Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. T Cell Lymphomas
2.1. Systemic Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALK+ ALCL)
2.1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
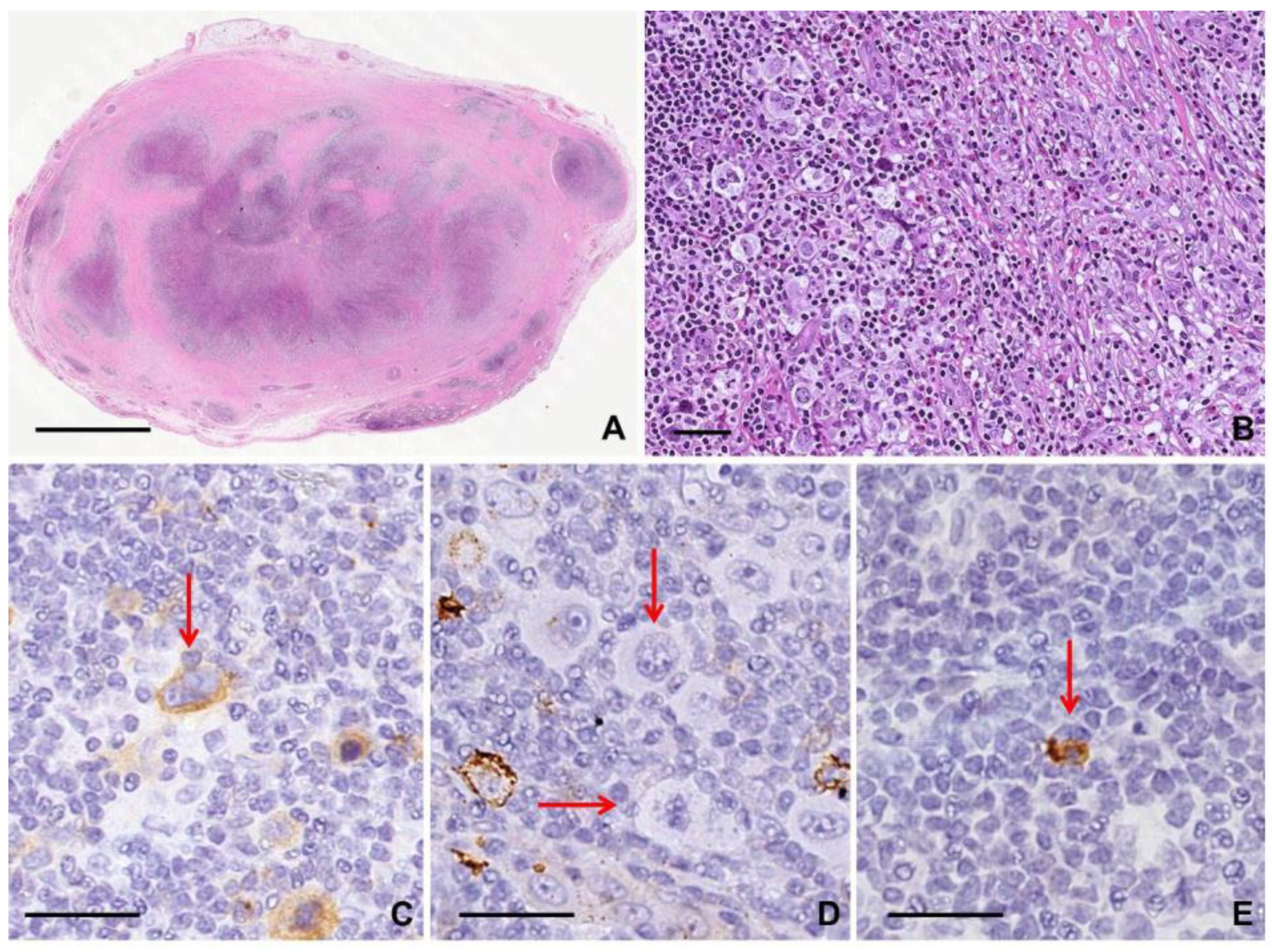
2.1.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
2.1.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
2.2. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Negative Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (ALK− ALCL)
2.2.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
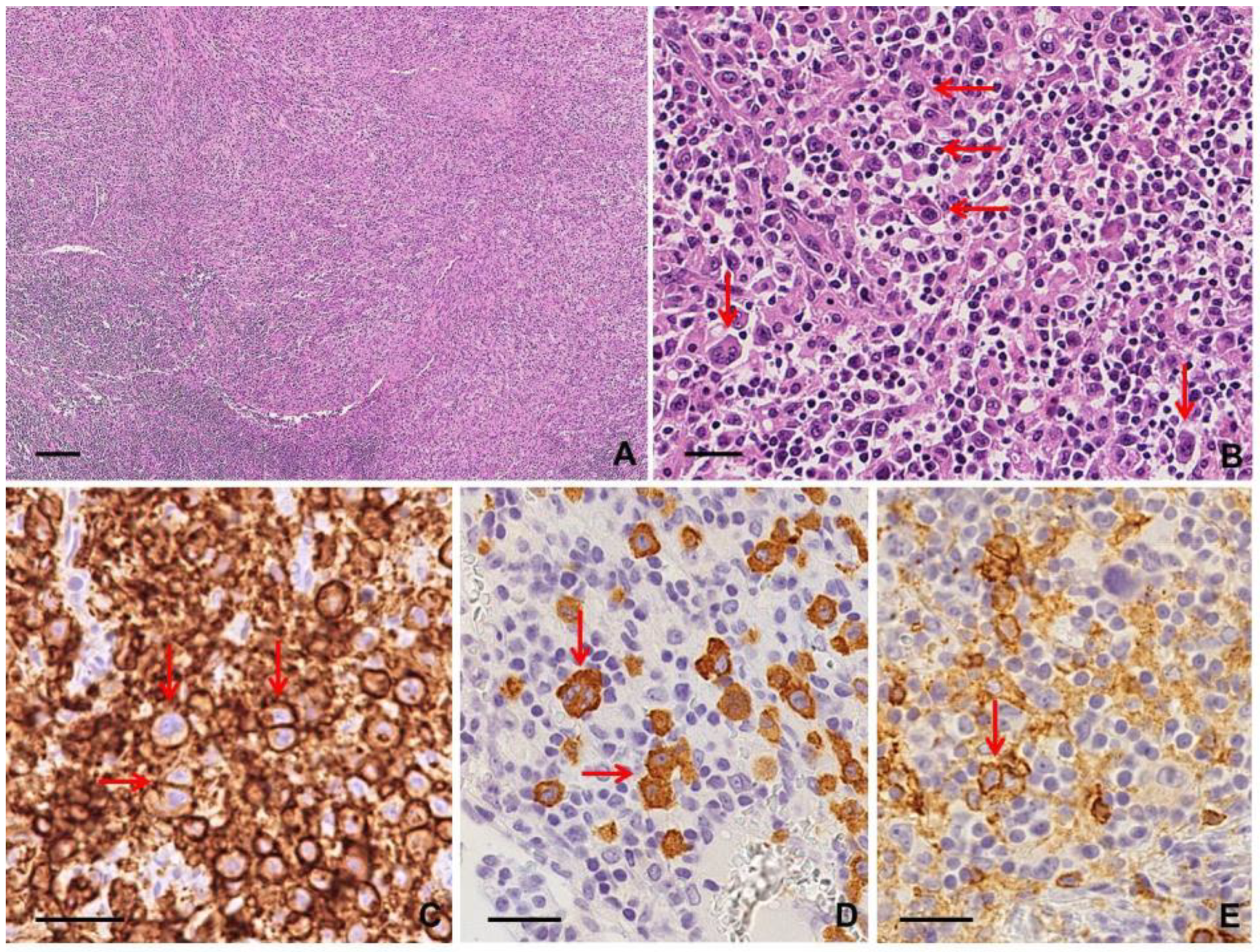
2.2.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
2.2.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
2.3. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
2.3.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
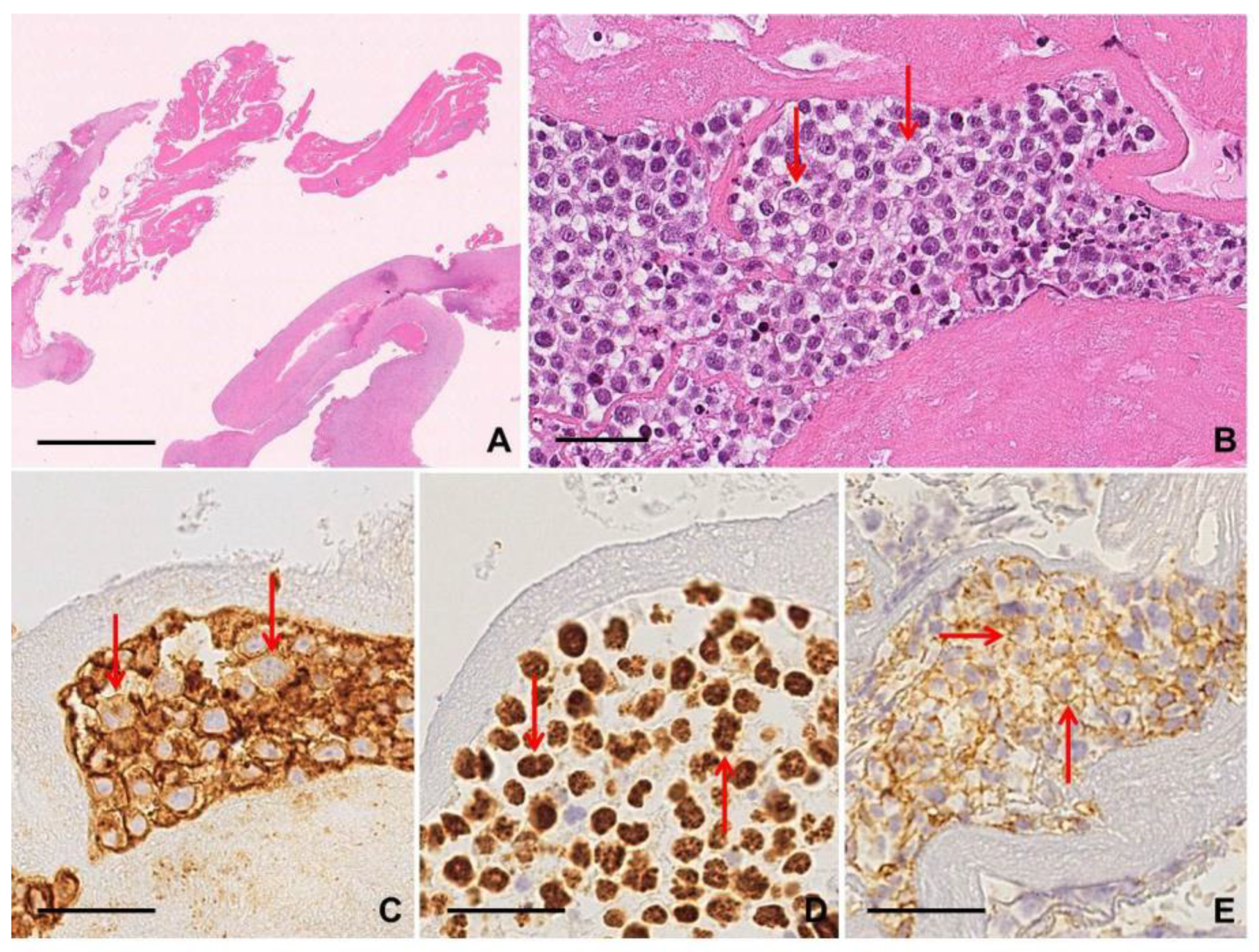
2.3.2. Histological and Cytological Findings and Immunophenotype
2.3.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
2.4. Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma (AITL)
2.4.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
2.4.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
2.4.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
2.5. Follicular Peripheral T cell Lymphoma (F-PTCL)
2.5.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
2.5.2. Histological Findings and immunophenotype
2.5.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3. B cell Lymphomas, High Grade
3.1. Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified (DLBCL, NOS)
3.1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.1.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.1.3. Clues into Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.2. T Cell/Histiocyte-Rich Large B Cell Lymphoma (THRLBCL)
3.2.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.2.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.2.3. Clues into Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.3. ALK-Positive Large B cell Lymphoma (ALK+ LBCL)
3.3.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.3.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.3.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.4. Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B Cell Lymphoma (PMBL)
3.4.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.4.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.4.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.5. Mediastinal Gray-Zone Lymphoma (GZL)
3.5.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.5.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.5.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.6. Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis (LG)
3.6.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.6.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.6.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.7. Primary Effusion Lymphoma (PEL)
3.7.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.7.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.7.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.8. EBV-Positive Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified (EBV+ DLBCL, NOS)
3.8.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.8.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.8.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
3.9. Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
3.9.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
3.9.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
3.9.3. Clues into Differential Diagnosis with cHL
4. B Cell Lymphomas, Low Grade
4.1. Follicular Lymphoma (FL)
4.1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
4.1.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
4.1.3. Clue for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
4.2. Primary Cutaneous Marginal Zone Lymphoma (PCMZL)
4.2.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
4.2.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
4.2.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
4.3. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma
4.3.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
4.3.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
4.3.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
4.4. Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma (PCFCL)
