Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples
Abstract
:1. Introduction
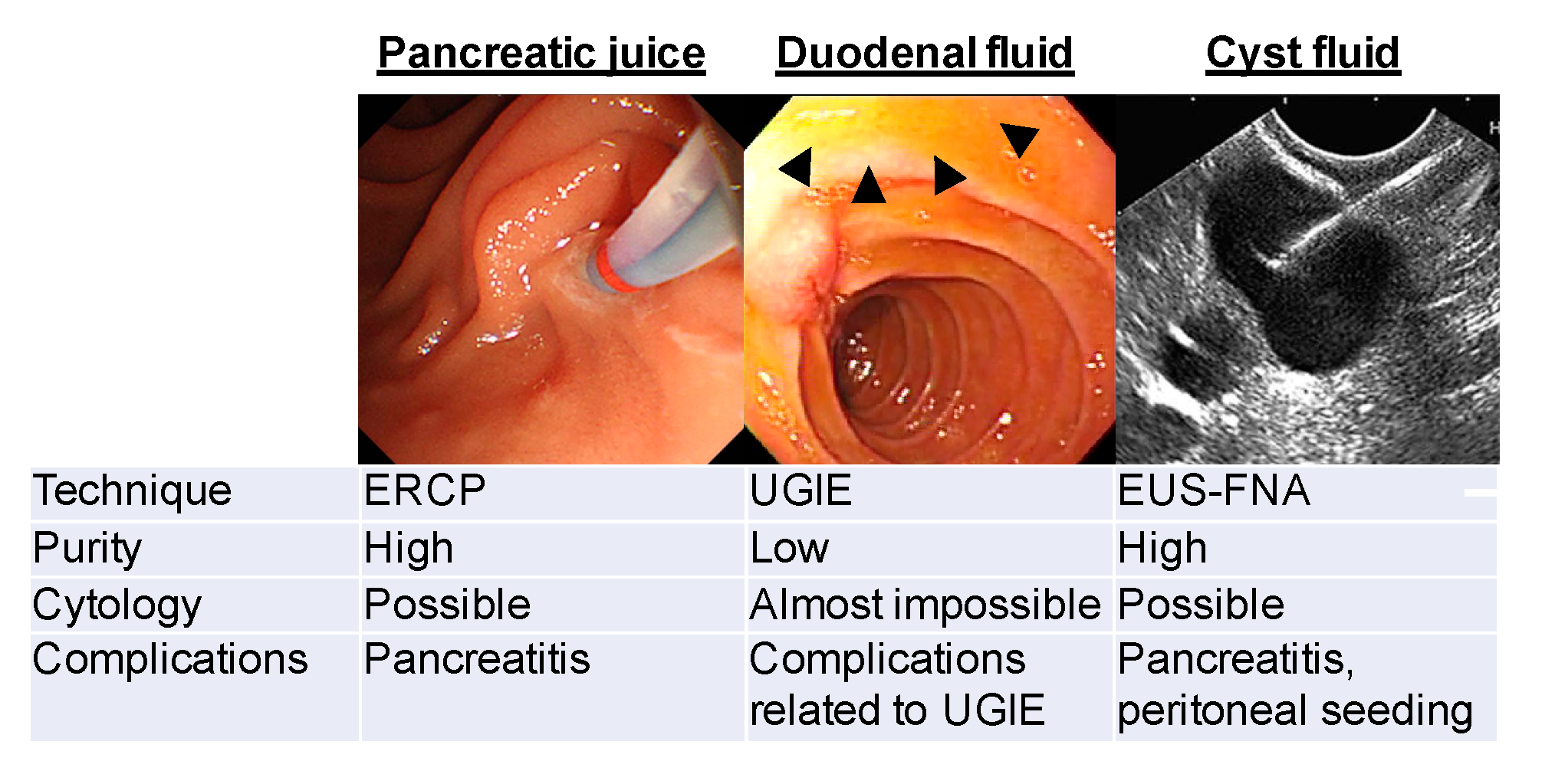
2. Methods of Collecting PJ/DF Samples
3. Genomic Analysis of PJ/DF for Early Detection of PDAC
3.1. Identification of Microscopic Precursor Lesions Using DF Samples
3.2. Screening for High-Grade Dysplasia and Invasive Cancer
3.3. Differentiation of Cystic Lesions of the Pancreas
3.4. Biomarker Proteins in PJ/DF from Patients with PDAC
3.5. Analysis of miRNA in Pancreatic Juice
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer, J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chari, S.T. Detecting early pancreatic cancer: Problems and prospects. Semin. Oncol. 2007, 34, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhi, A.D.; Koay, E.J.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2024–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohuchida, K.; Ohtsuka, T.; Mizumoto, K.; Hashizume, M.; Tanaka, M. Pancreatic Cancer: Clinical Significance of Biomarkers. Gastrointest. Tumors 2013, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cotton, P.B.; Cremer, M.; Robberecht, P.; Christophe, J. Proceedings: Biochemical studies on pure pancreatic juice obtained by duodenoscopic cannulation of the pancreatic duct in conscious patients. Gut 1974, 15, 838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabenstein, T.; Hahn, E.G. Post-ERCP pancreatitis: Is the endoscopist’s experience the major risk factor? JOP 2002, 3, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandervoort, J.; Soetikno, R.M.; Tham, T.C.; Wong, R.C.; Ferrari, A.P.; Montes, H.; Roston, A.D.; Slivka, A.; Lichtenstein, D.R.; Ruymann, F.W.; et al. Risk factors for complications after performance of ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmunzer, B.J.; Scheiman, J.M.; Lehman, G.A.; Chak, A.; Mosler, P.; Higgins, P.D.; Hayward, R.A.; Romagnuolo, J.; Elta, G.H.; Sherman, S.; et al. A randomized trial of rectal indomethacin to prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1414–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raimondo, M.; Imoto, M.; DiMagno, E.P. Is a rapid endoscopic secretin stimulation test useful to differentiate patients with pancreatic disease from disease controls? Pancreas 1999, 19, 435. [Google Scholar]
- Conwell, D.L.; Zuccaro, G.; Vargo, J.J.; Morrow, J.B.; Obuchowski, N.; Dumot, J.A.; Trolli, P.A.; Burton, A.; O’laughlin, C.; Van Lente, F. An endoscopic pancreatic function test with cholecystokinin-octapeptide for the diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 1, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kono, H.; Nagayoshi, Y.; Ideno, N.; Aso, T.; Kozono, S.; Ohuchida, K.; Takahata, S.; Nakamura, M.; et al. A minimally invasive and simple screening test for detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using biomarkers in duodenal juice. Pancreas 2013, 42, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideno, N.; Ohtsuka, T.; Matsunaga, T.; Kimura, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Tamura, K.; Aso, T.; Aishima, S.