A Molecular Perspective on Colistin and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Mode of Action, Resistance Genetics, and Phenotypic Susceptibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
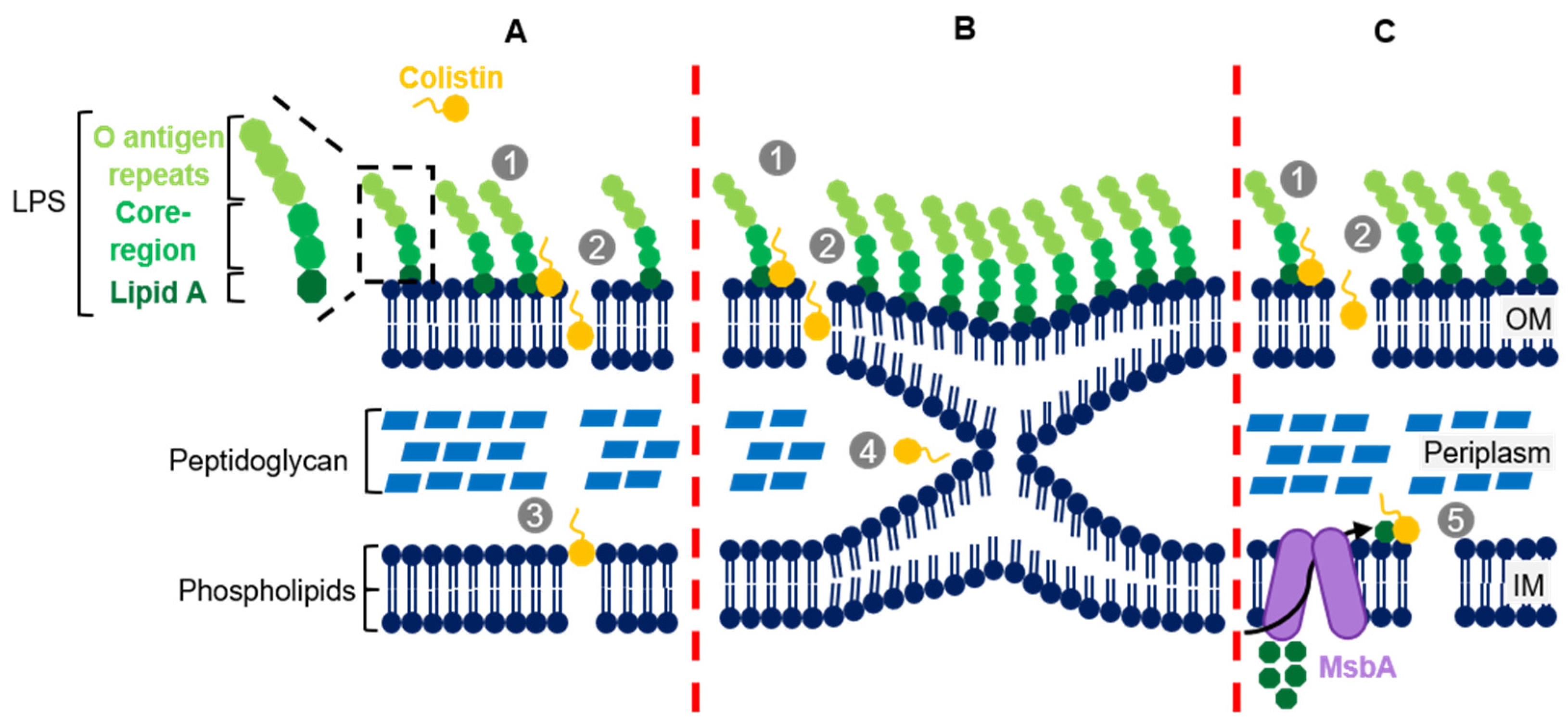
2. Colistin’s Structure and Mechanism of Action
3. Colistin Resistance Mechanisms in K. pneumoniae
3.1. Chromosomal Mutations Leading to LPS Modification
3.2. Capsule
3.3. Efflux Pumps
3.4. Plasmid-Mediated Resistance
4. Quantifying Colistin Susceptibility for K. pneumoniae
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyles, C.; Boerlin, P. Horizontally transferred genetic elements and their role in pathogenesis of bacterial disease. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S. Klebsiella Infections. Medscape 2019. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/219907-print (accessed on 8 November 2020).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance in Europe 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Haeggman, S.; Löfdahl, S.; Paauw, A.; Verhoef, J.; Brisse, S. Diversity and evolution of the class A chromosomal beta-lactamase gene in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2400–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon-Venezia, S.; Kondratyeva, K.; Carattoli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae: A major worldwide source and shuttle for antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 252–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, A. Mobilization of Carbapenemase-Mediated Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Brunel, J.M.; Dubus, J.C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Rolain, J.M. Colistin: An update on the antibiotic of the 21st century. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosillo, N.; Taglietti, F.; Granata, G. Treatment Options for Colistin Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Present and Future. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Antimicrobial Consumption in the EU/EEA, Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji, B.T.; Pogue, J.M.; Zavascki, A.P.; Paul, M.; Daikos, G.L.; Forrest, A.; Giacobbe, D.R.; Viscoli, C.; Giamarellou, H.; Karaiskos, I.; et al. International Consensus Guidelines for the Optimal Use of the Polymyxins: Endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy (ACCP), European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID), Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA), International Society for Anti-infective Pharmacology (ISAP), Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM), and Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists (SIDP). Pharmacotherapy 2019, 39, 10–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, Y.; Kurosawa, A.; Tsuchiya, A.; Takakura, K. A new antibiotic ‘colistin’ produced by spore-forming soil bacteria. J. Antibiot. 1950, 3, 457–458. [Google Scholar]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P. Polymyxins: Antibacterial Activity, Susceptibility Testing, and Resistance Mechanisms Encoded by Plasmids or Chromosomes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 30, 557–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhouma, M.; Beaudry, F.; Thériault, W.; Letellier, A. Colistin in Pig Production: Chemistry, Mechanism of Antibacterial Action, Microbial Resistance Emergence, and One Health Perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghapour, Z.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ganbarov, K.; Bialvaei, A.Z.; Mahmood, S.S.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, M.; Asgharzadeh, M.; Yousefi, B.; Kafil, H.S. Molecular mechanisms related to colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkov, T.; Thompson, P.E.; Nation, R.L.; Li, J. Structure-activity relationships of polymyxin antibiotics. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1898–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Qin, W.; Lin, J.; Fang, S.; Qiu, J. Antibacterial mechanisms of polymyxin and bacterial resistance. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 679109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausell, A.; Garcia-Subirats, M.; Pujol, M.; Busquets, M.A.; Rabanal, F.; Cajal, Y. Gram-negative outer and inner membrane models: Insertion of cyclic cationic lipopeptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deris, Z.Z.; Swarbrick, J.D.; Roberts, K.D.; Azad, M.A.; Akter, J.; Horne, A.S.; Nation, R.L.; Rogers, K.L.; Thompson, P.E.; Velkov, T.; et al. Probing the penetration of antimicrobial polymyxin lipopeptides into gram-negative bacteria. Bioconj. Chem. 2014, 25, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausell, A.; Rabanal, F.; Garcia-Subirats, M.; Asunción Alsina, M.; Cajal, Y. Membrane Association and Contact Formation by a Synthetic Analogue of Polymyxin B and Its Fluorescent Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 4465–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.-P.S.; Hancock, R.E.W. The relationship between peptide structure and antibacterial activity. Peptides 2003, 24, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R.F.; Sa-Correia, I.; Valvano, M.A. Lipopolysaccharide modification in Gram-negative bacteria during chronic infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, A.; Klöckner, A.; Becce, M.; Hagart, K.L.H.; Evans, L.E.; Furniss, R.C.D.; Mavridou, D.A.I.; Larrouy-Maumus, G.J.; Stevens, M.M.; Edwards, A.M. Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. bioRxiv 2020, 479618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, M.; Hancock, R.E.; Kelly, N.M. Antiendotoxin activity of cationic peptide antimicrobial agents. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 4922–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, K.; Sharma, M.; Vijay, S.; Shome, B.R. Understanding policy dilemmas around antibiotic use in food animals & offering potential solutions. Indian J. Med. Res. 2019, 149, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Ban on Antibiotics as Growth Promoters in Animal Feed Enters into Effect; EC: Brussels, Belguim, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Model List of Essential Medicines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Categorisation of Antibiotics in the European Union; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rojas, L.J.; Salim, M.; Cober, E.; Richter, S.S.; Perez, F.; Salata, R.A.; Kalayjian, R.C.; Watkins, R.R.; Marshall, S.; Rudin, S.D.; et al. Colistin Resistance in Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Laboratory Detection and Impact on Mortality. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 64, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, A.B.; Doorduijn, D.J.; Mills, G.; Rogers, M.R.C.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Rooijakkers, S.H.M.; Willems, R.J.L.; Bengoechea, J.A.; van Schaik, W. Evolution of Colistin Resistance in the Klebsiella pneumoniae Complex Follows Multiple Evolutionary Trajectories with Variable Effects on Fitness and Virulence Characteristics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01958-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrophanov, A.Y.; Jewett, M.W.; Hadley, T.J.; Groisman, E.A. Evolution and Dynamics of Regulatory Architectures Controlling Polymyxin B Resistance in Enteric Bacteria. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breazeale, S.D.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Raetz, C.R. Oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid in extracts of polymyxin-resistant Escherichia coli. Origin of lipid a species modified with 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2886–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, A.M.; Goulian, M. Feedback inhibition in the PhoQ/PhoP signaling system by a membrane peptide. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Peng, H.-L. Molecular characterization of the PhoPQ-PmrD-PmrAB mediated pathway regulating polymyxin B resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, M.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Jones, M.B.; Marshall, S.H.; Rudin, S.D.; van Duin, D.; Kaye, K.; Jacobs, M.R.; Bonomo, R.A.; Adams, M.D. Genomic and transcriptomic analyses of colistin-resistant clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae reveal multiple pathways of resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Lin, T.-L.