Localization Accuracy of Ultrasound-Actuated Needle with Color Doppler Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
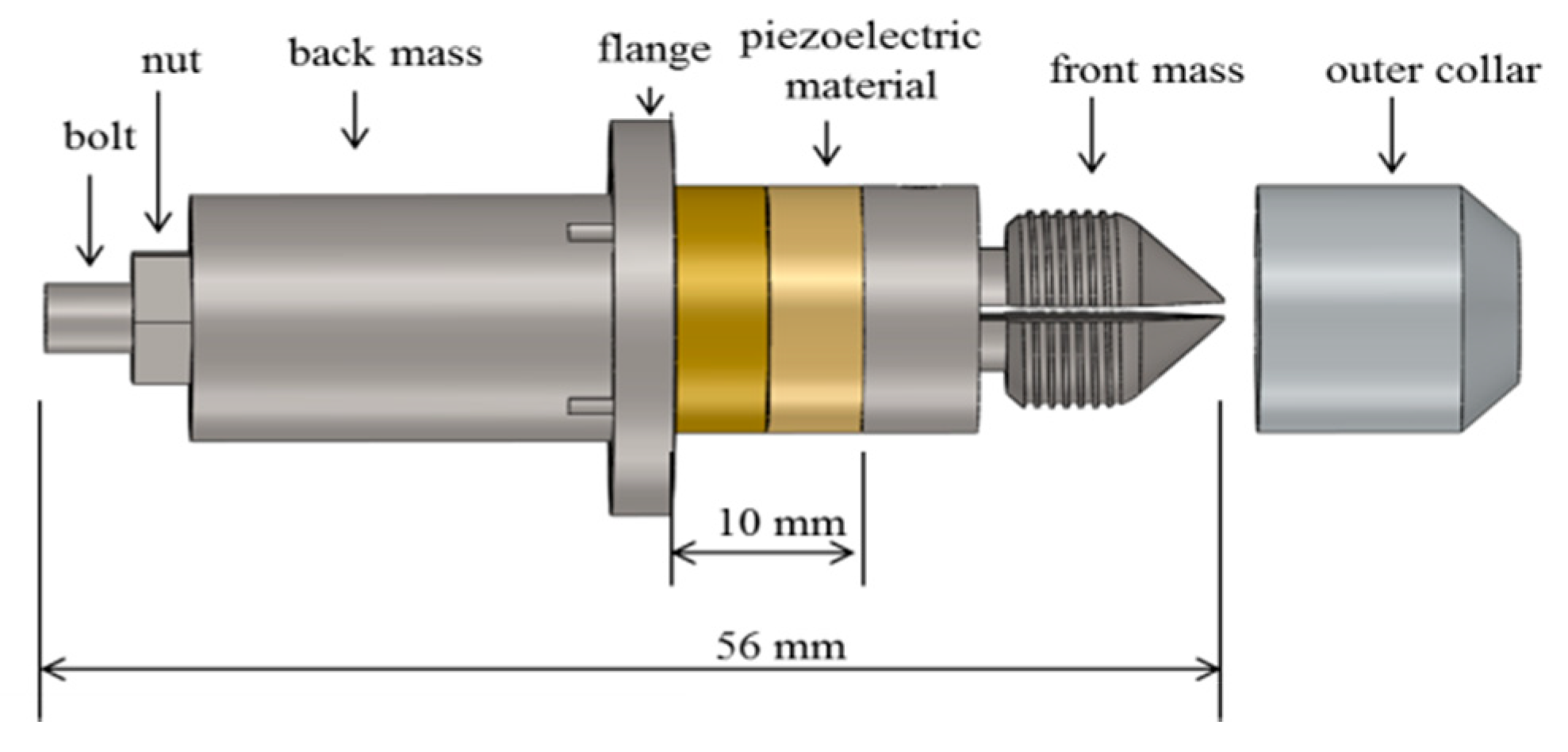
2.1. Fabrication and Characterization of Needle Actuation Transducer
2.2. Overall Experimental Setup
2.3. Needle Visibility Test
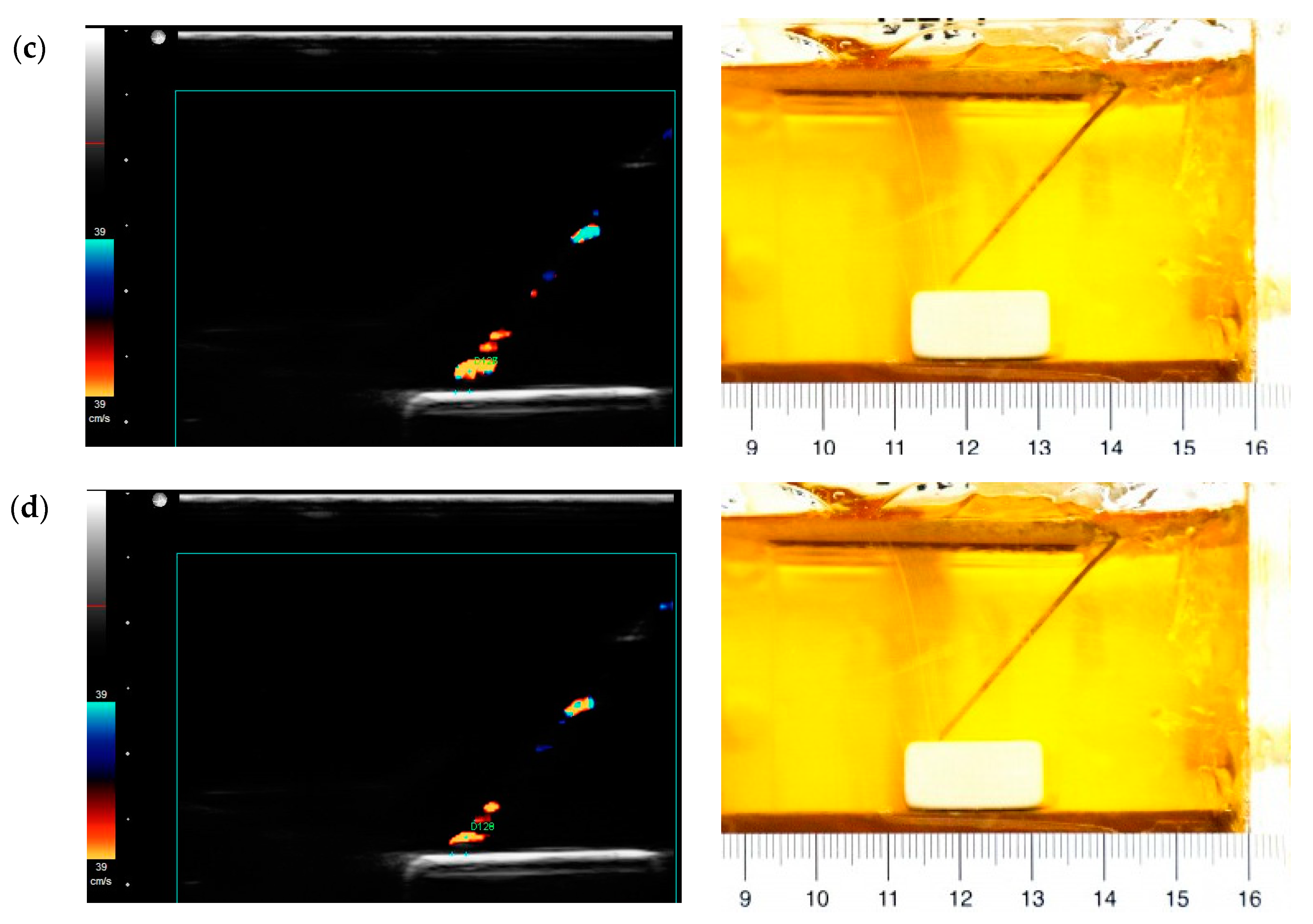
2.4. Needle Accuracy Test: Color Doppler vs. Photographic
2.5. Needle Accuracy Test: Color Doppler vs. Greyscale
3. Results
3.1. Needle Visibility Test: Effect of Drive Voltage on Needle Visibility
3.2. Needle Visibility Test: Effect of Insertion Angle on Needle Visibility
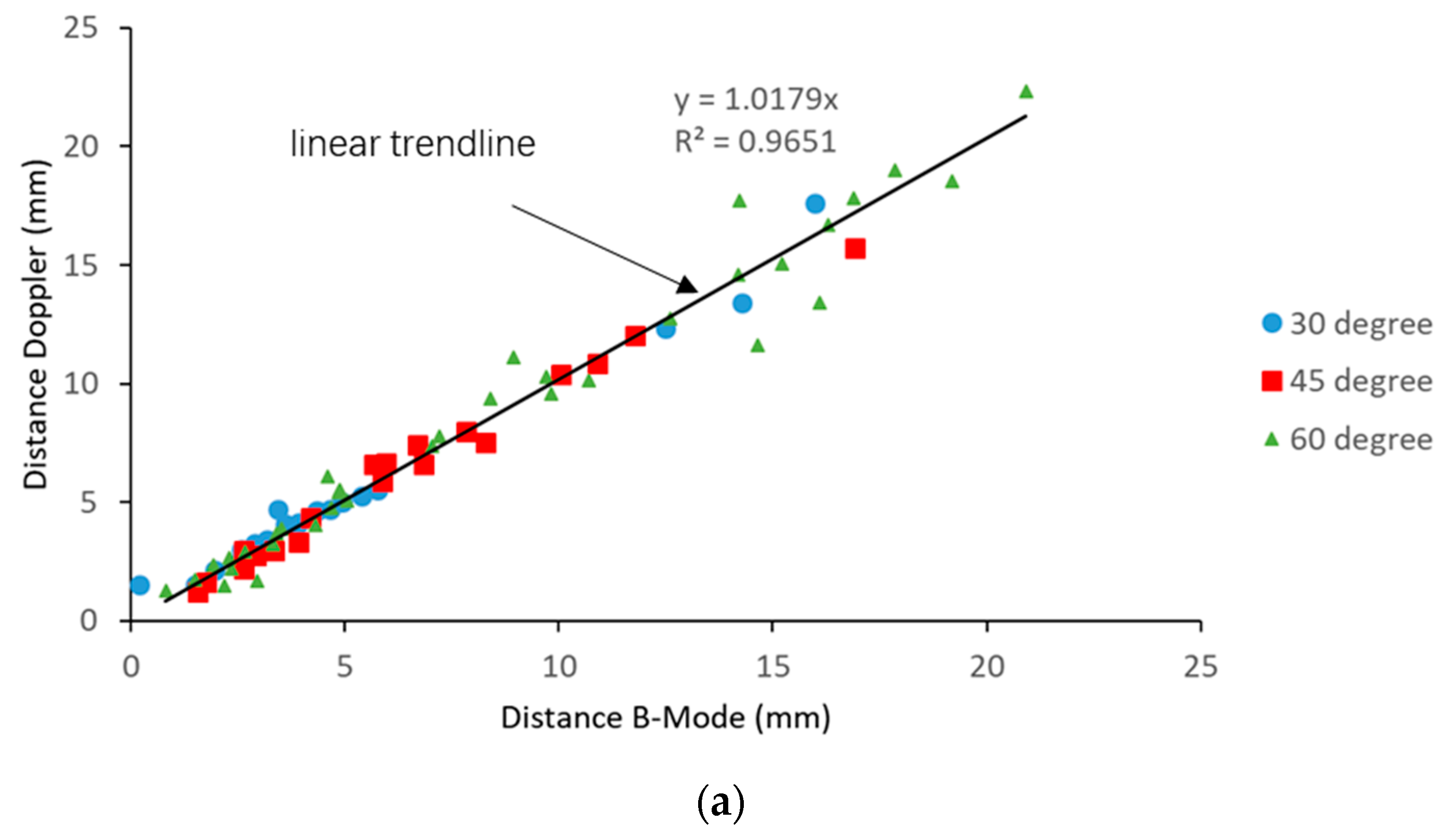
3.3. Needle Accuracy Test: Color Doppler vs. Photographic
3.4. Needle Accuracy Test: Color Doppler vs. Greyscale
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baloch, Z.W.; Tam, D.; Langer, J.; Mandel, S.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Gupta, P.K. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of the thyroid: Role of on-site assessment and multiple cytologic preparations. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2000, 23, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhofer, P.; Greher, M.; Kapral, S. Ultrasound guidance in regional anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 94, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rha, D.-W.; Im, S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, S.-K. Needle Insertion into the Tibialis Posterior: Ultrasonographic Evaluation of an Anterior Approach. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munirama, S.; Joy, J.; Columb, M.; Habershaw, R.; Eisma, R.; Corner, G.; Cochran, S.; McLeod, G.A. A randomised, single-blind technical study comparing the ultrasonic visibility of smooth-surfaced and textured needles in a soft embalmed cadaver model. Anaesthesia 2014, 70, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abolhassani, N.; Patel, R.V. Deflection of a flexible needle during insertion into soft tissue. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 3858–3861. (In English). [Google Scholar]
