Molecular Analysis of Liquid-Based Cytological Specimen Using Virtually Positive Sputum with Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Cell Treatment
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Extraction of DNA and RNA and qPCR
- Actin sense 5′-CTCTTCCAGCCTTCCTTCCT-3′
- Actin antisense 5′-AGCACTGTGTTGGCGTACAG-3′
- EGFR sense 5′-GCAATATCAGCCTTAGGTGCGGCT-3′
- EGFR antisense 5′-CATAGAAAGTGAACATTTAGGATGTG-3′
- TTF-1 sense 5′-GGACGACTTGGAACGGTTTA-3′
- TTF-1 antisense 5′-TTGTCTGCACTCTCAATGCC-3′
2.5. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutation Detection
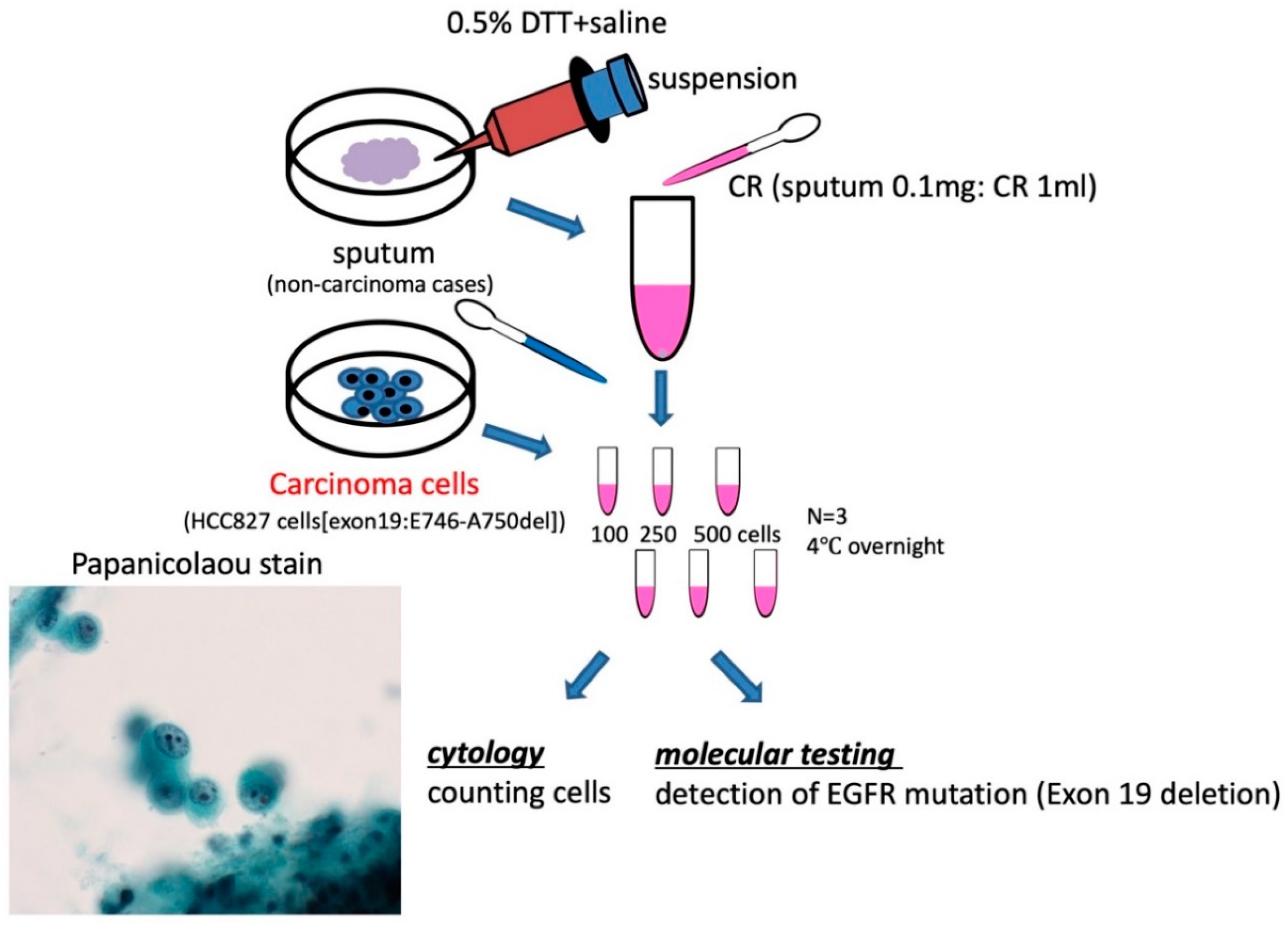
2.6. Specimens of Sputum and Cytological Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficiency of DNA and RNA Extraction
3.2. Immunocytochemistry of Liquid-Based Cytology (LBC)
3.3. DNA Detection Sensitivity
3.4. Detection of EGFR Mutation
3.5. Detection of EGFR DNA Mutation from Sputum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lynch, T.J.; Bell, D.W.; Sordella, R.; Gurubhagavatula, S.; Okimoto, R.A.; Brannigan, B.W.; Harris, P.L.; Haserlat, S.M.; Supko, J.G.; Haluska, F.G.; et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2129–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikova, K.; Guo, A.; Zeng, Q.; Possemato, A.; Yu, J.; Haack, H.; Nardone, J.; Lee, K.; Reeves, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 2007, 131, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guibert, N.; Tsukada, H.; Hwang, D.H.; Chambers, E.; Cibas, E.S.; Bale, T.; Supplee, J.; Ulrich, B.; Sholl, L.M.; Paweletz, C.P.; et al. Liquid biopsy of fine-needle aspiration supernatant for lung cancer genotyping. Lung Cancer 2018, 122, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, U.; de Rosa, N.; Bellevicine, C.; Rocco, D.; Vitiello, F.; Piantedosi, F.V.; Illiano, A.; Nappi, O.; Troncone, G. EGFR mutations detection on liquid-based cytology: Is microscopy still necessary? J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, U.; de Rosa, N.; Rocco, D.; Bellevicine, C.; Crispino, C.; Illiano, A.; Piantedosi, F.V.; Nappi, O.; Troncone, G. EGFR and KRAS mutations detection on lung cancer liquid-based cytology: A pilot study. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.P.; Zhou, Y.; Jakubowski, M.A.; Wang, Z.; Brainard, J.A.; Klein, R.D.; Farver, C.F.; Almeida, F.A.; Cheng, Y.W. Next-generation sequencing of liquid-based cytology non-small cell lung cancer samples. Cancer Cytopathol. 2017, 125, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Hou, L.K.; Ren, S.X.; Su, B.; Chen, G. High feasibility of liquid-based cytological samples for detection of EGFR mutations in Chinese patients with NSCLC. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 7885–7889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, T.; Guo, H.; Ying, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Detection of EGFR and KRAS gene mutations using suspension liquid-based cytology specimens in metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106685–106692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Asano, A.; Shimada, K.; Tatsumi, Y.; Obayashi, C.; Konishi, N. Evaluation of RNA and DNA extraction from liquid-based cytology specimens. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2016, 44, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Yamashita, K.; Satoh, Y. Reducing DNA damage by formaldehyde in liquid-based cytology preservation solutions to enable the molecular testing of lung cancer specimens. Cancer Cytopathol. 2018, 126, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyers, C.L. Opportunities and challenges in the development of kinase inhibitor therapy for cancer. