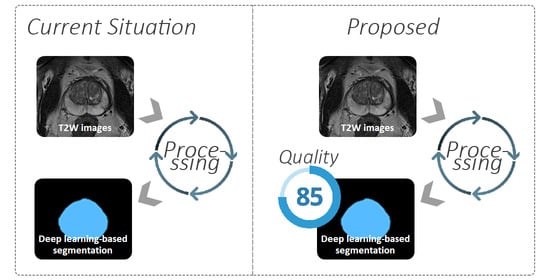
A Quality Control System for Automated Prostate Segmentation on T2-Weighted MRI
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Prostate Segmentation
2.3. Reference Quality Scores
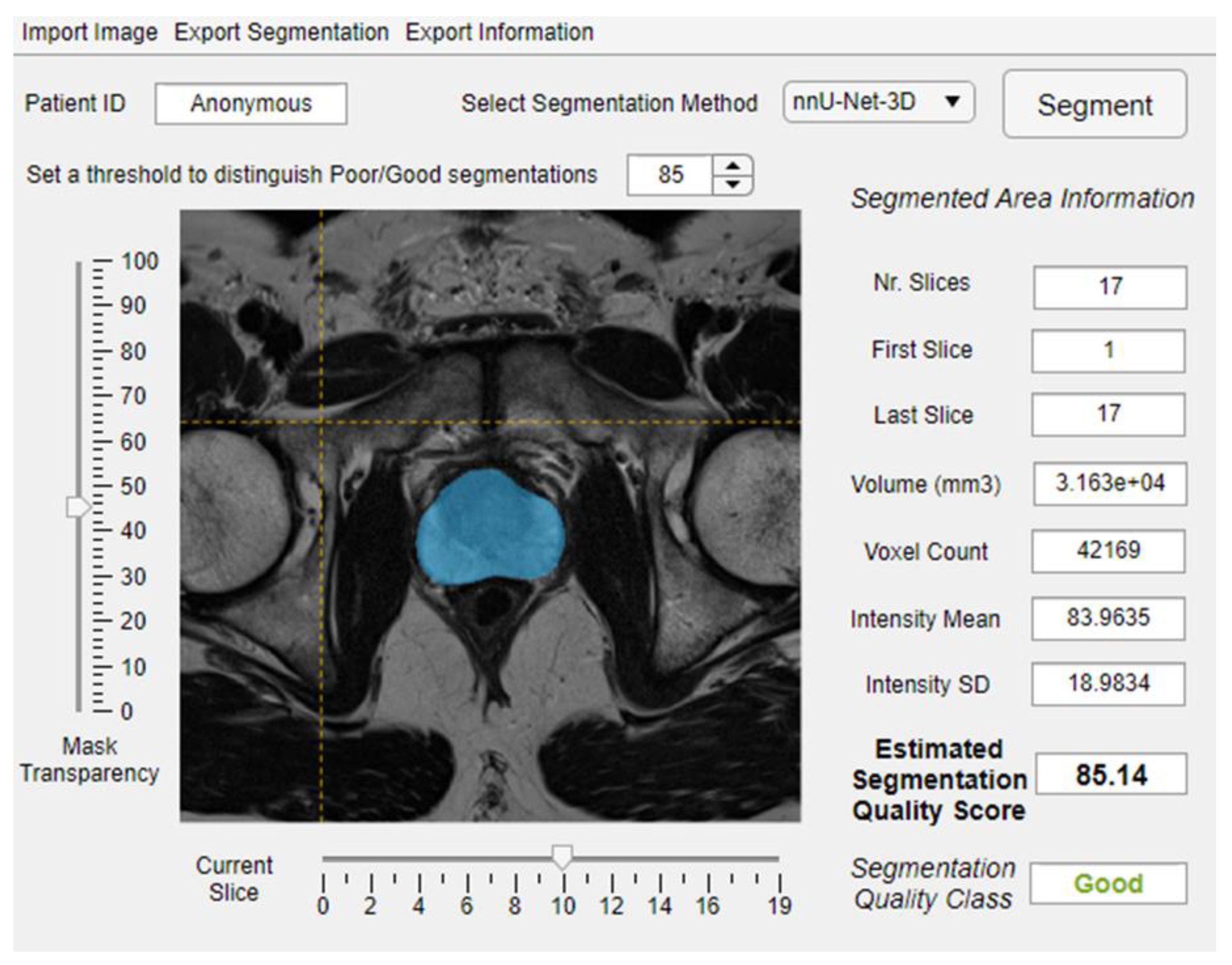
2.4. Quality Control System
2.4.1. Data Preparation
2.4.2. Model Training, Optimizing and Testing
3. Results
3.1. Reference Quality Scores
3.2. Training and Optimization
3.3. Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Richenberg, J.; Clements, R.; Choyke, P.; Verma, S.; Villeirs, G.; Rouviere, O.; Logager, V.; Futterer, J.J. ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur. Radiol. 2012, 22, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System: 2015, Version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruprecht, O.; Weisser, P.; Bodelle, B.; Ackermann, H.; Vogl, T.J. MRI of the prostate: Interobserver agreement compared with histopathologic outcome after radical prostatectomy. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litjens, G.; Debats, O.; Barentsz, J.; Karssemeijer, N.; Huisman, H. Computer-aided detection of prostate cancer in MRI. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 33, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Burtt, K.; Turkbey, B.; Choyke, P.; Summers, R.M. Computer aided-diagnosis of prostate cancer on multiparametric MRI: A technical review of current research. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 789561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrock, T.; Vos, P.C.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.A.; Barentsz, J.O.; Huisman, H.J. Prostate cancer: Computer-aided diagnosis with multiparametric 3-T MR imaging—Effect on observer performance. Radiology 2013, 266, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemaitre, G.; Marti, R.; Freixenet, J.; Vilanova, J.C.; Walker, P.M.; Meriaudeau, F. Computer-Aided Detection and diagnosis for prostate cancer based on mono and multi-parametric MRI: A review. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 60, 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-Net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Jäger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Automated Design of Deep Learning Methods for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.08128. [Google Scholar]
