Time and Mode of Epidemic HCV-2 Subtypes Spreading in Europe: Phylodynamics in Italy and Albania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
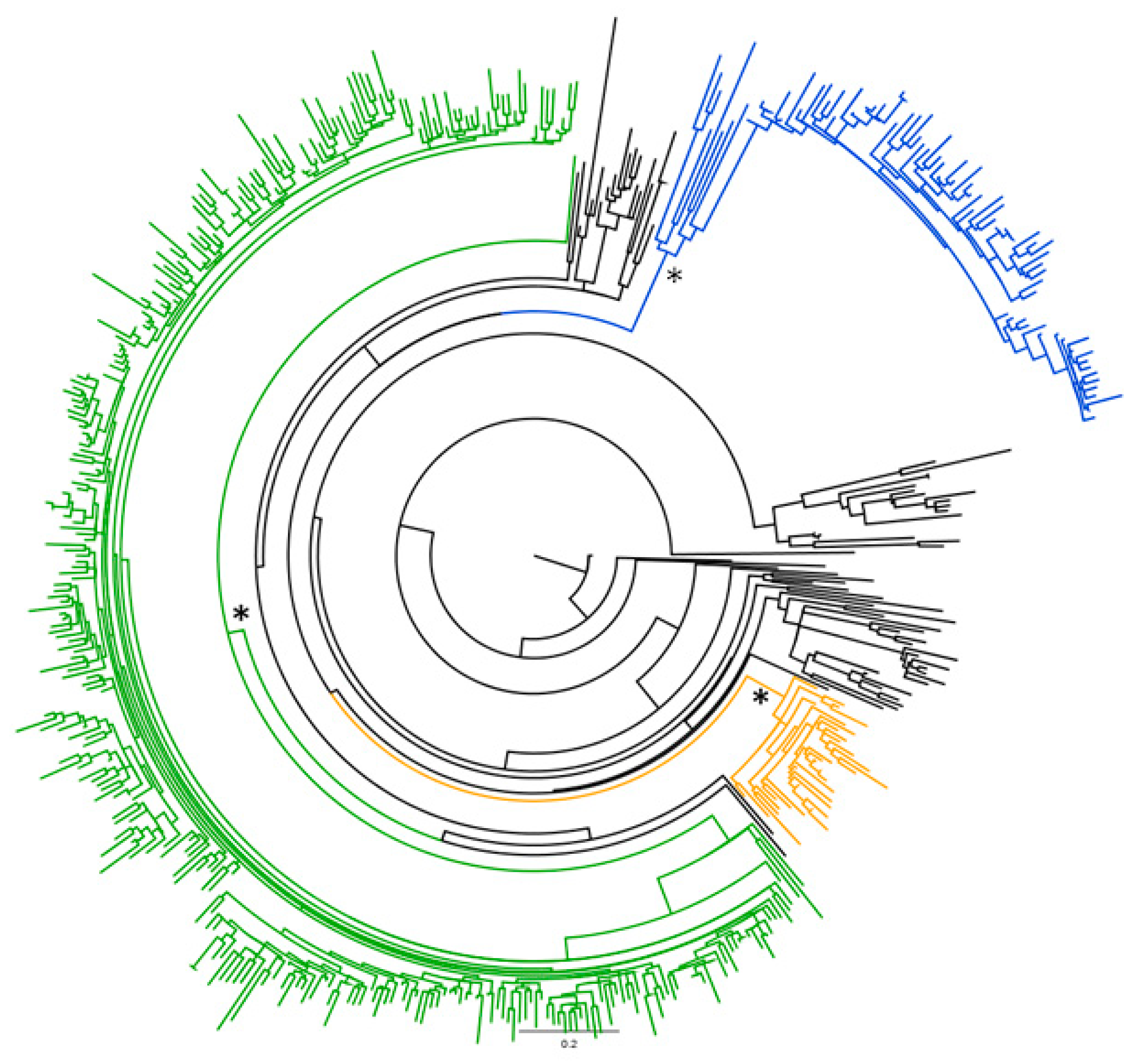
2.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Global HCV-2 Dataset
2.2. Likelihood Mapping of the Main Dataset
2.3. Phylogeographical and Phylodynamic Analyses
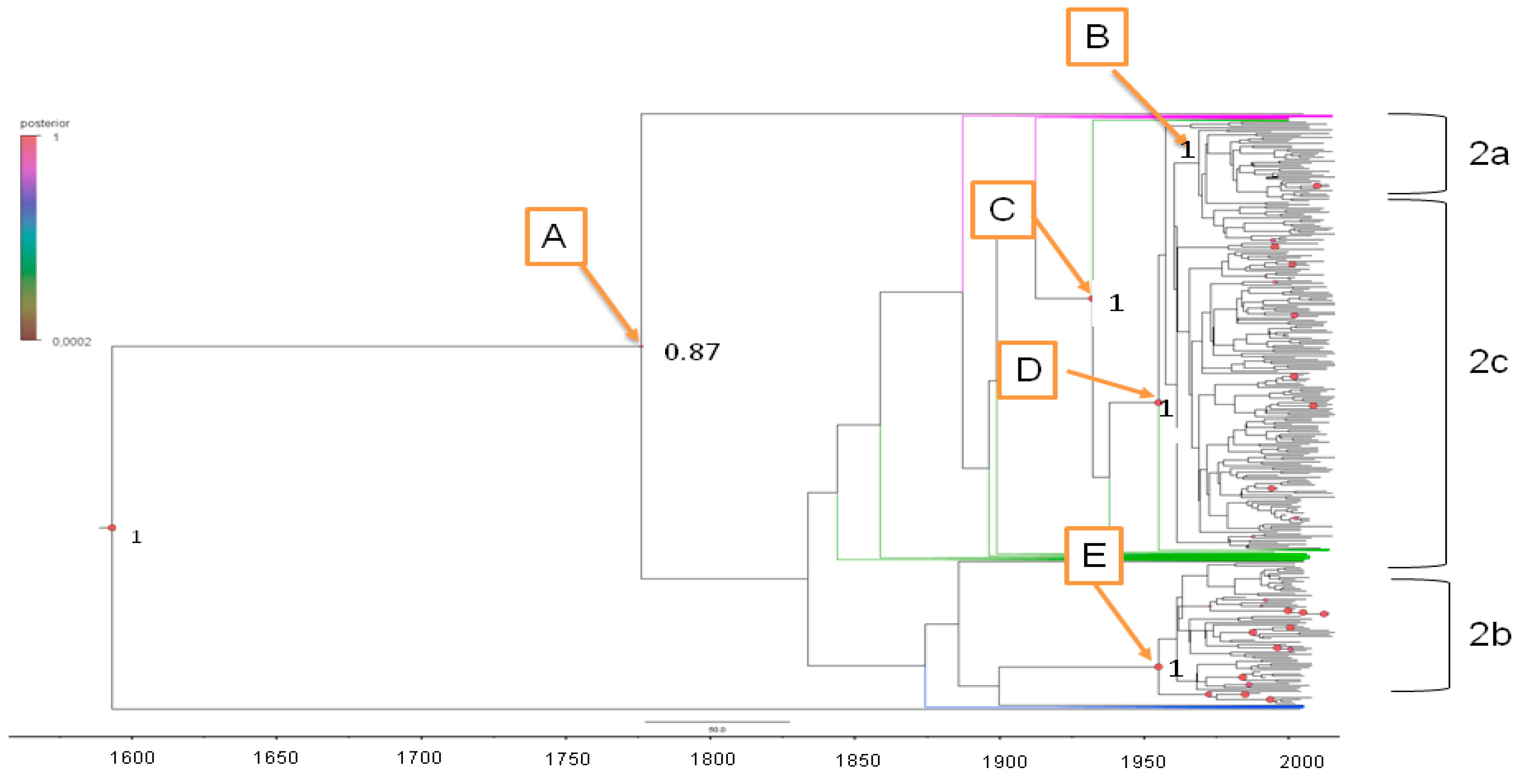
2.3.1. Estimated Substitution Rates and tMRCA
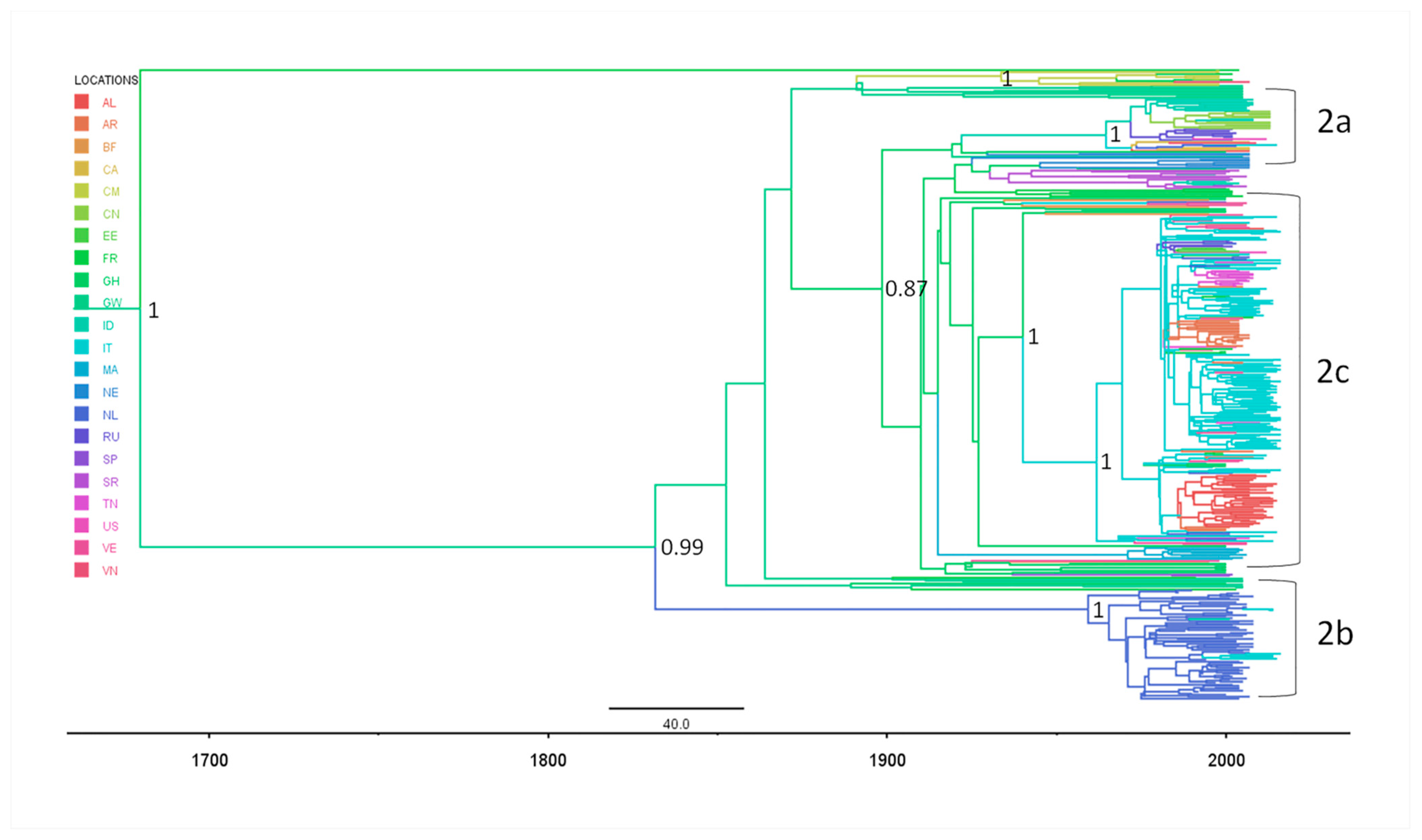
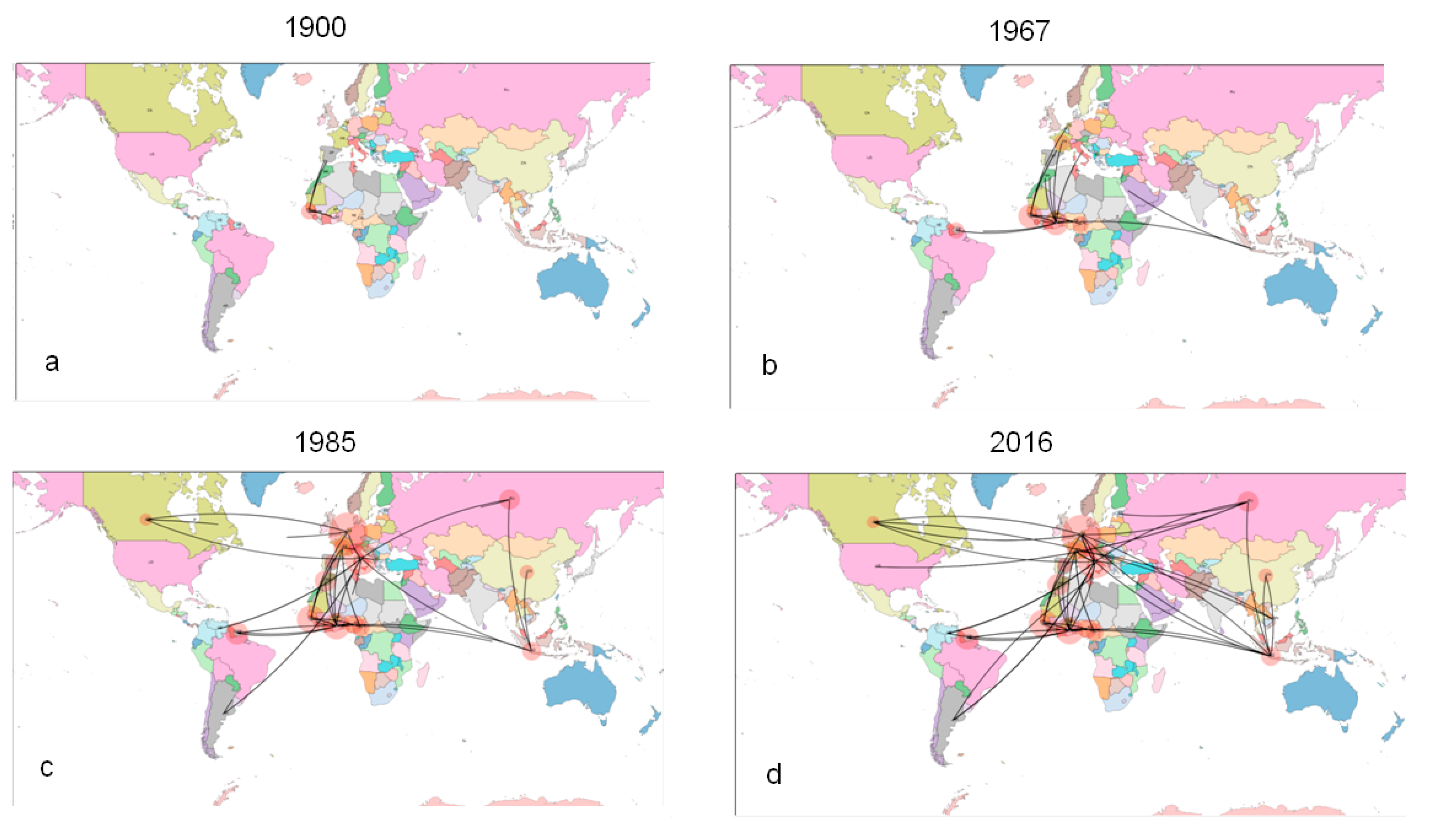
2.3.2. Phylogeography of HCV-2
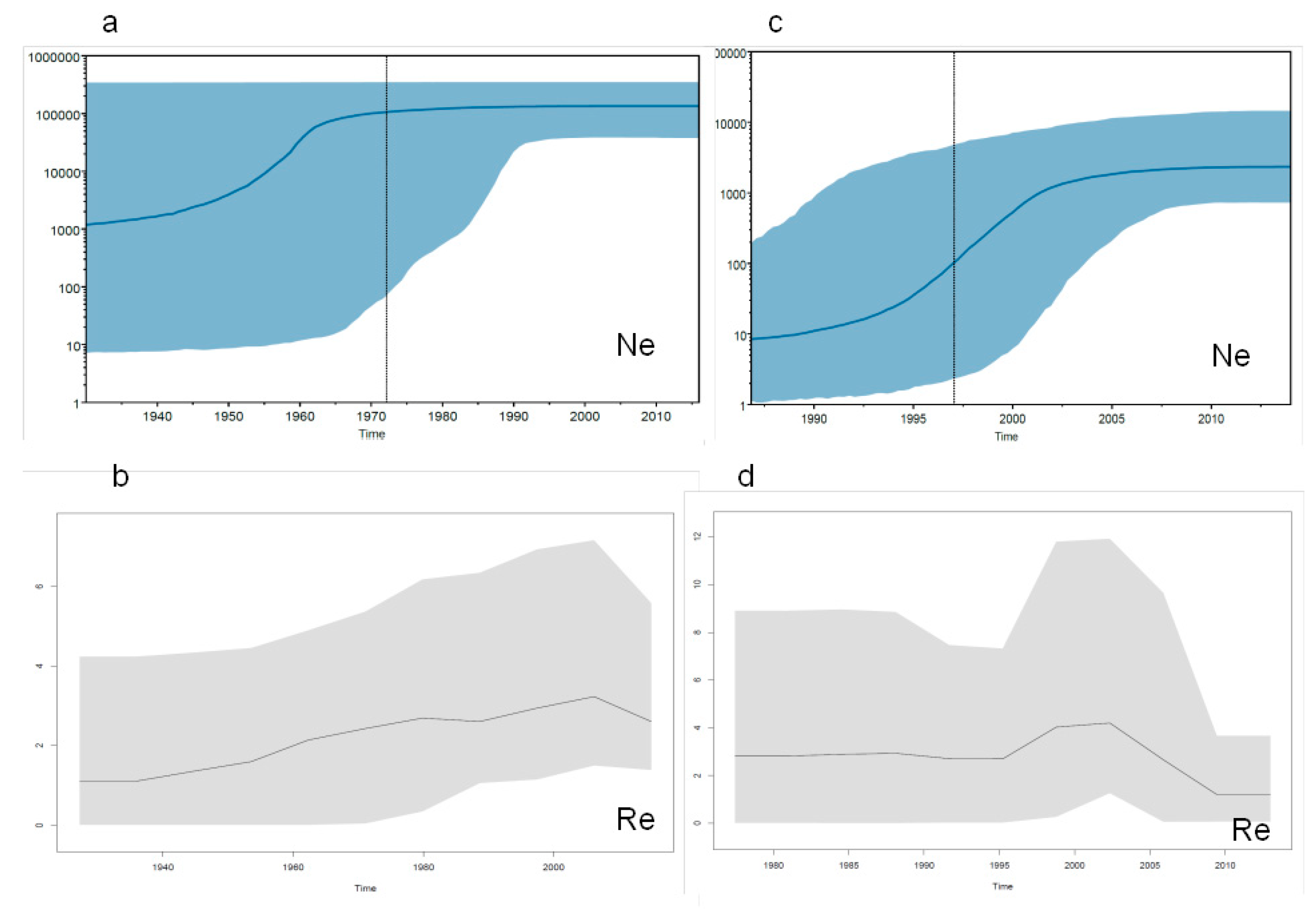
2.3.3. Evolutionary Demography and R0/Re Estimates in Italy and Albania
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. HCV-2 Positive Patients and Sequences
4.3. Sample Processing and HCV RNA Sequencing
4.4. HCV-2 NS5B Datasets
4.5. Likelihood Mapping Analysis
4.6. Bayesian Phylogenetic and Phylogeographical Reconstructions
4.7. Birth-Death Skyline Plot Estimate of Effective Reproduction Number (Re)
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GT | Genotype |
| AL | Albania |
| AR | Argentine |
| BF | Burkina Faso |
| CA | Canada |
| CM | Cameroon |
| CN | China |
| EE | Estonia |
| FR | France |
| GH | Ghana |
| GW | Guinea Bissau |
| ID | Indonesia |
| IT | Italy |
| MA | Morocco |
| NE | Nigeria |
| NL | The Netherlands |
| RU | Russia |
| SP | Spain |
| SR | Suriname |
| TN | Tunisia |
| US | The United States |
| VE | Venezuela |
| VN | Vietnam |
| HPD | High Posterior Density |
| tMRCA | Time of the Most Recent Common Ancestor |
| GTR+I+G | Generalized time reversible + proportion of invariable sites + gamma distribution |
| YA | Years Ago |
References
- Snow, K.K.; Bell, M.C.; Stoddard, A.M.; Curto, T.M.; Wright, E.C.; Dienstag, J.L. Processes to manage analyses and publications in a phase III multicenter randomized clinical trial. Trials 2014, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesmero, E.; Thorpe, I.F. Using the Hepatitis C Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase as a Model to Understand Viral Polymerase Structure, Function and Dynamics. Viruses 2015, 7, 3974–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2014, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pybus, O.G.; Markov, P.V.; Wu, A.; Tatem, A.J. Investigating the endemic transmission of the hepatitis C virus. Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global distribution and prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2015, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, P. Genetic diversity and evolution of hepatitis C virus – 15 years on. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, T.M.; Bhardwaj, N.; Hedskog, C.; Chodavarapu, K.; Camus, G.; McNally, J.; Brainard, D.; Miller, M.D.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Global epidemiology of HCV subtypes and resistance-associated substitutions evaluated by sequencing-based subtype analyses. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantaloube, J.F.; Gallian, P.; Laperche, S.; Elghouzzi, M.H.; Piquet, Y.; Bouchardeau, F.; Jordier, F.; Biagini, P.; Attoui, H.; de Micco, P. Molecular characterization of genotype 2 and 4 hepatitis C virus isolates in French blood donors. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, F.; Nicot, F.; Sandres-Sauné, K.; Dubois, M.; Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Alric, L.; Peron, J.M.; Pasquier, C.; Izopet, J. Genetic diversity of HCV genotype 2 strains in south western France. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, P.V.; van de Laar, T.J.; Thomas, X.V.; Aronson, S.J.; Weegink, C.J.; van den Berk, G.E.; Prins, M.; Pybus, O.G.; Schinkel, J. Colonial history and contemporary transmission shape the genetic diversity of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 in Amsterdam. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 7677–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldeda, M.; Baume, J.; Tamalet, C.; Bizhga, M.; Colson, P. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in Tirana, Albania. Int. J. Infect. Dis.: IJID: Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2014, 18, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Kondili, L.A.; Çuko, L.; Chionne, P.; Candido, A.; Madonna, E.; Dentico, P.; Resuli, B.; Taliani, G.; Brunetto, M.R.; Rapicetta, M. Hepatitis B, C and Delta virus infections in Albanian patients with chronic liver disease: Evaluation of possible changes during the last 10 years. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzziello, A.; Loquercio, G.; Sabatino, R.; Balaban, D.V.; Ullah Khan, N.; Piccirillo, M.; Rodrigo, L.; di Capua, L.; Guzzo, A.; Labonia, F.; et al. Prevalence of Hepatitis C virus genotypes in nine selected European countries: A systematic review. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doçi, P.; Ebranati, E.; Zehender, G.; Dragusha, E.; Fiaschi, L.; Carta, V.; Veo, C.; Bino, S.; Seferi, I.; Shkjezi, R. Prevalence of HCV virus genotypes in Albania. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2017, 6, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansaldi, F.; Bruzzone, B.; Salmaso, S.; Rota, M.C.; Durando, P.; Gasparini, R.; Icardi, G. Different seroprevalence and molecular epidemiology patterns of hepatitis C virus infection in Italy. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 76, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roffi, L.; Ricci, A.; Ogliari, C.; Scalori, A.; Minola, E.; Colloredo, G.; Donada, C.; Ceriani, R.; Rinaldi, G.; Paris, B.; et al. HCV genotypes in Northern Italy: A survey of 1368 histologically proven chronic hepatitis C patients. J. Hepatol. 1998, 29, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, G.; Ansaldi, F.; Biagi, C.; D’Agaro, P.; Comar, M.; Crocè, L.; Tiribelli, C.; Campello, C. Changing molecular epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in Northeast Italy. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 68, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bortolotti, F.; Guido, M.; Zancan, L.; Gussetti, N. Long-term outcome of hepatitis C in children. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagnino, V.; Stroffolini, T.; Rapicetta, M.; Costantino, A.; Kondili, L.A.; Menniti-Ippolito, F.; Caroleo, B.; Costa, C.; Griffo, G.; Loiacono, L.