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ohuchida, K.; et al. Clinical significance of GNAS mutation in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas with concomitant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2015, 44, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Asano, K.; Kimura, H.; Ohuchida, K.; Kitada, H.; Ideno, N.; Mori, Y.; Tokunaga, S.; Oda, Y.; et al. S100P in Duodenal Fluid Is a Useful Diagnostic Marker for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaga, M.; Sadakari, Y.; Almario, J.A.; Borges, M.; Lennon, A.M.; Shin, E.J.; Canto, M.I.; Goggins, M. Using an endoscopic distal cap to collect pancreatic fluid from the ampulla (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 86, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-Del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okabe, Y.; Kaji, R.; Ishida, Y.; Tsuruta, O.; Sata, M. The management of the pancreatic cystic neoplasm: The role of the EUS in Japan. Dig. Endosc 2011, 23 (Suppl. 1), 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, B.C.; Baron, T.H.; Adler, D.G.; Davila, R.E.; Egan, J.; Hirota, W.K.; Leighton, J.A.; Qureshi, W.; Rajan, E.; Zuckerman, M.J.; et al. ASGE guideline: The role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and the management of cystic lesions and inflammatory fluid collections of the pancreas. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2005, 61, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, M.; Matthaei, H.; Wu, J.; Hong, S.M.; Yu, J.; Borges, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Maitra, A.; Kinzler, K.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. Presence of somatic mutations in most early-stage pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 730–733.e739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M.; Parsons, J.; Kern, S.E. Progression model for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2969–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Sadakari, Y.; Kanda, M.; Maitani, K.; Borges, M.; Canto, M.I.; Goggins, M. Mutant KRAS and GNAS DNA Concentrations in Secretin-Stimulated Pancreatic Fluid Collected from the Pancreatic Duct and the Duodenal Lumen. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2014, 5, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshleman, J.R.; Norris, A.L.; Sadakari, Y.; Debeljak, M.; Borges, M.; Harrington, C.; Lin, E.; Brant, A.; Barkley, T.; Almario, J.A.; et al. KRAS and guanine nucleotide-binding protein mutations in pancreatic juice collected from the duodenum of patients at high risk for neoplasia undergoing endoscopic ultrasound. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 963–969.e964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, M.; Sadakari, Y.; Borges, M.; Topazian, M.; Farrell, J.; Syngal, S.; Lee, J.; Kamel, I.; Lennon, A.M.; Knight, S.; et al. Mutant TP53 in duodenal samples of pancreatic juice from patients with pancreatic cancer or high-grade dysplasia. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 11, 719–730.e715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Sadakari, Y.; Shindo, K.; Suenaga, M.; Brant, A.; Almario, J.A.N.; Borges, M.; Barkley, T.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Ford, M.; et al. Digital next-generation sequencing identifies low-abundance mutations in pancreatic juice samples collected from the duodenum of patients with pancreatic cancer and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Gut 2017, 66, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singhi, A.D.; McGrath, K.; Brand, R.E.; Khalid, A.; Zeh, H.J.; Chennat, J.S.; Fasanella, K.E.; Papachristou, G.I.; Slivka, A.; Bartlett, D.L.; et al. Preoperative next-generation sequencing of pancreatic cyst fluid is highly accurate in cyst classification and detection of advanced neoplasia. Gut 2018, 67, 2131–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Matthaei, H.; Maitra, A.; Dal Molin, M.; Wood, L.