Subjective Versus Quantitative Methods of Assessing Breast Density
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mammographic Cases
2.2. Subjective Density Assessment
2.3. Quantitative Assessment
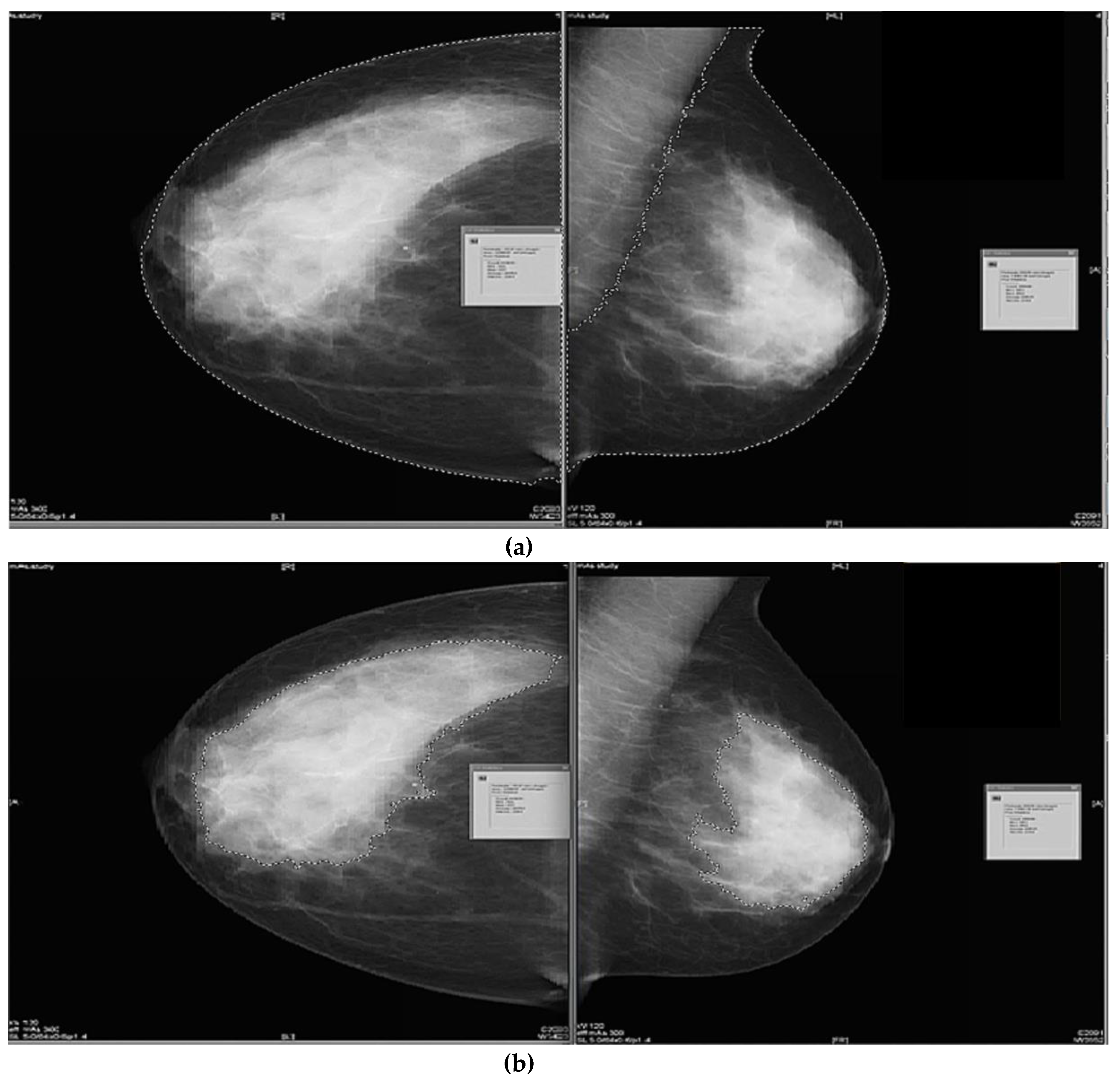
2.3.1. Semi-Subjective Density Assessment
2.3.2. Semi-Objective Density Assessment
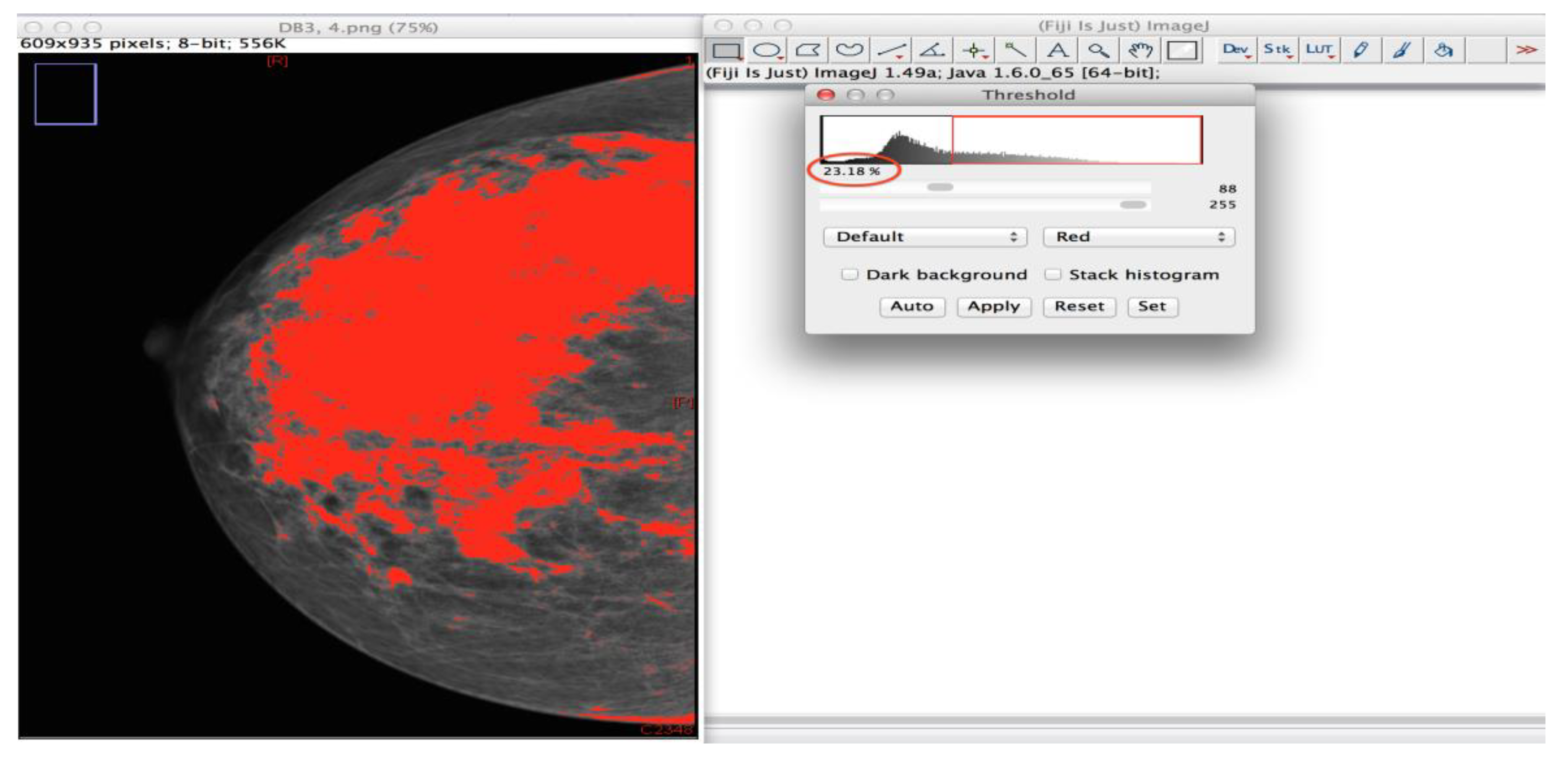
2.3.3. Automated Objective Density Assessment
2.4. Time Difference between Methods
2.5. Amended, BI-RADS Scale
2.6. Distractors within Cases That Impacted the Radiologists’ Breast Density Decisions
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. MBD Assessments
3.2. Time Analysis
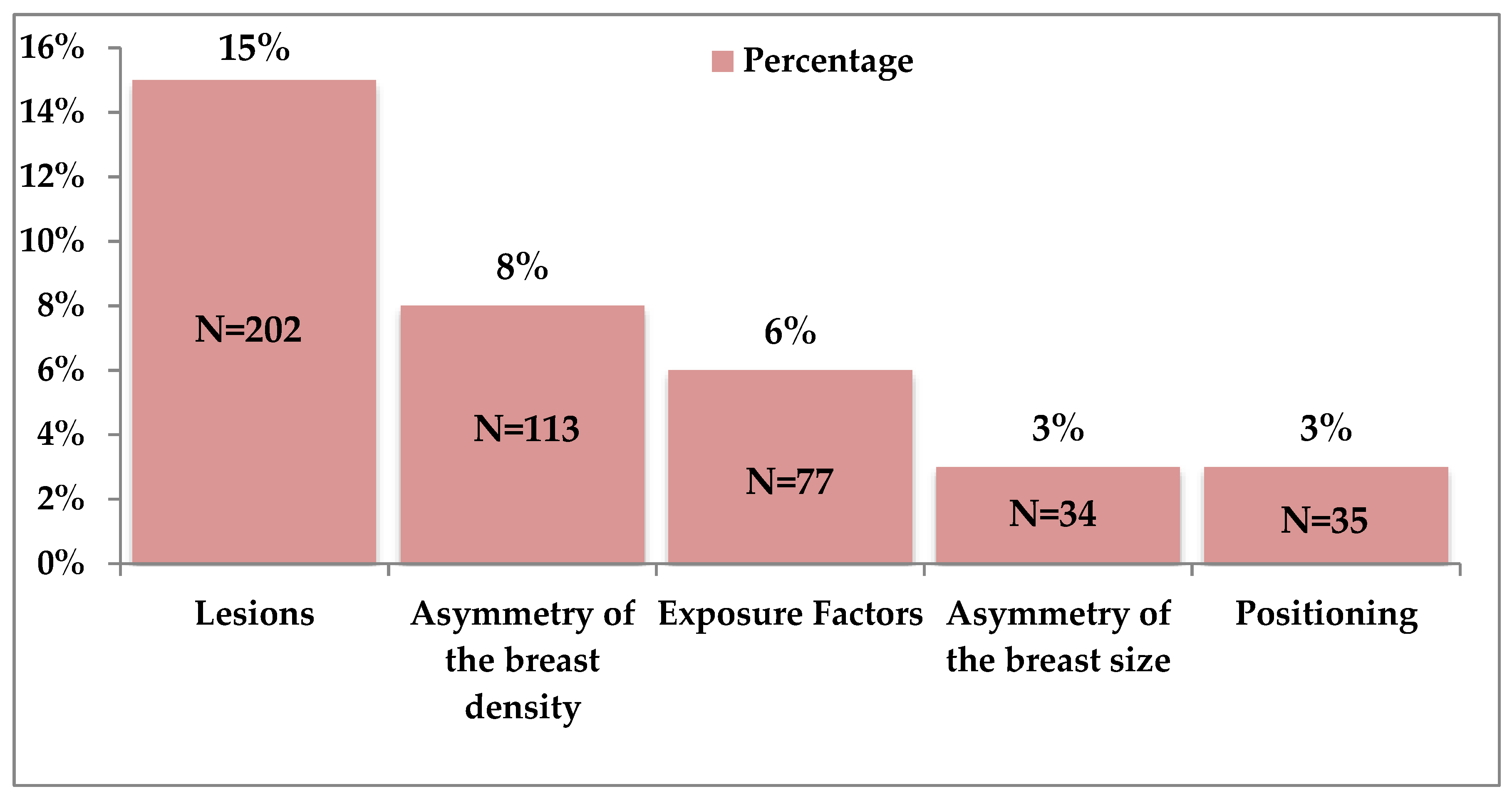
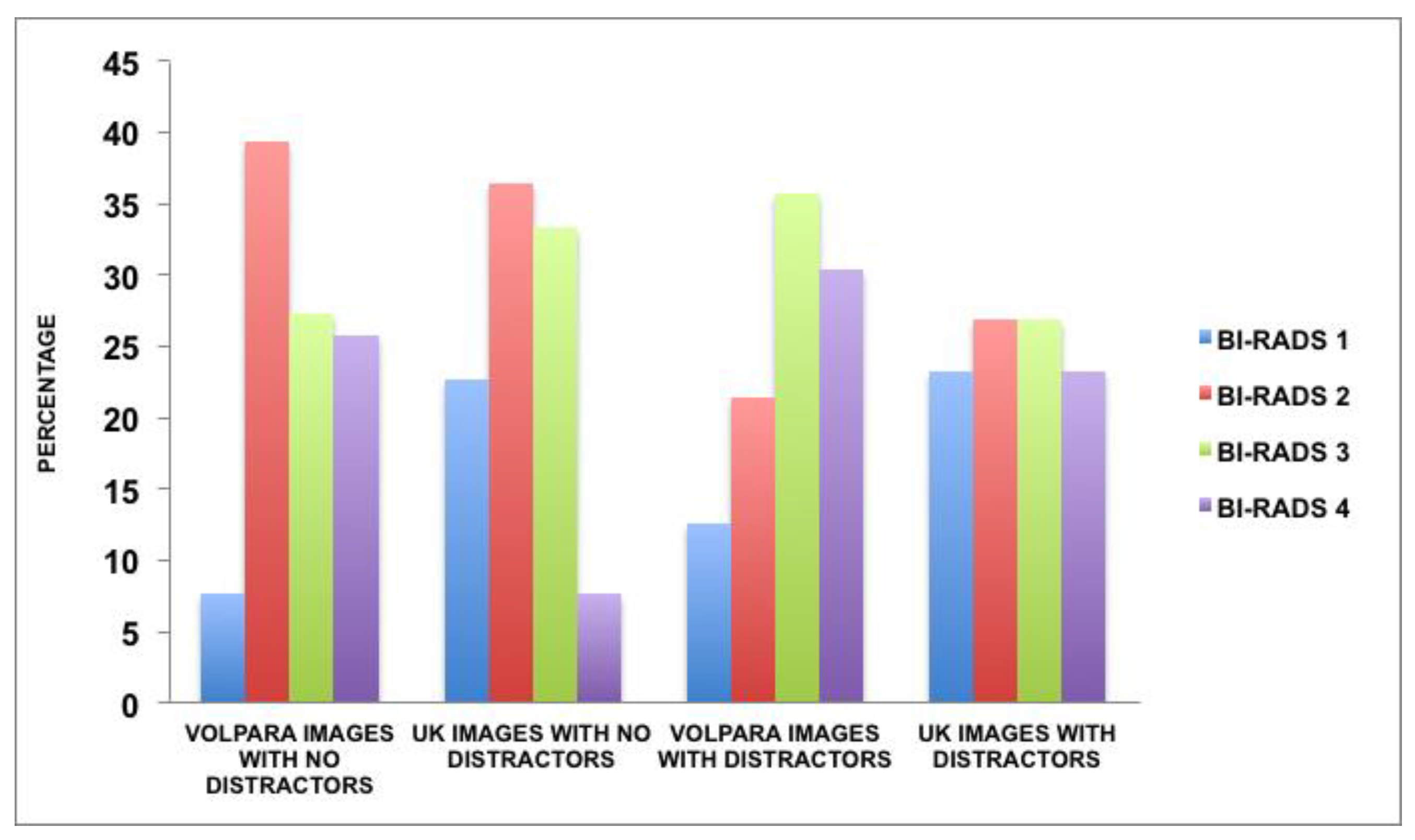
3.3. Image Distractors Influencing MBD Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaffe, M.J. Mammographic density. Measurement of mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziv, E.; Shepherd, J.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Kerlikowske, K. Mammographic breast density and family history of breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, P.A.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Yankaskas, B.C.; Kerlikowske, K.; Rosenberg, R.; Rutter, C.M.; Geller, B.M.; Abraham, L.A.; Taplin, S.H.; Dignan, M.; et al. Individual and combined effects of age, breast density, and hormone replacement therapy use on the accuracy of screening mammography. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, I.; Thurfjell, E.; Holmberg, L. Effect of estrogen and estrogen-progestin replacement regimens on mammographic breast parenchymal density. J. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 15, 3201–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yankaskas, B.C.; Cleveland, R.J.; Schell, M.J.; Kozar, R. Association of Recall Rates with Sensitivity and Positive Predictive Values of Screening Mammography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2001, 177, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurfjell, E. Breast density and the risk of breast cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroudi, S.; Kadir, T.; Brady, M. Automatic classification of mammographic parenchymal patterns: A statistical approach. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEEE Cat. No.03CH37439), Cancun, Mexico, 17–21 September 2003; Available online: http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~timork/Mammo/embs511.