End-to-End, Pixel-Wise Vessel-Specific Coronary and Aortic Calcium Detection and Scoring Using Deep Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition and Identification of CAC
2.3. Splitting of Dataset and Preprocessing
2.4. Deep Learning Model
2.5. Model Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
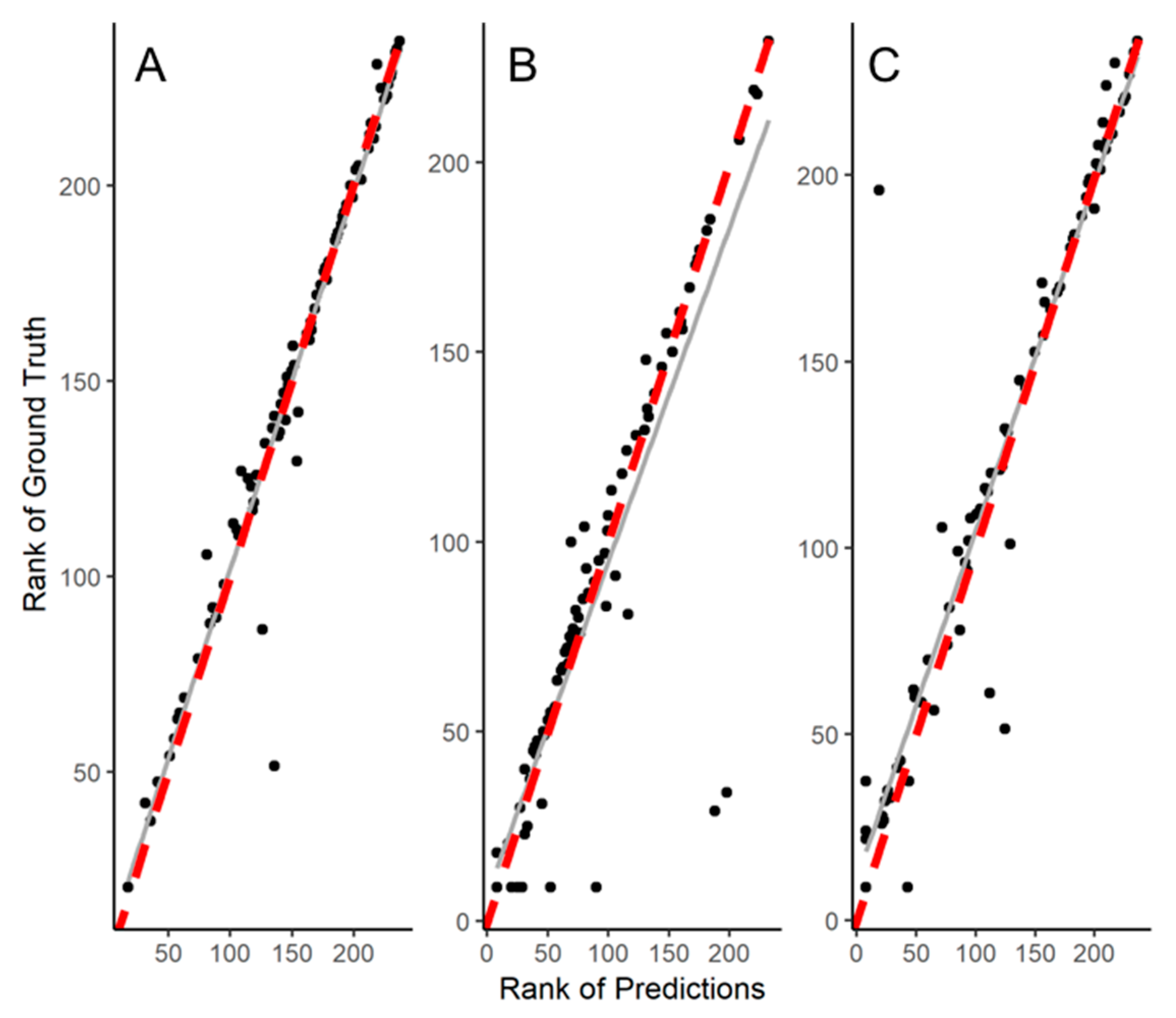
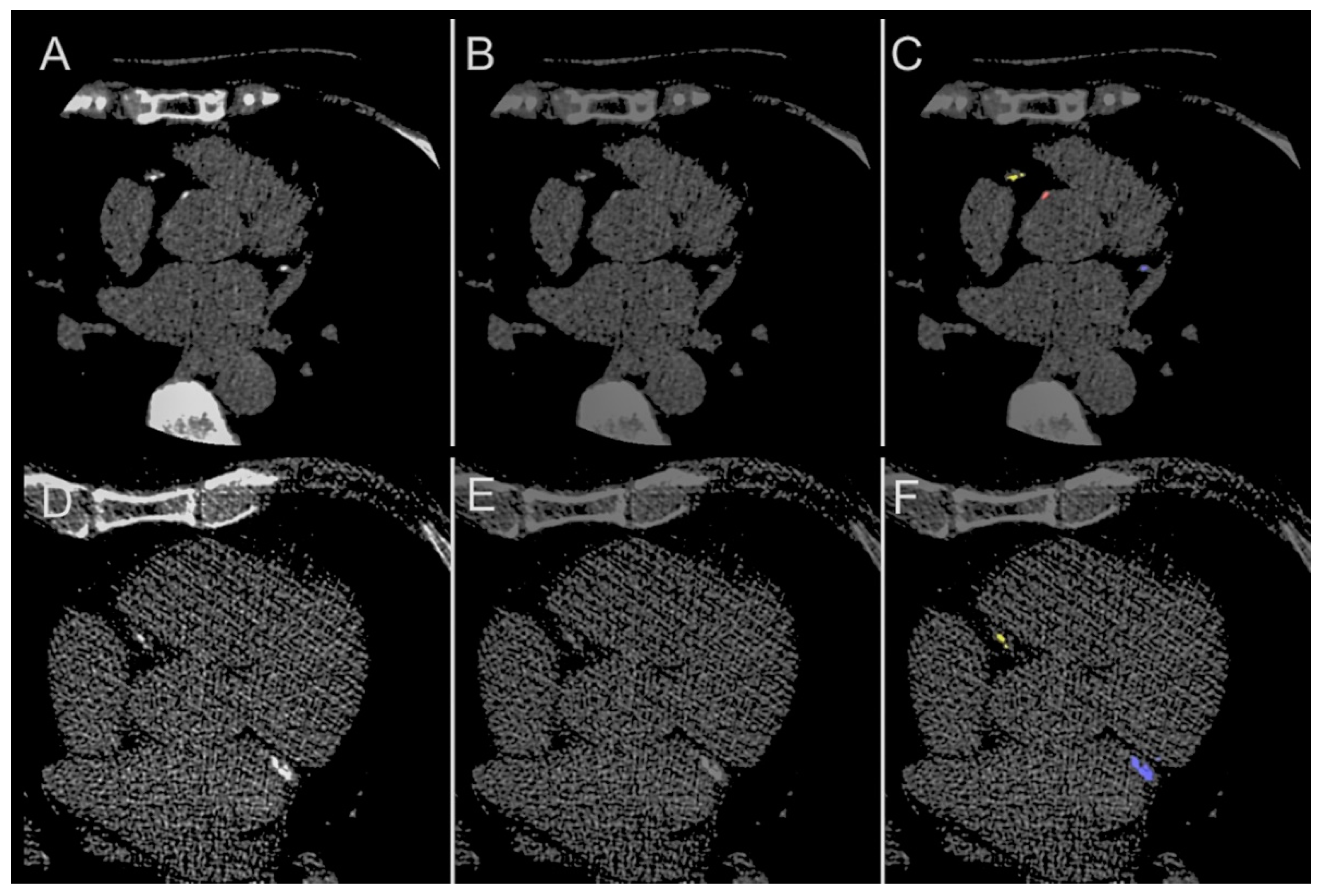
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaha, M.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Tota-Maharaj, R.T.; Dardari, Z.A.; Wong, N.D.; Kronmal, R.A.; Eng, J.; Post, W.S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Nasir, K. Improving the CAC Score by Addition of Regional Measures of Calcium Distribution: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2016, 9, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agatston, A.S.; Janowitz, W.R.; Hildner, F.J.; Zusmer, N.R.; Viamonte, M.; Detrano, R. Quantification of coronary artery calcium using ultrafast computed tomography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1990, 15, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.J.; Min, J.K.; Nasir, K.; Xie, J.X.; Berman, D.S.; Miedema, M.D.; Whelton, S.P.; Dardari, A.Z.; Rozanski, A.; Rumberger, J.; et al. Sex differences in calcified plaque and long-term cardiovascular mortality: Observations from the CAC Consortium. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3727–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, L.J.; Narula, J.; Chandrashekhar, Y. The Never-Ending Story on Coronary Calcium: Is it predictive, punitive, or protective? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1283–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, G.; Al’Aref, S.J.; van Assen, M.; Kim, T.S.; Van Rosendael, A.; Kolli, K.K.; Dwivedi, A.; Maliakal, G.; Pandey, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Machine learning in cardiac CT: Basic concepts and contemporary data. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2018, 12, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinton, G. Deep Learning—A Technology with the Potential to Transform Health Care. JAMA 2018, 320, 1101–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, A.; Hartaigh, B.