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2998–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; von Mehren, M.; Blanke, C.D.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Eisenberg, B.; Roberts, P.J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Tuveson, D.A.; Singer, S.; Janicek, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J.; Talpaz, M.; Resta, D.J.; Peng, B.; Buchdunger, E.; Ford, J.M.; Lydon, N.B.; Kantarjian, H.; Capdeville, R.; Ohno-Jones, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a specific inhibitor of the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slamon, D.J.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Shak, S.; Fuchs, H.; Paton, V.; Bajamonde, A.; Fleming, T.; Eiermann, W.; Wolter, J.; Pegram, M.; et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paez, J.G.; Janne, P.A.; Lee, J.C.; Tracy, S.; Greulich, H.; Gabriel, S.; Herman, P.; Kaye, F.J.; Lindeman, N.; Boggon, T.J.; et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science 2004, 304, 1497–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L.; et al. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from "never smokers" and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, L.; Gisfredi, S.; Ursino, S.; Camacci, T.; Baldini, E.; Melfi, F.; Fontanini, G. Mutational analysis in cytological specimens of advanced lung adenocarcinoma: A sensitive method for molecular diagnosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 1086–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malapelle, U.; Bellevicine, C.; Zeppa, P.; Palombini, L.; Troncone, G. Cytology-based gene mutation tests to predict response to anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy: A review. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, S.; Boggon, T.J.; Dayaram, T.; Janne, P.A.; Kocher, O.; Meyerson, M.; Johnson, B.E.; Eck, M.J.; Tenen, D.G.; Halmos, B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.A.; Politi, K.A.; Riely, G.J.; Somwar, R.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Varmus, H. Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Waltman, B.A.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Digumarthy, S.; Turke, A.B.; Fidias, P.; Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Gettinger, S.; Cosper, A.K.; et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, ra26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.O.; Oh, I.J.; Kho, B.G.; Park, H.Y.; Chang, J.S.; Park, C.K.; Shin, H.J.; Lim, J.H.; Kwon, Y.S.; Kim, Y.I.; et al. Feasibility of re-biopsy and EGFR mutation analysis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, R.; Kenmotsu, H.; Serizawa, M.; Koh, Y.; Wakuda, K.; Ono, A.; Taira, T.; Naito, T.; Murakami, H.; Isaka, M.; et al. Frequency of EGFR T790M mutation and multimutational profiles of rebiopsy samples from non-small cell lung cancer developing acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in Japanese patients. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Malhotra, K.P.; Husain, N.; Gupta, A.; Anand, N. The utility of cytology in the diagnosis of adenocarcinoma lung: A tertiary care center study. J. Cytol. 2015, 32, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubers, A.J.; Prinsen, C.F.; Sozzi, G.; Witte, B.I.; Thunnissen, E. Molecular sputum analysis for the diagnosis of lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Liao, J.; Gao, L.; Shen, J.; Guarnera, M.A.; Zhan, M.; Fang, H.