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Tagliafico, A.; Tagliafico, G.; Tosto, S.; Chiesa, F.; Martinoli, C.; Derchi, L.E.; Calabrese, M. Mammographic density estimation: Comparison among BI-RADS categories, a semi-automated software and a fully automated one. Breast 2009, 18, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickles, E.; D’Orsi, C.; Bassett, L.; Al, E. ACR BI-RADS ® Mammography. In ACR BI-RADS ® Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; Reston, V.A., Ed.; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Byng, J.W.; Boyd, N.F.; Fishell, E.; A Jong, R.; Yaffe, M.J. The quantitative analysis of mammographic densities. Phys. Med. Boil. 1994, 39, 1629–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, V.; Highnam, R.; Perry, N.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I. Comparison of a new and existing method of mammographic density measurement: Intramethod reliability and associations with known risk factors. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, J.; Szekely, L.; Eriksson, L.; Heddson, B.; Sundbom, A.; Czene, K.; Hall, P.; Humphreys, K. High-throughput mammographic-density measurement: A tool for risk prediction of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovio, U.; Li, J.; Aitken, Z.; Humphreys, K.; Czene, K.; Moss, S.; Hall, P.; McCormack, V.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I. Comparison of fully and semi-automated area-based methods for measuring mammographic density and predicting breast cancer risk. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1908–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eng, A.; Gallant, Z.; Shepherd, J.A.; McCormack, V.; Li, J.; Dowsett, M.; Vinnicombe, S.; Allen, S.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I. Digital mammographic density and breast cancer risk: A case-control study of six alternative density assessment methods. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerlikowske, K.; Ichikawa, L.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Buist, D.S.M.; Vacek, P.M.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Yankaskas, B.; Carney, P.A.; Ballard-Barbash, R. Longitudinal Measurement of Clinical Mammographic Breast Density to Improve Estimation of Breast Cancer Risk. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2007, 99, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.E.; Helvie, M.A.; Zhou, C.; Roubidoux, M.A.; Bailey, J.E.; Paramagul, C.; Blane, C.E.; Klein, K.A.; Sonnad, S.S.; Chan, H.