Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Index and Reference Test
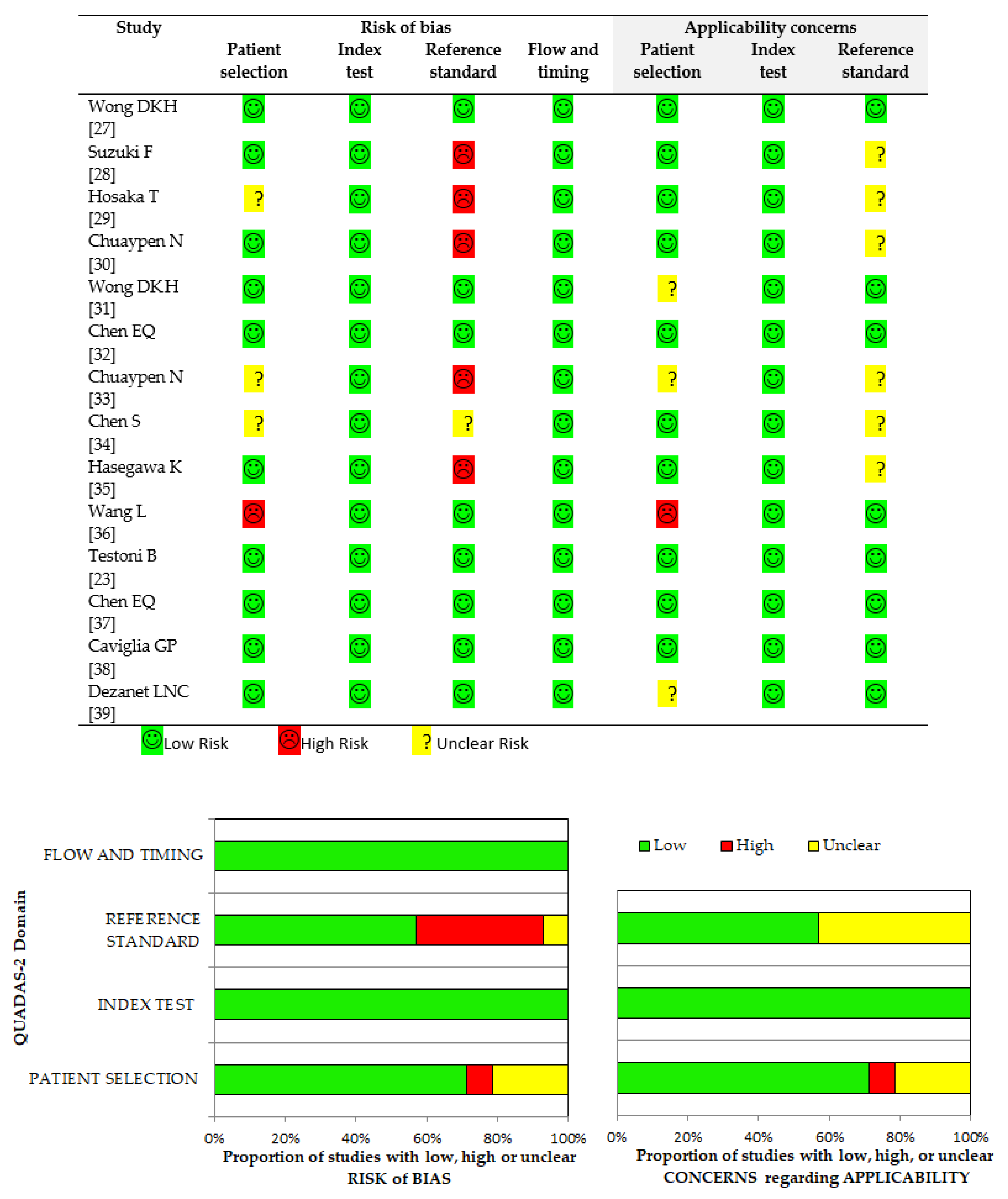
2.4. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Study Population
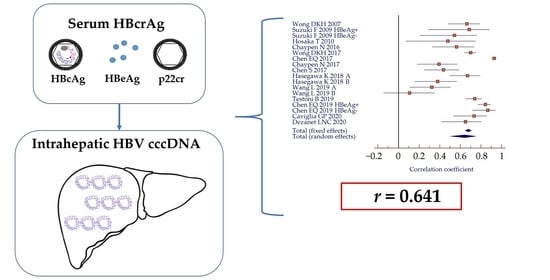
3.2. Correlation between Serum HBcrAg and Intrahepatic HBV cccDNA
3.3. Comparison between HBcrAg and HBsAg Performance
3.4. Performance of HBcrAg According to HBeAg-Positivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seto, W.K.; Lo, Y.R.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Yuen, M.F. Chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2018, 392, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; Global Hepatitis Programme: Geneva, Switzerland, April 2017; Available online: http://www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ (accessed on 21 November 2020).