- Chin, K.J.; Perlas, A.; Chan, V.W.; Brull, R. Needle Visualization in Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia: Challenges and Solutions. Reg. Anesthesia Pain Med. 2008, 33, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.K.; Kingston, J.E.; Domizio, P.; Norton, A.J.; Reznek, R.H. Imaging-Guided Core Biopsy for the Diagnosis of Malignant Tumors in Pediatric Patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 176, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, P.L.; Narayana, V.; McShan, D.L.; Winfield, R.J.; McLaughlin, P.W. Source placement error for permanent implant of the prostate. Med. Phys. 1997, 24, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Schwab, A.; McLeod, G.; Corner, G.; Cochran, S.; Eisma, R.; Soames, R. Echogenic Regional Anaesthesia Needles: A Comparison Study in Thiel Cadavers. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebard, S.; Hocking, G. Echogenic Technology Can Improve Needle Visibility During Ultrasound-Guided Regional Anesthesia. Reg. Anesthesia Pain Med. 2011, 36, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.A.; Soo, M.S.; Mengoni, P. Sonographically guided percutaneous interventions of the breast using a steerable ultrasound beam. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheung, S.; Rohling, R. Enhancement of needle visibility in ultrasound-guided percutaneous procedures. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2004, 30, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.; Ernst, S.; Grust, A.; Furst, G.; Dall, P.; Modder, U. Real-time compound imaging: Improved visibility of biopsy needles and localization wires as compared to single-line ultrasonography. Rofo-Fortschritte Auf Dem Gebiet Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Bildgebenden Verfahren 2001, 173, 368–372. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fronheiser, M.P.; Wolf, P.D.; Idriss, S.F.; Nelson, R.C.; Lee, W.; Smith, S.W. Real-Time 3D Color Flow Doppler for Guidance of Vibrating Interventional Devices. Ultrason. Imaging 2004, 26, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettenbach, J.; Kronreif, G.; Figl, M.; Birkfellner, W.; Hanel, R.; Bergmann, H. Robot-assisted biopsy using ultrasound guidance: Initial results from in vitro tests. Eur. Radiol. 2004, 15, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, B.C.H. Facilitating needle alignment in-plane to an ultrasound beam using a portable laser unit. Reg. Anesthesia Pain Med. 2007, 32, 84–88. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.E. Ultrasonic Imaging of Biopsy Needle. U.S. Patent No. 5,095,910, 17 March 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Feld, R.; Needleman, L.; Goldberg, B.B. Use of needle-vibrating device and color Doppler imaging for sonographically guided invasive procedures. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1997, 168, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, C.D.; McGahan, J.P.; Clark, K.J. Color Doppler ultrasonographic detection of a vibrating needle system. J. Ultrasound Med. 1997, 16, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.; Cardon, L.; Vilkomerson, D.; Lipson, D.; Wong, J.; Leonardorodriguez, L.; Thomas, J.D.; Griffin, B.P. Localization of needle tip with color doppler during pericardiocentesis: In vitro validation and initial clinical application†. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2001, 14, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.; Cochran, S.; Huang, Z.; Corner, G.; McLeod, G.; Carena, P. Medical Apparatus and Its Visualization. U.S. Patent Application No. 14/777,514, 11 March 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Y.; Hilgers, A.; Sadiq, M.; Cochran, S.; Corner, G.; Huang, Z. Modelling and characterisation of a ultrasound-actuated needle for improved visibility in ultrasound-guided regional anaesthesia and tissue biopsy. Ultrasonics 2016, 69, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, X.C.; Sadiq, M.; Corner, G.; Cochran, S.; Huang, Z.H. Reduced Penetration Force through Ultrasound Activation of a Standard Needle an Experimental and Computational Study. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Prague, Czech Republic, 21–25 July 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1428–1431. [Google Scholar]