- Zavala-Romero, O.; Breto, A.L.; Xu, I.S.R.; Chang, Y.C.C.; Gautney, N.; Pra, A.D.; Abramowitz, M.C.; Pollack, A.; Stoyanova, R. Segmentation of prostate and prostate zones using deep learning A multi-MRI vendor analysis. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Lei, Y.; Tian, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Patel, P.; Jani, A.B.; Mao, H.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; et al. Deeply supervised 3D fully convolutional networks with group dilated convolution for automatic MRI prostate segmentation. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Wang, X.; Kim, J.; Khadra, M.; Fulham, M.; Feng, D. A propagation-DNN: Deep combination learning of multi-level features for MR prostate segmentation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 170, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. In International Conference on Medical image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Toth, R.; van de Ven, W.; Hoeks, C.; Kerkstra, S.; van Ginneken, B.; Vincent, G.; Guillard, G.; Birbeck, N.; Zhang, J.; et al. Evaluation of prostate segmentation algorithms for MRI: The PROMISE12 challenge. Med. Image Anal. 2014, 18, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato, S.G., 3rd; Huisman, H.; Drukker, K.; Hadjiiski, L.; Kirby, J.S.; Petrick, N.; Redmond, G.; Giger, M.L.; Cha, K.; Mamonov, A.; et al. PROSTATEx Challenges for computerized classification of prostate lesions from multiparametric magnetic resonance images. J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 044501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaev, I. Fully Convolutional Neural Network with Residual Connections for Automatic Segmentation of Prostate Structures from MR Images. Available online: https://grand-challenge-public.s3.amazonaws.com/evaluation-supplementary/40/d70ba7d1-bc95-439e-a81e-7f1a4ed5fda0/18_MBIOS.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2020).