- Charre, C.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Scholtès, C. Non-invasive biomarkers for chronic hepatitis B virus infection management. Antivir. Res. 2019, 169, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Olivero, A.; Ngatchou, D.; Saracco, G.M.; Smedile, A. Long-term results of chronic hepatitis B antiviral treatment with nucleos(t)ide analogues: A single center experience. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2019, 65, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M. HBV cccDNA: Viral persistence reservoir and key obstacle for a cure of chronic hepatitis B. Gut 2015, 64, 1972–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caviglia, G.; Abate, M.L.; Tandoi, F.; Ciancio, A.; Amoroso, A.; Salizzoni, M.; Saracco, G.; Rizzetto, M.; Romagnoli, R.; Smedile, A. Quantitation of HBV cccDNA in anti-HBc-positive liver donors by droplet digital PCR: A new tool to detect occult infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armandi, A.; Rosso, C.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Caviglia, G. Moving towards core antigen for the management of patients with overt and occult HBV infection. Panminerva Med. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudi, I.; Inoue, T.; Tanaka, Y. Novel biomarkers of Hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma: Clinical significance of HBcrAg and M2BPGi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Exosomes mediate hepatitis B virus (HBV) transmission and NK-cell dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, L. Exosomes modulate the viral replication and host immune responses in HBV infection. Biomed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 2103943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Noviello, D.; Olivero, A.; Rosso, C.; Troshina, G.; Ciancio, A.; Rizzetto, M.; Saracco, G.; Smedile, A. hepatitis B core-related antigen kinetics in chronic hepatitis B virus genotype D-infected patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues or pegylated-interferon-α. Hepatol. Res. 2017, 47, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werle–Lapostolle, B.; Bowden, S.; Locarnini, S.; Wursthorn, K.; Petersen, J.; Lau, G.; Trepo, C.; Marcellin, P.; Goodman, Z.; Delaney, W.E.; et al. Persistence of cccDNA during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B and decline during adefovir dipivoxil therapy. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.J.; Nguyen, T.; Iser, D.; Ayres, A.; Jackson, K.; Littlejohn, M.; Slavin, J.; Bowden, S.; Gane, E.J.; Abbott, W.; et al. Serum hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B e antigen titers: Disease phase influences correlation with viral load and in-trahepatic hepatitis B virus markers. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1933–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cai, Q.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Z. Different Mechanisms May Exist for HBsAg synthesis and secretion during various phases of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Noviello, D.; Pellicano, R.; Olivero, A. Role of serum hepatitis B core-related antigen in chronic hepatitis B infection. Minerva Biotecnol. 2018, 30, 29–35. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, L.Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Cheung, K.-S.; Seto, W.-K.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Review article: Hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg): An emerging marker for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveri, F.; Surace, L.; Cavallone, D.; Colombatto, P.; Ricco, G.; Salvati, N.; Coco, B.; Romagnoli, V.; Gattai, R.; Salvati, A.; et al. Long-term outcome of inactive and active, low viraemic HBeAg-negative-hepatitis B virus infection: Benign course towards HBsAg clearance. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1622–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro-Barciela, M.; Bes, M.; Rodríguez-Frías, F.; Tabernero, D.; Ruiz, A.; Casillas, R.; Vidal-González, J.; Homs, M.; Nieto, L.; Sauleda, S.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen is more accurate than hepatitis B surface antigen to identify inactive carriers, regardless of hepatitis B virus genotype. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Höner Zu Siederdissen, C.; Maasoumy, B.; Cornberg, M. New viral biomarkers for Hepatitis B: Are we able to change practice? J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svicher, V.; Salpini, R.; Malagnino, V.; Piermatteo, L.; Alkhatib, M.; Cerva, C.; Sarmati, L. New markers in monitoring the reactivation of hepatitis B virus infection in immunocompromised hosts. Viruses 2019, 11, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beudeker, B.J.B.; Groothuismink, Z.M.A.; de Man, R.A.; Witjes, C.D.M.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Boonstra, A.; Sonneveld, M.J. Hepatitis B core-related antigen levels predict recurrence-free survival in patients with HBV-associated early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from a Dutch long-term follow-up study. J. Viral. Hepat. 2021, 28, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, B.; Lebossé, F.; Scholtes, C.; Berby, F.; Miaglia, C.; Subic, M.; Loglio, A.; Facchetti, F.; Lampertico, P.; Levrero, M.; et al. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen (HBcrAg) correlates with covalently closed circular DNA transcriptional activity in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.M. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Tanaka, Y.; Lai, C.-L.; Mizokami, M.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.-F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigens as markers for monitoring chronic hepatitis B infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3942–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, F.; Miyakoshi, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Kumada, H. Correlation between serum hepatitis B virus core-related antigen and intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosaka, T.; Suzuki, F.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Kawamura, Y.; Yatsuji, H.; Sezaki, H.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; et al. HBcrAg is a predictor of post-treatment recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma during antiviral therapy. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuaypen, N.; Posuwan, N.; Payungporn, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinkai, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen as a treatment predictor of pegylated interferon in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. Liver Int. 2016, 36, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Cheung, K.-S.; Chong, C.-K.; Huang, F.-Y.; Fung, J.; Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Hepatitis B virus core-related antigen as a surrogate marker for covalently closed circular DNA. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.-Q.; Feng, S.; Wang, M.-L.; Liang, L.-B.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Du, L.-Y.; Yan, L.-B.; Tao, C.-M.; Tang, H. Serum hepatitis B core-related antigen is a satisfactory surrogate marker of intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA in chronic hepatitis B. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chuaypen, N.; Posuwan, N.; Chittmittraprap, S.; Hirankarn, N.; Treeprasertsuk, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Shinkai, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Tangkijvanich, P. Predictive role of serum HBsAg and HBcrAg kinetics in patients with HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B receiving pegylated interferon-based therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 306.e7–306.