Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Diagnostic Challenges: Understanding the Clinical Phenotype of the Puerto Rican RSPH4A Founder Mutation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Electron Microscopy Findings
3.3. RSPH4A Genetic Sequencing
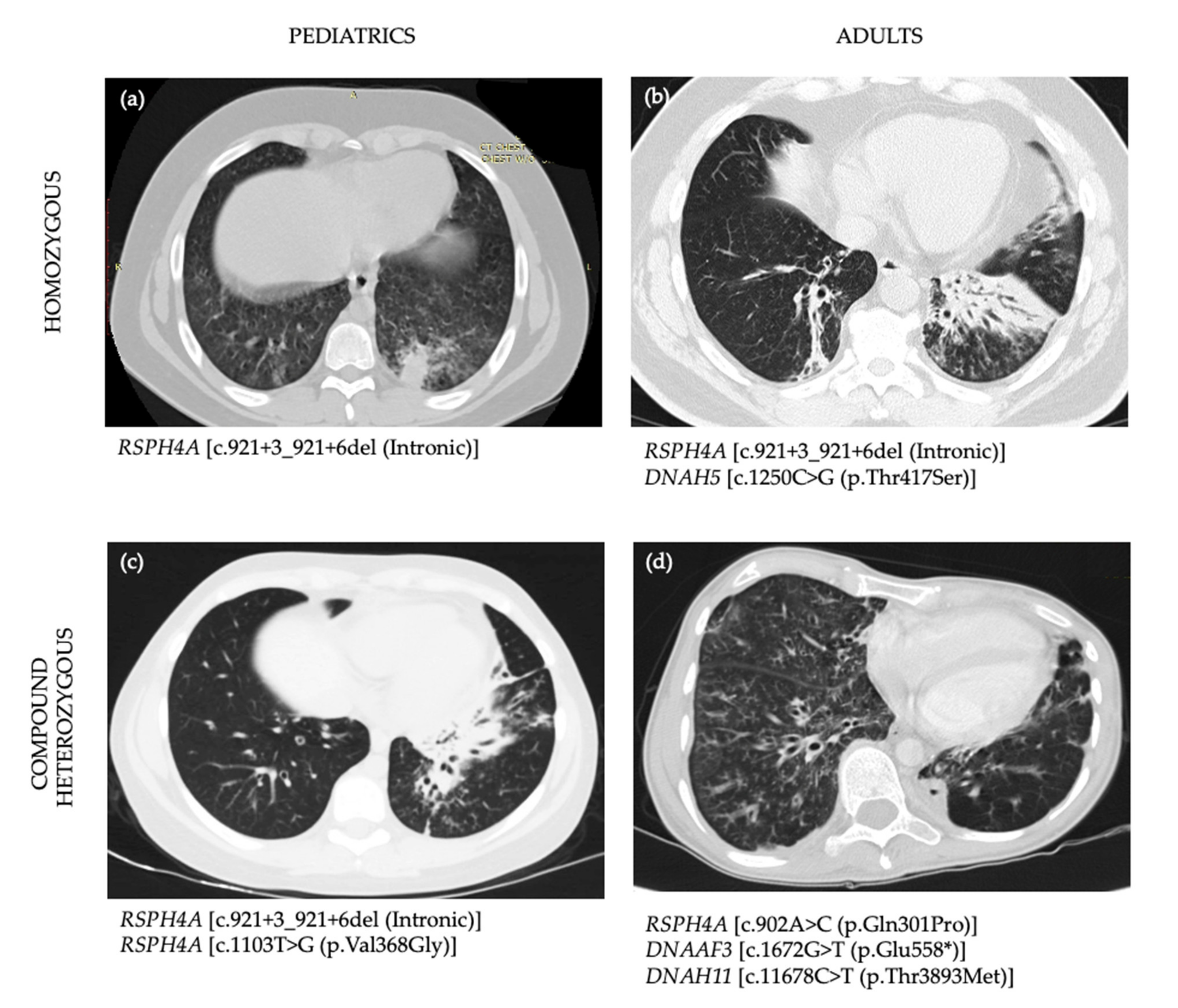
3.4. Imaging
3.5. Pulmonary Function Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCD | Primary ciliary dyskinesia |
| nNO | nasal nitric oxide |
| HRCT | High-resolution chest computer tomography |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| GLI | Global lung function initiative-2012 |
| LLL | Left lower lobe |
| RLL | Right lower lobe |
| RML | Right middle lobe |
| RUL | Right upper lobe |
| VUS | Variant of unknown significance |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 second |
| RV | Residual Volume |
| TLC | Total Lung Capacity |
| sRAW | Specific airway resistance |
| RDS | Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
Appendix A
| Case | Sex | Age (y) | Laterality Defects | Ciliary Defects | Ethnicity | Chronic Cough | Neonatal RDS | Bronchiectasis on HRCT | Chronic Rhinorrhea | Chronic SecretoryOM | Hearing Loss | FEV1 (%) | Affected PCD Gene | Base Change | Amino-Acid Change | Zygocity | Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homozygous Genetic Variants | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | M | 1 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | - | Y | N | Y | - | RSPH4A CCDC151 DNAH5 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.619C > T c.1250C > G | Intronic p.Arg207Trp p.Thr417Ser | Homo Hete Hete | Pathogenic VUS VUS |
| 2 | F | 7 | 0 | R* | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | 106 | RSPH4A DNAH11 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.3133C > T | Intronic p.Arg1045* | Homo Hete | Pathogenic Pathogenic |
| 3 | F | 11 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 79 | RSPH4A CCDC114 DNAH11 GAS8 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.203C > T c.8093T > C Deletion | Intronic p.Ala68Val p.Leu2698Ser Exons 9-11 | Homo Hete Hete Hete | Pathogenic VUS VUS VUS |
| 4 | M | 15 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 72 | RSPH4A | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del | Intronic | Homo | Pathogenic |
| 5 | M | 51 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | 62 | RSPH4A DNAH5 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.1250C > G | Intronic p.Thr417Ser | Homo Hete | Pathogenic VUS |
| 6 | F# | 35 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | 36 | RSPH4A DNAAF2 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.58G > C | Intronic p.Val20Leu | Homo Hete | Pathogenic VUS |
| 7 | F | 26 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | - | Y | N | - | 53 | RSPH4A | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del | Intronic | Homo | Pathogenic |
| 8 | F | 19 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Y | 59 | RSPH4A | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del | Intronic | Homo | Pathogenic |
| Compound Heterozygous Genetic Variants | |||||||||||||||||
| 9 | M | 13 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | 60 | RSPH4A RSPH4A DNAH8 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.1103T > G c.9839A > T | Intronic p.Val368Gly p.Gln3280Leu | Hete Hete Hete | Pathogenic Pathogenic^ VUS |