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in the general population: A community-based survey in southern Italy. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, G.; Lamberti, A.; Quirino, A.; Focà, D.; Giancotti, A.; Barreca, G.S.; Guadagnino, V.; Liberto, M.C. Changes in the prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotype 4 in Calabria, Southern Italy. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 42, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistello, M.; Maggi, F.; Vatteroni, L.; Cecconi, N.; Panicucci, F.; Bresci, G.P.; Gambardella, L.; Taddei, M.; Bionda, A.; Tuoni, M.; et al. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes in Italy. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenci, M.; Massi, M.; Alderisio, M.; De Soccio, G.; Recchia, O. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes and increase of type 4 in central Italy: An update and report of a new method of HCV genotyping. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pontisso, P.; Ruvoletto, M.G.; Nicoletti, M.; Tisminetzky, S.; Gerotto, M.; Levrero, M.; Artini, M.; Baldi, M.; Ballardini, G.; Barbara, L.; et al. Distribution of three major hepatitis C virus genotypes in Italy. A multicentre study of 495 patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Viral Hepat. 1995, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paschale, M.; Casiraghi, M.A.; Biagiotti, S.; Rossi, U.; Zanetti, A.R. Association between neonatal blood microtransfusions in the 1960s and hepatitis C virus infection. Lancet 2000, 356, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, J.I.; Sauleda, S.; Quer, J. The changing epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection in Europe. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 148–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markov, P.V.; Pepin, J.; Frost, E.; Deslandes, S.; Labbé, A.C.; Pybus, O.G. Phylogeography and molecular epidemiology of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 in Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2086–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Forbi, J.C.; Sue, A.; Layden, J.E.; Switzer, W.M.; Opare-Sem, O.K.; Phillips, R.O.; Khudyakov, Y.E. A re-evaluation of the origin of hepatitis C virus genotype 2 in West Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Saarma, U.; Barnett, R.; Haile, J.; Shapiro, B. The effect of inappropriate calibration: Three case studies in molecular ecology. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, J.P.; Lawlor, E.; Davidson, F.; Holmes, E.C.; Yap, P.L.; Simmonds, P. Molecular epidemiology of an outbreak of infection with hepatitis C virus in recipients of anti-D immunoglobulin. Lancet 1995, 345, 1211–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, O.G.; Charleston, M.A.; Gupta, S.; Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Harvey, P.H. The epidemic behavior of the hepatitis C virus. Science 2001, 292, 2323–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, K.M.; Chan, C.H.; Tanaka, M.M. Connecting within-host dynamics to the rate of viral molecular evolution. Virus Evol. 2015, 1, vev013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Scholle, S.O.; Ypma, R.J.; Lloyd, A.L.; Koelle, K. Viral substitution rate variation can arise from the interplay between within-host and epidemiological dynamics. Am. Nat. 2013, 182, 494–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Lewis, M.; Egan, J.F.; Hall, W.W.; Desmyter, J.; Vandamme, A.M. Different population dynamics of human T cell lymphotropic virus type II in intravenous drug users compared with endemically infected tribes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13253–13258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streicker, D.G.; Lemey, P.; Velasco-Villa, A.; Rupprecht, C.E. Rates of viral evolution are linked to host geography in bat rabies. PLoS Pathog 2012, 8, e1002720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanada, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Gojobori, T. A large variation in the rates of