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Jia, J.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, M.; Feng, H.; Guan, W.; Ji, J.; Gao, Z.; Gao, C. Clinical evaluation of hepatitis B core-related antigen in chronic hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Takashima, T.; Aizawa, N.; Takata, R.; Yoh, K.; et al. Proposed model for the prediction of intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA level in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Deng, J.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, H. Correlation of HBcrAg with intrahepatic hepatitis B virus Total DNA and covalently closed circular DNA in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01303–e01318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, E.Q.; Wang, M.L.; Tao, Y.C.; Wu, D.B.; Liao, J.; He, M.; Tang, H. Serum HBcrAg is better than HBV RNA and HBsAg in reflecting intrahepatic covalently closed circular DNA. J. Viral. Hepat. 2019, 26, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, G.; Olivero, A.; Ciancio, A.; Tandoi, F.; Troshina, G.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Younes, R.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Smedile, A.; et al. Analytical and clinical evaluation of a novel assay for anti-HBc IgG measurement in serum of subjects with overt and occult HBV infection. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dezanet, L.N.C.; Maylin, S.; Gabassi, A.; Rougier, H.; Miailhes, P.; Lascoux-Combe, C.; Chas, J.; Girard, P.M.; Delaugerre, C.; Zoulim, F.; et al. Correlation of serum hepatitis B core-related antigen with hepatitis B virus total intrahepatic DNA and co-valently closed circular-DNA viral load in HIV-hepatitis B coinfection. AIDS 2020, 34, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.T.; Han, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, F.M.; Jing, X.; Du, Z. Enhanced specificity of real-time PCR for measurement of hepatitis B virus cccDNA using restriction endonuclease and plasmid-safe ATP-dependent DNase and selective primers. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 169, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, B.; Ni, Y.; Lempp, F.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Urban, S. T5 Exonuclease hydrolysis of hepatitis B virus replicative intermediates allows reliable quantification and fast drug efficacy testing of covalently closed circular DNA by PCR. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01117-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Xi, J.; Liu, H.; Liao, H.; Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Lu, F. Over-gap PCR amplification to identify presence of replication-competent HBV DNA from integrated HBV DNA: An updated occult HBV infection definition. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durantel, D.; Zoulim, F. New antiviral targets for innovative treatment concepts for hepatitis B virus and hepatitis delta virus. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Abate, M.L.; Pellicano, R.; Smedile, A. Chronic hepatitis B therapy: Available drugs and treatment guidelines. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2016, 61, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Spyrou, E.; Smith, C.I.; Ghany, M.G. Hepatitis B: Current status of therapy and future therapies. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, B.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F. Challenges to a cure for HBV infection. Semin. Liver Dis. 2017, 37, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Pellicano, R.; Saracco, G.; Smedile, A. Hepatitis B core-related antigen: A serum biomarker for intrahepatic covalently-closed-circular DNA. Clin. Lab. 2018, 64, 411–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooddell, C.I.; Yuen, M.F.; Chan, H.L.; Gish, R.G.; Locarnini, S.A.; Chavez, D.; Given, B.D.; Hamilton, J.; Kanner, S.B.; Lai, C.L.; et al. RNAi-based treatment of chronically infected patients and chimpanzees reveals that integrated hepatitis B virus DNA is a source of HBsAg. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaan0241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milich, D.; Liang, T.J. Exploring the biological basis of hepatitis B e antigen in hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2003, 38, 1075–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Ohno, N.; Terada, N.; Rokuhara, A.; Matsumoto, A.; Yagi, S.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Ohno, S.; Maki, N. Hepatitis B Virus DNA-negative Dane Particles Lack Core Protein but Contain a 22-kDa Precore Protein without C-terminal Arginine-rich Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21713–21719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brunetto, M.R.; Marcellin, P.; Cherubini, B.; Yurdaydin, C.; Farci, P.; Hadziyannis, S.J.; Rothe, V.; Regep, L.; Bonino, F. Response to peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) in HBeAg-negative CHB: On-treatment kinetics of HBsAg serum levels vary by HBV genotype. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetto, M.R.; Carey, I.; Maasoumy, B.; Marcos, C.; van Halewijn, G.; Caviglia, G.P.; Loglio, A.; Cavallone, D.; Scholtes, C.; Smedile, A.; et al. Evaluation of HBV core-related antigen(s) for improving discrimination between HBeAg-negative subjects with chronic infection B versus chronic hepatitis B. Analysis of multicenter data. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1183A–1184A. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Zhang, X.; Lu, W.; Wang, Y.-B.; Weng, Q.-C.; Feng, Y. Distinct patterns of serum hepatitis B core-related antigen during the natural history of chronic hepatitis B. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, L.Y.; Cloherty, G.; Wong, D.K.; Gersch, J.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Yuen, M.F. HBV RNA profiles in chronic hepatitis B patients under different disease phases and anti-viral therapy. Hepatology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, I.; Gersch, J.; Wang, B.; Moigboi, C.; Kuhns, M.; Cloherty, G.; Dusheiko, G.; Agarwal, K. Pregenomic HBV RNA and hepatitis B core-related antigen predict outcomes in hepatitis B e antigen–negative chronic hepatitis B patients suppressed on nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy. Hepatology 2020, 72, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study | Country | Year | Patients (n) | HBeAg (+/−) | HBV Genotype | Therapy | HBcrAg | HBsAg | HBV cccDNA | r * p-Value | r ** p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wong DKA [27] | China | 2007 | 54 | 17/37 | n.a. | No | 1180 (<1.0–9.0 × 105) kU/mL | n.a. | 1.3 (<0.002–23.3) copies/cell | r = 0.664 p < 0.001 | n.a. |
| Suzuki F [28] | Japan | 2009 | 44 | 16/28 | n.a. | No | 5.05 ± 1.62 Log U/mL e+: 6.53 ± 1.14 Log U/mL e−: 4.20 ± 1.18 Log U/mL | n.a. n.a. n.a. | 4.46 ± 0.87 Log copies/mg e+: 4.88 ± 1.06 Log copies/mg e−: 4.23 ± 0.64 Log copies/mg | n.a. r = 0.687 p = 0.003 r = 0.542 p = 0.003 | n.a. n.a. n.a. |
| Hosaka T [29] | Japan | 2010 | 55 A | 23/32 | C = 51 Other = 9 | 30 LAM 17 LAM + ADV 8 ETV | 5.0 (<3.0–> 6.8) Log U/mL | n.a. | 4.2 (3.0–5.0) Log copies/µg B | r = 0.479 p = 0.028 B | n.a. |
| Chuaypen N [30] | Thailand | 2016 | 46 | 46/0 | B = 5 C = 41 | No | 8.1 (7.7–8.4) Log U/mL | 3.9 (3.7–4.1) Log IU/mL | 1.6 (1.2–1.9) copies/cEq | r = 0.564 p = 0.001 | r = 0.424 p = 0.020 |
| Wong DKA [31] | China | 2017 | 138 | 77/61 | B = 40 C = 82 n.a. = 16 | Baseline 1 year NAs 6–12 years NAs | 586 (1–1.1 × 107) kU/mL C | 3.3 (−1.3–5.9) Log IU/mL C | 1.1 (0.005–258) copies/cell C | r = 0.70 p < 0.001 C | r = 0.40 p < 0.001 C |