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Analysis of small nucleolar RNAs in sputum for lung cancer diagnosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjuman, N.; Li, N.; Guarnera, M.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Evaluation of lung flute in sputum samples for molecular analysis of lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2013, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Ma, J.; Guarnera, M.A.; Fang, H.; Cai, L.; Jiang, F. Digital PCR quantification of miRNAs in sputum for diagnosis of lung cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liao, J.; Guarnera, M.A.; Fang, H.; Cai, L.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Analysis of MicroRNAs in sputum to improve computed tomography for lung cancer diagnosis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Todd, N.W.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, M.; Fang, H.; Peng, H.; Alattar, M.; Deepak, J.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Altered miRNA expression in sputum for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 67, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.; Su, J.; Guarnera, M.A.; Zhang, H.; Cai, L.; Zhou, R.; Stass, S.A.; Jiang, F. Sputum microRNA biomarkers for identifying lung cancer in indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodules. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Todd, N.W.; Yu, L.; Fang, H.; Jiang, F. Early detection of squamous cell lung cancer in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1157–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Todd, N.W.; Xing, L.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Fang, H.; Zhang, J.; Katz, R.L.; Jiang, F. Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2870–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Achten, R.; Drijkoningen, M. Use of liquid-based cytology in serous fluids: A comparison with conventional cytopreparatory techniques. Acta Cytol. 2004, 48, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Hwang, J.Y.; Son, S.M.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Kim, E.J.; Han, H.S.; An, J.Y.; Han, J.H.; Lee, O.J. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy between CellprepPlus(R) and ThinPrep(R) liquid-based preparations in effusion cytology. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2014, 42, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.D.; Bizzarro, T.; Schmitt, F.; Longatto-Filho, A. The role of liquid-based cytology and ancillary techniques in pleural and pericardic effusions: An institutional experience. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015, 123, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottger, F.; Schaaij-Visser, T.B.; de Reus, I.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; Nagel, R.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Thunnissen, E.; Smit, E.F.; Jimenez, C.R. Proteome analysis of non-small cell lung cancer cell line secretomes and patient sputum reveals biofluid biomarker candidates for cisplatin response prediction. J. Proteom. 2019, 196, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, S.J.; Lewis, K.E.; Beckmann, M.; Allison, G.G.; Ghosal, R.; Lewis, P.D.; Mur, L.A. The metabolomic detection of lung cancer biomarkers in sputum. Lung Cancer 2016, 94, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubers, A.J.; Heideman, D.A.; Yatabe, Y.; Wood, M.D.; Tull, J.; Taron, M.; Molina, M.A.; Mayo, C.; Bertran-Alamillo, J.; Herder, G.J.; et al. EGFR mutation analysis in sputum of lung cancer patients: A multitechnique study. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, S.E.; Kurbatov, L.K.; Zavialova, M.G.; Zgoda, V.G.; Archakov, A.I. [Omics technologies in diagnostics of lung adenocarcinoma]. Biomed. Khimiya 2017, 63, 181–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cell Counts (Percentage of Mutant Cells) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1975 (T790M, L858R) | 5 | 10 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| H1299 (wild type) | 495 | 490 | 475 | 975 | 2475 |