- Sadiq, M.R.; Cochran, S.; Liao, X.; Huang, Z. Enhanced US-guided needle intervention through ultrasound actuation of a standard needle. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Chicago, IL, USA, 3–6 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Xia, C.; Cochran, S.; Huang, Z. Improved Performance of d(31)-Mode Needle-Actuating Transducer With PMN-PT Piezocrystal. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control. 2018, 65, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bland, J.; Altman, D. Comparing methods of measurement: Why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet 1995, 346, 1085–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1999, 8, 135–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, P.; Cui, J.I. Using the Bland–Altman method to measure agreement with repeated measures. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bude, R.O.; Adler, R.S. An easily made, low-cost, tissue-like ultrasound phantom material. J. Clin. Ultrasound 1995, 23, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fornage, B.D. A simple phantom for training in ultrasound-guided needle biopsy using the freehand technique. J. Ultrasound Med. 1989, 8, 701–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Othman, N.S.; Jaafar, M.S.; Rahman, A.A.; Sazlinayati, E. Ultrasound propagation speed of polymer gel mimicked human soft tissue in 23 days. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology, Shanghai, China, 15–17 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Abolhassani, N.; Patel, R.; Moallem, M. Needle insertion into soft tissue: A survey. Med. Eng. Phys. 2007, 29, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.N.; Peiffer, J.S.; Halmann, N.; Delaney, L.; Owen, C.A.; Hersh, J. Ultrasound-Guided Needle Technique Accuracy: Prospective Comparison of Passive Magnetic Tracking Versus Unassisted Echogenic Needle Localization. Reg. Anesthesia Pain Med. 2017, 42, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]