synonymous substitution for RNA viruses and its relationship to a diversity of viral infection and transmission modes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2004, 21, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.R.; Parker, J.; Lemey, P.; Salemi, M.; Katzourakis, A.; Pybus, O.G. The mode and tempo of hepatitis C virus evolution within and among hosts. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salemi, M.; Vandamme, A.M. Hepatitis C virus evolutionary patterns studied through analysis of full-genome sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 2002, 54, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marascio, N.; Ciccozzi, M.; Equestre, M.; Lo Presti, A.; Costantino, A.; Cella, E.; Bruni, R.; Liberto, M.C.; Pisani, G.; Zicca, E.; et al. Back to the origin of HCV 2c subtype and spreading to the Calabria region (Southern Italy) over the last two centuries: A phylogenetic study. Infect. Genet. Evol.: J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2014, 26, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hundie, G.B.; Raj, V.S.; GebreMichael, D.; Pas, S.D.; Haagmans, B.L. Genetic diversity of hepatitis C virus in Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, O.G.; Cochrane, A.; Holmes, E.C.; Simmonds, P. The hepatitis C virus epidemic among injecting drug users. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifazi, C.; Sabatino, D. Albanian migration to Italy: What official data and survey results can reveal. J. Ethn. Migr. Stud. 2003, 29, 967–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehender, G.; Sorrentino, C.; Lai, A.; Ebranati, E.; Gabanelli, E.; Lo Presti, A.; Vujoševic, D.; Lauševic, D.; Terzić, D.; Shkjezi, R.; et al. Reconstruction of the evolutionary dynamics of hepatitis C virus subtypes in Montenegro and the Balkan region. Infect. Genet. Evol. J. Mol. Epidemiol. Evol. Genet. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Nakano, T.; Smallwood, G.A.; Heffron, T.G.; Robertson, B.H.; Hagedorn, C.H. A refined long RT-PCR technique to amplify complete viral RNA genome sequences from clinical samples: Application to a novel hepatitis C virus variant of genotype 6. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 126, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimmer, K.; von Haeseler, A. Likelihood-mapping: A simple method to visualize phylogenetic content of a sequence alignment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6815–6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; von Haeseler, A. TREE-PUZZLE: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Suchard, M.A.; Xie, D.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemey, P.; Suchard, M.; Rambaut, A. Reconstructing the initial global spread of a human influenza pandemic: A Bayesian spatial-temporal model for the global spread of H1N1pdm. PLoS Curr 2009, 1, RRN1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchard, M.A.; Weiss, R.E.; Sinsheimer, J.S. Bayesian selection of continuous-time Markov chain evolutionary models. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes Factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielejec, F.; Baele, G.; Vrancken, B.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Lemey, P. SpreaD3: Interactive Visualization of Spatiotemporal History and Trait Evolutionary Processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2167–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, T.; Kühnert, D.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Drummond, A.J. Birth-death skyline plot reveals temporal changes of epidemic spread in HIV and hepatitis C virus (HCV). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Italian Patients (208) | Albanian Patients (37) | Significant (p) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (SD)-Years | 72 years (15.2) | 50.5 (14.3) | <0.05 |
| Males proportion: absolute number (%) | 81 (38.9) | 20 (54.1) | - |
| Females proportion:absolute number (%) | 127 (61.1) | 17 (45.9) | 0.09 |
| Not-known risk-absolute number (%) | 158 (75.9) | 31 (83.7) | 0.3 |
| Iatrogenic risk-absolute number (%) | 34 (16.3) | 6 (16.2) | - |