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-T. Amino Acid Substitutions of CrrB Responsible for Resistance to Colistin through CrrC in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Rasmussen, P.K.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Cai, T.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Xie, Z.; Ding, X.; Niu, L.; et al. Proteomic Changes of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Response to Colistin Treatment and crrB Mutation-Mediated Colistin Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e02200-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaidane, N.; Bonnin, R.A.; Mansour, W.; Girlich, D.; Creton, E.; Cotellon, G.; Chaouch, C.; Boujaafar, N.; Bouallegue, O.; Naas, T. Genomic Insights into Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from a Tunisian Teaching Hospital. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01601-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Jayol, A.; Poirel, L. Rapid Detection of Polymyxin Resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Lehours, P.; Poirel, L.; Dubois, V. Comparison of methods for detection of plasmid-mediated and chromosomally encoded colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, T.L.; Pan, Y.J.; Wang, Y.P.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. Colistin resistance mechanisms in Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from Taiwan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2909–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Diene, S.M.; Kempf, M.; Berrazeg, M.; Bakour, S.; Gupta, S.K.; Thongmalayvong, B.; Akkhavong, K.; Somphavong, S.; Paboriboune, P.; et al. Worldwide emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae from healthy humans and patients in Lao PDR, Thailand, Israel, Nigeria and France owing to inactivation of the PhoP/PhoQ regulator mgrB: An epidemiological and molecular study. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragasam, A.K.; Shankar, C.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Biswas, I.; Nabarro, L.E.B.; Inbanathan, F.Y.; George, B.; Verghese, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Causing Bacteremia from India—A First Report. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, P.; Veeraraghavan, B.; Devanga Ragupathi, N.K.; Inbanathan, F.Y.; Khurana, S.; Bhardwaj, N.; Kumar, S.; Sagar, S.; Gupta, A. Multiple mutations in lipid-A modification pathway & novel fosA variants in colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Sci. OA 2018, 4, Fso319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.J.; Ko, K.S. Mutant prevention concentrations of colistin for Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbelle, N.M.; Feldman, C.; Sekyere, J.O.; Maningi, N.E.; Modipane, L.; Essack, S.Y. Pathogenomics and Evolutionary Epidemiology of Multi-Drug Resistant Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Pretoria, South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Pelegrin, A.C.; Mirande, C.; Brkic, S.; Cirkovic, I.; Goossens, H.; Rossolini, G.M.; van Belkum, A. Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem- and Colistin-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates From Serbia: Predominance of ST101 Strains Carrying a Novel OXA-48 Plasmid. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Brink, A.; Poirel, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with alterations in the PhoPQ regulatory system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannatelli, A.; Giani, T.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Conte, V.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Vatopoulos, A.; Rossolini, G.M. MgrB inactivation is a common mechanism of colistin resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirel, L.; Jayol, A.; Bontron, S.; Villegas, M.-V.; Ozdamar, M.; Türkoglu, S.; Nordmann, P. The mgrB gene as a key target for acquired resistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 70, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeili, M.; Javani, A.; Moradi, J.; Jafari, Z.; Feizabadi, M.M.; Babaei, E. MgrB Alterations Mediate Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Iran. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli, A.; Di Pilato, V.; Giani, T.; Arena, F.; Ambretti, S.; Gaibani, P.