| Total counts | 500 (1%) | 500 (2%) | 500 (5%) | 1000 (2.5%) | 2500 (1%) |
| N.D. | N.D. | T790M(+), L858R(+) | N.D. | N.D. | |
| Clinical Diagnosis/Symptom | Cell Counts | LBC (Cytology and Molecular Testing) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cell Counts | HCC827 (% of HCC827 Cells) | Total HCC827 Cell Counts (All Fields) | Epithelial Cells (/HPF) | Other Cells * (/HPF) | DNA Amount (μg) | EGFR (Ex 19 del) | ||
| Case 1 | Bronchial asthma | 7000 | 100 (1.43) | 31 | 76 | 31 | 9.81 × 10−3 | (+) |
| 250 (3.57) | 89 | 88 | 39 | 19.1 × 10−3 | (+) | |||
| 500 (7.14) | 192 | 79 | 34 | 20.3 × 10−3 | (+) | |||
| Case 2 | Bronchiectasis | 23,000 | 100 (0,43) | 3 | 93 | 43 | 1.86 | (−) |
| Bloody sputum | 250 (1.09) | 32 | 96 | 56 | 1.59 | (−) | ||
| 500 (2.17) | 54 | 101 | 56 | 1.34 | (+) | |||
| Case 3 | Bronchiectasis | 80,000 | 100 (0.13) | 40 | 171 | 5 | 2.69 | (−) |
| Bloody sputum | 250 (0.31) | 37 | 159 | 4 | 2.87 | (−) | ||
| 500 (0.63) | 89 | 162 | 3 | 3.81 | (−) | |||
| Case 4 | Emphysema | 172,000 | 100 (0.06) | 0 | 116 | 5 | 2.63 | (−) |
| Pneumonia | 250 (0.15) | 9 | 123 | 4 | 4.39 | (−) | ||
| 500 (0.29) | 6 | 110 | 5 | 4.28 | (−) | |||
| Cell Line | Cell Counts | LBC (Cytology and Molecular Testing) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cell Counts | HCC827/H1975 (% of Cancer Cells) | Total Cancer Cell Counts (All Fields) | DNA Amount (μg) | EGFR (T790M) | EGFR (Ex 19 del) | ||
| Case 5 | HCC827 | 8000 | 500 (6.25) | 81 | 1.17 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (6.25) | 36 | 0.93 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 1000 (12.5) | 85 | 0.82 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 2000 (25.0) | 445 | 0.17 | (+) | |||
| Case 6 | HCC827 | 10,000 | 500 (5.00) | 89 | 1.70 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (5.00) | 32 | 1.96 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 1000 (10.0) | 69 | 1.65 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 2000 (20.0) | 371 | 1.26 | (−) | |||
| Case 7 | HCC827 | 15,500 | 500 (3.23) | 97 | 0.98 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (3.23) | 41 | 0.83 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 1000 (6.45) | 129 | 0.58 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 2000 (12.9) | 330 | 0.54 | (+) | |||
| Case 8 | HCC827 | 33,500 | 500 (1.49) | 15 | 4.19 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (1.49) | 29 | 2.10 | (−) | |||
| Case 9 | HCC827 | 9000 | 500 (5.56) | 10 | 0.78 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (5.56) | 7 | 0.77 | (−) | |||
| Case 10 | HCC827 | 27,000 | 500 (1.85) | 14 | 1.22 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (1.85) | 22 | 1.11 | (−) | |||
| Case 11 | HCC827 | 15,500 | 500 (3.23) | 24 | 2.52 | (+) | |
| H1975 | 500 (3.23) | 47 | 2.61 | (−) | |||
| Case 12 | HCC827 | 15,000 | 500 (3.33) | 52 | 4.47 | (−) | |
| H1975 | 500 (3.33) | 48 | 3.11 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 1000 (6.67) | 122 | 2.34 | (−) | |||
| H1975 | 2000 (13.3) | 367 | 2.15 | (−) | |||
| Case 13 | HCC827 | 20,000 | 500 (2.50) | 11 | 4.50 | (+) | |
| Case 14 | HCC827 | 38,000 | 500 (1.85) | 8 | 1.50 | (+) | |