Ó.; Knaapen, P.; Leipsic, J.; Shaw, L.J.; Andreini, D.; Pontone, G.; Raman, S.; Khan, M.A.; Ridner, M.; et al. Rationale and Design of the CREDENCE Trial: Computed TomogRaphic evaluation of atherosclerotic DEtermiNants of myocardial IsChEmia. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-J.; Lin, F.Y.; Lee, S.-E.; Andreini, D.; Bax, J.; Cademartiri, F.; Chinnaiyan, K.; Chow, B.J.; Conte, E.; Cury, R.C.; et al. Coronary Atherosclerotic Precursors of Acute Coronary Syndromes. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, D.B.; Berman, D.S.; Budoff, M.J.; Carr, J.J.; Gerber, T.C.; Hecht, H.S.; Hlatky, M.A.; Hodgson, J.M.; Lauer, M.S.; Miller, J.M.; et al. ACCF/ACR/AHA/NASCI/SAIP/SCAI/SCCT 2010 Expert Consensus Document on Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2663–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weininger, M.; Ritz, K.S.; Schoepf, U.J.; Flohr, T.G.; Vliegenthart, R.; Costello, P.; Hahn, D.; Beissert, M. Interplatform Reproducibility of CT Coronary Calcium Scoring Software. Radiology 2012, 265, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, B.D.; Wolterink, J.M.; Leiner, T.; De Jong, P.A.; Lessmann, N.; Leiner, I. Direct Automatic Coronary Calcium Scoring in Cardiac and Chest CT. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolterink, J.M.; Leiner, T.; Takx, R.A.P.; Viergever, M.A.; Isgum, I. Automatic Coronary Calcium Scoring in Non-Contrast-Enhanced ECG-Triggered Cardiac CT with Ambiguity Detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1867–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isgum, I.; Prokop, M.; Niemeijer, M.; Viergever, M.A.; van Ginneken, B. Automatic Coronary Calcium Scoring in Low-Dose Chest Computed Tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2012, 31, 2322–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano-Espinosa, C.; González, G.; Washko, G.R.; Cazorla, M.; Estépar, S.J.R. Automated Agatston score computation in non-ECG gated CT scans using deep learning. Proc. SPIE 2018, 10574, 105742K. [Google Scholar]