| Other risks -absolute number (%) | 16 (7.6) | - | - |
| Node | Clade | tMRCA | Lower tMRCA | Upper tMRCA | Year Mean | Lower Year | Upper Year | Location | Location Probability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | 434.7 | 223 | 684 | 1574 | 1332 | 1793 | Gwinea | 0.49 | |
| A | 227.2 | 137 | 639 | 1781 | 1377 | 1879 | Ghana | 0.89 | |
| B | HCV-2b | 61.03 | 49 | 75 | 1948 | 1941 | 1967 | Netherlands | 0.99 |
| C | 83.86 | 61.2 | 109.2 | 1925 | 1906.8 | 1954.8 | Ghana | 0.99 | |
| D | HCV-2c | 60.9 | 44.2 | 79.7 | 1948 | 1936.3 | 1971.8 | Italy | 0.83 |
| E | HCV-2a | 56.2 | 39.4 | 73.1 | 1954 | 1942.9 | 1976.6 | Indonesia | 0.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebranati, E.; Mancon, A.; Airoldi, M.; Renica, S.; Shkjezi, R.; Dragusha, P.; Della Ventura, C.; Ciccaglione, A.R.; Ciccozzi, M.; Bino, S.; et al. Time and Mode of Epidemic HCV-2 Subtypes Spreading in Europe: Phylodynamics in Italy and Albania. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020327
Ebranati E, Mancon A, Airoldi M, Renica S, Shkjezi R, Dragusha P, Della Ventura C, Ciccaglione AR, Ciccozzi M, Bino S, et al. Time and Mode of Epidemic HCV-2 Subtypes Spreading in Europe: Phylodynamics in Italy and Albania. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020327
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbranati, Erika, Alessandro Mancon, Martina Airoldi, Silvia Renica, Renata Shkjezi, Pranvera Dragusha, Carla Della Ventura, Anna Rita Ciccaglione, Massimo Ciccozzi, Silvia Bino, and et al. 2021. "Time and Mode of Epidemic HCV-2 Subtypes Spreading in Europe: Phylodynamics in Italy and Albania" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020327
APA StyleEbranati, E., Mancon, A., Airoldi, M., Renica, S., Shkjezi, R., Dragusha, P., Della Ventura, C., Ciccaglione, A. R., Ciccozzi, M., Bino, S., Tanzi, E., Micheli, V., Riva, E., Galli, M., & Zehender, G. (2021). Time and Mode of Epidemic HCV-2 Subtypes Spreading in Europe: Phylodynamics in Italy and Albania. Diagnostics, 11(2), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020327