| Case 15 | HCC827 | 8500 | 500 (5.88) | 45 | 0.83 | (+) | |
| Case 16 | H1975 | 14,500 | 2000 (13.8) | 369 | 0.56 | (+) | |
| Case 17 | H1975 | 19,000 | 2000 (10.5) | 256 | 3.24 | (−) | |
| Case 18 | H1975 | 17,000 | 2000 (11.8) | 164 | 7.53 | (−) | |
| Case 19 | H1975 | 18,500 | 2000 (10.8) | 196 | 1.95 | (−) | |
| Case 20 | H1975 | 13,000 | 2000 (15.4) | 186 | 1.13 | (−) | |
| Cell Line | Cell Counts | LBC (Cytology and Molecular Testing) | NGS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Cell Counts | HCC827/H1975 (% of Cancer Cells) | Total Cancer Cell Counts (All Fields) | DNA Amount (μg) | EGFR Mutation (F-PHFA) | Cancer Hot Spot Panel v2 | ||
| Case 5 | HCC827 | 8000 | 500 (6.25) | 81 | 1.17 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| H1975 | 2000 (25.0) | 445 | 0.17 | T790M+/L858R+ | T790M+/L858R+ | ||
| Case 6 | HCC827 | 10,000 | 500 (5.00) | 89 | 1.70 | Ex19 del + | (−) |
| H1975 | 2000 (20.0) | 371 | 1.26 | (−) | (−) | ||
| Case 7 | HCC827 | 15,500 | 500 (3.23) | 97 | 0.98 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| H1975 | 2000 (12.9) | 330 | 0.54 | T790M+/L858R+ | (−) | ||
| Case 8 | HCC827 | 33,500 | 500 (1.49) | 15 | 4.19 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 9 | HCC827 | 9000 | 500 (5.56) | 10 | 0.78 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 10 | HCC827 | 27,000 | 500 (1.85) | 14 | 1.22 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 11 | HCC827 | 15,500 | 500 (3.23) | 24 | 2.52 | Ex19 del + | (−) |
| Case 12 | HCC827 | 15,000 | 500 (3.33) | 52 | 4.47 | (−) | (−) |
| H1975 | 2000 (13.3) | 367 | 2.15 | (−) | (−) | ||
| Case 13 | HCC827 | 20,000 | 500 (2.50) | 11 | 4.50 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 14 | HCC827 | 38,000 | 500 (1.85) | 8 | 1.50 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 15 | HCC827 | 8500 | 500 (5.88) | 45 | 0.83 | Ex19 del + | p.E746_A750del (ELREA/−) |
| Case 16 | H1975 | 14,500 | 2000 (13.8) | 369 | 0.56 | T790M+/L858R+ | T790M+/L858R+ |
| Case 17 | H1975 | 19,000 | 2000 (10.5) | 256 | 3.24 | (−) | |
| Case 18 | H1975 | 17,000 | 2000 (11.8) | 164 | 7.53 | (−) | |
| Case 19 | H1975 | 18,500 | 2000 (10.8) | 196 | 1.95 | (−) | |
| Case 20 | H1975 | 13,000 | 2000 (15.4) | 186 | 1.13 | (−) | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, T.; Fujii, T.; Tatsumi, S.; Sugimoto, A.; Sekita-Hatakeyama, Y.; Shimada, K.; Yamazaki, M.; Hatakeyama, K.; Ohbayashi, C. Molecular Analysis of Liquid-Based Cytological Specimen Using Virtually Positive Sputum with Adenocarcinoma Cells. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020084
Nishikawa T, Fujii T, Tatsumi S, Sugimoto A, Sekita-Hatakeyama Y, Shimada K, Yamazaki M, Hatakeyama K, Ohbayashi C. Molecular Analysis of Liquid-Based Cytological Specimen Using Virtually Positive Sputum with Adenocarcinoma Cells. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020084
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Takeshi, Tomomi Fujii, Shigenobu Tatsumi, Aya Sugimoto, Yoko Sekita-Hatakeyama, Keiji Shimada, Masaharu Yamazaki, Kinta Hatakeyama, and Chiho Ohbayashi. 2020. "Molecular Analysis of Liquid-Based Cytological Specimen Using Virtually Positive Sputum with Adenocarcinoma Cells" Diagnostics 10, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020084
APA StyleNishikawa, T., Fujii, T., Tatsumi, S., Sugimoto, A., Sekita-Hatakeyama, Y., Shimada, K., Yamazaki, M., Hatakeyama, K., & Ohbayashi, C. (2020). Molecular Analysis of Liquid-Based Cytological Specimen Using Virtually Positive Sputum with Adenocarcinoma Cells. Diagnostics, 10(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020084