| Parameter | 20% Gelatin Phantom | Porcine Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| Greyscale frequency | 10.0 MHz | 10.0 MHz |
| Doppler frequency | 6.6 MHz | 4.0 MHz |
| Depth | 5.0 cm | 5.0 cm |
| Sector | 100% | 100% |
| Greyscale gain | 55% | 60% |
| Doppler gain | 50% | 60% |
| Frame rate | 8 Hz | 7 Hz |
| PRF /WF | 4 kHz/1440 Hz | 4 kHz/840 Hz |
| Assumed speed of ultrasound | 1540 ms−1 | 1540 ms−1 |
| Insertion Angle | Total Number of Paired Measurements | Number of Excluded Measurement | Average Axis Error (mm) | Standard Deviation (SD) (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30° | 27 | 7 | −0.59 | 0.38 |
| 45° | 37 | 9 | −0.58 | 0.44 |
| 60° | 30 | 9 | −0.32 | 0.32 |
| All angles | 94 | 25 | −0.50 | 0.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, T.; McLeod, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, Z.; Cui, Y. Localization Accuracy of Ultrasound-Actuated Needle with Color Doppler Imaging. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121020
Jiang T, McLeod G, Huang Z, Zhu X, Jiao Y, Li X, Shen Z, Cui Y. Localization Accuracy of Ultrasound-Actuated Needle with Color Doppler Imaging. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121020
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Tingyi, Graeme McLeod, Zhihong Huang, Xinle Zhu, Yang Jiao, Xinze Li, Zhitian Shen, and Yaoyao Cui. 2020. "Localization Accuracy of Ultrasound-Actuated Needle with Color Doppler Imaging" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121020
APA StyleJiang, T., McLeod, G., Huang, Z., Zhu, X., Jiao, Y., Li, X., Shen, Z., & Cui, Y. (2020). Localization Accuracy of Ultrasound-Actuated Needle with Color Doppler Imaging. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121020