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Rossolini, G.M. In vivo evolution to colistin resistance by PmrB sensor kinase mutation in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae is associated with low-dosage colistin treatment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4399–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayol, A.; Poirel, L.; Brink, A.; Villegas, M.V.; Yilmaz, M.; Nordmann, P. Resistance to colistin associated with a single amino acid change in protein PmrB among Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates of worldwide origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4762–4766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Brink, A.; Villegas, M.V.; Dubois, V.; Poirel, L. High-Level Resistance to Colistin Mediated by Various Mutations in the crrB Gene among Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01423-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli, A.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Giani, T.; Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Ambretti, S.; Gaibani, P.; Rossolini, G.M. In vivo emergence of colistin resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae producing KPC-type carbapenemases mediated by insertional inactivation of the PhoQ/PhoP mgrB regulator. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5521–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zowawi, H.M.; Forde, B.M.; Alfaresi, M.; Alzarouni, A.; Farahat, Y.; Chong, T.M.; Yin, W.F.; Chan, K.G.; Li, J.; Schembri, M.A.; et al. Stepwise evolution of pandrug-resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, R.; Khan, E.; Gonzalez, G.; Hasan, R.; Schneiders, T. Genetic regulation of the ramA locus and its expression in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, S.; Nikaido, E.; Nakashima, R.; Sakurai, K.; Fujiwara, D.; Fujii, I.; Nishino, K. The crystal structure of multidrug-resistance regulator RamR with multiple drugs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Majumdar, S.; Yu, J.; Fookes, M.; McAteer, S.P.; Llobet, E.; Finn, S.; Spence, S.; Monaghan, A.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Ingram, R.J.; et al. Elucidation of the RamA Regulon in Klebsiella pneumoniae Reveals a Role in LPS Regulation. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, M.A.; Vargas, M.A.; Regueiro, V.; Llompart, C.M.; Albertí, S.; Bengoechea, J.A. Capsule polysaccharide mediates bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 7107–7114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llobet, E.; Tomás, J.M.; Bengoechea, J.A. Capsule polysaccharide is a bacterial decoy for antimicrobial peptides. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llobet, E.; Campos, M.A.; Giménez, P.; Moranta, D.; Bengoechea, J.A. Analysis of the networks controlling the antimicrobial-peptide-dependent induction of Klebsiella pneumoniae virulence factors. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 3718–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V.B.; Rajamohan, G. KpnEF, a new member of the Klebsiella pneumoniae cell envelope stress response regulon, is an SMR-type efflux pump involved in broad-spectrum antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 4449–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang-Kan, X.; Neuberger, A.; van Veen, H.W.; Pos, K.M.; Piddock, L.J.V.; Luisi, B.F. Multidrug efflux pumps: Structure, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.B.; Singh, B.B.; Priyadarshi, N.; Chauhan, N.K.; Rajamohan, G. Role of Novel Multidrug Efflux Pump Involved in Drug Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.; Mallette, E.; Clarke, B.R.; Kimber, M.S.; Whitfield, C. The Klebsiella pneumoniae O12 ATP-binding Cassette (ABC) Transporter Recognizes the Terminal Residue of Its O-antigen Polysaccharide Substrate. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 9748–9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, W.; Minato, Y.; Dodan, H.; Onishi, M.; Tsuchiya, T.; Kuroda, T. Characterization of MATE-type multidrug efflux pumps from Klebsiella pneumoniae MGH78578. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, J.X.; Lin, Z.W.; Sun, X.; Lin, W.H.