- Klein, S.; van der Heide, U.A.; Lips, I.M.; van Vulpen, M.; Staring, M.; Pluim, J.P.W. Automatic segmentation of the prostate in 3D MR images by atlas matching using localized mutual information. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimann, T.; van Ginneken, B.; Styner, M.A.; Arzhaeva, Y.; Aurich, V.; Bauer, C.; Beck, A.; Becker, C.; Beichel, R.; Bekes, G.; et al. Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2009, 28, 1251–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, S.S.; Dowling, J.A.; Shen, K.K.; Raniga, P.; Pluim, J.P.; Greer, P.B.; Salvado, O.; Fripp, J. Patient specific prostate segmentation in 3-d magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tustison, N.J.; Avants, B.B.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J.C. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunoqrot, M.R.S.; Nketiah, G.A.; Selnaes, K.M.; Bathen, T.F.; Elschot, M. Automated reference tissue normalization of T2-weighted MR images of the prostate using object recognition. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, E104–E107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, A.; Sehgal, C.M.; Greenleaf, J.F. Use of Gray Value Distribution of Run Lengths for Texture Analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 1990, 11, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, G.; Fertil, B.; Navarro, C.; Pereira, S.; Cau, P.; Levy, N.; Sequeira, J.; Mari, J. Texture Indexes and Gray Level Size Zone Matrix. Application to Cell Nuclei Classification. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Information Processing, Minsk, Belarus, Minsk, Belarus, 19–21 May 2009; pp. 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.J.; Wee, W.G. Neighboring Gray Level Dependence Matrix for Texture Classification. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1983, 23, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadasun, M.; King, R. Textural Features Corresponding to Textural Properties. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical Methods for Assessing Agreement between Two Methods of Clinical Measurement. Lancet 1986, 1, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayadevan, R.; Zhou, S.; Priester, A.M.; Delfin, M.; Marks, L.S. Use of MRI-ultrasound Fusion to Achieve Targeted Prostate Biopsy. J. Vis. Exp. 2019, 146, e59231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salembier, C.; Villeirs, G.; De Bari, B.; Hoskin, P.; Pieters, B.R.; Van Vulpen, M.; Khoo, V.; Henry, A.; Bossi, A.; De Meerleer, G.; et al. ESTRO ACROP consensus guideline on CT- and MRI-based target volume delineation for primary radiation therapy of localized prostate cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xie, H.H.; Wang, H.H.; Han, C.; Yang, J.J.; Lin, Z.Y.; Li, Y.F.; He, Q.; Wang, R.; Cui, Y.P.; et al. MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for the Preoperative Prediction of Extracapsular Extension of Prostate Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, X.D.; Li, M.; Dong, D.; Feng, Z.Y.; Zhang, P.P.; Ke, Z.; You, H.J.; Han, F.F.; Ma, H.; Tian, J.; et al. Multi-parametric MRI-based radiomics signature for discriminating between clinically significant and insignificant prostate cancer: Cross-validation of a machine learning method. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 115, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, L.; Mao, L.; Li, X.; Yan, W.; Xiao, Y.; Lei, J.; Sun, H.; Jin, Z. Radiomics Based on Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Predict Extraprostatic Extension of Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2014, 8689, 818–833. [Google Scholar]