-P. Mammographic Density Measured with Quantitative Computer-aided Method: Comparison with Radiologists’ Estimates and BI-RADS Categories. Radiology 2006, 240, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, C.M.; Van Gils, C.H.; A Sellers, T.; Ghosh, K.; Pruthi, S.; Brandt, K.R.; Pankratz, V.S. Mammographic density, breast cancer risk and risk prediction. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, J.A.; Kerlikowske, K.; Ma, L.; Duewer, F.; Fan, B.; Wang, J.; Malkov, S.; Vittinghoff, E.; Cummings, S.R.; Malkov, S. Volume of mammographic density and risk of breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2011, 20, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.-H.; Yip, C.-H.; Taib, N.A.M. Standardisation of clinical breast-density measurement. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo-Proulx, O.; Mawdsley, G.; Patrie, J.T.; Yaffe, M.J.; A Harvey, J. Reliability of Automated Breast Density Measurements. Radiology 2015, 275, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youk, J.H.; Gweon, H.M.; Son, E.J.; Kim, J.-A. Automated Volumetric Breast Density Measurements in the Era of the BI-RADS Fifth Edition: A Comparison With Visual Assessment. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 206, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpara Solutions Receives FDA Clearance for Volpara Density Maps. Volpara Solutions. 2016. Available online: https://volparasolutions.com/about-volpara/news/volpara-solutions-receives-fda-clearance-for-volpara-density-maps-designed-to-help-identify-the-risk-of-breast-density-masking-a-potential-cancer/ (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Gweon, H.M.; Youk, J.H.; Kim, J.-A.; Son, E.J. Radiologist Assessment of Breast Density by BI-RADS Categories Versus Fully Automated Volumetric Assessment. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 201, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na Lee, H.; Sohn, Y.M.; Han, K. Comparison of mammographic density estimation by Volpara software with radiologists’ visual assessment: Analysis of clinical–radiologic factors affecting discrepancy between them. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, K.; The, J.; Griff, J.; Oliver, L.; Mahal, R.; Saady, M.; Velasquez, M.V. Impact of quantitative breast density on experienced radiologists’ assessment of mammographic breast density Aims and objectives. In Electronic Presentation Online System; European Congress of Radiology: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: http://www.bocaradiology.com/data1/BreastDensityCAD.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2017).