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, G.B.; Deng, Q.W.; Qu, D.; Yu, Z.J. Overexpression of OqxAB and MacAB efflux pumps contributes to eravacycline resistance and heteroresistance in clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, J.; Zhao, J.; Cui, J.; Wang, R.; Liu, Y. Effects of Efflux Pump Inhibitors on Colistin Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 3215–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.K.; Ko, K.S. Effect of carbonyl cyanide 3-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) on killing Acinetobacter baumannii by colistin. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naha, S.; Sands, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Roy, C.; Rameez, M.J.; Saha, B.; Dutta, S.; Walsh, T.R.; Basu, S. KPC-2-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST147 in a neonatal unit: Clonal isolates with differences in colistin susceptibility attributed to AcrAB-TolC pump. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ruan, Z.; Hua, X.; Zhou, H.; Yu, Y. Tigecycline susceptibility and the role of efflux pumps in tigecycline resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Sekyere, J.; Amoako, D.G. Carbonyl Cyanide m-Chlorophenylhydrazine (CCCP) Reverses Resistance to Colistin, but Not to Carbapenems and Tigecycline in Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Lin, T.L.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, J.T. A putative RND-type efflux pump, H239_3064, contributes to colistin resistance through CrrB in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkadlec, J.; Kalova, A.; Brajerova, M.; Gelbicova, T.; Karpiskova, R.; Smelikova, E.; Nyc, O.; Drevinek, P.; Krutova, M. The Intestinal Carriage of Plasmid-Mediated Colistin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae in Tertiary Care Settings. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osei Sekyere, J. Mcr colistin resistance gene: A systematic review of current diagnostics and detection methods. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Li, H.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, R.; Walsh, T.R.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y. Novel Plasmid-Mediated Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-3 in Escherichia coli. mBio 2017, 8, e00543-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wei, W.; Lei, S.; Lin, J.; Srinivas, S.; Feng, Y. An Evolutionarily Conserved Mechanism for Intrinsic and Transferable Polymyxin Resistance. mBio 2018, 9, e02317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Liu, L.; Wei, L.; Kang, M.; Zong, Z. Identification of novel mobile colistin resistance gene mcr-10. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, L.M.; Gaballa, A.; Guldimann, C.; Sullivan, G.; Henderson, L.O.; Wiedmann, M. Identification of Novel Mobilized Colistin Resistance Gene mcr-9 in a Multidrug-Resistant, Colistin-Susceptible Salmonella enterica Serotype Typhimurium Isolate. mBio 2019, 10, e00853-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView Version 4: A Multiplatform Graphical User Interface for Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Building. Mol. Biol. Evolut. 2009, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, gkab301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.S.; Elshafiee, E.A.; Khalefa, H.S.; Kadry, M.; Hamza, D.A. Evidence of colistin resistance genes (mcr-1 and mcr-2) in wild birds and its public health implication in Egypt. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Tascini, C.; Cannatelli, A.; Henrici De Angelis, L.; Fortunato, S.; Giani, T.; Menichetti, F.; Rossolini, G.M. mcr-1.2, a New mcr Variant Carried on a Transferable Plasmid from a Colistin-Resistant KPC Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Strain of Sequence Type 512. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5612–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, L.; Baron, S.A.; Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.-M. Co-occurrence of Variants of mcr-3 and mcr-8 Genes in a Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolate From Laos. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, S.; Shen, J.