- Valindria, V.V.; Lavdas, I.; Bai, W.; Kamnitsas, K.; Aboagye, E.O.; Rockall, A.G.; Rueckert, D.; Glocker, B. Reverse Classification Accuracy: Predicting Segmentation Performance in the Absence of Ground Truth. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, R.; Valindria, V.V.; Bai, W.; Oktay, O.; Kainz, B.; Suzuki, H.; Sanghvi, M.M.; Aung, N.; Paiva, J.M.; Zemrak, F.; et al. Automated quality control in image segmentation: Application to the UK Biobank cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging study. J. Cardiovasc. Magn. Reson. 2019, 21, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy, A.G.; Conjeti, S.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Bayesian QuickNAT: Model uncertainty in deep whole-brain segmentation for structure-wise quality control. NeuroImage 2019, 195, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Model | N | MAE ± SD | IQR | Slope | Intercept | Rho | Correlation p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | 584 | 5.37 ± 11.02 | 9.32 | 0.72 | 22.40 | 0.70 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—U-Net | 89 | 5.48 ± 9.04 | 7.20 | 0.67 | 27.83 | 0.49 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—V-Net | 89 | 5.91 ± 8.21 | 6.80 | 0.40 | 50.43 | 0.43 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—nnU-Net-2D | 89 | 5.14 ± 6.04 | 5.96 | 0.40 | 51.25 | 0.41 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—nnU-Net-3D | 89 | 5.89 ± 7.79 | 5.64 | 0.47 | 44.97 | 0.40 | <0.001 |
| In-house—U-Net | 57 | 9.55 ± 17.24 | 22.95 | 0.86 | 7.92 | 0.70 | <0.001 |
| In-house—V-Net | 57 | 6.58 ± 13.01 | 12.33 | 1.07 | −9.55 | 0.55 | <0.001 |
| In-house—nnU-Net-2D | 57 | 8.18 ± 14.2 | 21.26 | 0.71 | 21.99 | 0.67 | <0.001 |
| In-house—nnU-Net-3D | 57 | 8.35 ± 19.02 | 14.78 | 0.75 | 20.73 | 0.48 | <0.001 |
| Sub-Results Combination | N | MAE ± SD | IQR | Slope | Intercept | Rho | Correlation p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROSTATEx—U-Net | 89 | 5.24 ± 5.28 | 6.20 | 0.36 | 52.69 | 0.50 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—V-Net | 89 | 5.50 ± 4.67 | 5.33 | 0.27 | 61.28 | 0.38 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—nnU-Net-2D | 89 | 5.41 ± 4.46 | 5.37 | 0.26 | 62.80 | 0.43 | <0.001 |
| PROSTATEx—nnU-Net-3D | 89 | 4.85 ± 5.76 | 6.12 | 0.35 | 57.17 | 0.50 | <0.001 |
| In-house—U-Net | 57 | 7.27 ± 12.61 | 19.84 | 0.73 | 17.59 | 0.76 | <0.001 |
| In-house—V-Net | 57 | 4.39 ± 6.64 | 6.47 | 0.59 | 34.65 | 0.70 | <0.001 |
| In-house—nnU-Net-2D | 57 | 4.84 ± 12.4 | 17.78 | 0.78 | 16.90 | 0.87 | <0.001 |
| In-house—nnU-Net-3D | 57 | 5.76 ± 20.79 | 10.17 | 1.02 | −3.50 | 0.74 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunoqrot, M.R.S.; Selnæs, K.M.; Sandsmark, E.; Nketiah, G.A.; Zavala-Romero, O.; Stoyanova, R.; Bathen, T.F.; Elschot, M. A Quality Control System for Automated Prostate Segmentation on T2-Weighted MRI. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090714
Sunoqrot MRS, Selnæs KM, Sandsmark E, Nketiah GA, Zavala-Romero O, Stoyanova R, Bathen TF, Elschot M. A Quality Control System for Automated Prostate Segmentation on T2-Weighted MRI. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(9):714. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090714
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunoqrot, Mohammed R. S., Kirsten M. Selnæs, Elise Sandsmark, Gabriel A. Nketiah, Olmo Zavala-Romero, Radka Stoyanova, Tone F. Bathen, and Mattijs Elschot. 2020. "A Quality Control System for Automated Prostate Segmentation on T2-Weighted MRI" Diagnostics 10, no. 9: 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090714
APA StyleSunoqrot, M. R. S., Selnæs, K. M., Sandsmark, E., Nketiah, G. A., Zavala-Romero, O., Stoyanova, R., Bathen, T. F., & Elschot, M. (2020). A Quality Control System for Automated Prostate Segmentation on T2-Weighted MRI. Diagnostics, 10(9), 714. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10090714