- Damases, C.N.; Brennan, P.C.; Mello-Thoms, C.; McEntee, M.F. Mammographic Breast Density Assessment Using Automated Volumetric Software and Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BIRADS) Categorization by Expert Radiologists. Acad. Radiol. 2016, 23, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.Y.; Kim, E.-K.; Kim, M.J.; Moon, H.J. Mammographic Density Estimation with Automated Volumetric Breast Density Measurement. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durning, M. Breast Density Notification Laws by State—Interactive Map. Diagnostic Imaging. 2016. Available online: http://www.diagnosticimaging.com/breast-imaging/breast-density-notification-laws-state-interactive-map (accessed on 3 June 2017).
- Alomaim, W.; O’Leary, D.; Ryan, J.; Rainford, L.; Evanoff, M.; Foley, S. Variability of Breast Density Classification Between US and UK Radiologists. J. Med Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2019, 50, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damases, C.N.; Hogg, P.; McEntee, M.F. Inter country analysis of breast density classification using visual grading. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20170064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, A.; Comas, M.; Macià, F.; Ferrer, F.; Murta-Nascimento, C.; Maristany, M.T.; Molins, E.; Sala, M.; Castells, X. Inter- and intraradiologist variability in the BI-RADS assessment and breast density categories for screening mammograms. Br. J. Radiol. 2012, 85, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, E.N.; Yepes, M. The conundrum of explaining breast density to patients. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2013, 80, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, J.; Stockton, D.; Godward, S. Impact of false-positive mammography on subsequent screening attendance and risk of cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraudeau, B.; Mary, J.Y. Planning a reproducibility study: How many subjects and how many replicates per subject for an expected width of the 95 per cent confidence interval of the intraclass correlation coefficient. Stat. Med. 2001, 20, 3205–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundel, H.L.; Polansky, M. Measurement of Observer Agreement. Radiology 2003, 228, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooms, E.; Zonderland, H.; Eijkemans, M.; Kriege, M.; Delavary, B.M.; Burger, C.; Ansink, A. Mammography: Interobserver variability in breast density assessment. Breast 2007, 16, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubern-Merida, A.; Kallenberg, M.; Platel, B.; Mann, R.M.; Martí, R.; Karssemeijer, N. Volumetric Breast Density Estimation from Full-Field Digital Mammograms: A Validation Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NEMA. Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) Part 14: Greyscale Standard Display Function; (NEMA) National Electrical Manufacturers Association: Rosslyn, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Byng, J.W.; Yaffe, M.J.; A Jong, R.; Shumak, R.S.; A Lockwood, G.; Tritchler, D.L.; Boyd, N.F. Analysis of mammographic density and breast cancer risk from digitized mammograms. Radiographics 1998, 18, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.; Guo, H.; Martin, L.J.; Sun, L.; Stone, J.; Fishell, E.; Jong, R.A.; Hislop, G.; Chiarelli, A.; Minkin, S.; et al. Mammographic Density and the Risk and Detection of Breast Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; Byng, J.W.; Jong, R.A.; Fishell, E.K.; Little, L.E.; Lockwood, G.A.; Tritchler, D.L.; Yaffe, M.J.; Miller, A.B. Quantitative Classification of Mammographic Densities and Breast Cancer Risk: Results From the Canadian National Breast Screening Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, J.M.; Lindfors, K.K.; Beatty, C.S.; Seibert, J.A. A breast density index for digital mammograms based on radiologists’ randing. J. Digit. Imaging 1998, 11, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Highnam, R.; Sauber, N.; Destounis, S.; Harvey, J.; McDonald, D. Breast Density into Clinical Practice. In Breast Imaging IWDM 2012 Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Maidment, A.D.A., Bakic, P.R., Gavenonis, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 7361, pp. 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Sharma, M.; Singla, V.; Khandelwal, N. Breast Density Estimation with Fully Automated Volumetric Method. Acad. Radiol. 2016, 23, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, J.S.; Czene, K.; Shepherd, J.A.; Leifland, K.; Heddson, B.; Sundbom, A.; Eriksson, M.; Li, J.; Humphreys, K.; Hall, P. Automated Measurement of Volumetric Mammographic Density: A Tool for Widespread Breast Cancer Risk Assessment. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, K.; Kallenberg, M.; Mann, R.; van Gils, C.; Karssemeijer, N. Stability of Volumetric Tissue Composition Measured in Serial Screening Mammograms. In International Workshop on Digital Mammography; Fujita, H., Hara, T., Muramatsu, C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8539, pp. 