4.4.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
4.4.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
4.4.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
5. Rare Lymphoproliferative Diseases
5.1. Nodal Involvement by CD30+ Cutaneous Lymphoproliferative Disorders (CD30+ LPDs)
5.1.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
5.1.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
5.1.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
5.2. Cutaneous Localization of AITL
5.2.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
5.2.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
5.2.3. Clues for Differential Diagnosis with cHL
5.3. Composite Lymphoma (CL)
5.4. EBV-Positive Mucocutaneus Ulcer (EBV+ MCU)
5.4.1. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
5.4.2. Histological Findings and Immunophenotype
5.4.3. Clues for differential diagnosis with cHL
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABVD | Doxorubicin, Bleomycin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine |
| AITL | Angioimmunoblastic T cell Lymphoma |
| ALCT | Anaplastic Large T cell Lymphoma |
| ALK+ ALCL | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |
| ALK− ALCL | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-negative Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |
| ALK+ LBCL | Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-positive Large B cell Lymphoma |
| BIA-ALCL | Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |
| BM | Bone Marrow |
| C-ALCL | Primary Cutaneous Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma |
| CD | Castleman Disease |
| CD30+ LPDs | CD30+ Cutaneous Lymphoproliferative Disorders |
| cHL | classical Hodgkin Lymphoma |
| CHOP | Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine, and Prednisone |
| CL | Composite Lymphoma |
| CLL/SLL | Chronic Lymphocytes Leukemia/Small lymphocytes lymphoma |
| DLBCL, NOS | Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified |
| EBER | EBV-encoded small RNA |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr Virus |
| EBV+ DLBCL | EBV-positive Diffuse Large B cell Lymphoma, not otherwise specified |
| EBV+ MCU | EBV-positive mucocutaneus ulcer |
| FDC | follicular dendritic cell |
| FL | Follicular Lymphoma |
| F-PTCL | Follicular Peripheral T cell Lymphoma |
| GZL | Gray Zone Lymphoma |
| HHV8 | Human Herpes Virus 8 |
| IGH | Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain |
| LBCL | Large B cell Lymphoma |
| LDH | Serum Lactase Dehydrogenase |
| LG | Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis |
| LyP | Lymphomatoid Papulosis |
| LMP1 | Latent Membrane Protein-1 |
| MALT | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Lymphoma |
| MCL | Mantle Cell Lymphoma |
| MF | Mycosis Fungoides |
| NLPHL | Nodular Lymphocytes Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma |
| NHL | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| PCMZL | Primary Cutaneous Marginal Zone Lymphoma |
| PCFCL | Primary Cutaneous Follicle Center Lymphoma |
| PEL | Primary Effusion Lymphoma |
| PMBL | Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B cell Lymphoma |
| PTCL | Peripheral T cell lymphoma |
| RSC | Reed–Sternberg Cell |
| RSLC | Reed–Sternberg-like cells |
| TCR | T cell Receptor |
| TFH | T-follicular helper derived |
| THRLBCL | T cell/Histiocyte-Rich Large B cell Lymphoma |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Connors, J.M.; Cozen, W.; Steidl, C.; Carbone, A.; Hoppe, R.T.; Flechtner, H.; Bartlett, N.L. Hodgkin Lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2020, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C. The Reed-Sternberg cell in classical Hodgkin’s disease. Hematol. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullet, M.R.; Bagg, A. Recent insights into the biology of Hodgkin lymphoma: Unraveling the mysteries of the Reed-Sternberg cell. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 7, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidl, C. Exposing Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells. Blood 2017, 129, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Malley, D.P.; Dogan, A.; Fedoriw, Y.; Medeiros, L.J.; Ok, C.Y.; Salama, M.E. American Registry of Pathology Expert Opinions: Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 39, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salati, M.; Cesaretti, M.; Macchia, M.; El Mistiri, M.; Federico, M. Epidemiological Overview of Hodgkin Lymphoma across the Mediterranean Basin. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 6, e2014048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piris, M.A.; Medeiros, L.J.; Chang, K.J. Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Review of Pathological Features and Recent Advances in Pathogenesis. Pathology 2020, 52, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relecom, A.; Federico, M.; Connors, M.J.; Coiffier, B.; Biasoli, I.; Moccia, A.; Salles, G.; McKee, T.; Miralbell, R.; Borchmann, P.; et al. Resources-Stratified Guidelines for Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Jaffe, S.A.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Arber, D.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; et al. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, Revised 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton, R.; Cairo, M.S.; Cotter, F.E. Childhood, Adolescent and Young Adult non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: State of the Science. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Khan, D.; Hall, G.W.; Collins, G.P. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase-Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Current and Future Perspectives in Adult and Paediatric Disease. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshaid, L.; Xu, M.L. ALCL by Any Other Name: The Many Facets of Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Pathology 2020, 52, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventaki, V.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Lim, S.M. Pathology and genetics of anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 37, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.L.; Hanby, A.M.; Wells, C.; Calaminici, M.; Johnson, L.; Turton, P.; Deb, R.; Provenzano, E.; Shaaban, A.; Ellis, I.O.; et al. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): An Overview of Presentation and Pathogenesis and Guidelines for Pathological Diagnosis and Management. Histopathology 2019, 75, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, G.S.; Deapen, D.; Taylor, C.R.; Pinter-Brown, L.; House-Lightner, S.R.; Andersen, J.S.; Carlson, G.; Lechner, M.G.; Epstein, A.L. Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Occurring in Women With Breast Implants: Analysis of 173 Cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2015, 135, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, C.; Delas, A.; Gaulard, P.; Haioun, C.; Moreau, A.; Xerri, L.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Rousset, T.; Quintin-Roue, I.; Petrella, T.; et al. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Two Distinct Clinicopathological Variants with Different Outcomes. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.W.; Medeiros, L.J.; Butler, C.E.; Hunt, K.K.; Fanale, M.A.; Horwitz, S.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Liu, J.; Morgan, E.A.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; et al. Complete Surgical Excision Is Essential for the Management of Patients with Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, L.A.; Michel, R.P.; Auger, M. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma and Effusions: A Review with Emphasis on the Role of Cytopathology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2020. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, M.; Chiba, S.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M. Recent Progress in the Understanding of Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2017, 57, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leval, L. Approach to Nodal-Based T-cell Lymphomas. Pathology 2020, 52, 78–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Venkataraman, G.; Vijnovich-Baron, A.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas of follicular T-helper cell derivation with Hodgkin/Reed–Sternberg cells of B-cell lineage: Both EBV-positive and EBV-negative variants exist. Am. J.Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Goncharova, O.; Portyanko, A. CD30 Expression in Neoplastic T Cells of Follicular T Cell Lymphoma Is a Helpful Diagnostic Tool in the Differential Diagnosis of Hodgkin Lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 32, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Bennani, N.; Feldman, A.L. Lymphoma classification update: T-cell lymphomas, Hodgkin lymphomas, and histiocytic/dendritic cell neoplasms. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Young, K.H.; Medeiros, L.J. Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Pathology 2018, 50, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Barta, S.K. Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma: 2019 Update on Diagnosis, Risk Stratification, and Treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukswai, N.; Lyapichev, K.; Khoury, J.D.; Medeiros, L.J. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma variants: An update. Pathology 2020, 52, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommalapati, A.; Tella, S.H.; Go, R.S.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Goyal, G. T Cell/Histiocyte-Rich Large B Cell Lymphoma: Incidence, Demographic Disparities, and Long-Term Outcomes. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, S.; Eichenauer, D.A. Nodular Lymphocyte Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma: Pathology, Clinical Course and Relation to T-cell/histiocyte Rich Large B-cell Lymphoma. Pathology 2020, 52, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Hu, S.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Reddy, V.; Sanmann, J.N.; Smith, L.M.; Chen, M.; Gao, Z.; et al. ALK-positive Large B-cell Lymphoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 26 Cases with Review of Additional 108 Cases in the Literature. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.P.; Wang, K.F.; Xia, Y.; Bi, X.W.; Sun, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.M.; Jiang, W.Q. Racial Patterns of Patients with Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma: SEER Analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e4054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladily, N.T.; Mansour, A.; Alsughayer, A.; Sughayer, M.; Medeiros, L.J. The Utility of CD83, Fascin and CD23 in the Differential Diagnosis of Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma Versus Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 40, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, K.; Venkataraman, G. Challenges in the Diagnosis of Gray Zone Lymphomas. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2019, 12, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilichowska, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Ferry, J.A.; Hemminger, J.; Chang, H.; Kanakry, J.A.; Sehn, L.H.; Feldman, T.; Abramson, J.S.; Kritharis, A.; et al. Clinicopathologic Consensus Study of Gray Zone Lymphoma With Features Intermediate Between DLBCL and Classical HL. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2600–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkozy, C.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Damotte, D. Gray-zone Lymphoma Between cHL and Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Histopathologic Series From the LYSA. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.Y.; Pittaluga, S.; Dunleavy, K.; Grant, N.; White, T.; Jiang, L.; Davies-Hill, T.; Raffeld, M.; Wilson, W.H.; Jaffe, E.S. Lymphomatoid Granulomatosis-A Single Institute Experience: Pathologic Findings and Clinical Correlations. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillet, S.; Gérard, L.; Meignin, V.; Agbalika, F.; Cuccini, W.; Denis, B.; Katlama, C.; Galicier, L.; Eric Oksenhendler, E. Classic and extracavitary primary effusion lymphoma in 51 HIV-infected patients from a single institution. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, P.; Zanelli, M.; Zizzo, M.; Carosi, I.; Di Candia, L.; Sperandeo, M.; Lacedonia, D.; Fesce, V.F.; Ascani, S.; Graziano, P. Primary effusion lymphoma metachronous to Multicentric Castleman disease in an immunocompetemt patient. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 153024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Beltran, B.E.; Miranda, R.N.; Young, K.H.; Chavez, J.C.; Sotomayor, E.M. EBV-positive Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified: 2018 Update on Diagnosis, Risk-Stratification and Management. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Salas, Y.I.; Pachas, C.; Becker-Hecker, R.; Vega, F.; Miranda, R.N. Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated B-cell Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Lymphomas: A Review. Pathology 2020, 52, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, B.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Ott, G.; Xerri, L.; Kuzu, I.; Chan, J.K.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E. Mantle Cell Lymphoma-A Spectrum From Indolent to Aggressive Disease. Virchows Arch. 2016, 468, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, N.C.; Kahl, B. Evolving Treatment Strategies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2018, 31, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.Y.; Seymour, J.F.; Wang, M.L. Mantle Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, S.; Uppal, G.; Wang, Z.X.; Gong, J.Z. Mantle Cell Lymphoma with Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells: Review With Illustrative Case. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2019, 27, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashkandi, H.; Petrova-Drus, K.; Batlevi, C.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Roshal, M.; Sen, F.; Yao, J.; Baik, J.; Bilger, A.; Singh, J.; et al. Divergent Clonal Evolution of a Common Precursor to Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2019, 5, a004259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Raffeld, M.; Richter, M.; Krugmann, J.; Burek, C.; Hartmann, E.; Rudiger, T.; Jaffe, E.S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; et al. IgVH mutational status and clonality analysis of Richter’s transformation: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma in association with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) represent 2 different pathways of disease evolution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.; Quinn, F.; Illyes, G.; Walker, J.; Castriciano, G.; O’Sullivan, P.; Grant, C.; Vandenberghe, E.; Bird, B.; Flavin, R. Composite blastoid variant of mantle cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 25, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Chen, W.W.; Sorbara, L.; Davies-Hill, T.; Pittaluga, S.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Hodgkin lymphoma variant of Richter transformation: Morphology, Epstein–Barr virus status, clonality, and survival analysis-with comparison to Hodgkin-like lesion. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 55, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Roulland, S.; Gloghini, A.; Younes, A.; von Keudell, G.; López-Guillermo, A.; Fitzgibbon, J. Follicular Lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis Primers 2019, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshna, K.M.; Qian, W.; Smith, P.; Braganca, N.; Lowry, L.; Patrick, P.; Warden, J.; Stevens, L.; Pocock, C.F.; Miall, F.; et al. Rituximab versus a Watch-And-Wait Approach in Patients With Advanced-Stage, Asymptomatic, Non-Bulky Follicular Lymphoma: An Open-Label Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Gelvez, J.C.; Smith, L.B. Reed-Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2015, 139, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayerl, M.G.; Bentley, G.; Bellan, C.; Leoncini, L.; Ehmann, W.C.; Palutke, M. Lacunar and Reed-Sternberg-like cells in follicular lymphomas are clonally related to the centrocytic and centroblastic cells as demonstrated by laser capture microdissection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 122, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hope, B.C.; Pincus, L.B. Primary Cutaneous B-cell Lymphomas. Clin Lab Med 2017, 37, 547–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreuder, M.I.; van den Brand, M.; Hebeda, K.M.; Groenen, P.J.T.A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Scheijen, B. Novel Developments in the Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma. J. Hematop. 2017, 10, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Torres, L.; Manso, R.; Cieza-Díaz, D.E.; Jo, M.; Kilany Pérez, L.; Montenegro-Damaso, T.; Eraña, I.; Lorda, M.; Suarez Massa, D.; Machan, S.; et al. Large Cells With CD30 Expression and Hodgkin-like Features in Primary Cutaneous Marginal Zone B-Cell Lymphoma: A Study of 13 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, C.M.; Yang, A.; Fraga, G. Blastic marginal zone lymphoma: A clinical and pathological study of 8 cases and review of the literature. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2013, 35, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tees, M.T.; Flinn, M.T. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma: Two Faces of the Same Disease. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2017, 10, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.A.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Asplund, S.L.; McKenn, R.W.; Howard, M.S.; Kroft, S.H. Immunophenotype Does Not Correlate with Lymph Node Histology in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2002, 26, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, D.; Hudnall, S.D.; Aisenberg, A.; Jacobson, J.O.; Harris, N.H. Richter’s transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia with Hodgkin’s-like cells is associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Mod. Pathol. 1994, 7, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- De Leval, L.; Vivario, M.; De Prijck, B.; Zhou, Y.; Boniver, J.; Harris, N.L.; Isaacson, P.; Du, M.Q. Distinct clonal origin in two cases of Hodgkin’s lymphoma variant of Richter’s syndrome associated With EBV infection. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbay, R.M.; Jain, N.; Loghavi, S.; Medeiros, L.J.; Khoury, J.D. Histologic Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic leukemia/small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockorny, B.; Codreanu, I.; Dasanu, C.A. Hodgkin lymphoma as Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A retrospective analysis of world literature. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 156, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 63 Haverkos, B.; Tyler, K.; Gru, A.A.; Winardi, F.K.; Frederickson, J.; Hastings, J.; Elkins, C.; Zhang, X.; Xu-Welliver, M.; Wong, H.K.; et al. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphoma: Management and patterns of recurrence at the multimodality cutaneous lymphoma clinic of the Ohio state university. Oncologist 2015, 20, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amitay-Laish, I.; Tavallaee, M.; Kim, J.; Hoppe, R.T.; Million, L.; Feinmesser, M.; Fenig, E.; Wolfe, M.E.L.; Hodak, E.; Kim, Y.H. Paediatric primary cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma: Does it differ from the adult counterpart? Br. J. Dermal. 2016, 176, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, A.L.; Querfeld, C.; Horwitz, S.; Pulitzer, M.; Moskowitz, A.; Myskowski, P.L. Primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas: Part II. Therapy and future directions. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 343.e1–343.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldarweesh Fatima, A.; Diana, O. Primary Cutaneous Follicle Centre Lymphoma with Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg like Cells: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Hematol. 2017, 2017, 9549428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, E.M.; Huh, J. Reed-Sternberg-like cells in follicular lymphoma. Blood Res. 2014, 49, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lezama, L.S.; Gratzinger, D. Nodal Involvement by CD30 + Cutaneous Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Its Challenging Differentiation from Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarisbrick, J.J.; Prince, H.M.; Vermeer, M.H.; Quaglino, P.; Horwitz, S.; Porcu, P.; Stadler, R.; Wood, G.S.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Pham-Ledard, A.; et al. Cutaneous Lymphoma International Consortium Study of Outcome in Advanced Stages of Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome: Effect of specific prognostic markers on survival and development of a prognostic model. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3766–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.; LeeHarris, N.; Vardiman, J.W. (Eds.) Hematopathology; Saunders/Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 454–472, 588–603, 604–616. [Google Scholar]