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y. Emergence of a novel mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-8, in NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2018, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Lei, C.W.; Zhang, A.Y.; Wang, H.N. Novel plasmid-mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-7.1 in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1791–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turlej-Rogacka, A.; Xavier, B.B.; Janssens, L.; Lammens, C.; Zarkotou, O.; Pournaras, S.; Goossens, H.; Malhotra-Kumar, S. Evaluation of colistin stability in agar and comparison of four methods for MIC testing of colistin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuschek, E.; Åhman, J.; Webster, C.; Kahlmeter, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of colistin—Evaluation of seven commercial MIC products against standard broth microdilution for Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter spp. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Committee for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of antibacterial agents by broth dilution. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2003, 9, ix–xv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Recommendations for MIC Determination of Colistin (Polymyxin E) As Recommended by the Joint CLSI-EUCAST Polymyxin Breakpoints Working Group; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters—Version 9.0; EUCAST: Växjö, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement. M100-S24; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Schurek, K.N.; Sampaio, J.L.M.; Kiffer, C.R.V.; Sinto, S.; Mendes, C.M.F.; Hancock, R.E.W. Involvement of pmrAB and phoPQ in Polymyxin B Adaptation and Inducible Resistance in Non-Cystic Fibrosis Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 4345–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.S.; Murray, C.K.; Griffith, M.E.; McElmeel, M.L.; Fulcher, L.C.; Hospenthal, D.R.; Jorgensen, J.H. Susceptibility of acinetobacter strains isolated from deployed U.S. military personnel. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 376–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, D.; Salamera, J.; Quale, J. Irreproducible and uninterpretable Polymyxin B MICs for Enterobacter cloacae and Enterobacter aerogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 4106–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard—Ninth Edition. M07-A9; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, January 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sader, H.S.; Rhomberg, P.R.; Flamm, R.K.; Jones, R.N. Use of a surfactant (polysorbate 80) to improve MIC susceptibility testing results for polymyxin B and colistin. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prim, N.; Rivera, A.; Coll, P.; Mirelis, B. Is Colistin Susceptibility Testing Finally on the Right Track? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02067-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafopoulou, K.; Zarkotou, O.; Dimitroulia, E.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Gennimata, V.; Pournaras, S.; Tsakris, A. Comparative Evaluation of Colistin Susceptibility Testing Methods among Carbapenem-Nonsusceptible Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii Clinical Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4625–4630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezadi, F.; Ardebili, A.; Mirnejad, R. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing for Polymyxins: Challenges, Issues, and Recommendations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01390-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindler, J.A.; Humphries, R.M. Colistin MIC Variability by Method for Contemporary Clinical Isolates of Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1678–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, J.S.; Murray, C.K.; Jorgensen, J.H. Colistin heteroresistance in acinetobacter and its association with previous colistin therapy. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meletis, G.; Tzampaz, E.; Sianou, E.; Tzavaras, I.; Sofianou, D. Colistin heteroresistance in carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 946–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falagas, M.E.; Makris, G.C.; Dimopoulos, G.; Matthaiou, D.K. Heteroresistance: A concern of increasing clinical significance? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2008, 14, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Rayner, C.R.; Nation, R.L.; Owen, R.J.; Spelman, D.; Tan, K.E.; Liolios, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 2946–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarzembowski, T.; Wiśniewska, K.; Jóźwik, A.; Witkowski, J. Heterogeneity of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains (MRSA) characterized by flow cytometry. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 78–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Halfawy, O.M.; Valvano, M.A. Antimicrobial heteroresistance: An emerging field in need of clarity. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrancianu, C.O.; Popa, L.I.; Bleotu, C.; Chifiriuc, M.C. Targeting Plasmids to Limit Acquisition and Transmission of Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, P.; Köse, Ş.; Dao, S.; Ganbarov, K.; Tanomand, A.; Dal, T.; Aghazadeh, M.; Ghotaslou, R.; Ahangarzadeh Rezaee, M.; Yousefi, B.; et al. How CRISPR-Cas System Could Be Used to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Gene | Function | Mutation 1 | No. of Isolates Harboring the Mutation [Reference] |
|---|---|---|---|
| phoQ | Part of the two-component system PhoP/PhoQ that modulate the expression of arnBCADTEF operon, by activation of PmrA/PmrB through PmrD. | ∆Lys2-Leu6 | 9 [43] |
| Arg16Cys | 1 [44]; 1 [45] | ||
| Leu26Pro | 1 [46] | ||
| Leu96Pro | 1 [47] | ||
| Asp146Gly | 5 [48] | ||
| Asp150Gly | 1 [46]; 3 [48]; 8 [49] | ||
| Ser174Asn | 1 [50] | ||
| Val258Phe | 1 [46] | ||
| Leu348Gln | 2 [47] | ||
| Gly385Ser | 1 [47] | ||
| Ser405Arg | 1 [51] | ||
| His406Tyr | 2 [51] | ||
| Asp434Asn | 1 [40] | ||
| Val446Gly | 1 [52] | ||
| phoP | Part of the two-component system PhoP/PhoQ that modulate the expression of arnBCADTEF operon, by activation of PmrA/PmrB through PmrD. | Val3Phe | 1 [46] |
| Leu26Gln | 1 [47] | ||
| Ser86Leu | 1 [46] | ||
| Arg114Ala | 8 [49]; 7 [48] | ||
| Arg128Ala | 1 [48] | ||
| Asp191Tyr | 1 [45]; 1 [53] | ||
| mgrB | Encodes a small protein that negatively regulate the PhoPQ signaling system. | Val1Ala | 1 [49] |
| Lys2 * | 1 [52]; 3 [44] | ||
| ∆Lys2-Val7 | 1 [43] | ||
| Lys3 * | 1 [52] | ||
| Leu9 * | 1 [47] | ||
| ∆Ala10 | 2 [48] | ||
| Ile13 * | 1 [47] | ||
| Ala14Ser | 2 [47] | ||
| Trp20Arg | 1 [44] | ||
| Leu24His | 1 [54]; 1 [49] | ||
| ∆Leu24Asn | 1 [43] | ||
| Val26 * | 1 [47] | ||
| Met27Lys | 1 [44] | ||
| Cys28Phe | 1 [47]; 10 [43] | ||
| Cys28Tyr | 1 [40]; 1 [54]; 1 [47]; 1 [46]; 1 [52] | ||
| Cys28Ser | 37 [52] | ||
| Cys28 * | 3 [44]; 1 [47]; 1 [55]; 2 [48] | ||
| Gln30 * | 6 [44]; 1 [47]; 2 [55]; 7 [56]; 1 [52] | ||
| Asp31Asn | 1 [47] | ||
| Phe35Ile | 1 [47] | ||
| Gly37Ser | 5 [54] | ||
| Cys39Tyr | 1 [44] | ||
| Cys39 * | 2 [56] | ||
| ∆Thr40 | 2 [43] | ||
| ∆Ile41 | 2 [43] | ||
| Asn42Tyr/Lys43lle | 1 [44]; 1 [45] | ||
| Ile45Thr | 1 [44]; 1 [45] | ||
| Pro46Ser | 1 [44] | ||
| Trp47Arg | 1 [44] | ||
| * 48Tyr | 3 [46] | ||
| pmrA | Part of the two-component system PmrA/PmrB which modulate the expression of arnBCADTEF operon and pmrC gene which ones modifies lipid A. | Glu35Als | 2 [47] |
| Ser42Asn | 1 [47] | ||
| Gly53Cys | 1 [47]; 1 [44]; 1 [45] | ||
| Gly53Ser | 2 [44]; 2 [45] | ||
| Glu57Gly | 1 [52] | ||
| Ser64Thr | 3 [51] | ||
| Met66Ile | 1 [51] | ||
| Ala217Val | 5 [43]; 1 [51] | ||
| pmrC | Catalyses the addition of a phosphoethanolamine moiety to the lipid A. | Ser25Gly | 6 [43] |
| Cys27Phe | 3 [43]; 4 [49]; 1 [48] | ||
| Val39Leu | 7 [49]; 5 [48] | ||
| Val42Leu | 1 [49]; 3 [48] | ||
| Leu50Val | 2 [43] | ||
| Pro135Ala | 2 [43] | ||
| Val138Ile | 13 [43] | ||
| Ala148Thr | 13 [43] | ||
| Arg152His | 2 [49]; 2 [48] | ||
| Arg155His | 1 [48] | ||
| Ser204Phe | 13 [43] | ||
| Ser257Leu | 1 [49]; 2 [48] | ||
| Ser260Leu | 1 [49]; 2 [48] | ||
| Ala279Gly | 2 [49]; 5 [48] | ||
| Gln319Arg | 7 [43]; 4 [49] | ||
| Glu354Lys | 13 [43] | ||
| Gly469Val | 13 [43] | ||
| Asp477Asn | 2 [49]; 2 [48] | ||