| Chen EQ [32] | China | 2017 | 139 | 111/28 | B = 88 C = 51 | No | 9.23 ± 2.86 Log U/mL | 4.15 ± 0.86 Log IU/mL | 7.33 ± 1.03 Log copies/106 cells | r = 0.929 p < 0.001 | r = 0.742 p < 0.001 |
| Chuaypen N [33] | Thailand | 2018 | 121 D | 0/121 | B = 25 C = 96 | No | R: 4.1 ± 1.3 Log U/mL NR: 4.4 ± 1.1 Log U/mL | R: 3.2 ± 0.4 Log IU/mL NR: 3.6 ± 0.5 Log IU/mL | R: 0.4 ± 0.9 Log copies/cEq NR: 0.4 ± 1.2 Log copies/cEq | r = 0.393 p = 0.009 | r = 0.040 p = 0.737 |
| Chen S [34] | China | 2018 | 160 E | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | 5.10 (1.96–8.50) Log U/mL | 250 (0.14–250) IU/mL | n.a. | r = 0.436 p < 0.001 F | n.a. |
| Hasegawa K [35] | Japan | 2018 | 126 G | n.a. | n.a. | Untreated, n = 57 (A) previous NAs, n = 69 (B) | A: 3.0 (2.0–7.0) Log U/mL B: 4.1 (2.0–7.0) Log U/mL | A: 1692.7 (0.05–91960.7) IU/mL B: 1050.0 (0.05–71583.0) IU/mL | A: 3.0 (1.5–5.8) Log copies/µg B: 3.4 (1.7–4.8) Log copies/µg | A: r = 0.67 p < 0.001 B: r = 0.38 p = 0.007 | A: r = 0.59 p < 0.001 B: r = 0.32 p = 0.007 |
| Wang L [36] | China | 2019 | 82 | 82/0 (A); 44/12 (B) | n.a. | Baseline (A) 2 years NAs (B) | A: 7.97 ± 0.96 Log U/mL B: 5.74 ± 1.10 Log U/mL | A: 4.05 ± 0.64 Log IU/mL B: 3.32 ± 0.90 Log IU/mL | A: 0.67 ± 0.74 Log copies/cell B: −0.94 ± 0.60 Log copies/cell | A: r = 0.323 H p < 0.001 B: r = 0.108 p = 0.403 | A: r = 0.152 p = 0.172 B: r = 0.39 p = 0.002 |
| Testoni B [23] | France | 2019 | 130 | 36/94 | A = 20 B = 4 C = 13 D = 51 E = 14 F = 3 | No | 5.3 (4.0–7.6) Log U/mL e+: 8 (7.3–8.3) Log U/mL e−: 4.0 (3.7–4.9) Log U/mL | 3.9 (3.4–4.3) Log IU/mL e+: 4.61 (4.1–5.2) Log IU/mL e−: 3.74 (3.2–4.1) Log IU/mL | 0.15 (0.06–1.34) copies/cell e+: 6.3 (1.4–18.1) copies/cell e−: 0.09 (0.03–0.2) copies/cell | r = 0.74 p <0.001 I e+: r = 0.80 p <0.001 L e− CH: r = 0.25 p = n.s. I e− CI: r = 0.47 p = 0.05 I | r = 0.26 p = 0.044 I e+: r = 0.33 p = 0.01 L e− CH: r = −0.4 p = 0.01 I e− CI: r = −0.03 p = n.s. I |
| Chen EQ [37] | China | 2019 | 110 | 85/25 | B = 68 C = 42 | No | e+: 10.30 (6.00–12.30) Log U/mL e−: 5.40 (3.28–7.20) Log U/mL | e+: 4.59 (0.82–5.10) Log IU/mL e−: 3.49 (0.99–4.01) Log IU/mL | e+: 7.46 (5.11–8.17) Log copies/106 cells e−: 6.03 (5.00–6.85) Log copies/106 cells | e+: r = 0.843 p < 0.001 e−: r = 0.865 p < 0.001 | e+: r = 0.710 p < 0.001 e−: r = 0.579 p = 0.002 |
| Caviglia GP [38] | Italy | 2020 | 35 | 0/35 | D = 35 | No | 3.8 ± 1.8 Log U/mL | 3.13 ± 1.31 Log IU/mL | 3.11 ± 1.14 Log copies/105 cells | r = 0.733 p < 0.001 | r = 0.624 p < 0.001 |
| Dezanet LNC [39] | France | 2020 | 31 M | 22/9 | A = 11 D = 1 E = 1 G = 4 n.a. = 14 | NAs + ART (n = 22) | 5.5 (3.1–7.0) Log U/mL | 4.0 (3.2–4.5) Log IU/mL | 0.26 (0.0–2.89) copies/cell | r = 0.65 p < 0.001 e+: r = 0.40 p = 0.07 e−: r = 0.22 p = 0.5 | r = 0.68 p < 0.001 e+: r = 0.42 p = 0.10 e−: r = 0.68 p = 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caviglia, G.P.; Armandi, A.; Rosso, C.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Pellicano, R.; Fagoonee, S. Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020187
Caviglia GP, Armandi A, Rosso C, Ribaldone DG, Pellicano R, Fagoonee S. Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020187
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaviglia, Gian Paolo, Angelo Armandi, Chiara Rosso, Davide Giuseppe Ribaldone, Rinaldo Pellicano, and Sharmila Fagoonee. 2021. "Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020187
APA StyleCaviglia, G. P., Armandi, A., Rosso, C., Ribaldone, D. G., Pellicano, R., & Fagoonee, S. (2021). Hepatitis B Core-Related Antigen as Surrogate Biomarker of Intrahepatic Hepatitis B Virus Covalently-Closed-Circular DNA in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics, 11(2), 187. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020187