| 10 | F# | 33 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | N | Y | Y | N | - | 24 | RSPH4A DNAAF3 DNAH11 | c.902A > C c.1672G > T c.11678C > T | p.Gln301Pro p.Glu558* p.Thr3893Met | Hete Hete Hete | VUS VUS VUS |
| 11 | F | 5 | 0 | - | Hispanic | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | - | RSPH4A CCDC65 DNAH1 DNAH11 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.771G > T c.9646C > G c.3288G > A | Intronic p.Glu257Asp p.Leu3216Val p.Met1096Ile | Hete Hete Hete Hete | Pathogenic VUS VUS VUS |
| 12 | M | 2 | 0 | CA | Hispanic | Y | Y | - | Y | N | - | - | RSPH4A DNAAF4 DNAH11 DNAH5 | c.921 + 3_921 + 6del c.186C > G c.8888C > A c.12709G > T | Intronic p.Ser62Arg p.Ser2963Tyr p.Val4237Phe | Hete Hete Hete Hete | Pathogenic VUS VUS VUS |
| Heterozygous Genetic Variants | |||||||||||||||||
| 13 | F | 3 | 0 | - | Hispanic | Y | N | - | Y | N | - | - | RSPH4A | c.902A > C | p.Gln301Pro | Hete | VUS |
References
- Knowles, M.R.; Daniels, L.A.; Davis, S.D.; Zariwala, M.A.; Leigh, M.W. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Recent Advances in Diagnostics, Genetics, and Characterization of Clinical Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, M.W.; Horani, A.; Kinghorn, B.; O’Connor, M.G.; Zariwala, M.A.; Knowles, M.R. Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD): A genetic disorder of motile cilia. Transl. Sci. Rare Dis. 2019, 4, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zariwala, M.A.; Knowles, M.R.; Leigh, M.W. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia; GeneReviews: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Davis, S.D.; Polineni, D.; Manion, M.; Rosenfeld, M.; Dell, S.D.; Chilvers, M.A.; Ferkol, T.W.; Zariwala, M.A.; Sagel, S.D.; et al. Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, e24–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.G.; Griffiths, A.; Iyer, N.P.; Shapiro, A.J.; Wilson, K.C.; Thomson, C.C. Summary for Clinicians: Diagnosis of Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, G.J.; Carter, E.R. Chronic Suppurative Lung Disease in Children: Definition and Spectrum of Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Leigh, M.W. Value of transmission electron microscopy for primary ciliary dyskinesia diagnosis in the era of molecular medicine: Genetic defects with normal and non-diagnostic ciliary ultrastructure. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2017, 41, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castleman, V.H.; Romio, L.; Chodhari, R.; Hirst, R.A.; De Castro, S.C.; Parker, K.A.; Ybot-Gonzalez, P.; Emes, R.D.; Wilson, S.W.; Wallis, C.; et al. Mutations in Radial Spoke Head Protein Genes RSPH9 and RSPH4A Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia with Central-Microtubular-Pair Abnormalities. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 84, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilvers, M.A.; Rutman, A.; O’Callaghan, C. Ciliary beat pattern is associated with specific ultrastructural defects in primary ciliary dyskinesia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Marin, X.M.; Ostrowski, L.E. Cilia and Mucociliary Clearance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a028241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.J.; Davis, S.D.; Ferkol, T.; Dell, S.D.; Rosenfeld, M.; Olivier, K.N.; Sagel, S.D.; Milla, C.; Zariwala, M.A.; Wolf, W.; et al. Laterality Defects Other Than