| Asp480Asn | 1 [48] | ||
| ∆Leu521-Gly523 | 1 [49] | ||
| pmrB | Part of the two-component system PmrA/PmrB that modulate the expression of arnBCADTEF operon and pmrC gene which ones modifies lipid A. | ∆Arg14 | 1 [50] |
| Leu17Gln | 1 [44] | ||
| Leu82Arg | 2 [57] | ||
| Ser85Arg | 3 [47] | ||
| Thr140Pro | 1 [47] | ||
| Asp150His | 4 [49] | ||
| Thr157Pro | 1 [43]; 2 [44]; 2 [49]; 2 [46]; 2 [50]; 1 [58]; 2 [45]; 1 [48]; 1 [52] | ||
| Ser205Pro | 2 [47] | ||
| Ser208Asn | 1 [50] | ||
| ∆Tyr209 | 1 [50] | ||
| Thr246Ala | 9 [43]; 4 [51]; 2 [49]; 3 [48] | ||
| Arg256Gly | 4 [43]; 4 [49]; 9 [46]; 1 [48] | ||
| Lys280Leu | 1 [46] | ||
| Leu339Cys | 1 [51] | ||
| His340Ile | 1 [51] | ||
| Asn341Thr | 1 [51] | ||
| Arg342Asp | 1 [51] | ||
| Gln343Ser | 1 [51] | ||
| Leu344Pro | 8 [49]; 7 [48] | ||
| Pro346Gln | 1 [51] | ||
| arnA | Bifunctional enzyme that belongs to arnBCADTEF operon. It promotes oxidative decarboxylation of UDP-glucuronic acid to UDP-4-keto-arabinose and the addition of a formyl group to UDP-l-Ara4N to form UDP-l-4-formamido-arabinose. | Ser18Ala | 1 [48] |
| Leu161Cys | 1 [48] | ||
| Thr185Ala | 1 [48] | ||
| Ile260Leu | 8 [49]; 8 [48] | ||
| Asn442Lys | 8 [49]; 8 [48] | ||
| arnB | Belong to arnBCADTEF operon and catalyzes the conversion of UDP-4-keto-arabinose into UDP-4-amino-4-deoxy-l- arabinose. | Gly47Asp | 2 [49]; 4 [48] |
| Ala112Asp | 4 [49]; 7 [48] | ||
| Ile126Val | 2 [49]; 4 [48] | ||
| Asp285Glu | 2 [49]; 3 [48] | ||
| arnC | Belong to arnBCADTEF operon and catalyses the transfer of 4-deoxy-4-formamido-l-arabinose from UDP to undecaprenyl phosphate. | Ser19Thr | 2 [49]; 3 [48] |
| Ser30Thr | 6 [49]; 5 [48] | ||
| arnT | Belong to arnBCADTEF operon and catalyzes the transfer of the l-Ara4N moiety of the glycolipid undecaprenyl phosphate-alpha-l-Ara4N to lipid A. | Ala55Gly | 8 [48] |
| Ser56Leu | 8 [48] | ||
| Ala57Arg | 8 [48] | ||
| Thr58Tyr | 8 [48] | ||
| Tyr59Phe | 9 [48] | ||
| Leu114Met | 1 [48] | ||
| Ile117Val | 1 [48] | ||
| Gln156His | 8 [49] | ||
| Arg157Ser | 7 [49] | ||
| Arg158Ser | 1 [49] | ||
| Arg372Lys | 6 [49]; 3 [48] | ||
| Ile474Asn | 2 [49]; 3 [48] | ||
| arnD | Belong to arnBCADTEF operon catalyses the deformylation of 4-deoxy-4-formamido-l-arabinose-phosphoundecaprenol to 4-amino-4-deoxy-l-arabinose-phosphoundecaprenol. | Trp52Leu | 1 [49] |
| Val53Ile | 1 [49] | ||
| Ile94Leu | 4 [49] | ||
| Ser164Pro | 2 [49] | ||
| Ile300Val | 4 [49] | ||
| crrB | crrB encodes for a signal-transducing histidine kinase CrrB belonging to the CrrA/CrrB two-component system that is responsible by lipid A modification through the upregulation of PmrA/PmrB. | Gln10Leu | 1 [40]; 2 [41] |
| Tyr31His | 1 [41] | ||
| Ala35Val | 1 [51] | ||
| Tyr36His | 1 [51] | ||
| Phe84Ser | 1 [59] | ||
| Leu94Met | 1 [40] | ||
| Trp140Arg | 1 [41] | ||
| Asn141Ile | 2 [41] | ||
| Asn141Tyr | 1 [45]; 1 [59] | ||
| Pro151Ser | 1 [41] | ||
| Pro151Leu | 1 [45]; 1 [59] | ||
| Gly183Val | 1 [45]; 1 [59] | ||
| Ser195Asn | 1 [41] | ||
| Asn388Asp | 1 [51] | ||
| Ser379Pro | 1 [51] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elias, R.; Duarte, A.; Perdigão, J. A Molecular Perspective on Colistin and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Mode of Action, Resistance Genetics, and Phenotypic Susceptibility. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071165
Elias R, Duarte A, Perdigão J. A Molecular Perspective on Colistin and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Mode of Action, Resistance Genetics, and Phenotypic Susceptibility. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(7):1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071165
Chicago/Turabian StyleElias, Rita, Aida Duarte, and João Perdigão. 2021. "A Molecular Perspective on Colistin and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Mode of Action, Resistance Genetics, and Phenotypic Susceptibility" Diagnostics 11, no. 7: 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071165
APA StyleElias, R., Duarte, A., & Perdigão, J. (2021). A Molecular Perspective on Colistin and Klebsiella pneumoniae: Mode of Action, Resistance Genetics, and Phenotypic Susceptibility. Diagnostics, 11(7), 1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11071165







