yanagida, T. Myxobolus nagaraensis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) causes abdominal distension of freshwater goby Rhinogobius sp. OR type from the Nagara Riber. Fish. Sci. 2007, 73, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Huang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gu, Z. Morphological plasticity in Myxobolus Bütschli, 1882: A taxonomic dilemma case and renaming of a parasite species of the common carp. Parasit. Vectors 2018, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshina, T. On the new myxosporidian parasite of the genus Myxosoma, M. salmonis n. sp. infecting the scales of the dog salmon (Oncorhynchus keta). Seibutsu 1949, 4, 106–109. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Kudo, R.R. tributions to the study of parasitic protozoa. II. Myxobolus toyamai nov. spec.; a new myxosporidian parasite in Cyprinus carpio L. J. Parasitol. 1917, 3, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Ogawa, K. The resurrection of Myxobolus toyamai with a validation of a stunted polar capsule based on morphological evidence. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Yokoyama, H.; Wang, J.G.; Li, A.H.; Gong, X.N.; Ryu-Hasegawa, A.; Iwashita, M.; Ogawa, K. Utilization of tissue habitats by Myxobolus wulii Landsberg & Lom, 1991 in different carp hosts and disease resistance in allogynogenetic gibel carp: Redescription of M. wulii from China and Japan. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egusa, S. Myxobolus buri sp. n. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) parasitic in the brain of Seriola quinqueradiata Temminck et Schlegel. Fish Pathol. 1985, 19, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, Y.; Sorimachi, M.; Ogawa, K.; Kearn, G.C. Myxobolus spirosulcatus n. sp. (Myxosporea, Bivalvulida) infecting the bile duct of the yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata from Japan. Syst. Parasitol. 1995, 31, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Freeman, M.A.; Yoshinaga, T.; Ogawa, K. Myxobolus buri, the myxosporean parasite causing scoliosis of yellowtail, is synonymous with Myxobolus acanthogobii infecting the brain of the yellowfin goby. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Freeman, M.A.; Itoh, N.; Fukuda, Y. Spinal curvature of cultured Japanese mackerel Scomber japonicus associated with a brain myxosporean, Myxobolus acanthogobii. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 66, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Fukuda, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Ogawa, K. A PCR method to detect Myxobolus acanthogobii (Myxozoa: Myxosporea), the causative agent of skeletal deformities of marine fishes. Fish Pathol. 2005, 40, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusa, S.; Maeno, Y.; Sorimachi, M. A new species of Myxozoa, Myxobolus episquamalis sp. nov. infecting the scales of the mullet, Mugil cephalus L. Fish Pathol. 1990, 25, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurakhno, V.M.; Ovcharenko, M.O. Study of Myxosporea (Myxozoa), infecting worldwide mullets with description of a new species. Parasitol. Res. 2014, 113, 3661–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Maeno, Y.; Sorimachi, M.; Ogawa, K.; Egusa, S. Myxobolus spinacurvatura sp. n. (Myxosporea: Bivalvulida) parasitic in deformed mullet, Mugil cephalus. Fish Pathol. 1990, 25, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Yanagida, T.; Freeman, M.A.; Kaatagiri, T.; Hosokawa, A.; Endo, M.; Hirai, M.; Takagi, S. Molecular diagnosis of Myxobolus spirosulcatus associated with encephalomyelitis of culured yellowtail, Seriola quinqueradiata Temminck & Schlegel. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Urawa, S.; Grabner, D.; Shirakashi, S. Henneguya cartilaginis n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) in the head cartilage of masu salmon Oncorhynchus masou masou. Parasitol. Int. 2012, 61, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T. Notes on some Myxosporidia in freshwater fishes. Zool. Mag. 1936, 48, 595–601. [Google Scholar]
- Nitta, M.; Ishikawa, T. New Japanese record of Henneguya postexilis (Cnidaria: Myxobolidae) from gills of alien channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus (Siluriformes: Ictaluridae) in Japan. Species Divers. 2024, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Kawakami, H.; Yasuda, H.; Tanaka, S. Henneguya lateolabracis sp. n. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea), the causative agent of cardiac henneguyosis in Chinese sea bass Lateolabrax sp. Fish. Sci. 2003, 69, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, H.; Itoh, N.; Tanaka, S. Henneguya pagri n. sp. (Myxozoa: Myxosporea) causing cardiac henneguyosis in red sea bream, Pagrus major (Temminck & Schlegel). J. Fish Dis. 2005, 28, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S. Myxosporidiosis of Japanese eel. Zool. Mag. 1915, 27, 372–383. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Hine, P.M. Review of some species of Myxidium Bütschli, 1882 (Myxosporea) from eels (Anguilla spp.). J. Protozool. 1980, 27, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasri, M.; Hoffman, G.L. Review of Myxidium (Protozoa: Myxozoa: Myxosporea). Protozool Abstr. 1982, 6, 61–91. [Google Scholar]
- Nagasawa, K.; Umino, T.; Mizuno, K. A checklist of the parasites of eels (Anguilla spp.) (Anguilliformes: Anguillidae) in Japan (1915–2007). J. Grad. Sch. Biosp. Sci. Hiroshima Univ. 2007, 46, 91–121. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, S. On a myxosporidian parasitic in the fin of Japanese eel. Zool. Mag. 1916, 28, 271–272. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Moser, M.; Noble, E.R.; Lee, R.S. The genus Myxidium (Protozoa: Myxosporidia) in macrourid fishes. J. Parasitol. 1976, 62, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székely, C.; Shaharom, F.; Cech, G.; Mohamed, K.; Zin, N.A.M.; Borkhanuddin, M.H.; Ostoros, G.; Molnár, K. Myxozoan infection of the Malaysian mahseer, Tor tambroides, of Tasik Kenyir Reservoir, Malaysia: Description of a new species Myxobolus tambroides sp.n. Parasitol. Res. 2012, 111, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seenappa, D.; Manohar, L. Five new species of Myxobolus (Myxosporea: Protozoa), parasitic in Cirrhina mrigala (Hamilton) and Labeo rohita (Hamilton), with a note on a new host record for M. curmucae Seenappa & Manohar, 1980. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 1981, 28, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukhimenko, S.S. New species of myxosporidians in the genus Myxobolus (Myxosporidia, Myxobolidae) from cyprinid fishes of the Amur River. Parazitologiia 1986, 20, 416–421. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).