- Shadmi, R.; Mazo, V.; Bregman-Amitai, O.; Elnekave, E. Fully-convolutional deep-learning based system for coronary calcium score prediction from non-contrast chest CT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 2018, pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lessmann, N.; van Ginneken, B.; Zreik, M.; de Jong, P.A.; de Vos, B.D.; Viergever, M.A.; Išgum, I. Automatic Calcium Scoring in Low-Dose Chest CT Using Deep Neural Networks with Dilated Convolutions. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Lee, K.; Shin, E.; Choy, G.; Do, S. How much data is needed to train a medical image deep learning system to achieve necessary high accuracy? arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06348. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, G.; della Latta, D.; Martini, N.; Valvano, G.; Gori, A.; Ripoli, A.; Susini, C.L.; Landini, L.; Chiappino, D. An automatic deep learning approach for coronary artery calcium segmentation. In Proceedings of the EMBEC & NBC 2017 Joint Conference of the European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference (EMBEC) and the Nordic-Baltic Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Medical Physics (NBC), Tampere, Finland, 11–15 June 2017; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristic | Total |
|---|---|
| N | 377 |
| Age, years (SD) | 64.2 ± 9.8 |
| Female (%) | 33.16 |
| Diabetes Mellitus (%) | 29.71 |
| Dyslipidemia (%) | 56.50 |
| Hypertension (%) | 64.19 |
| Smoker (%) | 32.36 |
| LAD calcification (%) | 74.87 |
| RCA calcification (%) | 55.82 |
| LCx calcification (%) | 57.41 |
| Triple vessel calcification (%) | 46.03 |
| Aortic calcification (%) | 85.41 |
| CACS 0 (%) | 11.39 |
| CACS 1–99 (%) | 11.39 |
| CACS 100–399 (%) | 24.05 |
| CACS ≥ 400 (%) | 53.16 |
| Structure | Category | Dice Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Quartile (1st, 3rd) | p | ||
| Total coronary (LAD + RCA + LCx) | Overall | 0.952 | (0.921, 0.981) | - |
| Male | 0.948 | (0.920, 0.981) | 0.350 | |
| Female | 0.965 | (0.933, 0.980) | ||
| Age < 65 years | 0.950 | (0.913, 0.981) | 0.742 | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 0.957 | (0.930, 0.977) | ||
| LAD | Overall | 0.971 | (0.930, 1.000) | - |
| Male | 0.963 | (0.919, 1.000) | 0.058 | |
| Female | 0.988 | (0.968, 1.000) | ||
| Age < 65 years | 0.970 | (0.941, 0.999) | 0.980 | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 0.975 | (0.911, 1.000) | ||
