Motor Pathophysiology Related to Dyspnea in COPD Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
Abstract
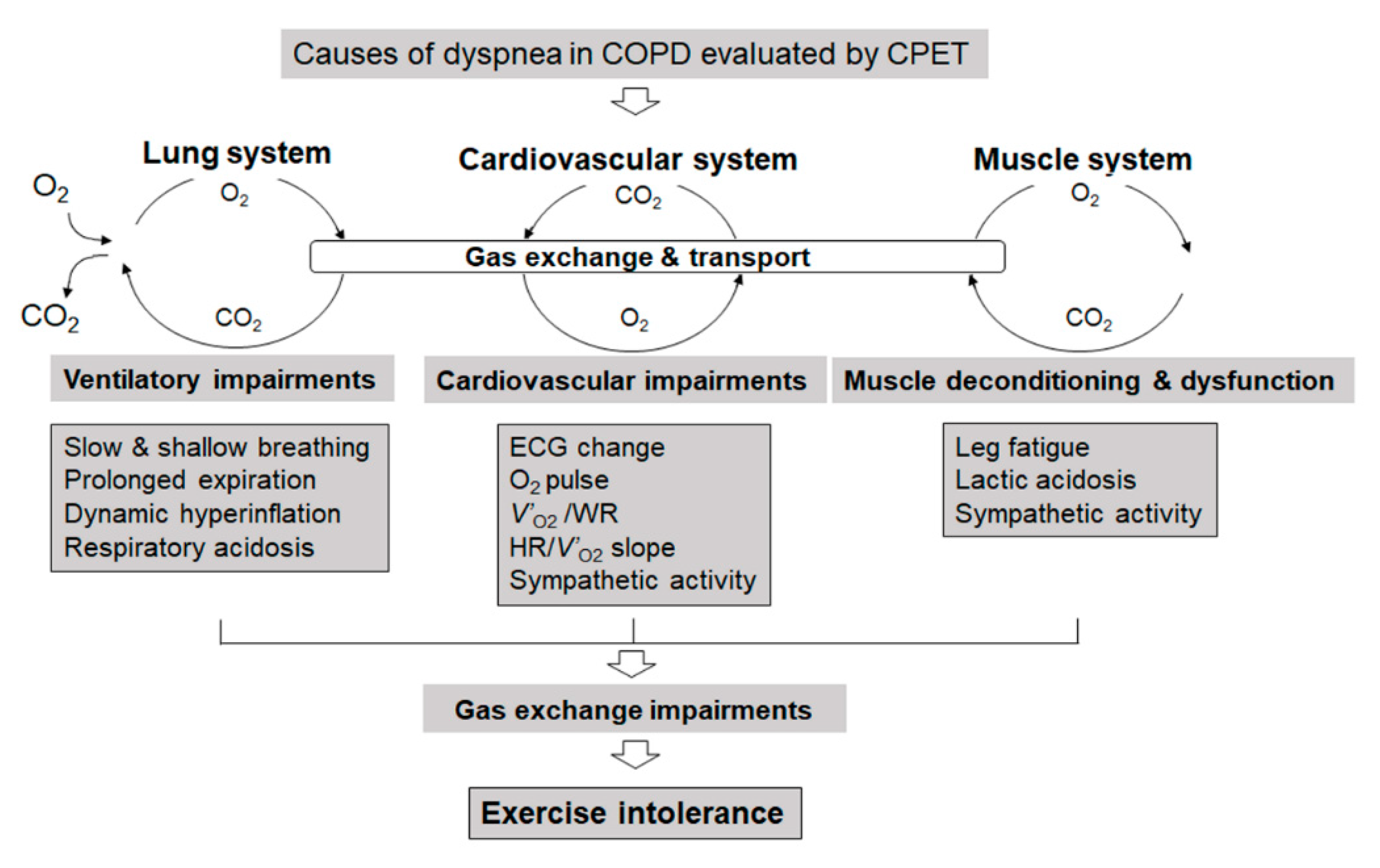
1. Introduction
2. Exercise Tolerance and Exercise-Limiting Factors
2.1. Exertional Dyspnea Due to Cardiovascular Disorders
2.2. Measures and Treatment of Lower Limb Fatigue
2.3. Exertional Dyspnea Due to Ventilatory Impairment
2.3.1. Improving Ventilatory Impairments to Reduce Exertional Dyspnea
2.3.2. Reducing Ventilatory Demand to Reduce Exertional Dyspnea
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Laveneziana, P.; Webb, K.A.; Ora, J.; Wadell, K.; O′Donnell, D.E. Evolution of dyspnea during exercise in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Impact of critical volume constraints. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 184, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Hiraga, T.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Tateishi, Y. Effects of oxygen on exertional dyspnoea and exercise performance in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respirology 2012, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Lam, M.; Webb, K.A. Measurement of symptoms, lung hyperinflation, and endurance during exercise in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 158, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Milne, K.M.; James, M.D.; de Torres, J.P.; Neder, J.A. Dyspnea in COPD: New Mechanistic Insights and Management Implications. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, W.Q.; Man, S.F.; Senthilselvan, A.; Sin, D.D. Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and systemic inflammation: A systematic review and a meta-analysis. Thorax 2004, 59, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanfleteren, L.E.; Spruit, M.A.; Groenen, M.; Gaffron, S.; van Empel, V.P.; Bruijnzeel, P.L.; Rutten, E.P.; Roodt, J.O.; Wouters, E.F.; Franssen, F.M. Clusters of comorbidities based on validated objective measurements and systemic inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, T.; Crook, S.; Kaltsakas, G.; Louvaris, Z.; Berton, D.; Urquhart, D.S.; Kampouras, A.; Rabinovich, R.A.; Verges, S.; Kontopidis, D.; et al. ERS statement on standardisation of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in chronic lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laviolette, L.; Laveneziana, P. Exercise Testing in the prognostic evaluation of patients with lung and heart diseases. In Clinical Exercise Testing (ERS Monograph); Palange, P., Laveneziana, P., Neder, J.A., Ward, S.A., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 222–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman, K.; Hansen, J.; Sue, D.; Stringer, W.; Sietsema, K.; Sun, X.-G. Principles of Exercise Testing and Interpretation: Including Pathophysiology and Clinical Applications, 5th ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Puente-Maestu, L.; Palange, P.; Casaburi, R.; Laveneziana, P.; Maltais, F.; Neder, J.A.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Onorati, P.; Porszasz, J.; Rabinovich, R.; et al. Use of exercise testing in the evaluation of interventional efficacy: An official ERS statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 429–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, H.; Miki, K.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Oshitani, Y.; Nishida, K.; Sawa, N.; Tsujino, K.; Maekura, R. Dyspnea and the Varying Pathophysiologic Manifestations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing With Arterial Blood Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neder, J.A.; Berton, D.C.; Arbex, F.F.; Alencar, M.C.; Rocha, A.; Sperandio, P.A.; Palange, P.; O’Donnell, D.E. Physiological and clinical relevance of exercise ventilatory efficiency in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1602036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.B.; Collins, S.; Stickland, M.K. Measurement and Interpretation of Exercise Ventilatory Efficiency. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherald, J.; Sattler, C.; Garcia, G.; Laveneziana, P. Ventilatory response to exercise in cardiopulmonary disease: The role of chemosensitivity and dead space. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraga, T.; Maekura, R.; Okuda, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Hirotani, A.; Kitada, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Yokota, S.; Ito, M.; Ogura, T. Prognostic predictors for survival in patients with COPD using cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2003, 23, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oga, T.; Nishimura, K.; Tsukino, M.; Hajiro, T.; Ikeda, A.; Mishima, M. Relationship between different indices of exercise capacity and clinical measures in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Heart Lung 2002, 31, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oga, T.; Nishimura, K.; Tsukino, M.; Sato, S.; Hajiro, T. Analysis of the factors related to mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Role of exercise capacity and health status. Am. J. Respir Crit Care Med. 2003, 167, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgür, E.S.; Nayci, S.A.; Özge, C.; Taşdelen, B. An integrated index combined by dynamic hyperinflation and exercise capacity in the prediction of morbidity and mortality in COPD. Respir. Care 2012, 57, 1452–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, K.; Maekura, R.; Hiraga, T.; Miki, K.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Tateishi, Y.; Mori, M. Identification of three exercise-induced mortality risk factors in patients with COPD. COPD 2014, 11, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guazzi, M.; Adams, V.; Conraads, V.; Halle, M.; Mezzani, A.; Vanhees, L.; Arena, R.; Fletcher, G.F.; Forman, D.E.; Kitzman, D.W.; et al. EACPR/AHA Scientific Statement. Clinical recommendations for cardiopulmonary exercise testing data assessment in specific patient populations. Circulation 2012, 126, 2261–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekura, R.; Hiraga, T.; Miki, K.; Kitada, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Miki, M.; Tateishi, Y. Differences in physiological response to exercise in patients with different COPD severity. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, R.C.; Jones, P.W. A comparison of the visual analogue scale and modified Borg scale for the measurement of dyspnoea during exercise. Clin. Sci. 1989, 76, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Hiraga, T.; Hashimoto, H.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Fushitani, K.; Motone, M. Acidosis and raised norepinephrine levels are associated with exercise dyspnoea in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology 2009, 14, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirotani, A.; Maekura, R.; Okuda, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Moriguchi, K.; Kitada, S.; Hiraga, T.; Ito, M.; Ogura, T.; Ogihara, T. Exercise-induced electrocardiographic changes in patients with chronic respiratory diseases: Differential diagnosis by 99mTc-tetrofosmin SPECT. J. Nucl. Med. 2003, 44, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Rutten, F.H.; Cramer, M.J.; Grobbee, D.E.; Sachs, A.P.; Kirkels, J.H.; Lammers, J.W.; Hoes, A.W. Unrecognized heart failure in elderly patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, K.; Yoshimoto, D.; Hagan, G.W.; Jones, P.W. Prevalence of airflow limitation in outpatients with cardiovascular diseases in Japan. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2014, 9, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostoni, P.; Casaburi, R. Patterns of cariopulmonary response to exercise in cardiac diseses In Clinical Exercise Testing (ERS Monograph); Palange, P., Laveneziana, P., Neder, J.A., Ward, S.A., Eds.; European Respiratory Society: Sheffield, UK, 2018; pp. 160–174. [Google Scholar]
- Nery, L.E.; Wasserman, K.; French, W.; Oren, A.; Davis, J.A. Contrasting cardiovascular and respiratory responses to exercise in mitral valve and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases. Chest 1983, 83, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G.; Bluemke, D.A.; Ahmed, F.S.; Carr, J.J.; Enright, P.L.; Hoffman, E.A.; Jiang, R.; Kawut, S.M.; Kronmal, R.A.; Lima, J.A.; et al. Percent emphysema, airflow obstruction, and impaired left ventricular filling. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, M.; Barr, R.G.; Lima, J.A.; Hoffman, E.A.; Bluemke, D.A.; Carr, J.J.; Chahal, H.; Enright, P.L.; Jain, A.; Prince, M.R.; et al. Percent emphysema and right ventricular structure and function: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis-Lung and Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis-Right Ventricle Studies. Chest 2013, 144, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppoolse, R.; Schols, A.M.; Baarends, E.M.; Mostert, R.; Akkermans, M.A.; Janssen, P.P.; Wouters, E.F. Interval versus continuous training in patients with severe COPD: A randomized clinical trial. Eur. Respir. J. 1999, 14, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, T.J.C.; Lindley, M.R.; Ferguson, R.A.; Constantin, D.; Singh, S.J.; Bolton, C.E.; Evans, R.A.