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Weighted kappa: Nominal scale agreement with provision for scaled disagreement or partial credit. Psychol. Bull. 1968, 70, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, K.O.; Wong, S.P. Forming inferences about some intraclass correlation coefficients. Psychological Methods. 1996, 1, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, K. On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a correlated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supposed to have arisen from random sampling. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1900, 50, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosall, N.K.; Gosall, G.S. The Doctor’s Guide to Critical Appraisal, 3rd ed.; PasTest: Knutsford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sauber, N.; Chan, A.; Highnam, R. BI-RADS breast density classification-an international standard? In European Congress of Radiology; Electronic Presentation Online System: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Highnam, R.; Brady, S.M.; Yaffe, M.J.; Karssemeijer, N.; Harvey, J. Robust Breast Composition Measurement-VolparaTM. In 10th International Conference on Digital Mammography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.B.; Moore, S.; Polk, S.; Shtatland, E.; Elmore, J.G.; Fletcher, S.W. Increased patient concern after false-positive mammograms: Clinician documentation and subsequent ambulatory visits. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, H.; Lång, K.; Rosso, A.; Borgquist, S.; Zackrisson, S.; Timberg, P. Measuring mammographic density: Comparing a fully automated volumetric assessment versus European radiologists’ qualitative classification. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 4354–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destounis, S.; Arieno, A.; Morgan, R.; Roberts, C.; Chan, A. Qualitative Versus Quantitative Mammographic Breast Density Assessment: Applications for the US and Abroad. Diagnostics 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Waal, D.; Heeten, G.J.D.; Pijnappel, R.M.; Schuur, K.H.; Timmers, J.M.H.; Verbeek, A.L.M.; Broeders, M.J.M. Comparing Visually Assessed BI-RADS Breast Density and Automated Volumetric Breast Density Software: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Breast Cancer Screening Setting. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L. The Density Conundrum: Does Legislation Help or Hurt? J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2013, 10, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, M.A.; Walker, E.; Abujudeh, H.H. Understanding and Confronting Our Mistakes: The Epidemiology of Error in Radiology and Strategies for Error Reduction. Radiographics 2015, 35, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, N.S.; Raza, S.; Mackesy, M.; Birdwell, R.L. Breast Density: Clinical Implications and Assessment Methods. Radiographics 2015, 35, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffers, A.M.; Sieh, W.; Lipson, J.A.; Rothstein, J.H.; McGuire, V.; Whittemore, A.S.; Rubin, D.L. Breast Cancer Risk and Mammographic Density Assessed with Semiautomated and Fully Automated Methods and BI-RADS. Radiology 2016, 282, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivaramakrishna, R.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chilcote, W.A.; Powell, K.A. Automatic Segmentation of Mammographic Density. Acad. Radiol. 2001, 8, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couwenberg, A.M.; Verkooijen, H.M.; Li, J.; Pijnappel, R.M.; Charaghvandi, K.R.; Hartman, M.; Van Gils, C.H. Assessment of a fully automated, high-throughput mammographic density measurement tool for use with processed digital mammograms. Cancer Causes Control. 2014, 25, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevrhal, S.; Shepherd, J.A.; Smith-Bindman, R.; Cummings, S.; Kerlikowske, K. Accuracy of mammographic breast density analysis: Results of formal operator training. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2002, 11, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Engeland, S.; Snoeren, P.; Huisman, H.; Boetes, C.; Karssemeijer, N. Volumetric breast density estimation from full-field digital mammograms. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 2006, 25, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, V.; Dos-Santos-Silva, I. Breast Density and Parenchymal Patterns as Markers of Breast Cancer Risk: A Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2006, 15, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokate, M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Kallenberg, M.G.; Bosch, M.A.A.J.V.D.; Peeters, P.H.M.; Van Gils, C.H. Volumetric Breast Density from Full-Field Digital Mammograms and Its Association with Breast Cancer Risk Factors: A Comparison with a Threshold Method. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2010, 19, 3096–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Eagleman, D.M.; Tse, P.U.; Buonomano, D.; Janssen, P.; Nobre, A.C.; Holcombe, A.O. Time and the Brain: How Subjective Time Relates to Neural Time. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 10369–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodine, C.F.; Mello-Thoms, C.; Kundel, H.L.; Weinstein, S.P. Time Course of Perception and Decision Making During Mammographic Interpretation. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2002, 179, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheddad, A.; Czene, K.; Eriksson, M.; Li, J.; Easton, D.; Hall, P.; Humphreys, K. Area and Volumetric Density Estimation in Processed Full-Field Digital Mammograms for Risk Assessment of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Breast Density | Image Sets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | D | E | Repeated Cases | |
| BI-RADS 1 | 14% | 25% | 22% | 17% | 22% | 7% |
| BI-RADS 2 | 36% | 17% | 22% | 28% | 25% | 57% |
| BI-RADS 3 | 36% | 39% | 39% | 39% | 36% | 21% |
| BI-RADS 4 | 14% | 19% | 17% | 17% | 17% | 14% |
| Breast Density | Researcher | VOLPARA |
|---|---|---|
| BI-RADS 1 | 16% | 10% |
| BI-RADS 2 | 29% | 31% |
| BI-RADS 3 | 41% | 31% |
| BI-RADS 4 | 14% | 28% |
| Subjects | VOLPARA | Hand Delineation | ImageJ |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA radiologists | 0.639 * | 0.632 * | 0.752 * |
| UK radiologists | 0.589 * | 0.680 * | 0.768 * |
| Subjects | VOLPARA |
|---|---|
| Hand Delineation | 0.597 * |
| ImageJ | 0.603 * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alomaim, W.; O’Leary, D.; Ryan, J.; Rainford, L.; Evanoff, M.; Foley, S. Subjective Versus Quantitative Methods of Assessing Breast Density. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050331
Alomaim W, O’Leary D, Ryan J, Rainford L, Evanoff M, Foley S. Subjective Versus Quantitative Methods of Assessing Breast Density. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(5):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050331
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlomaim, Wijdan, Desiree O’Leary, John Ryan, Louise Rainford, Michael Evanoff, and Shane Foley. 2020. "Subjective Versus Quantitative Methods of Assessing Breast Density" Diagnostics 10, no. 5: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050331
APA StyleAlomaim, W., O’Leary, D., Ryan, J., Rainford, L., Evanoff, M., & Foley, S. (2020). Subjective Versus Quantitative Methods of Assessing Breast Density. Diagnostics, 10(5), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10050331