| RCA | Overall | 0.963 | (0.889, 0.991) | - |
| Male | 0.951 | (0.880, 1.000) | 0.633 | |
| Female | 0.977 | (0.923, 0.991) | ||
| Age < 65 years | 0.964 | (0.874, 0.999) | 0.875 | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 0.959 | (0.899, 0.987) | ||
| LCx | Overall | 0.955 | (0.894, 1.000) | - |
| Male | 0.954 | (0.887, 1.000) | 0.388 | |
| Female | 0.958 | (0.942, 0.998) | ||
| Age < 65 years | 0.954 | (0.905, 0.999) | 0.897 | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 0.955 | (0.887, 1.000) | ||
| Aortic | Overall | 0.832 | (0.759, 0.897) | |
| Male | 0.802 | (0.760, 0.905) | 0.996 | |
| Female | 0.834 | (0.764, 0.883) | ||
| Age < 65 years | 0.833 | (0.776, 0.933) | 0.204 | |
| Age ≥ 65 years | 0.793 | (0.756, 0.862) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, G.; Al’Aref, S.J.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, J.K.; Tan, S.Y.; Lin, F.Y.; Chang, H.-J.; Shaw, L.J.; Baskaran, L.; on behalf of the CREDENCE and ICONIC Investigators. End-to-End, Pixel-Wise Vessel-Specific Coronary and Aortic Calcium Detection and Scoring Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020215
Singh G, Al’Aref SJ, Lee BC, Lee JK, Tan SY, Lin FY, Chang H-J, Shaw LJ, Baskaran L, on behalf of the CREDENCE and ICONIC Investigators. End-to-End, Pixel-Wise Vessel-Specific Coronary and Aortic Calcium Detection and Scoring Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020215
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Gurpreet, Subhi J. Al’Aref, Benjamin C. Lee, Jing Kai Lee, Swee Yaw Tan, Fay Y. Lin, Hyuk-Jae Chang, Leslee J. Shaw, Lohendran Baskaran, and on behalf of the CREDENCE and ICONIC Investigators. 2021. "End-to-End, Pixel-Wise Vessel-Specific Coronary and Aortic Calcium Detection and Scoring Using Deep Learning" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020215
APA StyleSingh, G., Al’Aref, S. J., Lee, B. C., Lee, J. K., Tan, S. Y., Lin, F. Y., Chang, H.-J., Shaw, L. J., Baskaran, L., & on behalf of the CREDENCE and ICONIC Investigators. (2021). End-to-End, Pixel-Wise Vessel-Specific Coronary and Aortic Calcium Detection and Scoring Using Deep Learning. Diagnostics, 11(2), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020215