Situs Inversus Totalis in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Chest 2014, 146, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, S.; Yoshiba, S.; Watanabe, D.; Ikeuchi, S.; Goto, T.; Marshall, W.F.; Hamada, H. De Novo Formation of Left–Right Asymmetry by Posterior Tilt of Nodal Cilia. PLoS Biol. 2005, 3, e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stannard, W.; Rutman, A.; Wallis, C.; O’Callaghan, C. Central Microtubular Agenesis Causing Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, M.A.; Leigh, M.W.; Davis, S.D.; Armstrong, M.C.; Carson, J.L.; Hazucha, M.; Dell, S.D.; Eriksson, M.; Collins, F.S.; Knowles, M.R.; et al. Founder Mutation inRSPH4AIdentified in Patients of Hispanic Descent with Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.R.; Crapo, R.; Hankinson, J.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.; Enright, P.; Van Der Grinten, C.P.M.; Gustafsson, P.; et al. General considerations for lung function testing. Eur. Respir. J. 2005, 26, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, M.M.; Milian, L.; Armengot-Carceller, M.; Carda, C. Gene Mutations in Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Related to Otitis Media. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escabasse, V.; Coste, A.; Chauvin, P.; Fauroux, B.; Tamalet, A.; Garabedian, E.-N.; Escudier, E.; Roger, G. Otologic Features in Children With Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 136, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, D.A.; Hildebrandt, F. Ciliopathies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 9, a028191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristics | Value (N = 13) |
|---|---|
| Gender (F/M), N (%) | 8 (62) |
| Age, median ± SD, (years) | 13 ± 15.2 |
| Ethnicity, N (%), Hispanics, Puerto Ricans | 13 (100) |
| PCD-related symptoms/sign N (%) | - |
| Year-round wet cough | 13 (100) |
| Year-round daily nasal congestion | 13 (100) |
| Neonatal respiratory distress | 9 (69) |
| Hearing loss | 9 (69) |
| Bronchiectasis | 8/9 (89) |
| Chronic secretory otitis media | 4 (30) |
| Infertility | 2 (15) |
| Laterality defects | 0 (0) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Jesús-Rojas, W.; Reyes-De Jesús, D.; Mosquera, R.A. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Diagnostic Challenges: Understanding the Clinical Phenotype of the Puerto Rican RSPH4A Founder Mutation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020281
De Jesús-Rojas W, Reyes-De Jesús D, Mosquera RA. Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Diagnostic Challenges: Understanding the Clinical Phenotype of the Puerto Rican RSPH4A Founder Mutation. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020281
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Jesús-Rojas, Wilfredo, Dalilah Reyes-De Jesús, and Ricardo A. Mosquera. 2021. "Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Diagnostic Challenges: Understanding the Clinical Phenotype of the Puerto Rican RSPH4A Founder Mutation" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020281
APA StyleDe Jesús-Rojas, W., Reyes-De Jesús, D., & Mosquera, R. A. (2021). Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia Diagnostic Challenges: Understanding the Clinical Phenotype of the Puerto Rican RSPH4A Founder Mutation. Diagnostics, 11(2), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020281