- Willemze, R.; Hodak, E.; Zinzani, P.L.; Specht, L.; Ladetto, M. ESMO Guidelines Committee. Primary cutaneous lymphomas: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. 4), iv30–iv40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, M.; Tomita, A.; Takata, K.; Shimoyama, Y.; Yoshino, T.; Tomita, Y.; Nakamura, S. Primary cutaneous CD30 positive T-cell lymphoproliferative disorders with aberrant expression of PAX5: Report of three cases. Pathol. Int. 2012, 62, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ge, S.; Mei, S.; Li, H.; Jing, X.; Zhang, C. The Histologic, Immunohistochemical, and Genetic Features of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Aberrant T-cell/B-cell Antigen Expression. Hum. Pathol. 2019, 84, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberle, F.C.; Song, J.Y.; Xi, L.; Raffeld, M.; Harris, N.L.; Wilson, W.H.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. Nodal involvement by cutaneous CD30-positive T-cell lymphoma mimicking classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel, P.; Laroche, L.; Courville, P.; Larroche, C.; Wechsler, J.; Lenormand, B.; Delfau, M.H.; Bodemer, C.; Bagot, M.; Joly, P. Cutaneous Involvement in Patients with Angioimmunoblastic Lymphadenopathy With Dysproteinemia: A Clinical, Immunohistological, and Molecular Analysis. Arch. Dermatol. 2000, 136, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, V.; Dereure, O.; René, C.; Tempier, A.; Durand, L.; Alame, M.; Cacheux, V.; Costes-Martineau, V. Cutaneous Localization of Angioimmunoblastic T-cell Lymphoma May Masquerade as B-cell Lymphoma or Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Histologic Diagnostic Pitfall. J. Cutan Pathol. 2019, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclaire Alirkilicarslan, L.; Dupuy, A.; Pujals, A.; Parrens, M.; Vergier, B.; Robson, A.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Ingen-Housz-Oro, S.; Chosidow, O.; Haioun, C.; et al. Expression of TFH Markers and Detection of RHOA p.G17V and IDH2 p.R172K/S Mutations in Cutaneous Localizations of Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Vilela, D.; Izquierdo-Garcia, F.M. Angioimmunoblastic Lymphadenopathy-Like T-cell Lymphoma: Cutaneous Clinical Onset with Prominent Granulomatous Reaction. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 699–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, R.J.; McCalmont, T.H.; Ai, W.Z.; Fox, L.P.; Treseler, P.; Pincus, L.B. Use of an Expanded Immunohistochemical Panel to Distinguish Cutaneous Hodgkin Lymphoma from Histopathologic Imitators. J. Cutan Pathol. 2012, 39, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hendrickson, M.D.; Dorfman, R.F. Composite lymphoma. Cancer 1977, 41, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumala, S.; Esposito, M.; Fuchs, A. An unusual variant of composite lymphoma: A short case report and review of the literature. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 1376–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Zettl, A.; Rüdiger, T.; Marx, A.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Ott, G. Composite marginal zone B-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: A clinicopathological study of 12 cases. Histopathology 2005, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppers, R.; Duhrsen, U.; Hansmann, M.L. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of composite lymphomas. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e435–e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caleo, A.; Sanchez-Aguilera, A.; Rodriguez, S. Composite Hodgkin lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma: Two clonally unrelated tumours. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Kalla, H.; Balasubramanian, M.; Brodsky, I.; Gladstone, D.; Hou, J.S. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma concurrently evolving in a patient with marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the spleen. Ann. Diagn Pathol. 2008, 12, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aussedat, G.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Stamatoullas, A. Composite and Sequential Lymphoma Between Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Primary Mediastinal lymphoma/diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, a Clinico-Pathological Series of 25 Cases. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 189, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; Ladewig, E.; Schiavoni, G.; Penson, A.; Fortini, E.; Pettirossi, V.; Wang, Y.; Rosseto, A.; Venanzi, A.; Vlasevska, S.; et al. Pervasive mutations of JAK-STAT pathway genes in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienand, K.; Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.; Wu, D.