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Steiner, M.C. Submaximal Eccentric Cycling in People With COPD: Acute Whole-Body Cardiopulmonary and Muscle Metabolic Responses. Chest 2020, 159, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watz, H.; Pitta, F.; Rochester, C.L.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; ZuWallack, R.; Troosters, T.; Vaes, A.W.; Puhan, M.A.; Jehn, M.; Polkey, M.I.; et al. An official European Respiratory Society statement on physical activity in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1521–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agusti, A.; Soriano, J.B. COPD as a systemic disease. COPD 2008, 5, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, K.F.; Watz, H. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celli, B.R.; Locantore, N.; Tal-Singer, R.; Riley, J.; Miller, B.; Vestbo, J.; Yates, J.C.; Silverman, E.K.; Owen, C.A.; Divo, M.; et al. Emphysema and extrapulmonary tissue loss in COPD: A multi-organ loss of tissue phenotype. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, F.; Decramer, M.; Casaburi, R.; Barreiro, E.; Burelle, Y.; Debigaré, R.; Dekhuijzen, P.N.; Franssen, F.; Gayan-Ramirez, G.; Gea, J.; et al. An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: Update on limb muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, e15–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Nakazato, M.; Kimura, H.; Murakami, S.; Ohnishi, S.; Hiraga, T.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; et al. Ghrelin treatment of cachectic patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, I.H. Sarcopenia: Origins and clinical relevance. J. Nutr. 1997, 127, 990s–991s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studenski, S.A.; Peters, K.W.; Alley, D.E.; Cawthon, P.M.; McLean, R.R.; Harris, T.B.; Ferrucci, L.; Guralnik, J.M.; Fragala, M.S.; Kenny, A.M.; et al. The FNIH sarcopenia project: Rationale, study description, conference recommendations, and final estimates. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschöp, M.; Smiley, D.L.; Heiman, M.L. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 2000, 407, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazato, M.; Murakami, N.; Date, Y.; Kojima, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K.; Matsukura, S. A role for ghrelin in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 2001, 409, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Tsuchihashi, T.; Fujii, K.; Abe, I.; Iida, M. Central ghrelin modulates sympathetic activity in conscious rabbits. Hypertension 2002, 40, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Mori, M.; Kangawa, K. Effects of ghrelin treatment on exertional dyspnea in COPD: An exploratory analysis. J. Physiol. Sci. 2015, 65, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Nagaya, N.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Motone, M.; Hiraga, T.; Mori, M.; et al. Effects of ghrelin treatment on exercise capacity in underweight COPD patients: A substudy of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ghrelin treatment. BMC Pulm. Med. 2013, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macklem, P.T. Therapeutic implications of the pathophysiology of COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 35, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neder, J.A.; Arbex, F.F.; Alencar, M.C.; O’Donnell, C.D.; Cory, J.; Webb, K.A.; O’Donnell, D.E. Exercise ventilatory inefficiency in mild to end-stage COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, D.S.; Brancatisano, T.; Engel, L.A. Chest wall mechanics during exercise in patients with severe chronic air-flow obstruction. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1984, 129, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, A.; Alghamdi, B.J.; Ciavaglia, C.E.; Elbehairy, A.F.; Webb, K.A.; Ora, J.; Neder, J.A.; O’Donnell, D.E. Common Mechanisms of Dyspnea in Chronic Interstitial and Obstructive Lung Disorders. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, C.J.; Luo, Y.M.; Steier, J.; Rafferty, G.F.; Polkey, M.I.; Moxham, J. Neural respiratory drive and breathlessness in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 45, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Guenette, J.A.; Maltais, F.; Webb, K.A. Decline of resting inspiratory capacity in COPD: The impact on breathing pattern, dyspnea, and ventilatory capacity during exercise. Chest 2012, 141, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, W.A.; Olafsson, S.; Hyatt, R.E. Ventilatory mechanics and expiratory flow limitation during exercise in patients with obstructive lung disease. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Revill, S.M.; Webb, K.A. Dynamic hyperinflation and exercise intolerance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, D.E.; Webb, K.A. Exertional breathlessness in patients with chronic airflow limitation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 148, 1351–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, K.; Cox, T.A.; Sietsema, K.E. Ventilatory regulation of arterial H(+) (pH) during exercise. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 190, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Tateishi, Y.; Mori, M. Exertional acidotic responses in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: The mechanisms of exertional dyspnea. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2013, 185, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.A.; Wagner, P.D. Exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laveneziana, P.; Webb, K.A.; Wadell, K.; Neder, J.A.; O’Donnell, D.E. Does expiratory muscle activity influence dynamic hyperinflation and exertional dyspnea in COPD? Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 199, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, K.; Tsujino, K.; Edahiro, R.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Kagawa, H.; Oshitani, Y.; Ohara, Y.; Hosono, Y.; et al. Exercise tolerance and balance of inspiratory-to-expiratory muscle strength in relation to breathing timing in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Breath Res. 2018, 12, 036008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Tsujino, K.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Kagawa, H.; Oshitani, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Matsuki, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kida, H. Managing COPD with expiratory or inspiratory pressure load training based on a prolonged expiration pattern. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, J.E.; Yuan, R.; Suzuki, M.; Seyednejad, N.; Elliott, W.M.; Sanchez, P.G.; Wright, A.C.; Gefter, W.B.; Litzky, L.; Coxson, H.O.; et al. Small-airway obstruction and emphysema in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, W.G.; Hutchinson, D.; Newby, J.P.; Hamstra, R.; Durrance, J. Major Airway Collapsibility in the Pathogenesis of Obstructive Emphysema. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1963, 46, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, H.; Norlander, K.; Berglund, L.; Janson, C.; Malinovschi, A.; Nordvall, L.; Nordang, L.; Emtner, M. Prevalence of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction and exercise-induced laryngeal obstruction in a general adolescent population. Thorax 2015, 70, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakin, R.C.; Metzger, W.J.; Haughey, B.H. Upper airway obstruction presenting as exercise-induced asthma. Chest 1984, 86, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landwehr, L.P.; Wood, R.P.; Blager, F.B.; Milgrom, H. Vocal cord dysfunction mimicking exercise-induced bronchospasm in adolescents. Pediatrics 1996, 98, 971–974. [Google Scholar]
- McFadden, E.R., Jr.; Zawadski, D.K. Vocal cord dysfunction masquerading as exercise-induced asthma. a physiologic cause for “choking” during athletic activities. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 153, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olin, J.T.; Clary, M.S.; Fan, E.M.; Johnston, K.L.; State, C.M.; Strand, M.; Christopher, K.L. Continuous laryngoscopy quantitates laryngeal behaviour in exercise and recovery. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, M.; Haji, G.S.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Tanner, R.J.; Hopkinson, N.S.; Polkey, M.I.; Hull, J.H. Dynamic laryngeal narrowing during exercise: A mechanism for generating intrinsic PEEP in COPD? Thorax 2015, 70, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosselink, R.; De Vos, J.; van den Heuvel, S.P.; Segers, J.; Decramer, M.; Kwakkel, G. Impact of inspiratory muscle training in patients with COPD: What is the evidence? Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 37, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, N. Inspiratory muscle training in stable COPD patients: Enough is enough? Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charususin, N.; Gosselink, R.; Decramer, M.; Demeyer, H.; McConnell, A.; Saey, D.; Maltais, F.; Derom, E.; Vermeersch, S.; Heijdra, Y.F.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of adjunctive inspiratory muscle training for patients with COPD. Thorax 2018, 73, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, K.; Jelusic, D.; Wittmann, M.; Krämer, B.; Huber, V.; Fuchs, S.; Lehbert, N.; Wingart, S.; Stojanovic, D.; Göhl, O.; et al. Inspiratory muscle training does not improve clinical outcomes in 3-week COPD rehabilitation: Results from a randomised controlled trial. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Miki, K.; Matsuki, T.; Fukushima, K.; Oshitani, Y.; Kagawa, H.; Tsujino, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Miki, M.; Kida, H. Intolerance to and limitations of inspiratory muscle training in patients with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A report of two cases. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 101210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobst, K.; Chen, J.H.; McPherson, K.; Arrowsmith, J.; Brown, V.; Efthimiou, J.; Fletcher, H.J.; Maciocia, G.; Mole, P.; Shifrin, K.; et al. Controlled trial of acupuncture for disabling breathlessness. Lancet 1986, 2, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Muro, S.; Ando, Y.; Omori, T.; Shiota, T.; Endo, K.; Sato, S.; Aihara, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Suzuki, S.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of acupuncture in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): The COPD-acupuncture trial (CAT). Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnie, B.; Barbe, T.; De Ridder, E.; Van Oosterwijck, J.; Cools, A.; Danneels, L. The influence of dry needling of the trapezius muscle on muscle blood flow and oxygenation. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2012, 35, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinbara, H.; Okubo, M.; Sumiya, E.; Fukuda, F.; Yano, T.; Kitade, T. Effects of manual acupuncture with sparrow pecking on muscle blood flow of normal and denervated hindlimb in rats. Acupunct. Med. 2008, 26, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekura, T.; Miki, K.; Miki, M.; Kitada, S.; Maekura, R. Clinical Effects Of Acupuncture On The Pathophysiological Mechanism Of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease During Exercise. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2019, 14, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casaburi, R.; Porszasz, J.; Burns, M.R.; Carithers, E.R.; Chang, R.S.; Cooper, C.B. Physiologic benefits of exercise training in rehabilitation of patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laveneziana, P.; Palange, P. Physical activity, nutritional status and systemic inflammation in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Maekura, R.; Kitada, S.; Miki, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawabe, T.; Kagawa, H.; Oshitani, Y.; Satomi, A.; et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD improves exercise time rather than exercise tolerance: Effects and mechanisms. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2017, 12, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, C.L.; Vogiatzis, I.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Marciniuk, D.D.; Puhan, M.A.; Spruit, M.A.; Masefield, S.; Casaburi, R.; Clini, E.M.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Policy Statement: Enhancing Implementation, Use, and Delivery of Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.L.; Lin, Z.K.; Weng, H.D.; Qi, Q.F.; Lu, J.; Liu, K.X. Effectiveness of meditative movement on COPD: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miki, K. Motor Pathophysiology Related to Dyspnea in COPD Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020364
Miki K. Motor Pathophysiology Related to Dyspnea in COPD Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020364
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiki, Keisuke. 2021. "Motor Pathophysiology Related to Dyspnea in COPD Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020364
APA StyleMiki, K. (2021). Motor Pathophysiology Related to Dyspnea in COPD Evaluated by Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing. Diagnostics, 11(2), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020364