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Goggins, M.; Canto, M.I.; Schulick, R.D.; Edil, B.H.; et al. Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 92ra66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanda, M.; Knight, S.; Topazian, M.; Syngal, S.; Farrell, J.; Lee, J.; Kamel, I.; Lennon, A.M.; Borges, M.; Young, A.; et al. Mutant GNAS detected in duodenal collections of secretin-stimulated pancreatic juice indicates the presence or emergence of pancreatic cysts. Gut 2013, 62, 1024–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolny, P.; Elwing, H.; Nilsson, L.A. The CEA concentration in duodenal fluid in patients with pancreatic disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1977, 12, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, K.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kondo, M.; Thiele, H.G. Immunological diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by assaying carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in pure pancreatic juice. Hepatogastroenterology 1980, 27, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Nakaizumi, A.; Uehara, H.; Takenaka, A.; Uedo, N.; Sakai, N.; Yano, H.; Ohigashi, H.; Ishikawa, O.; Ishiguro, S.; Sugano, K.; et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer by cytology and measurement of oncogene and tumor markers in pure pancreatic juice aspirated by endoscopy. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Grønborg, M.; Bunkenborg, J.; Kristiansen, T.Z.; Jensen, O.N.; Yeo, C.J.; Hruban, R.H.; Maitra, A.; Goggins, M.G.; Pandey, A. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human pancreatic juice. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirono, S.; Tani, M.; Kawai, M.; Okada, K.; Miyazawa, M.; Shimizu, A.; Kitahata, Y.; Yamaue, H. The carcinoembryonic antigen level in pancreatic juice and mural nodule size are predictors of malignancy for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugge, W.R.; Lewandrowski, K.; Lee-Lewandrowski, E.; Centeno, B.A.; Szydlo, T.; Regan, S.; del Castillo, C.F.; Warshaw, A.L. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: A report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Tani, M.; Onishi, H.; Kinoshita, H.; Ueno, M.; Hama, T.; Yamaue, H. Clinicopathological features of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: The differential diagnosis from benign entities. Arch. Surg. 2004, 139, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maire, F.; Voitot, H.; Aubert, A.; Palazzo, L.; O’Toole, D.; Couvelard, A.; Levy, P.; Vidaud, M.; Sauvanet, A.; Ruszniewski, P.; et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: Performance of pancreatic fluid analysis for positive diagnosis and the prediction of malignancy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 2871–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Egami, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Fujii, K.; Konomi, H.; Nagai, E.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tsuneyoshi, M.; Tanaka, M. S100P is an early developmental marker of pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5411–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, R.; Pan, S.; Cooke, K.; Moyes, K.W.; Bronner, M.P.; Goodlett, D.R.; Aebersold, R.; Brentnall, T.A. Comparison of pancreas juice proteins from cancer versus pancreatitis using quantitative proteomic analysis. Pancreas 2007, 34, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, M.; Cui, Y.Z.; Song, G.H.; Zong, M.J.; Zhou, X.Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, J.X. Proteomic analysis identifies MMP-9, DJ-1 and A1BG as overexpressed proteins in pancreatic juice from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, Z.; Yang, A.; Deng, R.; Mai, C.; Sang, X.; Faber, K.N.; Lu, X. Comparative proteomic analysis of human pancreatic juice: Methodological study. Proteomics 2007, 7, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Sato, N.; Nabae, T.; Takahata, S.; Toma, H.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bloomston, M.; Frankel, W.L.; Petrocca, F.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Liu, C.G.; Bhatt, D.; Taccioli, C.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007, 297, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greither, T.; Grochola, L.F.; Udelnow, A.; Lautenschläger, C.; Würl, P.; Taubert, H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Kayashima, T.; Fujita, H.; Moriyama, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Ueda, J.; Nagai, E.; Hashizume, M.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA expression as a predictive marker for gemcitabine response after surgical resection of pancreatic cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadakari, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Tsutsumi, K.; Takahata, S.; Nakamura, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA expression analyses in preoperative pancreatic juice samples of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. JOP 2010, 11, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Allenson, K.; Castillo, J.; San Lucas, F.A.; Scelo, G.; Kim, D.U.; Bernard, V.; Davis, G.; Kumar, T.; Katz, M.; Overman, M.J.; et al. High prevalence of mutant KRAS in circulating exosome-derived DNA from early-stage pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Sadakari, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Okayama, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Gotoh, Y.; Saeki, K.; Mori, Y.; Nakata, K.; Miyasaka, Y.; et al. Pancreatic Juice Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Tandon, M.; Alevizos, I.; Illei, G.G. The Majority of microRNAs detectable in serum and saliva is concentrated in exsosomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Authors (Ref) | Year | Control Cohort | Number of Unique Proteins in PJ from PDAC | Identified Protein Previously Undescribed in PDAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grønborg et al. [31] | 2004 | N/A | 170 | pg96, Azurocidin |
| Chen et al. [37] | 2007 | Chronic pancreatitis | 21 | Plasminogen, NCAM L1, Caldecrin |
| Tian et al. [38] | 2008 | Cancer-free | 24 | DJ-1, AIBG |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ideno, N.; Mori, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Ohtsuka, T. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121056
Ideno N, Mori Y, Nakamura M, Ohtsuka T. Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(12):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121056
Chicago/Turabian StyleIdeno, Noboru, Yasuhisa Mori, Masafumi Nakamura, and Takao Ohtsuka. 2020. "Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples" Diagnostics 10, no. 12: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121056
APA StyleIdeno, N., Mori, Y., Nakamura, M., & Ohtsuka, T. (2020). Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer: Role of Biomarkers in Pancreatic Fluid Samples. Diagnostics, 10(12), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10121056