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Zumla, F.; Ducar, M.D.; Thorner, A.R.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis of flow-sorted Hodgkin Reed Sternberg cells reveals additional genetic bases of immune evasion. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.L.; Lu, J.Y. Composite Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma of the Stomach: Case Report and Literature Review. World J. Gastroenterol 2013, 19, 6304–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellan, C.; Lazzi, S.; Zazzi, M.; Lalinga, A.V.; Palummo, N.; Galieni, P.; Marafioti, T.; Tonini, T.; Cinti, C.; Leoncini, L.; et al. Immunoglobulin gene rearrangement analysis in composite hodgkin disease and large B-cell lymphoma: Evidence for receptor revision of immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes in Hodgkin-Reed-Sternberg cells? Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2002, 11, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wilczynski, S.P.; Chang, K.L.; Weiss, L.M. Composite recurrent hodgkin lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: One clone, two faces. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 126, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.J.; Banerjee, S.S.; Cook, Y. Composite mantle-cell lymphoma and classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Histopathology 2006, 48, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Crescenzi, B.; Schneider, M. Subclonal evolution of a classical Hodgkin lymphoma from a germinal center B-cell-derived mantle cell lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gualco, G.; Chioato, L.; van-Den-Berg, A.; Weiss, L.M.; Bacchi, C.E. Composite lymphoma: EBV-positive classic Hodgkin lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: A case report. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2009, 17, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, A.; Miyoshi, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Arakawa, F.; Kawano, R.; Muta, H.; Sugita, Y.; Akashi, K.; Ohshima, K. Composite Lymphoma of Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma and Hodgkin Lymphoma, Mixed Cellularity Type, Pathological and Molecular Analysis. Pathol. Int. 2017, 67, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedobitek, G.; Baumann, I.; Brabletz, T.; Lisner, R.; Winkelmann, C.; Helm, G.; Kirchner, T. Hodgkin’s disease and peripheral T-cell lymphoma: Composite lymphoma with evidence of Epstein–Barr virus infection. J. Pathol. 2000, 191, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.; Venkataraman, G.; Raffeld, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV positive mucocutaneous ulcer-a study of 26 cases associated with various sources of immunosuppression. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2010, 34, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natkunam, Y.; Goodlad, J.R.; Chadburn, A.; de Jong, D.; Gratzinger, D.; Chan, J.K.; Said, J.; Jaffe, E.S. EBV-Positive B-Cell Proliferations of Varied Malignant Potential: 2015 SH/EAHP Workshop Report-Part 1. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 147, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Torres, L.; Eraña, I.; Gil-Redondo, R.; Gómez de la Riva, I.; Manso, R.; Pajares, R.; Córdoba, R.; Machan, S.; Ara, M.; Requena, L.; et al. The Spectrum of EBV-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer: A Study of 9 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.; Thakral, B.; Yohe, S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr.; Singh, C.; Spears, M.; McKenna, R.W. EBV-positive mucocutaneous ulcer in organ transplant recipients: A localized indolent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parente, P.; Zanelli, M.; Sanguedolce, F.; Mastracci, L.; Graziano, P. Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121019
Parente P, Zanelli M, Sanguedolce F, Mastracci L, Graziano P. Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121019
Chicago/Turabian StyleParente, Paola, Magda Zanelli, Francesca Sanguedolce, Luca Mastracci, and Paolo Graziano. 2020. "Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121019
APA StyleParente, P., Zanelli, M., Sanguedolce, F., Mastracci, L., & Graziano, P. (2020). Hodgkin Reed–Sternberg-Like Cells in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121019





